- Article
Therapeutic Potential of Exportin 1 and Aurora Kinase A Inhibition in Multiple Myeloma Cells
- Seiichi Okabe,
- Yuko Tanaka and
- Daigo Akahane
- + 4 authors
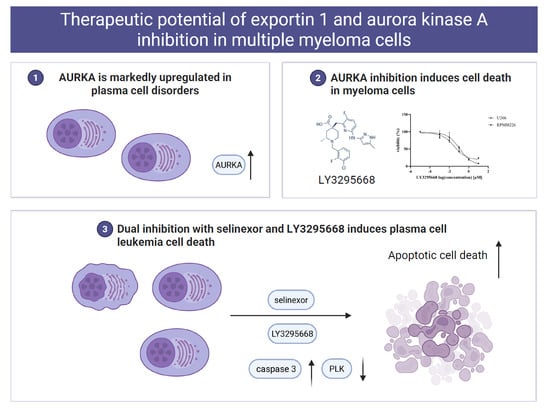
Background/Objectives: Aurora kinases (AURKs) are key regulators of mitosis, and their dysregulation contributes to plasma cell disorders, including multiple myeloma (MM) and plasma cell leukemia (PCL). Methods: The expression and prognostic relevance of AURK family members were examined, and the therapeutic potential of AURKA inhibition was evaluated. Results: Gene expression analysis demonstrated significant upregulation of AURKA in PCL. Treatment of MM cells with the selective AURKA inhibitor LY3295668 induced dose-dependent cytotoxicity, caspase-3/7 activation, and cellular senescence. Similarly, selinexor, a selective exportin-1 inhibitor, elicited dose-dependent cytotoxicity and apoptosis. Combined treatment with LY3295668 and selinexor significantly improved apoptosis compared with either agent alone, and AURKA knockdown further sensitized MM cells to selinexor, thereby increasing apoptosis. In bortezomib-resistant MM cells and primary PCL samples, the combination therapy induced cytotoxicity and caspase-3/7 activation. Conclusions: These findings underscore AURKA expression as a prognostic marker in plasma cell disorders and support the therapeutic potential of combining AURKA inhibition with selinexor for bortezomib-resistant MM and PCL. To explore biomarker-driven strategies for optimizing therapeutic outcomes, future studies are warranted.
9 January 2026