- Review
Applications of Image Recognition in Intelligent Agricultural Engineering: A Comprehensive Review
- Yujie Xue,
- Junyi Li and
- Tingkun Chen
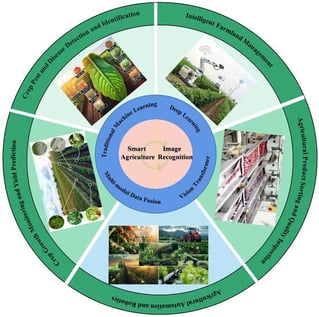
Confronted with the severe imperatives to food security posed by a growing population and the urgent need for sustainable development amid climate change, traditional agricultural models face significant resource-intensive efficiency bottlenecks. Deep learning-based image recognition is driving a future-oriented intelligent agricultural revolution by enabling high-throughput phenotyping and autonomous decision-making across the production chain. This paper systematically reviews key advancements in image recognition within modern agriculture, mapping the fundamental paradigm shift from traditional hand-crafted feature engineering to adaptive deep feature learning. We critically analyze technological implementation and performance across five core application scenarios: high-precision pest and disease diagnosis, spatio-temporal growth monitoring and yield prediction through multi-source image fusion, agricultural robots for automated harvesting, non-destructive quality inspection of products, and intelligent precision management of farmland. The review further identifies critical challenges hindering large-scale technology adoption, primarily centered on the high costs of constructing high-quality agricultural datasets and model robustness in complex field environments. Consequently, this study provides a comprehensive and forward-looking reference for advancing the deep integration of vision technology, thereby offering a strategic path toward achieving more intelligent, efficient, and sustainable global agricultural production systems in the digital era.
24 February 2026