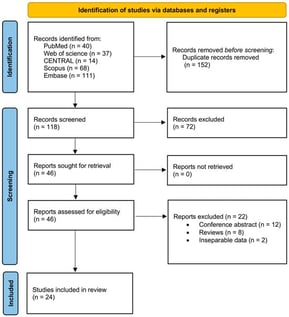
- Systematic Review
Intraocular Inflammation Following Intravitreal Faricimab: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Jumanah Qedair,
- Asmaa A. Youssif and
- Hashem Abu Serhan
- + 1 author
Background/Objectives: To evaluate the incidence, characteristics, and clinical outcomes of intraocular inflammation (IOI) associated with intravitreal faricimab (IVF) in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD) and diabetic macular edema (DME). Methods: Following PRISMA guidelines, a comprehensive search of PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, Embase, and CENTRAL databases was performed from their inception to February 2025. Using the random-effects model, weighted proportions, standardized mean differences, and weighted log odds ratios (OR) were pooled and calculated. A two-tailed p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant. The χ2 (z) test and the Higgins I2 test were used to assess studies heterogeneity. Results: We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of 24 studies (4761 patients; 5652 eyes). The most common diagnoses were nAMD (n = 4782, 94.6%) and DME (n = 845, 37.1%). The pooled proportion for IOI incidence in eyes receiving IVF was 3.0% (95% CI: 1.0–6.0). The odds of developing IOI did not differ significantly between the DME and nAMD groups (OR: 1.13, p = 0.78). Unspecified IOI was the most common sign (n = 210, 2.9% [95% CI: 1.2–7.3]), followed by anterior uveitis (n = 80, 1.9% [95% CI: 0.1–34.8]), vitritis (n = 63, 2.9% [95% CI: 0.2–32.1]), retinal hemorrhage (n = 27, 0.7% [95% CI: 0.0–15.3]), and endophthalmitis (n = 8, 0.5% [95% CI: 0.3–1.1]). Conclusions: While IVF demonstrates therapeutic efficacy, our findings highlight a clinically relevant risk of IOI. We, therefore, recommend vigilant clinical monitoring in patients receiving this therapy.
26 January 2026