Potential Association of the CSMD1 Gene with Moderate Intellectual Disability, Anxiety Disorder, and Obsessive–Compulsive Personality Traits
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
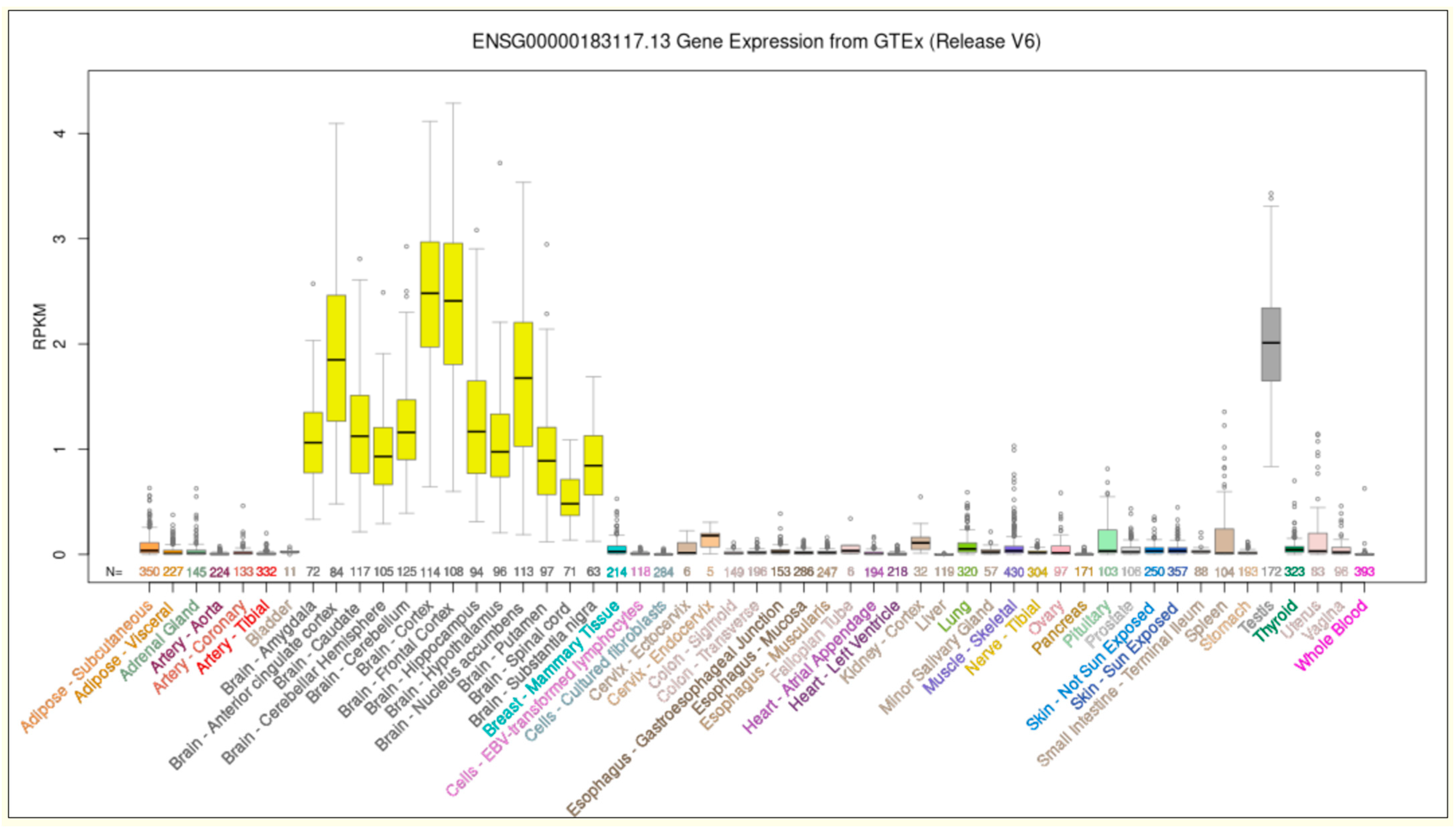
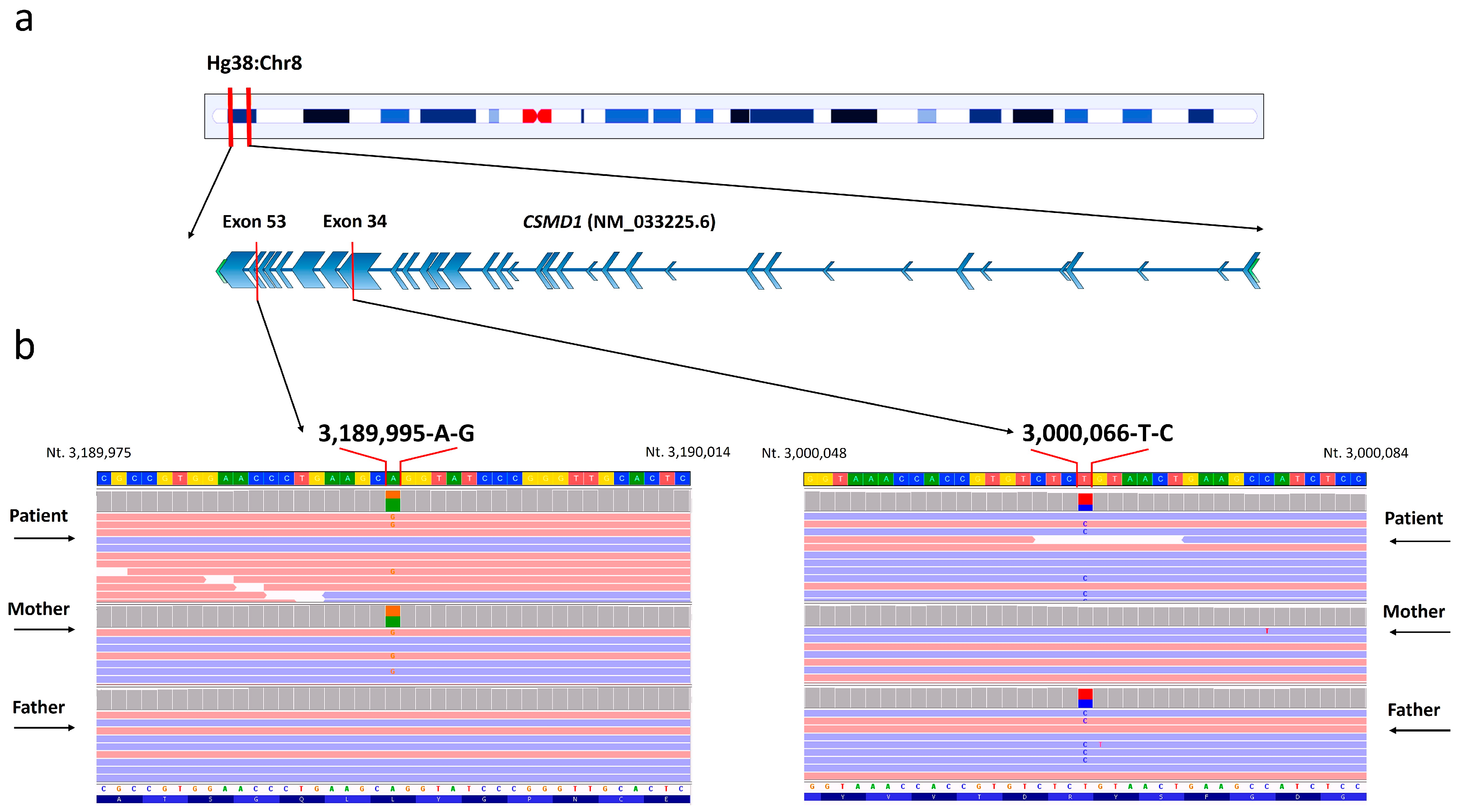
2.1. Clinical Data
2.2. Genetic Variant Detection
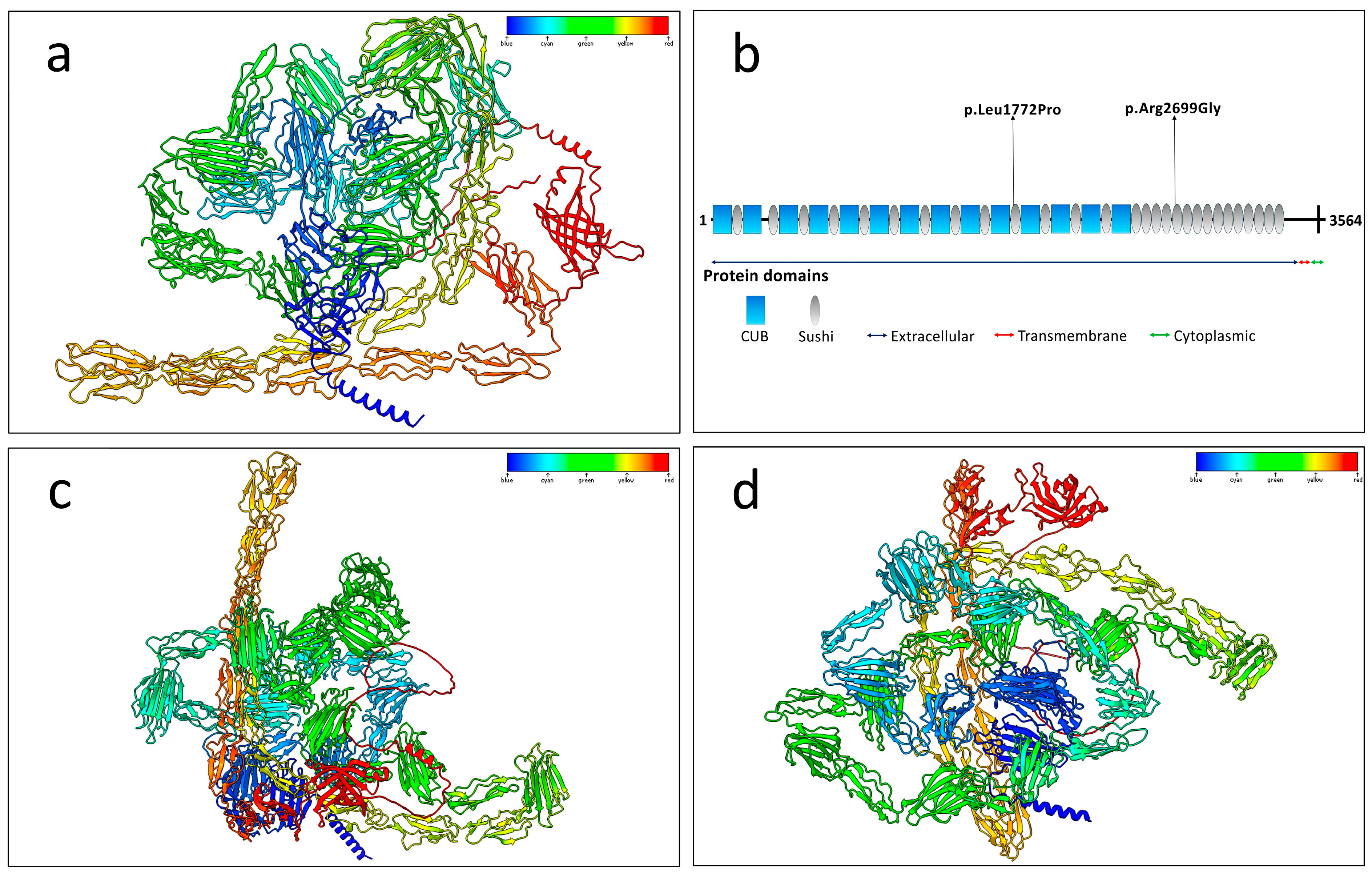
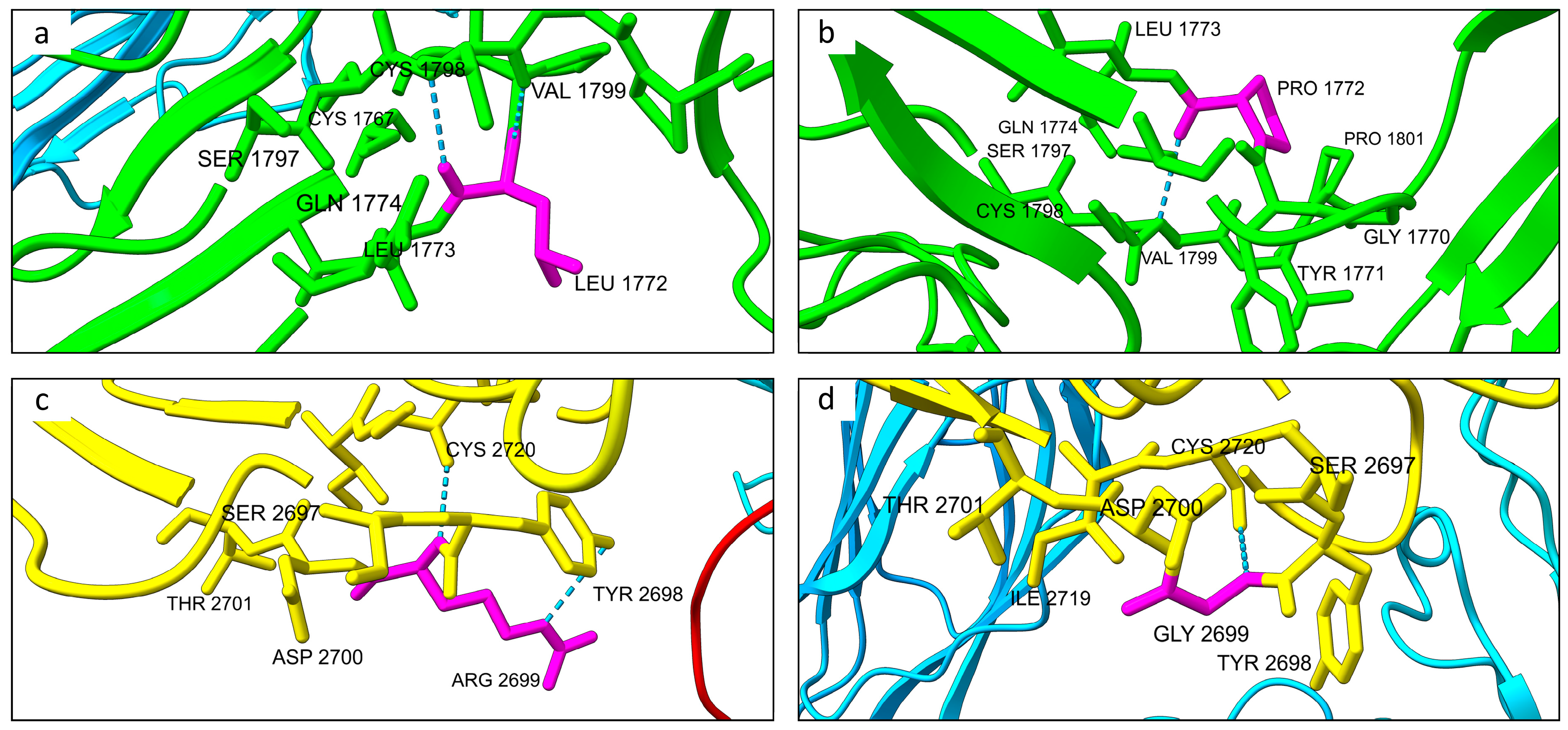
2.3. Protein Structure Prediction and Hydrogen Bonding Alterations
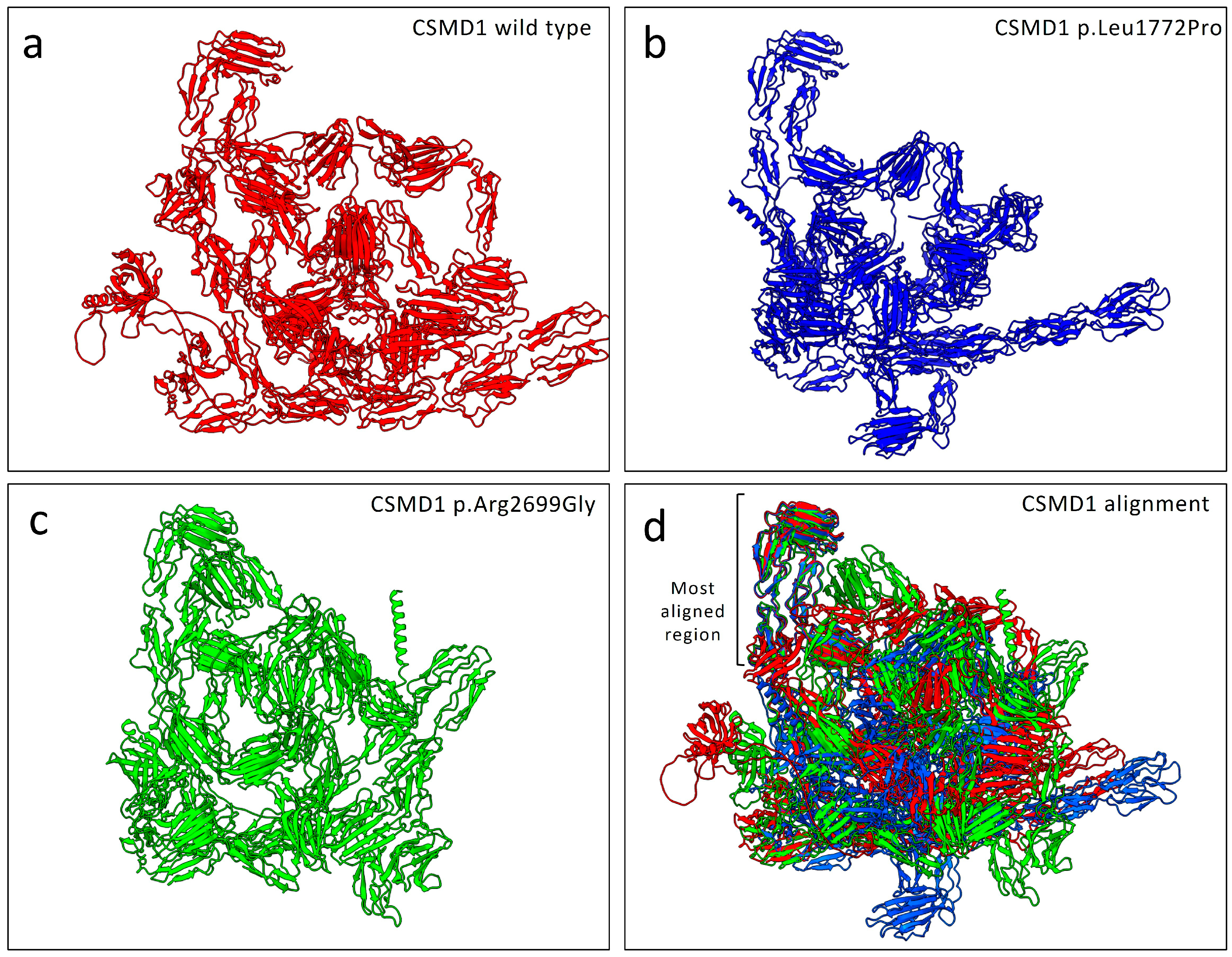
2.4. Structural Alignment and Stability Predictions
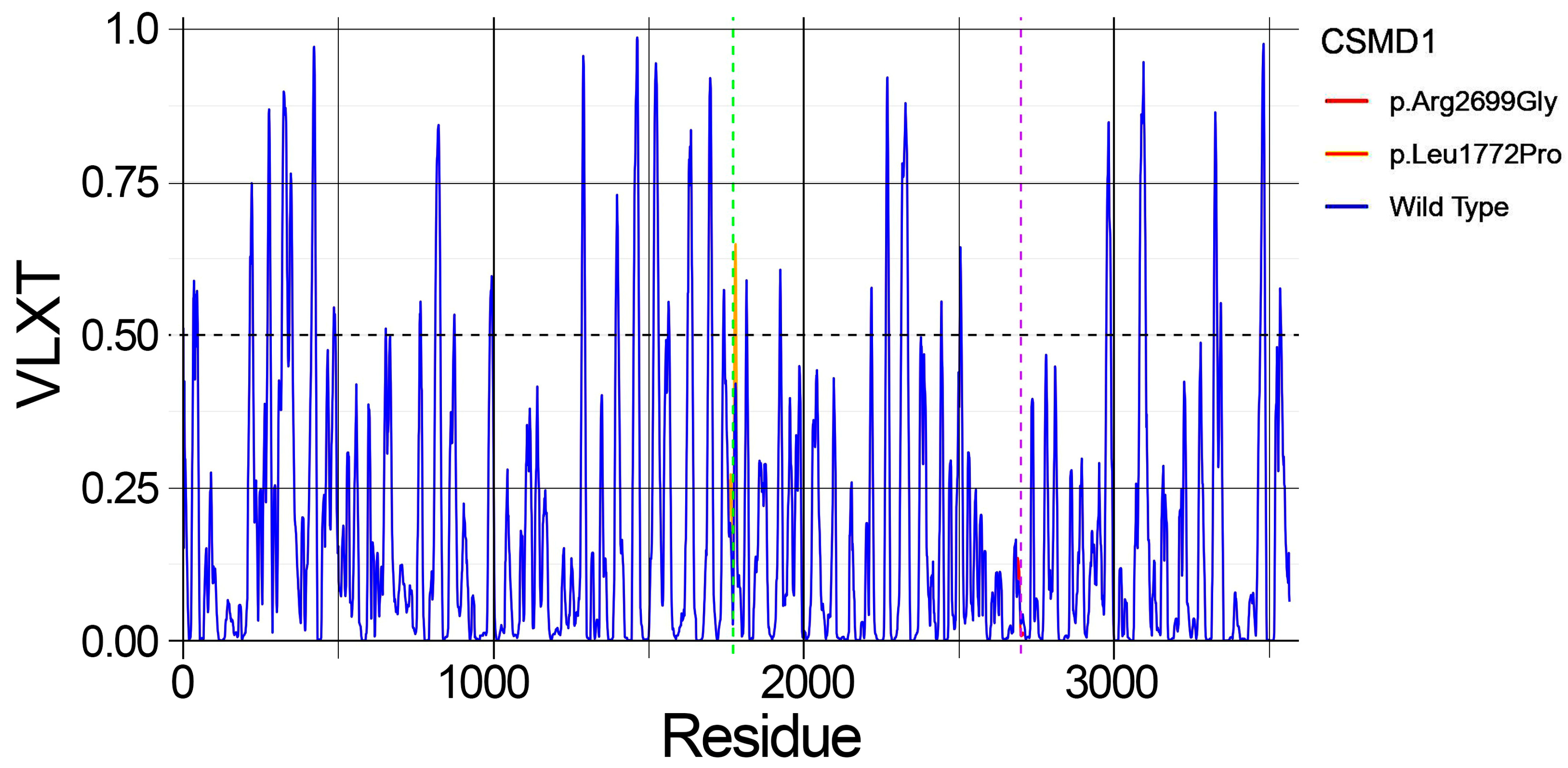
2.5. Predicted Structural Disorder
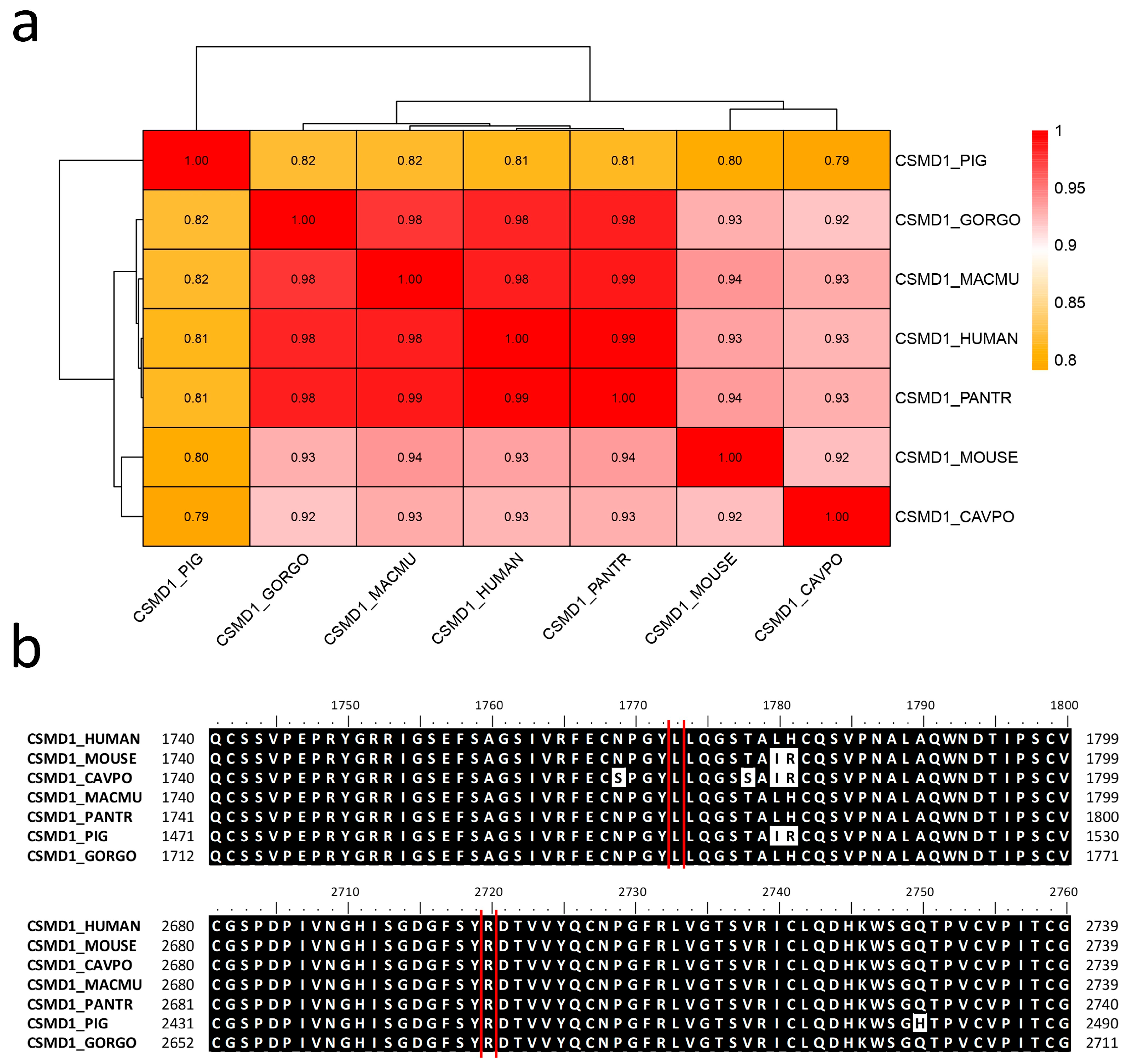
2.6. Allele Frequency and Evolutionary Conservation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Library Preparation and Whole-Exome Sequencing (WES)
4.2. Variant Identification and Filtering
4.3. Inheritance Pattern and Allele Frequencies
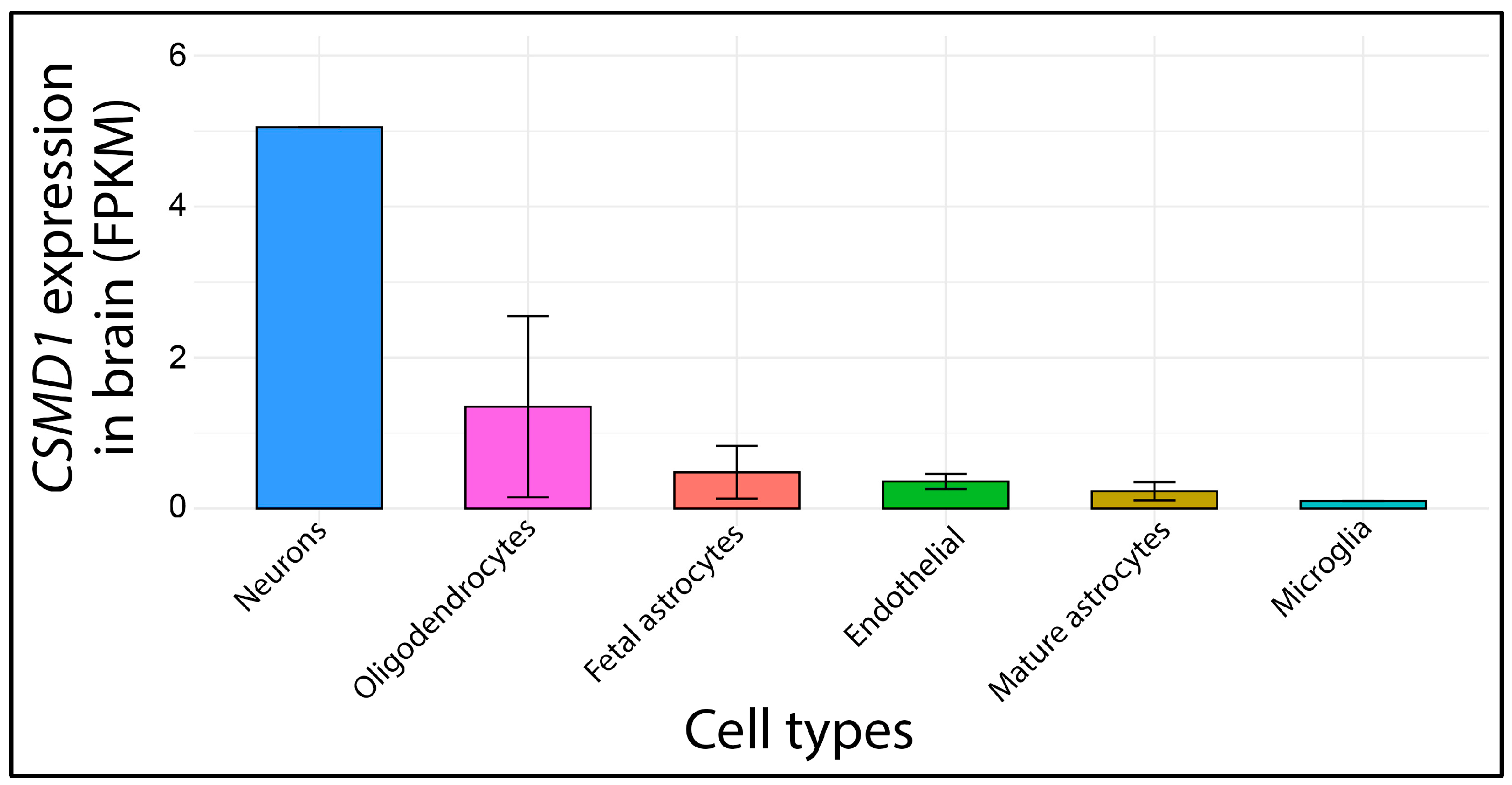
4.4. Gene Expression and Functional Domain Analysis
4.5. Impact of Mutations on Protein Structure
4.6. Protein Structure Prediction and Modeling
4.7. Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis
4.8. Brain Expression Profile Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACMG | American College of Medical Genetics |
| CSMD1 | CUB and Sushi domain-containing protein 1 |
| HGMD | Human Gene Mutation Database |
| WES | Whole-exome sequencing |
References
- Benoit, M.E.; Tenner, A.J. Complement Protein C1q-Mediated Neuroprotection Is Correlated with Regulation of Neuronal Gene and MicroRNA Expression. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 3459–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.D.; Coulthard, L.G.; Woodruff, T.M. Complement Dysregulation in the Central Nervous System during Development and Disease. Semin. Immunol. 2019, 45, 101340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulthard, L.G.; Hawksworth, O.A.; Woodruff, T.M. Complement: The Emerging Architect of the Developing Brain. Trends Neurosci. 2018, 41, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraus, D.M.; Elliott, G.S.; Chute, H.; Horan, T.; Pfenninger, K.H.; Sanford, S.D.; Foster, S.; Scully, S.; Welcher, A.A.; Holers, V.M. CSMD1 Is a Novel Multiple Domain Complement-Regulatory Protein Highly Expressed in the Central Nervous System and Epithelial Tissues. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 4419–4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federico, C.; Pappalardo, A.M.; Ferrito, V.; Tosi, S.; Saccone, S. Genomic Properties of Chromosomal Bands Are Linked to Evolutionary Rearrangements and New Centromere Formation in Primates. Chromosome Res. 2017, 25, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulino, G.M.; Bruno, F.; Sturiale, V.; Brancato, D.; Ragusa, D.; Tosi, S.; Saccone, S.; Federico, C. From FISH to Hi-C: The Chromatin Architecture of the Chromosomal Region 7q36.3, Frequently Rearranged in Leukemic Cells, Is Evolutionary Conserved. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, E.J.; Morris, D.W.; Hargreaves, A.; Fahey, C.; Greene, C.; Garavan, H.; Gill, M.; Corvin, A.; Donohoe, G. Neural Effects of the CSMD1 Genome-wide Associated Schizophrenia Risk Variant Rs10503253. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2013, 162, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.S.; Rusch, J.; Lima, A.C.; Usmani, A.; Huang, N.; Lepamets, M.; Vigh-Conrad, K.A.; Worthington, R.E.; Mägi, R.; Wu, X.; et al. Rare Mutations in the Complement Regulatory Gene CSMD1 Are Associated with Male and Female Infertility. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermis Akyuz, E.; Bell, S.M. The Diverse Role of CUB and Sushi Multiple Domains 1 (CSMD1) in Human Diseases. Genes 2022, 13, 2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, C.; Crimm, H.; Meeh, P.; Croshaw, R.; Barbar, T.; Vandersteenhoven, J.J.; Butler, W.; Buckhaults, P. Somatic Mutations to CSMD1 in Colorectal Adenocarcinomas. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2008, 7, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shull, A.Y.; Clendenning, M.L.; Ghoshal-Gupta, S.; Farrell, C.L.; Vangapandu, H.V.; Dudas, L.; Wilkerson, B.J.; Buckhaults, P.J. Somatic Mutations, Allele Loss, and DNA Methylation of the Cub and Sushi Multiple Domains 1 (CSMD1) Gene Reveals Association with Early Age of Diagnosis in Colorectal Cancer Patients. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, N.; Wang, C.; Zhang, T.; Su, H.; Liu, H.; Yang, H.H.; Giffen, C.; Hu, Y.; Taylor, P.R.; Goldstein, A.M. CSMD1 Shows Complex Patterns of Somatic Copy Number Alterations and Expressions of MRNAs and Target Micro RNAs in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athanasiu, L.; Giddaluru, S.; Fernandes, C.; Christoforou, A.; Reinvang, I.; Lundervold, A.J.; Nilsson, L.-G.; Kauppi, K.; Adolfsson, R.; Eriksson, E.; et al. A Genetic Association Study of CSMD1 and CSMD2 with Cognitive Function. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 61, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Håvik, B.; Le Hellard, S.; Rietschel, M.; Lybæk, H.; Djurovic, S.; Mattheisen, M.; Mühleisen, T.W.; Degenhardt, F.; Priebe, L.; Maier, W.; et al. The Complement Control-Related Genes CSMD1 and CSMD2 Associate to Schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 70, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohoe, G.; Walters, J.; Hargreaves, A.; Rose, E.J.; Morris, D.W.; Fahey, C.; Bellini, S.; Cummins, E.; Giegling, I.; Hartmann, A.M.; et al. Neuropsychological Effects of the CSMD1 Genome-wide Associated Schizophrenia Risk Variant Rs10503253. Genes Brain Behav. 2013, 12, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koiliari, E.; Roussos, P.; Pasparakis, E.; Lencz, T.; Malhotra, A.; Siever, L.J.; Giakoumaki, S.G.; Bitsios, P. The CSMD1 Genome-Wide Associated Schizophrenia Risk Variant Rs10503253 Affects General Cognitive Ability and Executive Function in Healthy Males. Schizophr. Res. 2014, 154, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fu, X.; Tang, Z.; Li, C.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, D.; Zhu, C. Altered Expression of the CSMD1 Gene in the Peripheral Blood of Schizophrenia Patients. BMC Psychiatry 2019, 19, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, V.M.; Nepal, C.; Ersland, K.M.; Holdhus, R.; Nævdal, M.; Ratvik, S.M.; Skrede, S.; Håvik, B. Neuropsychological Deficits in Mice Depleted of the Schizophrenia Susceptibility Gene CSMD1. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, M.L.; Wilton, D.K.; Fox, R.G.; Carey, A.; Hsu, Y.-H.H.; Hu, R.; Jäntti, H.J.; Fahey, J.B.; Muthukumar, A.K.; Salla, N.; et al. CSMD1 Regulates Brain Complement Activity and Circuit Development. Brain Behav. Immun. 2024, 119, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beek, J.; Elward, K.; Gasque, P. Activation of Complement in the Central Nervous System. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 992, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahel, P.F.; Barnum, S.R. The Role of the Complement System in CNS Inflammatory Diseases. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2006, 2, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpanini, S.M.; Torvell, M.; Morgan, B.P. Therapeutic Inhibition of the Complement System in Diseases of the Central Nervous System. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekna, M.; Pekny, M. The Complement System: A Powerful Modulator and Effector of Astrocyte Function in the Healthy and Diseased Central Nervous System. Cells 2021, 10, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Luo, S.; Jiang, M.; Chen, Y.; Ren, R.; Wu, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhou, P.; Qin, J.; Liao, W. CSMD1 Is a Causative Gene of Developmental and Epileptic Encephalopathy and Generalized Epilepsies. Genes Dis. 2024, 12, 101473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sloan, S.A.; Clarke, L.E.; Caneda, C.; Plaza, C.A.; Blumenthal, P.D.; Vogel, H.; Steinberg, G.K.; Edwards, M.S.B.; Li, G.; et al. Purification and Characterization of Progenitor and Mature Human Astrocytes Reveals Transcriptional and Functional Differences with Mouse. Neuron 2016, 89, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werren, E.A.; Peirent, E.R.; Jantti, H.; Guxholli, A.; Srivastava, K.R.; Orenstein, N.; Narayanan, V.; Wiszniewski, W.; Dawidziuk, M.; Gawlinski, P.; et al. Biallelic Variants in CSMD1 Are Implicated in a Neurodevelopmental Disorder with Intellectual Disability and Variable Cortical Malformations. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzimanolis, A.; Foteli, S.; Stefanatou, P.; Ntigrintaki, A.-A.; Ralli, I.; Kollias, K.; Nikolaou, C.; Gazouli, M.; Stefanis, N.C. Deregulation of Complement Components C4A and CSMD1 Peripheral Expression in First-Episode Psychosis and Links to Cognitive Ability. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 272, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musumeci, A.; Vinci, M.; Treccarichi, S.; Ragalmuto, A.; Bruno, G.; Tinniriello, G.; Farina, J.; Federico, C.; Saccone, S.; Calì, F.; et al. Potential Role of ABCF2 Gene in Pudendal Nerve Neuropathy and Interstitial Cystitis. Genes 2025, 16, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenson, P.D.; Mort, M.; Ball, E.V.; Chapman, M.; Evans, K.; Azevedo, L.; Hayden, M.; Heywood, S.; Millar, D.S.; Phillips, A.D.; et al. The Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD®): Optimizing Its Use in a Clinical Diagnostic or Research Setting. Hum. Genet. 2020, 139, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence Variants: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T. BioEdit: An Important Software for Molecular Biology. GERF Bull. Biosci. 2011, 2, 60–61. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Musumeci, A.; Vinci, M.; Treccarichi, S.; Greco, D.; Rizzo, B.; Gloria, A.; Federico, C.; Saccone, S.; Musumeci, S.A.; Calì, F. Potential Association of the CSMD1 Gene with Moderate Intellectual Disability, Anxiety Disorder, and Obsessive–Compulsive Personality Traits. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094297
Musumeci A, Vinci M, Treccarichi S, Greco D, Rizzo B, Gloria A, Federico C, Saccone S, Musumeci SA, Calì F. Potential Association of the CSMD1 Gene with Moderate Intellectual Disability, Anxiety Disorder, and Obsessive–Compulsive Personality Traits. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094297
Chicago/Turabian StyleMusumeci, Antonino, Mirella Vinci, Simone Treccarichi, Donatella Greco, Biagio Rizzo, Angelo Gloria, Concetta Federico, Salvatore Saccone, Sebastiano Antonino Musumeci, and Francesco Calì. 2025. "Potential Association of the CSMD1 Gene with Moderate Intellectual Disability, Anxiety Disorder, and Obsessive–Compulsive Personality Traits" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094297
APA StyleMusumeci, A., Vinci, M., Treccarichi, S., Greco, D., Rizzo, B., Gloria, A., Federico, C., Saccone, S., Musumeci, S. A., & Calì, F. (2025). Potential Association of the CSMD1 Gene with Moderate Intellectual Disability, Anxiety Disorder, and Obsessive–Compulsive Personality Traits. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094297









