- Case Report
Pulse Waveform Changes During Vasopressor Therapy Assessed Using Remote Photoplethysmography: A Case Series
- Mara Klibus,
- Viktorija Serova and
- Olegs Sabelnikovs
- + 3 authors
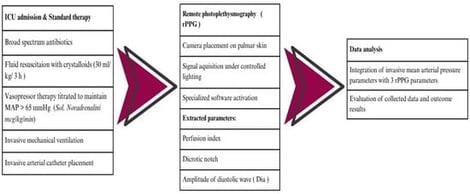
Background/Objectives: Septic shock involves severe circulatory and microcirculatory dysfunction and often requires vasopressors to maintain adequate mean arterial pressure (MAP). Conventional monitoring mainly reflects macrocirculation and may not capture changes in vascular tone or microcirculation. Remote photoplethysmography (rPPG) is a contactless optical method that analyzes peripheral pulse waveforms and may offer additional physiological insight during vasopressor therapy. The aim of this study was to assess the feasibility of rPPG for detecting pulse waveform changes associated with norepinephrine administration in septic shock. Methods: Prospective case series included three adult patients (n = 3) with septic shock admitted to the intensive care unit at Pauls Stradins Clinical University Hospital, Riga, Latvia. All patients received standard sepsis treatment, including fluid resuscitation and titrated norepinephrine to maintain MAP ≥ 65 mmHg. Continuous invasive arterial pressure monitoring was performed alongside rPPG signal acquisition from the palmar skin surface under controlled lighting. From averaged rPPG waveforms, perfusion index (PI), dicrotic notch amplitude (c-wave), and diastolic wave amplitude (d-wave) were extracted. Correlations between norepinephrine dose, MAP, and rPPG parameters were explored. Results: Increasing norepinephrine doses were associated with higher MAP and PI in all patients. Dicrotic notch and diastolic wave amplitude decreased consistently. These changes occurred alongside macrocirculatory stabilization and are consistent with increased vascular tone and altered arterial compliance. Conclusions: rPPG demonstrated feasibility for detecting pulse waveform changes during norepinephrine therapy in septic shock; however, larger controlled studies are required for validation.
30 January 2026