Progress in the Application of Iron-Based Plant Derived Biochar Catalyst for Fenton-like Remediation of Organic Wastewater: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preparation of Iron-Based Plant-Derived Biochar
2.1. Biomass Sources of Plant-Derived Biochar
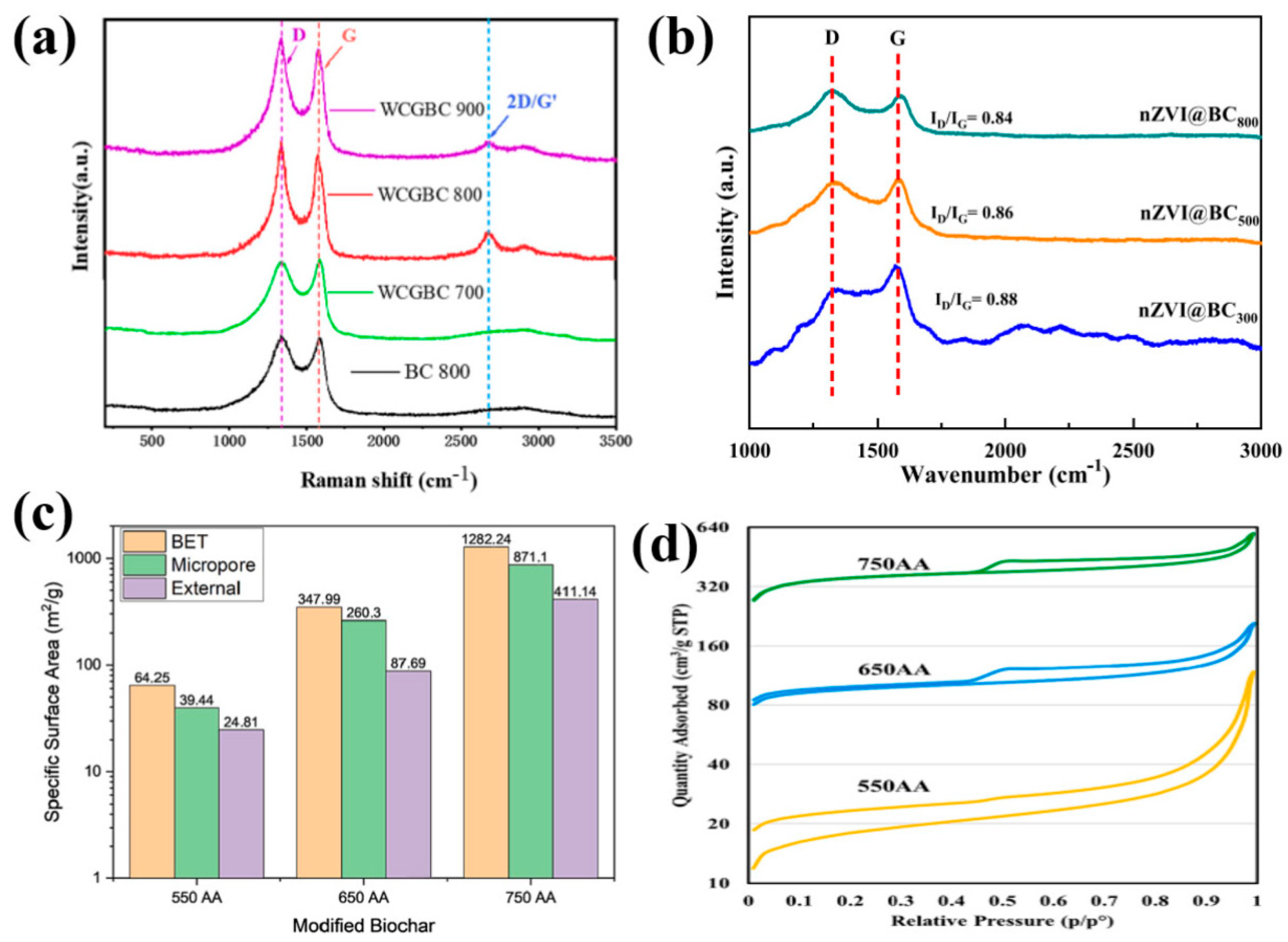
2.2. The Influence of Factors on the Performance of Biochar
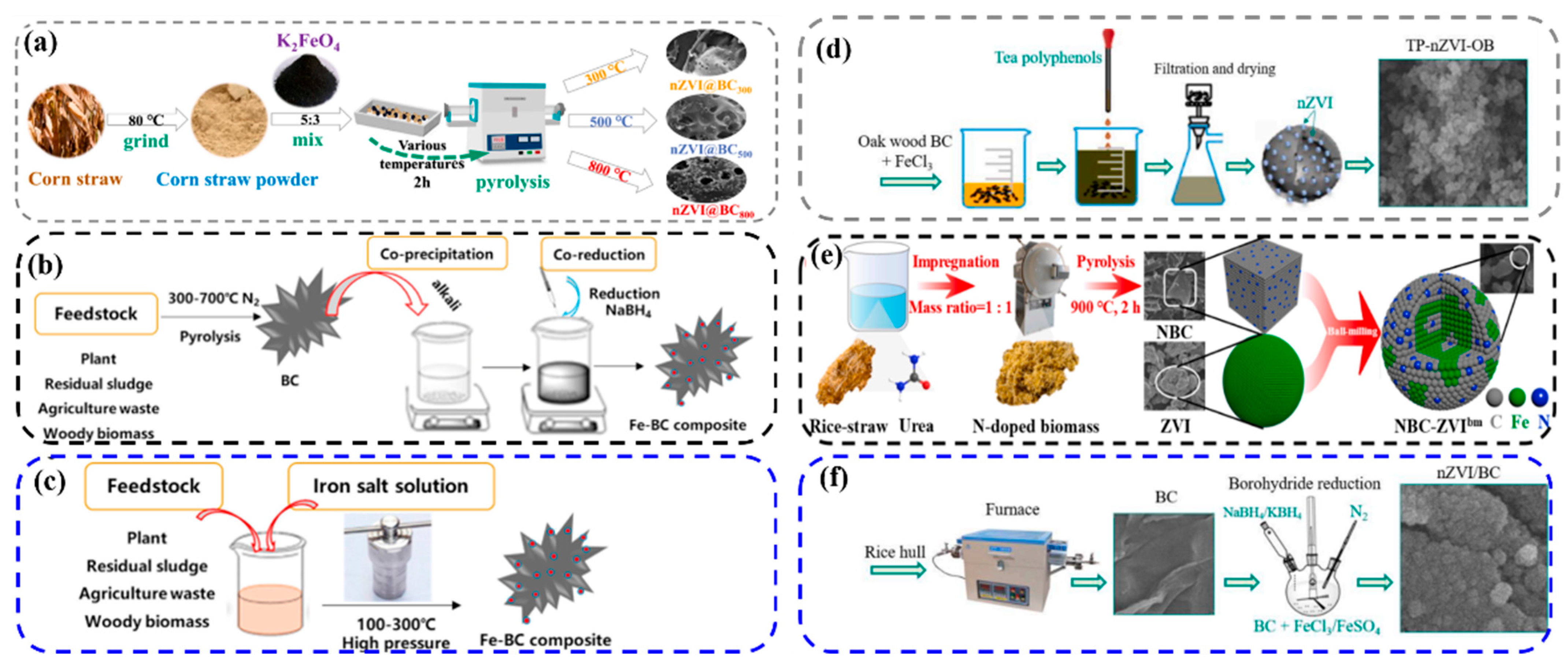
2.3. Strategies for Synthesizing Iron-Based Plant-Based Biochar
2.3.1. One-Step Pyrolysis
2.3.2. Co-Precipitation
2.3.3. Hydrothermal Process
2.3.4. Green Synthesis Process
2.3.5. Ball Milling Process
2.3.6. Chemical Reduction Process
3. Application of Iron-Based Plant-Based Biochar in Fenton-like Applications
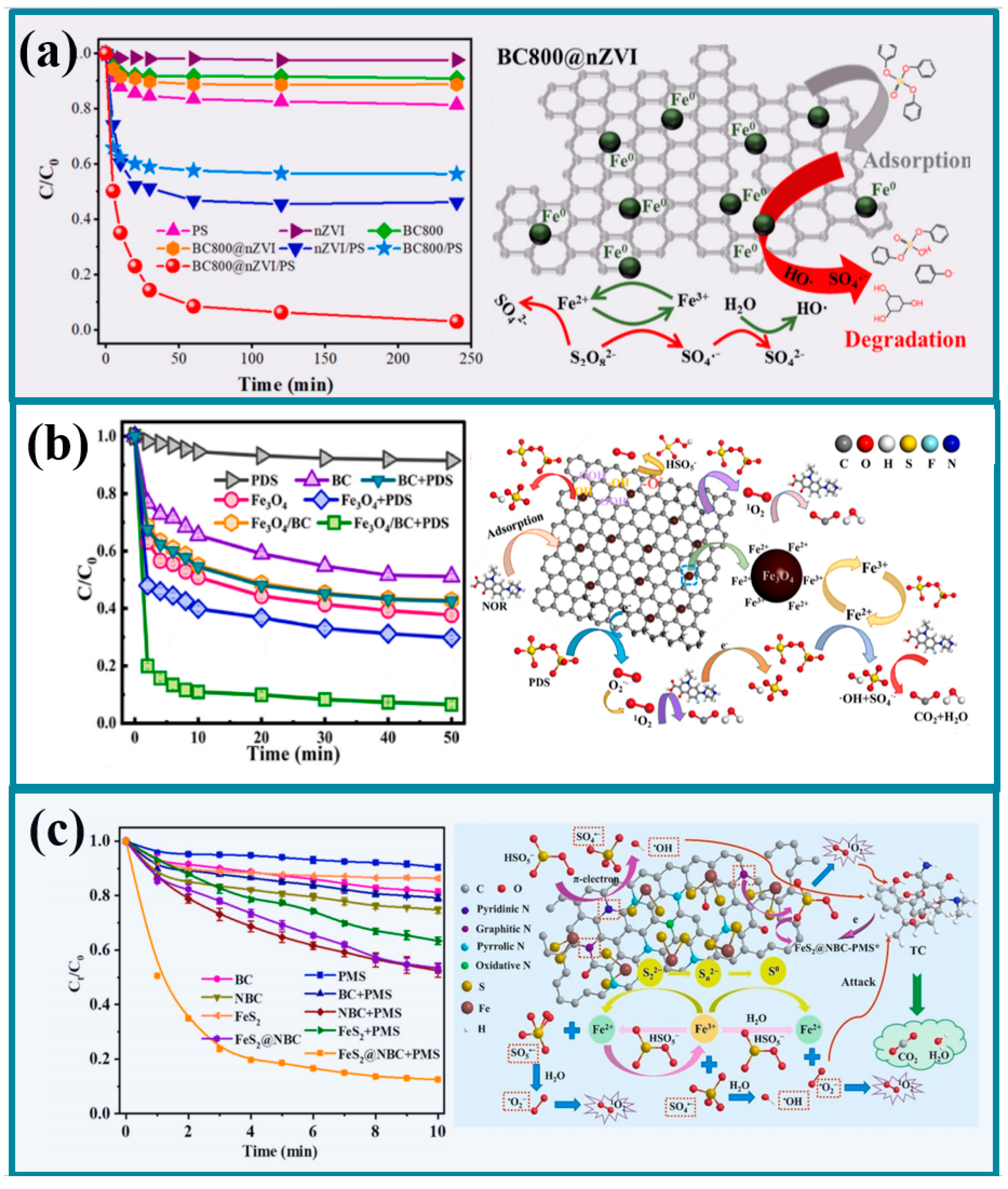
3.1. Iron-Based Monometallic Plant-Based Biochar
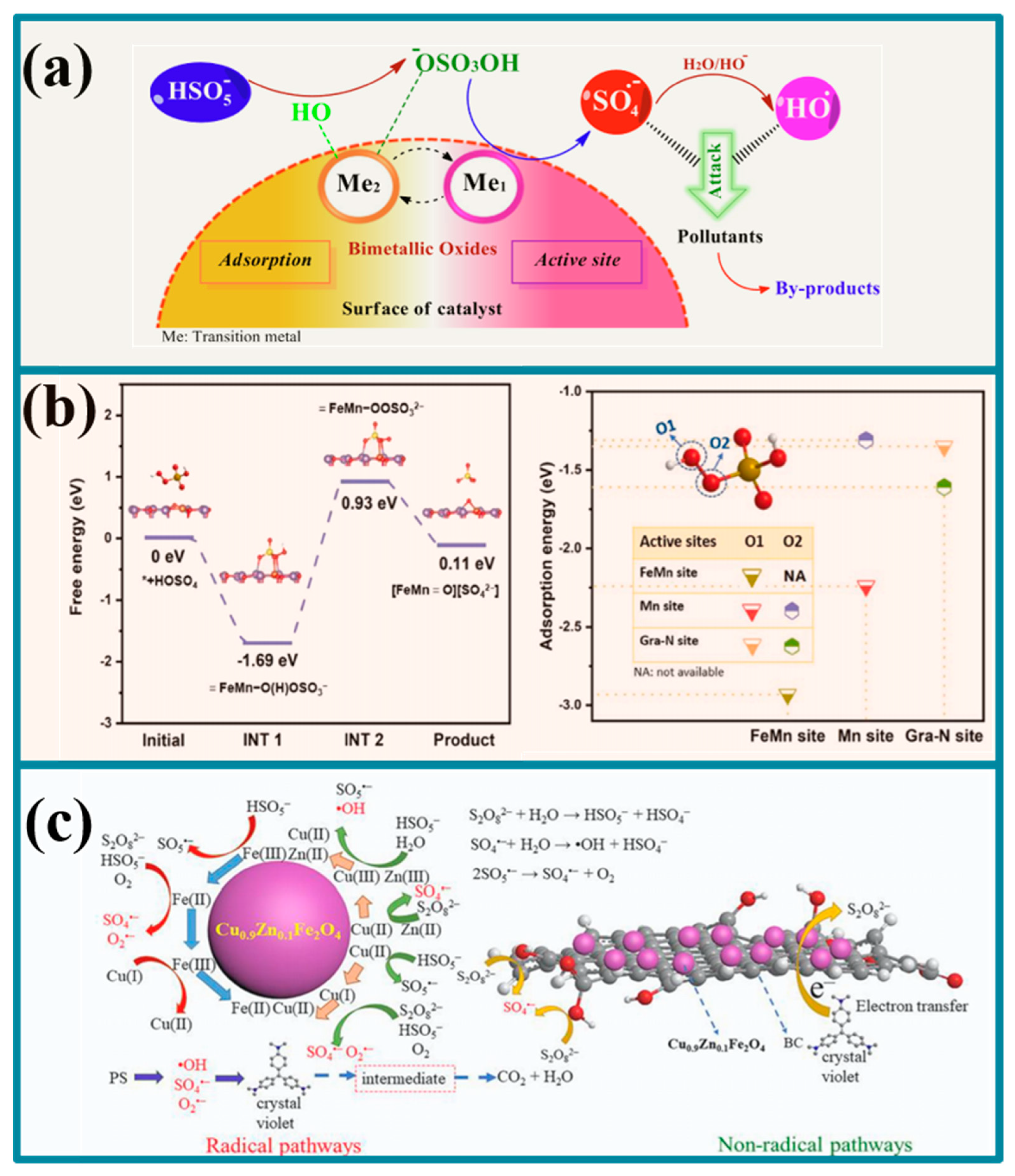
3.2. Iron-Based Polymetallic Plant-Based Biochar
3.3. Iron-Based Plant-Based Biochar Composites
3.4. Evaluation and Comparison of Different Catalyst Systems
4. Application and Performance of Fe-Biochar Composites in Photo-Fenton Systems
4.1. Light Source and Operational Conditions
4.2. Photocatalytic Degradation of Emerging and Persistent Pollutants
4.3. Matrix Effects and Reusability
5. Activation Mechanism
5.1. Radical Pathways
5.2. Non-Radical Pathways
5.2.1. 1O2 Pathway
5.2.2. Direct Electron Transfer
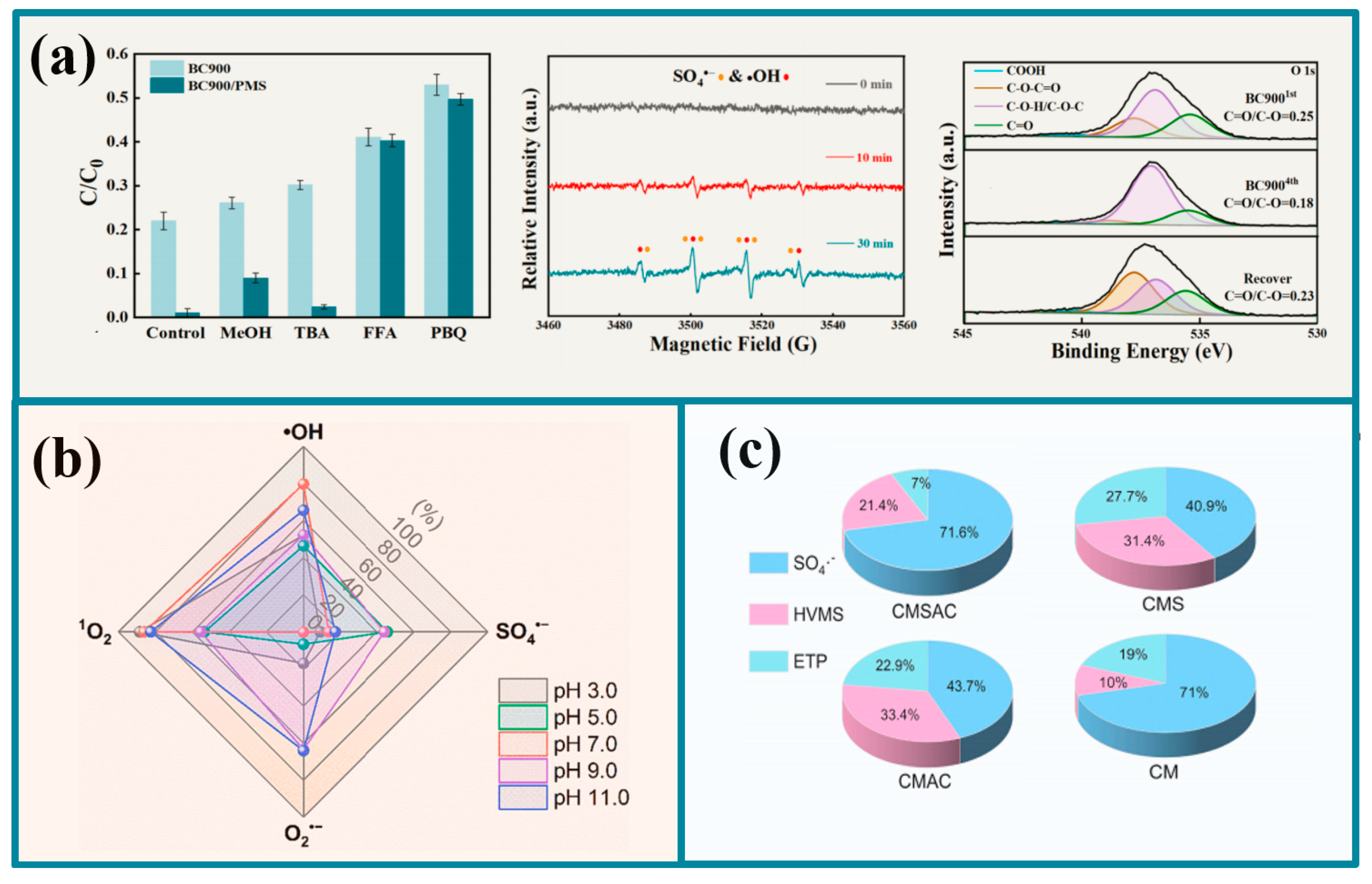
5.2.3. High-Value Metals
6. Challenges and Mitigation Strategies of Iron-Based Biochar Catalysts in Industrial-Scale Applications
6.1. Cost–Benefit and Scale-Up Assessment
6.2. Metal Dissolution and Secondary Pollution Control
- Encapsulation of Fe nanoparticles within graphitic carbon layers to shield against acid attack;
- Formation of stable oxides (Fe3O4, γ-Fe2O3) rather than free FeO;
- Sulfidation to produce FeSx species with low solubility;
- Surface complexation with oxygen- or nitrogen-containing functional groups to strengthen metal–support interactions (MSI);
- Post-treatment annealing at 500–600 °C to enhance crystallinity and reduce labile Fe sites.
6.3. Applicability to Real Water Matrices
- Baseline tests in deionized water to quantify intrinsic catalytic kinetics.
- Simulated water matrices containing common inorganic ions (Cl− ≈ 50 mg L−1, HCO3− ≈ 200 mg L−1, Ca2+ ≈ 100 mg L−1) and NOM (5–10 mg L−1 TOC) to assess interference.
- Actual water samples (e.g., river water, secondary effluent) to verify field applicability.
6.4. Toxicity and Transformation Product Assessment
- Identification of intermediates via GC–MS or LC–MS coupled with accurate mass spectrometry (MS/MS).
- Quantification of total organic carbon (TOC) to evaluate mineralization.
- Ecotoxicity assays such as Daphnia magna immobilization, Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata algal growth inhibition, or Vibrio fischeri luminescence inhibition (OECD standard tests).
- Computational toxicology tools (QSAR models, ECOSAR) for predicting the potential hazards of intermediates.
6.5. Catalyst Stability and Longevity
7. Conclusions and Perspective
- Durability and leaching control: Improve metal–support interaction via structural encapsulation or sulfidation to enable long-term operation with Fe release below regulatory limits and consistent catalytic activity over multiple reuse cycles.
- Standardized performance metrics: Establish reporting guidelines that include Fe leaching per cycle, photon-normalized kinetics, total organic carbon (TOC) removal, and toxicity evaluation of intermediates to enable fair comparison across studies.
- Cost–benefit assessment: To explore the economic cost of iron-based plant biochar in organic wastewater treatment, especially in large-scale production scenarios, and to weigh the pollutant removal efficiency against the cost, so as to help promote its practical application.
- Metal dissolution control: Closely monitor the metal dissolution condition in the catalyst use, strictly control it according to the emission standard, prevent secondary pollution, and ensure the environmental treatment effect and environmental safety.
- Research on the suitability of actual water bodies: In view of the complexity of the actual water body environment, strengthen the application research in natural water bodies, precisely analyze the impact of actual water body factors on the treatment effect, and enhance the practicality of the technology.
- Enhanced toxicity risk assessment: Emphasize the assessment of toxicity and biological hazards of intermediate products, fill the gaps in existing research, avoid secondary pollution and biological toxicity caused by more toxic intermediate products in the treatment process, and safeguard ecological safety.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xia, P.; Wang, C.; He, Q.; Ye, Z.; Sirés, I. MOF-derived single-atom catalysts: The next frontier in advanced oxidation for water treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohantorabi, M.; Moussavi, G.; Giannakis, S. A review of the innovations in metal- and carbon-based catalysts explored for heterogeneous peroxymonosulfate (PMS) activation, with focus on radical vs. non-radical degradation pathways of organic contaminants. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 411, 127957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Xia, P.; Duan, X.; He, Q.; Sirés, I.; Ye, Z. Accelerating Fe(III)/Fe(II) redox cycling in heterogeneous electro-Fenton process via S/Cu-mediated electron donor-shuttle regime. Appl. Catal. B 2024, 342, 123457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ma, C.; Wu, D.; Liu, X.; Li, N.; Fan, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Peng, W. Coating CoFe2O4 shell on Fe particles to increase the utilization efficiencies of Fe and peroxymonosulfate for low-cost Fenton-like reactions. Water Res. 2023, 244, 120542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, X.; Sun, K.; Lin, C.; Ma, J.; He, M.; Ouyang, W. Persulfate-based advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) for organic-contaminated soil remediation: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 836–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Yu, G.; Wen, X.; Chi, T.; Wang, G.; Su, Y.; Deng, F.; et al. Fe-based metal organic frameworks (Fe-MOFs) for organic pollutants removal via photo-Fenton: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tang, J. Fe-based Fenton-like catalysts for water treatment: Catalytic mechanisms and applications. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 332, 115755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tang, J. Fe-based Fenton-like catalysts for water treatment: Preparation, characterization and modification. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yao, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Q. Catalytic activity and mechanism of typical iron-based catalysts for Fenton-like oxidation. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 136972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parastaev, A.; Muravev, V.; Huertas Osta, E.; van Hoof, A.J.F.; Kimpel, T.; Kosinov, N.A.; Hensen, E.J.M. Boosting CO2 hydrogenation via size-dependent metal–support interactions in cobalt/ceria-based catalysts. Nat. Catal. 2020, 3, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Jiang, W.; Liu, X.; He, Y.; He, C.; Tang, T.; Zhang, J.; Hu, J. Molecularly Engineered Strong Metal Oxide–Support Interaction Enables Highly Efficient and Stable CO2 Electroreduction. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 13227–13235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Wang, B.; Chen, M.; Wu, P.; Lee, X.; Xing, Y. Invasive plants as potential sustainable feedstocks for biochar production and multiple applications: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 164, 105204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Li, K.; Xu, X.; Zhang, J.; Xue, Y. Efficiently catalytic degradation of tetracycline via persulfate activation with plant-based biochars: Insight into endogenous mineral self-template effect and pyrolysis catalysis. Chemosphere 2023, 337, 139309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, F.; Cheng, B.; Jin, Z.; Dai, Z.; Wang, B.; Yang, L.; Jiang, X. Hierarchical porous biochar from plant-based biomass through selectively removing lignin carbon from biochar for enhanced removal of toluene. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Bhattu, M.; Liew, R.K.; Verma, M.; Brar, S.K.; Bechelany, M.; Jadeja, R. Transforming rice straw waste into biochar for advanced water treatment and soil amendment applications. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 37, 103932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaida, M.; Verma, S.; Talukdar, S.; Kumar, N.; Mahtab, M.; Naushad, M.; Farooqi, I. Critical analysis of the role of various iron-based heterogeneous catalysts for advanced oxidation processes: A state of the art review. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 374, 121259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, A.; Khalid, A.; Qayyum, W.; Bibi, R.; Qamar, M.; Zahid, M.; Farhan, A.; Rayaroth, M.; Cichocki, Ł.; Boczkaj, G. FeS-based nanocomposites: A promising approach for sustainable environmental remediation—Focus on adsorption and photocatalysis—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Lu, Q.; Lu, D.; Yi, Z.; Zhou, Y. Iron-based biochar as efficient persulfate activation catalyst for emerging pollutants removal: A review. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 108357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yuan, S.; Dai, X.; Dong, B. Application, mechanism and prospects of Fe-based/ Fe-biochar catalysts in heterogenous ozonation process: A review. Chemosphere 2023, 319, 138018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Peng, A.; Chu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Huang, H.; Mi, Y.; Xia, D.; Wu, X.; Ye, Z.; Tao, Y.; et al. Sustainable remediation of Cr(VI)-contaminated soil by soil washing and subsequent recovery of washing agents using biochar supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 921, 171107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alchouron, J.; Fuentes, A.B.; Guerreiro, C.; Hodara, K.; Gatti, M.; Pittman, C., Jr.; Mlsna, T.; Chludil, H.; Vega, A. The feedstock anatomical properties determine biochar adsorption capacities: A study using woody bamboos (Bambuseae) and methylene blue as a model molecule. Chemosphere 2024, 362, 142656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almojil, S.F.; Almohana, A.I. Abatement of methylene blue and diazinon pesticide from synthetic solutions using magnetic biochar from pistachio shells modified with MOF-808. Environ. Res. 2025, 267, 120542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Wang, X.; Geng, M.; Chen, D.; Lin, H.; Zhang, H. Catalytic oxidation of clofibric acid by peroxydisulfate activated with wood-based biochar: Effect of biochar pyrolysis temperature, performance and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 374, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ao, Z.; Sun, H.; Duan, X.; Wang, S. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by carbonaceous oxygen groups: Experimental and density functional theory calculations. Appl. Catal. B 2016, 198, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Sun, H.; Ao, Z.; Zhou, L.; Wang, G.; Wang, S. Unveiling the active sites of graphene-catalyzed peroxymonosulfate activation. Carbon 2016, 107, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Korshin, G.; Yang, B. Insights into the mechanism of nonradical reactions of persulfate activated by carbon nanotubes: Activation performance and structure-function relationship. Water Res. 2019, 157, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Huang, X.; Ma, F.; Wang, L.; Duan, X.; Wang, S. Catalytic Removal of Aqueous Contaminants on N-Doped Graphitic Biochars: Inherent Roles of Adsorption and Nonradical Mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8649–8658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Nie, G.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, H.; Duan, X.; Wang, S. The Intrinsic Nature of Persulfate Activation and N-Doping in Carbocatalysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6438–6447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, W.; Xiong, L.; Nie, G.; Zhang, H.; Duan, X.; Wang, S. Insights into the Electron-Transfer Regime of Peroxydisulfate Activation on Carbon Nanotubes: The Role of Oxygen Functional Groups. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, P.; Nanda, S.; Pant, K.; Naik, S.; Kozinski, J.; Dalai, A. Evaluation of the physiochemical development of biochars obtained from pyrolysis of wheat straw, timothy grass and pinewood: Effects of heating rate. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 104, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Břendová, K.; Tlustoš, P.; Száková, J.; Habart, J. Biochar Properties from different materials of plant origin. Eur. Chem. Bull 2012, 1, 535–539. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, N.S.; Jalil, A.A.; Izzuddin, N.M.; Bahari, M.B.; Hatta, A.H.; Kasmani, R.M.; Norazahar, N. Recent advances in lignocellulosic biomass-derived biochar-based photocatalyst for wastewater remediation. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2024, 163, 105670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Xue, J.; Sun, M.; Li, K.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Superefficient non-radical degradation of benzo[a]pyrene in soil by Fe-biochar composites activating persulfate. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 481, 148585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Liu, L.; He, D.; Wu, J.; Yang, W.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Su, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Highly graphitized biochar as nonmetallic catalyst to activate peroxymonosulfate for persistent quinclorac removal in soil through both free and non-free radical pathways. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 148082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, L.; Guo, H.; Yang, Y.Y.; Dong, Z.T.; Wu, Q.; Yi, C.; Niu, G.G.; Yan, M.; Wang, J.J.; Feng, L.S.; et al. Surface electric fields-enhanced biochar: A dual-action adsorbent and PMS activator for sulfamethoxazole removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 358, 130370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohman, G.A.N.; Aziz, M.A.; Nawaz, A.; Elgzoly, M.A.; Hossain, M.M.; Razzak, S.A. High-performance biochar from Chlorella pyrenoidosa algal biomass for heavy metals removal in wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 341, 126870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaeni, J.R.J.; Lim, J.W.; Wang, Z.; Ding, D.; Chua, Y.S.; Ng, S.L.; Oh, W.D. In situ nitrogen functionalization of biochar via one-pot synthesis for catalytic peroxymonosulfate activation: Characteristics and performance studies. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 241, 116702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, W.; Liu, B.; Wu, Q.; Luo, H.; Zhao, Q.; Si, Q.; Sseguya, F.; Ren, N. Edge-nitrogenated biochar for efficient peroxydisulfate activation: An electron transfer mechanism. Water Res. 2019, 160, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Wang, G.; Peng, C.; Tan, J.; Wan, J.; Sun, P.; Li, Q.; Ji, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y.; et al. Recent advances of carbon-based nano zero valent iron for heavy metals remediation in soil and water: A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 127993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, D.W.; Yoon, K.; Ahn, Y.; Sun, Y.; Tsang, D.C.; Hou, D.; Ok, Y.S.; Song, H. Fabrication and environmental applications of multifunctional mixed metal-biochar composites (MMBC) from red mud and lignin wastes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 374, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; How, Z.T.; Huang, Z.; El-Din, M.G. Biochar/iron oxide composite as an efficient peroxymonosulfate catalyst for the degradation of model naphthenic acids compounds. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qin, Y.; Jia, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Pan, Y.; Sun, J. Preparation and application of Fe/biochar (Fe-BC) catalysts in wastewater treatment: A review. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, J.; Yang, Z. Efficient catalytic degradation of alkanes in soil by a novel heterogeneous Fenton catalyst of functionalized magnetic biochar. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Shen, T.; Xu, P.; Wang, J.; Shi, F.; Cao, M.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, G. Exploring the mechanism of norfloxacin removal and active species evolution by coupling persulfate activation with biochar hybridized Fe3O4 composites. Chemosphere 2024, 347, 140666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Shi, Y.; Lv, S.; Liang, Y.; Xiao, P. Peroxymonosulfate activation by tea residue biochar loaded with Fe3O4 for the degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride: Performance and reaction mechanism. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 18525–18538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvaraj, R.; Nagendran, V.; Murugesan, G.; Goveas, L.C.; Varadavenkatesan, T.; Samanth, A.; Vinayagam, R.; Brindhadevi, K. Synthesis of magnetic biochar composite using Vateria indica fruits through in-situ one-pot hydro-carbonization for Fenton-like catalytic dye degradation. Environ. Res. 2024, 250, 118414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayğılı, G.A.; Sayğılı, H. Fabrication of a magnetic hydrochar composite via an in situ one-pot hydrocarbonization strategy for efficient herbicide removal. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2022, 128, 109302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, L.; Zhang, P.; Fan, M.; Xu, X.; Wang, C.; Tang, J.; Sun, H. Efficient degradation of p-nitrophenol by Fe@pomelo peel-derived biochar composites and its mechanism of simultaneous reduction and oxidation process. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 129213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, W.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Xie, X. Activation of peroxymonosulfate with natural pyrite-biochar composite for sulfamethoxazole degradation in soil: Organic matter effects and free radical conversion. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 133895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiao, X.; Liu, N.; Lv, J.; Yang, Y. Enhanced removal of aqueous Cr(VI) by a green synthesized nanoscale zero-valent iron supported on oak wood biochar. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, P.; Zhang, P.; Wang, C.; Jia, H.; Sun, H. Incorporation of N-doped biochar into submicron zero-valent iron for efficient peroxydisulfate activation in soil remediation: Performance and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 482, 148832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, A.; Xiang, M.; Xu, S.; Dong, C.; Chang, Z. Fe3O4 loaded on ball milling biochar enhanced bisphenol a removal by activating persulfate: Performance and activating mechanism. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 319, 115661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xie, L.; Ma, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, T. Ball milling enhanced Cr(VI) removal of zero-valent iron biochar composites: Functional groups response and dominant reduction species. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 137174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Liu, X.; Tang, J.; Zhang, S. Biochar-supported nanosized zero-valent iron (nZVI/BC) composites for removal of nitro and chlorinated contaminants. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tang, J.; Yu, C.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L. Efficient degradation of anthracene in soil by carbon-coated nZVI activated persulfate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 431, 128581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Weng, C.; Bai, W.; Jiao, Y.; Kaegi, R.; Lowry, G.V. Reactivity, Selectivity, and Long-Term Performance of Sulfidized Nanoscale Zerovalent Iron with Different Properties. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 5936–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, J.; Yan, Y.; Ma, R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Shen, Y.; Ullah, H.; Lu, L. Removal of organophosphorus flame retardant by biochar-coated nZVI activating persulfate: Synergistic mechanism of adsorption and catalytic degradation. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 331, 121880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, W.; Tang, Q.; Fan, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, H. Boosting peroxymonosulfate activation with a composite of highly dispersed FeS2 nanoparticles anchored on N-doped biochar for efficient tetracycline degradation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jiang, X.; Xie, R.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Jiang, W. A novel porous biochar-supported Fe-Mn composite as a persulfate activator for the removal of acid red 88. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 250, 117232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Qin, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, P.; Zeng, G. Fe-Mn oxycarbide anchored on N-doped carbon for enhanced Fenton-like catalysis: Importance of high-valent metal-oxo species and singlet oxygen. Appl. Catal. B 2024, 340, 123204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Chen, C.; Huang, Q.; Lu, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, P.; Liang, J.; Hu, H.; Gan, T. Zinc-doped and biochar support strategies to enhance the catalytic activity of CuFe2O4 to persulfate for crystal violet degradation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 38775–38793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J. Magnetic 2D/2D oxygen doped g-C3N4/biochar composite to activate peroxymonosulfate for degradation of emerging organic pollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimian, F.; Lovato, G.; Alvarado-Morales, M.; Ashraf, M.T.; Rodrigues, J.A.D.; Tsapekos, P.; Angelidaki, I. Iron limitation effect on H2/CO2 biomethanation: Experimental and model analysis. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila-Barnard, S.; Dasgupta, S.; Cheng, V.; Reddam, A.; Wiegand, J.L.; Volz, D.C. Tris (1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate disrupts the trajectory of cytosine methylation within developing zebrafish embryos. Environ. Res. 2022, 211, 1113078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Li, D.; Lei, X.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yan, Q.; Wang, J.; He, G. H2O brace molecules to slip stack: Transform ACQ to AIE for latent fingerprints recognition. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 137933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, H.; Cao, S.; Guo, W.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Guo, C.; Chen, G.; Chang, B.; Bai, Y.; et al. Reversible anionic redox and spinel-layered coherent structure enable high-capacity and long-term cycling of Li-rich cathode. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Cantor, J.F.; Gimello, O.; Guerrero-Fajardo, C.-A.; Di Renzo, F.; Petitjean, H.; Riviere, M.; Gérardin, C.; Tanchoux, N. Synthesis of alkyl-branched fatty acids by isomerization on micro-mesoporous ferrierite-based zeolitic materials. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2024, 344, 123602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.T.; Li, T.; Deng, S.K.; Spain, J.C.; Zhou, N.Y. A cytochrome P450 system initiates 4-nitroanisole degradation in Rhodococcus sp. strain JS3073. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 458, 131886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Yan, Q.; Liu, Q.; Li, D.; Chen, Y.; He, G. Bright green emission non-conjugated polymer dots: pH trigged hydrogel for specific adsorption of anionic dyes and visual detection of tert-butylhydroquinone. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 292, 121023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.C. Selective laser melting manufactured porous Fe-based metallic glass matrix composite with remarkable catalytic activity and reusability. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 19, 100543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchi, F.S.; Ambrosetti, M.; Balzarotti, R.; Bracconi, M.; Groppi, G.; Tronconi, E. Rich H2 catalytic oxidation as a novel methodology for the evaluation of mass transport properties of 3D printed catalyst supports. Catal. Today 2022, 383, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Jing, L.; Wang, T.; Kong, X.; Quan, R.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, R.; Zhu, H. Multi-level porous layered biochar modified cobalt-iron composite as a reusable synergistic activator of peroxymonosulfate for enhanced tetracycline degradation. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2022, 132, 104209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Shao, B.; Yan, M.; Liu, Z.; Liang, Q.; He, Q.; Wu, T.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Huang, J.; et al. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by biochar-based catalysts and applications in the degradation of organic contaminants: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 416, 128829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Sun, Z.; Zhen, Y.; Zhu, S.; Yang, C.; Lu, J.; Tian, Y.; Zhong, D.; Ma, J. Oxygen Vacancy-Induced Nonradical Degradation of Organics: Critical Trigger of Oxygen (O2) in the Fe–Co LDH/Peroxymonosulfate System. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 15400–15411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.B.; Dai, C.; Wang, Z.; You, X.; Duan, Y.; Lai, X.; Fu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Maimaitijiang, M.; Leong, K.H.; et al. Resource utilization of rice straw to prepare biochar as peroxymonosulfate activator for naphthalene removal: Performances, mechanisms, environmental impact and applicability in groundwater. Water Res. 2023, 244, 120555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Ai, L.; Ran, J.; Tu, S.; Liu, A.; Jiang, J. Two-dimensional MBene combined with cobalt nanoparticles enabling highly efficient peroxymonosulfate activation for ornidazole degradation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 128647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cai, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, S.; Luo, F.; Yang, L.; Yu, J.; Chi, R.; Chen, Z. Accelerating of Fe2+ regeneration in Fenton reaction by biochar: Pivotal roles of carbon defects as electron donor and shuttle. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 128945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, D.; Bai, X. Binary MOFs-derived Mn-Co3O4 for efficient peroxymonosulfate activation to remove sulfamethoxazole: Oxygen vacancy-assisted high-valent cobalt-oxo species generation. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 479, 147886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, S.; Sun, Y.; Qian, J. Discerning the Relevance of Singlet Oxygen in Pollutant Degradation in Peroxymonosulfate Activation Processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 14005–14012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Liu, L.; Li, W.; Lan, Y.; Li, Y. Reutilization of waste self-heating pad by loading cobalt: A magnetic and green peroxymonosulfate activator for naphthalene degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 439, 129572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhan, J.; Yu, G.; Wang, Y. Assessment of the validity of the quenching method for evaluating the role of reactive species in pollutant abatement during the persulfate-based process. Water Res. 2022, 221, 118730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Yu, Y.; Lei, X.; Liang, X.; Cheng, S.; Ouyang, G.; Yang, X. Assessing the Use of Probes and Quenchers for Understanding the Reactive Species in Advanced Oxidation Processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 5433–5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Hou, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Hao, Y. MOF-derived CuCo carbon microspheres assembled with nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes as PMS activator for the efficient degradation of p-nitrophenol. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 129107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xiong, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, Y.; Qian, Y.; Lai, B. Iron active sites encapsulated in N-doped graphite for efficiently selective degradation of emerging contaminants via peroxymonosulfate (PMS) activation: Inherent roles of adsorption and electron-transfer dominated nonradical mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 444, 136623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Cai, Y.; Wang, S. Peroxymonosulfate-activated molecularly imprinted bimetallic MOFs for targeted removal of PAHs and recovery of biosurfactants from soil washing effluents. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 443, 136412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Kang, W.; Li, T.; Wang, H. Plant Polyphenol-Driven Polymerization-Confinement Strategy toward Ultrahighly Loaded Atomically Dispersed FeCo Bimetallic Catalysts for Singlet Oxygen-Dominated Fenton-like Reactions. ACS ES&T Eng. 2024, 4, 2263–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wei, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, P.; Yao, G.; Liu, Y.; Lai, B.; Song, Y. CoFe2O4@BC as a heterogeneous catalyst to sustainably activate peroxymonosulfate for boosted degradation of enrofloxacin: Properties, efficiency and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 345, 127349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Gong, H.; Fu, K.; Jia, J.; Zhu, N. Overcoming metals redox rate limitations in spinel oxide-driven Fenton-like reactions via synergistic heteroatom doping and carbon anchoring for efficient micropollutant removal. Water Res. 2024, 261, 122020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Ren, X.; Zhao, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, X.; Song, X.; Li, X.; Liu, B.; Xiong, Z.; Lai, B. Modulating Electronic Structure Engineering of Atomically Dispersed Cobalt Catalyst in Fenton-like Reaction for Efficient Degradation of Organic Pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 14071–14081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, Z.; He, S.; Shi, L.; Guo, K.; Fang, J. Reinvestigation on High-Valent Cobalt for the Degradation of Micropollutants in the Co(II)/Peroxymonosulfate System: Roles of Co(III). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 3564–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Fu, K.; Fu, Y.; Liu, X.; Luo, S.; Yin, K.; Luo, J. Manipulating High-Valent Cobalt-Oxo Generation on Co/N Codoped Carbon Beads via PMS Activation for Micropollutants Degradation. ACS ES&T Eng. 2023, 3, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wen, X.; Lang, J.; Wei, Y.; Miao, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, B.; Long, M.; Alvarez, P.J.J.; Zhang, L. CoN1O2 Single-Atom Catalyst for Efficient Peroxymonosulfate Activation and Selective Cobalt(IV)=O Generation. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2023, 135, e202303267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valizadeh, B.; Ashtiani, F.Z.; Fouladitajar, A.; Dabir, B.; Baraghani, S.S.M.; Armand, S.B.; Salari, B.; Kouchakiniya, N. Scale-up economic assessment and experimental analysis of MF–RO integrated membrane systems in oily wastewater treatment plants for reuse application. Desalination 2015, 347, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.U.; Asghar, M.; Rauf, A.; Najam, T.; Shaaban, I.A.; Shah, S.S.A.; Nazir, M.A. MOF/Graphene interfaces in catalytic water splitting: Recent breakthroughs and future outlook. Fuel 2026, 405, 136800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, W.; Xu, X.; Zhan, C.; Lu, W.; Jia, D.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Gan, F.; Li, M. Recent advances of antibiotics degradation in different environment by iron-based catalysts activated persulfate: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 103075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalenbach, M.; Kasian, O.; Ledendecker, M.; Speck, F.D.; Mingers, A.M.; Mayrhofer, K.J.; Cherevko, S. The electrochemical dissolution of noble metals in alkaline media. Electrocatalysis 2018, 9, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanaik, A.; Sukla, L.B.; Pradhan, D.; Samal, D.K. Microbial mechanism of metal sulfide dissolution. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 30, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikawa, S.; Minamimoto, H.; Li, X.; Murakoshi, K. Nanoscale control of plasmon-active metal nanodimer structures via electrochemical metal dissolution reaction. Nanotechnology 2017, 29, 045702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niinipuu, M.; Bergknut, M.; Boily, J.F.; Rosenbaum, E.; Jansson, S. Influence of water matrix and hydrochar properties on removal of organic and inorganic contaminants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 30333–30341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Noh, J.H.; Park, J.W.; Yoon, S.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Son, H.J.; Lee, W.; Maeng, S.K. Integrating biological ion exchange with biological activated carbon treatment for drinking water: A novel approach for NOM removal, trihalomethane formation potential, and biological stability. Water Res. 2023, 245, 120598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, G.; Chen, B.; Lin, W.; Zhang, B. 3D-QSAR-aided toxicity assessment of synthetic musks and their transformation by-products. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 557530–557542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samy, M.; Mensah, K.; Alalm, M.G. A review on photodegradation mechanism of bio-resistant pollutants: Analytical methods, transformation products, and toxicity assessment. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 1033351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulenburg, H.; Stankov, S.; Schünemann, V.; Radnik, J.; Dorbandt, I.; Fiechter, S.; Bogdanoff, P.; Tributsch, H. Catalysts for the oxygen reduction from heat-treated iron (III) tetramethoxyphenylporphyrin chloride: Structure and stability of active sites. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 9034–9041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berahim, N.H.; Zabidi, N.A.M.; Ramli, R.M.; Suhaimi, N.A. The Activity and Stability of Promoted Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 Catalyst for CO2 Hydrogenation to Methanol. Processes 2023, 11, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghogia, A.C.; Durupt, A.; Guicheret, B.; Cayez, S.; Machado, B.F.; Soulantica, K.; Serp, P.; Philippe, R.; Minh, D.P. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis on carbon-supported Co catalysts coated on metallic foams. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 114, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Preparation Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| One-step pyrolysis | Easy to operate and highly controllable | Limitations, high equipment requirements, more impurities |
| Co-precipitation | Highly controllable and homogeneous active site | More impurities, longer time spent |
| Hydrothermal carbonization | Gentle and environmentally friendly conditions | High equipment requirements and low yield |
| Green synthesis | Environmentally friendly, highly sustainable, low toxicity | Low throughput and poor repeatability |
| Ball milling | Easy handling, homogeneous active site | Poor controllability, easy to destroy the original structure |
| Chemical reduction | Material homogeneity, controllability, efficient synthesis | High cost of reducing agents, environmental hazards |
| Catalyst Class | Typical Strengths (Bench Scale) | Practical Limitations | Scalability and Field Applicability (Assessment) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monometallic Fe–biochar | High removal (>90%) for many organics; low cost; simple one-step pyrolysis routes | Fe leaching at low pH; faster decay in real waters; sometimes lower mineralization | High scalability (simple synthesis), moderate field readiness if leaching is controlled and non-radical pathways are present |
| Bimetallic/multimetallic Fe–M–biochar | Faster Fe(III)/Fe(II) cycling; lower oxidant demand; better cyclic stability | More complex synthesis; dopant cost; need to monitor secondary metals | Moderate–high scalability (co-pyrolysis/impregnation possible), good field potential with stable Fe/M binding and reuse ≥5 cycles |
| Composites | Highest activity/mineralization; non-radical selectivity; strong matrix tolerance | Multi-step fabrication; yield and cost penalties | Moderate scalability (requires process optimization), high field promise for recalcitrant pollutants/complex matrices |
| Component | Typical Range or Consideration | Economic Implication | Recommended Optimization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Feedstock | Agricultural or forestry waste, 0–50 USD t−1 | Low cost; supply chain stability critical | Prioritize local biomass sources |
| Energy input | Pyrolysis 400–800 °C | Dominant cost contributor | Moderate temperature, waste-heat recovery |
| Iron precursor | FeCl3, Fe(NO3)3, FeSO4 (0.2–1.0 USD kg−1) | Moderate; scalable | Recycle iron-containing wastewater |
| Activation agents | KOH, H3PO4, etc. | Costly and corrosive | Explore physical activation or one-pot synthesis |
| Catalyst recovery | Magnetic separation or filtration | Low cost per reuse | Design for magnetic recyclability |
| Comparison with homogeneous Fenton | Requires pH ≈ 3, generates sludge | Biochar avoids excess sludge | Emphasize stability and reusability |
| Stability Factor | Underlying Cause | Evaluation Method | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Iron leaching | Weak Fe–C interaction; acidic pH; valence cycling | ICP-OES/MS for dissolved Fe per cycle; total Fe elution over ≥5 cycles | Graphitic encapsulation; Fe3O4/Fe2O3 crystallization; sulfidation (FeSx stabilization) |
| Surface fouling | Adsorption of NOM, carbonate, chloride, or reaction intermediates | FTIR/XPS before/after cycles; TGA for carbonaceous deposits | Pre-filtration; periodic regeneration |
| Structural degradation | Breakage of carbon matrix under mechanical or chemical stress | SEM/TEM imaging after reuse; BET analysis | Pelletization; binder; magnetic recovery to limit abrasion |
| Oxidant overuse | Excess PMS/H2O2 generating ROS attack on catalyst itself | Adsorption capacity/reduction in BET area over time | Optimize oxidant dosage; promote non-radical pathways |
| Redox fatigue | Fe(III)/Fe(II) cycling imbalance; insufficient electron supply | XPS Fe 2p or Fe K-edge XANES before/after cycles | Introduce electron mediators |
| Mechanical attrition | Stirring, fluidization, abrasion losses | Mass balance; size distribution analysis; wet sieving | Use of magnetic Fe-biochar for rapid collection; integration into fixed-bed reactors |
| pH instability | Operating at low or fluctuating pH | Measure pH trend during cycles; correlate with Fe release | Design for neutral-pH operation (photo-Fenton, non-radical pathways) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Zhang, D.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, B.; Sun, L. Progress in the Application of Iron-Based Plant Derived Biochar Catalyst for Fenton-like Remediation of Organic Wastewater: A Review. Molecules 2025, 30, 4549. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234549
Wang X, Zhang D, Cheng Y, Wu B, Sun L. Progress in the Application of Iron-Based Plant Derived Biochar Catalyst for Fenton-like Remediation of Organic Wastewater: A Review. Molecules. 2025; 30(23):4549. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234549
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiao, Dongqing Zhang, Yan Cheng, Binkui Wu, and Lanyi Sun. 2025. "Progress in the Application of Iron-Based Plant Derived Biochar Catalyst for Fenton-like Remediation of Organic Wastewater: A Review" Molecules 30, no. 23: 4549. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234549
APA StyleWang, X., Zhang, D., Cheng, Y., Wu, B., & Sun, L. (2025). Progress in the Application of Iron-Based Plant Derived Biochar Catalyst for Fenton-like Remediation of Organic Wastewater: A Review. Molecules, 30(23), 4549. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234549





