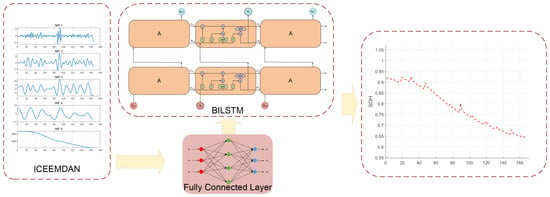
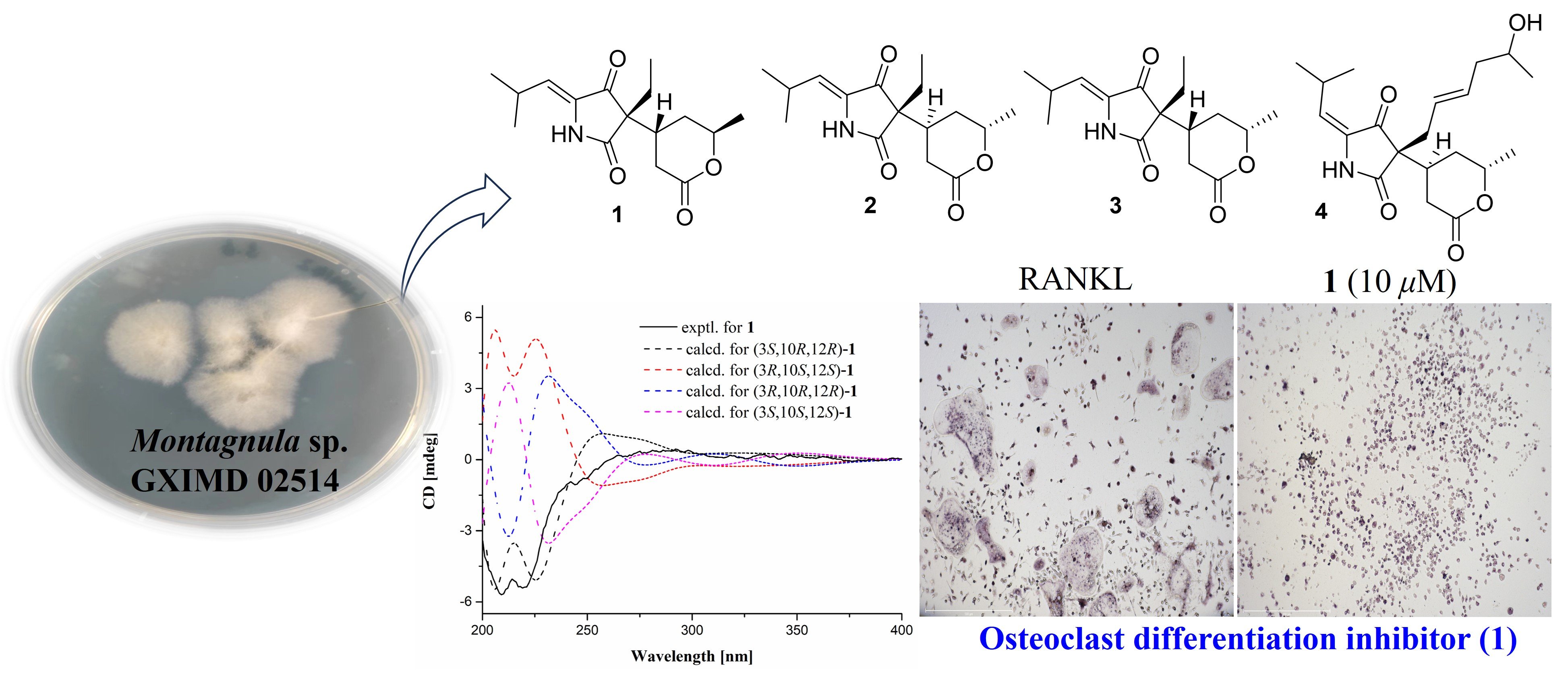
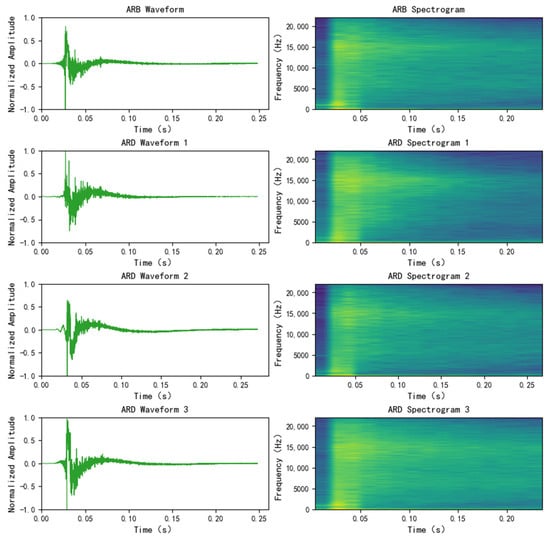
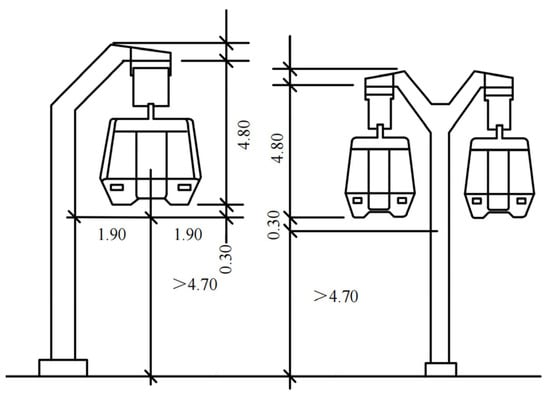
Open Access Journals
-
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT
FACTOR
4.9 -
 Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT
FACTOR
2.5 -
 Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT
FACTOR
3.3 -
 JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT
FACTOR
2.9 -
 Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT
FACTOR
3.5 -
 Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT
FACTOR
3.2 -
 Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT
FACTOR
3.2 -
 Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT
FACTOR
2.6 -
 Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT
FACTOR
3.1 -
 Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT
FACTOR
4.6 -
 Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT
FACTOR
2.8 -
 Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT
FACTOR
2.2 -
 Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT
FACTOR
4.4 -
 Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT
FACTOR
4.1 -
 Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT
FACTOR
5.1 -
 Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT
FACTOR
4.1 -
 Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT
FACTOR
2.7 -
 Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT
FACTOR
2.7 -
 Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT
FACTOR
5.0 -
 Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT
FACTOR
3.0 -
 Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT
FACTOR
3.3 -
 Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT
FACTOR
3.9 -
 Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT
FACTOR
4.9 -
 Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT
FACTOR
4.2 -
 Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT
FACTOR
3.4 -
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT
FACTOR
2.2 -
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT
FACTOR
3.2 -
 JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT
FACTOR
2.8 -
 Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT
FACTOR
3.6 -
 Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT
FACTOR
2.4 -
 Biology
IMPACT
Biology
IMPACT
FACTOR
3.5 -
 Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT
FACTOR
5.2 -
 Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
FACTOR
4.8 -
 Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT
FACTOR
3.4 -
 Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT
FACTOR
4.3 -
 Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT
FACTOR
2.6 -
 Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT
FACTOR
2.1 -
 Behavioral Sciences
IMPACT
Behavioral Sciences
IMPACT
FACTOR
2.5 -
 Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT
FACTOR
3.0 -
 Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT
FACTOR
2.5 -
 Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT
FACTOR
4.8 -
 Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
FACTOR
5.5 -
 IJERPH
IJERPH
-
 Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT
FACTOR
3.5 -
 Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT
FACTOR
6.6 -
 Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT
FACTOR
2.8 -
 Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT
FACTOR
2.8 -
 Pathogens
IMPACT
Pathogens
IMPACT
FACTOR
3.3 -
 Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT
FACTOR
2.8 -
 Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT
FACTOR
0.6 -
 Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT
FACTOR
3.7 -
 Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT
FACTOR
2.5 -
 Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT
FACTOR
3.0 -
 Machines
IMPACT
Machines
IMPACT
FACTOR
2.5 -
 Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT
FACTOR
2.2 -
 Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT
FACTOR
2.3 -
 Systems
IMPACT
Systems
IMPACT
FACTOR
3.1 -
 Insects
IMPACT
Insects
IMPACT
FACTOR
2.9 -
 Veterinary Sciences
IMPACT
Veterinary Sciences
IMPACT
FACTOR
2.3 -
 Entropy
IMPACT
Entropy
IMPACT
FACTOR
2.0 -
 Antibiotics
IMPACT
Antibiotics
IMPACT
FACTOR
4.6 -
 CIMB
IMPACT
CIMB
IMPACT
FACTOR
3.0 -
 Aerospace
IMPACT
Aerospace
IMPACT
FACTOR
2.2 -
 Catalysts
IMPACT
Catalysts
IMPACT
FACTOR
4.0 -
 Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT
FACTOR
3.4 -
 Photonics
IMPACT
Photonics
IMPACT
FACTOR
1.9