Artificially Engineered Synthetic Biomarkers Revolutionizing Early Diagnosis of Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
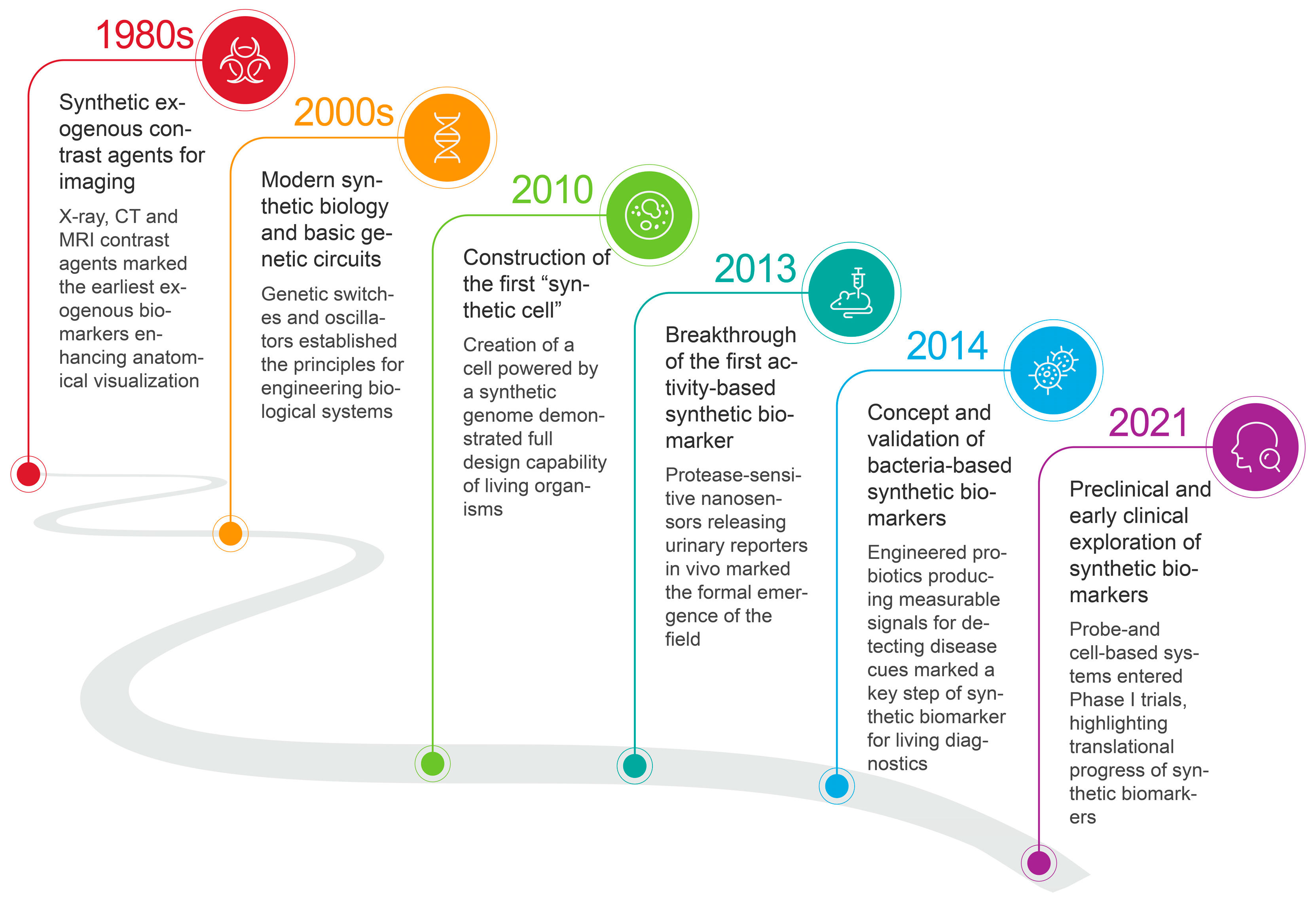
2. Advent of Synthetic Biomarkers
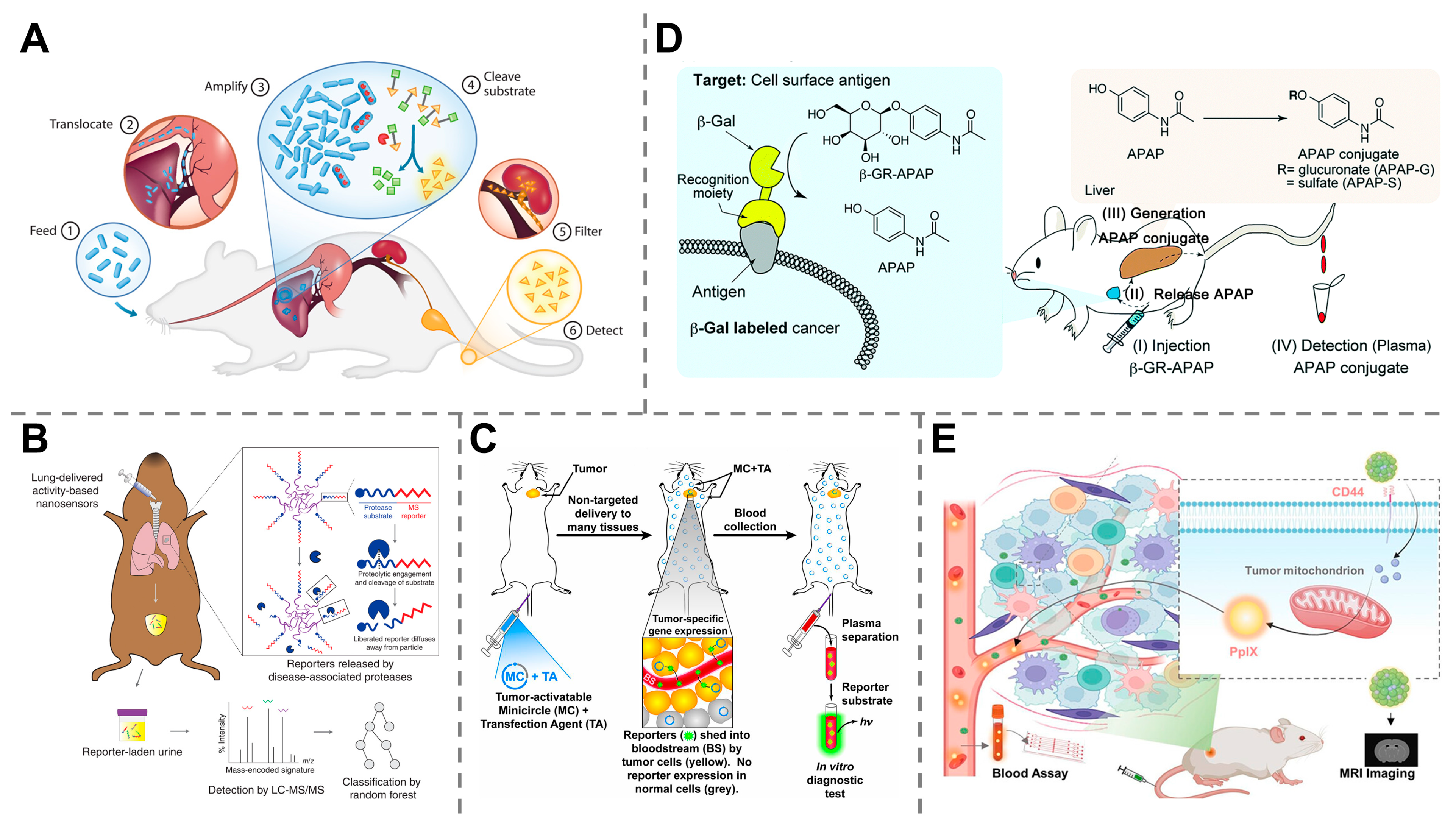
3. Mechanistic Categories of Synthetic Biomarkers
3.1. Engineered Nanoparticles
3.2. Activity-Based Probes
3.3. Genetically Encoded Probes
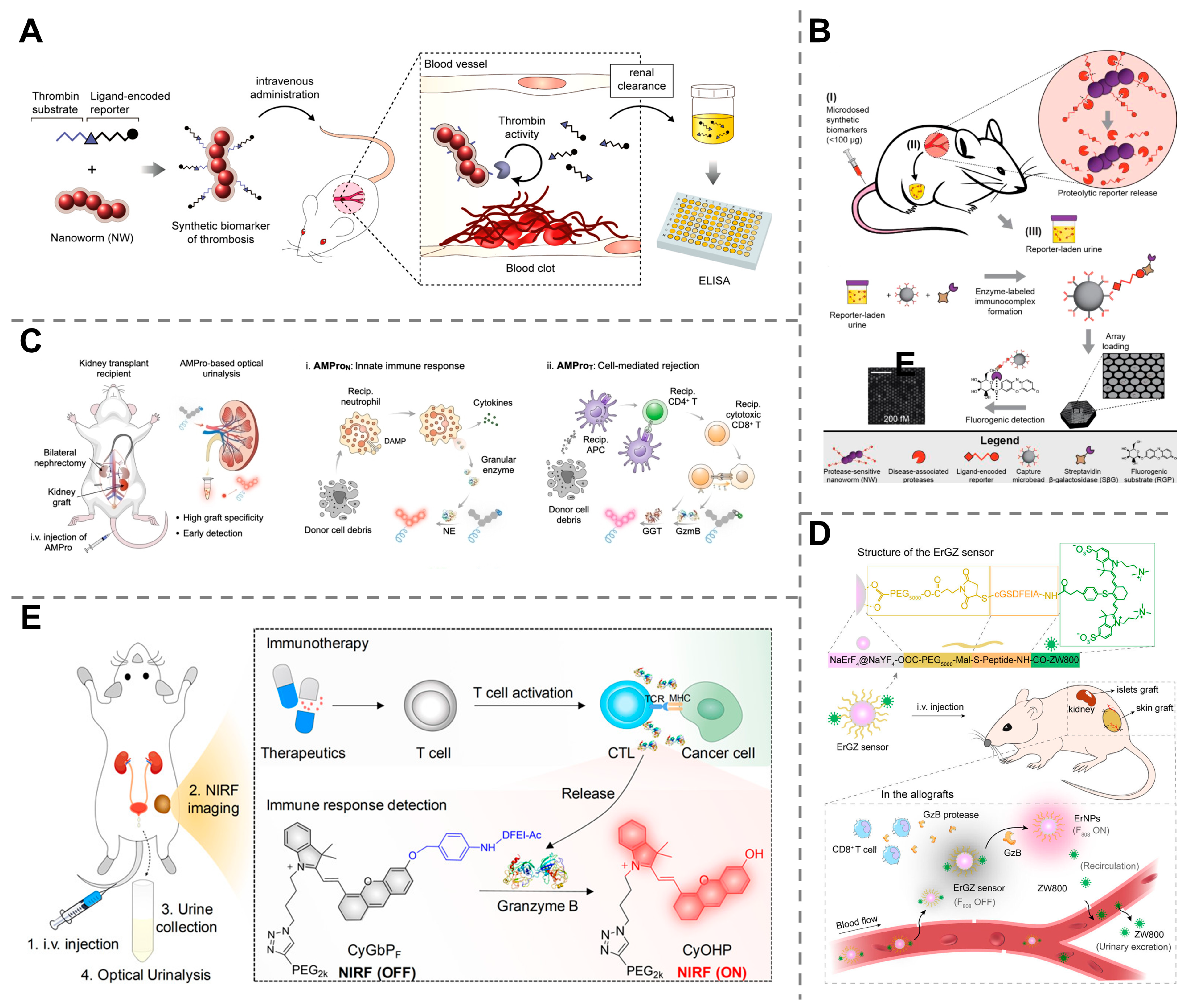
4. Applications of Synthetic Biomarkers in Disease Diagnosis
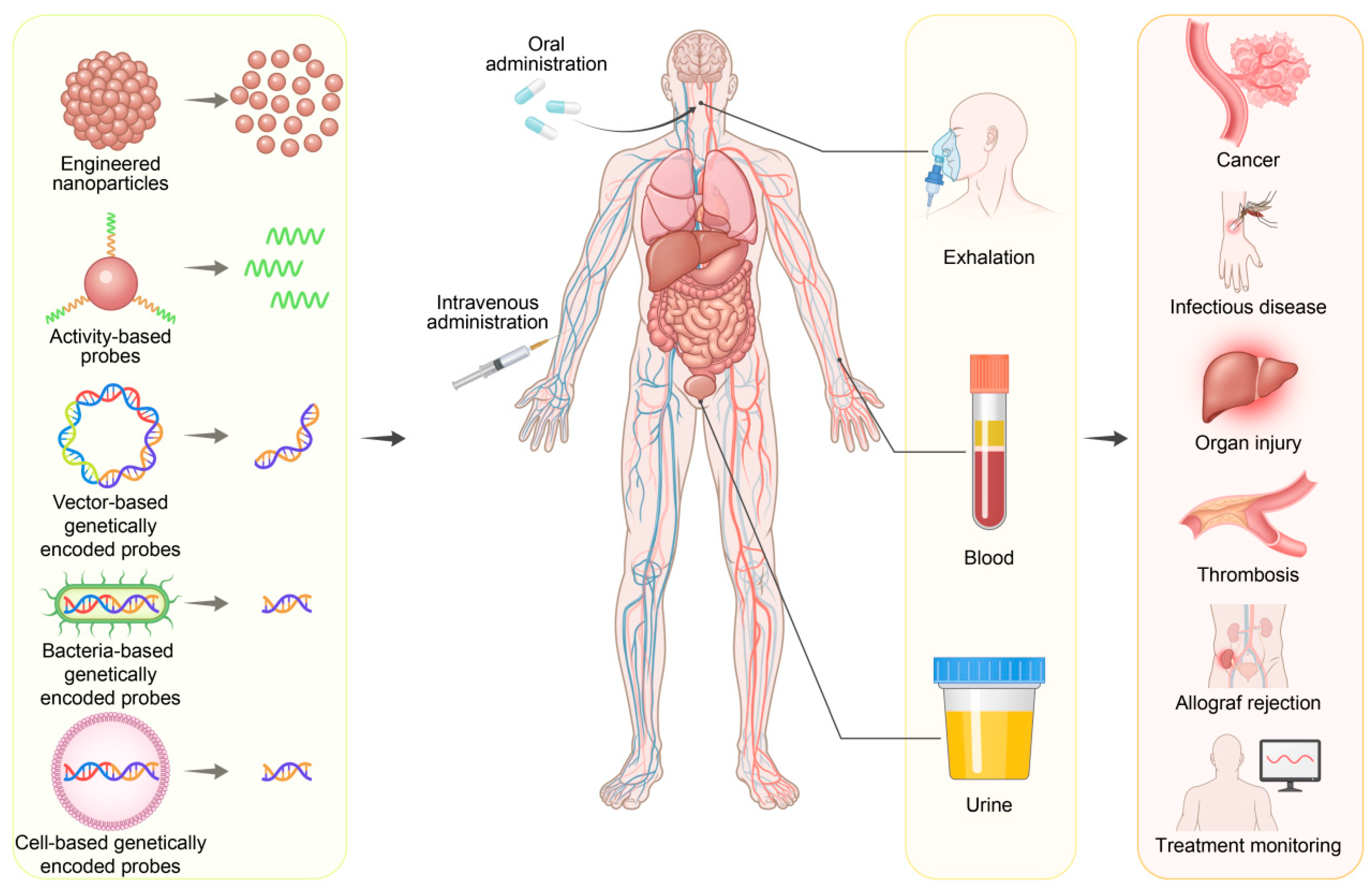
4.1. Detection Modalities of Synthetic Biomarkers
4.2. Early Detection of Cancers
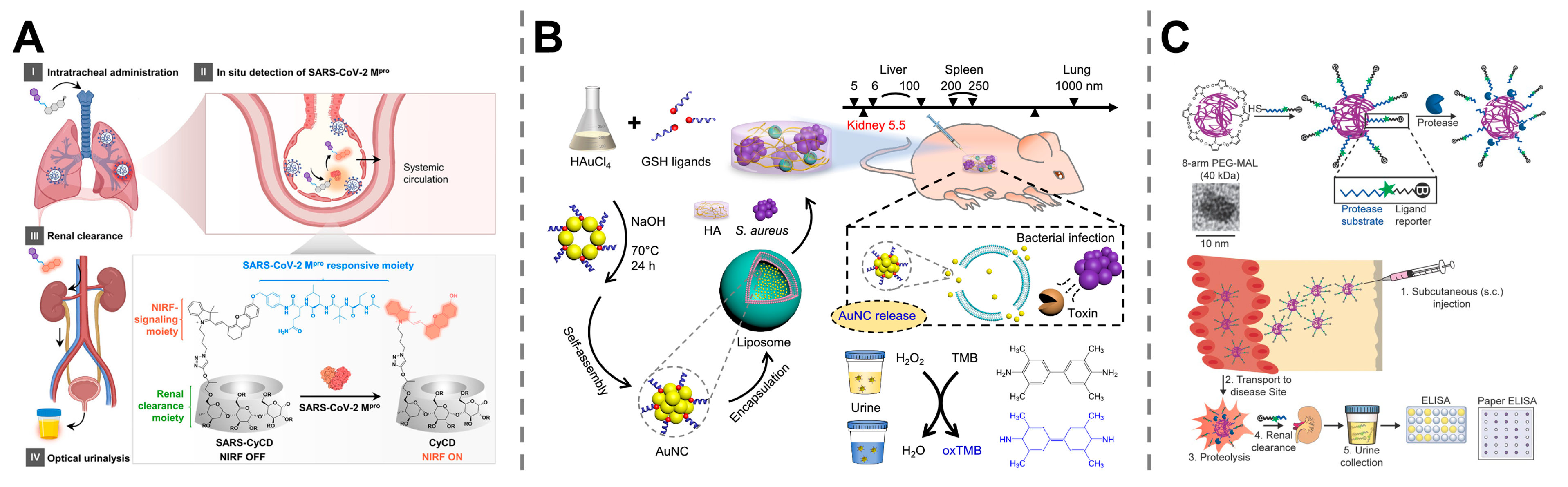
4.3. Detection of Infectious Diseases
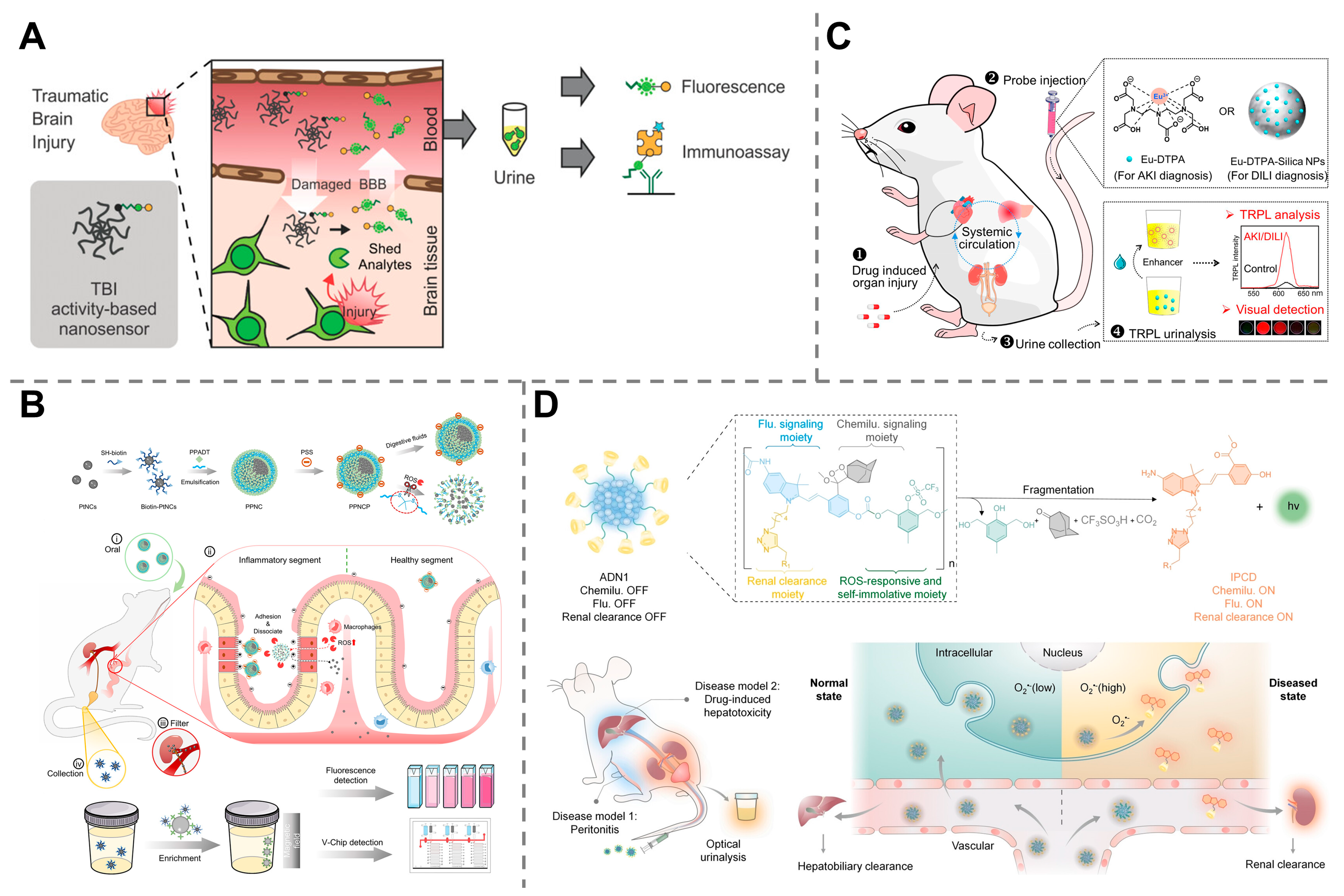
4.4. Monitoring of Organ Dysfunction and Injury
4.5. Other Diagnostic Applications
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| PET | Positron emission tomography |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| NP | Nanoparticle |
| ABP | Activity-based probe |
| APN | Aminopeptidase N |
| CTC | Circulating tumor cell |
| cfDNA | Cell-free tumor DNA |
| V-Chip | Volumetric bar-chart chip |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| AUC | Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve |
| MSC | Mesenchymal stem cell |
| PtNC | Platinum nanocluster |
| AuNC | Gold nanocluster |
| PEG | Poly(ethylene glycol) |
| AKI | Acute kidney injury |
| TBI | Traumatic brain injury |
| PPNCP | Platinum nanomarker superparticle |
| DTPA | Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid |
| NKC | Natural killer cell |
| fCAL | Fecal calprotectin |
| AATD | Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency |
| β-gal | Beta-galactosidase |
| hGluc | Humanized Gaussia luciferase |
| CTL | Cytotoxic T lymphocyte |
| GzmB | Granzyme B |
| GGT | γ-glutamyl transpeptidase |
References
- Crosby, D.; Bhatia, S.; Brindle, K.M.; Coussens, L.M.; Dive, C.; Emberton, M.; Esener, S.; Fitzgerald, R.C.; Gambhir, S.S.; Kuhn, P.; et al. Early detection of cancer. Science 2022, 375, eaay9040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, R.C.; Antoniou, A.C.; Fruk, L.; Rosenfeld, N. The future of early cancer detection. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Liu, X.; Feng, S.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Gao, Y. Synthesis and Biomedical Applications of Covalent Organic Frameworks for Disease Diagnosis and Therapy. ChemBioChem 2025, 26, e202400807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maajani, K.; Jalali, A.; Alipour, S.; Khodadost, M.; Tohidinik, H.R.; Yazdani, K. The Global and Regional Survival Rate of Women with Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Breast Cancer 2019, 19, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaquinto, A.N.; Sung, H.; Miller, K.D.; Kramer, J.L.; Newman, L.A.; Minihan, A.; Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.L. Breast Cancer Statistics, 2022. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 524–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Gole, J.; Gore, A.; He, Q.; Lu, M.; Min, J.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, T.; et al. Non-invasive early detection of cancer four years before conventional diagnosis using a blood test. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, B.; Keshavarz, M.; Wales, D.; Darzi, A.; Yeatman, E. Orthogonal Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering/Field-Effect Transistor Detection of Breast and Colorectal Cancer-Derived Exosomes using Graphene as a Tag-Free Diagnostic Template. Adv. NanoBiomed Res. 2023, 3, 2300055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Luo, W.; Luan, X.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, Y.; He, B.; Gao, Y.; Song, Y. Detecting telomerase activity at the single-cell level using a CRISPR-Cas12a-based chip. Lab Chip 2024, 25, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.; Cao, X.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Song, Y.; He, B. Ultrasensitive Detection of Extracellular Vesicles Based on Metal–Organic Framework DNA Biobarcodes Triggered G-Quadruplex Coupled with Rolling Circle Amplification Assay. ACS Sens. 2025, 10, 2136–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, A.; Kakiuchi, N.; Yoshizato, T.; Nannya, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Takeuchi, Y.; Shiozawa, Y.; Sato, Y.; Aoki, K.; Kim, S.K.; et al. Age-related remodelling of oesophageal epithelia by mutated cancer drivers. Nature 2019, 565, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwabi-Addo, B.; Chung, W.; Shen, L.; Ittmann, M.; Wheeler, T.; Jelinek, J.; Issa, J.-P.J. Age-Related DNA Methylation Changes in Normal Human Prostate Tissues. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 3796–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paggi, M.G.; Vona, R.; Abbruzzese, C.; Malorni, W. Gender-related disparities in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 2010, 298, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, G.A.; Ghosh, S.; Gamboa, L.; Patriotis, C.; Srivastava, S.; Bhatia, S.N. Synthetic biomarkers: A twenty-first century path to early cancer detection. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Mire, J.; Kong, Y.; Chang, M.; Hassounah, H.A.; Thornton, C.N.; Sacchettini, J.C.; Cirillo, J.D.; Rao, J. Rapid point-of-care detection of the tuberculosis pathogen using a BlaC-specific fluorogenic probe. Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Pan, R.; Li, P.; Guan, Q.; Ao, J.; Wang, K.; Xu, L.; Liang, X.; Jin, X.; Zhang, C.; et al. Hydrogen Peroxide-Responsive Nanoprobe Assists Circulating Tumor Cell Identification and Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 5966–5975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jongkhumkrong, J.; Thaveesangsakulthai, I.; Sukbangnop, W.; Kulsing, C.; Sooksimuang, T.; Aonbangkhen, C.; Sahasithiwat, S.; Sriprasart, T.; Palaga, T.; Chantaravisoot, N.; et al. Helicene-Hydrazide Encapsulated Ethyl Cellulose as a Potential Fluorescence Sensor for Highly Specific Detection of Nonanal in Aqueous Solutions and a Proof-of-Concept Clinical Study in Lung Fluid. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 49495–49507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hu, R.; Yang, C.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, S.; Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Cai, X.; Li, S.; et al. An ultrasensitive bioluminogenic probe of γ-Glutamyltranspeptidase in vivo and in human serum for tumor diagnosis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 98, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Ma, A. A high-selectivity NIR fluorescent probe for detection of nitric oxide in saliva samples and living cells imaging. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 374, 132790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Cao, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dong, R.; Zhu, M.; Gao, P.; Wang, X.; Cai, J.; Zuo, X. Circ_0008315 promotes tumorigenesis and cisplatin resistance and acts as a nanotherapeutic target in gastric cancer. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenck, J.; Sonanini, D.; Cotton, J.M.; Rammensee, H.-G.; la Fougère, C.; Zender, L.; Pichler, B.J. Advances in PET imaging of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2023, 23, 474–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.C.; Tang, Z.; Eremina, O.E.; Sofias, A.M.; Lammers, T.; Lovell, J.F.; Zavaleta, C.; Cai, W.; Cormode, D.P. Nanomaterial-based contrast agents. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2023, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, D.; Zhang, H.; Hu, G.; Guo, B. Recent development of contrast agents for magnetic resonance and multimodal imaging of glioblastoma. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, T.C.; Anton, N.; Attia, M.F. CT and X-ray contrast agents: Current clinical challenges and the future of contrast. Acta Biomater. 2023, 171, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Magaud, P.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, F.; Yang, J.; Baldas, L.; Song, Y. Nanocatalysis meets microfluidics: A powerful platform for sensitive bioanalysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 158, 116887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-González, D.; Merkoçi, A. Nanomaterial-based devices for point-of-care diagnostic applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 4697–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Cao, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Q.; Cheng, J.; Shen, Y.; He, K. Enhancing hepatocellular carcinoma therapy with DOX-loaded SiO2 nanoparticles via mTOR-TFEB pathway autophagic flux inhibition. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2025, 23, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Nie, G. Multifunctional biomolecule nanostructures for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 766–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhong, X.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, L. Inorganic nanomaterials with rapid clearance for biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 8669–8742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, G.A.; Von Maltzahn, G.; Murugappan, G.; Abudayyeh, O.; Mo, S.; Papayannopoulos, I.A.; Sverdlov, D.Y.; Liu, S.B.; Warren, A.D.; Popov, Y.; et al. Mass-encoded synthetic biomarkers for multiplexed urinary monitoring of disease. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Pu, K. Molecular imaging and disease theranostics with renal-clearable optical agents. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 1095–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Pu, K. Artificial urinary biomarker probes for diagnosis. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2024, 2, 425–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; Cai, Y.; Cheng, P.; Zheng, L.; Pu, K. Body fluid diagnostics using activatable optical probes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2025, 54, 3906–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Fang, L.; Lv, D.; Chen, L.; Zhang, B.; Wu, D. Design and synthesis of Ag NPs/chitosan-starch nano-biocomposite as a modern anti-human malignant melanoma drug. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 236, 123823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selmani, A.; Kovačević, D.; Bohinc, K. Nanoparticles: From synthesis to applications and beyond. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 303, 102640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farka, Z.; Juřík, T.; Kovář, D.; Trnková, L.; Skládal, P. Nanoparticle-Based Immunochemical Biosensors and Assays: Recent Advances and Challenges. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 9973–10042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykman, L.; Khlebtsov, N. Gold nanoparticles in biomedical applications: Recent advances and perspectives. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2256–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yuan, Z.; Shi, S.; Chen, X.; Yu, S.; Qi, X.; Deng, T.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, D.; Xu, S.; et al. Microneedle patches incorporating zinc-doped mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with betamethasone dipropionate for psoriasis treatment. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Cheng, S.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y. Membrane engineering of cell membrane biomimetic nanoparticles for nanoscale therapeutics. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Schüth, F.; Lozano, D.; Colilla, M.; Manzano, M. Engineering mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery: Where are we after two decades? Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 5365–5451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Ke, B.; Tian, Q.; Gao, Y.; Zhai, Q.; Zhang, W. Targeting AURKA with multifunctional nanoparticles in CRPC therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, R.H.; Gao, W.; Zhang, L. Targeting drugs to tumours using cell membrane-coated nanoparticles. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.-Y.; Wu, F.-G.; Chen, X. Antibody-Incorporated Nanomedicines for Cancer Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2109210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, S.; Wang, X.; Tao, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Song, Y. Microfluidic synthesis of hemin@ZIF-8 nanozyme with applications in cellular reactive oxygen species detection and anticancer drug screening. Lab Chip 2024, 24, 3521–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhu, M.; Dong, R.; Cao, D.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Cai, J.; Zuo, X. TH-302-loaded nanodrug reshapes the hypoxic tumour microenvironment and enhances PD-1 blockade efficacy in gastric cancer. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wu, D.; Lv, D.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, B. Supported of gold nanoparticles on carboxymethyl lignin modified magnetic nanoparticles as an efficient catalyst for reduction of nitroarenes and treatment of human melanoma. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 270, 132250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Pu, K. Molecular Probes for Autofluorescence-Free Optical Imaging. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 13086–13131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Song, Y.; Xiao, H.; Song, E. Enzyme-activated apoptotic bodies-encapsulated NSET biomimetic probe for wash-free detection of intracellular pathogen in synovial fluid and monitoring therapy effect of septic arthritis. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 485, 149539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Pan, Y.; Liu, X.; Gao, Y.; Luan, X.; Zeng, F.; Zhou, D.; Long, W.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y. Hypoxia-Responsive Platinum Supernanoparticles for Urinary Microfluidic Monitoring of Tumors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202114239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Li, J.; He, S.; Huang, J.; Pu, K. A Renal-Clearable Macromolecular Reporter for Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging of Bladder Cancer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 4415–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, S.X.; Aeran, R.; Liao, W.; Lu, M.; Polovin, G.; Pone, E.J.; Zhao, W. Exogenous marker-engineered mesenchymal stem cells detect cancer and metastases in a simple blood assay. Stem Cell Res. Amp. Ther. 2015, 6, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panteli, J.T.; Van Dessel, N.; Forbes, N.S. Detection of tumors with fluoromarker-releasing bacteria. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, M.M.; Sloane, B.F. multifunctional enzymes in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergers, G.; Fendt, S.-M. The metabolism of cancer cells during metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 162–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho, E.; Batlle, E.; Clevers, H. Signaling pathways in intestinal development and cancer. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2004, 20, 695–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Y.; Du, Z.; Xu, S.; Wang, X.; Wei, S.; Tao, Y.; Li, B.; Jiang, J.; et al. p53 Modulates the Gut-Liver Axis via PI3K/AKT/Wnt Signaling Pathways in Type 2 Diabetes. FASEB J. 2025, 39, e70898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimany, A.P.; Bhatia, S.N. Activity-Based Diagnostics: An Emerging Paradigm for Disease Detection and Monitoring. Trends Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 450–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, K.E.; Francis, S.; Carlson, E.E. Activity-Based Probe for Histidine Kinase Signaling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 9150–9153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbowuro, A.A.; Huston, W.M.; Gamble, A.B.; Tyndall, J.D.A. Proteases and protease inhibitors in infectious diseases. Med. Res. Rev. 2018, 38, 1295–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, G.A. Matrix metalloproteinases and their multiple roles in neurodegenerative diseases. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudani, J.S.; Warren, A.D.; Bhatia, S.N. Harnessing protease activity to improve cancer care. Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol. 2018, 2, 353–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissleder, R.; Tung, C.-H.; Mahmood, U.; Bogdanov, A. In vivo imaging of tumors with protease-activated near-infrared fluorescent probes. Nat. Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.; Miller, J.S.; Sun, J.; Yu, W.W.; Colvin, V.L.; Drezek, R.; West, J.L. Protease-activated quantum dot probes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 334, 1317–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarty, N.S.; Graham, A.E.; Studená, L.; Ledesma-Amaro, R. Multiplexed CRISPR technologies for gene editing and transcriptional regulation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Song, Y. Harnessing Gene Editing Technology for Tumor Microenvironment Modulation: An Emerging Anticancer Strategy. Chem. A Eur. J. 2024, 30, e202402485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nora, L.C.; Westmann, C.A.; Martins-Santana, L.; Alves, L.D.F.; Monteiro, L.M.O.; Guazzaroni, M.E.; Silva-Rocha, R. The art of vector engineering: Towards the construction of next-generation genetic tools. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 125–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P Teixeira, A.; Fussenegger, M. Engineering mammalian cells for disease diagnosis and treatment. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 55, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, R.M.; Wright, J.A.; Ng, J.Q.; Goyne, J.M.; Suzuki, N.; Lee, Y.K.; Ichinose, M.; Radford, G.; Ryan, F.J.; Kumar, S.; et al. Engineered bacteria detect tumor DNA. Science 2023, 381, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riglar, D.T.; Giessen, T.W.; Baym, M.; Kerns, S.J.; Niederhuber, M.J.; Bronson, R.T.; Kotula, J.W.; Gerber, G.K.; Way, J.C.; Silver, P.A. Engineered bacteria can function in the mammalian gut long-term as live diagnostics of inflammation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huyn, S.T.; Burton, J.B.; Sato, M.; Carey, M.; Gambhir, S.S.; Wu, L. A Potent, Imaging Adenoviral Vector Driven by the Cancer-selective Mucin-1 Promoter That Targets Breast Cancer Metastasis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3126–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, S.Y.; Lee, A.S.G. The future of blood-based biomarkers for the early detection of breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 92, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Leevan, E.; Ahmed, J.; Ko, B.; Shin, S.; De Souza, A.; Takebe, N. Blood-based multi-cancer detection: A state-of-the-art update. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2024, 48, 101059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yin, Y.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y. Nanomaterial-assisted microfluidics for multiplex assays. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Long, W.; Wang, Y.; Han, Y.; Zeng, F.; Li, J.; He, B.; Song, Y.; Gao, Y. A portable microfluidic platform for ultra-sensitive detection of ovarian cancer biomarkers via cascade signal amplification. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 503, 158289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Song, Y. Microfluidics-Based Urine Biopsy for Cancer Diagnosis: Recent Advances and Future Trends. ChemMedChem 2022, 17, e202200422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshi, M.; Murthy, V.; Takahashi, H.; Huyser, M.; Okano, M.; Tokumaru, Y.; Rashid, O.M.; Matsuyama, R.; Endo, I.; Takabe, K. Urine as a Source of Liquid Biopsy for Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Shao, K.; Wang, T. Detection of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from exhaled breath as noninvasive methods for cancer diagnosis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 2759–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.D. Application of Electronic-Nose Technologies and VOC-Biomarkers for the Noninvasive Early Diagnosis of Gastrointestinal Diseases. Sensors 2018, 18, 2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Sun, A.; Zhang, X.; Hu, L.; Wang, H. A wash-free red fluorescent probe for real-time monitoring of mitochondrial viscosity changes and tumor imaging. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2025, 268, 113182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Wu, C.; Saqib, M.; Hao, R. Single-molecule fluorescence methods for protein biomarker analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 3655–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinen, A.B.; Guan, C.M.; Ferrer, J.R.; Barnaby, S.N.; Merkel, T.J.; Mirkin, C.A. Nanoparticle Probes for the Detection of Cancer Biomarkers, Cells, and Tissues by Fluorescence. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 10530–10574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagit, O.; Hildebrandt, N. Fluorescence Sensing of Circulating Diagnostic Biomarkers Using Molecular Probes and Nanoparticles. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Gao, Y.; Song, Y. Sucrose-Powered Liposome Nanosensors for Urinary Glucometer-Based Monitoring of Cancer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202404493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danino, T.; Prindle, A.; Kwong, G.A.; Skalak, M.; Li, H.; Allen, K.; Hasty, J.; Bhatia, S.N. Programmable probiotics for detection of cancer in urine. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 289ra284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkpatrick Jesse, D.; Warren Andrew, D.; Soleimany Ava, P.; Westcott Peter, M.K.; Voog Justin, C.; Martin-Alonso, C.; Fleming Heather, E.; Tammela, T.; Jacks, T.; Bhatia Sangeeta, N. Urinary detection of lung cancer in mice via noninvasive pulmonary protease profiling. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaaw0262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Xu, M.; Hu, Y.; Liu, J.; Cheng, P.; Zeng, Z.; Pu, K. Ingestible Artificial Urinary Biomarker Probes for Urine Test of Gastrointestinal Cancer. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2314084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Cheng, P.; Pu, K. Activatable near-infrared probes for the detection of specific populations of tumour-infiltrating leukocytes in vivo and in urine. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 7, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, L.; Zhao, R.T.; Welch, N.L.; Tan, E.K.W.; Zhong, Q.; Harzallah, N.S.; Ngambenjawong, C.; Ko, H.; Fleming, H.E.; Sabeti, P.C.; et al. CRISPR-Cas-amplified urinary biomarkers for multiplexed and portable cancer diagnostics. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2023, 18, 798–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, J.; Liew, S.S.; Hu, Y.; Xu, M.; Pu, K. Urinary bioorthogonal reporters for the monitoring of the efficacy of chemotherapy for lung cancer and of associated kidney injury. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2025, 9, 686–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Sun, N.; Li, Q.; Yang, J.; Yang, X.; Liu, D. Self-Referenced Synthetic Urinary Biomarker for Quantitative Monitoring of Cancer Development. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loynachan, C.N.; Soleimany, A.P.; Dudani, J.S.; Lin, Y.; Najer, A.; Bekdemir, A.; Chen, Q.; Bhatia, S.N.; Stevens, M.M. Renal clearable catalytic gold nanoclusters for in vivo disease monitoring. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronald, J.A.; Chuang, H.-Y.; Dragulescu-Andrasi, A.; Hori, S.S.; Gambhir, S.S. Detecting cancers through tumor-activatable minicircles that lead to a detectable blood biomarker. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3068–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishihara, T.; Kuno, S.; Nonaka, H.; Tabata, S.; Saito, N.; Fukuda, S.; Tomita, M.; Sando, S.; Soga, T. Beta-galactosidase-responsive synthetic biomarker for targeted tumor detection. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 11745–11748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, X.; Gao, Y.; Pan, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zeng, F.; He, G.; He, B.; Ye, D.; Song, Y. Bifunctional Nanoassembly Enables Metabolism-Driven Microfluidic Blood Screening Guided by MRI Localization for Cancer Monitoring. Anal. Chem. 2025, 97, 3395–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, R.E.; Mahmud, A.S.; Miller, I.F.; Rajeev, M.; Rasambainarivo, F.; Rice, B.L.; Takahashi, S.; Tatem, A.J.; Wagner, C.E.; Wang, L.-F.; et al. Infectious disease in an era of global change. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morens, D.M.; Folkers, G.K.; Fauci, A.S. The challenge of emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases. Nature 2004, 430, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casanova, J.-L.; Abel, L. Mechanisms of viral inflammation and disease in humans. Science 2021, 374, 1080–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilt, E.E.; Ferrieri, P. Next Generation and Other Sequencing Technologies in Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Genes 2022, 13, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Rothman, R.E. PCR-based diagnostics for infectious diseases: Uses, limitations, and future applications in acute-care settings. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2004, 4, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, S.S.; Zeng, Z.; Cheng, P.; He, S.; Zhang, C.; Pu, K. Renal-Clearable Molecular Probe for Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging and Urinalysis of SARS-CoV-2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 18827–18831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Najer, A.; Charchar, P.; Saunders, C.; Thanapongpibul, C.; Klöckner, A.; Chami, M.; Peeler, D.J.; Silva, I.; Panariello, L.; et al. Non-invasive in vivo sensing of bacterial implant infection using catalytically-optimised gold nanocluster-loaded liposomes for urinary readout. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudani, J.S.; Buss, C.G.; Akana, R.T.K.; Kwong, G.A.; Bhatia, S.N. Sustained-Release Synthetic Biomarkers for Monitoring Thrombosis and Inflammation Using Point-of-Care Compatible Readouts. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 2919–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buss, C.G.; Dudani, J.S.; Akana, R.T.K.; Fleming, H.E.; Bhatia, S.N. Protease activity sensors noninvasively classify bacterial infections and antibiotic responses. eBioMedicine 2018, 38, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellum, J.A.; Romagnani, P.; Ashuntantang, G.; Ronco, C.; Zarbock, A.; Anders, H.-J. Acute kidney injury. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gameiro, J.; Fonseca, J.A.; Outerelo, C.; Lopes, J.A. Acute Kidney Injury: From Diagnosis to Prevention and Treatment Strategies. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moledina, D.G.; Hall, I.E.; Thiessen-Philbrook, H.; Reese, P.P.; Weng, F.L.; Schröppel, B.; Doshi, M.D.; Wilson, F.P.; Coca, S.G.; Parikh, C.R. Performance of Serum Creatinine and Kidney Injury Biomarkers for Diagnosing Histologic Acute Tubular Injury. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 70, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Vlies, C.H.; Olthof, D.C.; Gaakeer, M.; Ponsen, K.J.; Van Delden, O.M.; Goslings, J.C. Changing patterns in diagnostic strategies and the treatment of blunt injury to solid abdominal organs. Int. J. Emerg. Med. 2011, 4, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryashev, J.A.; Madias, M.I.; Kandell, R.M.; Lin, Q.X.; Kwon, E.J. An Activity-Based Nanosensor for Minimally-Invasive Measurement of Protease Activity in Traumatic Brain Injury. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2300218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Yin, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Yang, J.; Pan, Y.; Song, Y. Orally Administered Platinum Nanomarkers for Urinary Monitoring of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 18503–18514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Li, M.; Ni, S.; Yang, K.; Li, S.; Li, R.; Zheng, W.; Tu, D.; Chen, X.; Yang, H. Ultrasensitive Urinary Diagnosis of Organ Injuries Using Time-Resolved Luminescent Lanthanide Nano-bioprobes. Nano Lett. 2023, 23, 1878–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, B.; Yu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhu, L.; Yi, S.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, J. Size-Transformable Superoxide-Triggered Nanoreporters for Crosstalk-Free Dual Fluorescence/Chemiluminescence Imaging and Urinalysis in Living Mice. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202305812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xian, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Pu, K.; Wang, H. A Renally Clearable Activatable Polymeric Nanoprobe for Early Detection of Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2201357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzorati, D.; Mainardi, L.; Sedda, G.; Gasparri, R.; Spaggiari, L.; Cerveri, P. A review of exhaled breath: A key role in lung cancer diagnosis. J. Breath Res. 2019, 13, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Peng, Y.; Duan, Y. Diagnosis of breast cancer based on breath analysis: An emerging method. Crit. Rev. Oncol. /Hematol. 2013, 87, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, L.W.; Anahtar, M.N.; Ong, T.-H.; Hern, K.E.; Kunz, R.R.; Bhatia, S.N. Engineering synthetic breath biomarkers for respiratory disease. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolberg, A.S.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Weitz, J.I.; Jaffer, I.H.; Agnelli, G.; Baglin, T.; Mackman, N. Venous thrombosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nougier, C.; Benoit, R.; Simon, M.; Desmurs-Clavel, H.; Marcotte, G.; Argaud, L.; David, J.S.; Bonnet, A.; Negrier, C.; Dargaud, Y. Hypofibrinolytic state and high thrombin generation may play a major role in SARS-CoV2 associated thrombosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 2215–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lux, J.; Vezeridis, A.M.; Hoyt, K.; Adams, S.R.; Armstrong, A.M.; Sirsi, S.R.; Mattrey, R.F. Thrombin-Activatable Microbubbles as Potential Ultrasound Contrast Agents for the Detection of Acute Thrombosis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 37587–37596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.Y.; Kwong, G.A.; Warren, A.D.; Wood, D.K.; Bhatia, S.N. Nanoparticles That Sense Thrombin Activity As Synthetic Urinary Biomarkers of Thrombosis. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 9001–9009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, A.D.; Gaylord, S.T.; Ngan, K.C.; Dumont Milutinovic, M.; Kwong, G.A.; Bhatia, S.N.; Walt, D.R. Disease Detection by Ultrasensitive Quantification of Microdosed Synthetic Urinary Biomarkers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 13709–13714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.-L.; Wang, R.-l.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Q.; Li, X.-L.; He, Q.; Zhu, J.-Q. Granzyme B–Producing B Cells Function as a Feedback Loop for T Helper Cells in Liver Transplant Recipients with Acute Rejection. Inflammation 2021, 44, 2270–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Yi, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Q.; Song, Y.; Ding, M.; Deng, C.; Chen, Y.; Xie, Y.; et al. Granzyme B-responsive fluorescent probe for non-invasive early diagnosis of transplant rejection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 232, 115303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronca, V.; Wootton, G.; Milani, C.; Cain, O. The Immunological Basis of Liver Allograft Rejection. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, C.; He, S.; Wang, H.; Pu, K. Renal clearable polyfluorophore nanosensors for early diagnosis of cancer and allograft rejection. Nat. Mater. 2022, 21, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, P.; Wang, R.; He, S.; Yan, P.; Huang, H.; Chen, J.; Shen, J.; Pu, K. Artificial Urinary Biomarkers for Early Diagnosis of Acute Renal Allograft Rejection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202306539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Pei, P.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, F. Noninvasive Early Diagnosis of Allograft Rejection by a Granzyme B Protease Responsive NIR-II Bioimaging Nanosensor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202301696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Li, J.; Lyu, Y.; Huang, J.; Pu, K. Near-Infrared Fluorescent Macromolecular Reporters for Real-Time Imaging and Urinalysis of Cancer Immunotherapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 7075–7082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Vázquez, S.; Lozano-Torres, B.; García-Fernández, A.; Galiana, I.; Perez-Villalba, A.; Martí-Rodrigo, P.; Palop, M.J.; Domínguez, M.; Orzáez, M.; Sancenón, F.; et al. A renal clearable fluorogenic probe for in vivo β-galactosidase activity detection during aging and senolysis. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshehri, S.; Alahmari, K.A.; Alasiry, A. A Comprehensive Evaluation of AI-Assisted Diagnostic Tools in ENT Medicine: Insights and Perspectives from Healthcare Professionals. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, P.-J. Determinants of physicians’ intention to use AI-assisted diagnosis: An integrated readiness perspective. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2023, 147, 107868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Biomarker | Potential Targets | Advantages | Disadvantages | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Engineered nanoparticles | Disease-related physiological conditions, ROS, pH, hypoxia, metabolites |
|
|
|
| Activity-based probes | Enzymatic activities, redox states |
|
| |
| Bacteria-based genetically encoded probes | Tumor microenvironment, specific promoter activity |
|
| |
| Mammalian cell-based genetically encoded probes |
|
| ||
| Vector-based genetically encoded probes |
|
| ||
| Conventional endogenous biomarkers | Naturally occurring proteins, nucleic acids, cells, metabolites, exosomes |
|
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, A.; Wei, M.; Yu, K.; Heng, S.; Zhao, X.; Jian, W.; Zhao, J.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y. Artificially Engineered Synthetic Biomarkers Revolutionizing Early Diagnosis of Diseases. Molecules 2025, 30, 4532. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234532
Wang A, Wei M, Yu K, Heng S, Zhao X, Jian W, Zhao J, Gao Y, Wang Y. Artificially Engineered Synthetic Biomarkers Revolutionizing Early Diagnosis of Diseases. Molecules. 2025; 30(23):4532. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234532
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Anyun, Min Wei, Keying Yu, Siying Heng, Xinyue Zhao, Wenxi Jian, Jinsong Zhao, Yanfeng Gao, and Yanping Wang. 2025. "Artificially Engineered Synthetic Biomarkers Revolutionizing Early Diagnosis of Diseases" Molecules 30, no. 23: 4532. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234532
APA StyleWang, A., Wei, M., Yu, K., Heng, S., Zhao, X., Jian, W., Zhao, J., Gao, Y., & Wang, Y. (2025). Artificially Engineered Synthetic Biomarkers Revolutionizing Early Diagnosis of Diseases. Molecules, 30(23), 4532. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234532






