- Article
DECAF: Deconvoluted Extracted Ion Chromatogram-Based Quantification of Therapeutic Oligonucleotides
- Piotr Prostko,
- Youzhong Liu and
- Dirk Valkenborg
- + 3 authors
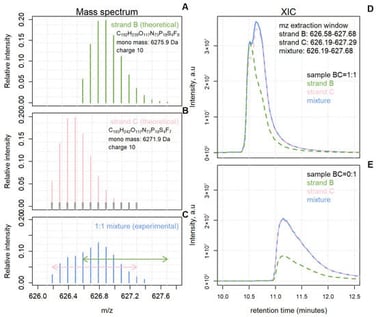
Accurate quantification in LC–MS experiments becomes challenging when analytes overlap both chromatographically and in mass spectra, as conventional extracted ion chromatogram-based methods can yield biased results by double-counting shared isotope signals. This limitation is particularly relevant for oligonucleotides, where degradation products and synthetic impurities frequently co-elute with the intended full-length product, complicating relative quantification. To address this, we developed DECAF, a straightforward and computationally efficient procedure for deconvoluting overlapping isotope patterns directly from MS1 data. The method models experimental isotope distributions as mixtures of theoretical templates across retention time, generating deconvoluted ion chromatograms whose peak areas accurately reflect the contributions of individual components. We demonstrate the utility of DECAF on two pharmaceutically relevant oligonucleotide mixture datasets, where it reliably estimated mixing proportions and enabled visualisation of component-specific elution profiles. Analysis of a typical sample required one to two minutes, underscoring the method’s practical efficiency. DECAF provides a transparent and accessible alternative to existing commercial software, with promising applications in pharmaceutical analysis and quality control.
6 February 2026