COVID-19 Vaccine Development and Vaccination
A topical collection in Vaccines (ISSN 2076-393X). This collection belongs to the section "COVID-19 Vaccines and Vaccination".
Viewed by 425077Editors
Interests: viral immunology; vaccines; therapeutics; RSV; influenza; RNAi; miRNA
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: the requirements for the generation and maintenance of resident memory CD8 T cells
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
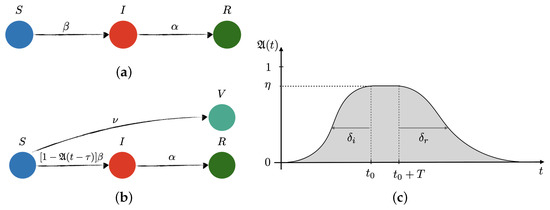
COVID-19 vaccines significantly reduce the risk of illness or death from the disease. Each vaccine stimulates the immune system to produce antibodies that combat the virus. The vaccines utilize a harmless version of a structure resembling the spike protein found on the surface of the virus. In the United States, the following COVID-19 vaccines are available:
- Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine (2024–2025 formula) for individuals aged 6 months and older.
- Moderna COVID-19 vaccine (2024–2025 formula) for individuals aged 6 months and older.
- Novavax COVID-19 vaccine (2024–2025 formula) for individuals aged 12 years and older.
These vaccines have received emergency use authorization or approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). This collection on “COVID-19 Vaccine Development and Vaccination” will showcase recent efforts to develop, test, and administer vaccines against SARS-CoV-2.
Prof. Dr. Ralph Tripp
Dr. Scott Anthony
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Vaccines is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.