- Article
A Low-Noise Equalizing Transimpedance Amplifier for LED-Limited Visible Light Communication
- Neethu Mohan,
- Diaaeldin Abdelrahman and
- Mohamed Atef
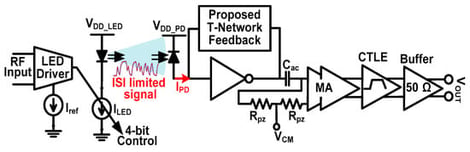
Solid-state lighting, especially light-emitting diodes (LEDs), is revolutionizing indoor lighting due to its energy efficiency, long lifespan, low heat output, and enhanced color rendering. LEDs can quickly adjust light intensity, enabling the development of visible light communication (VLC) technology. However, the modulation bandwidth of phosphor-converted white LEDs commonly used for illumination is limited, potentially affecting the speed of the VLC links. This paper presents a receiver-side equalization technique to overcome bandwidth limitations in VLC links due to LEDs. The proposed approach utilizes a novel transimpedance amplifier with an embedded T-network shunt-feedback equalizer (TIA-TE) to introduce adjustable high-frequency peaking in the TIA’s frequency response. By incorporating this peaking, the system’s bandwidth is extended without sacrificing important performance parameters like gain, noise, or power dissipation. The TIA-TE is followed by a main amplifier and a standalone continuous-time linear equalizer (CTLE) for further signal conditioning, while a 50 Ω buffer interfaces the receiver with measurement equipment. Post-layout simulations in a 0.35 µm CMOS process validate the approach. Using a 4 pF photodiode, the system bandwidth was initially limited by the LED’s 3 MHz modulation bandwidth. The proposed TIA-TE extends the bandwidth to 8.4 GHz without sacrificing the gain or power dissipation. The subsequent CTLE further extends the bandwidth to 14 MHz. The receiver front end achieves a mid-band transimpedance of 110 dBΩ and an input-referred noise current of 7.2 nArms, while dissipating 2.48 mW (excluding the 50 Ω buffer). Simulated 28 Mb/s NRZ eye diagrams demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed TIA-TE architecture for LED-limited VLC links.
1 March 2026