- Review
Unraveling the Potential of Photochemical Nanoplatforms in Tumor Microenvironments: Therapeutic Strategies for Gastrointestinal Malignancies
- Dongqi Li,
- Yingshu Cui and
- Xiaosong Li
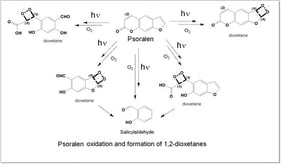
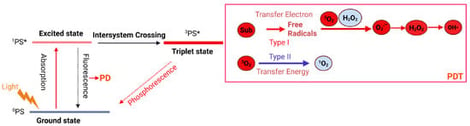
Gastrointestinal (GI) malignancies have caused tremendous disease burden around the world; however, conventional therapy strategies, such as radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy, have achieved limited efficacy in the diagnosis and treatment. In further exploration of GI tumors, the complexity and heterogeneity of the tumor microenvironment (TME) have been increasingly recognized. Appropriate strategies to modulate the TME are necessary to enhance the therapeutic effect. Photosensitizers (PSs) are chemical substances that are activated at specific wavelengths of light to initiate photodynamic effects. Nanotechnology provides a platform for the targeted delivery of PSs and small-molecule drugs, enabling precise targeting and remodeling of the TME. In this review, we summarize the principles and mechanisms of photochemical reactions and elaborate on the effect of photochemical nanoplatforms in modulating the TME of GI tumors. Finally, we discuss the potential value of photochemical nanoplatforms for diagnosing GI malignancies.
4 March 2026



![Basis of cw pump–probe TR RR experiments on BR. (A) Simplified scheme of the photocycle of BR. Spectral and kinetic data were taken from the literature [2,3]. The individual states are indicated by the commonly used notation, with the numbers referring to the absorption maxima. The photochemical and thermal reactions are characterized by the red and black arrows/symbols, respectively. The approximate lifetimes of the individual reaction steps are indicated. (B) Principle of pump–probe TR RR spectroscopy using a flowing sample with the velocity v and the pump (red) and Raman probe beam (green) separated by the distance Δs. The beam diameter, defined by the intensity drop to
1
/
e
2
of the maximum laser power, must be larger for the pump (dP) than for the Raman probe beam (dR).](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/photochem/photochem-06-00009/article_deploy/html/images/photochem-06-00009-ag-550.jpg)