- Review
Alloimmunization in Pregnancy: A Practical Guide for Transfusion Medicine
- Palma Manduzio,
- Luigi Ciccone and
- Tommaso Granato
- + 5 authors
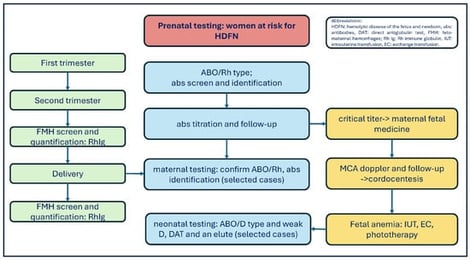
Background: Feto-maternal hemorrhages (FMHs) due to placenta disruption and bleeding from fetal maternal circulation can lead to life-threatening fetal anemia. These hemorrhages are more often of small volume and remain unreported. Sensitization to fetal red blood cell (RBC) antigens can occur during pregnancy, at delivery, or after invasive procedures. The sensitized mother produces IgG antibodies (abs) that cross the placenta and cause the hemolysis of fetal RBCs, release of hemoglobin, and increased levels of unconjugated bilirubin in the fetus or neonate. The result is hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (HDFN). Methods: In this study, we aim to provide a structured overview of RBC alloimmunization in pregnancy. A literature search was conducted using PubMed. English articles published from January 2010 to October 2025 were selected by the authors. The contributing manuscripts focused on managing RBC alloimmunization in pregnancy, FMH screening and quantification, antenatal and postnatal testing, Rh immune globulin (Rh Ig or Anti-D) prophylaxis, and national registry data. Results: Frequencies of RBC abs vary among American, Caucasian, and Asian populations because of genetic diversity, different antibody detection and antibody identification methods, and FMH tests. More specifically, the erythrocyte rosette is a simple screening test for FMH. A positive rosette must be quantified by the Kleihauer–Betke (KB) or flow cytometry (FC). The KB results may be overestimated or underestimated. The advantages of FC include high accuracy, specificity, and repeatability. Ultimately, anti-D prophylaxis protocol varies from country to country. Conclusion: Maternal alloimmunization is an uncommon and highly variable event. Although introducing anti-D prophylaxis has decreased the Rh immunization rate, it is still an unmet medical need. In brief, mitigation strategies for RBC alloimmunization risk include accurate maternal and neonatal testing at different time points, adequate Rh immune globulin prophylaxis in D-negative pregnant women, preventing sensitizing events, adopting a conservative transfusion policy, and upfront ABO and Rh (C/c, E/e) and Kell matching in females under 50 years of age.
13 January 2026