- Review
Economic and Optimisation Modelling of Energy Storage Systems: A Review
- Andrew J. Hutchinson,
- Chris M. Harrison and
- Andrew Forsyth
- + 7 authors
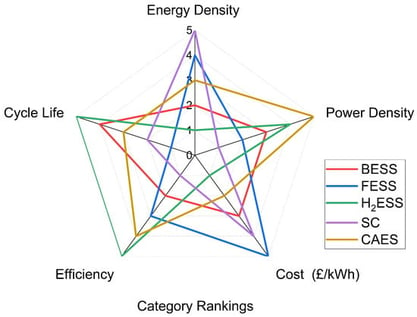
Demand for new solutions to emerging issues faced by the electricity generation, demand and supply industries continues to increase with the introduction of increasing proportions of variable renewable energy and changing system demands. Energy storage systems represent a key part of the solution as stakeholders attempt to move towards a ‘net zero’ system. Within research, studies into the techno-economic optimisation of varied energy storage technologies for different applications continue to play a significant role in this changing landscape. A key aspect of this research is the modelling and simulation of such systems, often with the goal of optimising their parameters for deploying in specific roles and services. This paper presents an extensive analysis of the current economic outlook for five major energy storage technologies, highlighting the significant variation in quoted costs within the literature. It presents a unique and novel perspective by considering economic and optimisation modelling from both a technology and application-centric approach. It explores the different approaches available for performing economic analysis on energy storage systems, providing a novel overview of the advantages of various approaches along with examples from the literature on how these studies are implemented. Finally, the paper explores optimisation studies, giving an in-depth explanation of different approaches used in the optimisation of energy storage systems and reviewing prominent uses within the literature. The paper concludes with a consideration of the main challenges that face the field of techno-economic energy storage studies and provides recommendations on areas that require further research.
28 February 2026