Generation of New Knock-Out Mouse Strains of Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1
Abstract
1. Introduction
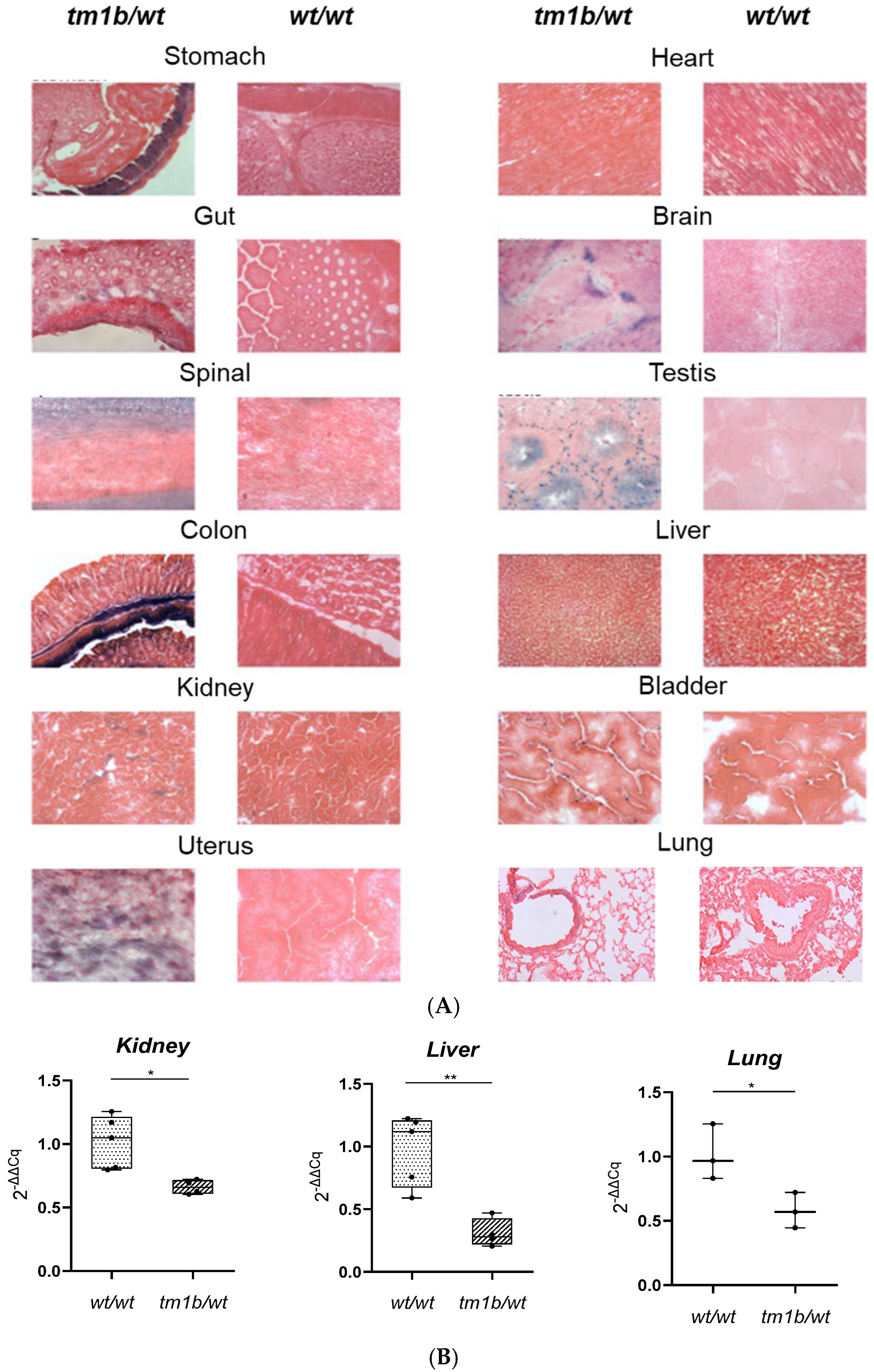
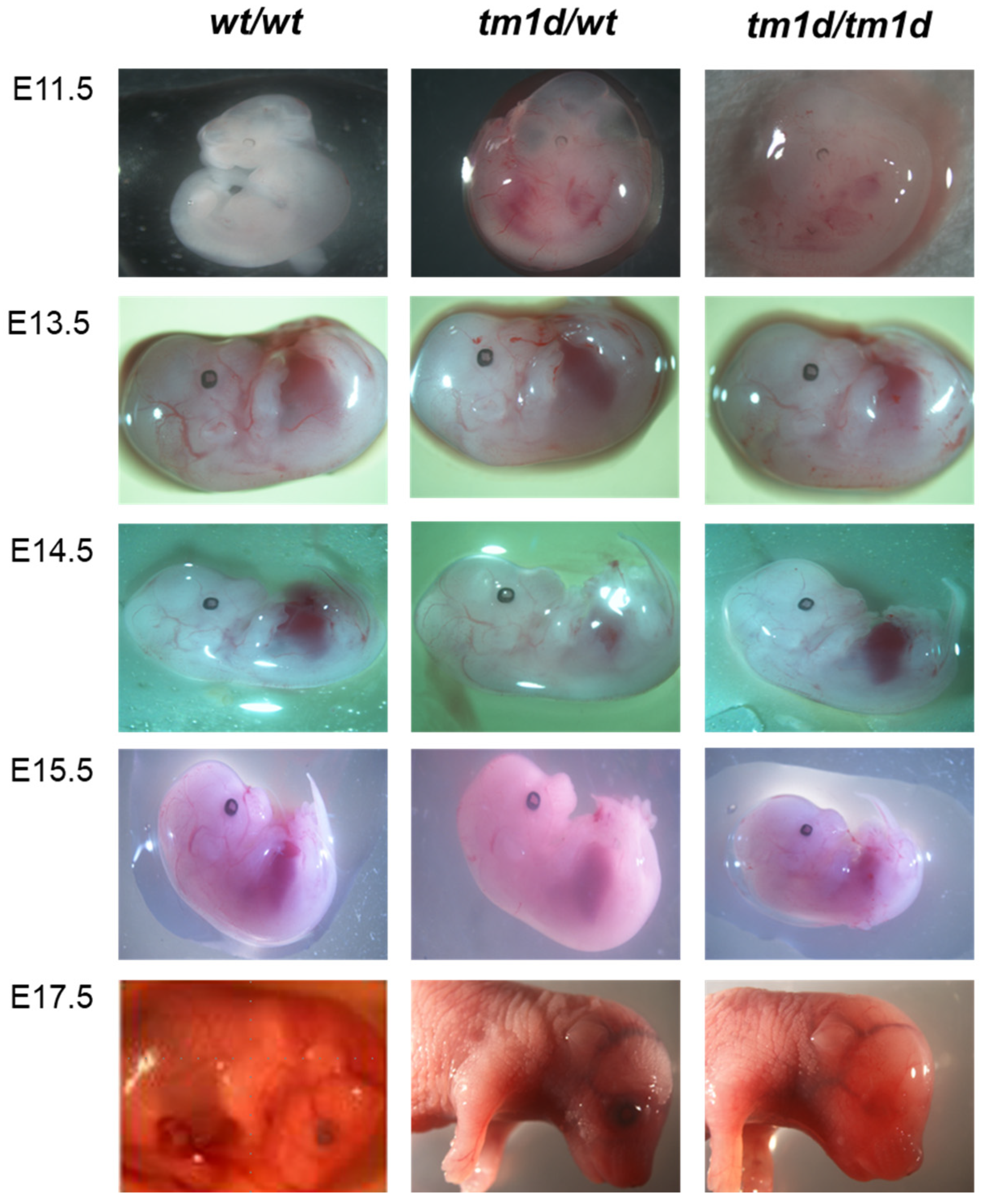
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Mice Breeding
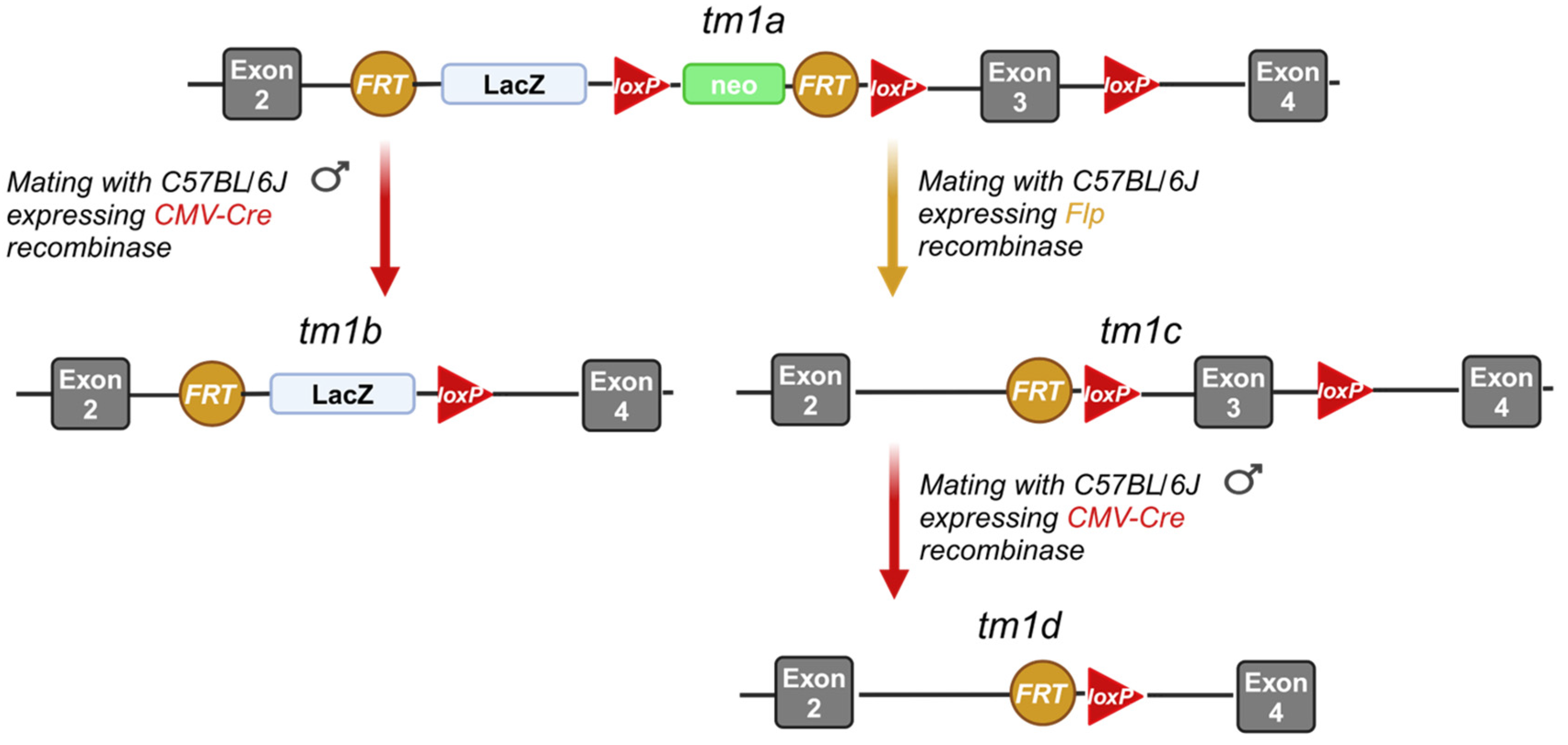
3.2. Generation of the Lpar1tm1a, Lpar1tm1b, Lpar1tm1c, and Lpar1tm1d Mouse Strains
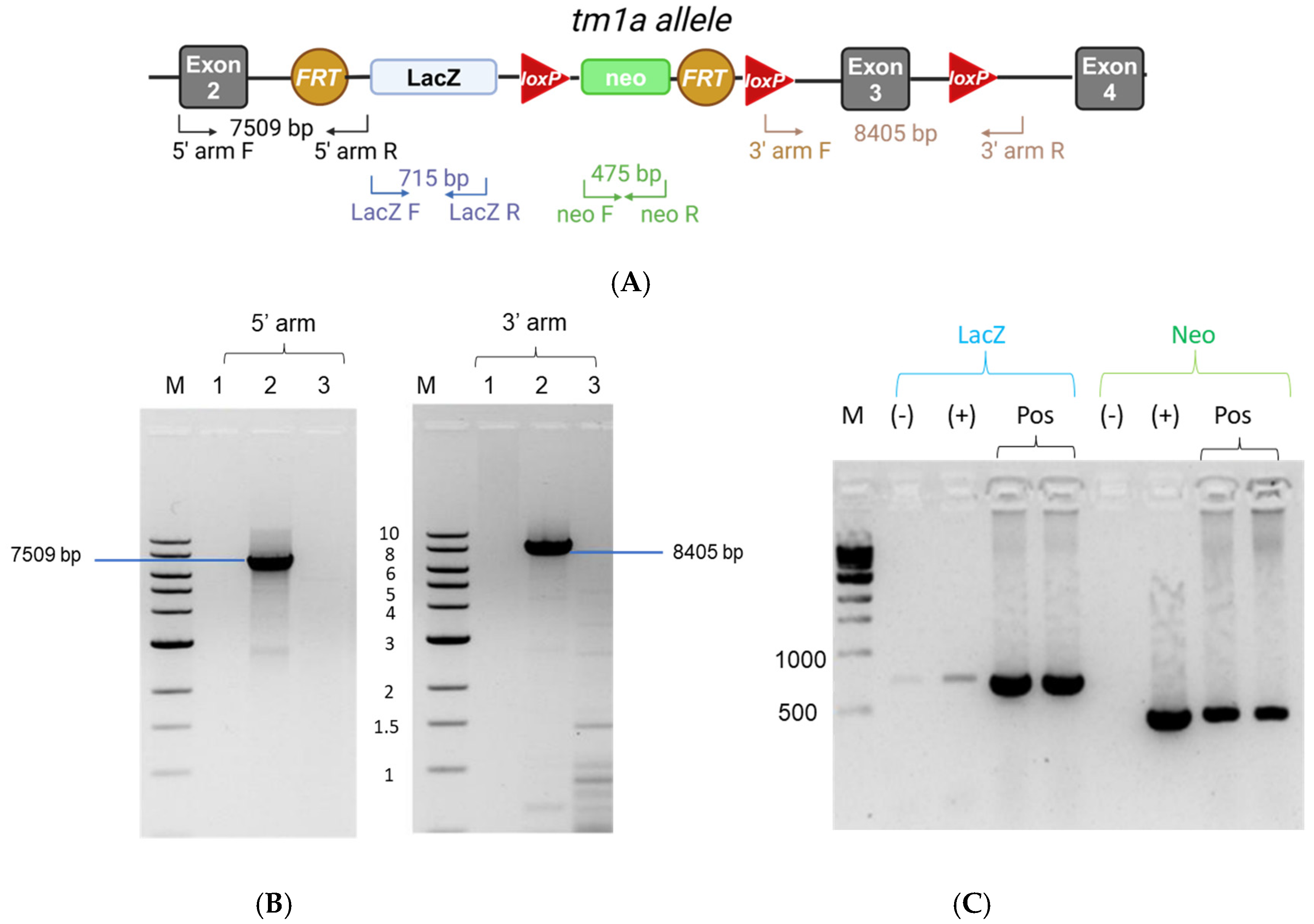
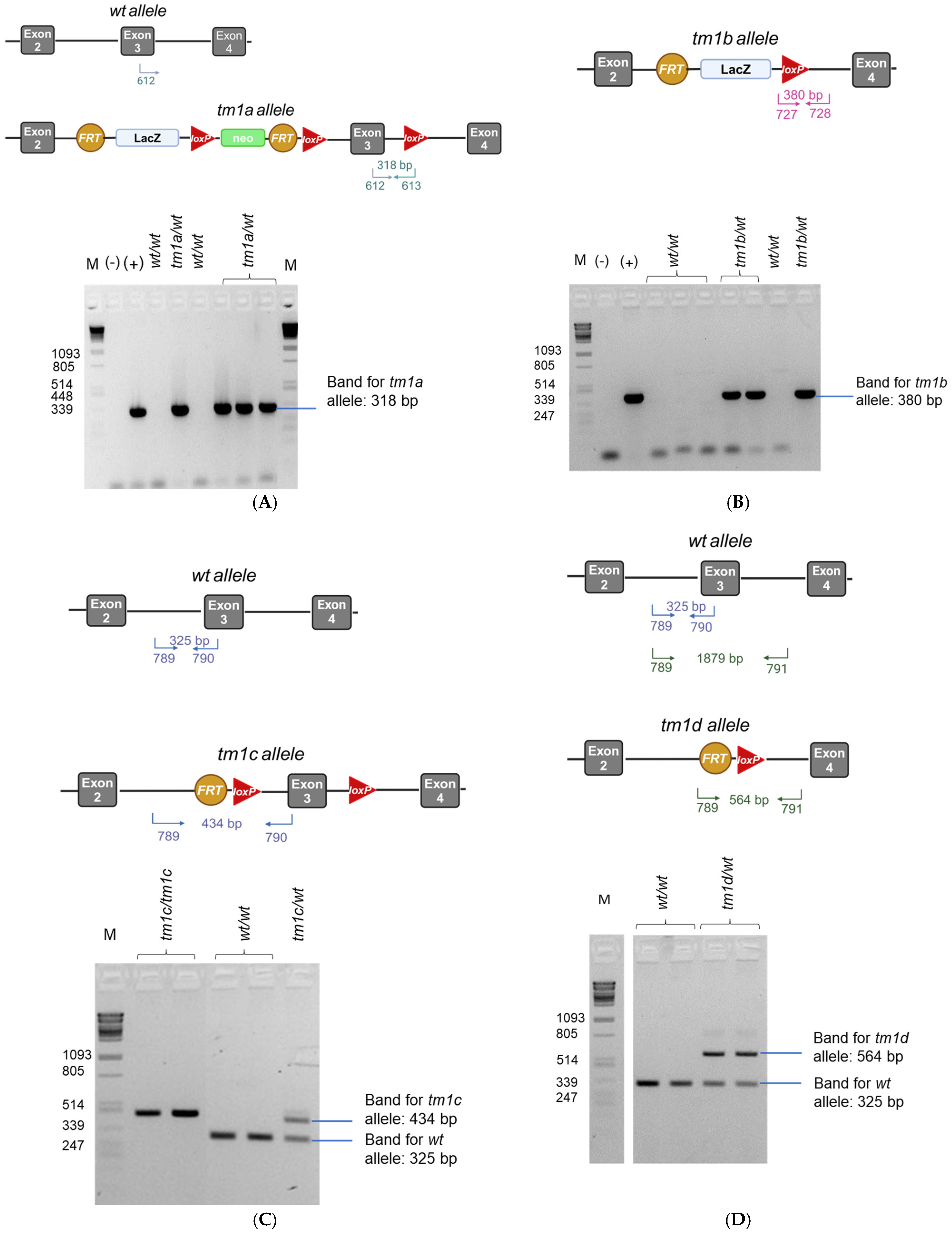
3.3. DNA Extraction, Long-Range PCR, and Genotyping PCR
3.4. Isolation and Imaging of E11.5–E17.5 Embryos
3.5. RNA Isolation-Reverse Transcription-Real Time PCR
3.6. Tissue Processing, H&E Staining, and Imaging
3.7. X-Gal Staining
3.7.1. Protocol for Cryosections
3.7.2. Protocol for Paraffin Sections (Lungs/Testis)
3.8. Biochemical Analysis
3.9. Statistical Analysis
3.10. Image Creation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATX | autotaxin |
| B2m | beta-2 microglobulin |
| CMV | Cytomegalovirus |
| DAG | Diacylglycerol |
| EMMA | European Mouse Mutant Archive |
| ES cells | Embryonic stem cells |
| EUCOMM | European Conditional Mouse Mutagenesis Program |
| IPF | Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| KO | knockout |
| LPA | Lysophosphatidic acid |
| LPAR1 | Lysophosphatidic acid Receptor 1 |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| PI3K | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-protein kinase B |
| PLC | phospholipase C |
| RA | rheumatoid arthritis |
| SRF | serum response factor |
| tm1a | targeted mutation 1a |
| TGF-β | transforming growth factor beta |
References
- Geraldo, L.H.M.; Spohr, T.; Amaral, R.F.D.; Fonseca, A.; Garcia, C.; Mendes, F.A.; Freitas, C.; dosSantos, M.F.; Lima, F.R.S. Role of lysophosphatidic acid and its receptors in health and disease: Novel therapeutic strategies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magkrioti, C.; Galaris, A.; Kanellopoulou, P.; Stylianaki, E.A.; Kaffe, E.; Aidinis, V. Autotaxin and chronic inflammatory diseases. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 104, 102327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaffe, E.; Magkrioti, C.; Aidinis, V. Deregulated Lysophosphatidic Acid Metabolism and Signaling in Liver Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magkrioti, C.; Antonopoulou, G.; Fanidis, D.; Pliaka, V.; Sakellaropoulos, T.; Alexopoulos, L.G.; Ullmer, C.; Aidinis, V. Lysophosphatidic Acid Is a Proinflammatory Stimulus of Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdes-Rives, S.A.; Gonzalez-Arenas, A. Autotaxin-Lysophosphatidic Acid: From Inflammation to Cancer Development. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 9173090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, J.H.; Weiner, J.A.; Post, S.R.; Chun, J. Ventricular zone gene-1 (vzg-1) encodes a lysophosphatidic acid receptor expressed in neurogenic regions of the developing cerebral cortex. J. Cell Biol. 1996, 135, 1071–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yung, Y.C.; Stoddard, N.C.; Chun, J. LPA receptor signaling: Pharmacology, physiology, and pathophysiology. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 1192–1214. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, H.; Lu, Y.; Shao, M.; Wu, T. Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptors: Biochemical and Clinical Implications in Different Diseases. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 3519–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estivill-Torrus, G.; Llebrez-Zayas, P.; Matas-Rico, E.; Santin, L.; Pedraza, C.; De Diego, I.; Del Arco, I.; Fernandez-Llebrez, P.; Chun, J.; De Fonseca, F.R. Absence of LPA1 signaling results in defective cortical development. Cereb. Cortex 2008, 18, 938–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shano, S.; Moriyama, R.; Chun, J.; Fukushima, N. Lysophosphatidic acid stimulates astrocyte proliferation through LPA1. Neurochem. Int. 2008, 52, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsbury, M.A.; Rehen, S.K.; Contos, J.J.; Higgins, C.M.; Chun, J. Non-proliferative effects of lysophosphatidic acid enhance cortical growth and folding. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fransson, J.; Gomez-Conde, A.I.; Romero-Imbroda, J.; Fernandez, O.; Leyva, L.; de Fonseca, F.R.; Chun, J.; Louapre, C.; Van-Evercooren, A.B.; Zujovic, V.; et al. Activation of Macrophages by Lysophosphatidic Acid through the Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1 as a Novel Mechanism in Multiple Sclerosis Pathogenesis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georas, S.N.; Berdyshev, E.; Hubbard, W.; Gorshkova, I.A.; Usatyuk, P.V.; Saatian, B.; Myers, A.C.; Williams, M.A.; Xiao, H.Q.; Liu, M.; et al. Lysophosphatidic acid is detectable in human bronchoalveolar lavage fluids at baseline and increased after segmental allergen challenge. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2007, 37, 311–322. [Google Scholar]
- Tager, A.M.; LaCamera, P.; Shea, B.S.; Campanella, G.S.; Selman, M.; Zhao, Z.; Polosukhin, V.; Wain, J.; Karimi-Shah, B.A.; Kim, N.D.; et al. The lysophosphatidic acid receptor LPA1 links pulmonary fibrosis to lung injury by mediating fibroblast recruitment and vascular leak. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Castelino, F.V.; Seiders, J.; Bain, G.; Brooks, S.F.; King, C.D.; Swaney, J.S.; Lorrain, D.S.; Chun, J.; Luster, A.D.; Tager, A.M. Amelioration of dermal fibrosis by genetic deletion or pharmacologic antagonism of lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 in a mouse model of scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, F.; Miller, D.D. Role of lysophosphatidic acid and its receptors in the kidney. Physiol. Genom. 2017, 49, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyabe, Y.; Miyabe, C.; Iwai, Y.; Takayasu, A.; Fukuda, S.; Yokoyama, W.; Nagai, J.; Jona, M.; Tokuhara, Y.; Ohkawa, R.; et al. Necessity of lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 for development of arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 2037–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyabe, Y.; Miyabe, C.; Iwai, Y.; Yokoyama, W.; Sekine, C.; Sugimoto, K.; Harigai, M.; Miyasaka, M.; Miyasaka, N.; Nanki, T. Activation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes derived from rheumatoid arthritis via lysophosphatidic acid-lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 cascade. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsaibia, M.J.; Boulanger, M.C.; Bouchareb, R.; Mkannez, G.; Le Quang, K.; Hadji, F.; Argaud, D.; Dahou, A.; Bosse, Y.; Koschinsky, M.L.; et al. OxLDL-derived lysophosphatidic acid promotes the progression of aortic valve stenosis through a LPAR1-RhoA-NF-kappaB pathway. Cardiovasc. Res. 2017, 113, 1351–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyabe, C.; Miyabe, Y.; Nagai, J.; Miura, N.N.; Ohno, N.; Chun, J.; Tsuboi, R.; Ueda, H.; Miyasaka, M.; Miyasaka, N.; et al. Abrogation of lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 ameliorates murine vasculitis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelsson Raja, A.; Wakimoto, H.; DeLaughter, D.M.; Reichart, D.; Gorham, J.; Conner, D.A.; Lun, M.; Probst, C.K.; Sakai, N.; Knipe, R.S.; et al. Ablation of lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 attenuates hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in a mouse model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2204174119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Han, Y.; Jenkin, K.; Lee, S.J.; Sasaki, M.; Klapproth, J.M.; He, P.; Yun, C.C. Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1 Is Important for Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function and Susceptibility to Colitis. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Ma, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Zheng, G.-Y.; Sun, Z.; Jiang, F.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Dang, A.; et al. Genetic and Functional Evidence Supports LPAR1 as a Susceptibility Gene for Hypertension. Hypertension 2015, 66, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obo, Y.; Yamada, T.; Furukawa, M.; Hotta, M.; Honoki, K.; Fukushima, N.; Tsujiuchi, T. Frequent mutations of lysophosphatidic acid receptor-1 gene in rat liver tumors. Mutat. Res. 2009, 660, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huyghe, J.R.; Bien, S.A.; Harrison, T.A.; Kang, H.M.; Chen, S.; Schmit, S.L.; Conti, D.V.; Qu, C.; Jeon, J.; Edlund, C.K.; et al. Discovery of common and rare genetic risk variants for colorectal cancer. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magkrioti, C.; Oikonomou, N.; Kaffe, E.; Mouratis, M.A.; Xylourgidis, N.; Barbayianni, I.; Megadoukas, P.; Harokopos, V.; Valavanis, C.; Chun, J.; et al. The Autotaxin-Lysophosphatidic Acid Axis Promotes Lung Carcinogenesis. Cancer. Res. 2018, 78, 3634–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Chen, C.C. Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor Antagonists and Cancer: The Current Trends, Clinical Implications, and Trials. Cells 2021, 10, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Feng, J.; Lu, M.; Tang, W.; Han, J.; Luo, X.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, L. microRNA-501-5p promotes cell proliferation and migration in gastric cancer by downregulating LPAR1. J. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 121, 1911–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.; Yoshikawa, K.; Tanabe, E.; Kitayoshi, M.; Fukui, R.; Fukushima, N.; Tsujiuchi, T. Opposite roles of LPA1 and LPA3 on cell motile and invasive activities of pancreatic cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 2012, 33, 1739–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Cao, G.; Bai, H.; Zhang, Z. LPAR1 regulates the development of intratumoral heterogeneity in ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benesch, M.G.K.; Wu, R.; Tang, X.; Brindley, D.N.; Ishikawa, T.; Takabe, K. Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor Signaling in the Human Breast Cancer Tumor Microenvironment Elicits Receptor-Dependent Effects on Tumor Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Rebecca, V.W.; Kossenkov, A.V.; Connelly, T.; Liu, Q.; Gutierrez, A.; Xiao, M.; Li, L.; Zhang, G.; Samarkina, A.; et al. Neural Crest-Like Stem Cell Transcriptome Analysis Identifies LPAR1 in Melanoma Progression and Therapy Resistance. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 5230–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatraman, G.; Benesch, M.G.; Tang, X.; Dewald, J.; McMullen, T.P.; Brindley, D.N. Lysophosphatidate signaling stabilizes Nrf2 and increases the expression of genes involved in drug resistance and oxidative stress responses: Implications for cancer treatment. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 772–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, C.C. Lysophosphatidic Acid and Autotaxin-associated Effects on the Initiation and Progression of Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decato, B.E.; Leeming, D.J.; Sand, J.M.B.; Fischer, A.; Du, S.; Palmer, S.M.; Karsdal, M.; Luo, Y.; Minnich, A. LPA1 antagonist BMS-986020 changes collagen dynamics and exerts antifibrotic effects in vitro and in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corte, T.J.; Behr, J.; Cottin, V.; Glassberg, M.K.; Kreuter, M.; Martinez, F.J.; Ogura, T.; Suda, T.; Wijsenbeek, M.; Berkowitz, E.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Admilparant, an LPA(1) Antagonist in Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 211, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allanore, Y.; Distler, O.; Jagerschmidt, A.; Illiano, S.; Ledein, L.; Boitier, E.; Agueusop, I.; Denton, C.P.; Khanna, D. Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1 Antagonist SAR100842 for Patients With Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Eight-Week Placebo-Controlled Study Followed by a Sixteen-Week Open-Label Extension Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 1634–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Ali, F.N.; Ye, Z.; Zarzoso, J.; Rogowski, J.; Sun, Y.; Xin, Y. Pharmacokinetics of Fipaxalparant, a Small-Molecule Selective Negative Allosteric Modulator of Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1, and the Effect of Food in Healthy Volunteers. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2024, 13, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, S.; Sasaki, Y.; Koike, S.; Takemoto, A.; Seto, Y.; Haraguchi, M.; Ukaji, T.; Kawaguchi, T.; Sugawara, M.; Saito, M.; et al. Platelet-derived lysophosphatidic acid mediated LPAR1 activation as a therapeutic target for osteosarcoma metastasis. Oncogene 2021, 40, 5548–5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erstad, D.J.; Tager, A.M.; Hoshida, Y.; Fuchs, B.C. The autotaxin-lysophosphatidic acid pathway emerges as a therapeutic target to prevent liver cancer. Mol. Cell Oncol. 2017, 4, e1311827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rancoule, C.; Dusaulcy, R.; Treguer, K.; Gres, S.; Attane, C.; Saulnier-Blache, J.S. Involvement of autotaxin/lysophosphatidic acid signaling in obesity and impaired glucose homeostasis. Biochimie 2014, 96, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajitani, N.; Miyano, K.; Okada-Tsuchioka, M.; Abe, H.; Itagaki, K.; Hisaoka-Nakashima, K.; Morioka, N.; Uezono, Y.; Takebayashi, M. Identification of Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1 in Astroglial Cells as a Target for Glial Cell Line-derived Neurotrophic Factor Expression Induced by Antidepressants. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 27364–27370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, H.; Kajitani, N.; Okada-Tsuchioka, M.; Omori, W.; Yatsumoto, M.; Takebayashi, M. Antidepressant amitriptyline-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 activation is mediated by Src family tyrosine kinase, which leads to glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA expression in rat astroglial cells. Neuropsychopharmacol. Rep. 2019, 39, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contos, J.J.; Fukushima, N.; Weiner, J.A.; Kaushal, D.; Chun, J. Requirement for the lpA1 lysophosphatidic acid receptor gene in normal suckling behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13384–13389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.M.; Reavill, C.; Brown, G.; Brown, J.T.; Cluderay, J.E.; Crook, B.; Davies, C.H.; Dawson, L.A.; Grau, E.; Heidbreder, C.; et al. LPA1 receptor-deficient mice have phenotypic changes observed in psychiatric disease. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2003, 24, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, R.R.; Lin, M.E.; Bornhop, E.C.; Chun, J. Conditional Lpar1 gene targeting identifies cell types mediating neuropathic pain. Faseb J. 2020, 34, 8833–8842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, R.; Williams, N.A.; Kennedy, G.G.; Sanchez-Pavon, P.; Chun, J. Generation of an Lpar1-EGFP Fusion Knock-in Transgenic Mouse Line. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 79, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Paknejad, N.; Zhu, L.; Kihara, Y.; Ray, M.; Chun, J.; Liu, W.; Hite, R.K.; Huang, X.Y. Differential activation mechanisms of lipid GPCRs by lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine 1-phosphate. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradere, J.P.; Klein, J.; Gres, S.; Guigne, C.; Neau, E.; Valet, P.; Calise, D.; Chun, J.; Bascands, J.L.; Saulnier-Blache, J.S.; et al. LPA1 receptor activation promotes renal interstitial fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2007, 18, 3110–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Diaz, B.; Riquelme, R.; Varela-Nieto, I.; Jimenez, A.J.; de Diego, I.; Gomez-Conde, A.I.; Matas-Rico, E.; Aguirre, J.A.; Chun, J.; Pedraza, C.; et al. Loss of lysophosphatidic acid receptor LPA1 alters oligodendrocyte differentiation and myelination in the mouse cerebral cortex. Brain Struct. Funct. 2015, 220, 3701–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meduri, B.; Pujar, G.V.; Durai Ananda Kumar, T.; Akshatha, H.S.; Sethu, A.K.; Singh, M.; Kanagarla, A.; Mathew, B. Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) receptor modulators: Structural features and recent development. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 222, 113574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarnes, W.C.; Rosen, B.; West, A.P.; Koutsourakis, M.; Bushell, W.; Iyer, V.; Mujica, A.O.; Thomas, M.; Harrow, J.; Cox, T.; et al. A conditional knockout resource for the genome-wide study of mouse gene function. Nature 2011, 474, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwenk, F.; Baron, U.; Rajewsky, K. A cre-transgenic mouse strain for the ubiquitous deletion of loxP-flanked gene segments including deletion in germ cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995, 23, 5080–5081. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Farley, F.W.; Soriano, P.; Steffen, L.S.; Dymecki, S.M. Widespread recombinase expression using FLPeR (flipper) mice. Genesis 2000, 28, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ray, R.; Sinha, S.; Aidinis, V.; Rai, V. Atx regulates skeletal muscle regeneration via LPAR1 and promotes hypertrophy. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotopoulou, S.; Oikonomou, N.; Grigorieva, E.; Nikitopoulou, I.; Paparountas, T.; Thanassopoulou, A.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, Y.; Kontoyiannis, D.L.; Remboutsika, E.; et al. ATX expression and LPA signalling are vital for the development of the nervous system. Dev. Biol. 2010, 339, 451–464. [Google Scholar]

| (A) | |||||||
| Total Matings: 6 | Total Progeny | ||||||
| 49 (100%) | |||||||
| wt/wt | tm1d/wt | tm1d/tm1d | |||||
| Embryonic Day | Embryos | Expected | Embryos | Expected | Embryos | Expected | |
| 15 | 12–13 | 24 | 24–25 | 10 | 12–13 | ||
| 30.6% | 25% | 48.9% | 50% | 20.4% | 25% | ||
| E11.5 | 8 | ||||||
| 3 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 2 | ||
| 37.5% | 25% | 37.5% | 50% | 25% | 25% | ||
| E13.5 | 8 | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 1 | 2 | ||
| 12.5% | 25% | 75% | 50% | 12.5% | 25% | ||
| E14.5 | 11 | ||||||
| 6 | 2–3 | 4 | 5–6 | 1 | 2–3 | ||
| 54.5% | 25% | 36.4% | 50% | 9.1% | 25% | ||
| E15.5 | 12 | ||||||
| 4 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 3 | ||
| 33.3% | 25% | 33.3% | 50% | 33.3% | 25% | ||
| E17.5 | 4 | ||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | ||
| 0% | 25% | 50% | 50% | 50% | 25% | ||
| E17.5 | 6 | ||||||
| 1 | 1–2 | 5 | 3 | 0 | 1–2 | ||
| 16.7% | 25% | 83.3% | 50% | 0% | 25% | ||
| (B) | |||||||
| Total Matings | Total Progeny | ||||||
| 8 | 71 (100%) | ||||||
| wt/wt | tm1d/wt | tm1d/tm1d | |||||
| Born | Expected | Born | Expected | Born | Expected | ||
| 20 | 17–18 | 44 | 35–36 | 6 | 17–18 | ||
| 28.1% | 25% | 61.9% | 50% | 8.5% | 25% | ||
| 1♂tm1d/wt × 2♀tm1d/wt | 15 | ||||||
| 7 | 3–4 | 7 | 7–8 | 1 | 3–4 | ||
| 46.7% | 25% | 46.7% | 50% | 6.7% | 25% | ||
| 1♂tm1d/wt × 2♀tm1d/wt | 8 | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 1 | 2 | ||
| 12.5% | 25% | 75% | 50% | 12.5% | 25% | ||
| 1♂tm1d/wt × 2♀tm1d/wt | 6 | ||||||
| 0 | 1–2 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 1–2 | ||
| 0% | 25% | 100% | 50% | 0% | 25% | ||
| 1♂tm1d/wt × 2♀tm1d/wt | 6 | ||||||
| 4 | 1–2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 1–2 | ||
| 66.7% | 25% | 33.3% | 50% | 0% | 25% | ||
| 1♂tm1d/wt × 2♀tm1d/wt | 4 | ||||||
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | ||
| 50% | 25% | 50% | 50% | 0% | 25% | ||
| 1♂tm1d/wt × 2♀tm1d/wt | 6 | ||||||
| 1 | 1–2 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1–2 | ||
| 16.7% | 25% | 66.7% | 50% | 16.7% | 25% | ||
| 1♂tm1d/wt × 2♀tm1d/wt | 14 | ||||||
| 3 | 3–4 | 8 | 7 | 2 | 3–4 | ||
| 21.4% | 25% | 57.1% | 50% | 14.3% | 25% | ||
| 1♂tm1d/wt × 2♀tm1d/wt | 10 | ||||||
| 2 | 2–3 | 7 | 5 | 1 | 2–3 | ||
| 20% | 25% | 70% | 50% | 10% | 25% | ||
| Reaction and Expected Product Size | Primer | Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Long-Range PCR for 5′ arm (7509 bp) | 5′ arm F | TCATTCCTCCTCTTAGGCTCAACC |
| 5′ arm R | TGGGATAGGTCACGTTGGTGTAGA | |
| Long-Range PCR for 3′ arm (8405 bp) | 3′ arm F | CCCATGGATAGCCTATCCACTCCCTCATGC |
| 3′ arm R | CACACCTCCCCCTGAACCTGAAAC | |
| PCR for LacZ reporter gene (715 bp) | LacZ F | GATCCCGTCGTTTTACAACGTCGT |
| LacZ R | GAACTTCAGCCTCCAGTACAGCGC | |
| PCR for neomycin cassette (475 bp) | neo F | ATTGAACAAGATGGATTGCAC |
| neo R | CGTCCAGATCATCCTGATC |
| Genotyping and Expected Product(s) Size | Primer | Sequence (5′→3′) | Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lpar1tm1a wt allele: No band tm1a allele: 318 bp | 612 | GAGGATGTCTCGGCATAGTTCTGG | |
| 613 | TGAACTGATGGCGAGCTCAGACC | ||
| Lpar1tm1b wt allele: No band tm1b allele: 380 bp | 727 | CGGTCGCTACCATTACCAGT | |
| 728 | ACTGATGGCGAGCTCAGACC | ||
| Lpar1tm1c & Lpar1tm1d Lpar1tm1c: 789, 790 wt allele: 325 bp and 1879 bp, tm1c allele: 434 bp Lpar1tm1d: 789, 790, 791 wt allele: 325 bp, tm1d allele: 564 bp | 789 | GGATGCTATTTCTGGGGATGA | |
| 790 | ATACCCAATGCAGCCAAAAA | ||
| 791 | TCATGGACACTTGGACTAATGAA | ||
| Cre gene (233 bp) | Cre-F | CATTTGGGCCAGCTAAACAT | |
| Cre-R | TAAGCAATCCCCAGAAATGC | ||
| FlpE gene (600 bp) | FlpE-F | AGGGGCATACAGTACCAGAT | |
| FlpE-R | CCACACAGGGTTCCTTGTTT |
| Target Gene | Forward Primer (5′→3′) | Reverse Primer (5′→3′) | Annealing Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| B2m | TTCTGGTGCTTGTCTCACTGA | CAGTATGTTCGGCTTCCCATTC | 60 |
| Lpar1 | GAGGAATCGGGACACCATGAT | TGAAGGTGGCGCTCATCT | 59 |
| Lpar2 | GACCACACTCAGCCTAGTCAAGAC | CAGCATCTCGGCAGGAAT | 58 |
| Lpar3 | GCTCCCATGAAGCTAATGAAGACA | TACGAGTAGATGATGGGG | 59 |
| Lpar4 | AGTGCCTCCCTGTTTGTCTTC | GCCAGTGGCGATTAAAGTTGTAA | 53 |
| Lpar5 | ACCCTGGAGGTGAAAGTC | GACCACCATATGCAAACG | 54 |
| Lpar6 | GATCACTCTCTGCATCGCTGTTTC | CCCTGAACTTCAGAGAACCTGGAG | 65 |
| Gpr35 | AAGGCCCACCTGGAGTAGAA | CCACGTGAGGGTGCTGTTAC | 59 |
| Gpr87 | GGCCGCCACAATGAAAGAAAT | AAGAAACGCTTGGGGAGAGG | 59 |
| Trpv1 | GGCCGAGTTTCAGGGAGAAA | TATCTCGAGTGCTTGCGTCC | 59 |
| P2y10 | GGATGCAGTGGTTCTGGTCA | AGCAATTGGTGGGTGTTTCA | 59 |
| Rage | GGTCCACTGGATAAAGGATGGTG | TTTCCTGAGGTCCGTGGCTA | 59 |
| Pparg | GCTCGCAGATCAGCAGACTCT | GAGAAGCTGTTGGCGGAGAT | 59 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antonopoulou, G.; Magkrioti, C.; Chatzidaki, I.; Nastos, D.; Grammenoudi, S.; Bozonelos, K.; Aidinis, V. Generation of New Knock-Out Mouse Strains of Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062811
Antonopoulou G, Magkrioti C, Chatzidaki I, Nastos D, Grammenoudi S, Bozonelos K, Aidinis V. Generation of New Knock-Out Mouse Strains of Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062811
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntonopoulou, Georgia, Christiana Magkrioti, Ismini Chatzidaki, Dimitris Nastos, Sofia Grammenoudi, Konstantinos Bozonelos, and Vassilis Aidinis. 2025. "Generation of New Knock-Out Mouse Strains of Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062811
APA StyleAntonopoulou, G., Magkrioti, C., Chatzidaki, I., Nastos, D., Grammenoudi, S., Bozonelos, K., & Aidinis, V. (2025). Generation of New Knock-Out Mouse Strains of Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062811







