- Article
A Nation Veering off Course: Implications for Efficacy and Well-Being
- Kristina G. Chamberlin,
- J. Doris Dai and
- Stephanie A. Fryberg
- + 2 authors
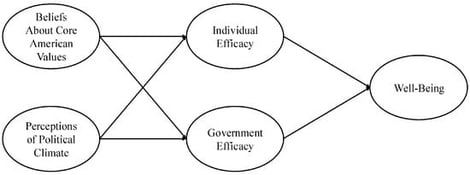
The United States has undergone rapid and, at times, unprecedented political changes in 2025. Recent national polling indicates that many Americans—across political parties—believe that the country is heading in the wrong direction. In a preregistered study with more than 7000 adults residing in the United States, we explored the implications of these widespread concerns for individuals’ psychological functioning. As theorized, individuals who believed that the political climate was worsening and viewed the United States as failing to live up to its core national values experienced lower efficacy, both in terms of their personal ability to influence politics (i.e., individual efficacy) and their confidence in the government to uphold its obligations to the nation and its residents (i.e., government efficacy). In turn, these individuals reported worse overall well-being and less effective coping in response to stressors related to the political climate. These relationships persisted after accounting for the participants’ 2024 presidential vote choice and political party affiliation. Together, these findings suggest that the political turbulence Americans are experiencing exerts a measurable, bipartisan toll on Americans’ psychological and social health.
10 March 2026