- Systematic Review
Systematic Review of Health Literacy and Health Behavior in Adolescents Research
- Saulius Sukys,
- Gerda Kuzmarskiene and
- Kristina Motiejunaite
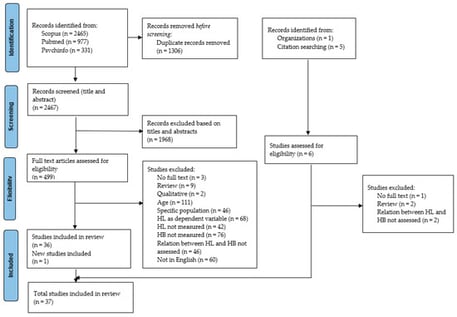
Background/Objectives: Despite the publication of several systematic reviews on adolescent health literacy, comprehensive evaluations of the relationship between health literacy and health-related behaviors are still limited. This systematic review sought to synthesize and critically appraise the available evidence on associations between health literacy and health behaviors among adolescents. Methods. A systematic search of three databases (Scopus, PubMed, and PsycINFO) was conducted in accordance with PRISMA guidelines. Thirty-seven eligible cross-sectional studies were selected for qualitative synthesis. Methodological quality was evaluated using the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale adapted for cross-sectional studies. Results: The 37 included studies encompassed 71,558 adolescents (mean age range 11.0–17.0 years) and were conducted primarily in Europe (n = 22), with additional studies from the USA (n = 5), Asia (n = 8), and cross-cultural settings (n = 2). Across studies, 11 HL instruments were used (including two eHealth literacy measures), most commonly the Health Literacy for School-aged Children scale (n = 14). Physical activity (n = 22), nutrition-related indicators (n = 26), and smoking/alcohol/drug outcomes (n = 16) were assessed using heterogeneous operationalisations. Overall, higher HL was more often associated with healthier behavioral profiles, with more consistent patterns for nutrition-related outcomes. Findings for physical activity and substance use were more heterogeneous and, in some cases, varied depending on the HL measurement approach (subjective vs. objective) and the behavioral reference period. Conclusions: Current evidence indicates that higher health literacy in adolescents is generally associated with more favorable health behaviors, particularly regarding nutrition-related indicators. However, study heterogeneity and the predominance of cross-sectional designs limit comparability and causal inference. Future research should prioritize standardized measurement tools and longitudinal designs to clarify directionality and underlying mechanisms.
18 February 2026