Determination and Dissection of DNA-Binding Specificity for the Thermus thermophilus HB8 Transcriptional Regulator TTHB099
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
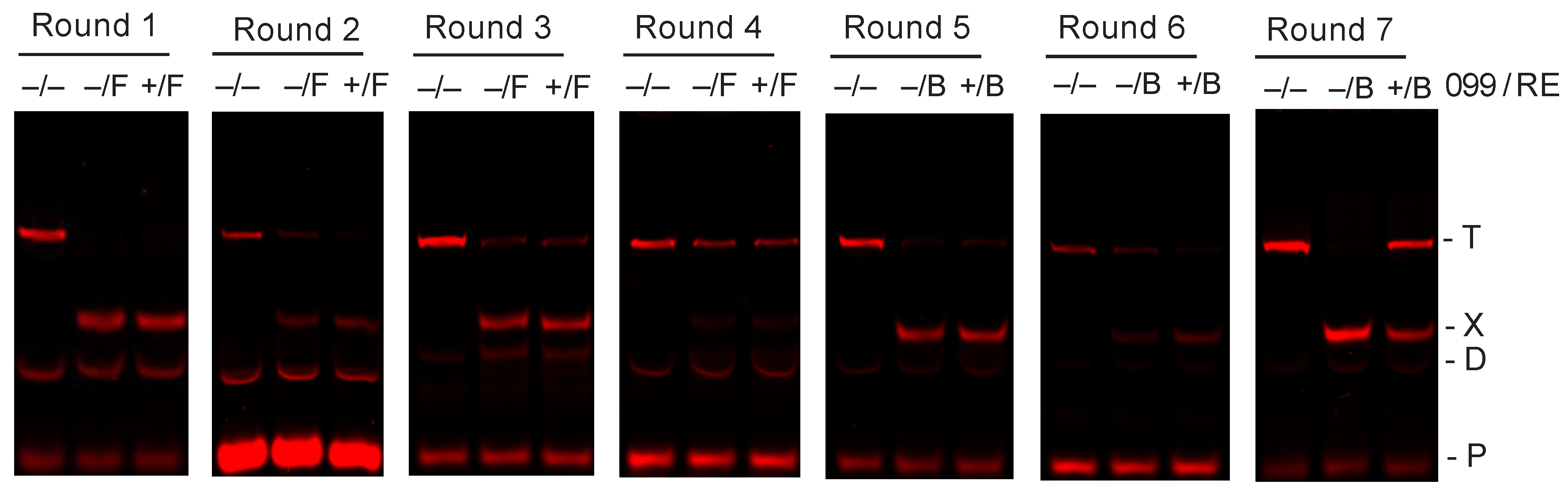
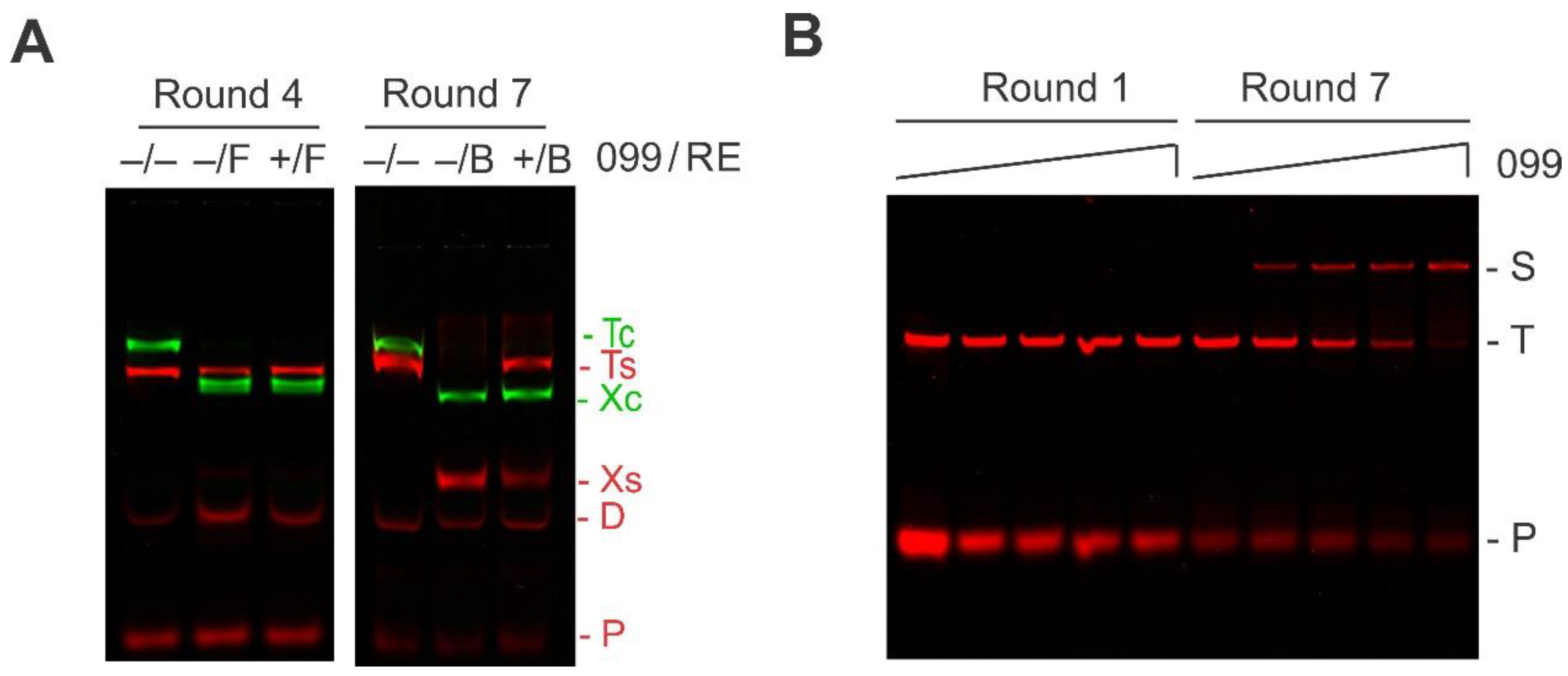
2.1. Preferred TTHB099-Binding Sequences Selected Via REPSA
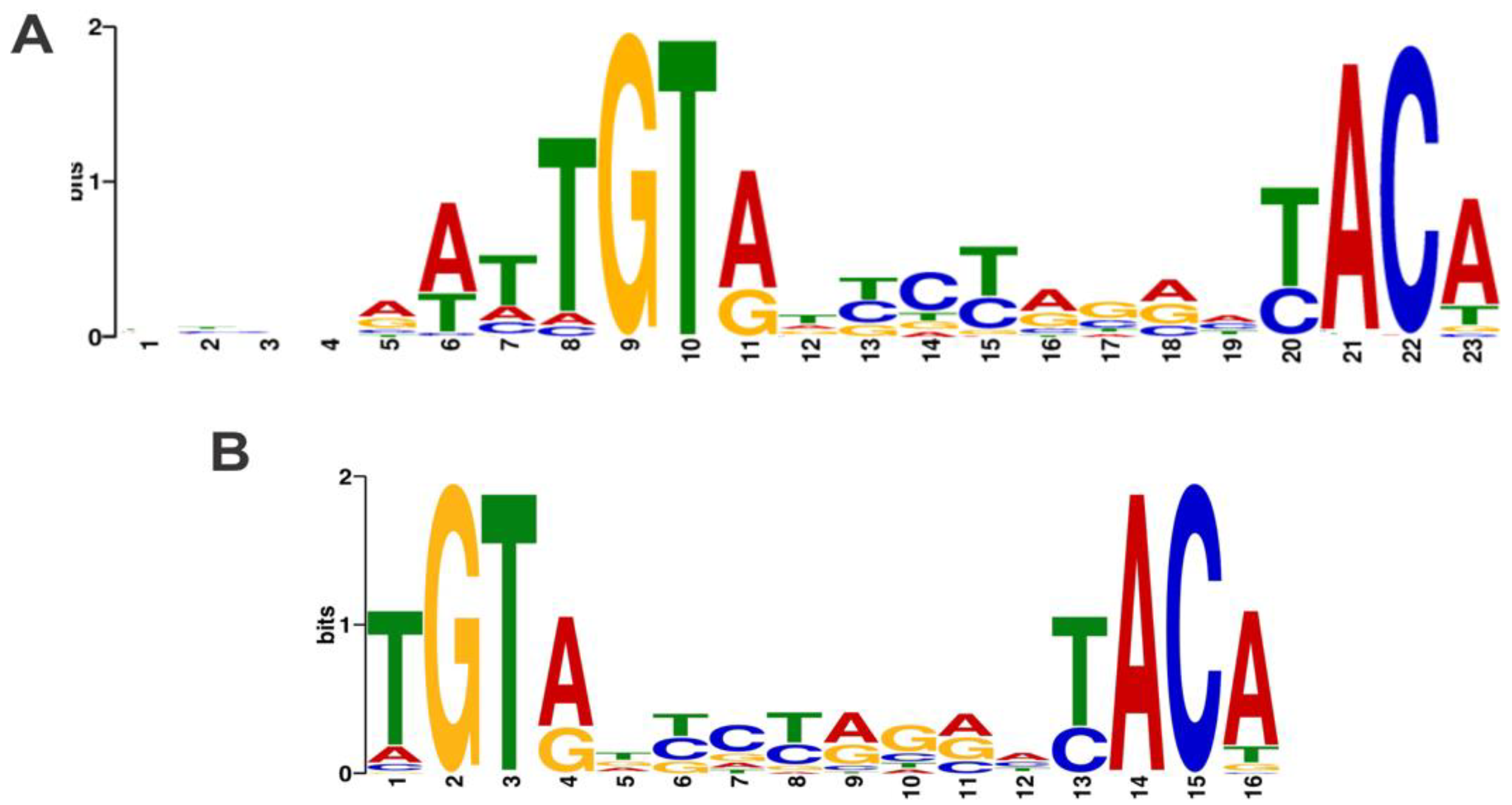
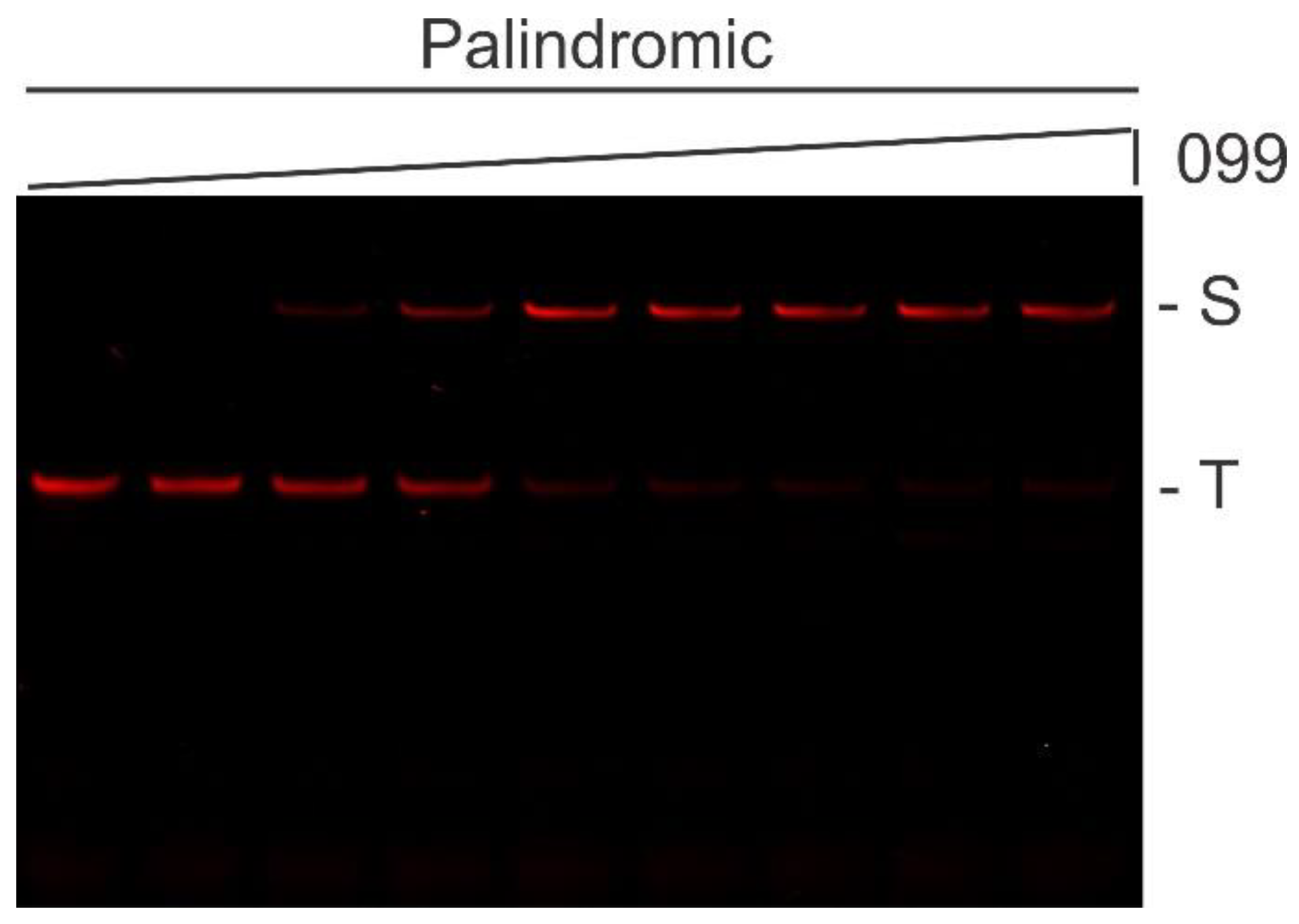
2.2. Identification and Characterization of TTHB099-Binding Motif
2.3. T. thermophilus HB8 Genome-Wide Mapping of the TTHB099-Binding Motif
2.4. Validation of Potential TTHB099-Regulated Genes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Oligonucleotides
4.2. TTHB099 Protein Expression and Purification
4.3. TTHB099-Consensus Sequence Determination
4.4. Protein-DNA Binding Assays
4.5. Bioinformatic Determination of Candidate Regulated Genes
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BLI | Biolayer Interferometry |
| cAMP | 3′,5′-cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate |
| CRP | Cyclic AMP Receptor Protein |
| DOOR2 | Database of PrOkaryotic OpeRons |
| EMSA | Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay |
| ETC | Electron Transport Chain |
| FIMO | Find Individual Motif Occurrences |
| GEO | Gene Expression Omnibus |
| IISRE | Type IIS Restriction Endonuclease |
| IRD7 | IRDye® 700 |
| ISP | Individual Sequencing Particle |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| MEME | Multiple Em for Motif Elicitation |
| NCBI | National Center for Biotechnology Information |
| PGM | Personal Genome Machine |
| REPA | Restriction Endonuclease Protection Assay |
| REPSA | Restriction Endonuclease Protection, Selection, and Amplification |
| TetR | Tetracycline Repressor Protein |
| TF | Transcription Factor |
| TFBS | Transcription Factor Binding Site |
| TSS | Transcription Start Site |
References
- Collado-Vides, J.; Magasanik, B.; Gralla, J.D. Control site location and transcriptional regulation in Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1991, 55, 371–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mejía-Almonte, C.; Busby, S.J.; Wade, J.T.; van Helden, J.; Arkin, A.P.; Stormo, G.D.; Eilbeck, K.; Palsson, B.O.; Galagan, J.E.; Collado-Vides, J. Redefining fundamental concepts of transcription initiation in bacteria. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Hoover, T.R. Transcriptional regulation at a distance in bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2001, 4, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, D.F.; Busby, S.J. The regulation of bacterial transcription initiation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Antonio, A.; Collado-Vides, J. Identifying global regulators in transcriptional regulatory networks in bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2003, 6, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. Orthologous transcription factors in bacteria have different functions and regulate different genes. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2007, 3, e175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-Zavaleta, A.; Salgado, H.; Gama-Castro, S.; Sánchez-Pérez, M.; Gómez-Romero, L.; Ledezma-Tejeida, D.; García-Sotelo, J.S.; Alquicira-Hernández, K.; Muñiz-Rascado, L.J.; Peña-Loredo, P. RegulonDB v 10.5: Tackling challenges to unify classic and high throughput knowledge of gene regulation in E. coli K-12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D212–D220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyke, M.W.; Beyer, M.D.; Clay, E.; Hiam, K.J.; McMurry, J.L.; Xie, Y. Identification of preferred DNA-binding sites for the Thermus thermophilus transcriptional regulator SbtR by the combinatorial approach REPSA. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Um, H.; Van Dyke, M.W. Identification and characterization of preferred DNA-binding sites for the Thermus thermophilus transcriptional regulator FadR. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.S.; Moncja, K.; Mckinnes, M.; Van Dyke, M.W. Identification and Characterization of Preferred DNA-Binding Sites for the Thermus thermophilus HB8 Transcriptional Regulator TTHA0973. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shell Cox, J.; Van Dyke, M.W. General and Genomic DNA-Binding Specificity for the Thermus thermophilus HB8 Transcription Factor TTHB023. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 94. [Google Scholar]
- Agari, Y.; Kuramitsu, S.; Shinkai, A. X-ray crystal structure of TTHB099, a CRP/FNR superfamily transcriptional regulator from Thermus thermophilus HB8, reveals a DNA-binding protein with no required allosteric effector molecule. Proteins 2012, 80, 1490–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardenbol, P.; Van Dyke, M.W. Sequence specificity of triplex DNA formation: Analysis by a combinatorial approach, restriction endonuclease protection selection and amplification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 2811–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dyke, M.; Gracien, I. Restriction endonuclease protection assays using infrared-fluorescent probes. Protocols.io 2020, bi5ikg4e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Elkan, C. Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers. Proc. Int. Conf. Intell. Syst. Mol. Biol. 1994, 2, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Concepcion, J.; Witte, K.; Wartchow, C.; Choo, S.; Yao, D.; Persson, H.; Wei, J.; Li, P.; Heidecker, B.; Ma, W.; et al. Label-free detection of biomolecular interactions using BioLayer interferometry for kinetic characterization. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2009, 12, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovych, N.; Tzeng, S.R.; Tonelli, M.; Ebright, R.H.; Kalodimos, C.G. Structural basis for cAMP-mediated allosteric control of the catabolite activator protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6927–6932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, C.E.; Bailey, T.L.; Noble, W.S. FIMO: Scanning for occurrences of a given motif. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1017–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Furumichi, M.; Morishima, K.; Tanabe, M. New approach for understanding genome variations in KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D590–D595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.R.; Hem, V.; Katz, K.S.; Ovetsky, M.; Wallin, C.; Ermolaeva, O.; Tolstoy, I.; Tatusova, T.; Pruitt, K.D.; Maglott, D.R. Gene: A gene-centered information resource at NCBI. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D36–D42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.; Dam, P.; Chou, J.; Olman, V.; Xu, Y. DOOR: A database for prokaryotic operons. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D459–D463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karp, P.D.; Billington, R.; Caspi, R.; Fulcher, C.A.; Latendresse, M.; Kothari, A.; Keseler, I.M.; Krummenacker, M.; Midford, P.E.; Ong, Q. The BioCyc collection of microbial genomes and metabolic pathways. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovyev, V.; Salamov, A. Automatic annotation of microbial genomes and metagenomic sequences. In Metagenomics and Its Applications in Agriculture, Biomedicine and Environmental Studies; Li, R.W., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 61–78. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, T.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Tomashevsky, M.; Marshall, K.A.; Phillippy, K.H.; Sherman, P.M.; Holko, M.; et al. NCBI GEO: Archive for functional genomics data sets—Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D991–D995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuze, M.R.; Karpinets, T.V.; Syed, M.H.; Beliaev, A.S.; Uberbacher, E.C. Binding motifs in bacterial gene promoters modulate transcriptional effects of global regulators CRP and ArcA. Gene Regul. Syst. Biol. 2012, 6, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, R.K.; Wolters, J.; Kröger, B.; Schultze, S.; Specht, T.; Erdmann, V.A. Does Thermus represent another deep eubacterial branching? Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1989, 11, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiba, H. Autoregulation of the Escherichia coli crp gene: CRP is a transcriptional repressor for its own gene. Cell 1983, 32, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galan-Vasquez, E.; Sanchez-Osorio, I.; Martinez-Antonio, A. Transcription factors exhibit differential conservation in bacteria with reduced genomes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Balleza, E.; Lopez-Bojorquez, L.N.; Martínez-Antonio, A.; Resendis-Antonio, O.; Lozada-Chávez, I.; Balderas-Martínez, Y.I.; Encarnación, S.; Collado-Vides, J. Regulation by transcription factors in bacteria: Beyond description. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 33, 133–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, T.; Fujita, N.; Yamamoto, K.; Ishihama, A. Novel roles of cAMP receptor protein (CRP) in regulation of transport and metabolism of carbon sources. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Iyer, M.S.; Srinivasan, S.; Seshasayee, A.S.; Venkatesh, K.V. Elucidating the regulatory role of CRP in coordinating protein biosynthesis machinery with metabolism that defines growth optimality in Escherichia coli. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Gosset, G.; Barabote, R.; Gonzalez, C.S.; Cuevas, W.A.; Saier, M.H. Functional interactions between the carbon and iron utilization regulators, Crp and Fur, in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, H.; Kondo, M.; Usui, N.; Usui, T.; Ohzeki, H.; Yamazaki, R.; Washioka, M.; Nakamura, A.; Hoshino, T.; Hakamata, W. Involvement of CarA/LitR and CRP/FNR family transcriptional regulators in light-induced carotenoid production in Thermus thermophilus. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 2451–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ebright, R.H. Structural basis of transcription activation. Science 2016, 352, 1330–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarenko, V.; Liu, Y.; Ninfa, A.; Studitsky, V.M. Action of prokaryotic enhancer over a distance does not require continued presence of promoter-bound σ54 subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyke, M. Direct Double-Stranded DNA Quantitation from PCR Reactions V.2. Protocols.io 2017, k5pcy5n. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyke, M.; Cox, J. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays using infrared-fluorescent DNA probes. Protocols.io 2018, mbdc2i6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
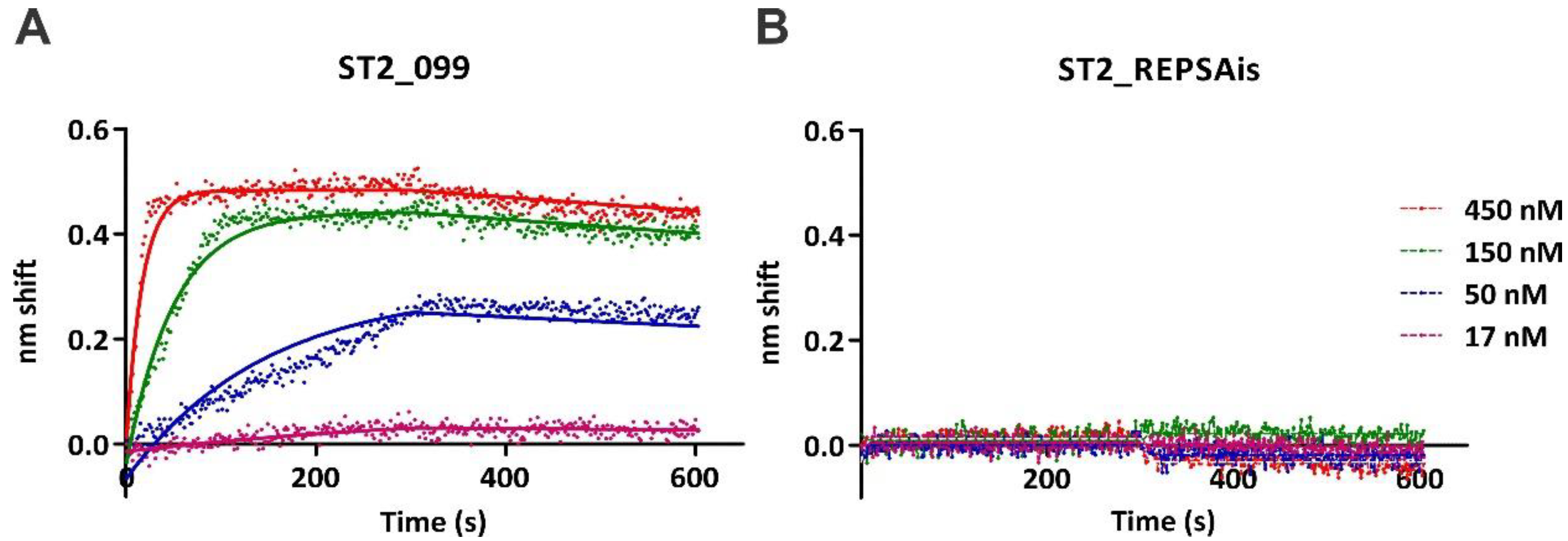
| Name | Sequence | kon (M−1s−1) | koff (s−1) | KD (M) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt | TGTATTCTAGAATACA | 131,308 | 2.907 × 10−4 | 2.214 × 10−9 | 0.9883 |
| m1 | gGTATTCTAGAATACA | 120,059 | 7.558 × 10−4 | 6.295 × 10−9 | 0.9895 |
| m2 | TtTATTCTAGAATACA | 112,773 | 3.785 × 10−3 | 3.356 × 10−8 | 0.9778 |
| m3 | TGaATTCTAGAATACA | 88,146 | 1.221 × 10−3 | 1.385 × 10−8 | 0.9824 |
| m4 | TGTcTTCTAGAATACA | 142,953 | 1.366 × 10−3 | 9.557 × 10−9 | 0.9817 |
| m5 | TGTAcTCTAGAATACA | 110,766 | 5.379 × 10−4 | 4.856 × 10−9 | 0.9879 |
| m6 | TGTATaCTAGAATACA | 125,945 | 7.064 × 10−4 | 5.608 × 10−9 | 0.9794 |
| m7 | TGTATTtTAGAATACA | 119,827 | 6.978 × 10−4 | 5.823 × 10−9 | 0.9805 |
| m8 | TGTATTCaAGAATACA | 115,299 | 7.848 × 10−4 | 6.807 × 10−9 | 0.9840 |
| wt + cAMP | TGTATTCTAGAATACA | 214,759 | 4.780 × 10−4 | 2.226 × 10−9 | 0.9231 |
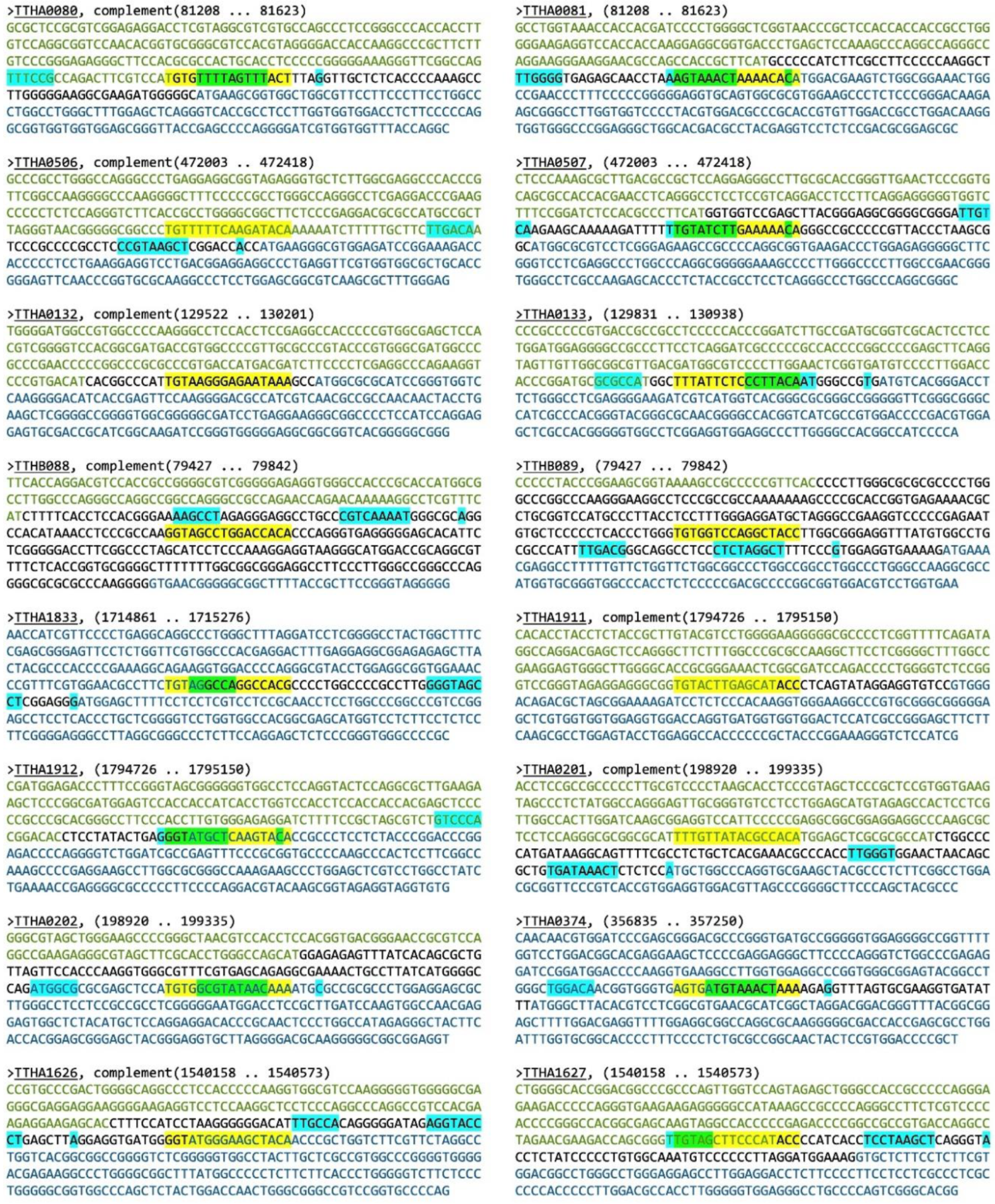
| Start | End | p-Value | Q-Value | Sequence | Loc | Gene | Op |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 81,408 | 81,423 | 4.03 × 10−6 | 1 | AGTAAACTAAAACACA | +1 | TTHA0081 | 1/3 |
| 81,408 | 81,423 | 4.03 × 10−6 | 1 | TGTGTTTTAGTTTACT | −48 | TTHA0080 | S |
| 32,704 | 32,719 | 5.82 × 10−6 | 1 | TGTGTACGAAATTACA | +434 | TTHA0030 | 1/2 |
| 472,203 | 472,218 | 7.74 × 10−6 | 1 | TGTATCTTGAAAAACA | −26 | TTHA0507 | S |
| 472,203 | 472,218 | 7.74 × 10−6 | 1 | TGTTTTTCAAGATACA | −56 | TTHA0506 | S |
| 130,005 | 130,020 | 1.01 × 10−5 | 1 | TTTATTCTCCCTTACA | −10 | TTHA0133 | 1/2 |
| 130,005 | 130,020 | 1.01 × 10−5 | 1 | TGTAAGGGAGAATAAA | −3 | TTHA0132 | S |
| 1506 | 1521 | 1.23 × 10−5 | 1 | AGTGAGATAACTCACA | −666 | TTHC003 | 1/3 |
| 1506 | 1521 | 1.23 × 10−5 | 1 | TGTGAGTTATCTCACT | +627 | TTHC002 | S |
| 79,627 | 79,642 | 1.30 × 10−5 | 1 | TGTGGTCCAGGCTACC | −78 | TTHB089 | 1/3 |
| 79,627 | 79,642 | 1.30 × 10−5 | 1 | GGTAGCCTGGACCACA | −162 | TTHB088 | S |
| 615,132 | 615,147 | 1.46 × 10−5 | 1 | GGTAGCCAGGGATACA | +909 | TTHA0647 | 4/4 |
| 1,715,061 | 1,715,076 | 1.65 × 10−5 | 1 | TGTAGGCCAGGCCACG | −33 | TTHA1833 | 1/2 |
| 609,145 | 609,160 | 1.83 × 10−5 | 1 | CGTGTCCCTGAACACA | +790 | TTHA0641 | 2/4 |
| 614,143 | 614,158 | 2.12 × 10−5 | 1 | TGTGCCTTTGGCCACA | +326 | TTHA0645 | 1/3 |
| 1,794,923 | 1,794,938 | 2.33 × 10−5 | 1 | GGTATGCTCAAGTACA | +13 | TTHA1912 | 1/2 |
| 1,794,923 | 1,794,938 | 2.33 × 10−5 | 1 | TGTACTTGAGCATACC | −19 | TTHA1911 | 1/4 |
| 1272 | 1287 | 2.61 × 10−5 | 1 | TGTAGCCCAGGCCAAA | +239 | TTHB003 | S |
| 1272 | 1287 | 2.61 × 10−5 | 1 | TTTGGCCTGGGCTACA | +536 | TTHB004 | 4/4 |
| 199,120 | 199,135 | 2.90 × 10−5 | 1 | TGTGGCGTATAACAAA | −17 | TTHA0202 | S |
| 199,120 | 199,135 | 2.90 × 10−5 | 1 | TTTGTTATACGCCACA | −103 | TTHA0201 | S |
| 357,035 | 357,050 | 3.43 × 10−5 | 1 | AGTGATGTAAACTAAA | −26 | TTHA0374 | S |
| 314,103 | 314,118 | 3.67 × 10−5 | 1 | TGTGTTGCAGGACCCA | +58 | TTHA0326 | 2/11 |
| 1,540,358 | 1,540,373 | 3.95 × 10−5 | 1 | TGTAGCTTCCCATACC | −67 | TTHA1627 | S |
| 1,540,358 | 1,540,373 | 3.95 × 10−5 | 1 | GGTATGGGAAGCTACA | +13 | TTHA1626 | S |
| Gene | Sequence | kon (M−1s−1) | koff (s−1) | KD (M) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TTHA0080/81 | TGTGTTTTAGTTTACT | 122,852 | 1.145 × 10−2 | 9.322 × 10−8 | 0.9817 |
| TTHA0506/07 | TGTTTTTCAAGATACA | 164,971 | 1.280 × 10−2 | 7.762 × 10−8 | 0.9718 |
| TTHA0132/33 | TGTAAGGGAGAATAAA | 96,736 | 2.140 × 10−2 | 2.212 × 10−7 | 0.9687 |
| TTHB088/89 | GGTAGCCTGGACCACA | 214,153 | 7.163 × 10−4 | 3.345 × 10−9 | 0.9805 |
| TTHA1833 | TGTAGGCCAGGCCACG | 332,611 | 1.013 × 10−3 | 3.046 × 10−9 | 0.9757 |
| TTHA1911/12 | TGTACTTGAGCATACC | 136,294 | 8.938 × 10−3 | 6.558 × 10−8 | 0.9806 |
| TTHA0201/02 | TTTGTTATACGCCACA | 57,231 | 4.464 × 10−2 | 7.801 × 10−7 | 0.9596 |
| TTHA0374 | AGTGATGTAAACTAAA | − | − | − | − |
| TTHA1626/27 | GGTATGGGAAGCTACA | 126,605 | 1.291 × 10−2 | 1.020 × 10−7 | 0.9759 |
| Operon | Gene | Role | LogFC | Adj. p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | TTHA0080 | hypothetical protein | 0.851 | 0.0268 |
| 1 | TTHA0081 | hypothetical protein | −0.202 | 0.421 |
| 2 | TTHA0082 | phosphoesterase | −0.176 | 0.463 |
| 3 | TTHA0083 | dimethyladenosine transferase | −0.219 | 0.336 |
| S | TTHA0506 | malate synthase | −0.454 | 0.0983 |
| S | TTHA0507 | IclR family transcriptional regulator, acetate operon repressor | 0.276 | 0.619 |
| S | TTHA0132 | hypothetical protein | 0.872 | 0.0295 |
| 1 | TTHA0133 | Short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase family oxidoreductase | −0.211 | 0.674 |
| 2 | TTHA0134 | NrdR family transcriptional regulator | −0.328 | 0.350 |
| S | TTHB088 | Zn-dependent hydrolase | −0.386 | 0.653 |
| 1 | TTHB089 | hypothetical protein | −0.779 | 0.0451 |
| 2 | TTHB090 | hypothetical protein | −0.0653 | 0.955 |
| 3 | TTHB091 | hypothetical protein | −0.217 | 0.674 |
| 1 | TTHA1833 | ABC transporter permease | −0.294 | 0.287 |
| 2 | TTHA1834 | ABC transporter ATP-binding protein | −0.195 | 0.567 |
| 1 | TTHA1911 | 3-isopropylmalate dehydratase large subunit | −0.817 | 0.0246 |
| 2 | TTHA1910 | homoaconitate hydratase small subunit | −1.14 | 0.0265 |
| 3 | TTHA1909 | hypothetical protein | −0.0793 | 0.790 |
| 4 | TTHA1908 | hypothetical protein | −0.0327 | 0.905 |
| 1 | TTHA1912 | hypothetical protein | 0.353 | 0.154 |
| 2 | TTHA1913 | hypothetical protein | 0.723 | 0.0284 |
| S | TTHA0201 | Mg2+ chelatase family protein | 0.141 | 0.698 |
| S | TTHA0202 | hypothetical protein | 0.454 | 0.0644 |
| S | TTHA0374 | hypothetical protein | 0.687 | 0.0421 |
| S | TTHA1626 | hypothetical protein | 2.62 | 2.10 × 10−3 |
| S | TTHA1627 | hypothetical protein | −1.20 | 0.0960 |
| Operon | Gene | Role | LogFC | Adj. p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | TTHA1498 | Elongation Factor G | +4.384 | 2.07 × 10−4 |
| 2 | TTHA1499 | MoxR-like protein | +5.067 | 7.03 × 10−5 |
| 3 | TTHA1500 | Phosphoenolpyruvate Synthase | +5.231 | 7.03 × 10−5 |
| 4 | TTHA1501 | Hemolysin III | +3.133 | 1.27 × 10−3 |
| 5 | TTHA1502 | Response Regulator_two-component system, OmpR family | +1.087 | 9.51 × 10−3 |
| 6 | TTHA1503 | Sensor Histidine Kinase | +0.369 | 2.46 × 10−1 |
| S | TTHA1836 | Isocitrate lyase | +4.423 | 1.52 × 10−4 |
| 1 | TTHA1838 | SufC protein, ATP-binding protein | −2.465 | 1.06 × 10−3 |
| 2 | TTHA1839 | SufB protein, membrane protein | −2.593 | 9.53 × 10−4 |
| 3 | TTHA1840 | SufD protein, membrane protein | −2.630 | 6.25 × 10−4 |
| 4 | TTHA1841 | Dioxygenase ferredoxin subunit | −2.419 | 2.59 × 10−3 |
| 1 | TTHA1133 | ba3-type cytochrome C oxidase polypeptide IIA | +1.311 | 4.37 × 10−2 |
| 2 | TTHA1134 | ba3-type cytochrome C oxidase polypeptide II | +2.944 | 7.89 × 10−3 |
| 3 | TTHA1135 | ba3-type cytochrome C oxidase polypeptide I | +4.269 | 1.27 × 10−3 |
| 1 | TTHA1136 | hypothetical protein | +1.910 | 1.29 × 10−3 |
| 2 | TTHA1137 | Major facilitator superfamily transporter | +2.300 | 9.53 × 10−4 |
| 1 | TTHA0251 | Elongation factor Tu | −1.254 | 1.17 × 10−2 |
| 1 | TTHA0250 | 50S ribosomal protein L33 | −1.139 | 8.04 × 10−3 |
| 2 | TTHA0249 | Preprotein translocase subunit SecE | −0.997 | 9.18 × 10−3 |
| 3 | TTHA0248 | Transcription antitermination protein NusG | −1.136 | 7.86 × 10−3 |
| 1 | TTHA0247 | 50S ribosomal protein L11 | −2.378 | 1.27 × 10−3 |
| 2 | TTHA0246 | 50S ribosomal protein L1 | −1.776 | 2.16 × 10−3 |
| 1 | TTHA0084 | NADH-quinone oxidoreductase subunit 7 | +1.083 | 8.73 × 10−3 |
| 2 | TTHA0085 | NADH dehydrogenase subunit B | +1.005 | 2.41 × 10−2 |
| 3 | TTHA0086 | NADH-quinone oxidoreductase subunit 5 | +1.251 | 1.06 × 10−2 |
| 4 | TTHA0087 | NADH-quinone oxidoreductase subunit 4 | +1.255 | 6.43 × 10−3 |
| 5 | TTHA0088 | NADH-quinone oxidoreductase subunit 2 | +0.693 | 4.43 × 10−2 |
| 6 | TTHA0089 | NADH-quinone oxidoreductase subunit 1 | +1.249 | 4.68 × 10−3 |
| 7 | TTHA0090 | NADH-quinone oxidoreductase subunit 3 | +1.248 | 5.76 × 10−3 |
| 8 | TTHA0091 | NADH-quinone oxidoreductase subunit 8 | +1.490 | 3.62 × 10−3 |
| 9 | TTHA0092 | NADH-quinone oxidoreductase subunit 9 | +1.502 | 2.21 × 10−3 |
| 10 | TTHA0093 | NADH-quinone oxidoreductase subunit 10 | +1.626 | 6.84 × 10−3 |
| 11 | TTHA0094 | NADH-quinone oxidoreductase subunit 11 | +1.043 | 6.39 × 10−3 |
| 12 | TTHA0095 | NADH-quinone oxidoreductase subunit 12 | +1.492 | 2.85 × 10−3 |
| 13 | TTHA0096 | NADH-quinone oxidoreductase subunit 13 | +1.679 | 3.34 × 10−3 |
| 14 | TTHA0097 | NADH-quinone oxidoreductase subunit 14 | +1.509 | 2.84 × 10−3 |
| 15 | TTHA0098 | arginyl-tRNA synthetase | +0.397 | 8.43 × 10−2 |
| 16 | TTHA0099 | serine protease | +0.106 | 6.09 × 10−1 |
| 17 | TTHA0100 | UDP-N-acetylmuramoylalanyl-D-glutamate--2,6-diaminopimelate ligase | +0.520 | 5.11 × 10−2 |
| S | TTHA1626 | hypothetical protein | +2.616 | 2.10 × 10−3 |
| S | TTHA1625 | Osmotically inducible protein OsmC | +1.206 | 3.65 × 10−3 |
| 1 | TTHA1628 | Iron ABC transporter substrate-binding protein | −2.947 | 1.83 × 10−3 |
| 2 | TTHA1629 | Iron ABC transporter permease | −2.344 | 1.68 × 10−3 |
| 3 | TTHA1630 | Iron ABC transporter ATP-binding protein | −0.796 | 1.69 × 10−2 |
| 4 | TTHA1631 | tRNA pseudouridine synthase A | −0.461 | 8.43 × 10−2 |
| S | TTHA0135 | MutT/nudix family protein | −1.369 | 6.82 × 10−3 |
| 1 | TTHA0206 | nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase subunit alpha 1 | +1.516 | 5.30 × 10−3 |
| 2 | TTHA0207 | nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase subunit alpha 2 | +1.596 | 2.85 × 10−3 |
| 3 | TTHA0208 | nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase subunit beta | +1.647 | 2.10 × 10−3 |
| 1 | TTHA0209 | 50S ribosomal protein L10 | −1.673 | 5.33 × 10−3 |
| 2 | TTHA0210 | 50S ribosomal protein L7/L12 | −1.326 | 8.74 × 10−3 |
| 1 | TTHB117 | putative type IV pilin | +1.125 | 4.09 × 10−2 |
| 2 | TTHB118 | secretion system protein | +1.450 | 3.74 × 10−3 |
| 3 | TTHB119 | prepilin-like protein | +1.429 | 5.85 × 10−3 |
| 4 | TTHB120 | hypothetical protein | +2.250 | 1.27 × 10−3 |
| 1 | TTHA1652 | maltose ABC transporter substrate-binding protein | +1.787 | 1.72 × 10−3 |
| 2 | TTHA1651 | maltose ABC transporter permease | +2.154 | 1.17 × 10−3 |
| 3 | TTHA1650 | maltose ABC transporter permease | +2.108 | 1.29 × 10−3 |
| 1 | TTHB186 | putative transcriptional regulator | +3.377 | 2.59 × 10−3 |
| 2 | TTHB187 | hypothetical protein | +2.036 | 7.58 × 10−3 |
| 1 | TTHB188 | hypothetical protein | +1.215 | 9.19 × 10−3 |
| 2 | TTHB189 | CRISPR-associated Cse2 family protein | +1.514 | 4.80 × 10−3 |
| 3 | TTHB190 | hypothetical protein | +1.671 | 6.62 × 10−3 |
| 4 | TTHB191 | hypothetical protein | +1.480 | 4.34 × 10−3 |
| 5 | TTHB192 | hypothetical protein | +1.669 | 4.68 × 10−3 |
| 6 | TTHB193 | hypothetical protein | +1.446 | 6.84 × 10 −3 |
| 7 | TTHB194 | hypothetical protein | +1.549 | 1.71 × 10−2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moncja, K.; Van Dyke, M.W. Determination and Dissection of DNA-Binding Specificity for the Thermus thermophilus HB8 Transcriptional Regulator TTHB099. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7929. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21217929
Moncja K, Van Dyke MW. Determination and Dissection of DNA-Binding Specificity for the Thermus thermophilus HB8 Transcriptional Regulator TTHB099. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(21):7929. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21217929
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoncja, Kristi, and Michael W. Van Dyke. 2020. "Determination and Dissection of DNA-Binding Specificity for the Thermus thermophilus HB8 Transcriptional Regulator TTHB099" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 21: 7929. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21217929
APA StyleMoncja, K., & Van Dyke, M. W. (2020). Determination and Dissection of DNA-Binding Specificity for the Thermus thermophilus HB8 Transcriptional Regulator TTHB099. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(21), 7929. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21217929






