Heparin Specifically Interacts with Basic BBXB Motifs of the Chemokine CCL21 to Define CCR7 Signaling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
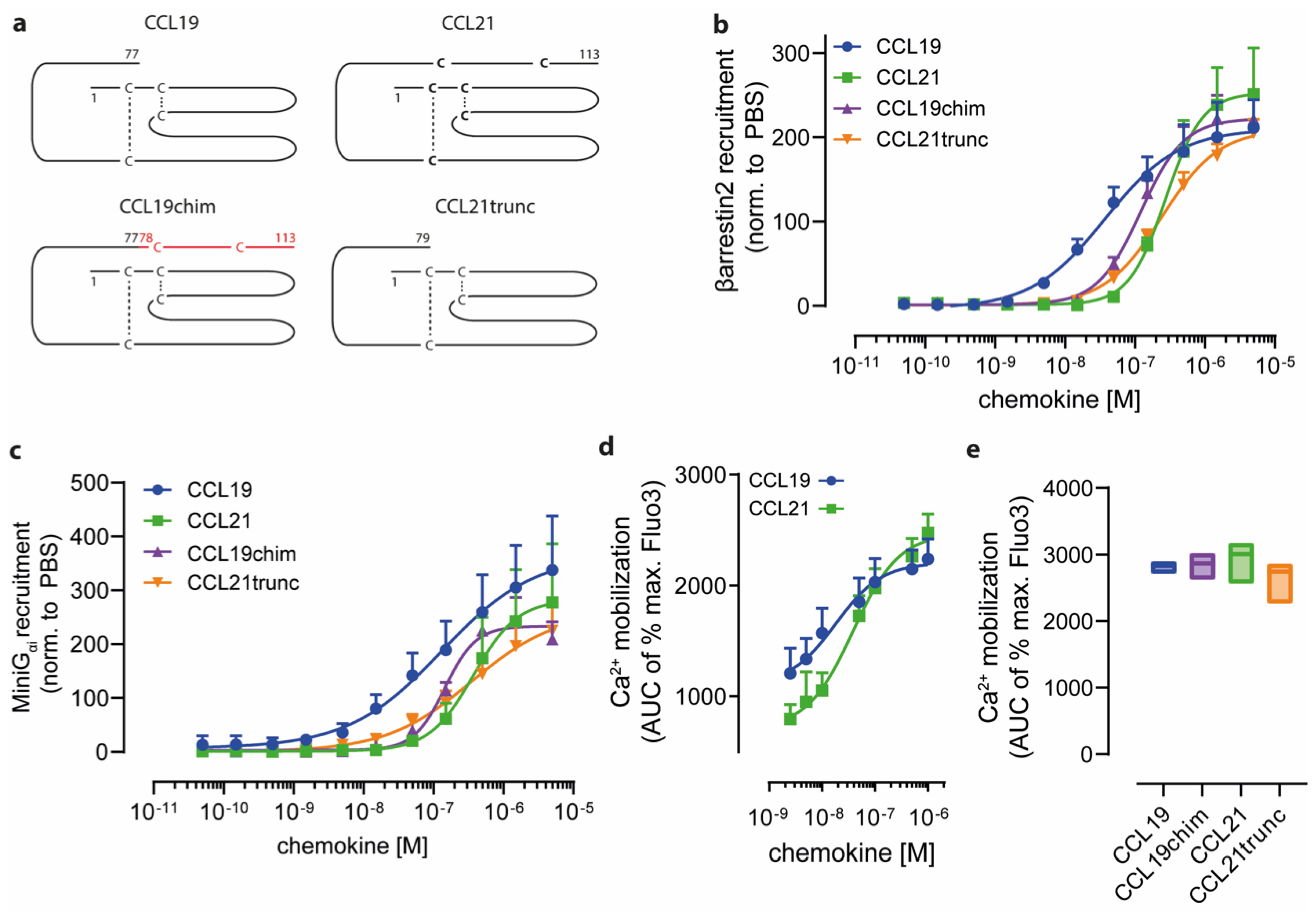
2.1. Charged C-Terminal Residues of CCL21 Only Partially Confer Ligand-Biased CCR7 Signaling
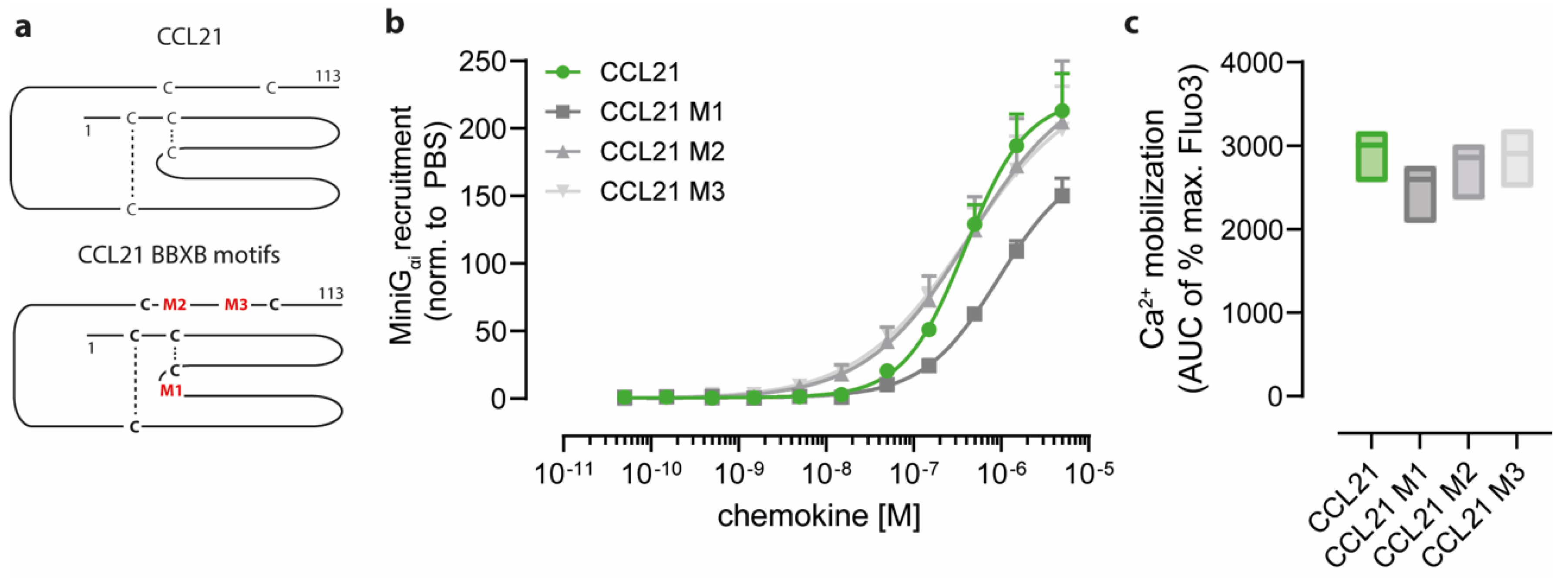
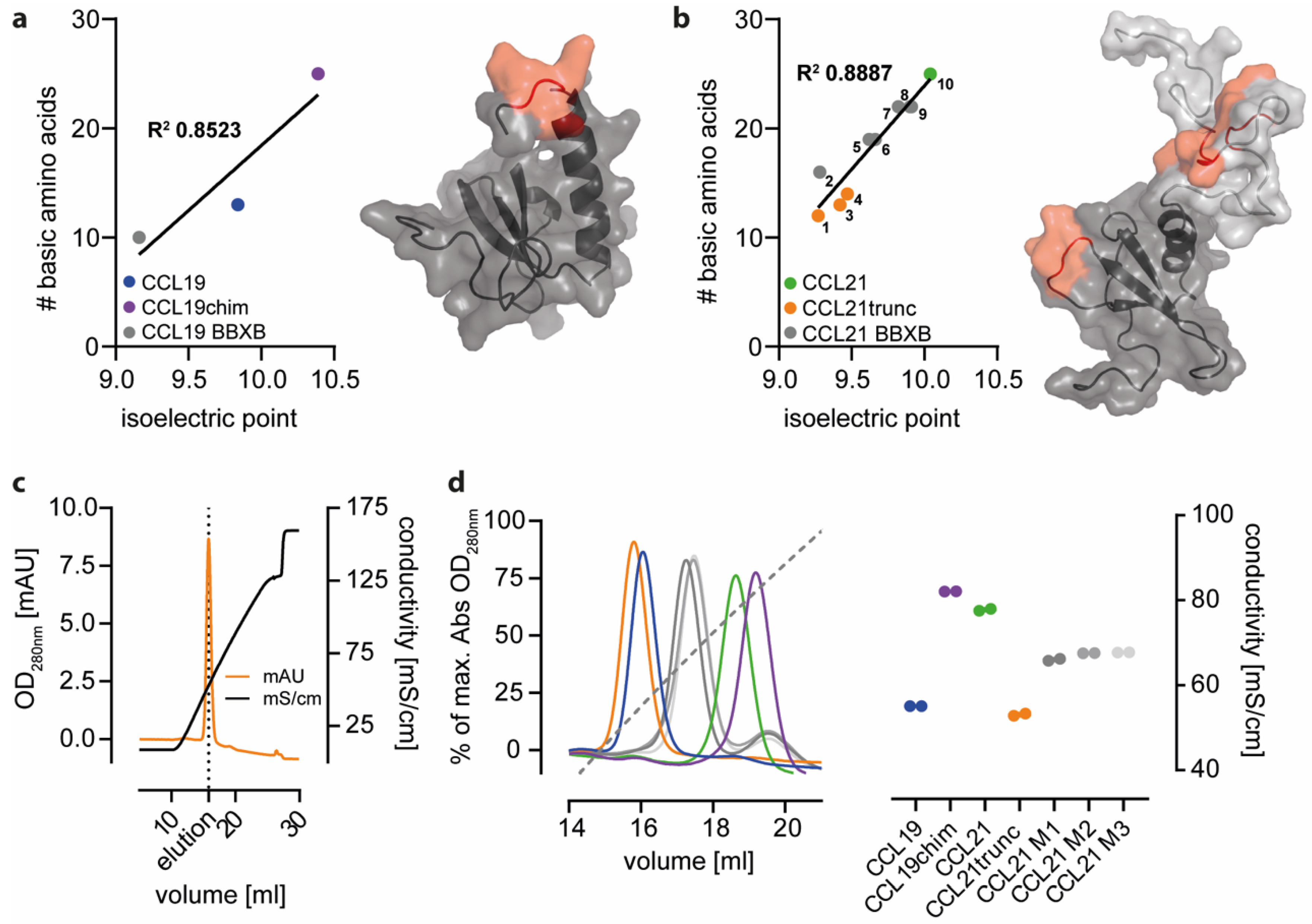
2.2. Positively Charged Amino Acids at the Surface of CCL21 Mediate Heparin Binding
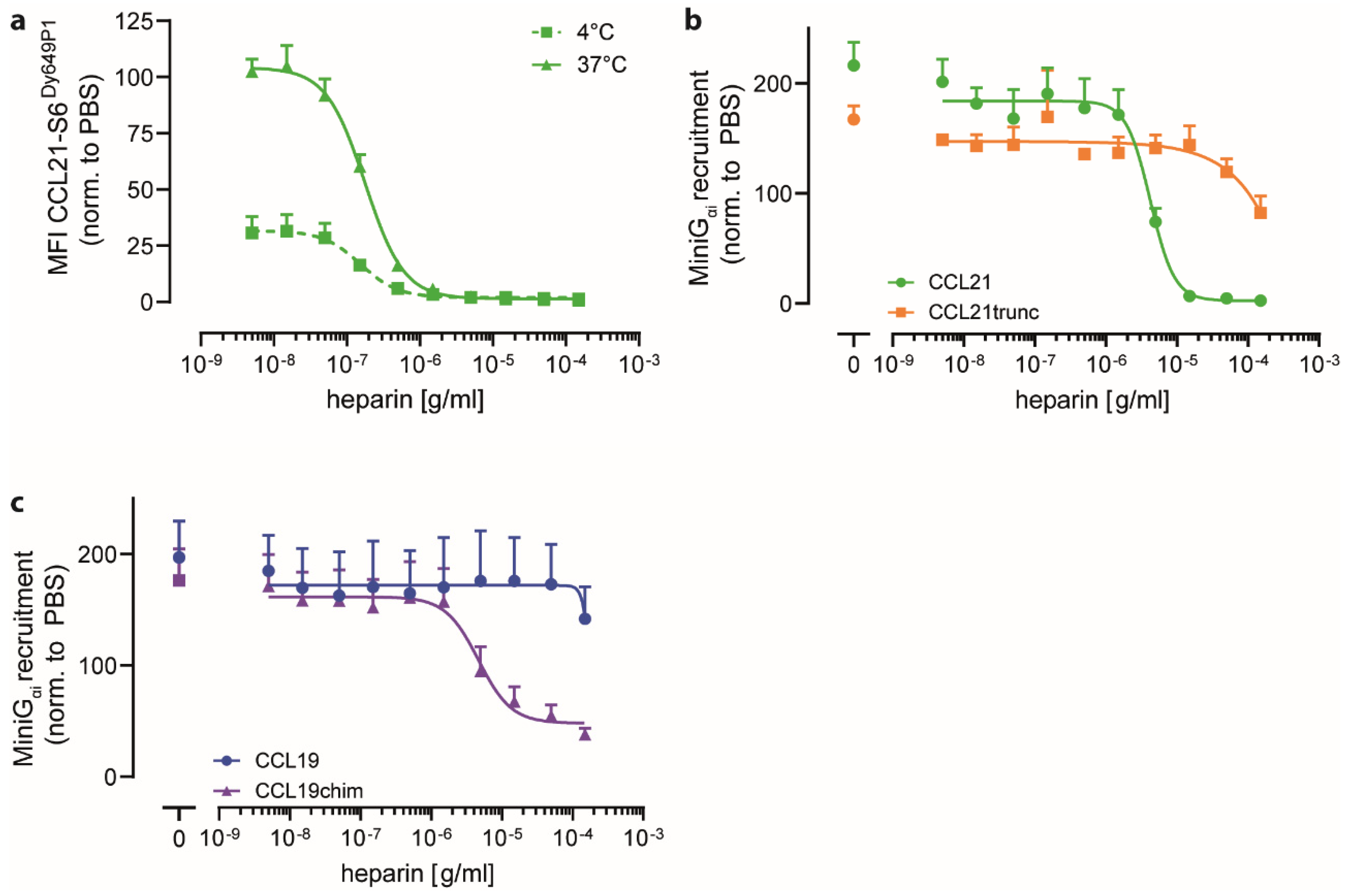
2.3. Heparin Interacts with CCL21′s C-terminus and Negatively Regulates CCR7 Signaling
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Plasmids
4.2. Chemokine Purification and Fluorescent Labeling
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Transient Transfection
4.5. MiniGαi and βarrestin2 Recruitment to CCR7
4.6. Mobilization of Intracellular Calcium
4.7. Heparin Binding Assays
4.8. Competition for Chemokine Binding to CCR7 and by Heparin
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hauser, M.A.; Legler, D.F. Common and biased signaling pathways of the chemokine receptor CCR7 elicited by its ligands CCL19 and CCL21 in leukocytes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 99, 869–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proudfoot, A.E.I.; Johnson, Z.; Bonvin, P.; Handel, T.M. Glycosaminoglycan Interactions with Chemokines Add Complexity to a Complex System. Pharmaceuticals 2017, 10, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, L.; Ehrengruber, M.U.; Clark-Lewis, I.; Baggiolini, M.; Rot, A. Binding to heparan sulfate or heparin enhances neutrophil responses to interleukin 8. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 7158–7162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, S.; Martínez-Burgo, B.; Sepuru, K.M.; Rajarathnam, K.; Kirby, J.A.; Sheerin, N.S.; Ali, S. Regulation of chemokine function: The roles of GAG-binding and post-translational nitration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, N.S.; Mancera, R.L. The structure of glycosaminoglycans and their interactions with proteins. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2008, 72, 455–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.; Hauschild, R.; Schwarz, J.; Moussion, C.; De Vries, I.; Legler, D.F.; Luther, S.A.; Bollenbach, T.; Sixt, M. Interstitial dendritic cell guidance by haptotactic chemokine gradients. Science 2013, 339, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, X.; Moseman, E.A.; Saito, H.; Petryanik, B.; Thiriot, A.; Hatakeyama, S.; Ito, Y.; Kawashima, H.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Lowe, J.B. Endothelial heparan sulfate controls chemokine presentation in recruitment of lymphocytes and dendritic cells to lymph nodes. Immunity 2010, 33, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legler, D.F.; Thelen, M. New insights in chemokine signaling. F1000Research 2018, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legler, D.F.; Matti, C.; Laufer, J.M.; Jakobs, B.D.; Purvanov, V.; Uetz-von Allmen, E.; Thelen, M. Modulation of Chemokine Receptor Function by Cholesterol: New Prospects for Pharmacological Intervention. Mol. Pharmacol. 2017, 91, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, C.E.; Nibbs, R.J.B. A guide to chemokines and their receptors. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 2944–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förster, R.; Davalos-Misslitz, A.C.; Rot, A. CCR7 and its ligands: Balancing immunity and tolerance. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, A.S.; Rosenkilde, M.M.; Hjortø, G.M. Biased signaling of G protein-coupled receptors—From a chemokine receptor CCR7 perspective. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2018, 258, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardi, G.; Lipp, M.; Baggiolini, M.; Loetscher, P. The T cell chemokine receptor CCR7 is internalized on stimulation with ELC, but not with SLC. Eur. J. Immunol. 2001, 31, 3291–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, C.; Groettrup, M.; Legler, D.F. Opposite fate of endocytosed CCR7 and its ligands: Recycling versus degradation. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 2314–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjortø, G.M.; Larsen, O.; Steen, A.; Daugvilaite, V.; Berg, C.; Fares, S.; Hansen, M.; Ali, S.; Rosenkilde, M.M. Differential CCR7 targeting in dendritic cells by three naturally occurring CC-chemokines. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, J.V.; Rot, A.; Luo, Y.; Narasimhaswamy, M.; Nakano, H.; Gunn, M.D.; Matsuzawa, A.; Quackenbush, E.J.; Dorf, M.E.; von Andrian, U.H. The CC chemokine thymus-derived chemotactic agent 4 (TCA-4, secondary lymphoid tissue chemokine, 6Ckine, exodus-2) triggers lymphocyte function–associated antigen 1–mediated arrest of rolling T lymphocytes in peripheral lymph node high endothelial venules. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassileva, G.; Soto, H.; Zlotnik, A.; Nakano, H.; Kakiuchi, T.; Hedrick, J.A.; Lira, S.A. The reduced expression of 6Ckine in the plt mouse results from the deletion of one of two 6Ckine genes. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 190, 1183–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, A.; Homey, B.; Soto, H.; Ge, N.; Catron, D.; Buchanan, M.E.; McClanahan, T.; Murphy, E.; Yuan, W.; Wagner, S.N. Involvement of chemokine receptors in breast cancer metastasis. Nature 2001, 410, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, H.E.; Gonzalez, E.B.; Maki, W.; Wu, M.T.; Hwang, S.T. Expression of CC chemokine receptor-7 and regional lymph node metastasis of B16 murine melanoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001, 93, 1638–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, K.; Leier, J.; Henning, G.; Dimmler, A.; Weißbach, R.; Hohenberger, W.; Förster, R. Prediction of lymph node metastasis in colorectal carcinoma by expressionof chemokine receptor CCR7. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 116, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashino, K.; Sadanaga, N.; Yamaguchi, H.; Tanaka, F.; Ohta, M.; Shibuta, K.; Inoue, H.; Mori, M. Expression of chemokine receptor CCR7 is associated with lymph node metastasis of gastric carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 2937–2941. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Legler, D.F.; Uetz-von Allmen, E.; Hauser, M.A. CCR7: Roles in cancer cell dissemination, migration and metastasis formation. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 54, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Truty, J.; Lawrence, R.; Johns, S.C.; Srinivasan, R.S.; Handel, T.M.; Fuster, M.M. A critical role for lymphatic endothelial heparan sulfate in lymph node metastasis. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, R.; Nagira, M.; Kitaura, M.; Imagawa, N.; Imai, T.; Yoshie, O. Secondary lymphoid-tissue chemokine is a functional ligand for the CC chemokine receptor CCR7. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 7118–7122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagira, M.; Imai, T.; Hieshima, K.; Kusuda, J.; Ridanpää, M.; Takagi, S.; Nishimura, M.; Kakizaki, M.; Nomiyama, H.; Yoshie, O. Molecular cloning of a novel human CC chemokine secondary lymphoid-tissue chemokine that is a potent chemoattractant for lymphocytes and mapped to chromosome 9p13. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 19518–19524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, A.S.; Adogamhe, P.E.; Laufer, J.M.; Legler, D.F.; Veldkamp, C.T.; Rosenkilde, M.M.; Hjortø, G.M. CCL19 with CCL21-tail displays enhanced glycosaminoglycan binding with retained chemotactic potency in dendritic cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018, 104, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussouras, N.A.; Hjortø, G.M.; Peterson, F.C.; Szpakowska, M.; Chevigné, A.; Rosenkilde, M.M.; Volkman, B.F.; Dwinell, M.B. Structural features of an extended C-terminal tail modulate the function of the chemokine CCL21. Biochemistry 2020, 59, 1338–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legler, D.F.; Thelen, M. Chemokines: Chemistry, Biochemistry and Biological Function. Chimia 2016, 70, 856–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.; Sandberg, J.L.; Ziarek, J.J.; Gerarden, K.P.; Rode, R.R.; Jensen, D.R.; McCaslin, D.R.; Peterson, F.C.; Veldkamp, C.T. Solution structure of CCL21 and identification of a putative CCR7 binding site. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 733–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumann, K.; Lämmermann, T.; Bruckner, M.; Legler, D.F.; Polleux, J.; Spatz, J.P.; Schuler, G.; Förster, R.; Lutz, M.B.; Sorokin, L. Immobilized chemokine fields and soluble chemokine gradients cooperatively shape migration patterns of dendritic cells. Immunity 2010, 32, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, N.; Loef, E.J.; Kelch, I.D.; Verdon, D.J.; Black, M.M.; Middleditch, M.J.; Greenwood, D.R.; Graham, E.S.; Brooks, A.E.; Dunbar, P.R. Plasmin and regulators of plasmin activity control the migratory capacity and adhesion of human T cells and dendritic cells by regulating cleavage of the chemokine CCL21. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2016, 94, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, M.A.; Kindinger, I.; Laufer, J.M.; Spate, A.K.; Bucher, D.; Vanes, S.L.; Krueger, W.A.; Wittmann, V.; Legler, D.F. Distinct CCR7 glycosylation pattern shapes receptor signaling and endocytosis to modulate chemotactic responses. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 99, 993–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiermaier, E.; Moussion, C.; Veldkamp, C.T.; Gerardy-Schahn, R.; De Vries, I.; Williams, L.G.; Chaffee, G.R.; Phillips, A.J.; Freiberger, F.; Imre, R. Polysialylation controls dendritic cell trafficking by regulating chemokine recognition. Science 2016, 351, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barmore, A.J.; Castex, S.M.; Gouletas, B.A.; Griffith, A.J.; Metz, S.W.; Muelder, N.G.; Populin, M.J.; Sackett, D.M.; Schuster, A.M.; Veldkamp, C.T. Transferring the C-terminus of the chemokine CCL21 to CCL19 confers enhanced heparin binding. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 477, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maione, T.E.; Gray, G.S.; Hunt, A.J.; Sharpe, R.J. Inhibition of tumor growth in mice by an analogue of platelet factor 4 that lacks affinity for heparin and retains potent angiostatic activity. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 2077–2083. [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarty, L.; Rogers, L.; Quach, T.; Breckenridge, S.; Kolattukudy, P.E. Lysine 58 and histidine 66 at the C-terminal α-helix of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 are essential for glycosaminoglycan binding. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 29641–29647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crijns, H.; Adyns, L.; Ganseman, E.; Cambier, S.; Vandekerckhove, E.; Pörtner, N.; Vanbrabant, L.; Struyf, S.; Gerlza, T.; Kungl, A. Affinity and Specificity for Binding to Glycosaminoglycans Can Be Tuned by Adapting Peptide Length and Sequence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, A.S.; Larsen, O.; Uetz-von Allmen, E.; Lückmann, M.; Legler, D.F.; Frimurer, T.M.; Veldkamp, C.T.; Hjortø, G.M.; Rosenkilde, M.M. Biased signaling of CCL21 and CCL19 does not rely on N-terminal differences, but markedly on the chemokine core domains and extracellular loop 2 of CCR7. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Okashah, N.; Inoue, A.; Nehmé, R.; Carpenter, B.; Tate, C.G.; Lambert, N.A. Mini G protein probes for active G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs) in live cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 7466–7473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, J.; Kawashima, H.; Willis, M.S.; Springer, T.A.; Hasegawa, H.; Yoshie, O.; Miyasaka, M. Chondroitin sulfate B exerts its inhibitory effect on secondary lymphoid tissue chemokine (SLC) by binding to the C-terminus of SLC. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2002, 1571, 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Hirose, J.; Kawashima, H.; Yoshie, O.; Tashiro, K.; Miyasaka, M. Versican interacts with chemokines and modulates cellular responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 5228–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Molino Del Barrio, I.; Meeson, A.; Cooke, K.; Malki, M.I.; Barron-Millar, B.; Kirby, J.A.; Ali, S. Contribution of Heparan Sulphate Binding in CCL21-Mediated Migration of Breast Cancer Cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, A.S.; Brandum, E.P.; Mikkelsen, J.M.; Orfin, K.A.; Boilesen, D.R.; Egerod, K.L.; Moussouras, N.A.; Vilhardt, F.; Kalinski, P.; Basse, P. The C-terminal peptide of CCL21 drastically augments CCL21 activity through the dendritic cell lymph node homing receptor CCR7 by interaction with the receptor N-terminus. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 6963–6978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amara, A.; Lorthioir, O.; Valenzuela, A.; Magerus, A.; Thelen, M.; Montes, M.; Virelizier, J.-L.; Delepierre, M.; Baleux, F.; Lortat-Jacob, H. Stromal cell-derived factor-1α associates with heparan sulfates through the first β-strand of the chemokine. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 23916–23925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proudfoot, A.E.; Fritchley, S.; Borlat, F.; Shaw, J.P.; Vilbois, F.; Zwahlen, C.; Trkola, A.; Marchant, D.; Clapham, P.R.; Wells, T.N. The BBXB motif of RANTES is the principal site for heparin binding and controls receptor selectivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 10620–10626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandum, E.P.; Jørgensen, A.S.; Calvo, M.B.; Spiess, K.; Peterson, F.C.; Yang, Z.; Volkman, B.F.; Veldkamp, C.T.; Rosenkilde, M.M.; Goth, C.K. Selective Boosting of CCR7-Acting Chemokines; Short Peptides Boost Chemokines with Short Basic Tails, Longer Peptides Boost Chemokines with Long Basic Tails. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artinger, M.; Gerken, O.J.; Purvanov, V.; Legler, D.F. Distinct Fates of Chemokine and Surrogate Molecule Gradients: Consequences for CCR7-Guided Dendritic Cell Migration. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 913366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artinger, M.; Matti, C.; Gerken, O.J.; Veldkamp, C.T.; Legler, D.F. A Versatile Toolkit for Semi-Automated Production of Fluorescent Chemokines to Study CCR7 Expression and Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matti, C.; Salnikov, A.; Artinger, M.; D’Agostino, G.; Kindinger, I.; Uguccioni, M.; Thelen, M.; Legler, D.F. ACKR4 recruits GRK3 prior to β-Arrestins but can scavenge chemokines in the absence of β-arrestins. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, C.; Eisele, P.S.; Schaeuble, K.; Groettrup, M.; Legler, D.F. Distinct motifs in the chemokine receptor CCR7 regulate signal transduction, receptor trafficking and chemotaxis. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121 Pt 16, 2759–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeuble, K.; Hauser, M.A.; Rippl, A.V.; Bruderer, R.; Otero, C.; Groettrup, M.; Legler, D.F. Ubiquitylation of the chemokine receptor CCR7 enables efficient receptor recycling and cell migration. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125 Pt 19, 4463–4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerken, O.J.; Artinger, M.; Legler, D.F. Shifting CCR7 towards Its Monomeric Form Augments CCL19 Binding and Uptake. Cells 2022, 11, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Artinger, M.; Gerken, O.J.; Legler, D.F. Heparin Specifically Interacts with Basic BBXB Motifs of the Chemokine CCL21 to Define CCR7 Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021670
Artinger M, Gerken OJ, Legler DF. Heparin Specifically Interacts with Basic BBXB Motifs of the Chemokine CCL21 to Define CCR7 Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(2):1670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021670
Chicago/Turabian StyleArtinger, Marc, Oliver J. Gerken, and Daniel F. Legler. 2023. "Heparin Specifically Interacts with Basic BBXB Motifs of the Chemokine CCL21 to Define CCR7 Signaling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 2: 1670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021670
APA StyleArtinger, M., Gerken, O. J., & Legler, D. F. (2023). Heparin Specifically Interacts with Basic BBXB Motifs of the Chemokine CCL21 to Define CCR7 Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(2), 1670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021670








