- Communication
Short Report: Treadmill Walking Differs from Overground Walking in Multiple Sclerosis
- Herbert Karpatkin,
- Jaya Rachwani and
- Lourdes Rodriguez
- + 4 authors
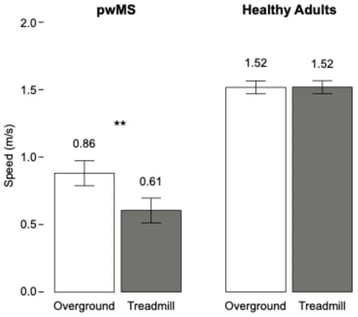
Background/Objectives: Gait impairment is a common finding in multiple sclerosis (MS). Clinicians have used both treadmill and overground walking for its evaluation and treatment. However, there is little evidence that these two types of walking are equivalent. Methods: An incidental finding from another study revealed differences between treadmill and overground walking speed in 24 persons with MS. We compared this to walking speed in healthy controls walking in the same two conditions. Results: Walking speed was significantly reduced on the treadmill relative to overground walking in persons with MS, while there was no difference between the two conditions for controls. Conclusions: Clinicians should consider that treadmill walking may not generalize to overground walking in this population.
16 January 2026