- Article
Differential Responsiveness of Human Skin Mast Cells to SCF and IL-33: Reduced Reactivity to SCF but Not to IL-33 in the Post-Mitotic Phase
- Manqiu Jin,
- Jean Schneikert and
- Magda Babina
- + 2 authors
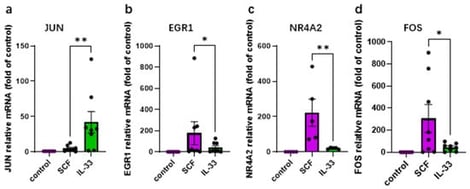
Skin mast cells (MCs) play a vital role in acute allergic reactions and also contribute to chronic dermatoses partially through cytokine production. Key growth factors (GFs), such as SCF and IL-33, orchestrate MC survival and activity. Whether early responses differ between these factors remains incompletely defined. In the skin, MCs are long-lived and can proliferate outside the body but eventually exit the cell cycle. It remains unclear whether post-mitotic MCs show altered sensitivity to GFs. MCs were isolated from human foreskin and cultured in the presence of SCF + IL-4. GF-deprived cells were stimulated with either SCF or IL-33. Signaling events were determined by immunoblot. Gene expression was studied by RT-qPCR, cytokine release by ELISA, comparing dividing (3–4 weeks) with post-mitotic “aged” MCs (≥6 weeks). SCF strongly induced genes like FOS, EGR1, and NR4A2, while IL-33 was particularly effective at inducing JUN. IL-33 also prompted significant cytokine production (TNF-α, CCL1 and IL-13), whereas the activation of LIF was confined to SCF. SCF favored KIT, ERK, AKT, and STAT5 activation, whereas IL-33 preferentially stimulated JNK and p38 pathways. Although post-mitotic MCs showed diminished overall responsiveness to SCF, and with interesting differences among modules, their cytokine response to SCF remained comparable. Intriguingly, after exiting the cell cycle, MCs showed heightened sensitivity to IL-33, evidenced by increased ERK activation and TNF-α production. Collectively, IL-33 and SCF elicit markedly different early responses in human skin MCs. Chronic exposure to SCF reduces the responsiveness to this GF without eliminating their reactivity, while non-dividing MCs become more sensitive to IL-33, possibly as a compensatory adaptation.
24 February 2026