- Article
A Two-Stage Hybrid Bioleaching Process for Selective Copper Extraction from Low-Grade, High-Arsenic Enargite Concentrates
- Jiehua Hu,
- Guidi Yang and
- Haibin He
- + 6 authors
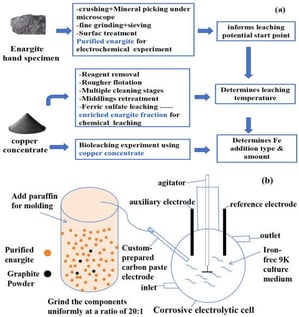
This study addresses the dual challenges of low copper recovery and persistent arsenic pollution in the bioleaching of low-grade, high-arsenic copper ores containing enargite (Cu3AsS4). Through integrated electrochemical, chemical, and biological investigations, a selective and environmentally sustainable two-stage hybrid leaching process was developed. Electrochemical analysis identified a critical oxidation threshold of ~750 mV governing enargite dissolution. Chemical leaching and X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) analysis revealed a temperature-dependent sulfur transformation pathway, enabling a staged thermal strategy: flotation below 40 °C to maximize hydrophobic elemental sulfur (S0) formation, and bioleaching at 40–55 °C to promote complete sulfur oxidation to sulfate. Optimization produced a two-stage process comprising 10-day chemical pre-leaching with FeSO4 (10.0 g/L Fe2+) followed by bioleaching, achieving 78.3% copper extraction while suppressing arsenic dissolution to approximately 10%. The use of FeSO4 instead of Fe2(SO4)3 reduces reagent costs by ~70%, saving an estimated CNY 47,250 daily at 1000 t/d scale. Leaching toxicity tests confirm residue As < 0.10 mg/L, meeting non-hazardous waste standards (GB5085.3-2007). This work provides the first integrated demonstration of electrochemical threshold control combined with temperature-dependent sulfur speciation for selective copper extraction from arsenic-bearing enargite ores, offering a scalable, reagent-economical, and environmentally sustainable metallurgical route.
13 March 2026




![Schematic diagram of EGS (modified from [38]).](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/processes/processes-14-00920/article_deploy/html/images/processes-14-00920-g001-550.jpg)