- Review
Natural Neurobiological Active Compounds in Parkinson’s Disease: Molecular Targets, Signaling Pathways, and Therapeutic Prospects
- Xue Wu,
- Linao Zhang and
- Peixin Guo
- + 9 authors
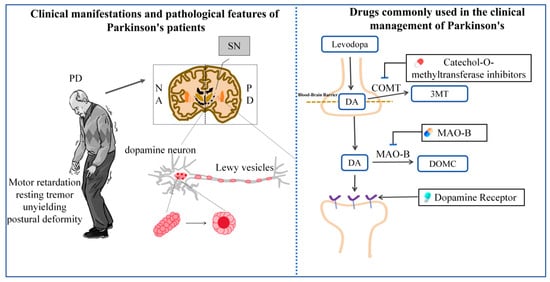
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative condition with a multifactorial etiology, characterized by dopaminergic neurons being selectively absent in the midbrain. Clinically, PD manifests primarily with core motor symptoms of resting tremor, bradykinesia, and muscle rigidity, and is often accompanied by non-motor symptoms including depression, cognitive impairment, and gastrointestinal dysfunction. Among the extensive relevant research, few have explored the precise pathogenic mechanisms underlying PD, and no curative treatment is available. Current pharmacological therapies mainly provide symptomatic relief by enhancing central dopaminergic function or modulating cholinergic activity; however, their long-term efficacy is frequently constrained by waning therapeutic response, drug tolerance, and adverse reactions. Accumulating evidence suggests that several naturally derived neuroactive compounds—such as gastrodin, uncarin, and paeoniflorin—demonstrate significant potential in combating PD. In this systematic review, we examined original research articles published from 2010 to 2025, retrieved from PubMed, Web of Science, and CNKI databases, using predefined keywords of Parkinson’s disease, neuroprotective herbal compounds, traditional medicine, multi-target mechanisms, natural product, autophagy, neuroinflammation, and oxidative stress. Studies were included if they specifically investigated the mechanistic actions of natural compounds in PD models. Conference abstracts, review articles, publications not in English or Chinese, and studies lacking clearly defined mechanisms were excluded. Analysis of the available literature reveals that natural neuroactive compounds may exert anti-PD effects through multiple mechanisms, e.g., inhibiting pathological α-synuclein aggregation, attenuating neuronal apoptosis, suppressing neuroinflammation, mitigating oxidative stress, and restoring mitochondrial dysfunction. This review provides insights that may inform the clinical application of natural bioactive compounds and guide their further development as potential therapeutic candidates against PD.
28 January 2026