-
 Progress in Gliotoxin Research
Progress in Gliotoxin Research -
 Fluorimetric Determination of Eosin Y in Water Samples and Drinks Using Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Liquid-Phase Microextraction
Fluorimetric Determination of Eosin Y in Water Samples and Drinks Using Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Liquid-Phase Microextraction -
 Synthesis, Structures and Corrosion Inhibition Properties of 4-Nitrophenylacetato-Rare-Earth(III) 1D Coordination Polymers
Synthesis, Structures and Corrosion Inhibition Properties of 4-Nitrophenylacetato-Rare-Earth(III) 1D Coordination Polymers -
 Catechins and Human Health: Breakthroughs from Clinical Trials
Catechins and Human Health: Breakthroughs from Clinical Trials
Journal Description
Molecules
Molecules
is a leading international, peer-reviewed, open access journal of chemistry, and is published semimonthly online by MDPI. The International Society of Nucleosides, Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids (IS3NA), Spanish Society of Medicinal Chemistry (SEQT) and International Society of Heterocyclic Chemistry (ISHC) are affiliated with Molecules and their members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, MEDLINE, PMC, Reaxys, CaPlus / SciFinder, MarinLit, AGRIS, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Biochemistry and Molecular Biology) / CiteScore - Q1 (Organic Chemistry)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 16.1 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Sections: published in 25 topical sections.
- Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about Molecules.
- Companion journal: Foundations.
- Journal Cluster of Chemical Reactions and Catalysis: Catalysts, Chemistry, Electrochem, Inorganics, Molecules, Organics, Oxygen, Photochem, Reactions, Sustainable Chemistry.
Impact Factor:
4.6 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
5.0 (2024)
Latest Articles
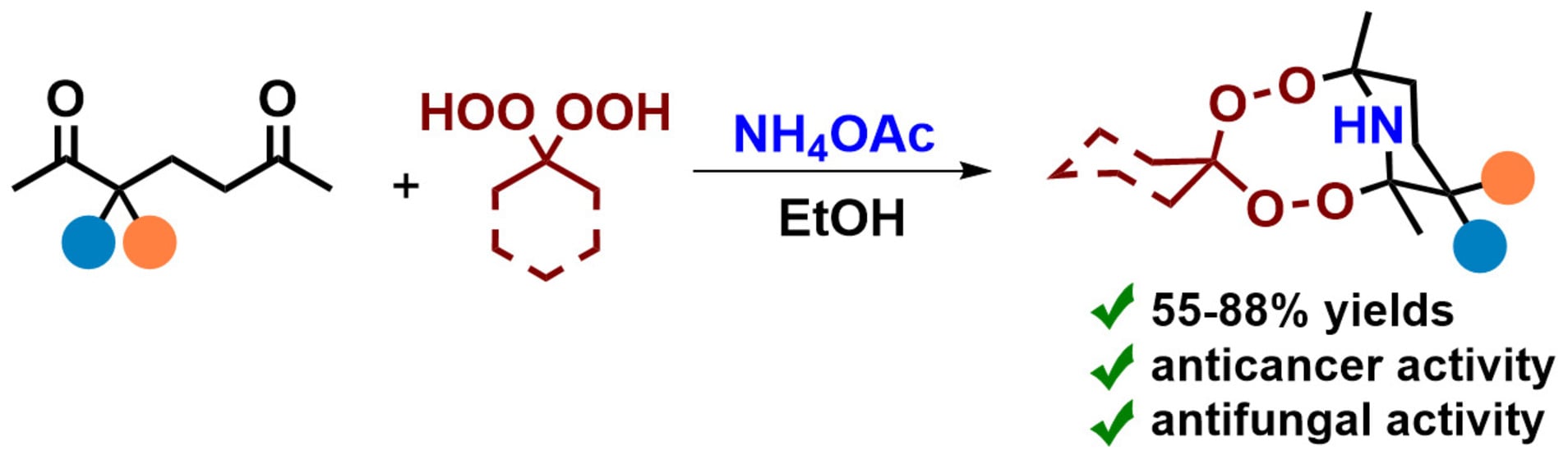
One-Pot Synthesis of Aminodiperoxides from 1,5-Diketones, Geminal Bishydroperoxides and Ammonium Acetate
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4703; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244703 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
Herein, we report an efficient one-pot synthesis of bridged aminodiperoxides via a three-component reaction of 1,5-diketones with geminal bishydroperoxides and ammonium acetate. The synthesized aminodiperoxides are stable despite containing an unprotected secondary NH-group adjacent to two peroxide functionalities. Under optimal conditions, the reaction
[...] Read more.
Herein, we report an efficient one-pot synthesis of bridged aminodiperoxides via a three-component reaction of 1,5-diketones with geminal bishydroperoxides and ammonium acetate. The synthesized aminodiperoxides are stable despite containing an unprotected secondary NH-group adjacent to two peroxide functionalities. Under optimal conditions, the reaction affords aminodiperoxides in high yields (up to 88%) with outstanding selectivity and high atom economy, thereby eliminating the need for column chromatographic purification. The synthesized aminodiperoxides exhibit potent cytotoxicity and remarkable selectivity toward Jurkat, K562, and A549 cancer cell lines, and are significantly superior to the clinically used anticancer agent camptothecin. Among all tested compounds, 3ec is the most promising candidate, exhibiting high activity and selectivity toward all tested cell lines (Jurkat: CC50 = 12.9 µM, SI = 67.09; K562: CC50 = 19.6 µM, SI = 44.28; A549: CC50 = 48.2 µM, SI = 17.98). Furthermore, a novel class of fungicidal compounds has been discovered. The aminodiperoxides exhibit fungicidal activity against phytopathogenic fungi, in some cases comparable to the commercial fungicide Triadimefon.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Organic Chemistry)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
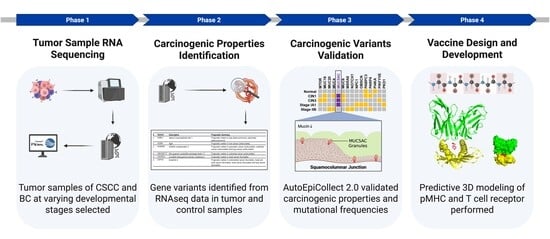
AutoEpiCollect 2.0: A Web-Based Machine Learning Tool for Personalized Peptide Cancer Vaccine Design
by
Clifford Kim, Nina Shelton, Madhav Samudrala, Kush Savsani and Sivanesan Dakshanamurthy
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4702; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244702 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
Personalized cancer vaccines are a key strategy for training the immune system to recognize and respond to tumor-specific antigens. Our earlier software release, AutoEpiCollect 1.0, was designed to accelerate the vaccine design process, but the identification of tumor-specific genetic variants remains a manual
[...] Read more.
Personalized cancer vaccines are a key strategy for training the immune system to recognize and respond to tumor-specific antigens. Our earlier software release, AutoEpiCollect 1.0, was designed to accelerate the vaccine design process, but the identification of tumor-specific genetic variants remains a manual process and is highly burdensome. In this study, we introduce AutoEpiCollect 2.0, an improved version with integrated genetic analysis capabilities that automate the identification and prioritization of tumorigenic variants from individual tumor samples. AutoEpiCollect 2.0 connects with RNA sequencing and cross-references the resulting RNAseq data for efficient determination of cancer-specific and prognostic gene variants. Using AutoEpiCollect 2.0, we conducted two case studies to design personalized peptide vaccines for two distinct cancer types: cervical squamous cell carcinoma and breast carcinoma. Case 1 analyzed five cervical tumor samples from different stages, ranging from CIN1 to cervical cancer stage IIB. CIN3 was selected for detailed analysis due to its pre-invasive status and clinical relevance, as it is the earliest stage where patients typically present symptoms. Case 2 examined five breast tumor samples, including HER2-negative, ER-positive, PR-positive, and triple-negative subtypes. In three of these breast samples, the same epitope was identified and was synthesized by identical gene variants. This finding suggests the presence of shared antigenic targets across subtypes. We identified the top MHC class I and class II epitopes for both cancer types. In cervical carcinoma, the most immunogenic epitopes were found in proteins expressed by HSPG2 and MUC5AC. In breast carcinoma, epitopes with the highest potential were derived from proteins expressed by BRCA2 and AHNAK2. These epitopes were further validated through pMHC-TCR modeling analysis. Despite differences in cancer type and tumor subtype, both case studies successfully identified high-potential epitopes suitable for personalized vaccine design. The integration of AutoEpiCollect 2.0 streamlined the variant analysis workflow and reduced the time required to identify key tumor antigens. This study demonstrates the value of automated data integration in genomic analysis for cancer vaccine development. Furthermore, by applying RNAseq in a standardized workflow, the approach enables both patient-specific and population-level vaccine design, based on statistically frequent gene variants observed across tumor datasets. AutoEpiCollect 2.0 is freely available as a website based tool for user to design vaccine.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Peptides in Anti-Cancer Treatments)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Green Synthesis of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles: Characterization and Evaluation of Their Potential for Photocatalytic and Dielectric Applications
by
Manal A. Awad, Khalid M. O. Ortashi, Wadha Alenazi, Fatimah S. Alfaifi and Asma A. Al-Huqail
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4701; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244701 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
This study investigated the dielectric and photocatalytic properties of green-synthesized titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs), which are widely utilized semiconductor materials known for their excellent optical, structural, and electronic characteristics. The TiO2 NPs were synthesized via a green precipitation method from
[...] Read more.
This study investigated the dielectric and photocatalytic properties of green-synthesized titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs), which are widely utilized semiconductor materials known for their excellent optical, structural, and electronic characteristics. The TiO2 NPs were synthesized via a green precipitation method from the aqueous extract of Cymbopogon proximus. A comprehensive set of analytical techniques—UV–Vis spectroscopy, XRD, FTIR, TEM, EDX, and DLS—was employed to determine their optical response, crystalline structure, functional groups, morphology, elemental composition, and particle size distribution. UV–Vis analysis revealed a characteristic absorption peak at 327 nm, and the band gap energy, calculated via the Tauc plot method, was 3.16 eV. The XRD results confirmed the formation of a tetragonal TiO2 phase with an average crystallite size of approximately 4 nm. TEM images further supported the spherical to quasitetragonal morphology and revealed that the aggregated clusters formed conjoint nanostructures. The photocatalytic activity of the TiO2 NPs was evaluated using a 0.5 mM RhB dye solution under UV–visible irradiation. The synthesized nanoparticles achieved a photodegradation efficiency of 97% after 50 h, with a corresponding rate constant of 0.073402 h−1, indicating their potential for effective photocatalytic pollutant removal. Furthermore, the dielectric behavior of the TiO2 NPs was examined at room temperature. The material exhibited a high dielectric constant at low frequencies due to interfacial (Maxwell–Wagner) polarization, along with frequency-dependent AC conductivity attributed to charge‒carrier hopping mechanisms. These dielectric properties, combined with strong photocatalytic performance, underscore the suitability of green-synthesized TiO2 NPs for applications in environmental remediation, energy-storage devices, and advanced technologies.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Theoretical Calculations on Hexagonal-Boron-Nitride-(h-BN)-Supported Single-Atom Cu for the Reduction of Nitrate to Ammonia
by
Guoliang Liu and Cen Hao
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4700; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244700 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
Nitrate (NO3−), as a stable nitrogen-containing compound, has caused serious harm to the ecological environment and human health. To reduce nitrate pollution, the catalytic reduction of nitrate (NO3RR) to ammonia (NH3) is a very promising solution.
[...] Read more.
Nitrate (NO3−), as a stable nitrogen-containing compound, has caused serious harm to the ecological environment and human health. To reduce nitrate pollution, the catalytic reduction of nitrate (NO3RR) to ammonia (NH3) is a very promising solution. Recently, single-atom catalysts (SACs) have received extensive attention due to their excellent activity and stability. Here, we study the nitrate catalytic reduction properties of hexagonal-boron-nitride-(h-BN)-supported single-atom Cu systematically and theoretically and compare it with monolayer h-BN. We find that (1) due to the stronger electronegativity of the N atom, Cu atom is preferentially doped at the N top site, resulting in the significant electron rearrangement; (2) the doped Cu atom at the N top site for monolayer h-BN can provide extra 3d-orbital electrons at the Fermi level, which can significantly enhance the conductivity, reduce the bandgap width, and increase the reducibility; (3) the NO3− ion preferentially adsorbs at the hollow site of monolayer h-BN, while the NO3− ion is adsorbed more strongly at the Cu top site of h-BN-supported single-atom Cu due to the abundant d-electron supply from the Cu atom; (4) single-atom Cu can significantly reduce the energy barrier of the rate-determining step (RDS) and increase the probability of nitrate reduction. In conclusion, h-BN-supported single-atom Cu exhibits excellent catalytic performance of NO3RR.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Computational and Theoretical Chemistry)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
The Use of Metabolic Inducers in Wheat to Increase the Nutritional and Functional Value of Grain
by
Wojciech Biszczak, Izabela Jośko, Michał Świeca, Karol Kraska, Małgorzata Haliniarz and Krzysztof Różyło
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4699; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244699 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Stimulation of plant metabolism is a research direction for increasing the nutritional and functional value of food. In a two-year field experiment with spring wheat, eight inducers from different groups (bio- and abiotic; exo- and endogenous) were used. The tested inducers had varied
[...] Read more.
Stimulation of plant metabolism is a research direction for increasing the nutritional and functional value of food. In a two-year field experiment with spring wheat, eight inducers from different groups (bio- and abiotic; exo- and endogenous) were used. The tested inducers had varied and significant effects on wheat grain yield and quality. Hydrogen peroxide, chitin, and chitosan hydrochloride increased phenolic content and antioxidant activity (by 13.7%, 15.7%, and 10.1%, respectively, compared to control). Analysis of the amino acid composition of caryopses flour showed a significant increase in the content of aspartic acid, alanine, phenylalanine, and arginine after the application of hydrogen peroxide. Application of chitosan hydrochloride, L-phenylalanine, and chitin resulted in an increase in APX gene expression, while sodium hypochlorite significantly decreased CAT gene expression. Potassium iodide and sodium hypochlorite significantly reduced grain yield (by 10.6% and 14.4%, respectively, compared to control) and also worsened quality parameters of grain. Hydrogen peroxide, chitin, and chitosan hydrochloride showed the greatest stimulatory potential, as their application did not worsen, and in some cases improved, yield parameters and increased the phenolic content and antioxidant activity of grain. Hydrogen peroxide further improved the amino acid composition of grains. However, further research is needed to understand the mechanisms of effects on plants and to optimize the use of these inducers in agricultural practice.
Full article
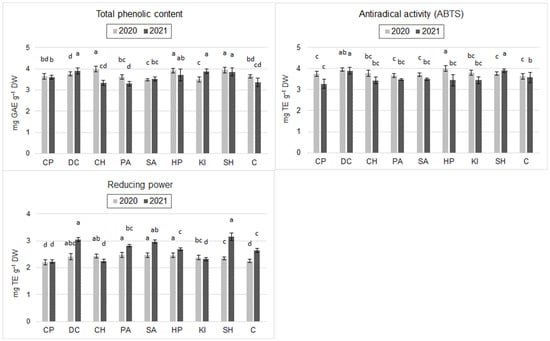
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Compounds on TiO2-Photocatalyst-Coated Concrete Surfaces
by
Katarzyna Bednarczyk and Artur Lewandowski
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4698; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244698 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
This study investigates the photocatalytic degradation of organic compounds on TiO2-coated concrete paving cubes, with a focus on their potential for environmental remediation in urban settings. The TiO2 P25 coating significantly enhanced the photocatalytic activity of the concrete surface, enabling
[...] Read more.
This study investigates the photocatalytic degradation of organic compounds on TiO2-coated concrete paving cubes, with a focus on their potential for environmental remediation in urban settings. The TiO2 P25 coating significantly enhanced the photocatalytic activity of the concrete surface, enabling effective degradation of model pollutants such as methylene blue. Various application methods were evaluated, including surface coating with and without impregnation, and bulk incorporation of TiO2 into the concrete matrix. Surface properties were assessed using contact angle measurements and absorption tests. Among all tested variants, the surface-coated and impregnated sample (SURF-IMP) showed the highest photocatalytic efficiency, achieving over 67% pollutant degradation. This variant also demonstrated the lowest water absorption and the highest contact angle, confirming improved surface hydrophobicity. In contrast, the bulk-modified sample (MIX) exhibited weaker performance due to limited surface accessibility of TiO2 particles. These findings highlight the importance of the application method in optimizing the performance of TiO2-functionalized concrete. The developed system offers a practical approach to integrating photocatalytic properties into paving materials for applications such as air purification, surface decontamination, and sustainable urban infrastructure.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nanomaterials in Photochemical Devices: Advances and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
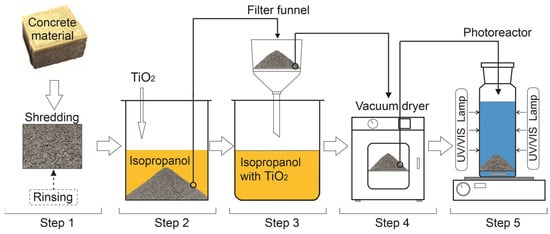
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Deep Eutectic Solvents as a Sustainable Approach for Silica Recovery from Rice Husk
by
Célio S. Faria-Júnior, Lucas dos Santos Silva, Armando L. C. Cunha, Filipe S. Buarque and Bernardo Dias Ribeiro
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4697; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244697 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
Rice husk is a lignocellulosic biomass rich in silica, which, when disposed of inappropriately, represents an environmental hazard. This study investigated the application of deep eutectic solvents (DES) as a green and efficient approach to the rice husk fractionation, combining the selective dissolution
[...] Read more.
Rice husk is a lignocellulosic biomass rich in silica, which, when disposed of inappropriately, represents an environmental hazard. This study investigated the application of deep eutectic solvents (DES) as a green and efficient approach to the rice husk fractionation, combining the selective dissolution of lignin and sugars with the purification of the silica-rich inorganic fraction. Six different DES were produced from choline chloride or betaine with different hydrogen bond donors and characterized for water content and pH. The DES based on carboxylic acids was more acidic, which favored the cleavage of ester and glycosidic bonds in the biomass. The TGA, XRF, SEM, and XRD analyses revealed that the lactic acid-based DES promoted better removal of lignin and mineral impurities, resulting in a purer silica with an amorphous morphology. The 110 °C condition was the most effective in preserving the thermal integrity of the organic (sugars and lignin) and inorganic (silica-rich ash) fractions. The results highlight the potential of DES as selective, sustainable, and tunable solvents for the valorization of agricultural waste, achieving biosilica with SiO2 purity exceeding 80% and lignin removal above 70%, reinforcing the potential of DES as sustainable solvents for agricultural waste valorization.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Chemistry with Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents: From Fundamentals to Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
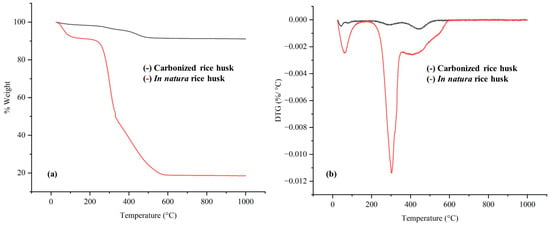
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Role of Scleroglucan Produced by Sclerotium rolfsii in Shaping the Microstructure, Rheology, and Flavour Profile of Full-Fat Yoghurts
by
Marika Magdalena Bielecka, Aneta Zofia Dąbrowska, Małgorzata Anna Majcher and Marek Aljewicz
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4696; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244696 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
This study evaluated the effects of different concentrations (0.25%, 0.5%, and 1.0% w/w) of highly purified (90%) β-glucan (scleroglucan—SCGL) produced by Sclerotium rolfsii on the physicochemical, rheological, microbiological, and sensory properties of full-fat yoghurt (3.2% fat). The fermentation dynamics, titratable
[...] Read more.
This study evaluated the effects of different concentrations (0.25%, 0.5%, and 1.0% w/w) of highly purified (90%) β-glucan (scleroglucan—SCGL) produced by Sclerotium rolfsii on the physicochemical, rheological, microbiological, and sensory properties of full-fat yoghurt (3.2% fat). The fermentation dynamics, titratable acidity, apparent viscosity, hardness, adhesiveness, colour, microstructure, and volatile compound profiles of the studied yoghurts were analysed. The addition of SCGL increased gel hardness and viscosity, while preserving its pseudoplastic flow behaviour (n = 0.10–0.15). In samples containing 1.0% SCGL, yield stress (τ0) increased from 0 Pa in the control to 739 Pa after 28 days of storage, pointing to the formation of a dense protein–polysaccharide network. The analysed polysaccharide slowed down lactose hydrolysis and acidification, but increased the counts of Streptococcus thermophilus (7.7 log CFU·g−1) compared to the control (5.8 log CFU·g−1). The volatile compound analysis showed increased acetaldehyde (5.6 mg·L−1) and diacetyl (5.0 mg·L−1) levels and reduced acetoin (~1.0 mg·L−1) concentration, which enhanced the intensity of the buttery aroma. The sensory evaluation revealed that yoghurts containing 1% SCGL had the most desirable smooth consistency and a balanced, fresh aroma, whereas yoghurts with lower SCGL concentrations (0.25–0.5%) were characterised by a mealy mouthfeel and thinner consistency. Scleroglucan proved to be an effective natural stabiliser and flavour modulator that improved the structure, stability, and sensory quality of full-fat yoghurts.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Characterization and Instrumental Analysis of Aroma-Active Compounds in Fermented Food and Beverage, the Second Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
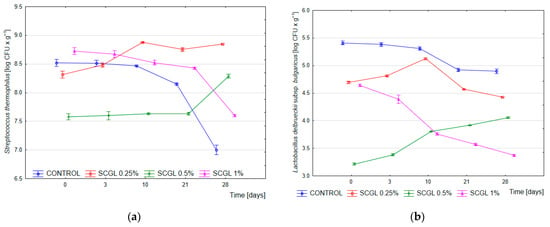
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comparative Study of Wild and Cultivated Lavandula dentata: Differences in Essential Oil Composition, Biological Activities, and Associated Microbial Communities
by
Siham Houssayni, Oumaima Akachoud, Btissam Zoubi, Meryem Youssfi, Anissa Lounès-Hadj Sahraoui, Frédéric Laruelle, Azucena Gonzalez Coloma, Maria Fe Andrés Yeves, Abderrazak Benkebboura, Hafida Bouamama and Ahmed Qaddoury
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4695; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244695 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
To ensure the preservation and sustainable use of Lavandula dentata L., we examined the impact of various growth conditions on the composition of essential oils extracted from the leaves of both cultivated and wild L. dentata. Additionally, we assessed the biological activities
[...] Read more.
To ensure the preservation and sustainable use of Lavandula dentata L., we examined the impact of various growth conditions on the composition of essential oils extracted from the leaves of both cultivated and wild L. dentata. Additionally, we assessed the biological activities of these essential oils, along with the biomass of the root and soil microorganisms. Gas chromatography analysis revealed 21 and 23 components in the EO of the wild and cultivated plants, accounting for over 98% of the total composition in both cases. The major compounds of wild EO were borneol (49.47%), eucalyptol (23.01%), β-pinene (3.95%), β-eudesmol (3.79%), and myrtenol (3.61%). In contrast, the EO extracted from cultivated plants was characterized by a high content of borneol (32.83%), isobornyl acetate (24.45%), eucalyptol (14.71%), and α-pinene (5.83%). Unique compounds were found in wild and cultivated EO, such as linalool, cis-verbenol, carveol, α-selinene, and terpinyl acetate or tricyclene, d-limonene, camphene hydrate, and isobornyl acetate, respectively. PLFA analysis revealed a higher microbial biomass in both soil (10.393 µg/g) and the roots (68.04 µg/g) of the wild plants compared to the cultivated ones (3.91 µg/g in soil and 62.04 µg/g in roots), driven especially by Gram-negative bacteria in soil, and by saprotrophic fungi in the roots. The biological activities of the essential oils showed some variations with growth conditions, with the wild EO generally exhibiting slightly higher antibacterial, antifungal, antioxidant, and nematicidal activities in certain assays. Overall, our findings indicate that the essential oils from wild and cultivated L. dentata exhibit comparable biological value, although some differences were observed. In particular, the wild EO tended to show significantly higher biological activities in certain assays, which may be associated with its distinct chemical composition and growth environment. However, these differences were moderate and not consistently significant across all tests. Therefore, properly managed cultivation can be a dependable alternative for producing L. dentata essential oil, helping to reduce pressure on natural populations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Essential Oils—Third Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
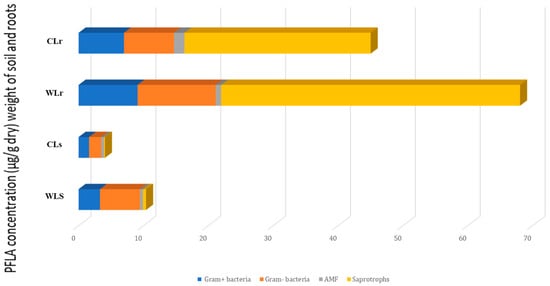
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Role of Noncovalent Interactions in the Infrared Spectra of Lignin Model Compounds: A DFT Study
by
Febdian Rusydi, Lusia Silfia Pulo Boli, Indri Badria Adilina, Wahyu Tri Cahyanto, Stewart F. Parker and Ferensa Oemry
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4694; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244694 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
Noncovalent interactions are key to the stability of lignin dimers, the primary components of bio-oil. However, their specific influence on the infrared spectra remains poorly understood. Using dispersion-corrected density-functional theory (APFD/6-311++G(d,p)), we conducted a comparative analysis of the structures and infrared spectra of
[...] Read more.
Noncovalent interactions are key to the stability of lignin dimers, the primary components of bio-oil. However, their specific influence on the infrared spectra remains poorly understood. Using dispersion-corrected density-functional theory (APFD/6-311++G(d,p)), we conducted a comparative analysis of the structures and infrared spectra of four lignin derivatives—benzene, phenol, anisole, and guaiacol—as monomers and dimers. Our study reveals that distinct vibrational shifts and newly emerging peaks observed in the calculated infrared spectra of the dimers can be attributed to the formation of σ···π and π···π stacking, hydrogen bonding, attractive van der Waals, and steric repulsion interactions. We extended the study to 3,3′-dimethoxy-1,1′-biphenyl-2,2′-diol, a guaiacyl moiety with a C–C linkage. The results indicate that the structure in which both guaiacol units adopt an anti–syn conformation is more stable—minimizing steric repulsion between hydroxyl groups—than configurations in which one guaiacol unit adopts either anti–anti or gauche–anti conformation. These differences are clearly reflected in their distinctive infrared spectral signatures.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Computational Spectroscopy, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
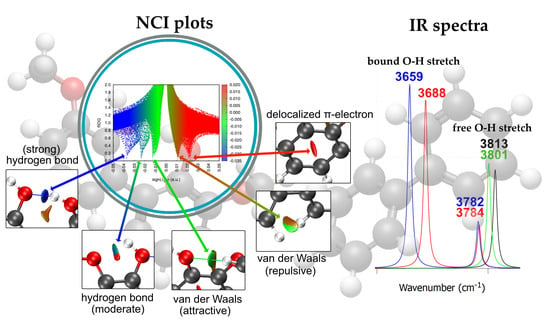
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Comparative Role of rGO, AgNWs, and rGO–AgNWs Hybrid Structure in the EMI Shielding Performance of Polyaniline/PCL-Based Flexible Films
by
Brankica Gajić, Marija Radoičić, Muhammad Yasir, Warda Saeed, Silvester Bolka, Blaž Nardin, Jelena Potočnik, Gordana Ćirić-Marjanović, Zoran Šaponjić and Svetlana Jovanović
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4693; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244693 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
The present study explores the comparative influence of reduced graphene oxide (rGO), silver nanowires (AgNWs), and their hybrid rGO–AgNWs on the electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding performance of polyaniline (PANI)-based flexible films prepared using a polycaprolactone (PCL) matrix. The nanocomposites were synthesized through in
[...] Read more.
The present study explores the comparative influence of reduced graphene oxide (rGO), silver nanowires (AgNWs), and their hybrid rGO–AgNWs on the electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding performance of polyaniline (PANI)-based flexible films prepared using a polycaprolactone (PCL) matrix. The nanocomposites were synthesized through in situ oxidative polymerization of aniline in the presence of individual or hybrid fillers, followed by their dispersion in the PCL matrix and casting of the corresponding films. Morphological and structural characterization (SEM, Raman, and FTIR spectroscopy) confirmed a uniform PANI coating on both rGO sheets and AgNWs, forming hierarchical 3D conductive networks. Thermal (TGA) and thermomechanical (TMA) analyses revealed enhanced thermal stability and stiffness across all composite systems, driven by strong interfacial interactions and restricted polymer chain mobility. Tmax increased from 437.9 °C for neat PCL to 487.9 °C for PANI/PCL, 480.6 °C for PANI/rGO/PCL, 499.4 °C for PANI/AgNWs/PCL and 495.0 °C for the hybrid PANI/rGO–AgNWs/PCL film. The gradual decrease in contact angle following the order PANI/AgNWs/PCL < PANI/rGO–AgNWs/PCL < PANI/rGO/PCL < PANI/PCL < PCL clearly indicates a systematic increase in surface polarity and surface energy with the incorporation of conductive nanofillers. Electrical conductivity reached 60.8 S cm−1 for PANI/rGO/PCL, gradually decreasing to 27.4 S cm−1 for PANI/AgNWs/PCL and 22.1 S cm−1 for the quaternary hybrid film. The EMI shielding effectiveness (SET) measurements in the X-band (8–12 GHz) demonstrated that the PANI/rGO/PCL film exhibited the highest attenuation (~7.2 dB). In contrast, the incorporation of AgNWs partially disrupted the conductive network, reducing SE to ~5–6 dB. The findings highlight the distinct and synergistic roles of 1D and 2D fillers in modulating the electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties of biodegradable polymer films, offering a sustainable route toward lightweight, flexible EMI shielding materials.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Metal and Metal Oxide Nanocomposites: From Synthesis to Applications in Biomedical & Environmental Technologies)
►▼
Show Figures
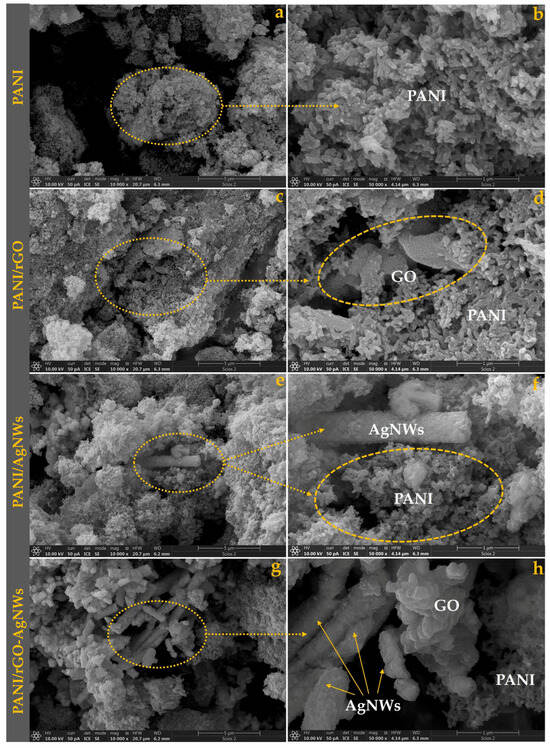
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Effects of Polyphenolic Extracts from Olive Mill Vegetation Water on Wild Boar Meat Patties
by
Caterina Altissimi, David Ranucci, Susanne Bauer, Raffaella Branciari, Roberta Galarini, Maurizio Servili, Rossana Roila and Peter Paulsen
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4692; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244692 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Game meats are particularly prone to oxidation and microbial spoilage due to their specific characteristics and the procedures required to obtain them. Various sustainable bioactive molecules derived from food industry by-products, such as olive mill wastewater, have the potential to enhance the stability
[...] Read more.
Game meats are particularly prone to oxidation and microbial spoilage due to their specific characteristics and the procedures required to obtain them. Various sustainable bioactive molecules derived from food industry by-products, such as olive mill wastewater, have the potential to enhance the stability and safety of game meats. The use of different levels of polyphenolic extracts from olive mill vegetation water, encapsulated through a freeze-drying process, was tested on wild boar meat patties as an antioxidant and antimicrobial. Two separate trials were performed. Trial 1 was carried out by adding different concentrations of polyphenolic extract (0, 1, and 2%) during the production of wild boar patties, and trial 2 by adding 1.5% salt and adding or not adding 2% polyphenolic extract. The first trial revealed antioxidant effects on the raw patties during storage time, both on colour (increasing in saturation index) and thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (0.306, 0.268, and 0.254 mg MDA/kg after 5 days of storage in the control with 1% and 2% polyphenolic extract groups, respectively). Oxidation was also reduced during cold storage of cooked patties. Trial 1 also revealed a dose-dependent antimicrobial effect, mainly on Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas spp. Trial 2 confirmed that salt plus extract addition had an overall higher antimicrobial effect than when singularly added, but with a moderate increase in the hardness of the products.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Fabrication of Novel MOF/HOF Composite for Efficient Degradation of Methylene Blue via Photo-Fenton-like Process
by
Yanfeng Zhang, Yong Huang, Han Leng and Xuwei Chen
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4691; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244691 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
The photo-Fenton process is an advanced oxidation method widely employed in environmental remediation. Herein, we developed a novel metal–organic framework@hydrogen-bonded organic framework (MOF/HOF) composite with excellent photo-Fenton-like activity for the efficient degradation of organic dye methylene blue (MB). Cu-based MOF (CuBTC) was firstly
[...] Read more.
The photo-Fenton process is an advanced oxidation method widely employed in environmental remediation. Herein, we developed a novel metal–organic framework@hydrogen-bonded organic framework (MOF/HOF) composite with excellent photo-Fenton-like activity for the efficient degradation of organic dye methylene blue (MB). Cu-based MOF (CuBTC) was firstly prepared via the solvothermal method, then melamine (MA) and trimesic acid (TMA)-based HOF (MA-TMA) was grown in situ on CuBTC with hydrogen bonding interactions to produce the MOF/HOF composite CuBTC-MA. The CuBTC-MA composite could catalyze H2O2 to produce active substances for efficient MB degradation. The degradation rate constant of the CuBTC-MA composite was 4.4 times and 16.7 times higher than that of CuBTC and MA-TMA. The remarkably enhanced performance was attributed to the synergistic effect between the efficient separation of electron–holes supported by the type-II heterojunction structure of the CuBTC-MA composite and the Cu(I)/Cu(II) inter-conversion. The CuBTC-MA composite demonstrated exceptional repeatability and maintained a stable performance across a broad pH range. This study provided a novel paradigm for engineering heterogeneous MOF/HOF heterostructures, demonstrating significant potential in advancing photo-Fenton-like catalytic systems for the efficient environmental remediation of organic pollutants through synergistic charge separation and radical generation mechanisms.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Determination, Adsorption and Degradation Mechanisms of Environmental Pollutants)
►▼
Show Figures
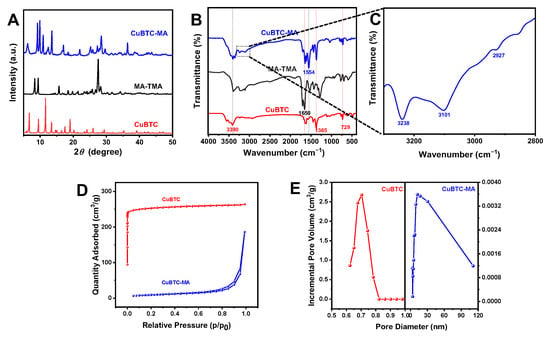
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Recovery of Lithium and Cobalt from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries Using a Deep Eutectic Solvent Based on Choline Chloride and Oxalic Acid (Oxaline)
by
Jessica M. Guamán-Gualancañay, Carlos F. Aragón-Tobar, Katherine Moreno, José-Luis Palacios and Diana Endara
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4690; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244690 - 7 Dec 2025
Abstract
The growing consumption of lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) in electronic devices and electric vehicles has led to a significant increase in waste containing valuable metals such as lithium and cobalt. Recovering these metals is essential to reducing dependence on primary sources and minimizing environmental
[...] Read more.
The growing consumption of lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) in electronic devices and electric vehicles has led to a significant increase in waste containing valuable metals such as lithium and cobalt. Recovering these metals is essential to reducing dependence on primary sources and minimizing environmental impact. In this study, the leaching of the cathode active material from discarded LIBs was evaluated using oxaline, a deep eutectic solvent (DES) composed of oxalic acid and choline chloride in a 1:1 molar ratio. The process began with the collection, discharge, washing, drying, and dismantling of the LIBs, followed by the separation of their components. Subsequently, the cathode active material was characterized, revealing a primary composition of cobalt (54.5%) and lithium (6.5%), with the presence of LiCoO2 confirmed by XRD analysis. Leaching experiments were conducted to evaluate the effects of temperature, time, and solid percentage, demonstrating that oxaline is effective for the selective leaching of lithium and cobalt. Under optimal conditions (90 °C, 1–2 wt.% cathode active material, 400 rpm), lithium underwent complete dissolution within the first hour, while cobalt achieved complete leaching by 4 h. Both metals were recovered as oxalates and separated based on differences in solubility. Oxaline proves to be an efficient and environmentally friendly alternative for the selective recovery of lithium and cobalt from LIB waste, supporting a circular economy in the management of critical metals.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Horizons in Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs): Synthesis, Characterization and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
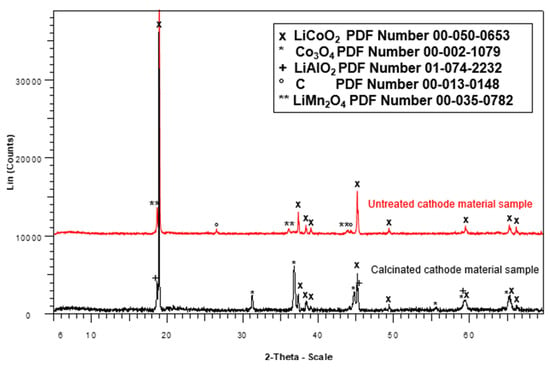
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Can Aquatic Plant Turions Serve as a Source of Arabinogalactans? Immunohistochemical Detection of AGPs in Turion Cells
by
Bartosz J. Płachno, Lubomír Adamec, Marcin Feldo, Piotr Stolarczyk and Małgorzata Kapusta
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4689; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244689 - 7 Dec 2025
Abstract
Turions (overwintering buds) as modified shoot apices constitute specialized vegetative structures that enable many aquatic vascular plants to withstand adverse environmental conditions such as low temperature, desiccation, or limited light availability. Turions serve as major storage sites for organic reserves, including sugars, proteins,
[...] Read more.
Turions (overwintering buds) as modified shoot apices constitute specialized vegetative structures that enable many aquatic vascular plants to withstand adverse environmental conditions such as low temperature, desiccation, or limited light availability. Turions serve as major storage sites for organic reserves, including sugars, proteins, fatty acids, and polyamines. Owing to their high content of energy-rich and nutritionally valuable compounds, turions represent a potential renewable resource for applications in biofuel production, animal feed, and the food industry. We investigated whether arabinogalactan proteins (AGPs) occur in aquatic plant turions and localized these compounds within specific tissues or cell types. This work was designed to evaluate whether stress-resistant storage organs may constitute a practical reservoir of AGPs. Considering the central role of AGPs in plant responses to abiotic stress, we hypothesized that turions, which routinely encounter cold, anoxia, and intermittent dehydration, would exhibit particularly high AGP accumulation. Mature turions of aquatic species (Aldrovanda vesiculosa, Utricularia australis, U. intermedia, and Caldesia parnassifolia) were used. Immunofluorescent labeling with AGP-specific antibodies (JIM8, JIM13, JIM14, LM2, MAC207) and confocal laser scanning microscopy were employed. In Aldrovanda vesiculosa and Caldesia parnassifolia, AGP epitopes were abundantly presented in cytoplasmic compartments. AGP epitopes occurred in secretory structures in turions of all examined species (trichomes of Aldrovanda and Utricularia, secretory ducts of Caldesia). In analyzing turions of four different species, we identified Aldrovanda vesiculosa turions as the most promising potential source of AGPs, also noting their high reserve potential for use in animal feed or the food industry.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Research on Chemical Composition and Activity of Natural Products, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
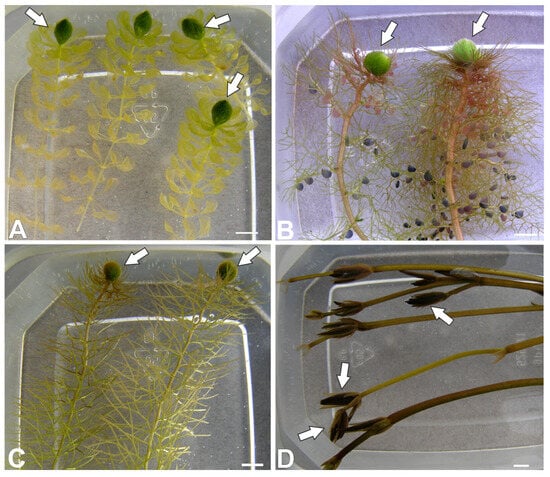

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Defining Aldol Chemoselectivity in the Presence of Henry Nucleophiles (Nitroalkanes)
by
Kritika B. Dwivedi, Patrick Knäbe, Nilesh N. Shitole, Aida H. Lakew, Ruslan Levochkin, Luis Paredes-Soler, Sofiia-Stefaniia Zhylinska, Diana Kochubei, Gabriela Guillena, Rafael Chinchilla, Diego A. Alonso and Thomas C. Nugent
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4688; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244688 - 7 Dec 2025
Abstract
This study evaluates the feasibility of achieving chemoselective aldol reactions over competing Henry reactions and employs competition experiments to establish proof of concept. A typical reaction involved using in-water reaction conditions where a concentrated organic layer containing an aldol nucleophile (1.5 equiv), a
[...] Read more.
This study evaluates the feasibility of achieving chemoselective aldol reactions over competing Henry reactions and employs competition experiments to establish proof of concept. A typical reaction involved using in-water reaction conditions where a concentrated organic layer containing an aldol nucleophile (1.5 equiv), a Henry nucleophile (1.5 equiv), an aldehyde electrophile (1.0 equiv), and a proline-based amino acid catalyst (2.5 mol%) constituted one phase, while the second phase was water (15 equiv). Highly enantioenriched aldol products were formed in practical yields, and a variety of Henry nucleophiles (nitroalkanes, allylic nitro compounds, and ethyl nitroacetate) were tolerated. This systematic examination of nitro compounds (pKa 5.5–10.0) established a pKa of ≈7.0 as the critical threshold at which nitronate formation results in Henry product formation under catalysis with 1. Reactions alternatively performed in MeOH/H2O (3:2 equiv) solvent combinations, at times, provided improved chemoselectivity or product dr over the use of water (15 equiv) alone but required longer reaction times to produce similar yields. Reactions constrained by solubility were investigated using mechanochemical methods, but these conditions failed to deliver practical yields of either competition product. In summary, defining this category of aldol chemoselectivity may provide new tactical opportunities for the synthesis of complex molecular targets.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Organic Chemistry—Third Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
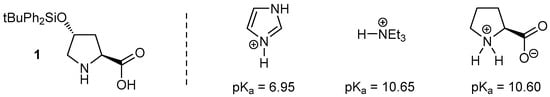
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Extracts from By-Products of the Fruit and Vegetable Industry as Ingredients Improving the Properties of Cleansing Gels
by
Agata Blicharz-Kania, Magdalena Iwanek and Anna Pecyna
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4687; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244687 - 7 Dec 2025
Abstract
This study aimed to evaluate the effect of adding extracts obtained from by-products on the physicochemical and functional properties of cleansing gels. Micellar extraction (2% decyl glucoside solution in water) was performed on secondary raw materials: banana peel (BP), pomegranate peel (PP), tomato
[...] Read more.
This study aimed to evaluate the effect of adding extracts obtained from by-products on the physicochemical and functional properties of cleansing gels. Micellar extraction (2% decyl glucoside solution in water) was performed on secondary raw materials: banana peel (BP), pomegranate peel (PP), tomato pomace (TP), and grape pomace (GP). The extracts were analyzed for soluble substances and active compounds (polyphenols, carotenoids, and vitamin C). Cleansing gels containing plant extracts were also prepared and evaluated for their color and physicochemical and functional properties. The extracts contained natural polyphenols (10.99–16.54 mg·100 mL−1), carotenoids (1.391–2.402 mg·mL−1), and vitamin C (0.651–1.529 mg·100 mL−1). The extract-enriched gels showed altered color (lower brightness, greater redness and yellowness), enhanced foaming properties, and modified viscosity (402.9–416.8 mPA for BP and GP; lower for PP and TP). The pH of the gels ranged from 5.391 to 5.917, which is within the physiological range of human skin. Dissolution times were reduced by up to 60% compared to the control, with PP extract producing the shortest time of 15.7 min. These results indicate that plant by-product extracts can improve both the functional performance and skin compatibility of cleaning gels.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Biologically Active Molecules: Extraction Strategies, Therapeutic Potential and Biomedical Perspective)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Molecular Mechanisms by Which Linear Versus Branched Alkyl Chains in Nonionic Surfactants Govern the Wettability of Long-Flame Coal
by
Boyu Li, Guochao Yan, Shaoqi Kong, Kuangkuang Wu and Yanheng Wang
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4686; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244686 - 7 Dec 2025
Abstract
Improving the wettability of coal dust with nonionic surfactants is crucial for mitigating environmental pollution. Here we compare two nonionic surfactants with distinct architectures—n-octyl-α-D-glucoside (OG) and Isooctyl glucoside (APG08)—to dissect how linear versus branched C8 chains govern the wetting of long-flame bituminous coal
[...] Read more.
Improving the wettability of coal dust with nonionic surfactants is crucial for mitigating environmental pollution. Here we compare two nonionic surfactants with distinct architectures—n-octyl-α-D-glucoside (OG) and Isooctyl glucoside (APG08)—to dissect how linear versus branched C8 chains govern the wetting of long-flame bituminous coal dust. Sedimentation and contact-angle measurements show that the linear OG, with reduced steric hindrance, assembles into a denser interfacial layer and delivers superior wetting. Corroborating spectroscopic and microscopic analyses (FTIR, XPS, and SEM) reveal that OG treatment increases hydroxyl functionalities and the O-element fraction at the coal surface; OG also drives stronger particle aggregation, consistent with markedly enhanced adsorption on coal. Molecular dynamics simulations further indicate tighter OG adsorption, a more homogeneous coal–water interfacial structure, and stronger binding of water to OG-modified surfaces. Collectively, these results identify chain linearity as a key design lever for nonionic glucosides and establish OG as a more effective wettability promoter for long-flame coal dust.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects of Aqueous Extracts from Green Leaves and Rhizomes of Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile on LPS-Stimulated RAW 246.7 Macrophages
by
Giulia Abruscato, Daniela Ganci, Federica Bellistrì, Roberto Chiarelli, Manuela Mauro, Aiti Vizzini, Vincenzo Arizza, Mirella Vazzana and Claudio Luparello
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4685; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244685 - 7 Dec 2025
Abstract
The marine angiosperm Posidonia oceanica (Linnaeus) Delile, 1813 is a rich source of phytotherapeutic compounds whose potential applications for human health remain largely uninvestigated. Here, we determined the differential impact of aqueous extracts from P. oceanica’s green leaves (GLE) and rhizomes (RE)
[...] Read more.
The marine angiosperm Posidonia oceanica (Linnaeus) Delile, 1813 is a rich source of phytotherapeutic compounds whose potential applications for human health remain largely uninvestigated. Here, we determined the differential impact of aqueous extracts from P. oceanica’s green leaves (GLE) and rhizomes (RE) on the inflammation-related mRNA expressions and protein levels, nitric oxide (NO) release, and endocytic activity in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. We also examined the influence of the extracts in modulating the activation of components of intracellular signaling pathways. Co-treatments of LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells in the presence of either GLE or RE resulted in a reduction in NO production, associated with a down-regulation of Nos2 expression, reduced levels of COX-2 and TNFα proteins, and a decrease in Nfkb1 expression and NF-κB activation. No effect was exerted on the release of IL-6. Moreover, co-exposures to LPS and the extracts led to an elevation in pJNK and pAKT levels alongside a reduction in pERK. In contrast to GLE, RE specifically lowered IL-1β production, induced a more robust increase in IL-10, positively influenced the endocytic function of RAW 264.7 cells, and drastically up-regulated the phosphorylation of p38. The data obtained indicate that GLE and RE exhibit considerable promise as prospective anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory agents.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Extracts from Natural Plants, 2nd Edition)
Open AccessReview
Rebalancing the Skin: The Microbiome, Acne Pathogenesis, and the Future of Natural and Synthetic Therapies
by
Maria Beatriz Oliveira, Ana Colette Maurício, Ana Novo Barros and Cláudia Botelho
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4684; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244684 - 7 Dec 2025
Abstract
The skin serves as a primary interface between the human body and the external environment, functioning both as a protective barrier and as a habitat for a complex and diverse microbiome. These microbial communities contribute to immune regulation, barrier integrity, and defence against
[...] Read more.
The skin serves as a primary interface between the human body and the external environment, functioning both as a protective barrier and as a habitat for a complex and diverse microbiome. These microbial communities contribute to immune regulation, barrier integrity, and defence against pathogens. Disruptions in this equilibrium can precipitate dermatological disorders such as acne vulgaris, which affects millions of adolescents and adults worldwide. This chronic inflammatory disorder of the pilosebaceous unit is driven by microbial dysbiosis, hyperkeratinisation, sebum overproduction, and inflammation. This review synthesizes data from over 100 sources to examine the interplay between the skin microbiome and acne pathogenesis, and to compare synthetic treatments, including retinoids, antibiotics, and hormonal therapies, with natural approaches such as polyphenols, minerals, and resveratrol. The analysis highlights the therapeutic convergence of traditional pharmacology and bioactive natural compounds, proposing microbiome-conscious and sustainable strategies for future acne management.
Full article

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Molecules Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal Browser-
arrow_forward_ios
Forthcoming issue
arrow_forward_ios Current issue - Vol. 30 (2025)
- Vol. 29 (2024)
- Vol. 28 (2023)
- Vol. 27 (2022)
- Vol. 26 (2021)
- Vol. 25 (2020)
- Vol. 24 (2019)
- Vol. 23 (2018)
- Vol. 22 (2017)
- Vol. 21 (2016)
- Vol. 20 (2015)
- Vol. 19 (2014)
- Vol. 18 (2013)
- Vol. 17 (2012)
- Vol. 16 (2011)
- Vol. 15 (2010)
- Vol. 14 (2009)
- Vol. 13 (2008)
- Vol. 12 (2007)
- Vol. 11 (2006)
- Vol. 10 (2005)
- Vol. 9 (2004)
- Vol. 8 (2003)
- Vol. 7 (2002)
- Vol. 6 (2001)
- Vol. 5 (2000)
- Vol. 4 (1999)
- Vol. 3 (1998)
- Vol. 2 (1997)
- Volumes not published by MDPI
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Biomass, Energies, Materials, Molecules, Nanomaterials, Polymers
Biomass for Energy, Chemicals and Materials
Topic Editors: Shaohua Jiang, Changlei Xia, Shifeng Zhang, Xiaoshuai HanDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topic in
J. Compos. Sci., Materials, Molecules, Nanomaterials, Polymers, Processes, Recycling
Science and Technology of Polymeric Blends, Composites, and Nanocomposites
Topic Editors: Roberto Scaffaro, Emmanuel Fortunato GulinoDeadline: 28 February 2026
Topic in
Cancers, IJMS, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Sci. Pharm., Current Oncology, Molecules
Recent Advances in Anticancer Strategies, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Hassan Bousbaa, Zhiwei HuDeadline: 31 March 2026
Topic in
Applied Nano, Catalysts, Materials, Nanomaterials, Polymers, Molecules
Application of Nanomaterials in Environmental Analysis
Topic Editors: Yonggang Zhao, Yun ZhangDeadline: 13 April 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Molecules
Advances in Sustainable Solvents for Greener Chemical Processes
Guest Editors: José Luis Todolí Torró, Gabriela GuillenaDeadline: 12 December 2025
Special Issue in
Molecules
Recent Advances in Development of Small Molecules to Fight Cancer—2nd Edition
Guest Editors: Giulia Bononi, Carlotta GranchiDeadline: 15 December 2025
Special Issue in
Molecules
Nano-Functional Materials for Sensor Applications—2nd Edition
Guest Editors: Li Fu, Aiwu WangDeadline: 15 December 2025
Special Issue in
Molecules
Heterocycles: Synthesis, Biological Activity, Pharmacokinetic Profiles, and Mechanism of Actions
Guest Editors: Guang Huang, Lucjan Strekowski, Xin LiDeadline: 15 December 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Molecules
Recent Advances in Flavors and Fragrances
Collection Editor: Luca Forti
Topical Collection in
Molecules
Natural Products as Leads or Drugs against Neglected Tropical Diseases
Collection Editors: Thomas J. Schmidt, Valeria Sülsen, Josphat Matasyoh
Topical Collection in
Molecules
Featured Reviews in Natural Products Chemistry
Collection Editors: Enrique Barrajón-Catalán, Vicente Micol, María Herranz-López
Topical Collection in
Molecules
Preanalytical Methods for Natural Products Production
Collection Editors: Young Hae Choi, Farid Chemat, Giancarlo Cravotto, Erica G. Wilson