- Article
Influenza A Virus Infection Induces Preferential Increases in Long-Chain Ceramides
- Savannah McKenna,
- Kwang Il Jung and
- Bumsuk Hahm
- + 3 authors
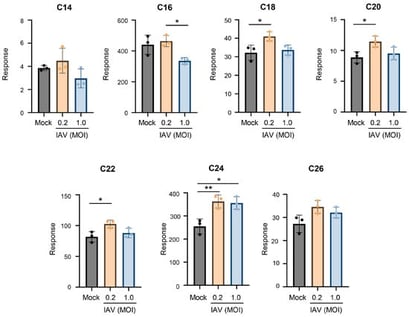
Influenza is a persistent public health concern worldwide. The elucidation of influenza A virus (IAV)–host interactions and the identification of host factors that regulate IAV infection would be beneficial for combating and treating the disease. Ceramides, comprising a host sphingolipid family, have been shown to regulate virus infections. However, the effect of IAV on individual ceramides remains unknown. This study aimed to investigate the changes in ceramide species during the infection of human lung epithelial A549 cells and human primary tracheal epithelial cells with IAV. We established a method utilizing UHPLC-MS analysis to measure individual ceramides (C14- to C26-ceramide). The results indicate that two main ceramide species, C16- and C24-ceramide, constitute approximately 80% of the ceramide population in human respiratory epithelial cells. Following IAV infection, these ceramides were found to undergo a shift in abundance, with a reduction in C16-ceramide and an increase in C24-ceramide, under various infection conditions. Primarily, IAV infection led to an increase in multiple long-chain ceramides. These findings could provide details for understanding how the ceramide system is disrupted during influenza virus infection and to further support the ongoing efforts to understand influenza–host interactions.
10 March 2026