Abstract
This study proposes an operational strategy to reduce building infiltration rates by predicting the infiltration rate in a variable air volume (VAV) system and implementing pressure control based on these predictions. To achieve this, a theoretical review of conventional VAV systems operations and its impact on building pressure differences was conducted. A method for predicting infiltration rate based on airflow variations in the VAV system was proposed and validated. Furthermore, a pressure control algorithm that utilizes the predicted infiltration rate was developed and evaluated. Previous studies were limited in capturing real-time envelope pressure differentials and changes in infiltration rate. However, this study predicted infiltration rate based on the exponential relationship between the difference in supply and return airflow rates and pressure differential, and verified its reliability against measured values. Furthermore, pressure control based on predicted infiltration rate reduced the infiltration rate by up to 46.1% compared with fan tracking and volumetric tracking control systems, while also reducing fan energy consumption by 94.7%, confirming its effectiveness in reducing cooling load.
1. Introduction
The pressure difference between the interior and exterior of a building is caused by wind, temperature differences between the interior and exterior, and the operation of air- conditioning systems [1]. This can cause unintended airflow through the building envelope, known as air infiltration or leakage. In particular, when there is a negative pressure difference between the interior and exterior, airflow from the exterior to the interior due to infiltration can cause unfiltered contaminated air from the exterior to enter the building. Infiltration occurring in the building envelope affects the indoor environment and building operation. According to a study by Du et al., analysis of air leakage in high-airtightness buildings under various climatic conditions in China revealed that heating energy demand due to winter infiltration can account for over 10% of the total building load [2]. Straube, J.F. emphasized the importance of building pressure management for moisture control, stating that indoor negative pressure promotes moisture penetration, and that moisture diffusion affects mold growth as well as the performance and structural integrity of building materials [3]. Previous studies have shown that condensation on the building envelope can cause problems such as increased heating and cooling energy consumption, poor indoor air quality, and moisture diffusion. One solution to these problems is to control the building pressure. The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) recommends maintaining buildings at positive pressure (1–20 Pa) to reduce condensation [4]. The main purpose of a heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning (HVAC) system is to maintain the indoor thermal environment and air quality by regulating the supply airflow rate, so the return airflow rate can be used to regulate the building pressure [5]. Appropriate return fan control in variable air volume (VAV) systems is required for building pressurization [6].
VAV system is a HVAC method used in a building’s heating and cooling system that maintains a constant-supply air temperature and changes the supply airflow rate according to load fluctuations [7]. Methods of controlling building pressure using VAV systems include fan tracking control (FT) and volumetric tracking control (VT) [8]. FT control operates the return fan at the same speed or slightly slower than the supply fan speed. In FT control of return fans, the supply and return fans operate at the same speed. VT control uses the airflow measurement of a duct or fan and adjusts dampers or fan speed to maintain a constant difference between the supply and return airflow rate. The control variable is the return airflow rate, and since it is set to follow the change in the VAV supply airflow rate, this method is called volume tracking control. Pang, X. et al.’s analyzed the impact of airflow and pressure control on the indoor environment and energy consumption under a VAV control system, and analyzed the basic operating principles of the system [9]. Li D. et al. addressed the relationship between airflow and duct pressure in variable airflow systems and suggested ways to save energy through fan speed control and duct pressure control [10]. In particular, this study effectively reduced the wear of terminal valves and fan energy consumption through a dual closed-loop control strategy in VAV systems. Liu, M. developed a variable speed drive volumetric tracking (VSDVT) control method utilizing VSD signals as a return fan control method for a VAV system [11]. This method efficiently controls the supply and return airflow rate in a VAV system. Simulations demonstrated that annual return fan energy consumption can be reduced by up to 50% and supply fan energy consumption by up to 30%.
Ke, Y.’s study analyzed the return fan control methods of VAV systems in six climate regions and explained how the appropriate selection of return fan control strategies according to the environment affects indoor air quality and energy efficiency [12]. The impact of climate-specific ventilation control strategies on energy efficiency was validated through experiments. Pang, X. et al.’s study analyzed the effects of airflow and pressure regulation through VAV system control methods on indoor environments and energy consumption, while also examining the system’s fundamental operating principles [10]. Various control variables of VAV systems were evaluated and classified as excellent, average, or poor, thereby establishing criteria for control performance assessment. Simulations demonstrated that energy consumption and thermal performance may vary significantly depending on the use of SAT reset, airflow control, and economic operation mode. While the study focused on evaluating the performance variability of existing systems, it did not propose new control algorithms or specific methods for performance improvement. Li D. et al.’s paper addressed the correlation between airflow and duct pressure in VAV systems, proposing methods to save energy through fan speed control and duct pressure regulation [8]. Notably, this study effectively reduced terminal valve wear and fan energy consumption in VAV systems using a dual closed-loop control strategy. Using experimental data, they modeled the dynamic temperature response to enhance adaptability to seasonal load variations. Liu, M. developed a VSDVT control method utilizing VSD signals as a ventilation fan control approach for variable air volume systems, efficiently regulating supply and return airflow rate in VAV systems [13]. Simulations demonstrated that this method could reduce annual ventilation fan energy consumption by up to 50% and supply fan energy consumption by up to 30%.
Infiltration occurs due to the pressure difference between the interior and exterior of a building, and pressure control requires considering the infiltration rate based on the real-time fluctuations in the building pressure difference. Previous studies have proposed and demonstrated various approaches to improve the control performance and energy efficiency of VAV systems. However, they have not specifically considered the envelope pressure difference caused by HVAC system operation and the resulting impact on infiltration. Furthermore, the real-time applicability of the proposed control strategy and its validation in the field have been lacking. Therefore, research on pressure control methods that consider infiltration rate in buildings remains urgently needed.
Pressure differentials within a building fluctuate constantly depending on the operating status of the HVAC system. To accurately track these changes, pressure sensors must be installed to continuously monitor indoor–outdoor pressure differentials [12,14]. However, the installation location of exterior wall pressure sensors influences measurement uncertainty. Therefore, it is recommended to install them at points where leakage is likely to occur or at locations away from other buildings or obstacles. However, finding such locations is difficult in densely built-up urban areas, and permanently installing pressure sensors on all exterior walls of existing buildings presents physical and economic constraints. Therefore, an alternative to physical pressure sensors is needed during the building operation phase.
To predict the infiltration rate occurring in the building envelope and develop a pressure control method for the VAV system, previous research on predicting building infiltration rate and controlling the return fan in VAV system was investigated. Max Sherman attempted to predict infiltration based on building airtightness by collecting infiltration rate data from more than 100,000 residential units and developing a regression model [15]. This model utilized a large database to analyze residential air leakage patterns, but its limitations included a failure to adequately account for changes in airflow through building exterior walls. Hrvoje Krstic conducted blower door tests on 58 residential buildings constructed between 1912 and 2013, establishing a database of airtightness performance and developing a model to predict airtightness performance based on window characteristics [16]. This model, also based on large-scale data, did not account for variations in airflow. On the other hand, Yongming Ji developed a model to predict infiltration in high-density, single-compartment buildings through an experimental approach [17]. However, this model suffers from the limitation of requiring real-time measurement of indoor–outdoor pressure differences, making it difficult to apply during actual building operation.
Previous studies have proposed and demonstrated various approaches to improve the control performance and energy efficiency of VAV systems. However, they did not specifically consider the impact of pressure differentials across the building envelope caused by HVAC system operation and the resulting infiltration rate. Furthermore, there was a lack of real-time applicability and verification of the proposed control strategies in actual environments. Considering these points, this study aims to propose an operational strategy that predicts infiltration rate during VAV system control and improves building infiltration by utilizing this prediction for ventilation fan control. To achieve this, a theoretical examination of existing VAV system operation and building pressure differentials was conducted, and a method for predicting infiltration rate based on VAV system airflow was developed and validated. Furthermore, a pressure control algorithm utilizing the predicted infiltration rate was derived and evaluated.
2. Predicting Infiltration Rate Using Supply and Return Airflow Rates
This section proposes a methodology for analyzing the relationship between supply and return airflow rates in VAV systems and building infiltration rate. To validate this approach, a target space equipped with a VAV system was selected to develop an airflow prediction model, and airtightness performance was measured with an air handling unit (AHU). Based on the experimental results, a method was established to predict building infiltration based on supply and return airflow rates.
2.1. Analysis of the Relationship Between Supply and Return Airflow Rates and Air Infiltration Rate
The airtightness of a building is an important factor in the infiltration of the building envelope [18]. During HVAC system operation, airflow within a building consists of supply airflow rate, return airflow rate, and leakage through the building envelope. According to the law of mass conservation, the sum of airflow entering a room equals the sum of airflow leaving it. That is, theoretically, the sum of the supply airflow rate from the AHU and the infiltration rate through the exterior walls equals the sum of the return airflow rate and the infiltration rate through the building envelope. Therefore, the difference between the supply airflow rate and the return airflow rate equals the airflow entering and exiting through the exterior walls. Based on this relationship, we aim to predict the infiltration rate using the supply and return airflow rates. [Figure 1] illustrates the prediction process, with details as follows.
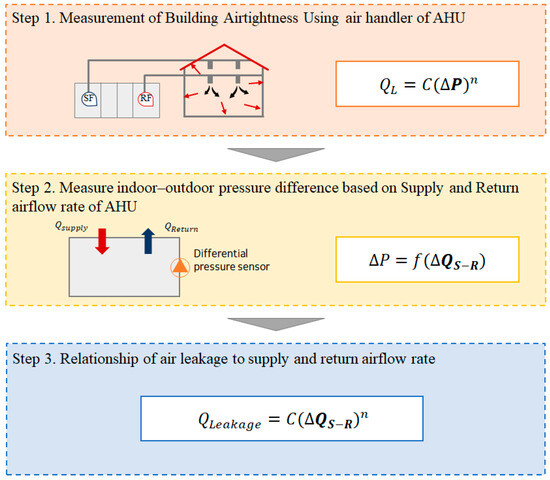
Figure 1.
Flowchart for predicting air leakage using supply and return airflow rates.
Step 1: Assess the airtightness of the building envelope using an AHU fan. To do this, a constant pressure difference (ΔP) is created between the indoor and outdoor areas, and the air leakage (QL) under these conditions is measured.
Step 2: The difference between the supply and return airflow rates is equal to the leakage through the building envelope. By directly measuring the supply and return airflow rates, the indoor/outdoor pressure difference can be predicted.
Step 3: By substituting the pressure difference (ΔP) obtained in the previous step into the Power Law, the relationship between the infiltration rate and the supply and return airflow rates can be established.
2.2. Experiment Overview
2.2.1. Target Space and System
The target space is a laboratory at Y University in Gyeongsan, Gyeongsangbuk-do, to analyze the relationship between the supply and the return airflow rates and pressure differential of a VAV system. The target space consists of two zones with equal areas, as shown in [Figure 2]. However, during the experiment, the internal door was left open, and the space was treated as a single unit for the experiment. The target space is AHU with VAV system, and the overview of the experimental target space is as shown in [Table 1]. The specifications of the target AHU fan are as shown in [Table 2].
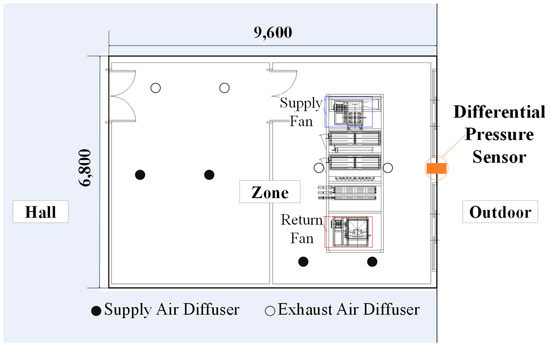
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the target space.

Table 1.
Overview of the experimental space.

Table 2.
Target AHU fan specifications.
To determine the airflow supplied and returned indoors and the resulting pressure differential, it is necessary to measure the airflow and pressure differential. Changes in airflow were measured by adjusting fan speed and VAV damper opening rate using the building automation system (BAS). The differential pressure sensor measuring the indoor–outdoor pressure difference is installed on the exterior wall of the target space. The specifications of the differential pressure sensor and airflow measurement device are presented in [Table 3].

Table 3.
Measurement sensor specifications.
2.2.2. Target Space Airtightness Performance Measurement
To measure the airtightness performance of the building envelope, which determines the building’s infiltration rate, the target space’s AHU was utilized. The AHU’s supply fan and return fan were used to pressurize and depressurize the interior, maintaining the pressure differential between the indoor and outdoor environments. Before pressurization, the exhaust diffusers were sealed with vinyl to prevent air leakage from the diffusers when the interior became pressurized. Conversely, the supply diffusers were sealed to prevent negative pressure from occurring, as shown in [Figure 3], and external air from entering the interior. The damper opening conditions for the HVAC system were set to 100% outside air during pressurization and 100% exhaust air during depressurization, with the damper closed to prevent outside air inflow.
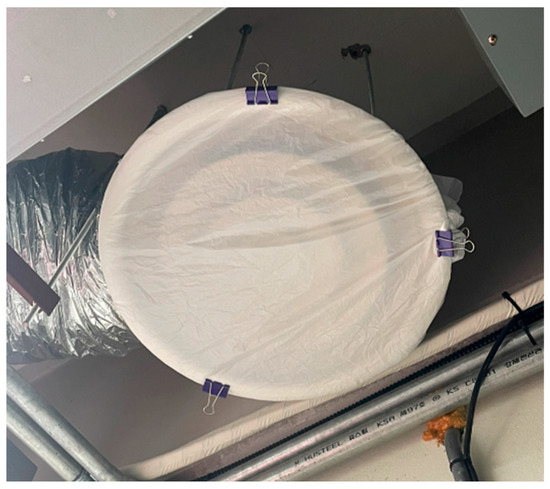

Figure 3.
Sealing the diffuser before pressurization/depressurization.
The leakage volume is related to the pressure difference and can be expressed in the form of Equation (1).
here,
: Leakage volume [m3/h]
: Leakage coefficient [m3/h∙Pa]
: Pressure difference [Pa]
: Leakage exponent [-]
The leakage coefficient () and leakage exponent () are variables related to the airtightness of the building, and the leakage exponent represents the airflow characteristics with a value between 0.5 and 1. Using the AHU’s fan to pressurize/depressurize the room, the fan airflow was measured at a pressure difference of 10 to 60 Pa. The results are shown in [Table 4]. The volumetric efficiency coefficient C was derived as 626.181 m3/h·Pa, and the volumetric efficiency index was derived as 0.5644. The airtightness performance of the target space was 6334 cubic meter per hour (CMH) for CMH50 and 26 times/h for ACH50 (air changes per hour at 50 Pa), and the leakage function equation derived based on the experimental results is as shown in Equation (2).

Table 4.
Pressurization/depressurization method measurement results.
2.2.3. Verification of the Prediction Method for Infiltration Rate
The infiltration rate was calculated by substituting the indoor–outdoor pressure difference values measured experimentally as a function of supply airflow rate changes into the leakage coefficient equation (2) derived from airtightness performance measurements with the AHU. [Figure 4] illustrates the relationship between the supply-to-return airflow rate difference and infiltration rate. Experimental results indicate that when the supply airflow rate exceeds the return airflow rate by approximately 3000 CMH, the infiltration rate reaches about 2000 CMH. Using the regression equation derived from the results, the building’s infiltration rate can be predicted based on the measured supply-to-return airflow rate difference.
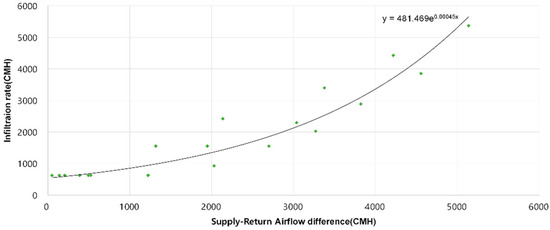
Figure 4.
Relationship between supply and return airflow rates differences and infiltration rate.
To verify the infiltration rate predicted by supply and return airflow rates, we compared it with the infiltration rate calculated from the pressure difference measured by a pressure sensor. We compared the infiltration rate calculated by substituting the pressure sensor readings with the infiltration rate predicted by changes in supply airflow rate during automatic HVAC operation at one-minute intervals over 80 min. The comparison results showed that the leakage volume predicted from supply and return airflow rates is proportional to the leakage volume calculated from the measured pressure differential. Since the pressure differential is negative, it is determined that leakage is occurring at the airflow rate shown in [Figure 5]. Although the calculation method for the infiltration rate derived from the relationship established in this study varies depending on the real-time changes in the HVAC conditions, the leakage volume calculated using the leakage function is measured as the same pressure difference regardless of the HVAC operating conditions, since the pressure difference sensor installed in the target space records only integer values.
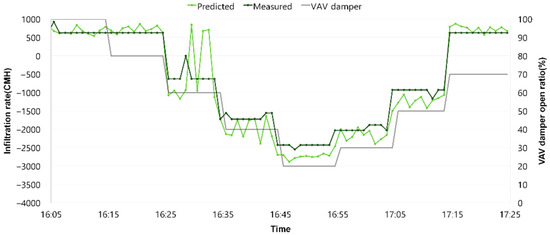
Figure 5.
Prediction and measurement comparison of infiltration rate.
The average error between predicted and measured infiltration rate is approximately 270 CMH. The coefficient of variation in the root mean squared error (CVRMSE) between the predicted and measured infiltration rate was 11.05%, showing better results than the guidelines of ASHRAE (≤30%) and IPMVP (≤20%). Therefore, the infiltration rate prediction model derived in this study, utilizing the relationship between supply and return airflow rates and the pressure difference in the AHU, is deemed suitable for predicting infiltration rate in occupied buildings.
3. Return Fan Control Method Using Infiltration Rate Prediction
We propose a return fan control scheme considering infiltration rate by utilizing pressure and infiltration prediction methods based on supply and return airflow rates in VAV systems. FT control, VT control, and the proposed operational scheme—all return fan control methods for VAV systems—are compared and analyzed through simulation. The target building’s facility systems and detailed data were modeled using TRNSYS 18 and TRNFLOW. This enables the derivation of simulation results and evaluation of the proposed algorithm.
3.1. Proposal of a Return Fan Control Algorithm Using Infiltration Prediction
This algorithm describes the process of generating a return fan control signal based on the relationships between supply airflow rate, return airflow rate, and infiltration rate. At the beginning of the algorithm, initial values such as supply airflow rate (Q_supply), return airflow rate (Q_return), leakage coefficient (), and leakage exponent () are provided as inputs. These values define the initial conditions of the system and provide the basic variables required for calculating supply and return airflow rates and leakage. Next, based on the difference between the supply airflow rate and the return airflow rate, the pressure difference between the indoor and outdoor airflow is predicted, providing the basic data needed to calculate the infiltration rate. The infiltration rate is calculated using the indoor/outdoor pressure difference. In this step, the infiltration is quantified using the leakage coefficient and leakage index. Based on the infiltration rate, the return airflow rate adjustment value (RA_control) is calculated. In this step, the adjusted return airflow rate is calculated by subtracting the infiltration rate from the supply airflow rate. This represents the new return airflow rate value that will be reflected in the return fan control. Next, it is checked whether the adjusted return airflow rate (RA_control) is greater than zero. In this step, the return airflow rate (Q_return) is adjusted according to the following conditions. If the adjusted return airflow rate (RA_control) is positive, Q_return is set to the RA_control value. Otherwise, the return airflow rate (Q_return) remains equal to the supply airflow rate (Q_supply). Finally, the adjusted return airflow rate (Q_return_new) is generated as output. This value is transmitted as a return fan control signal and applied to maintain indoor air pressure and air quality.
3.2. Evaluation of Return Fan Control Algorithm Using Infiltration Rate Prediction
3.2.1. Target Space and System Modeling
In this study, TRNSYS 18, a dynamic simulation program, was employed to analyze the energy consumption associated with the return fan control method of VAV system. To implement the VAV system in the target building described in [Figure 2], Type 23 (PID controller) was used to model the VAV terminal unit and the supply fan to automatically control them based on indoor temperature. TRNFLOW was also used to analyze airflow. [Figure 6] illustrates the simulation configuration and flowchart.
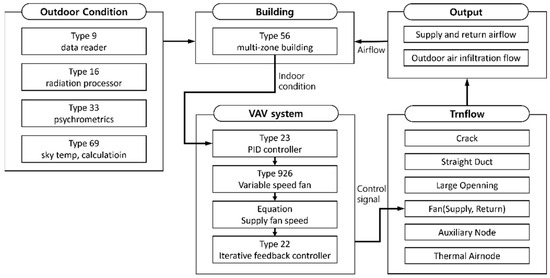
Figure 6.
Simulation configuration and flowchart.
3.2.2. Simulation Conditions
To estimate the airflow of VAV according to changes in indoor heat generation, the maximum occupancy of the target space was calculated. [Table 5] shows the conditions for calculating the occupancy of the target space. The maximum occupancy was calculated by applying the occupant density standard to the floor area. The indoor human heat generation was calculated based on the Korean Building Mechanical System Design Standard [19]. To compare the airflow and infiltration rate according to changes in heat generation, the occupancy rate was compared at 75% (Case A), 50% (Case B), and 25% (Case C) compared to the maximum occupancy, and three simulation occupancy cases were set. The occupancy was assumed to be in the room from 9:00 to 18:00 throughout the day.

Table 5.
Estimation of target space occupancy conditions.
The simulation was conducted from August 3 to 6, and during the simulation period, the outside temperature ranged from 23 °C to 32 °C. Since the outside wind can affect the indoor and outdoor pressure difference, the wind speed during occupancy hours (9:00 to 18:00) was set to not exceed 5 m/s.
3.3. Evaluation Results of Pressure Control Algorithm Using Infiltration Rate Prediction
3.3.1. Fan Tracking Control
In FT control, the indoor temperature in Cases A, B, and C was maintained within the set temperature of 24 ± 1 °C, satisfying the indoor thermal environment. [Figure 6] shows the changes in the supply airflow rate, return airflow rate, and fan frequency over time for Case A when operating with the fan tracking control method in the VAV system. In Case A of [Figure 7], the number of occupants was 30, the highest occupancy level, and the supply airflow rate and return airflow rate at this time were almost the same, averaging 1418 CMH and 1417 CMH, respectively.
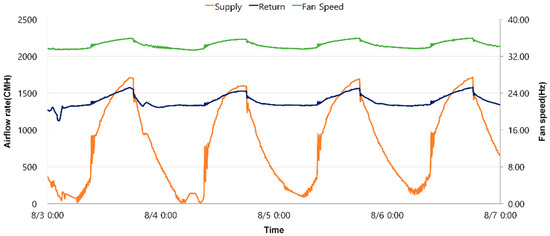
Figure 7.
Airflow and frequency during fan tracking control (Case A).
In Case B, where the number of occupants decreased to 20, the supply airflow rate decreased by about 13.8% to 1172 CMH, but the return airflow rate showed a tendency to slightly increase to 1370 CMH. In Case C, where the number of occupants decreased further to 10, the supply airflow rate decreased again to 993 CMH, but the return airflow rate decreased only by about 7%, showing a tendency for the difference with the supply airflow rate to gradually widen. In addition, an examination of the change in infiltration rate clearly showed a tendency to be inversely proportional to the number of occupants. The average infiltration rate in Case A was the lowest at 947 CMH, while it was the highest in Case C at 1167 CMH. This is because the smaller the number of occupants, the larger the indoor/outdoor pressure difference, resulting in more infiltration rate. In all cases, the infiltration rate decreased during the day according to the daily cycle and tended to increase at night when the outside temperature is low and the heating load is small.
3.3.2. Volumetric Tracking Control
In the VT control, the indoor temperature in Cases A, B, and C was maintained within the set temperature range 24 ± 1 °C, satisfying the indoor thermal environment. [Figure 8] shows the changes in the supply airflow rate and return airflow rate over time for Case A when operating with the VT control method in the VAV system. As shown in [Figure 8], when the number of occupants was 30, the supply airflow rate and return airflow rate were operated at the same rate of 1292 CMH each.
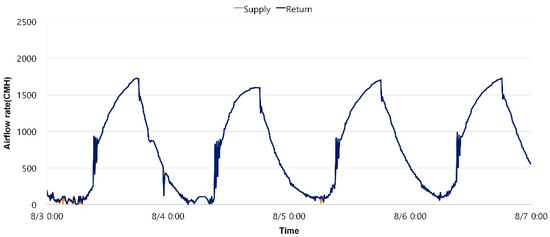
Figure 8.
Supply and return airflow rates when controlling VT (Case A).
When the occupancy decreased to 20, the supply and return airflow rates decreased by approximately 17.4% to 1068 CMH each. When the occupancy decreased to 10, the airflow decreased further by approximately 22.2% to 831 CMH. When VT control was used, the infiltration rate remained nearly constant regardless of the occupancy. Comparing infiltration rate with outdoor temperature also showed similar results, except during periods of high winds.
3.3.3. Proposed Pressure Control Algorithm
During the simulation period when the pressure control method considering infiltration rate was applied, the indoor temperature was stably maintained within the set temperature range 24 ± 1 °C, satisfying the indoor thermal environment. The Control_RA method dynamically adjusts the supply and return airflow rates considering the indoor and outdoor air infiltration rate, and shows the supply and return airflow rates when operating in this way. In [Figure 9], in a high occupancy state such as Case A, the supply and return airflow rates were 1197 CMH and 467 CMH on average, respectively. In Case C, when the occupancy rate decreased, they decreased to 694 CMH and 184 CMH on average, respectively. This indicates that the pressure control method considering infiltration rate efficiently adjusts the supply and ventilation demand while maintaining the indoor and outdoor pressure difference. The difference between the supply and return airflow rates was adjusted according to the change in the occupancy rate as a result of reflecting the infiltration rate. When the occupancy rate was high, the difference between the supply airflow rate and the return airflow rate was 730 CMH, and when the occupancy rate decreased to 50%, the difference decreased to 510 CMH. This contributes to suppressing infiltration rate by maintaining the indoor space in a positive pressure state.
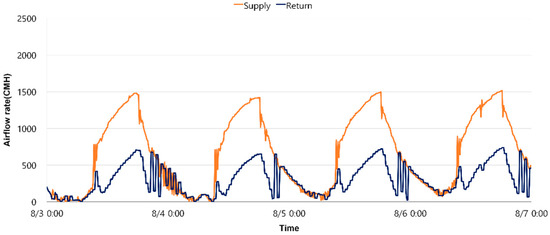
Figure 9.
Supply and return airflow rates under the proposed pressure control (Case A).
When the proposed pressure control was used, the change in infiltration rate according to the occupancy was almost constant even when the occupancy changed. When comparing the infiltration rate according to the outside temperature, a daily cycle was observed in which the infiltration rate decreased during the day and increased at night when the outside temperature was low and the heating load was small. In addition, when compared to the building envelope infiltration rate when the HVAC system was not operating, the infiltration rate was approximately 500 CMH lower on average when indoor occupants were present. This is believed to be because when the pressure control proposed in the VAV system was used, the return airflow rate was lower than the supply airflow rate, creating a positive pressure inside the room compared to the outside, which reduced the infiltration rate. In other words, it was confirmed that the infiltration rate decreased because the indoor–outdoor pressure difference decreased due to the operation of the HVAC system.
3.4. Analysis of Infiltration Rates According to Pressure Control
The characteristics of supply and return airflow rates by control method according to changes in the number of occupants were compared. In the case of the fan tracking control method, the supply airflow rate decreased in proportion to the indoor load as the number of occupants decreased from 30 to 20 and then to 10. However, the decrease in the return airflow rate was smaller than that of the supply airflow rate, and as a result, the difference between the supply and return airflow rates increased to 49 CMH, 198 CMH, and 441 CMH, respectively. On the other hand, the volumetric tracking control method is designed to always keep the supply and return airflow rates the same, so there was no difference between the supply and return airflow rates even when the number of occupants changed. Meanwhile, the proposed pressure control (Control_RA) method is designed to maintain positive indoor pressure by operating the return airflow rate lower than the supply airflow rate. When the number of occupants was 30, 20, and 10, the return airflow rate was operated lower than the supply airflow rate by approximately 721 CMH, 655 CMH, and 469 CMH, respectively.
[Figure 10] compares the average infiltration rate during the simulation period (9:00 to 18:00) according to the pressure control of the VAV system. In the case of fan tracking control, the infiltration rate increased from 904 CMH to 1122 CMH when the indoor occupancy decreased from 30 to 10.
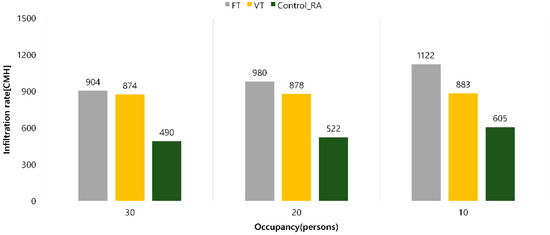
Figure 10.
Comparison of infiltration rate by occupant by pressure control.
When the proposed pressure control method was applied, when the number of occupants was 30, the Control_RA method showed an infiltration rate reduction effect of approximately 45.8% compared to the FT method and approximately 43.9% compared to the VT method. When the number of occupants was 20, the Control_RA method showed an infiltration rate reduction effect of approximately 46.7% compared to the FT method and approximately 40.5% compared to the VT method. When the number of occupants was 10, the Control_RA method showed an infiltration rate reduction effect of approximately 46.1% compared to the FT method and approximately 31.5% compared to the VT method. Therefore, it was confirmed that the infiltration rate reduction effect was more than 30% in all cases.
3.5. Energy Consumption Analysis
To estimate the total fan energy consumption in August according to fan control methods in VAV systems, the bin method was utilized. The bin method divides continuous data into ranges and analyzes the frequency of data occurrence within each range [20]. [Figure 11] shows the changes in supply airflow rate and return airflow rate according to outdoor temperature changes under fan tracking control. The occupancy load is 40, the maximum occupancy. In the high outdoor temperature range (35 °C to 27 °C), the supply airflow rate remains relatively high, and the return airflow rate also shows a similar trend. This is interpreted as a result of the high cooling load, which increases the supply airflow and correspondingly increases the return airflow rate. As the outdoor temperature decreases from 26 °C to 20 °C, the indoor–outdoor temperature difference narrows, reducing heating and cooling loads. Consequently, the supply airflow rate decreased, while the return airflow rate tends to remain constant. The difference between the supply airflow rate and the return airflow rate was greatest when the indoor load was low and the supply airflow rate was operated at the minimum airflow rate, generating an infiltration rate load of approximately 2000 CMH. The infiltration rate load caused by the increase in the return airflow rate compared to the supply airflow rate leads to an increase in the cooling load. When calculated with blank data, this increases by approximately 44% compared to the existing indoor load.
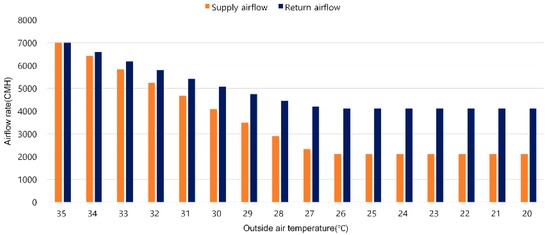
Figure 11.
Supply and return airflow rates during fan tracking control.
In volumetric tracking control, both the supply airflow rate and the return airflow rate remain constant depending on the outdoor temperature. Therefore, it is believed that no pressure difference occurs due to the operation of the HVAC system.
[Figure 12] shows the supply airflow rate and return airflow rate under the proposed pressure control. The proposed pressure control method assumes a slightly positive indoor/outdoor pressure difference of 5 Pa due to the supply and return airflow rates. The calculated difference between the supply and return airflow rates is approximately 1600 CMH. The return airflow rate is 1600 CMH less than the supply airflow rate across the entire outdoor temperature range.
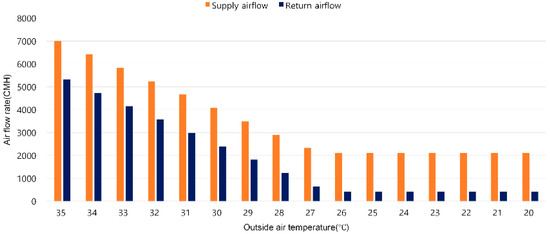
Figure 12.
Supply and return airflow rates under the proposed pressure control.
[Figure 13] shows the results of comparing the supply fan energy consumption by pressure control method (FT, VT, Control_RA) according to the occupancy level. When the energy consumption was analyzed by dividing the occupancy level into 40, 30, 20, 10, and 0 people, the FT method showed the highest energy consumption and the Control_RA method recorded the lowest consumption. Specifically, when the cooling load was high with 40 people in the room, the supply fan energy consumption of the FT method was 1204 kWh, that of the VT method was 1130 kWh, and that of the Control_RA method was 1073 kWh. When the room was not occupied, the FT method was 1092 kWh, the VT method was 1016 kWh, and the Control_RA method was 960 kWh.
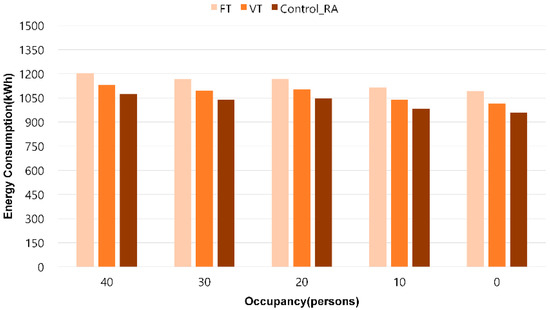
Figure 13.
August supply fan energy consumption.
[Figure 14] compares the ventilation fan energy consumption by pressure control method (FT, VT, Control_RA) according to the occupancy level. The analysis of energy consumption showed that the FT method had the highest energy consumption, and the Control_RA method had the lowest consumption. Specifically, when the occupancy level was 40, the return fan energy consumption for the FT method was 760 kWh, for the VT method was 289 kWh, and for the Control_RA method was 71 kWh. When the occupancy level was not occupied, the FT method consumed 684 kWh, the VT method 201 kWh, and the Control_RA method 36 kWh.
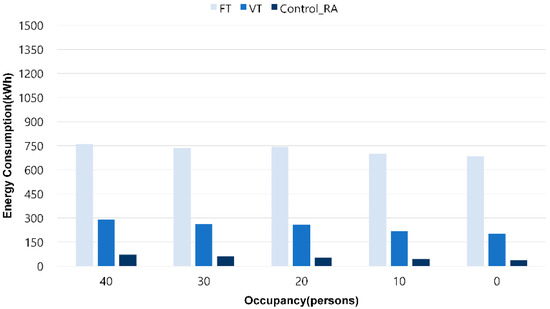
Figure 14.
August return fan energy consumption.
The energy savings from the supply and return fans increased with fewer occupants. The Control_RA method intentionally maintains the supply airflow rate higher than the return airflow rate, thereby creating a positive pressure state due to HVAC system operation, thereby reducing infiltration rate load and contributing to energy savings.
This study demonstrated that a pressure control strategy based on infiltration rate prediction effectively addresses the limitations of existing FT and VT methods, simultaneously reducing infiltration rate and improving energy efficiency. Future research should further validate the algorithm’s performance under various building conditions and environments and propose detailed design strategies to optimize it.
This study examined the relationship between supply and return airflow rates and infiltration rate in VAV systems, confirming that applying this relationship to pressure control can improve infiltration rate control and energy efficiency.
First, the difference between supply and return airflow rates and the indoor–outdoor pressure difference were experimentally derived as having an exponential relationship. This relationship was then applied to an airtightness-based leakage function to predict infiltration rate. This is significant as it overcomes the limitations of previous studies, which either relied on database-based airtightness values or focused solely on control performance.
Second, the proposed pressure control algorithm based on infiltration rate prediction significantly reduced infiltration rate compared to FT and VT methods under all conditions. It particularly improved the problem of increased infiltration rate due to negative pressure in the FT method, demonstrating an infiltration rate suppression effect of up to 46.1%. This demonstrates the effectiveness of the control strategy that maintains a positive indoor–outdoor pressure differential.
Third, from an energy consumption perspective, the reduced infiltration rate led to a decrease in cooling load. Significant savings were confirmed for both return and supply fans compared to existing control methods. Notably, return fan energy consumption was reduced by approximately 94.7% compared to the FT method, showing that infiltration rate prediction-based control is also advantageous in terms of energy efficiency.
However, this study only considered pressure changes caused by HVAC system operation and did not account for pressure variations due to external factors such as outdoor wind speed or indoor–outdoor temperature differences. Furthermore, since it relied on simulations based on TRNSYS and TRNFLOW, future verification of its applicability in actual systems is necessary.
4. Conclusions
This study proposes a method to predict infiltration rate based on supply and return airflow rates in VAV systems and demonstrates that applying this to pressure control algorithms can overcome limitations of existing control methods. The proposed algorithm reduces infiltration rate by up to 46.1% while maintaining indoor thermal comfort and significantly lowers fan energy consumption. The proposed method presents a new control strategy that reduces energy loss due to building envelope heat gain and enhances the efficiency of HVAC systems. To analyze the relationship between the supply and return airflow rates of a VAV system and the indoor–outdoor pressure differential in the target space, the indoor–outdoor pressure differential was measured by varying the supply and return airflow rates. Experimental results confirmed an exponential relationship between the indoor–outdoor pressure difference and the supply and return airflow rates difference, enabling prediction of the pressure difference using the derived equation. Substituting the relationship equations between supply and return airflow rates and pressure difference into the leakage coefficient derived from airtightness performance measurements allowed prediction of infiltration rate. The reliability of the predicted infiltration rate compared to measured values was confirmed. Furthermore, this study experimentally analyzed the relationship between supply and return airflow rates and heat gain, and evaluated its practical applicability by proposing a return fan operation plan utilizing this relationship. Compared to the conventional pressure control method, the proposed operation plan was confirmed to reduce both the building envelope infiltration rate and fan energy consumption. However, since the prediction model and control algorithm presented in this study only considered pressure changes caused by HVAC system operation, future research should develop a more precise algorithm that incorporates outdoor conditions (wind speed, indoor–outdoor temperature difference, etc.). Furthermore, applying and verifying automatic control in actual building systems is necessary to expand the practical applicability of this control scheme in the field. Additionally, the proposed pressure control strategy offers building operators reduced energy costs through decreased infiltration rate and lower fan power consumption while ensuring a stable indoor environment. For control device and fan manufacturers, developing smart controllers incorporating infiltration rate prediction capabilities can enhance product competitiveness. For institutions supplying facilities to buildings, it provides a basis for policies aimed at building energy savings and improved airtightness performance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, K.-W.K., H.-J.K. and Y.-H.C.; software, visualization, validation, formal analysis and writing—original draft, K.-W.K.; investigation, resources, writing—review and editing, M.-J.K., J.-H.L. and H.-J.K.; supervision and project administration, Y.-H.C.; funding acquisition, Y.-H.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the 2023 Yeungnam University Research Grant (223A380156); This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea(NRF) grant funded by the Korea government(MSIT) (RS-2025-00561486).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Kyung-Won Kim was employed by the company Enertec United. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- RDH Building Engineering Ltd. Air Leakage Control in Multi-Unit Residential Buildings: Development of Testing and Measurement Strategies to Quantify Air Leakage in MURBs; Project No. 5314.00; Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Ji, Y.; Duanmu, L.; Hu, S. A Case Study of Air Infiltration for Highly Airtight Buildings under the Typical Meteorological Conditions of China. Buildings 2024, 14, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straube, J.F.; Burnett, E.F.P. Building Science for Building Enclosures; Building Science Press: Westford, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- ASHRAE. ASHRAE Handbook—Applications, Ch. 47: Design and Application of Controls; American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc.: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Phalak, K.; Wang, G. Minimum outdoor air control and building pressurization with lack of airflow and pressure sensors in air-handling units. J. Archit. Eng. 2016, 22, 04015017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASHRAE. ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 62.1—Ventilation for Acceptable Indoor Air Quality; American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc.: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- ASHRAE. ASHRAE Handbook—HVAC Systems and Equipment, Ch. 46: VAV Systems; American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc.: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M. Variable speed drive volumetric tracking for airflow control in variable air volume systems. J. Sol. Energy Eng. 2003, 125, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Piette, M.A.; Zhou, N. Characterizing variations in variable air volume system controls. Energy Build. 2017, 135, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ahmat, M.; Cao, H.; Di, F. Optimization of double-closed-loop control of variable-air-volume air-conditioning system based on dynamic response model. Buildings 2024, 14, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, M.H.; McWilliams, J.A. Air Leakage of U.S. Homes: Model Prediction. In Proceedings of the Buildings X Conference—Thermal Performance of the Exterior Envelopes of Whole Buildings, Roomvent 2007 Session, Helsinki, Finland, 13–15 June 2007; Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, Y.P.; Mumma, S.A. Variable air volume ventilation control strategies analysed in six climate zones. Int. J. Energy Res. 1999, 23, 371–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poza-Casado, I.; Meiss, A.; Padilla-Marcos, M.Á.; Feijó-Muñoz, J. Airtightness and energy impact of air infiltration in residential buildings in Spain. Int. J. Vent. 2020, 20, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmotte, C. Airtightness of buildings—Considerations regarding place and nature of pressure taps. In Proceedings of the 40th AIVC–8th TightVent–6th venticool Conference, Ghent, Belgium, 15–16 October 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Krstić, H.; Koški, Ž.; Otković, I.I.; Španić, M. Application of neural networks in predicting airtightness of residential units. Energy Build. 2014, 84, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Duanmu, L.; Hu, S. Prediction model of air infiltration in single-zone buildings with high airtightness. Energy Built Environ. 2023, 4, 653–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, I.S.; Liu, M.; Liu, G. Application of fan airflow stations in air-handling units. Energy Eng. 2007, 104, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E779-10; Standard Test Method for Determining Air Leakage Rate by Fan Pressurization. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010.
- Ministry of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs (MLTM). Korean Building Mechanical System Design Standard; The Society of Air-Conditioning and Refrigerating Engineers of Korea (SAREK): Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2010.
- Lee, M.K.; Kim, J.T. Developing the prediction program of heat and cooling loads by modified bin methods. J. Korean Sol. Energy Soc. 2001, 21, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).

