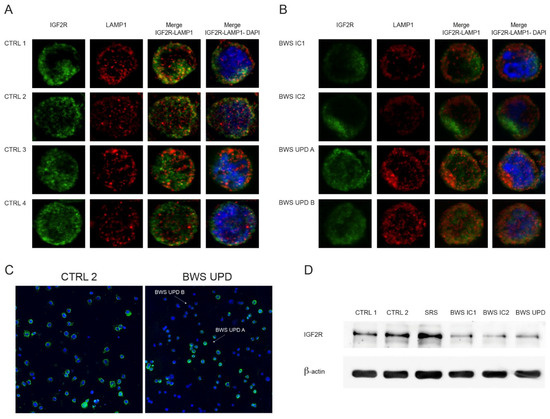
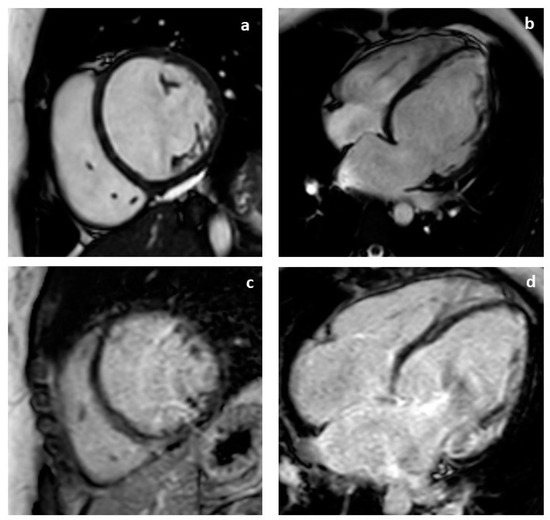
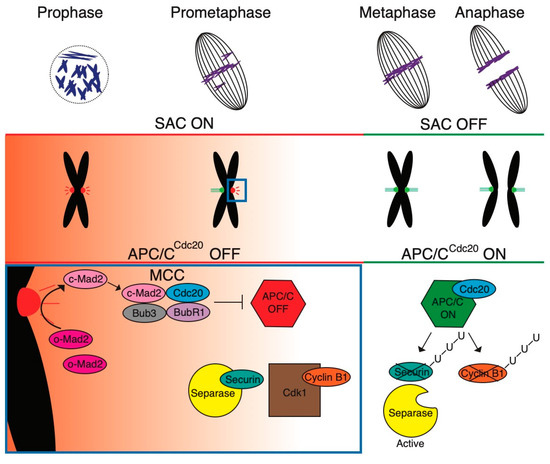
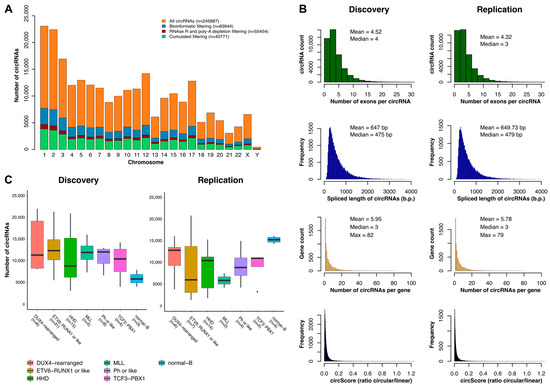
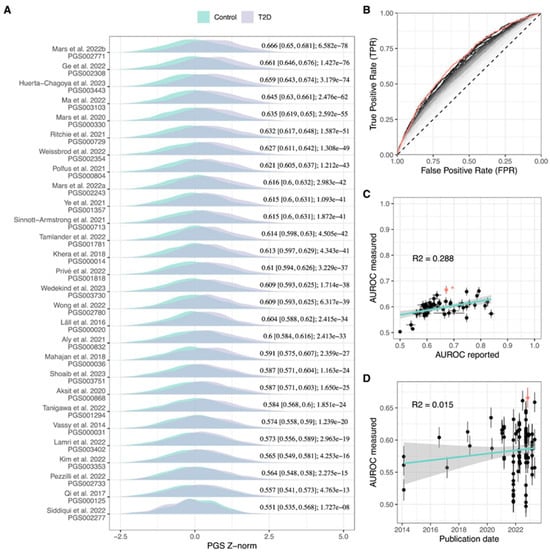
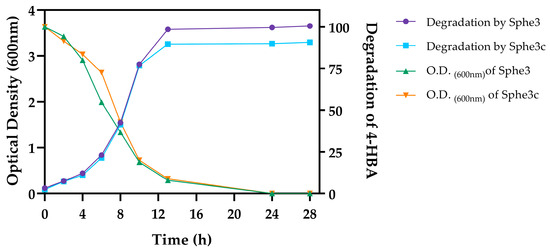
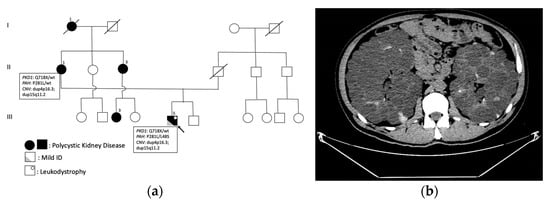
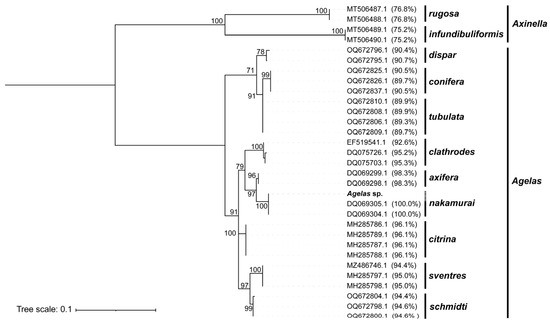
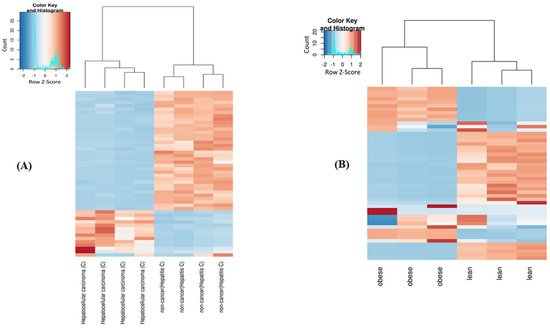
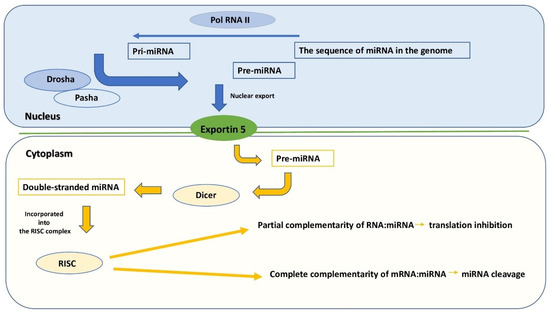
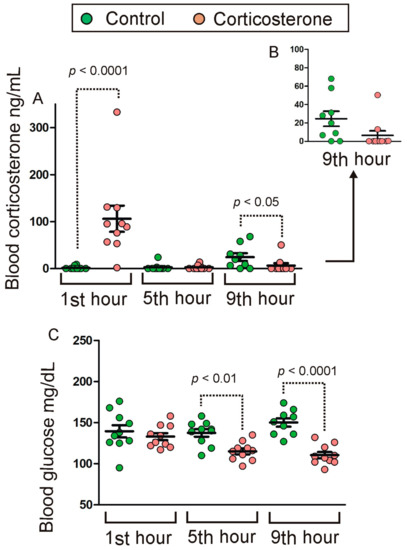
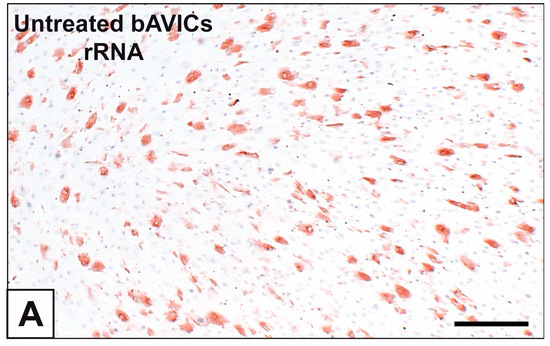
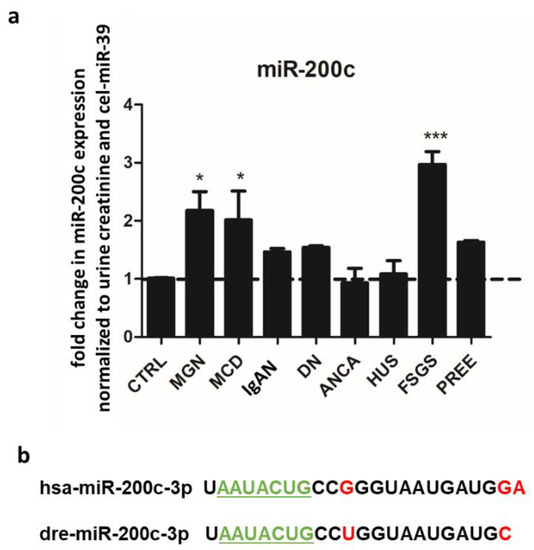
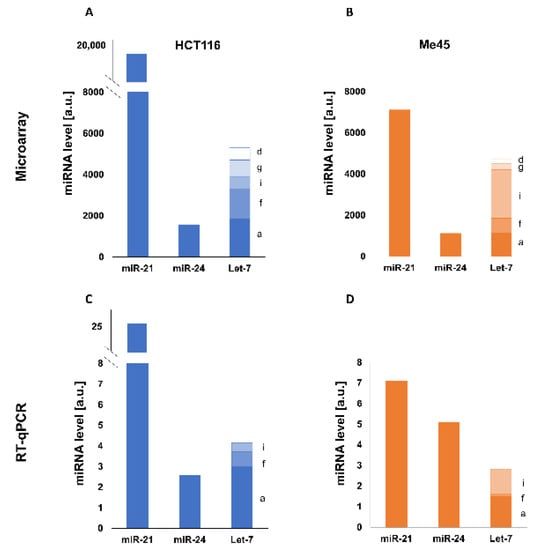
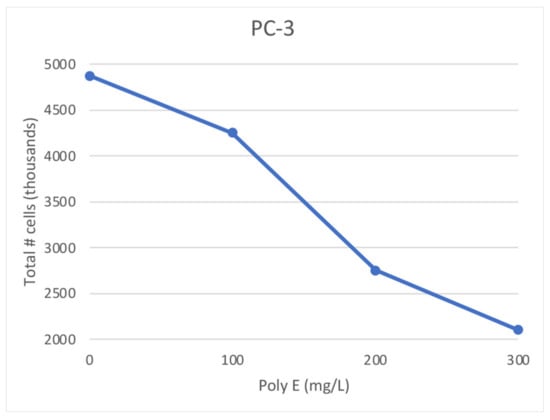
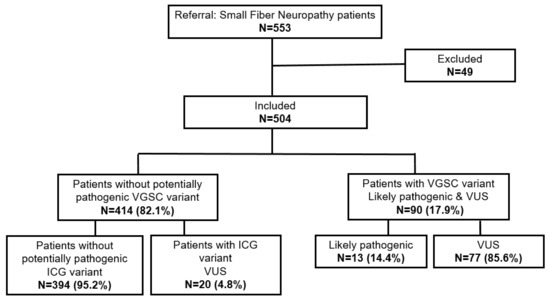
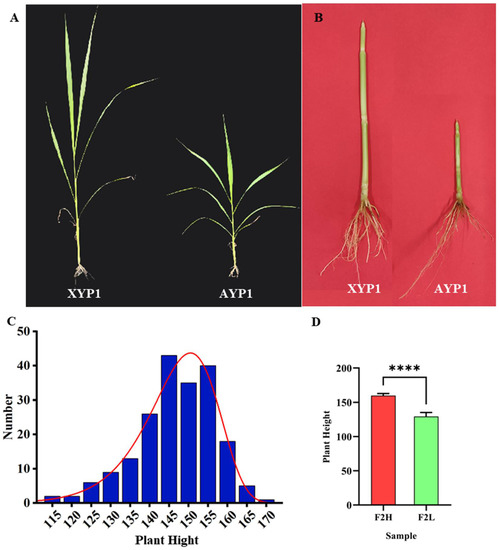
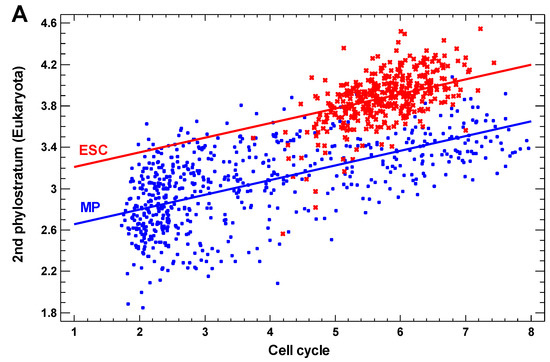
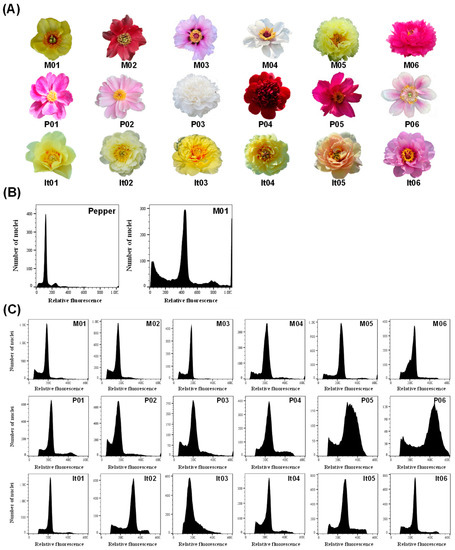
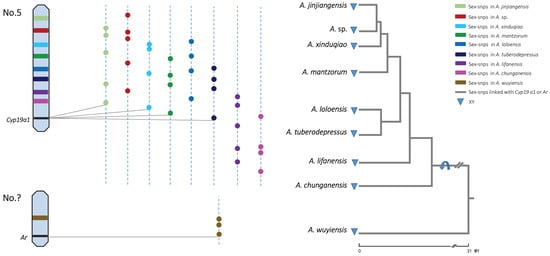
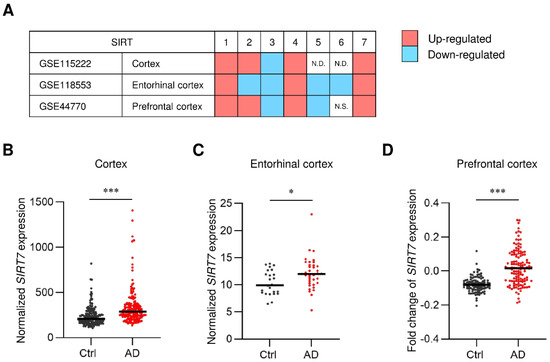
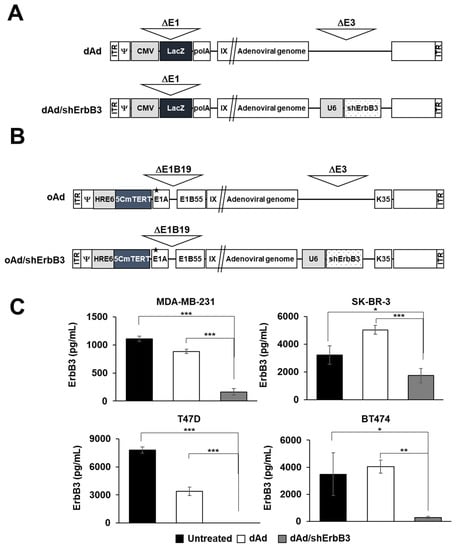
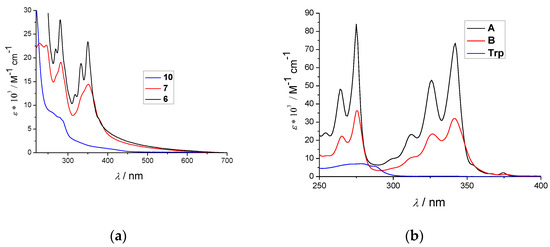
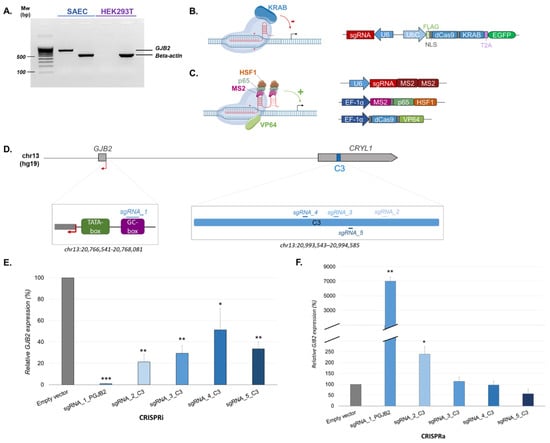
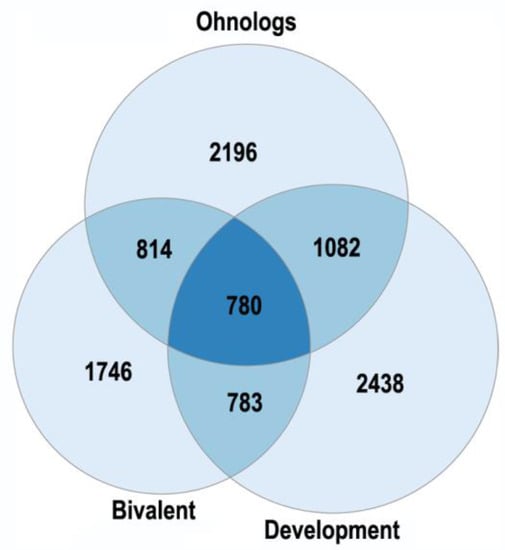
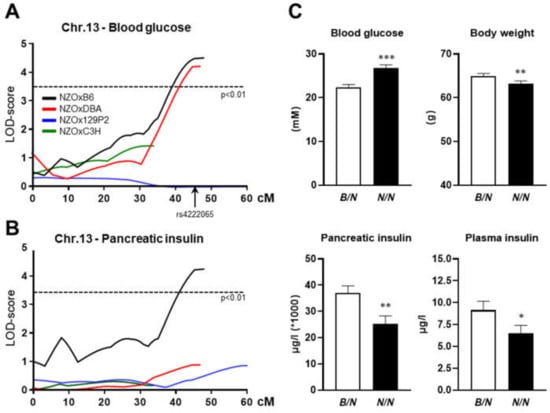
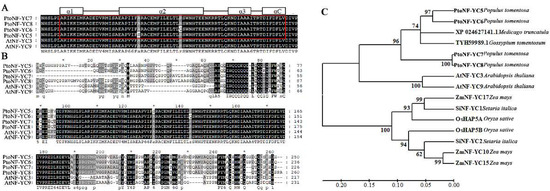
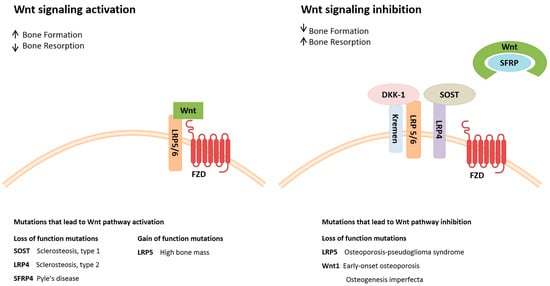
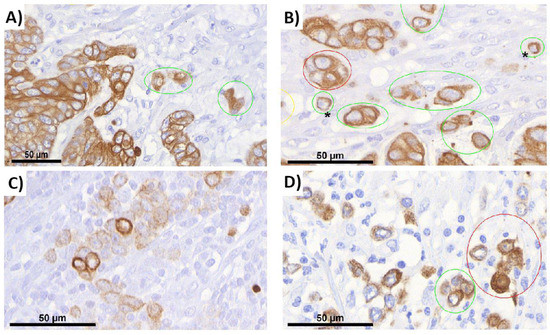
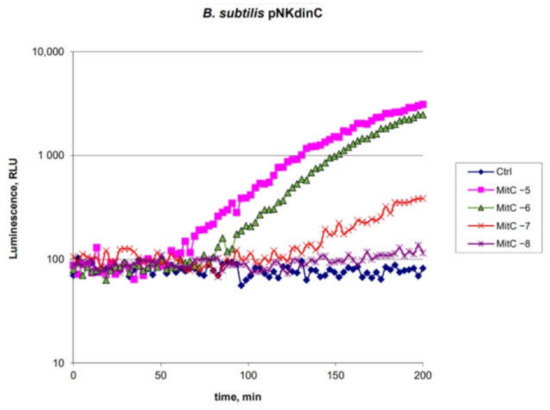
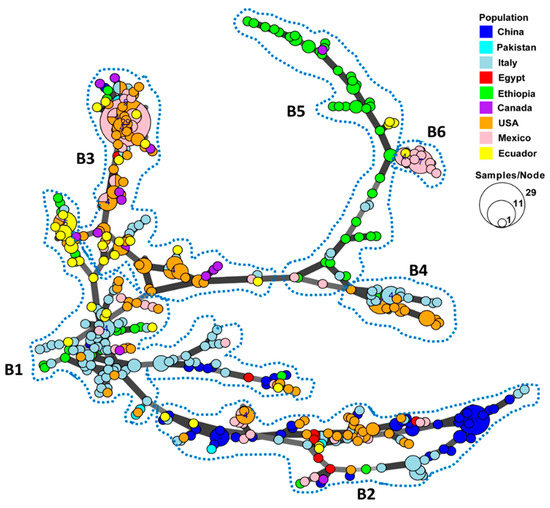
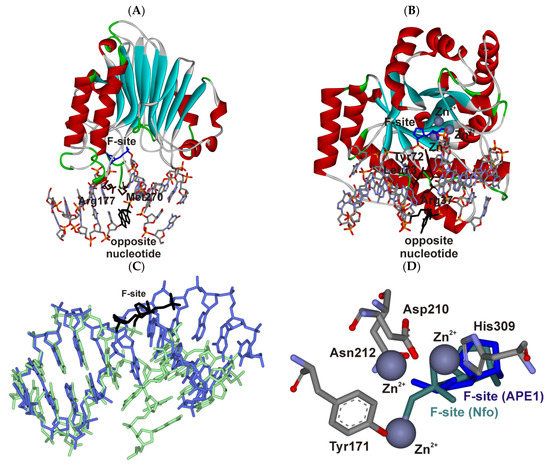
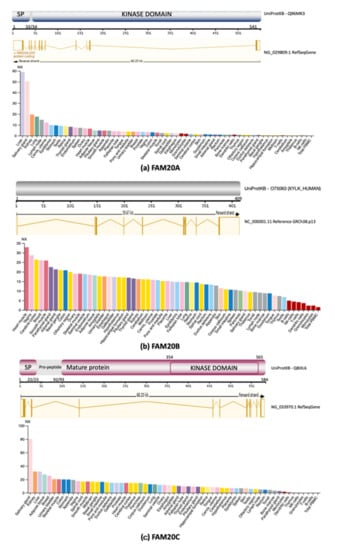
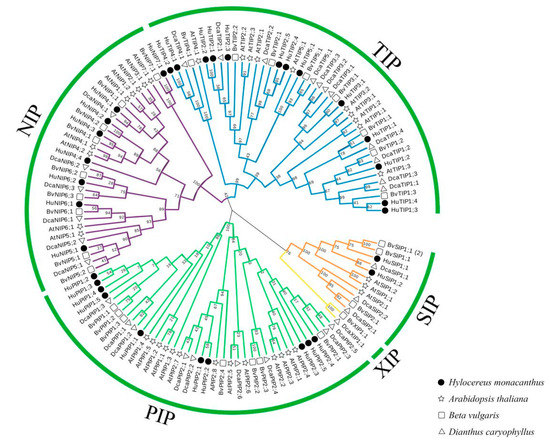
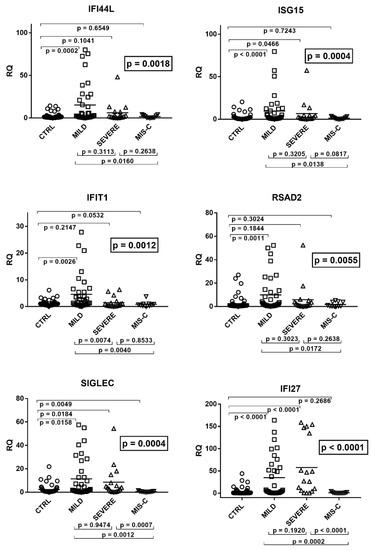
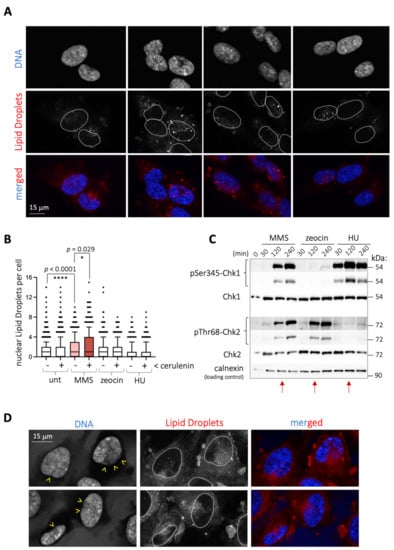
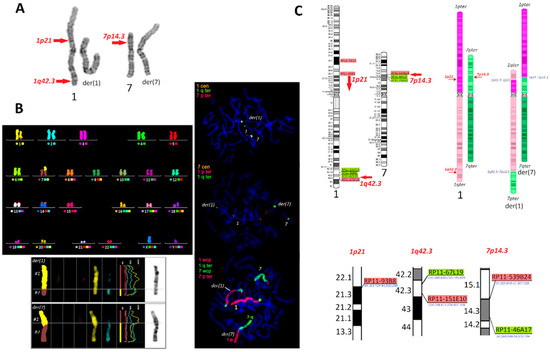
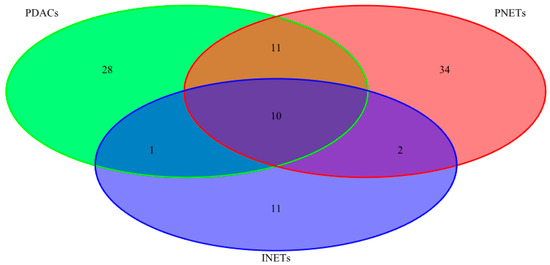
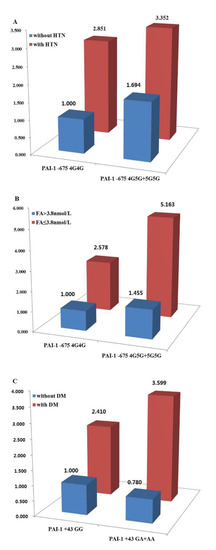
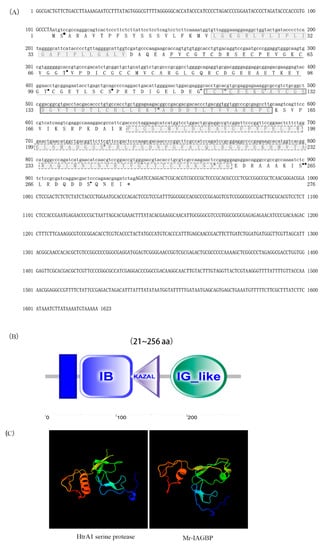
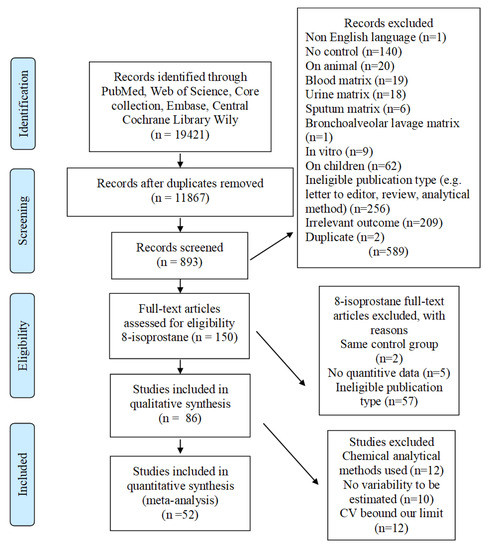
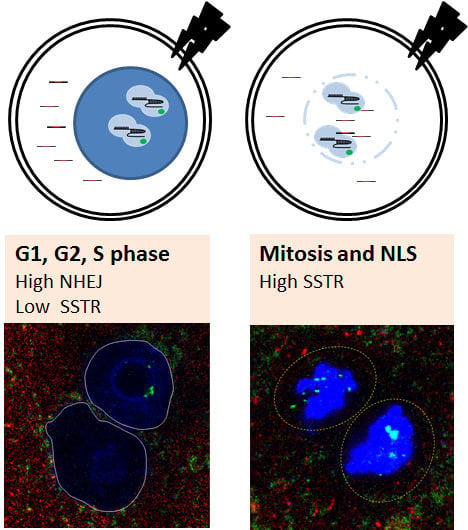
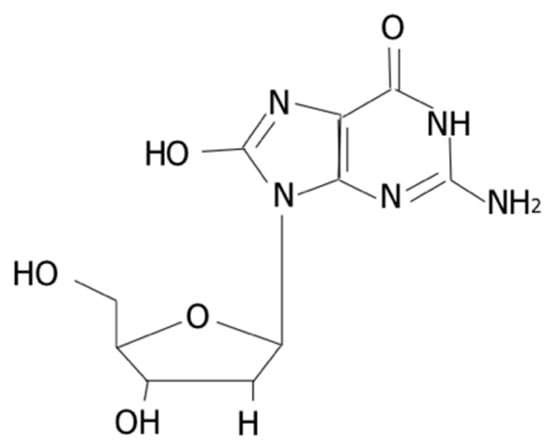
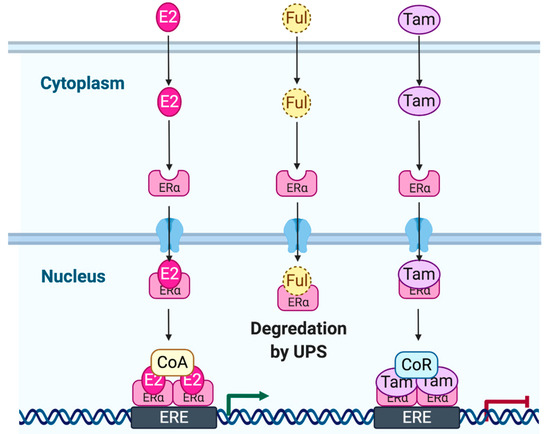
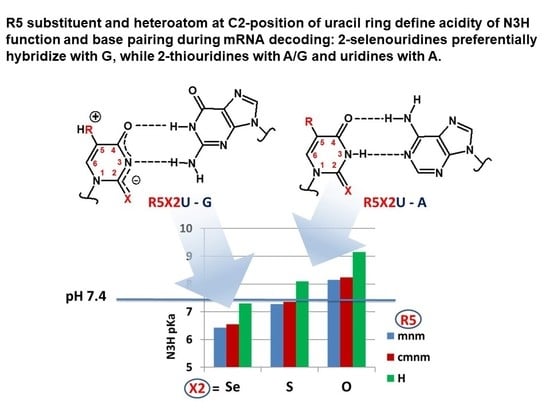
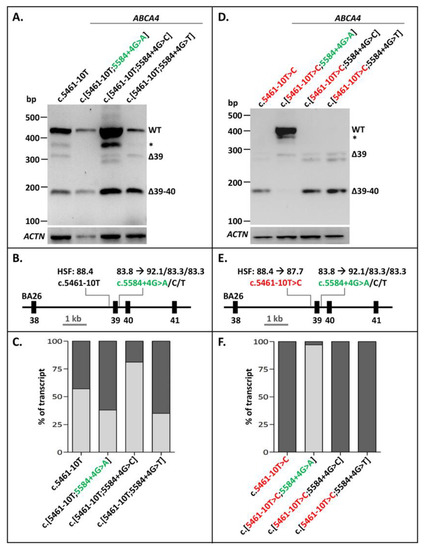
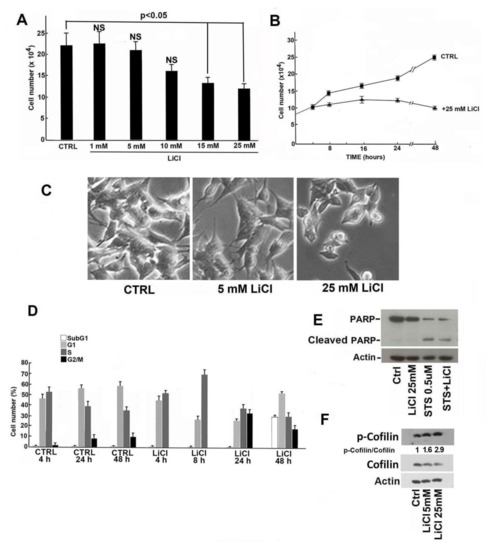
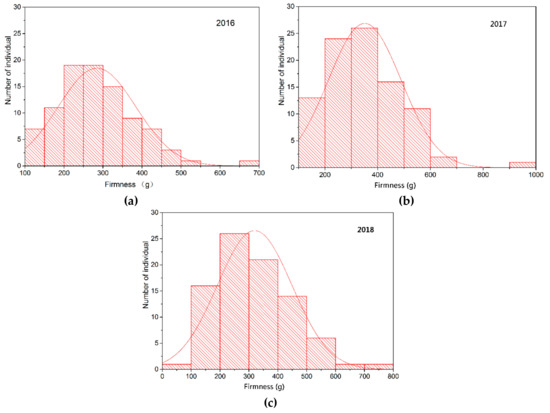
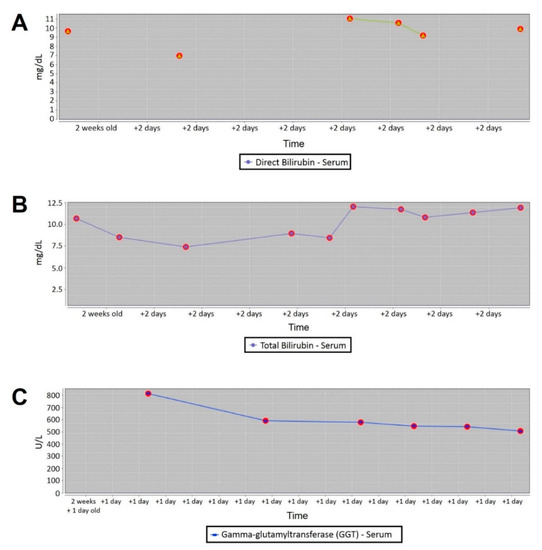
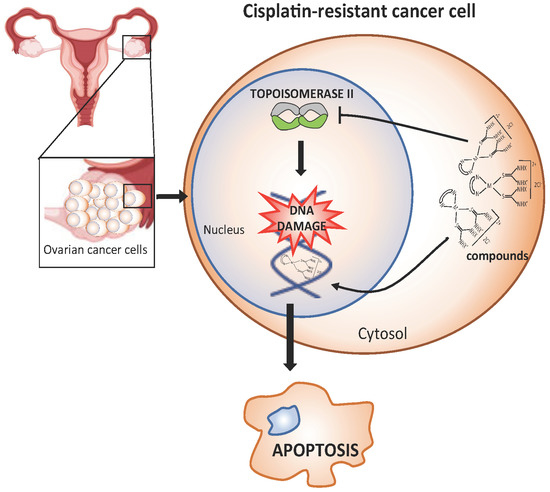
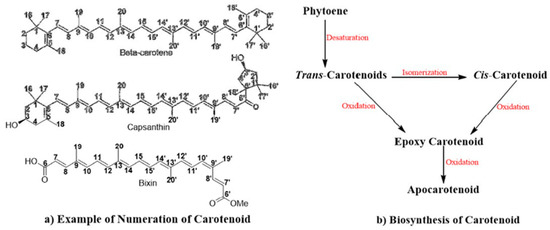
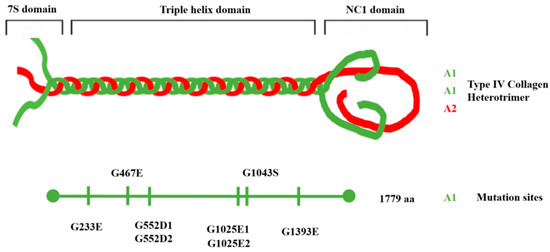
Feature Papers in Molecular Genetics and Genomics
A topical collection in International Journal of Molecular Sciences (ISSN 1422-0067). This collection belongs to the section "Molecular Genetics and Genomics".
Viewed by 906110Editors
2. Department of Translational Medicine, University of Piemonte Orientale, 28100 Novara, Italy
3. Interdisciplinary Research Center of Autoimmune Diseases (IRCAD), University of Piemonte Orientale, 28100 Novara, Italy
Interests: neurodegenerative diseases including Parkinson’s disease; Huntington’s disease; other movement disorders; Alzheimer’s disease; neuroimmune diseases including: multiple sclerosis, inflammatory neuropathies, myasthenia gravis
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
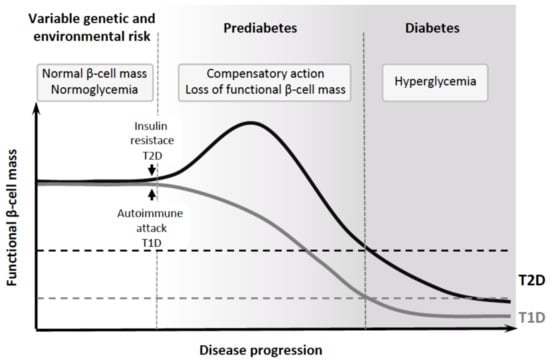
Interests: islet physiology; genetics of diabetes; cell regeneration; drug development
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: precision cancer medicine; precision immuno-oncoloy; precision oncology
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
This Topical Collection “Feature Papers in Molecular Genetics and Genomics” will collect high-quality research articles, short communications, and review articles in all the fields of molecular genetics and genomics. Since the aim of this Topical Collection is to illustrate, through selected works, frontier research in this field, we encourage Editorial Board Members of the Molecular Genetics and Genomics Section of the International Journal of Molecular Sciences to contribute papers reflecting the latest progress in their research field or to invite relevant experts and colleagues to do so. Topics include, but are not limited to, the following:
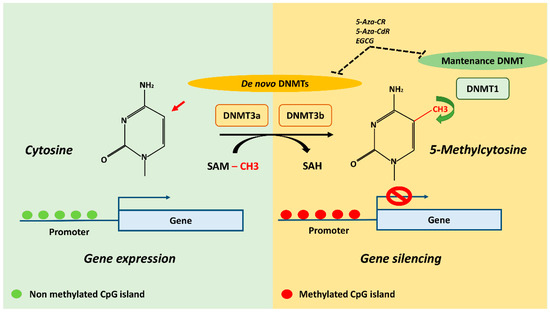
- Gene regulation, chromatin, and epigenetics
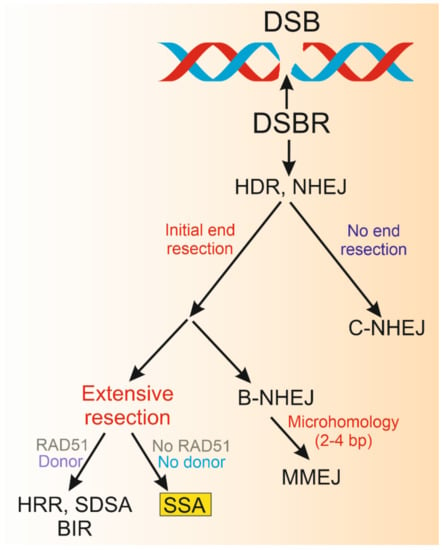
- Genome integrity, repair, and replication
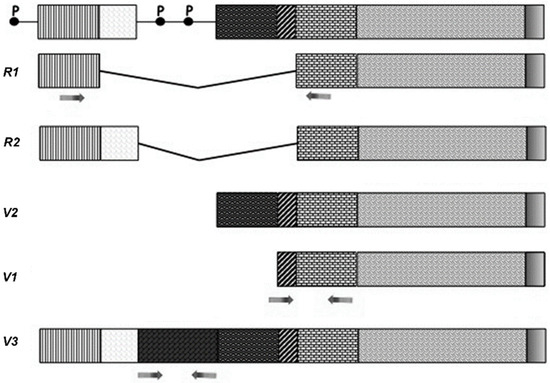
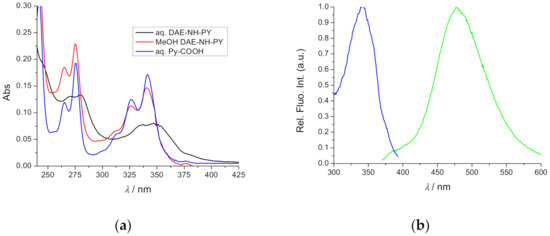
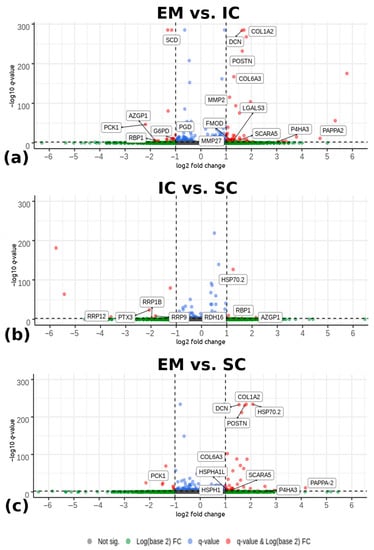
- Genes or genomes related to phenotypes and human physiopathology
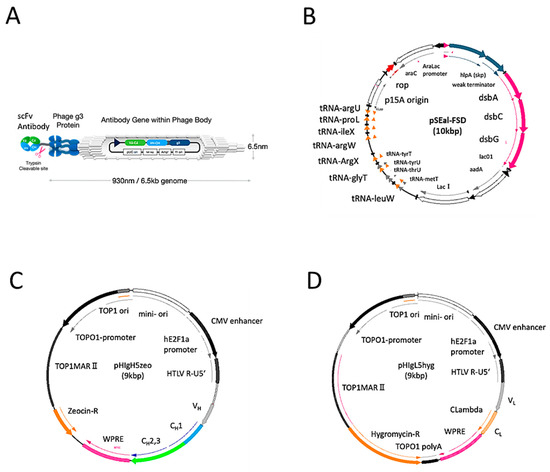
- Gene flow and transfer
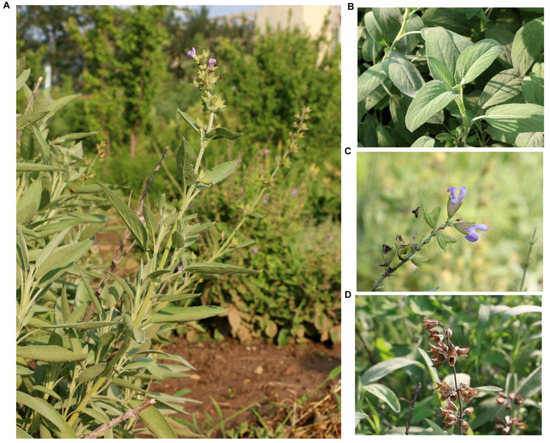
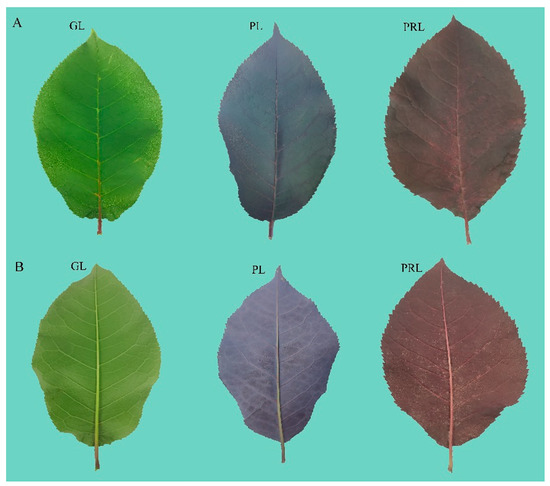
- Plant genetic studies
- Animal genetic studies
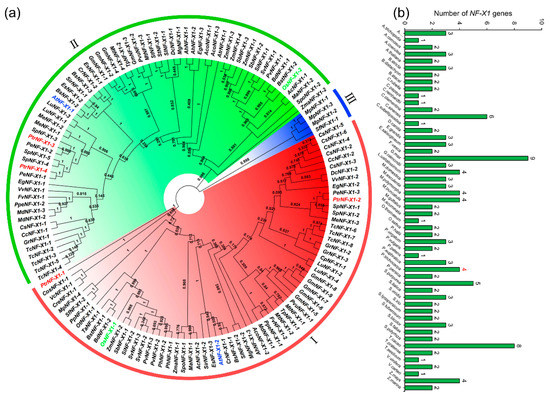
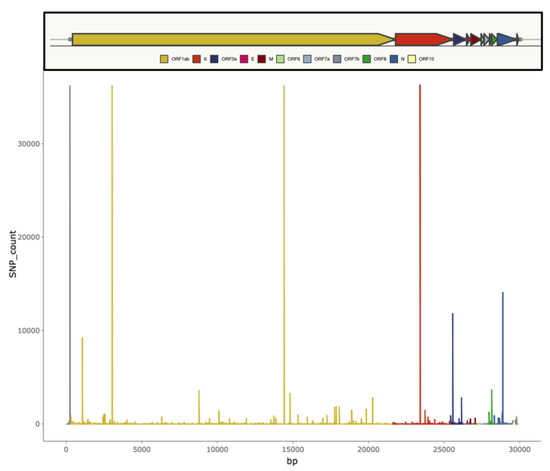
- Evolutionary genomics
Prof. Dr. Cristoforo Comi
Dr. Benoit Gauthier
Prof. Dr. Dimitrios Roukos
Prof. Dr. Alfredo Fusco
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. International Journal of Molecular Sciences is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. There is an Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal. For details about the APC please see here. Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.