- Article
Study on Co-Calcination of Vanadium-Chromium Slag and Artificial Marble Waste Slag Followed by Acid Leaching for Separation of Vanadium and Chromium
- Xiaoxin Xuan,
- Guangyu Zhang and
- Yang Chen
- + 2 authors
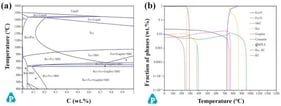
This study addresses the challenge of achieving efficient separation of vanadium and chromium from vanadium–chromium slag (VCS) while simultaneously tackling issues related to artificial granite waste residue (AGWR), such as its substantial stockpiling and associated air pollution. AGWR was used as a substitute calcination additive for calcium carbonate to achieve efficient separation through a calcination-leaching process. Orthogonal experiments were conducted to investigate the effects of AGWR addition amount, calcination temperature, and calcination time on the leaching behavior of vanadium and chromium. During calcination, vanadium reacts with CaO (a decomposition product of AGWR) to form acid-soluble calcium vanadate. Concurrently, chromium hydroxide decomposes into chromium oxide, which is poorly soluble in dilute acid. Subsequent leaching of the calcination product with dilute sulfuric acid leaches vanadium (V) into the solution, while chromium (Cr) remains in the residue, thus achieving separation. The experimental results showed that under the conditions of 30% AGWR addition; calcination at 850 °C for 1 h; leaching at 90 °C for 2 h with a liquid-to-solid ratio of 10:1 and a sulfuric acid concentration of 50 g·L−1; the leaching rate of vanadium reached 85.68%, whereas that of chromium was only 2.34%. These results demonstrate highly efficient separation of vanadium and chromium, offering valuable insights for resource recovery from both VCS and AGWR.
4 March 2026




![Schematic diagram showing the sources of VCS and AGWR [10,21]. (a) Sources of VCS; (b) Sources of AGWR.](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=470,h=317/https://mdpi-res.com/metals/metals-16-00291/article_deploy/html/images/metals-16-00291-g001-550.jpg)