-
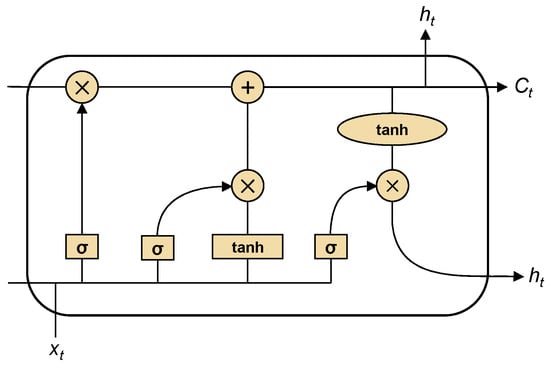
 Who Wins the Energy Race? Artificial Intelligence for Smarter Energy Use in Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Who Wins the Energy Race? Artificial Intelligence for Smarter Energy Use in Logistics and Supply Chain Management -
 A Critical Review of Green Hydrogen Production by Electrolysis: From Technology and Modeling to Performance and Cost
A Critical Review of Green Hydrogen Production by Electrolysis: From Technology and Modeling to Performance and Cost -
 A Large Eddy Simulation-Based Power Forecast Approach for Offshore Wind Farms
A Large Eddy Simulation-Based Power Forecast Approach for Offshore Wind Farms -
 Integrating Fish-Friendly Hydropower Solutions with the Nature Restoration Policy Through River Barrier Modification
Integrating Fish-Friendly Hydropower Solutions with the Nature Restoration Policy Through River Barrier Modification -
 Biogas Production in Agriculture: Technological, Environmental, and Socio-Economic Aspects
Biogas Production in Agriculture: Technological, Environmental, and Socio-Economic Aspects
Journal Description
Energies
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), Ei Compendex, RePEc, Inspec, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q1 (Control and Optimization)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 16.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Sections: published in 41 topical sections.
- Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about Energies.
- Companion journals for Energies include: Energy Storage and Applications and Bioresources and Bioproducts.
- Journal Cluster of Energy and Fuels: Energies, Batteries, Hydrogen, Biomass, Electricity, Wind, Fuels, Gases, Solar, ESA and Methane.
Latest Articles
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Deadline: 28 February 2026
Deadline: 10 March 2026
Deadline: 20 March 2026
Deadline: 31 March 2026
Conferences
Special Issues
Deadline: 5 February 2026
Deadline: 5 February 2026
Deadline: 5 February 2026
Deadline: 5 February 2026