Journal Description
Chemistry
Chemistry
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on chemistry published monthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Reliable service: rigorous peer review and professional production.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 15 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.2 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Extra benefits: no space constraints, no color charges.
- Journal Cluster of Chemical Reactions and Catalysis: Catalysts, Chemistry, Electrochem, Inorganics, Molecules, Organics, Oxygen, Photochem, Reactions, Sustainable Chemistry.
Impact Factor:
2.4 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.3 (2024)
Latest Articles
Effects of Vibrationally Treated Aqueous Media on the Kinetics of Methylene Blue Reduction by Ascorbic Acid
Chemistry 2026, 8(3), 33; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry8030033 - 3 Mar 2026
Abstract
As a primary reaction medium, water profoundly influences the kinetics and mechanisms of chemical processes. External physical treatments, such as vibration, can alter the physicochemical properties of water, thereby modifying reaction outcomes. This study aimed to investigate the effect of vibrational iterations (I0–I7)
[...] Read more.
As a primary reaction medium, water profoundly influences the kinetics and mechanisms of chemical processes. External physical treatments, such as vibration, can alter the physicochemical properties of water, thereby modifying reaction outcomes. This study aimed to investigate the effect of vibrational iterations (I0–I7) prepared using the “crossing” technology on the kinetics of the oxidation–reduction reaction between methylene blue and ascorbic acid, a standard model for evaluating external influences. Initial characterization revealed that while pH remained stable across all samples, electrical conductivity and dissolved oxygen levels deviated significantly from the control (intact water), with oxygen concentrations measuring either higher or lower than the control. Following the dissolution of methylene blue in these iterations, absorption spectroscopy was used to monitor decolorization kinetics. Different vibrational iterations influenced distinct kinetic parameters, including the rate constant, half-reaction time, and average reaction rate. Depending on the number of processing steps used to prepare the iterations, these parameters exhibited deviations ranging from 3% to 9% compared to the control. This suggests a complex relationship between the aqueous medium’s structural–dynamic properties and the reactants’ supramolecular organization. These findings underscore the potential of vibrational iterations as a tool for modulating chemical reaction kinetics through aqueous medium engineering. Further research is needed to elucidate the underlying mechanisms and expand the applicability of this approach to other systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Physical Chemistry and Chemical Physics)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Machine Learning and Approximated Estimation Approaches for Process Design in Drug Synthesis
by
Andrea Repetto, Gianguido Ramis and Ilenia Rossetti
Chemistry 2026, 8(3), 32; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry8030032 - 3 Mar 2026
Abstract
The continuous-flow technologies in organic synthesis for the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) are nowadays more and more applied. In-silico process design is a powerful tool able to support organic synthesis in the field of scale-up and process development. Process design feasibility
[...] Read more.
The continuous-flow technologies in organic synthesis for the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) are nowadays more and more applied. In-silico process design is a powerful tool able to support organic synthesis in the field of scale-up and process development. Process design feasibility and reliability depend on the availability of a well-defined chemical reaction kinetic scheme, information which is usually derived from experimental datasets collected on purpose. The latter approach is time-consuming and demanding in terms of resources. Different possibilities are here proposed to valorize widely available experimental data from explorative works with different approaches, depending on the nature, richness, and structure of the datasets. The kinetic parameters (i.e., reaction order, kinetic constant, and activation energy) of some interesting organic reactions have been approximately estimated by applying different computational methodologies, thanks to built-in experimental databases. The numerical algebra approach dealing with linear and non-linear regression analysis for the kinetic parameters has been initially considered and related to the database information for oseltamivir synthesis. The Bayesian statistic was applied to the ibuprofen case through the application of the Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) method for reaction order estimation. At last, a Machine Learning (ML) approach has been applied to the Rolipram and Pregabalin case study. The in-house developed T-ReX experimental kinetic constant database was exploited, with application of the k-Nearest neighbor algorithm for classification and regular expression pattern recognition. Advantages and limitations of the three approaches are discussed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue AI and Big Data in Chemistry)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Advances in Photodynamic Therapy: Photosensitizers, Biological Mechanisms, and Artificial Intelligence-Driven Innovation
by
Jadwiga Inglot, Dorota Bartusik-Aebisher, Katarzyna Bania, Klaudia Dynarowicz and David Aebisher
Chemistry 2026, 8(3), 31; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry8030031 - 2 Mar 2026
Abstract
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a minimally invasive therapeutic modality that combines a photosensitizer, light of an appropriate wavelength, and molecular oxygen to generate cytotoxic reactive oxygen species for selective tissue destruction. Over recent decades, PDT has evolved from early porphyrin-based systems to advanced
[...] Read more.
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a minimally invasive therapeutic modality that combines a photosensitizer, light of an appropriate wavelength, and molecular oxygen to generate cytotoxic reactive oxygen species for selective tissue destruction. Over recent decades, PDT has evolved from early porphyrin-based systems to advanced third-generation photosensitizers incorporating nanotechnology, targeting ligands, and activatable designs, significantly improving tumor selectivity, pharmacokinetics, and therapeutic efficacy. This article offers an in-depth look at the fundamental principles of PDT, including the roles of photosensitizers, light delivery systems, and oxygen dynamics, as well as the resulting biological effects such as direct tumor cell death, vascular shutdown, and immune activation. Clinical applications across oncology, dermatology, ophthalmology, and antimicrobial therapy are discussed, highlighting both established and emerging indications. Furthermore, the review critically examines recent advances in machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) applied to PDT, including treatment planning, dosimetry optimization, photosensitizer and nanoparticle design, real-time treatment monitoring, and outcome prediction. By integrating physics-based modeling, multimodal imaging, and artificial intelligence-driven approaches, PDT is transitioning toward adaptive, personalized photomedicine. This work outlines current challenges, future research directions, and the translational potential of AI-enabled PDT systems, emphasizing their role in improving precision, reproducibility, and clinical outcomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Modern Photochemistry and Molecular Photonics)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
A Dual-Passivation Strategy to Enhance Exciton Luminescence and Bimodal Anticounterfeiting in Red Perovskite Quantum Dots
by
Keyujia Zhong, Fang Lei, Shiqing Dang, Hongyang Zhang, Ying Shi and Haohong Chen
Chemistry 2026, 8(3), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry8030030 - 26 Feb 2026
Abstract
Perovskite quantum dots (PQDs) face significant performance limitations due to surface defects, which are not sufficiently addressed by conventional single-passivation methods. We introduce a dual-passivation strategy that synergistically combines bifunctional ligand 3-(N,N-dimethyloctadecylammonium)-propanesulfonate (SB3-18) treatment with silica coating to simultaneously passivate undercoordinated Pb2+
[...] Read more.
Perovskite quantum dots (PQDs) face significant performance limitations due to surface defects, which are not sufficiently addressed by conventional single-passivation methods. We introduce a dual-passivation strategy that synergistically combines bifunctional ligand 3-(N,N-dimethyloctadecylammonium)-propanesulfonate (SB3-18) treatment with silica coating to simultaneously passivate undercoordinated Pb2+ ions and bromine vacancies in red-emitting CsPb(Br/I)3 PQDs. This approach nearly triples the photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY, from 23% to 58%). Systematic structural, morphlogical, binding energy, Fermi level and optical analyses confirm effective defect suppression and enhanced exciton luminescence. The dual-passivated sample QDs:SB3-18@SiO2 also exhibit excellent environmental stability, retaining 85% of their initial emission after 30 min in air and exhibiting improved UV resistance. By combining the PQDs with a CGSO:Tb3+ mechanoluminescent phosphor, a composite film is fabricated with bimodal optical response—color-selective photoluminescence under UV excitation and stress-activated green emission upon scratching. This work presents a robust route to high-performance PQDs and demonstrates their potential for advanced anticounterfeiting and smart optical applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Chemistry of Materials)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
PDCG: A Diffusion Model Guided by Pre-Training for Molecular Conformation Generation
by
Yanchen Liu, Yameng Zheng, Amina Tariq, Xiaofei Nan, Lingbo Qu and Jinshuai Song
Chemistry 2026, 8(2), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry8020029 - 18 Feb 2026
Abstract
Background: While machine learning has advanced molecular conformation generation, existing models often suffer from limited generalization and inaccuracies, especially for complex molecular structures. These limitations hinder their reliability in downstream applications. Methods: We proposed a molecular conformation model combined with a molecular graph
[...] Read more.
Background: While machine learning has advanced molecular conformation generation, existing models often suffer from limited generalization and inaccuracies, especially for complex molecular structures. These limitations hinder their reliability in downstream applications. Methods: We proposed a molecular conformation model combined with a molecular graph pre-training module and a diffusion model (PDCG). Feature embeddings are obtained from a pre-trained model and concatenated with the molecular graph information. Fusion features are used for generating conformations in the model. The model was trained and evaluated on the GEOM-QM9 and GEOM-Drugs datasets. Results: PDCG significantly outperforms existing baselines, which shows markedly superior results. Furthermore, in downstream molecular property prediction tasks, conformations generated by PDCG yield results comparable to those derived from DFT-optimized geometries. Conclusions: Our work provides a robust and generalizable model for accurate conformation generation. PDCG offers a reliable tool for downstream computational tasks, such as the virtual screening of functional materials and drug-like molecules.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue AI and Big Data in Chemistry)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Self-Heating Performance of Magnetite Doped with Cobalt/Zinc Nanoparticles: Impact of Magnetic Field, Coating Agent, and Dispersing Solvent
by
Enaam A. Al-Harthi, Ghaida H. Munshi, Jamilah M. Al-Ahmari and Mohamed S. A. Darwish
Chemistry 2026, 8(2), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry8020028 - 16 Feb 2026
Abstract
Fabrication of magnetic materials via a facile and environmentally favorable process with high self-heating performance is quite favored for biomedical applications. To tackle this challenge, magnetic ferrite nanoparticles were developed through an ultrasonic-assisted coprecipitation process. Magnetite (Fe3O4), magnetite doped
[...] Read more.
Fabrication of magnetic materials via a facile and environmentally favorable process with high self-heating performance is quite favored for biomedical applications. To tackle this challenge, magnetic ferrite nanoparticles were developed through an ultrasonic-assisted coprecipitation process. Magnetite (Fe3O4), magnetite doped with cobalt nanoparticles (Co0.4Fe2.6O4), and magnetite doped with cobalt/zinc nanoparticles (Zn0.15Co0.25Fe2.6O4) were synthesized using ultrasonic-assisted coprecipitation techniques. Specific loss power (SLP) was estimated to optimize the heating influence under varied magnetic fields, coating agents, and dispersing solvents. Magnetite doped with cobalt/zinc nanoparticles demonstrated elevated SLP 110 W/g with preferable hyperthermic performance, where AMF conditions did not surpass the safety border for human exposure. The self-heating performance of magnetite doped with cobalt/zinc nanoparticles increased with increasing strength at a constant frequency. The self-heating performance of magnetite nanoparticles increased with increasing frequency at constant strength. Hence, the prepared magnetite doped with cobalt/zinc nanoparticles by the ultrasonic-assisted coprecipitation process can be appropriate for biomedical applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Recent Advances in Sustainable Materials for Energy and Environmental Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
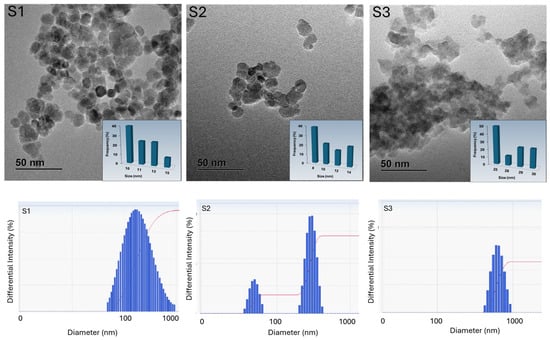
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Large Electrocaloric Effect in Stretched Relaxor Ferroelectric Polymers near Morphotropic Phase Boundary
by
Linxiao Xu, Yuquan Liu, Jiahong Li, Hangyao Wu, Yuanqi Wang, Ze Yuan, Ling Cheng, Yang Li, Huamin Zhou and Yang Liu
Chemistry 2026, 8(2), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry8020027 - 16 Feb 2026
Abstract
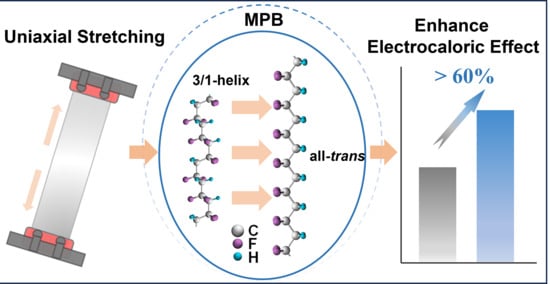
Use of the morphotropic phase boundary (MPB) is a promising approach to enhance the electrocaloric effect in ferroelectric polymers. This is usually achieved by a composition method, and polymer processing near the MPB to tune electrocaloric response has attracted little attention. Here, the
[...] Read more.
Use of the morphotropic phase boundary (MPB) is a promising approach to enhance the electrocaloric effect in ferroelectric polymers. This is usually achieved by a composition method, and polymer processing near the MPB to tune electrocaloric response has attracted little attention. Here, the relative stability between disordered 3/1-helix and ordered all-trans conformations is leveraged by uniaxial stretching to improve the electrocaloric effect in relaxor ferroelectric polymers under low electric fields. It is found that the stretching technique enables a considerably more enhanced electrocaloric response in polymer composition near the MPB at room temperature, compared with counterparts corresponding to the relaxor phase. The electrocaloric-induced temperature change is found to be 4.5 K under a low electric field of 50 MV m−1 in stretched relaxor ferroelectric polymers at room temperature, corresponding to a 60% enhancement over pristine counterparts. This result highlights the critical role of polymer processing in optimizing electrocaloric properties, especially near the MPB, and this can be extended to improve other functionalities, such as piezoelectric response, in relaxor ferroelectric polymers.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Phase Transition)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Surfactant Temperature-Dependent Critical Micelle Concentration Prediction with Uncertainty-Aware Graph Neural Network
by
Musa Sh. Adygamov, Emil R. Saifullin, Timur R. Gimadiev and Nikita Yu. Serov
Chemistry 2026, 8(2), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry8020026 - 15 Feb 2026
Abstract
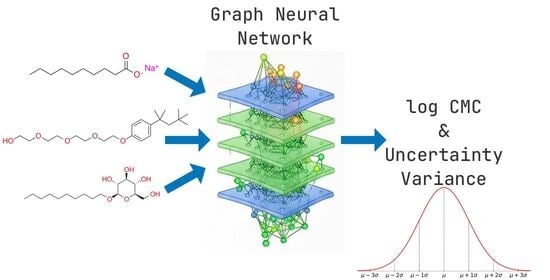
The critical micelle concentration (CMC) is a fundamental physicochemical property of surfactants with significant implications across multiple industries. This paper presents an uncertainty-aware graph neural network (GNN) that integrates molecular structure and temperature to simultaneously predict CMC values and prediction uncertainties. Trained on
[...] Read more.
The critical micelle concentration (CMC) is a fundamental physicochemical property of surfactants with significant implications across multiple industries. This paper presents an uncertainty-aware graph neural network (GNN) that integrates molecular structure and temperature to simultaneously predict CMC values and prediction uncertainties. Trained on a curated dataset of 2133 CMC values with temperature annotations, our GNN achieves comparatively similar performance on two external test sets from similar works. The model provides adequately calibrated uncertainty estimates that reliably quantify prediction confidence. This dual-output approach enables reliable CMC prediction with quantifiable confidence intervals, addressing a practical need for safety-critical applications where underestimation of uncertainty could have serious consequences.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Physical Chemistry and Chemical Physics)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
A Systematic Study of the Catalytic Decomposition Process of Ammonium Perchlorate and Its Decomposition Products Catalyzed by Copper and Copper Oxides
by
Guifeng Xiang, Xiaolin Tang, Chenhui Ma, Zeyu Zheng, Yifu Zhang and Chi Huang
Chemistry 2026, 8(2), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry8020025 - 13 Feb 2026
Abstract
To reveal the core mechanism of copper-based materials in catalyzing ammonium perchlorate (AP) decomposition, three copper-based materials with the simplest structures (Cu, Cu2O and CuO) are selected as research objects. This study systematically investigates their catalytic performances, gaseous product evolution, kinetic
[...] Read more.
To reveal the core mechanism of copper-based materials in catalyzing ammonium perchlorate (AP) decomposition, three copper-based materials with the simplest structures (Cu, Cu2O and CuO) are selected as research objects. This study systematically investigates their catalytic performances, gaseous product evolution, kinetic laws, and combustion behavior in AP decomposition. The results show that all three materials exhibit excellent catalytic activity, reducing the peak temperature of AP high-temperature decomposition to 325.1 °C, 329.9 °Cand 337.3 °C, respectively, with the catalytic activity order of Cu > Cu2O > CuO. Gaseous product analysis confirms that both temperature and catalyst type jointly regulate product distribution. Kinetic analysis shows that the activation energy of Cu and Cu2O catalytic processes exhibits a three-stage change of “increase-decrease-increase” (related to their own oxidation), while CuO shows a two-stage change, and the kinetic behaviors of the three are consistent in the later stage. Combustion experiments indicate that catalytic activity is positively correlated with combustion efficiency; the Cu-catalyzed system has the shortest combustion duration (383 ms) and the largest flame area. This study proposes the catalytic process of copper-based materials as “initial property regulation-unified active species (CuO) action”, providing theoretical support for the directional design of high-performance copper-based catalysts.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Catalysis)
►▼
Show Figures
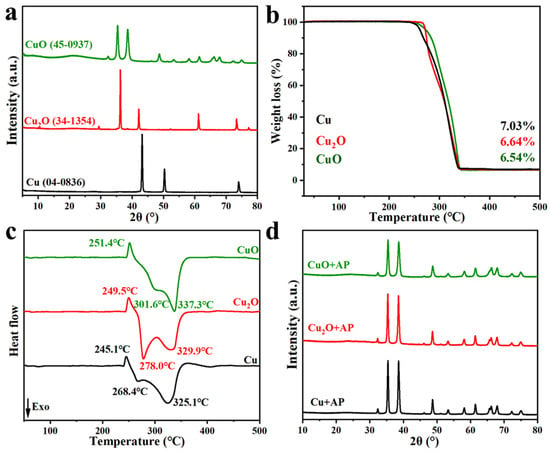
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Encryption Using Cholesteric Liquid Crystal Epoxy Film with Regionally Tailored Cross-Linking
by
Yingying Yi, Wenqian Yang, Yi Li, Wei Liu and Yonggang Yang
Chemistry 2026, 8(2), 24; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry8020024 - 13 Feb 2026
Abstract
Vividly colored cholesteric liquid crystal polymer network (CLCN) patterns based on epoxy resin are used in decorative and anti-counterfeiting applications. These films are typically prepared via cationic photopolymerization and post-polymerization to achieve a high cross-linking degree. In this work, the cross-linking degree is
[...] Read more.
Vividly colored cholesteric liquid crystal polymer network (CLCN) patterns based on epoxy resin are used in decorative and anti-counterfeiting applications. These films are typically prepared via cationic photopolymerization and post-polymerization to achieve a high cross-linking degree. In this work, the cross-linking degree is controlled by varying the UV irradiation dosage during photopolymerization. Following this, the reflection band of the CLCN film changes after removing non-cross-linked compounds with acetone. Leveraging the low cationic polymerization rate and the chain termination capability of methanol, a structurally colored CLCN film with regionally tailored cross-linking was fabricated. With the treatment of acetone, a colorful pattern was observed. Moreover, upon immersion in methanol, the film swelled, revealing a colorful pattern. After the evaporation of methanol, the pattern disappeared. Consequently, this CLCN film holds significant potential for information encryption applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Materials with Liquid–Crystalline Properties—Structure, Stimuli Responsiveness and Functionality)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Azomethines with Long Alkyl Chains: Synthesis, Characterization, Biological Properties and Computational Lipophilicity Assessment
by
Nikita Yu. Serov, Khasan R. Khayarov, Irina V. Galkina, Marina P. Shulaeva, Vyacheslav A. Grigorev and Timur R. Gimadiev
Chemistry 2026, 8(2), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry8020023 - 12 Feb 2026
Abstract
The search for new antibacterial agents is an important task due to the emergence of resistance to widely used drugs. Bromine-, chlorine-, and nitro-substituted phenyl ring azomethines with long alkyl chains (C12, C14, C16, and C18
[...] Read more.
The search for new antibacterial agents is an important task due to the emergence of resistance to widely used drugs. Bromine-, chlorine-, and nitro-substituted phenyl ring azomethines with long alkyl chains (C12, C14, C16, and C18) were synthesized and characterized using several experimental methods (NMR and IR spectroscopy, elemental analysis, mass spectrometry). Antibacterial and antifungal activity was tested on several cultures; the synthesized compounds show activity at the level of some commercial antiseptics. Lipophilicity (an important descriptor for predicting biological properties) of the experimentally synthesized and isomeric molecules was determined by three different approaches: quantum chemistry, machine learning (GraphormerLogP model), and an atom contribution model (RDKit library). The quantum-chemical method can account for any spatial arrangements and can be considered the most accurate of the approaches used, but it requires significant computational time. The atom contribution model is the fastest of the methods used, but it gives underestimated results, and different isomers have exactly the same values, in contrast to the quantum chemistry results. Machine learning-based methods (GraphormerLogP) demonstrate acceptable accuracy, sensitivity to isomerism, and orders-of-magnitude higher throughput, making them an optimal tool for high-throughput screening.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Theoretical and Computational Chemistry)
►▼
Show Figures
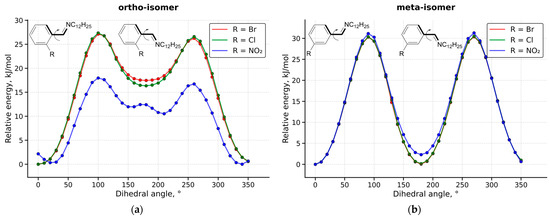
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Unsaturation and Chain Length of Methyl Esters on the Corrosion Behavior of Aluminum
by
Oscar Enrique Catalan-Montiel, Ana Karen Galvez-Larios, Isai Rosales-Cadena, América María Ramirez-Arteaga, Roy Lopez-Cecenes, Jesus Porcayo-Calderon and José Gonzalo Gonzalez-Rodriguez
Chemistry 2026, 8(2), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry8020022 - 12 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
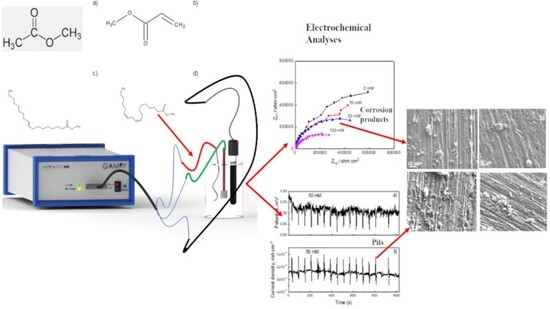
In this study, the corrosion behavior of pure aluminum in methyl esters with different degrees of unsaturation and chain lengths, as found in biodiesel, was investigated using electrochemical techniques. The methyl esters evaluated included methyl acrylate (C4H6O2)
[...] Read more.
In this study, the corrosion behavior of pure aluminum in methyl esters with different degrees of unsaturation and chain lengths, as found in biodiesel, was investigated using electrochemical techniques. The methyl esters evaluated included methyl acrylate (C4H6O2) and methyl linoleate (C19H34O2), which were added to methyl propionate (C4H8O2) and methyl oleate (C19H36O2), respectively. The electrochemical techniques employed were electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and electrochemical noise (EN), complemented by detailed scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analyses. The results indicated that both the corrosion rate and the susceptibility to localized corrosion, such as pitting, increased with higher degrees of unsaturation and longer alkyl chain lengths. The corrosion process remained under charge transfer control and was not directly influenced by these factors. However, the charge transfer resistance decreased with increasing unsaturation and chain length, consistent with the observed increase in corrosion rate.
Full article
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
An Optimal Synthetic Strategy for Conjugating Folic Acid with Manganese-Doped Silica Nanoparticles to Enhance Their Colloidal Stability
by
Anastasia P. Bebyakina, Zeai Huang, Olga D. Bochkova, Alexey S. Stepanov, Irek R. Nizameev, Kirill V. Kholin, Rustem R. Zairov, Ying Zhou and Asiya R. Mustafina
Chemistry 2026, 8(2), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry8020021 - 11 Feb 2026
Abstract
The inadequate biosafety of MRI contrast agents (CAs) remains a challenging issue. Both increasing the magnetic relaxivity of CAs and targeting them through conjugation with folates are promising approaches to addressing this issue. Silica nanoparticles (SNs) with Mn2+ ions specifically localized in
[...] Read more.
The inadequate biosafety of MRI contrast agents (CAs) remains a challenging issue. Both increasing the magnetic relaxivity of CAs and targeting them through conjugation with folates are promising approaches to addressing this issue. Silica nanoparticles (SNs) with Mn2+ ions specifically localized in the outer layer were selected as the target for further surface modification for the covalent attachment of folates. It was shown that when Mn-containing SNs are conjugated with folates via preliminary amino modification of the surface silanol groups, the folate-conjugated SNs suffer from colloidal instability. Thus, precoating Mn-containing SNs with unfolded BSA exposes surface amino groups that successfully conjugate with folates without loss of colloidal stability. Partial washout of surface-localized Mn2+ follows folate conjugation of Mn-containing SNs, although residual Mn2+ ions provide r1(2) relaxivities of 62.1 (160.4) mM−1s−1 at 0.47 T.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Organic and Organoelement Chemistry—A Themed Issue in Honor of Professor Oleg G. Sinyashin on the Occasion of His 70th Birthday)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceReview
Throwing Light on -O–O- Bond: Organic Peroxides in Visible-Light Photocatalysis
by
Diana V. Shuingalieva, Damir D. Karachev, Ksenia V. Skokova, Ivan M. Prosvetov, Dmitri I. Fomenkov, Vera A. Vil’ and Alexander O. Terent’ev
Chemistry 2026, 8(2), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry8020020 - 9 Feb 2026
Abstract
Visible-light photocatalysis enables the integration of classical electrophile/nucleophile chemistry with radical species (free radicals, radical cations, and radical anions) and metallocomplexes, significantly expanding the scope of organic transformations. Substrates capable of generating radicals via single-electron transfer (SET) are therefore of high value in
[...] Read more.
Visible-light photocatalysis enables the integration of classical electrophile/nucleophile chemistry with radical species (free radicals, radical cations, and radical anions) and metallocomplexes, significantly expanding the scope of organic transformations. Substrates capable of generating radicals via single-electron transfer (SET) are therefore of high value in this field. Among conventional radical precursors, organic peroxides occupy a distinctive position due to their unique reactivity. They can generate both oxygen-centered and carbon-centered radicals through either oxidative or reductive SET pathways. Furthermore, organic peroxides can act as radical precursors, nucleophiles, and oxidants. The review emphasizes the advancements of visible-light-mediated reactions utilizing the broad potential of organic peroxides for constructing various chemical bonds.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Featured Reviews, Perspectives, and Commentaries in Contemporary Chemistry)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Exploring Gardenia jasminoides Seed-Derived Natural Dyes for the Development of Functional Textiles
by
Amit Sarker, Mohammad Eanamul Haque Nizam, Mainul Morshed, Manoj Kanti Datta, Huiyu Jiang, Fiaz Hussain, Imran Ahmad Khan, Asfandyar Khan and Kashif Javed
Chemistry 2026, 8(2), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry8020019 - 6 Feb 2026
Abstract
Natural plant-based resources are rich in bioactive compounds that offer promising alternatives for developing sustainable, functional textiles. This study focuses on the extraction and application of natural dyes from Gardenia jasminoides as an eco-friendly substitute for conventional synthetic dyes. The dye was extracted
[...] Read more.
Natural plant-based resources are rich in bioactive compounds that offer promising alternatives for developing sustainable, functional textiles. This study focuses on the extraction and application of natural dyes from Gardenia jasminoides as an eco-friendly substitute for conventional synthetic dyes. The dye was extracted using methanol–water (50:50) and ethanol–water (50:50) solvent systems, alongside conventional aqueous extraction, followed by characterization through column chromatography. The characterization of the extracted powders confirmed the presence of gardenia yellow pigments with strong coloration potential. Among the tested extraction methods, ultrasonic-assisted methanol–water extraction (M.W.U.) exhibited the highest dye yield of 29.5%, followed by ethanol–water ultra-sound extraction (E.W.U.) at 24.9%, water ultrasound extraction (W.U.) at 18.35%, and the lowest yield obtained from the water-heater method (W.H.) at 18.25%. The dyed cotton fabrics were tested for color strength (K/S), CIELAB, colorfastness (washing, light, rubbing), and functional properties (antibacterial and vector protection) according to standard operating procedures. The results revealed that an optimal mordant concentration produced the maximum color strength (K/S = 1.7730), with good rubbing (4–5), washing (4–5), and light fastness (5). The dyed fabrics also exhibited excellent antibacterial activity against both Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli, as evaluated by the AATCC 100 test method. For instance, the vector protection property of the cotton dyed fabrics was also excellent, as confirmed by the cage test. Overall, the use of Gardenia jasminoides seed-based natural dye demonstrates not only desirable coloration and functional performance but also significant ecological advantages, reducing chemical pollution and supporting the transition toward environmentally sustainable textile processing.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Green and Sustainable Chemical Processes)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Study on the Catalytic Performance of Porous Cu/Cu2O Synthesized by One-Step Solvothermal Method for Thermal Decomposition of Ammonium Perchlorate
by
Bo Yang, Xiang Yang, Minghong Long, Yanzhi Yang and Xuechun Xiao
Chemistry 2026, 8(2), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry8020018 - 6 Feb 2026
Abstract
Porous Cu/Cu2O catalytic materials with a unique pore structure were successfully synthesized via a one-step solvothermal method using Cu-MOF-74 as the intermediate, followed by induced collapse and oxidation. The structural properties and catalytic performance of the as-prepared Cu/Cu2O materials
[...] Read more.
Porous Cu/Cu2O catalytic materials with a unique pore structure were successfully synthesized via a one-step solvothermal method using Cu-MOF-74 as the intermediate, followed by induced collapse and oxidation. The structural properties and catalytic performance of the as-prepared Cu/Cu2O materials in the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate (AP) were systematically investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area analysis, and thermogravimetry–differential scanning calorimetry (TG-DSC) combined with in situ thermogravimetry–mass spectrometry (TG-MS). The results show that the specific surface area of the Cu/Cu2O material is 46.6697 m2/g, and the average pore diameter is 9.4608 nm. Owing to the synergistic effect of Cu0/Cu+ dual sites on promoting electron transfer during AP thermal decomposition, the Cu/Cu2O catalyst exhibits excellent catalytic activity. Specifically, at a heating rate of 20 °C/min, the addition of 2 wt% Cu/Cu2O reduces the high-temperature decomposition temperature of AP from 473.1 °C to 321.1 °C (a decrease of 151.0 °C), lowers the thermal decomposition activation energy from 296.63 kJ/mol to 253.21 kJ/mol (a reduction of 43.42 kJ/mol), and increases the heat release by 617.8 J/g compared to pure AP. TG-MS analysis revealed that Cu/Cu2O accelerates the decomposition of AP by adsorbing and activating NH3 and HClO4 generated in the low-temperature decomposition stage, facilitating the formation of reactive intermediates such as ClOₓ and promoting the oxidation of nitrogen-containing species. This study demonstrates that the porous Cu/Cu2O material synthesized by the one-step solvothermal method is a promising catalyst for enhancing the thermal decomposition performance of AP in solid propellants.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Catalysis)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Synthesis, In Vitro Cytotoxicity Evaluation and GSK-3β Binding Study of Some Indole–Triazole-Linked Pyrazolone Derivatives
by
Ashok Madarakhandi, Sujeet Kumar, Nishith Teraiya, Gokulakrishnan Sakthivel, Basavaraj Metikurki, Veda B. Hacholli, Dominique Schols, Febina Ravindran, Bibha Choudhary and Subhas S. Karki
Chemistry 2026, 8(2), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry8020017 - 31 Jan 2026
Abstract
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK-3β) is a multifunctional serine/threonine kinase mediating multiple cellular functions, such as differentiation, apoptosis, and cell proliferation. Because of their ability to alter carcinogenic pathways, GSK-3β inhibitors are being explored for the development of anticancer molecules.
[...] Read more.
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK-3β) is a multifunctional serine/threonine kinase mediating multiple cellular functions, such as differentiation, apoptosis, and cell proliferation. Because of their ability to alter carcinogenic pathways, GSK-3β inhibitors are being explored for the development of anticancer molecules. In the present study, we synthesized and evaluated the cytotoxic properties of a series of twenty indole–triazole-linked pyrazolone derivatives, 10Aa–Ed. All derivatives were characterized by FTIR, 1H/13C NMR, and high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) methods. All compounds and standards, sunitinib and 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU), were screened against four adherent cell lines, including pancreatic adenocarcinoma (Capan-1), colorectal carcinoma (HCT-116), glioblastoma(LN229), and lung carcinoma (NCI-4460), and four non-adherent cell lines, including acute myeloid leukemia (HL-60), chronic myeloid leukemia (K562), T lymphoblast (MOLT4), and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (Z138). Among the screened derivatives, molecule 10Aa showed cytotoxicity against MOLT 4, Z138, and HL60 with CC50 values of 14.45 μM, 15.34 μM, and 17.56 μM, respectively. GSK-3β kinase inhibition was evaluated with the 10Aa, which is capable of inhibiting GSK-3β in a dose-dependent manner. Additionally, molecular docking was performed to estimate the correlation between invitro data and GSK-3β binding affinity. The outcomes of the invitro experiments demonstrated strong concordance with the insilico data. The discovery yielded compounds 10Aa and 10Cd, which can be modified to create effective anticancer agents that target GSK-3β.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Medicinal Chemistry)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Preparation of Dithiocarbamate and Carboxyl Co-Modified Chitosan and Its Adsorption of Heavy Metal Copper from Copper–Ammonia Wastewater
by
Chaoyang He, Tingting Jiang, Langbo Yi and Wenyong Hu
Chemistry 2026, 8(2), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry8020016 - 30 Jan 2026
Abstract
To address the challenge of removing copper from copper–ammonia complex wastewater in the printed circuit board (PCB) industry, this study employed natural chitosan (CTS) as the base material. Dithiocarbamate (DTC) groups were grafted onto CTS, followed by further carboxylation (-COOH) to produce two
[...] Read more.
To address the challenge of removing copper from copper–ammonia complex wastewater in the printed circuit board (PCB) industry, this study employed natural chitosan (CTS) as the base material. Dithiocarbamate (DTC) groups were grafted onto CTS, followed by further carboxylation (-COOH) to produce two novel adsorbents: DTC-CTS and DTC-CTS-COOH. The materials were characterized using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), SEM, and related techniques. The effects of solution pH, adsorption isotherms, kinetics, and regeneration performance were systematically investigated. Characterization results confirmed the successful introduction of DTC and carboxyl (-COOH) groups. Adsorption experiments demonstrated that DTC-CTS-COOH exhibited superior Cu2+ adsorption performance across pH 5–8, achieving a removal efficiency of (97.67 ± 1.3)% at pH 7. Its adsorption behavior followed the Langmuir model, with a maximum adsorption capacity (Qm) of 234.8 mg·g−1 at 318.15 K, significantly higher than that of DTC-CTS (183.6 mg·g−1). Adsorption kinetics conformed to a pseudo-second-order model, indicating rapid adsorption rates. After five adsorption-desorption cycles, DTC-CTS-COOH maintained a Cu2+ removal rate above 68.41%. The synergistic interaction between -COOH and DTC functional groups enhanced the adsorbent’s capacity, rate, and pH adaptability, demonstrating that DTC-CTS-COOH holds strong potential for application in the treatment of complex copper–ammonia wastewater.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Green and Environmental Chemistry)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Novel 1,4-Naphthoquinone-Zidovudine Hybrid: Design, Synthesis, and In Vitro Evaluation of Its Anti-Trypanosomatid and Cytotoxic Activities
by
Thiago de Souza Dias Silva, Afonso Santine M. M. Velez, Tiago Ribeiro Rodriguez, João Vitor da Costa Silva, Henrique Previtalli-Silva, Flávia de Oliveira Cardoso, Célio Geraldo Freire-de-Lima, Otávio Augusto Chaves, Debora Decote-Ricardo and Marco Edilson Freire de Lima
Chemistry 2026, 8(2), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry8020015 - 29 Jan 2026
Abstract
This work reports the synthesis and characterization of a new molecular hybrid 4, created by combining 1,4-naphthoquinone with the drug zidovudine (AZT) through an azide-alkyne cycloaddition reaction catalyzed by Cu1+. In vitro studies assessed the anti-trypanosomatid activity of hybrid 4
[...] Read more.
This work reports the synthesis and characterization of a new molecular hybrid 4, created by combining 1,4-naphthoquinone with the drug zidovudine (AZT) through an azide-alkyne cycloaddition reaction catalyzed by Cu1+. In vitro studies assessed the anti-trypanosomatid activity of hybrid 4, along with its precursors and synthetic intermediates (1, 2, and 3), against Trypanosoma cruzi (T. cruzi Tulahuen C2C4 LacZ), Trypanosoma brucei (T. b. brucei 427), and Leishmania infantum, as well as cytotoxicity in RAW 264.7 macrophages and LLC-MK2 cells. The biological results confirm the molecular design, showing that the new hybrid is effective against both epimastigotes and amastigotes of T. cruzi (IC50 = 22.26 ± 5.78 μM and 143.10 ± 5.79 μM, respectively), with approximately 4.5-fold better capacity than AZT to inhibit the epimastigote form. Additionally, the hybrid was also active against bloodstream T. b. brucei (IC50 = 54.47 ± 6.70 μM), with approximately 2.2-fold better capacity than AZT to inhibit this parasite. It also shows low toxicity in RAW 264.7 macrophages (CC50 > 200 μM) and LLC-MK2 cells (CC50 > 200 μM). For example, hybrid 4 exhibited approximately a 6.6-fold higher SI than 1,4-naphthoquinone 1 against T. cruzi amastigotes. In this context, the work contributes to the broader knowledge base guiding the design of hybrid molecules for antiparasitic chemotherapy. It provides a rational foundation for preparing subsequent, more potent analogues.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Rational Drug Design: From Target Identification to Drug Lead Compounds)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Thermo-Catalytic Carbon Dioxide Hydrogenation to Ethanol
by
Xianyu Meng, Ying Wang, Jie Li, Hongxing Wang, Chenglong Yu, Jia Guo, Zhuo Zhang, Qingli Qian and Buxing Han
Chemistry 2026, 8(2), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry8020014 - 28 Jan 2026
Abstract
The catalytic hydrogenation of carbon dioxide (CO2) represents a transformative approach for reducing greenhouse gas emissions while producing sustainable fuels and chemicals, with ethanol being particularly promising due to its compatibility with existing energy infrastructure. Despite significant progress in converting CO
[...] Read more.
The catalytic hydrogenation of carbon dioxide (CO2) represents a transformative approach for reducing greenhouse gas emissions while producing sustainable fuels and chemicals, with ethanol being particularly promising due to its compatibility with existing energy infrastructure. Despite significant progress in converting CO2 to C1 products (e.g., methane, methanol), selective synthesis of C2+ compounds like ethanol remains challenging because of competing reaction pathways and byproduct formation. Recent advances in thermo-catalytic CO2 hydrogenation have explored diverse catalyst systems including noble metals (Rh, Pd, Au, Ir, Pt) and non-noble metals (Co, Cu, Fe), supported on zeolites, metal oxides, perovskites, silica, metal–organic frameworks, and carbon-based materials. These studies reveal that catalytic performance hinges on the synergistic effects of multimetallic sites, tailored support properties and controlled reaction micro-environments to optimize CO2 activation, controlled hydrogenation and C−C coupling. Mechanistic insights highlight the critical balance between CO2 reduction steps and selective C−C bond formation, supported by thermodynamic analysis, advanced characterization techniques and theoretical calculations. However, challenges persist, such as low ethanol yields and undesired byproducts, necessitating innovative catalyst designs and optimized reactor configurations. Future efforts must integrate computational modeling, in situ/operando studies, and renewable hydrogen sources to advance scalable and economically viable processes. This review consolidates key findings, proposes potential reaction mechanisms, and outlines strategies for designing high-efficiency catalysts, ultimately providing reference for industrial application of CO2-to-ethanol technologies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Featured Reviews, Perspectives, and Commentaries in Contemporary Chemistry)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Chemistry, Gels, Nanomaterials, Polymers, Environments, Materials
Functionalized Materials for Environmental Applications
Topic Editors: Luca Burratti, Iole Venditti, Paolo ProspositoDeadline: 30 March 2026
Topic in
Biomolecules, Chemistry, IJMS, Molecules, Pharmaceuticals
Progress in Drug Design: Science and Practice
Topic Editors: Rui M. V. Abreu, Maria João QueirozDeadline: 30 April 2026
Topic in
Catalysts, ChemEngineering, Chemistry, Processes, Reactions, Sustainability
Green and Sustainable Catalytic Process
Topic Editors: Dmitry Yu. Murzin, Nataliya D. ShcherbanDeadline: 20 May 2026
Topic in
Chemistry, Molecules, IJMS, Biomolecules, Inorganics
Metal Ions in Health and Diseases: Current Progress and Future Challenges
Topic Editors: Massimiliano F. Peana, Carlo Santini, Maura PelleiDeadline: 31 May 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Chemistry
Fluorescent Chemosensors and Probes for Detection and Imaging
Guest Editor: Haishi CaoDeadline: 31 March 2026
Special Issue in
Chemistry
Design and Synthesis of Next-Generation Catalysts for Efficient Green Chemical Reactions
Guest Editor: Ming XuDeadline: 31 March 2026
Special Issue in
Chemistry
Oxygen-Containing Heterocyclic Compounds: Recent Advances in Chemistry
Guest Editors: Fernanda Proença, Elina Margarida Ribeiro MarinhoDeadline: 15 April 2026
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Chemistry
Featured Reviews, Perspectives, and Commentaries in Contemporary Chemistry
Collection Editor: Igor Alabugin









