Immunogenicity after a Third COVID-19 mRNA Booster in Solid Cancer Patients Who Previously Received the Primary Heterologous CoronaVac/ChAdOx1 Vaccine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
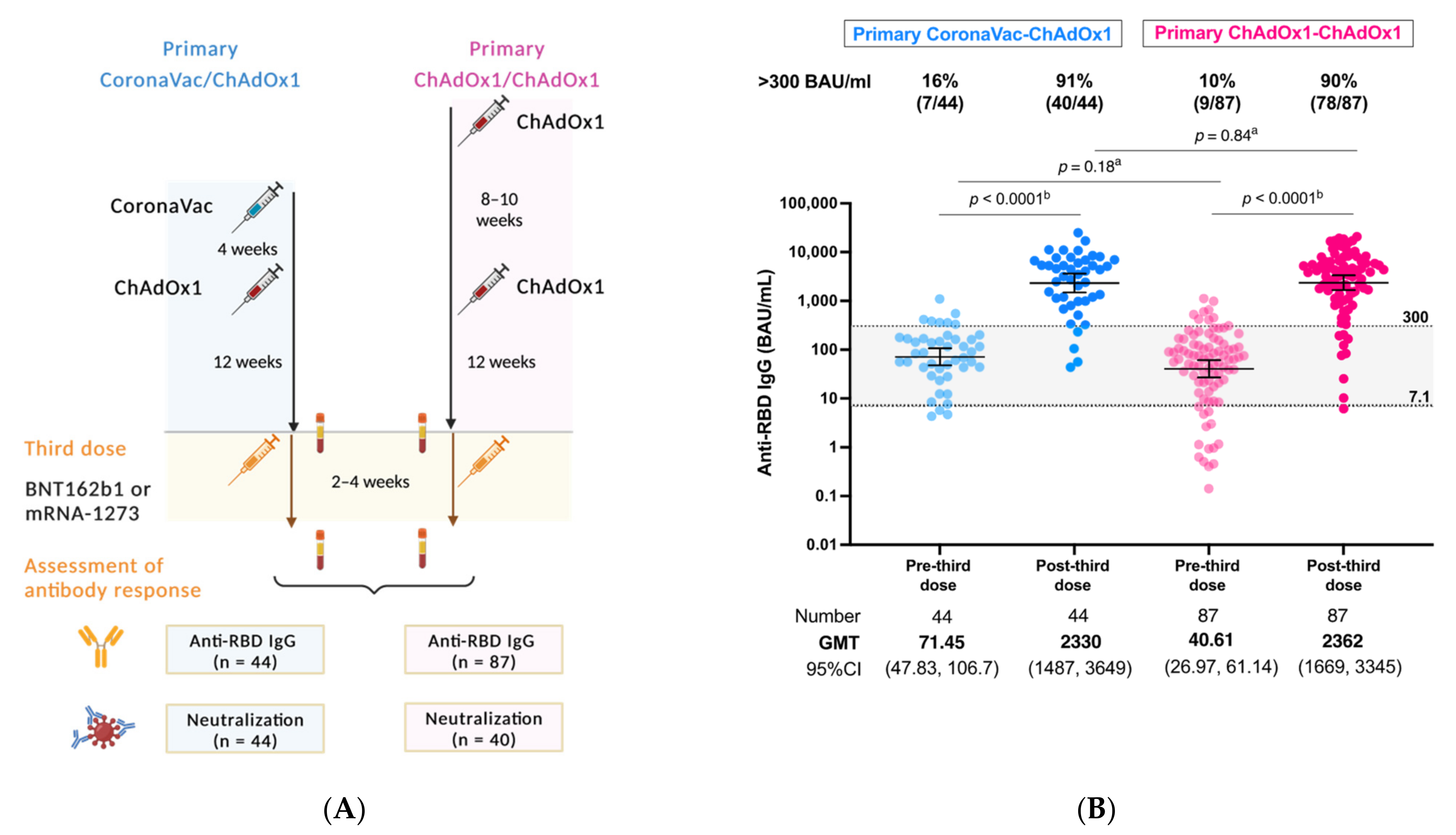
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Study End-Points
2.3. Assessment of SARS-CoV-2 Binding Antibody and Neutralization against Omicron Variant
2.4. Comparison with the Homologous ChAdOx1/ ChAdOx1 Vaccines
2.5. Comparison with Healthy Individuals
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Post-Third Dose SARS-CoV2 Binding Antibody Concentration Comparison between the Primary Series of CoronaVac/ChAdOx1 and ChAdOx1/ChAdOx1 Regimens
3.2. Post-Third Dose SARS-CoV2 Binding Antibody Levels between Solid Cancer Patients and Healthy Individuals Who Primed with the CoronaVac/ChAdOx1 Vaccination
3.3. Impact of Anticancer Treatment and Type of mRNA COVID-19 on Post-Third Dose Antibody Response
3.4. Safety
3.5. Neutralization against Omicron Variant of Concern
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Simple Summary
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giannakoulis, V.G.; Papoutsi, E.; Siempos, I.I. Effect of Cancer on Clinical Outcomes of Patients With COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis of Patient Data. JCO Glob. Oncol. 2020, 6, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, A.; Sengupta, R.; Locke, T.; Zaidi, S.K.; Campbell, K.M.; Carethers, J.M.; Jaffee, E.M.; Wherry, E.J.; Soria, J.C.; D’Souza, G.; et al. Priority COVID-19 Vaccination for Patients with Cancer while Vaccine Supply Is Limited. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linardou, H.; Spanakis, N.; Koliou, G.A.; Christopoulou, A.; Karageorgopoulou, S.; Alevra, N.; Vagionas, A.; Tsoukalas, N.; Sgourou, S.; Fountzilas, E.; et al. Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Patients with Cancer (ReCOVer Study): A Prospective Cohort Study of the Hellenic Cooperative Oncology Group. Cancers 2021, 13, 4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerril-Gaitan, A.; Vaca-Cartagena, B.F.; Ferrigno, A.S.; Mesa-Chavez, F.; Barrientos-Gutierrez, T.; Tagliamento, M.; Lambertini, M.; Villarreal-Garza, C. Immunogenicity and risk of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection after Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccination in patients with cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 160, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embi, P.J.; Levy, M.E.; Naleway, A.L.; Patel, P.; Gaglani, M.; Natarajan, K.; Dascomb, K.; Ong, T.C.; Klein, N.P.; Liao, I.C.; et al. Effectiveness of 2-Dose Vaccination with mRNA COVID-19 Vaccines Against COVID-19-Associated Hospitalizations Among Immunocompromised Adults—Nine States, January-September 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 1553–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.T.; La, J.; Branch-Elliman, W.; Huhmann, L.B.; Han, S.S.; Parmigiani, G.; Tuck, D.P.; Brophy, M.T.; Do, N.V.; Lin, A.Y.; et al. Association of COVID-19 Vaccination With SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Patients With Cancer: A US Nationwide Veterans Affairs Study. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbarya, A.; Sarel, I.; Ziv-Baran, T.; Agranat, S.; Schwartz, O.; Shai, A.; Nordheimer, S.; Fenig, S.; Shechtman, Y.; Kozlener, E.; et al. Efficacy of the mRNA-Based BNT162b2 COVID-19 Vaccine in Patients with Solid Malignancies Treated with Anti-Neoplastic Drugs. Cancers 2021, 13, 4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowronski, D.M.; Febriani, Y.; Ouakki, M.; Setayeshgar, S.; El Adam, S.; Zou, M.; Talbot, D.; Prystajecky, N.; Tyson, J.R.; Gilca, R.; et al. Two-dose SARS-CoV-2 vaccine effectiveness with mixed schedules and extended dosing intervals: Test-negative design studies from British Columbia and Quebec, Canada. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Baz, I.; Trobajo-Sanmartín, C.; Miqueleiz, A.; Guevara, M.; Fernández-Huerta, M.; Burgui, C.; Casado, I.; Portillo, M.E.; Navascués, A.; Ezpeleta, C.; et al. Product-specific COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness against secondary infection in close contacts, Navarre, Spain, April to August 2021. Euro. Surveill. 2021, 26, 2100894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.; Klemis, V.; Schub, D.; Mihm, J.; Hielscher, F.; Marx, S.; Abu-Omar, A.; Ziegler, L.; Guckelmus, C.; Urschel, R.; et al. Immunogenicity and reactogenicity of heterologous ChAdOx1 nCoV-19/mRNA vaccination. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1530–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros-Martins, J.; Hammerschmidt, S.I.; Cossmann, A.; Odak, I.; Stankov, M.V.; Morillas Ramos, G.; Dopfer-Jablonka, A.; Heidemann, A.; Ritter, C.; Friedrichsen, M.; et al. Immune responses against SARS-CoV-2 variants after heterologous and homologous ChAdOx1 nCoV-19/BNT162b2 vaccination. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1525–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanlapakorn, N.; Suntronwong, N.; Phowatthanasathian, H.; Yorsaeng, R.; Vichaiwattana, P.; Thongmee, T.; Auphimai, C.; Srimuan, D.; Thatsanatorn, T.; Assawakosri, S.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of heterologous and homologous inactivated and adenoviral-vectored COVID-19 vaccine regimens in healthy adults: A prospective cohort study. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2022, 18, 2029111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahasirimongkol, S.; Khunphon, A.; Kwangsukstid, O.; Sapsutthipas, S.; Wichaidit, M.; Rojanawiwat, A.; Wichuckchinda, N.; Puangtubtim, W.; Pimpapai, W.; Soonthorncharttrawat, S.; et al. The Pilot Study of Immunogenicity and Adverse Events of a COVID-19 Vaccine Regimen: Priming with Inactivated Whole SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine (CoronaVac) and Boosting with the Adenoviral Vector (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19) Vaccine. Vaccines 2022, 10, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Interim Statement on the Use of Additional Booster Doses of Emergency Use Listed mRNA Vaccines against COVID-19. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/17-05-2022-interim-statement-on-the-use-of-additional-booster-doses-of-emergency-use-listed-mrna-vaccines-against-covid-19 (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- ESMO. ESMO Statements on Vaccination against COVID-19 in People with Cancer. Available online: https://www.esmo.org/covid-19-and-cancer/covid-19-vaccination (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Chemaitelly, H.; Tang, P.; Hasan, M.R.; AlMukdad, S.; Yassine, H.M.; Benslimane, F.M.; Al Khatib, H.A.; Coyle, P.; Ayoub, H.H.; Al Kanaani, Z.; et al. Waning of BNT162b2 Vaccine Protection against SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Qatar. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, Y.; Mandel, M.; Bar-On, Y.M.; Bodenheimer, O.; Freedman, L.; Haas, E.J.; Milo, R.; Alroy-Preis, S.; Ash, N.; Huppert, A. Waning Immunity after the BNT162b2 Vaccine in Israel. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, e85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, N.; Stowe, J.; Kirsebom, F.; Toffa, S.; Rickeard, T.; Gallagher, E.; Gower, C.; Kall, M.; Groves, N.; O’Connell, A.M.; et al. COVID-19 Vaccine Effectiveness against the Omicron (B.1.1.529) Variant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1532–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntronwong, N.; Kanokudom, S.; Auphimai, C.; Assawakosri, S.; Thongmee, T.; Vichaiwattana, P.; Duangchinda, T.; Chantima, W.; Pakchotanon, P.; Chansaenroj, J.; et al. Effects of boosted mRNA and adenoviral-vectored vaccines on immune responses to omicron BA.1 and BA.2 following the heterologous CoronaVac/AZD1222 vaccination. J. Med. Virol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Minor, B.L.; Elliott, V.; Fernandez, M.; O’Neal, L.; McLeod, L.; Delacqua, G.; Delacqua, F.; Kirby, J.; et al. The REDCap consortium: Building an international community of software platform partners. J. Biomed. Inf. 2019, 95, 103208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Thielke, R.; Payne, J.; Gonzalez, N.; Conde, J.G. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—A metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J. Biomed. Inf. 2009, 42, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research. Toxicity Grading Scale for Healthy Adult and Adolescent Volunteers Enrolled in Preventive Vaccine Clinical Trials, Guidance for Industry. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/toxicity-grading-scale-healthy-adult-and-adolescent-volunteers-enrolled-preventive-vaccine-clinical (accessed on 8 January 2022).
- Suntronwong, N.; Assawakosri, S.; Kanokudom, S.; Yorsaeng, R.; Auphimai, C.; Thongmee, T.; Vichaiwattana, P.; Duangchinda, T.; Chantima, W.; Pakchotanon, P.; et al. Strong Correlations between the Binding Antibodies against Wild-Type and Neutralizing Antibodies against Omicron BA.1 and BA.2 Variants of SARS-CoV-2 in Individuals Following Booster (Third-Dose) Vaccination. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luangdilok, S.; Wanchaijiraboon, P.; Pakvisa, N.; Susiriwatananont, T.; Zungsontiporn, N.; Sriuranpong, V.; Namkanisorn, T.; Sainamthip, P.; Suntronwong, N.; Vichaiwattana, P.; et al. Immunogenicity and Omicron Neutralization Following a Third COVID-19 Vaccination in Solid Cancer Patients Previously Primed with Two Doses of Chadox1 Vaccine: A Prospective Cohort Study; SSRN: Rochester, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.A.; Ujjani, C.S.; Greninger, A.L.; Shadman, M.; Gopal, A.K. Immunogenicity of a heterologous COVID-19 vaccine after failed vaccination in a lymphoma patient. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1037–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ujjani, C.; Greninger, A.L.; Shadman, M.; Hill, J.A.; Lynch, R.C.; Warren, E.H.; Gopal, A.K. Heterologous SARS-CoV-2 vaccinations in patients with B-cell lymphoid malignancies. Am. J. Hematol. 2022, 97, E67–E69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, T.; Klemis, V.; Schub, D.; Schneitler, S.; Reichert, M.C.; Wilkens, H.; Sester, U.; Sester, M.; Mihm, J. Cellular immunity predominates over humoral immunity after homologous and heterologous mRNA and vector-based COVID-19 vaccine regimens in solid organ transplant recipients. Am. J. Transpl. 2021, 21, 3990–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goshen-Lago, T.; Waldhorn, I.; Holland, R.; Szwarcwort-Cohen, M.; Reiner-Benaim, A.; Shachor-Meyouhas, Y.; Hussein, K.; Fahoum, L.; Baruch, M.; Peer, A.; et al. Serologic Status and Toxic Effects of the SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 Vaccine in Patients Undergoing Treatment for Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palich, R.; Veyri, M.; Vozy, A.; Marot, S.; Gligorov, J.; Benderra, M.A.; Maingon, P.; Morand-Joubert, L.; Adjoutah, Z.; Marcelin, A.G.; et al. High seroconversion rate but low antibody titers after two injections of BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) vaccine in patients treated with chemotherapy for solid cancers. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1294–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voysey, M.; Clemens, S.A.C.; Madhi, S.A.; Weckx, L.Y.; Folegatti, P.M.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Baillie, V.L.; Barnabas, S.L.; Bhorat, Q.E.; et al. Safety and efficacy of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine (AZD1222) against SARS-CoV-2: An interim analysis of four randomised controlled trials in Brazil, South Africa, and the UK. Lancet 2021, 397, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creech, C.B.; Walker, S.C.; Samuels, R.J. SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines. JAMA 2021, 325, 1318–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Perez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, F.; Abolhassani, H.; Du, L.; Piralla, A.; Bertoglio, F.; de Campos-Mata, L.; Wan, H.; Schubert, M.; Cassaniti, I.; Wang, Y.; et al. Heterologous immunization with inactivated vaccine followed by mRNA-booster elicits strong immunity against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, A.P.S.; Janani, L.; Cornelius, V.; Aley, P.K.; Babbage, G.; Baxter, D.; Bula, M.; Cathie, K.; Chatterjee, K.; Dodd, K.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of seven COVID-19 vaccines as a third dose (booster) following two doses of ChAdOx1 nCov-19 or BNT162b2 in the UK (COV-BOOST): A blinded, multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 2258–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Cancer | Cancer | p-Value # | Healthy | p-Value * | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Series of Vaccination | CoronaVac-ChAdOx1 | ChAdOx1-ChAdOx1 | CoronaVac-ChAdOx1 | |||||
| (n = 44) | (n = 87) | (n = 107) | ||||||
| Age, years, median (IQR) | 57 | (48.5–65) | 57 | (48–65) | 0.774 | 41 | (35–48) | <0.001 |
| Sex | ||||||||
| Female | 24 | (55%) | 47 | (54%) | 0.955 | 46 | (43%) | 0.196 |
| Male | 20 | (45%) | 40 | (46%) | 61 | (57%) | ||
| BMI, kg/m2, median (IQR) | 21.7 | (19.5–25.5) | 23.1 | (21–26) | 0.238 | |||
| Cancer types | ||||||||
| Breast | 18 | (41%) | 36 | (41%) | 0.108 | |||
| Colorectal | 11 | (25%) | 33 | (38%) | ||||
| Head Neck | 6 | (14%) | 4 | (5%) | ||||
| Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic | 4 | (9%) | 5 | (6%) | ||||
| Esophagus/Gastric | 3 | (7%) | 1 | (1%) | ||||
| Genitourinary | 2 | (5%) | 2 | (2%) | ||||
| Lung | 0 | (0%) | 4 | (5%) | ||||
| Other | 0 | (0%) | 2 | (2%) | ||||
| Cancer treatment | ||||||||
| Chemotherapy | 29 | (66%) | 68 | (78%) | 0.131 | |||
| Hormonal therapy/Biologics | 15 | (34%) | 19 | (22%) | ||||
| Corticosteroid | ||||||||
| No/pre-medication | 41 | (93%) | 86 | (99%) | 0.110 | |||
| Therapeutic purpose | 3 | (7%) | 1 | (1%) | ||||
| Disease status | ||||||||
| Early | 20 | (45%) | 39 | (45%) | 0.695 | |||
| Locally advanced | 8 | (18%) | 11 | (13%) | ||||
| De novo metastasis | 10 | (23%) | 27 | (31%) | ||||
| Recurrence | 6 | (14%) | 10 | (11%) | ||||
| Co-morbidity | ||||||||
| Diabetes | 6 | (14%) | 11 | (13%) | 0.873 | |||
| Hypertension | 12 | (27%) | 18 | (21%) | 0.397 | |||
| Cardiovascular disease | 3 | (7%) | 2 | (2%) | 0.334 | |||
| Respiratory tract disease | 1 | (2%) | 2 | (2%) | 1.000 | |||
| Interval between first to second vaccine, days | 24 | (21–28) | 70 | (56–77) | <0.001 | 27 | (21–28) | 0.153 |
| Interval between second to third vaccine, days | 127.5 | (113.5–137) | 118 | (107–136) | 0.306 | 131 | (106–138) | 0.854 |
| Interval between third dose to blood collection, days | 14 | (14–14) | 14 | (14–14) | 0.211 | 14 | (14–14) | 0.544 |
| Type of third vaccine | ||||||||
| BNT162b2 (Pfizer) | 20 | (45%) | 31 | (36%) | 0.276 | 55 | (51%) | 0.507 |
| mRNA-1273 (Moderna) | 24 | (55%) | 56 | (64%) | 52 | (49%) | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luangdilok, S.; Wanchaijiraboon, P.; Pakvisal, N.; Susiriwatananont, T.; Zungsontiporn, N.; Sriuranpong, V.; Sainamthip, P.; Suntronwong, N.; Vichaiwattana, P.; Wanlapakorn, N.; et al. Immunogenicity after a Third COVID-19 mRNA Booster in Solid Cancer Patients Who Previously Received the Primary Heterologous CoronaVac/ChAdOx1 Vaccine. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10101613
Luangdilok S, Wanchaijiraboon P, Pakvisal N, Susiriwatananont T, Zungsontiporn N, Sriuranpong V, Sainamthip P, Suntronwong N, Vichaiwattana P, Wanlapakorn N, et al. Immunogenicity after a Third COVID-19 mRNA Booster in Solid Cancer Patients Who Previously Received the Primary Heterologous CoronaVac/ChAdOx1 Vaccine. Vaccines. 2022; 10(10):1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10101613
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuangdilok, Sutima, Passakorn Wanchaijiraboon, Nussara Pakvisal, Thiti Susiriwatananont, Nicha Zungsontiporn, Virote Sriuranpong, Panot Sainamthip, Nungruthai Suntronwong, Preeyaporn Vichaiwattana, Nasamon Wanlapakorn, and et al. 2022. "Immunogenicity after a Third COVID-19 mRNA Booster in Solid Cancer Patients Who Previously Received the Primary Heterologous CoronaVac/ChAdOx1 Vaccine" Vaccines 10, no. 10: 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10101613
APA StyleLuangdilok, S., Wanchaijiraboon, P., Pakvisal, N., Susiriwatananont, T., Zungsontiporn, N., Sriuranpong, V., Sainamthip, P., Suntronwong, N., Vichaiwattana, P., Wanlapakorn, N., Poovorawan, Y., Teeyapun, N., & Tanasanvimon, S. (2022). Immunogenicity after a Third COVID-19 mRNA Booster in Solid Cancer Patients Who Previously Received the Primary Heterologous CoronaVac/ChAdOx1 Vaccine. Vaccines, 10(10), 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10101613






