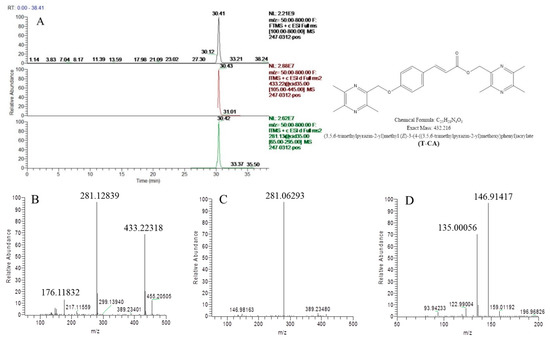
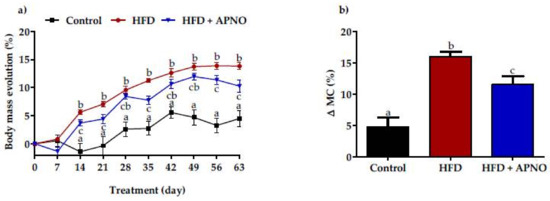
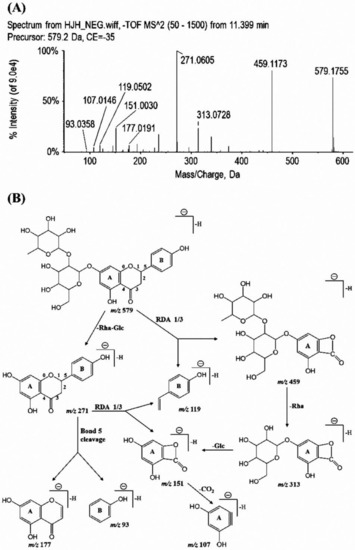
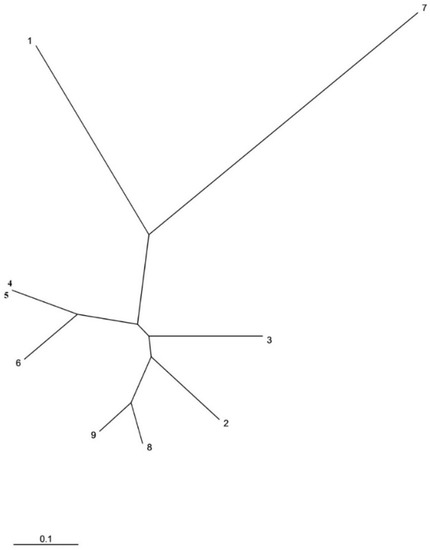
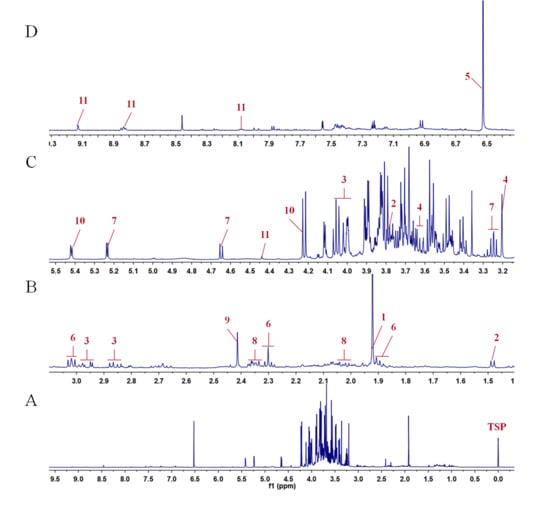
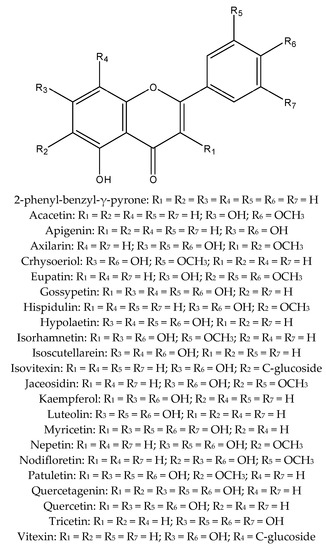
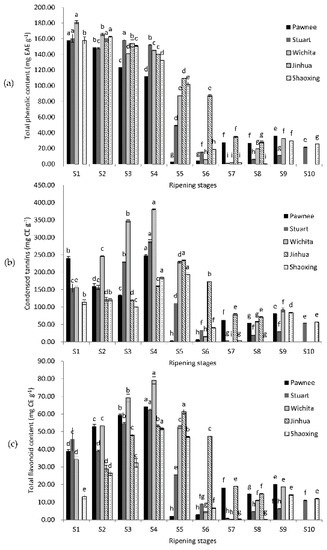
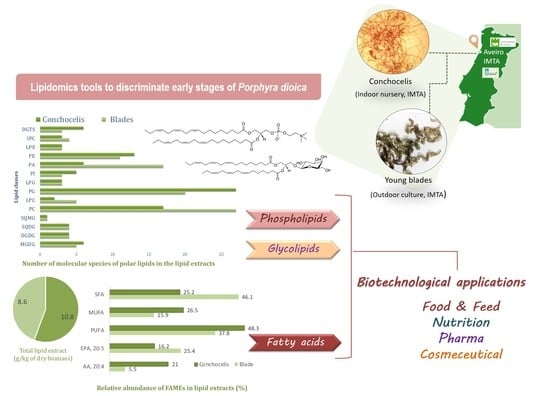
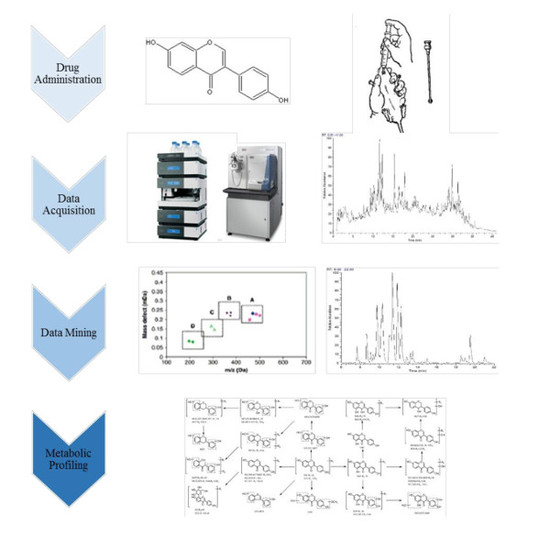
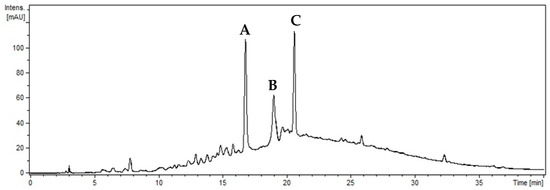
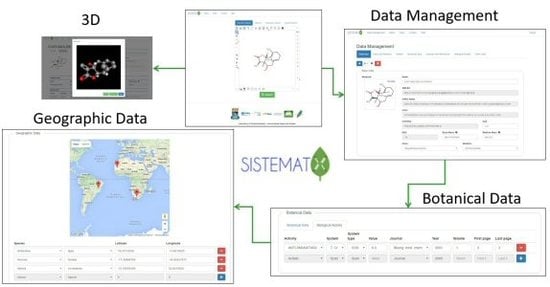
Phytochemicals: Biosynthesis, Metabolism and Biological Activities
A topical collection in Molecules (ISSN 1420-3049). This collection belongs to the section "Natural Products Chemistry".
Submission Status: Closed | Viewed by 1221830Editor
Interests: essential oils; bioactive phytochemicals; ethnopharmacology; antimicrobial resistance; one health; food security
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
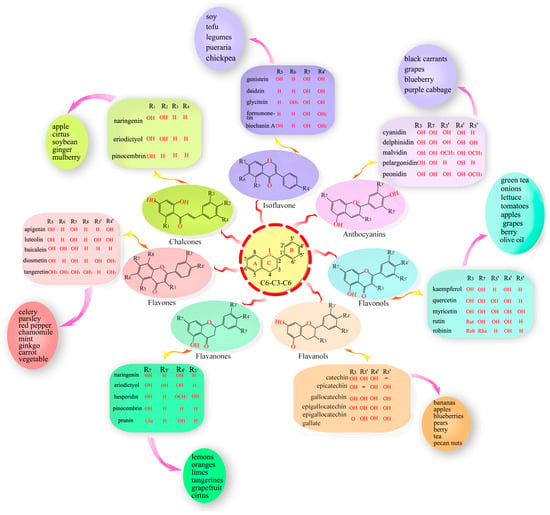
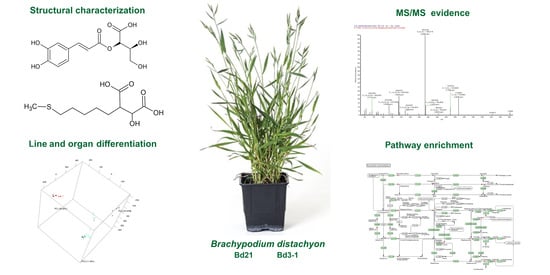
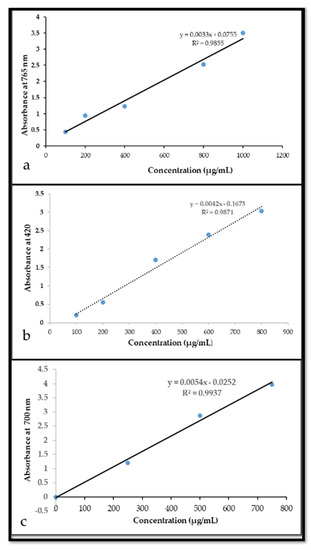
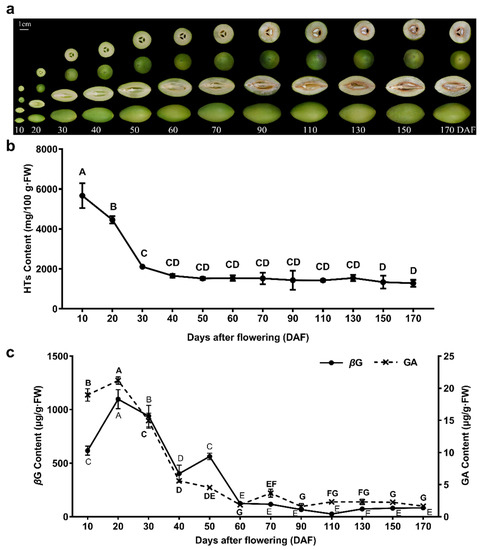
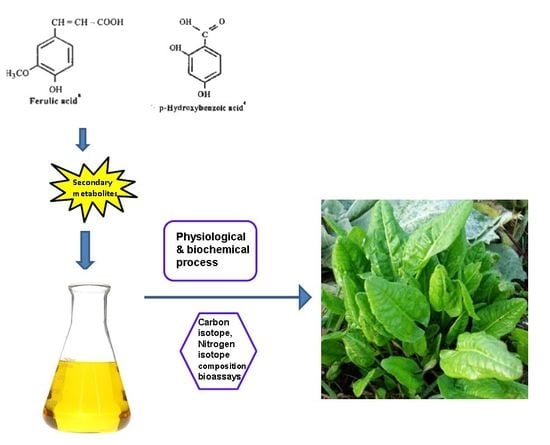
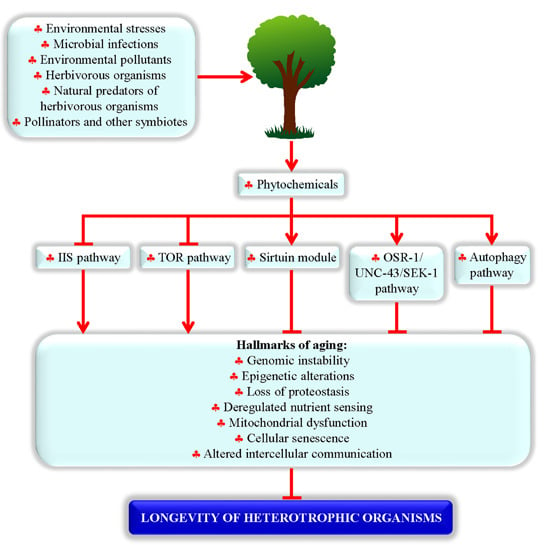
In their environment, plants have to cope with a plethora of stressful conditions such as pathogenic microorganisms, phytophagy, competitor plants, environmental pollutants and adverse climatic changes which have exerted a selective pressure on plant species and populations. In addition, coevolution, based on plant-microbe, plant-herbivore and plant-environment interactions, has represented a further force that has shaped evolving plants. Therefore, these sessile organisms have evolved a complex machinery in order to counteract harmful conditions, based on a number of sequential barriers which include both preformed and inducible chemical defenses. In evolutionary and ecological terms, chemical diversity has determined the successful of plants in their environment: these organisms synthesize secondary metabolites, i.e., phytochemicals, not only to defend themselves from their enemies, but also to secure the reproductive process, with pigments coloring flowers and volatile compounds attracting pollinators.
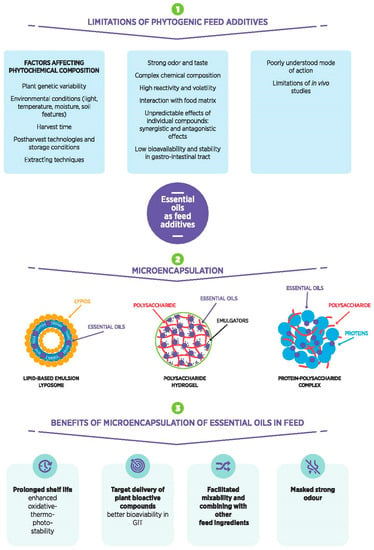
Efficacy of phytochemicals as defense metabolites mostly depends on their multiple molecular targets, both in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including receptors, ion channels, enzymes, structural macromolecules and nucleic acids. Consequently, secondary metabolites interfere with a number of cell processes such as cell cycle, mitosis, signaling pathways, protein synthesis and folding, programmed cell death, energy metabolism and so on. Not least because of this unique nature of phytochemicals, and because plant tissues contain hundreds of natural compounds, there exists a lower risk of developing phytochemical-resistant pathogens or insects compared with conventional agrochemicals or pharmaceuticals.
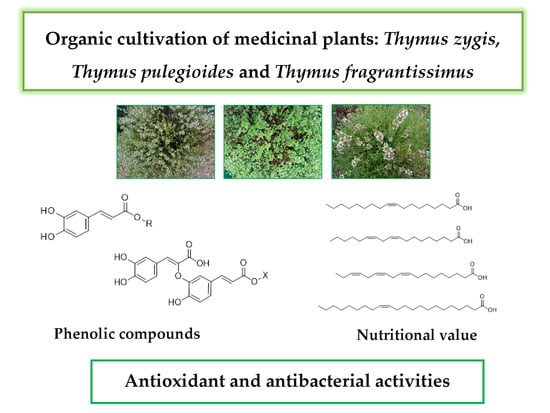
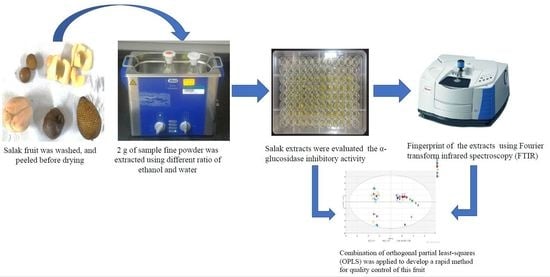
We invite investigators to submit both original research and review articles that explore all the aspects of plant secondary metabolism, with emphasis on functional roles of phytochemicals in plant organisms. We are also interested in contributions focusing on biological and pharmacological activities of secondary metabolites such as biocide, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anticancer activities, as well as on their roles in human nutrition as health-promoting agents.
Potential topics include, but are not limited to: stress metabolism; chemical ecology; plant stress physiology; plant defense mechanisms; xenobiotic metabolism; global climate changes; environmental pollution; medicinal and food plants; functional foods; nutraceuticals; essential oils
Prof. Dr. Marcello Iriti
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts for the topical collection can be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. All papers will be peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on this website. The topical collection considers regular research articles, short communications and review articles. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The article processing charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss francs).
Keywords
-
bioactive phytochemicals
-
natural products
-
botanicals
-
phytoalexins
-
secondary metabolites
-
melatonin