- Article
The Effect of Age and Symptom Duration on Patient-Reported Outcomes at 2- and 5-Year Follow-Up in Patients Undergoing Hip Arthroscopy for Femoroacetabular Impingement Syndrome
- Michael Moore,
- Samuel R. Montgomery and
- Thomas Youm
- + 4 authors
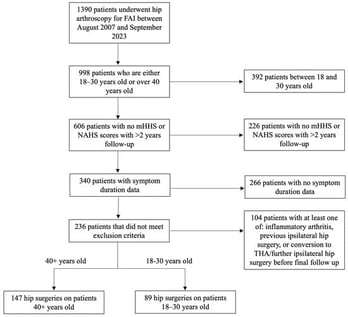
Background/Objectives: To determine whether patients under 30 years of age who have experienced symptoms for a duration of less than 1 year before undergoing hip arthroscopy (HA) for femoracetabular impingement (FAI) have better patient-reported outcomes than patients aged 40 years or older who have experienced symptoms for a duration of more than 1 year. Methods: This is a single-center, single-surgeon, retrospective analysis performed between August 2007 and May 2023 analyzing patients who underwent hip arthroscopy. Patients were divided into those who were 18 to 30 years old and patients that were 40 years and older. All patients who underwent primary hip arthroscopy for FAI and had completed mHHS or NAHS surveys prior to surgery with at least a 2-year follow-up were initially included in the study. Patients were excluded if they had no symptom duration information documented in their electronic medical record, a history of inflammatory arthritis, previous ipsilateral hip surgery, or future conversion to total hip arthroplasty (THA) before final follow-up. Results: A total of 236 hip arthroscopies were analyzed, including 147 patients ≥40 years and 89 patients 18–30 years, with symptom duration being significantly longer in the older cohort (28.4 vs. 17.5 months, p < 0.001). At 2 years, there was no difference in mHHS or NAHS between groups; however, younger patients with shorter symptom duration were more likely to achieve PASS for NAHS (87.5% vs. 58.7%, p = 0.036). At 5 years, the older cohort showed greater improvement in mHHS (33.1 vs. 22.9, p = 0.048), while patients 18–30 years continued to demonstrate higher absolute mHHS and NAHS at both 2 and 5 years. Regression analysis confirmed that increasing age was associated with lower PROs at follow-up. Conclusions: There was a significantly greater number of patients who achieved PASS for NAHS at 2-year follow-up for patients who were 18–30 years old with symptom duration ≤ 1 year compared to those aged 40+ years old with symptom duration ≥ 1 year. Additionally, patients ≥40 years old experienced a significantly longer symptom duration before surgery and had worse outcomes for mHHS and NAHS at 2- and 5-year follow-up compared to the 18–30 year cohort.
10 December 2025