- Article
Prostate Cancer Health Information on Google Using the Quality Evaluation Scoring Tool (Quest): A Cross-Sectional, Multilingual Analysis
- Nikola Jeker,
- Matthias Walter and
- Christian Wetterauer
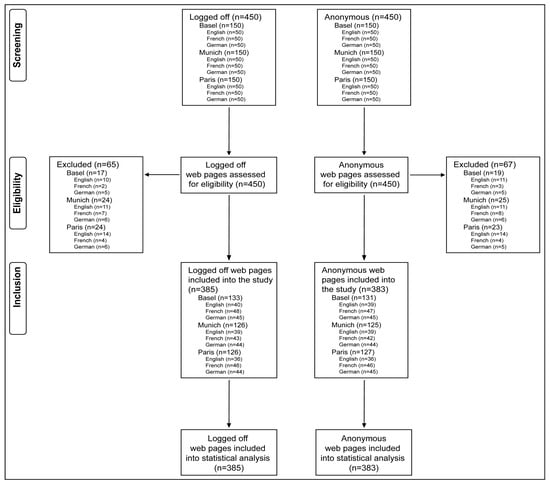
Background/Objectives: The internet is a major source of health information, including prostate cancer, but the quality of such content is inconsistent and may influence patient decision-making. This study aimed to evaluate the quality of online prostate cancer information by language, location, and user mode (“Logged off” vs. “Anonymous”) using the Google search engine. Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional, observational study between 5 and 11 December 2022, evaluating Google search results for prostate cancer information across three European cities (Basel, Munich, and Paris) and three languages (English, German, and French) in both “Logged off” and “Anonymous” user modes. A total of 900 websites (450 per mode) were retrieved and classified as: (1) university, (2) hospital, (3) governmental/medical societies, (4) industrial/commercial/NGOs, or (5) other. Website quality was assessed using the validated QUEST, which evaluates authorship, attribution, conflicts of interest, currency, and evidence. Inclusion rates and QUEST scores were compared across languages, locations, and categories using Kruskal-Wallis tests with multiple comparison adjustments. A total of 900 websites (450 per mode) were retrieved in English, German, and French from searches conducted in Basel, Munich, and Paris. Websites were classified as: (1) university, (2) hospital, (3) governmental/medical societies, (4) industrial/commercial/NGOs, or (5) other. Quality was assessed using the QUEST, which evaluates authorship, attribution, conflicts of interest, currency, and evidence. Inclusion rates and QUEST scores were compared across languages, locations, and categories using Kruskal-Wallis tests with multiple comparison adjustments. Results: Inclusion rates were high for both modes (Logged off: 86%; Anonymous: 85%). Location-based differences were significant for Basel (p = 0.04) and Paris (p = 0.02), while language-based differences were not significant. In “Logged off” mode, Category 1 achieved the highest median QUEST score (18.3), followed by 3 (17.8), while Category 2 scored lowest (14.2). Differences were significant (χ2 = 50, p < 0.001), particularly between Categories 2 vs. 3 and 2 vs. 4 (p < 0.001). Similar patterns were observed in the “Anonymous” mode. Conclusions: Online prostate cancer information varies substantially in quality. French-language sites, despite high inclusion rates, were of lower quality, while English and German content more frequently met high-quality standards. University websites were the most reliable, hospital websites the least. Language, location, and site type influence the accessibility and reliability of online prostate cancer information.
19 December 2025