- Article
Clinically Significant ISUP Upgrading in the Multiparametric MRI Era: Biopsy Tumor Burden Outperforms Complex Machine Learning Models in a Single-Center Exploratory Cohort
- Cristian Condoiu,
- Adelina Baloi and
- Razvan Bardan
- + 9 authors
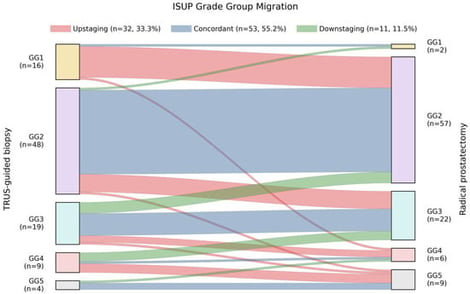
Background/Objectives: Despite multiparametric MRI (mpMRI)-guided biopsy, clinically significant upgrading (CSU) of ISUP Grade Group (GG) at radical prostatectomy (RP) remains common in prostate cancer (PCa). We aimed to identify predictors of CSU (biopsy GG ≤ 2 to RP GG ≥ 3) using routine preoperative variables, and to benchmark a parsimonious logistic model against multiple machine learning (ML) classifiers. Methods: In this single-center exploratory analysis, 96 consecutive PCa patients underwent pre-biopsy mpMRI, systematic ± MRI-targeted biopsy, and RP. Predictive modeling was restricted to biopsy GG 1–2 patients (n = 64). LASSO-guided feature selection and Firth-penalized logistic regression were used to build a locked reference model, evaluated against ML classifiers using cross-validated discrimination, calibration, and decision curve analysis. Results: CSU occurred in 10/64 patients (15.6%). Positive core ratio was the dominant independent predictor (adjusted OR 1.54 per 10% increase, 95% CI 1.10–2.17). PSA density (PSAD) showed a consistent positive association but did not retain independent significance. The locked two-variable model (AUC ≈ 0.75–0.79) outperformed all ML classifiers in discrimination, calibration, and net clinical benefit; however, the limited event count (n = 10) constrains model stability, and these findings require external validation. Conclusions: In a PCa mpMRI-informed diagnostic pathway, CSU is primarily driven by biopsy tumor burden. A simple logistic model based on positive core ratio and PSAD outperformed more complex ML approaches in this exploratory cohort, supporting integration of biopsy tumor burden metrics into preoperative risk stratification pending external validation.
24 February 2026






![IRX gene expression in hormone-sensitive cancer cell lines. (A) Expression of IRX1 in endometrial, ovarian, breast and prostate cancer cell lines from PCTA database and from qRT-PCR. (B) Expression of IRX2 in endometrial, ovarian, breast and prostate cancer cell lines from PCTA database and from qRT-PCR. (C) Expression of IRX3 in endometrial, ovarian, breast and prostate cancer cell lines from PCTA database and from qRT-PCR. (D) Expression of IRX4 in endometrial, ovarian, breast and prostate cancer cell lines from PCTA database and from qRT-PCR. (E) Expression of IRX5 in endometrial, ovarian, breast and prostate cancer cell lines from PCTA database and from qRT-PCR. (F) Expression of IRX6 in endometrial, ovarian, breast and prostate cancer cell lines from PCTA database and from qRT-PCR (PCTA [1], Log2(TPM + 1)). The quantitative expression of IRX genes in panel of prostate, breast, ovarian and endometrial cancer cell lines (LNCaP, C42B, SKOV3, CAOV3, Ishikawa, HEC-1A, MDA-MB-231, MCF-7). RPL32 was used as the endogenous housekeeping control. The relative fold expression was determined using the ΔΔCT method with respect to the lowest expression in cell lines for each IRX. (IRX1 with respect to LNCAP, IRX2 with respect to HEC-1A, IRX3 with respect to CAOV3, IRX4, IRX5 and IRX6 with respect to MDA-MB-231) (n = 3 biological and n = 3 technical replicates, mean ± SD).](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/cancers/cancers-18-00726/article_deploy/html/images/cancers-18-00726-g001-550.jpg)

