- Study Protocol
Probabilistic Safe Zone Mapping for S1 Screw Placement Using 1000 Lumbosacral CT Scans: A Study Protocol for a Bilateral, Two-Rater, Multi-Offset Anatomical Modeling Study
- Nikolai Ramadanov,
- Robert Hable and
- Roland Becker
- + 2 authors
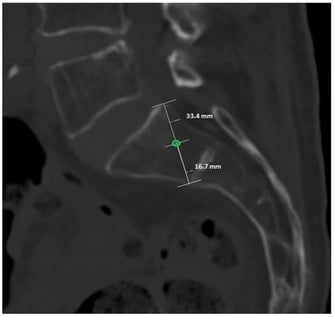
Background/Objectives: Safe placement of sacral vertebra 1 (S1) screws is essential in lumbosacral instrumentation and iliosacral fixation. Existing anatomical safe zones are largely based on averaged geometry and do not provide quantitative probability estimates for permissible deviations from an ideal entry point. This study aims to develop a probabilistic, computed tomography–based (CT-based) safe zone model for S1 screw placement. Methods: This retrospective imaging-based anatomical modeling study will analyze 1000 anonymized lumbosacral CT scans. A reproducible reference entry point will be defined on the lateral S1 projection, and bilateral offset-based virtual screw trajectories will be evaluated. Two independent raters will classify each trajectory as intraosseous or extraosseous. Probabilistic safety maps will be generated by aggregating binary classifications across offsets and directions. Interobserver reliability will be assessed using Cohen’s kappa, and anatomical influences will be analyzed using multivariable regression models. Results: The study is expected to generate continuous probabilistic safety maps illustrating the likelihood of intraosseous S1 screw placement across predefined offset distances and directions from the reference entry point. These maps are anticipated to demonstrate a gradual transition from high to low safety probabilities rather than a binary safe–unsafe boundary, and to identify anatomical factors influencing screw containment. Conclusions: This protocol describes a CT-based probabilistic modeling approach to S1 screw placement that aims to provide a more nuanced and quantitative definition of anatomical safe zones. If successful, the proposed method may improve preoperative planning and intraoperative decision-making by moving beyond averaged geometric constraints toward probability-informed screw placement.
7 February 2026