- Article
Analysis of Publications Related to Nursing Care in Patients Who Experience Organ and Tissue Transplantation Using the Bibliometric Method
- Hatice Gülsoy and
- Hatice Öntürk Akyüz
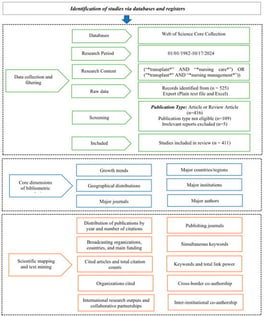
Background: This study was conducted to guide researchers by providing a global macroscopic perspective on the main characteristics of publications on nursing care in patients undergoing organ and tissue transplantation. Methods: The data obtained from the Web of Science (WoS) database in light of the determined keywords were analyzed using quantitative and qualitative criteria. The bibliometric analyses and visualizations were conducted using Microsoft Excel 365, VOSviewer (version 1.6.20), and the Biblioshiny interface within the R environment. Results: A total of 525 records were initially identified from the Web of Science database. After excluding meeting abstracts, editorials, and letters to ensure data quality, 411 publications (articles and reviews) were included in the final bibliometric analysis. The majority of these publications (87.6%) were published after 2005. The top five countries with the highest number of publications are the United States (USA), Brazil, China, Turkey, and Australia. Conclusions: This study is the first bibliometric analysis study to examine the trend of scientific publications indexed in Web of Science for nursing care in patients with organ and tissue transplantation processes. The findings have the potential to be used to improve the work of scientists conducting research in the field of nursing care.
24 February 2026