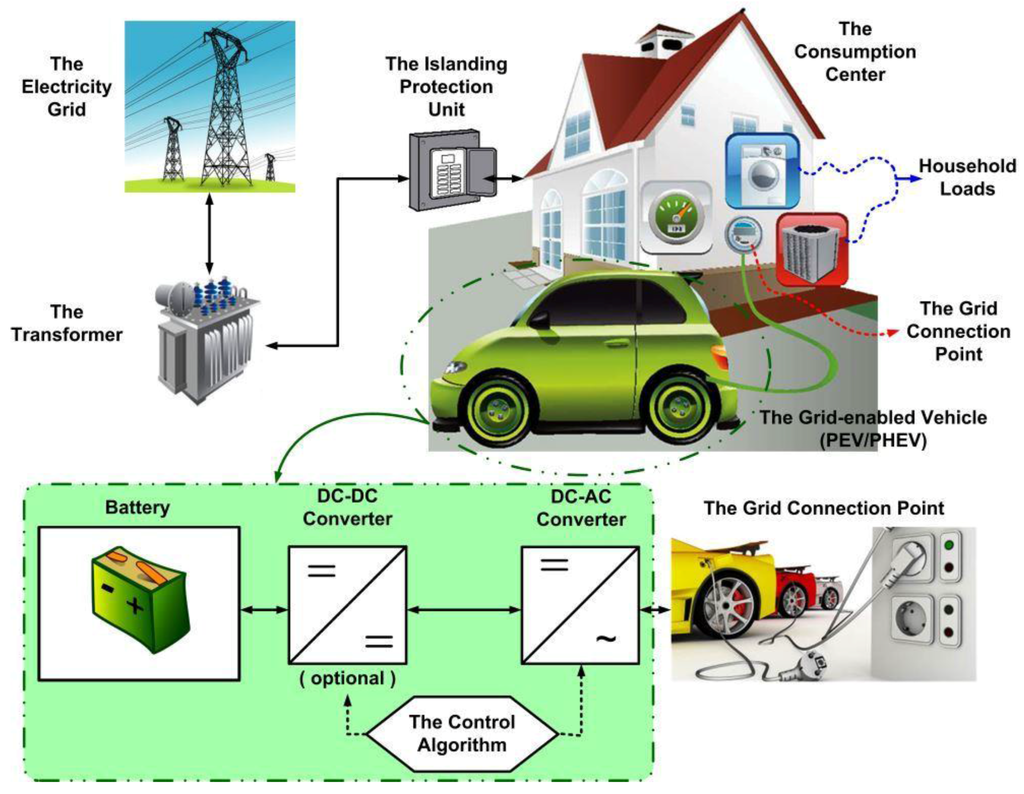
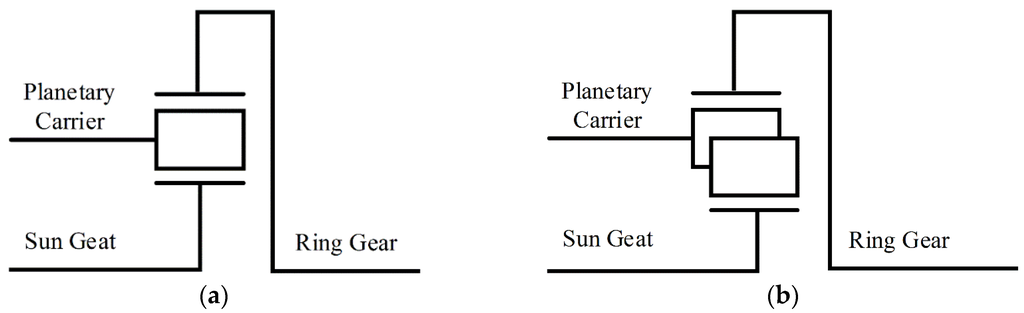
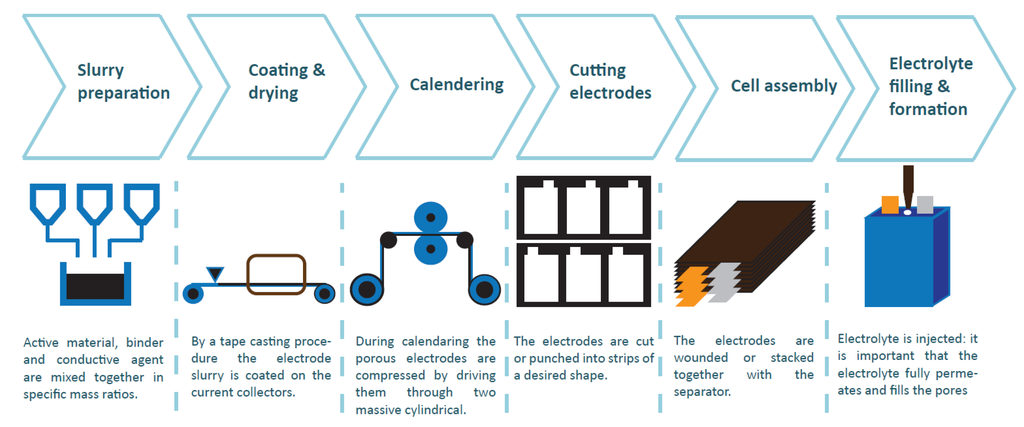
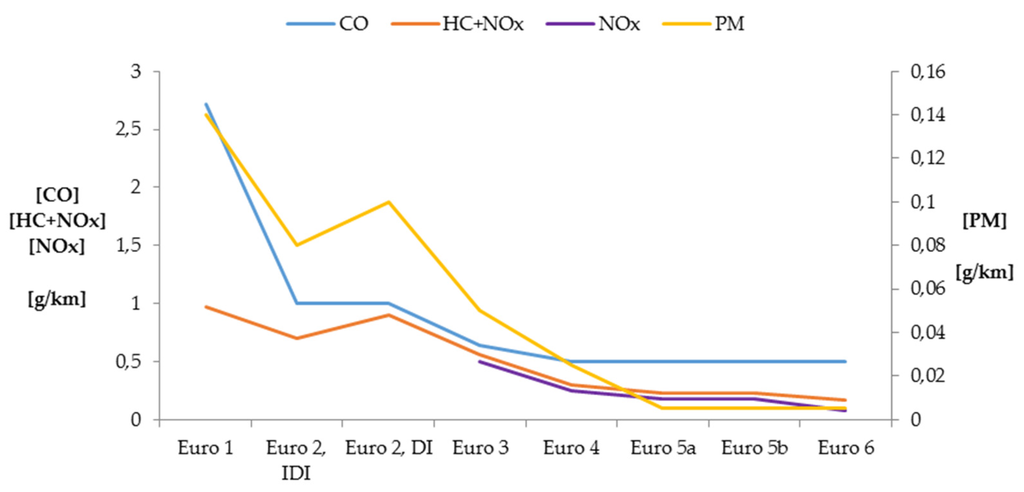
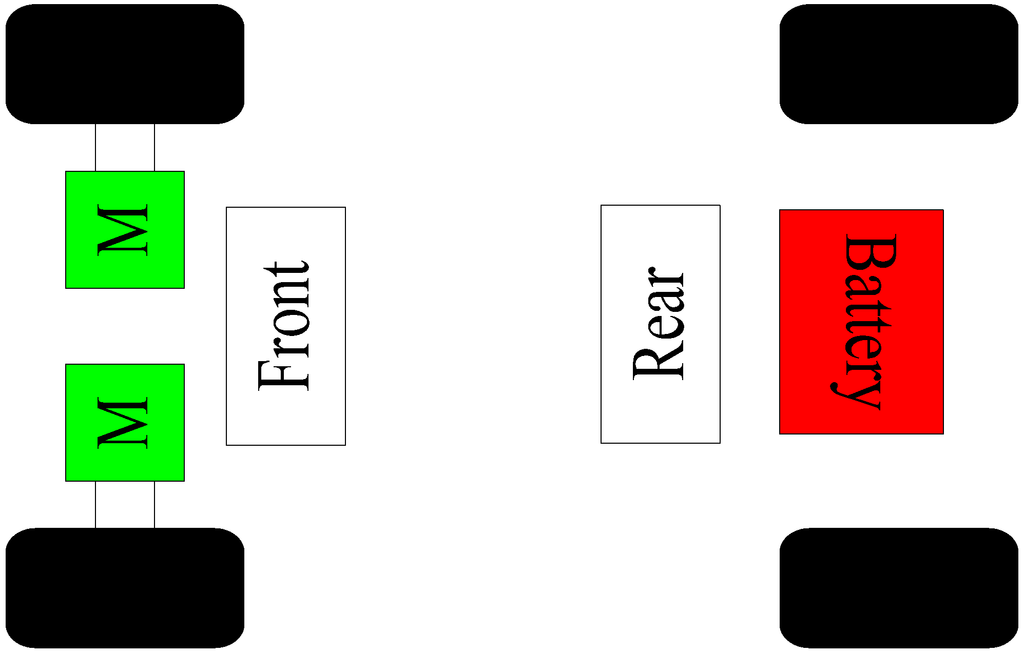
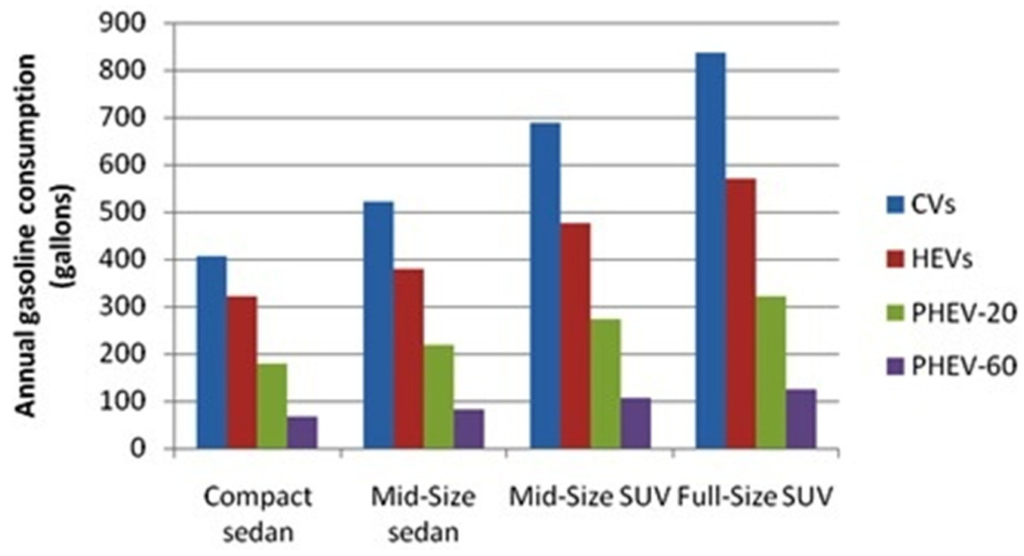
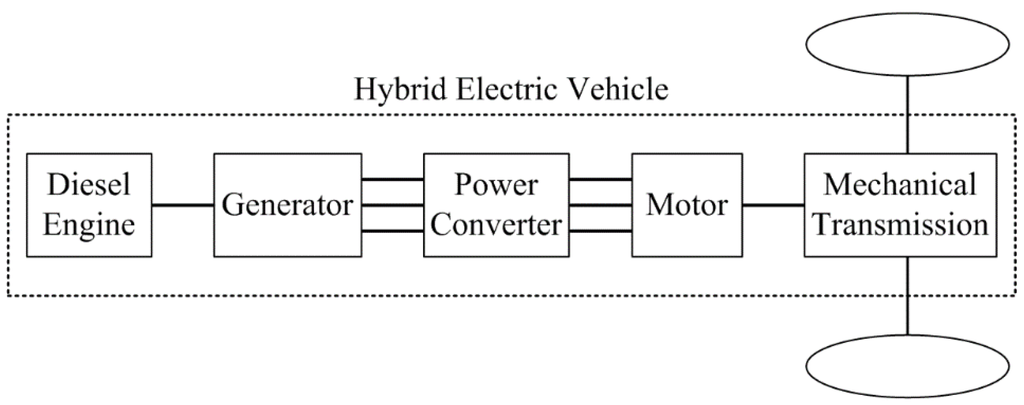
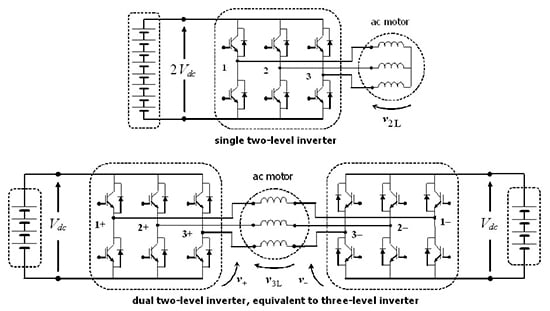
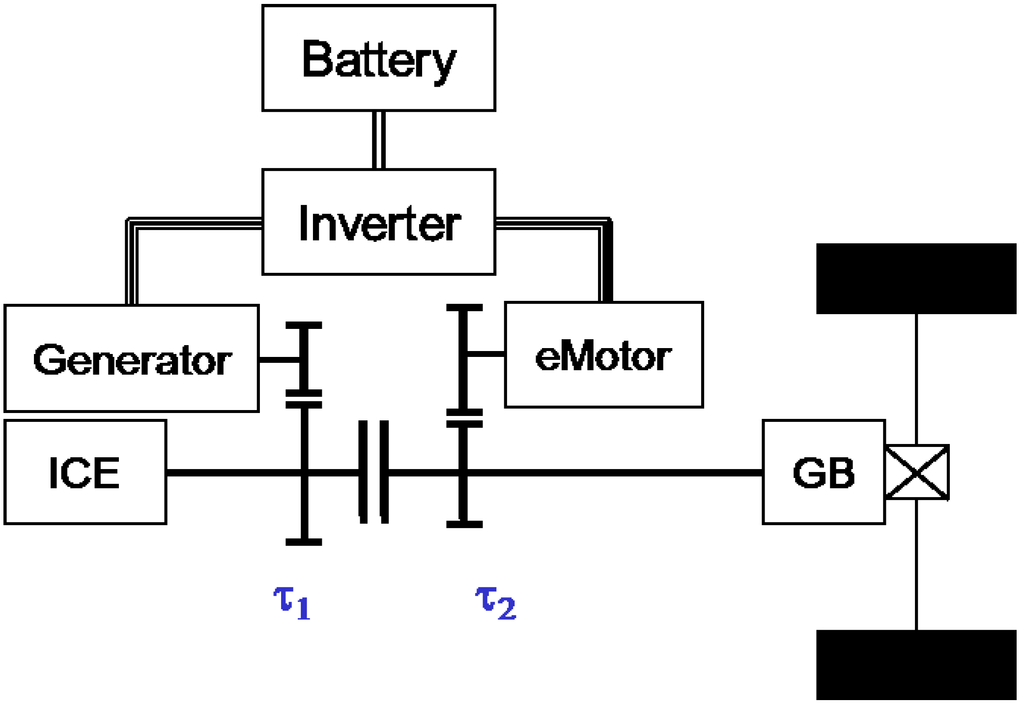
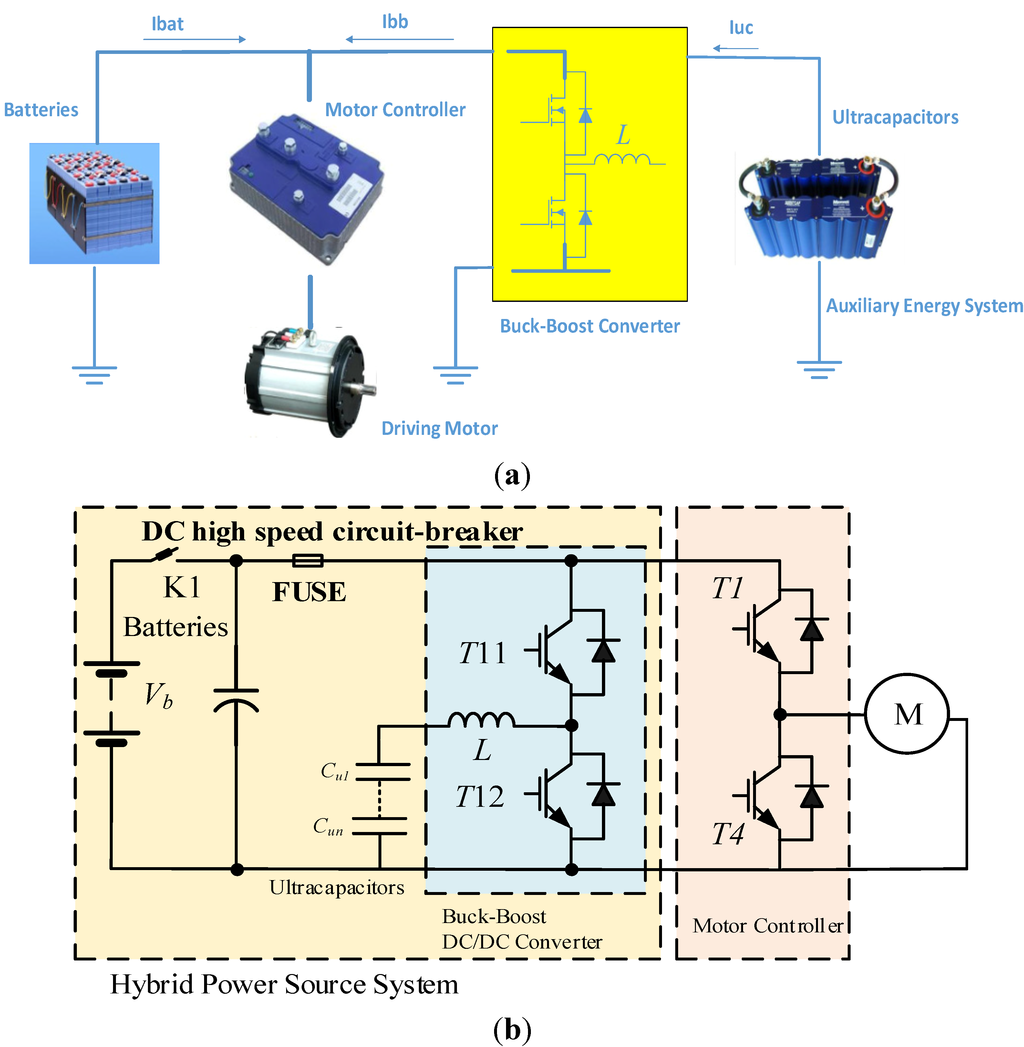
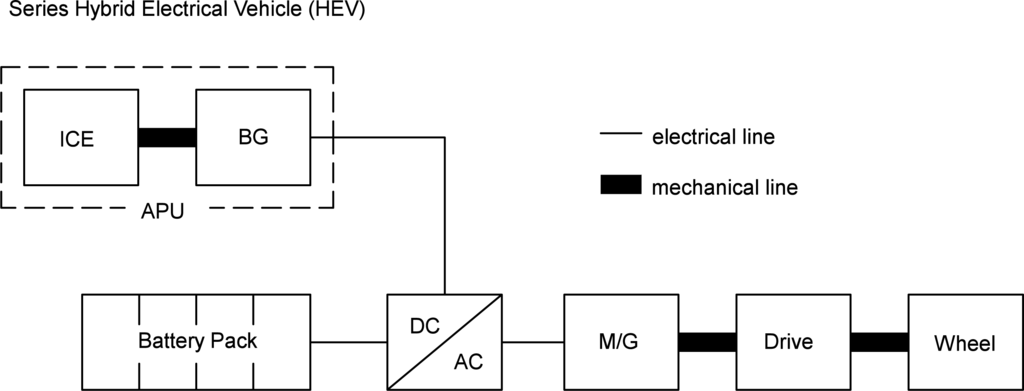
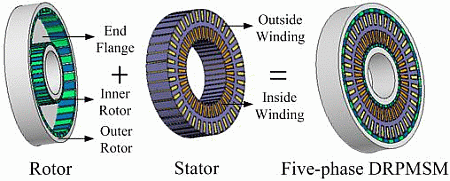
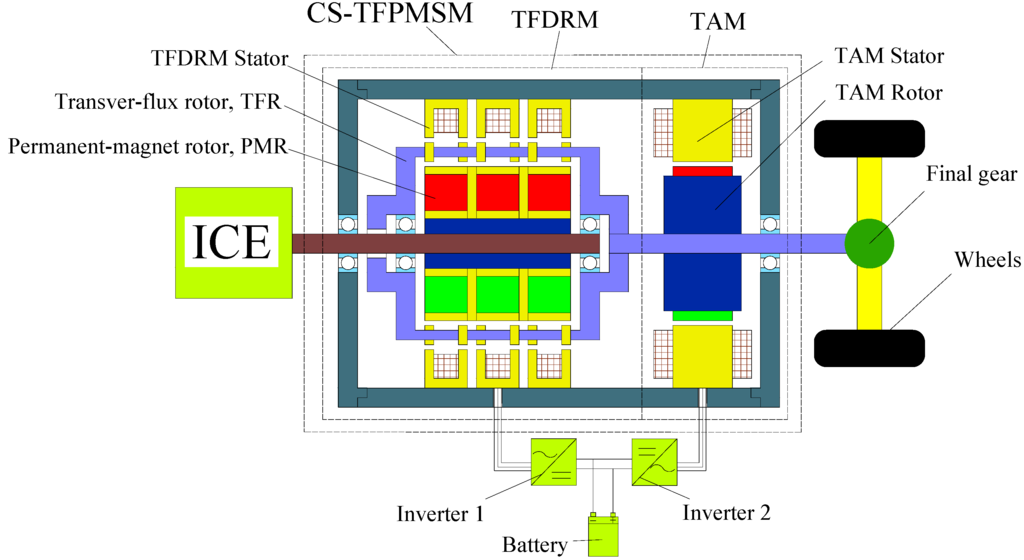
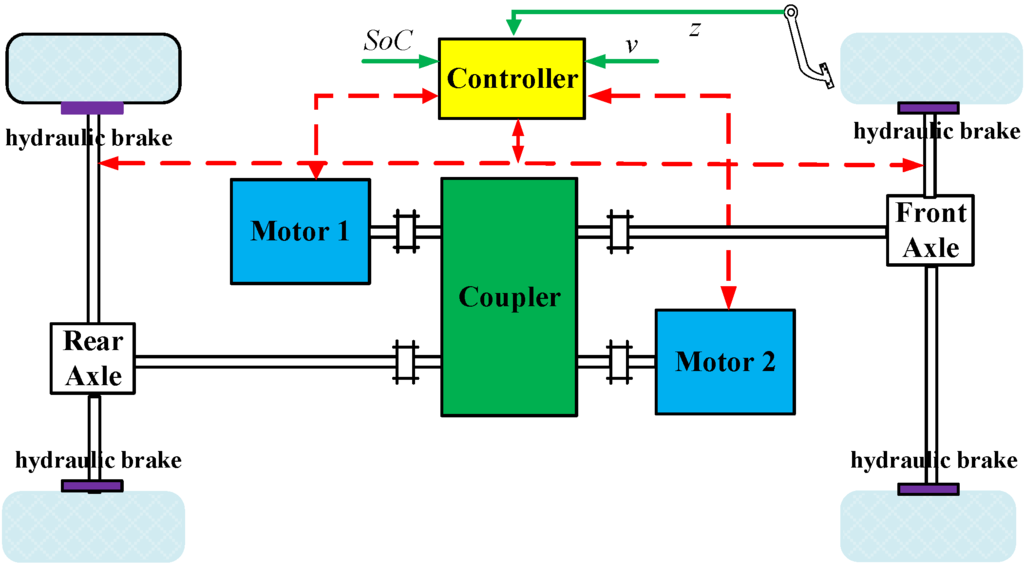
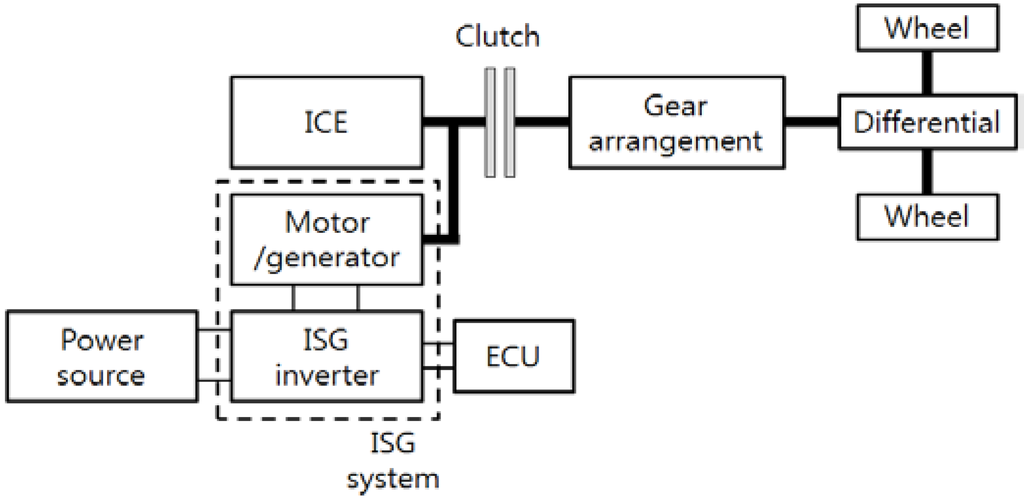
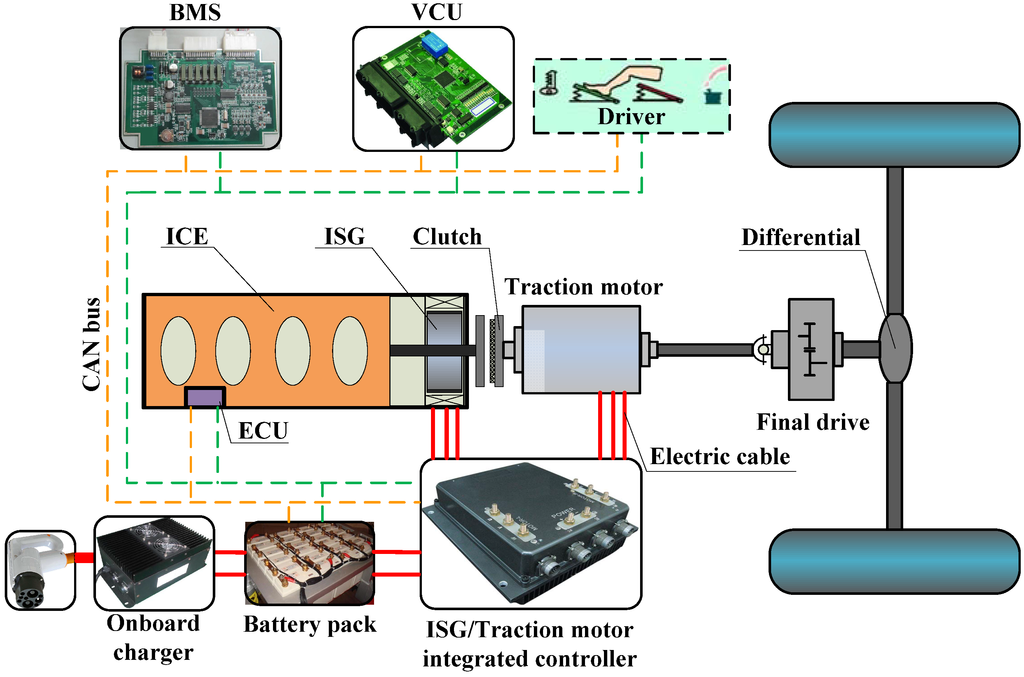
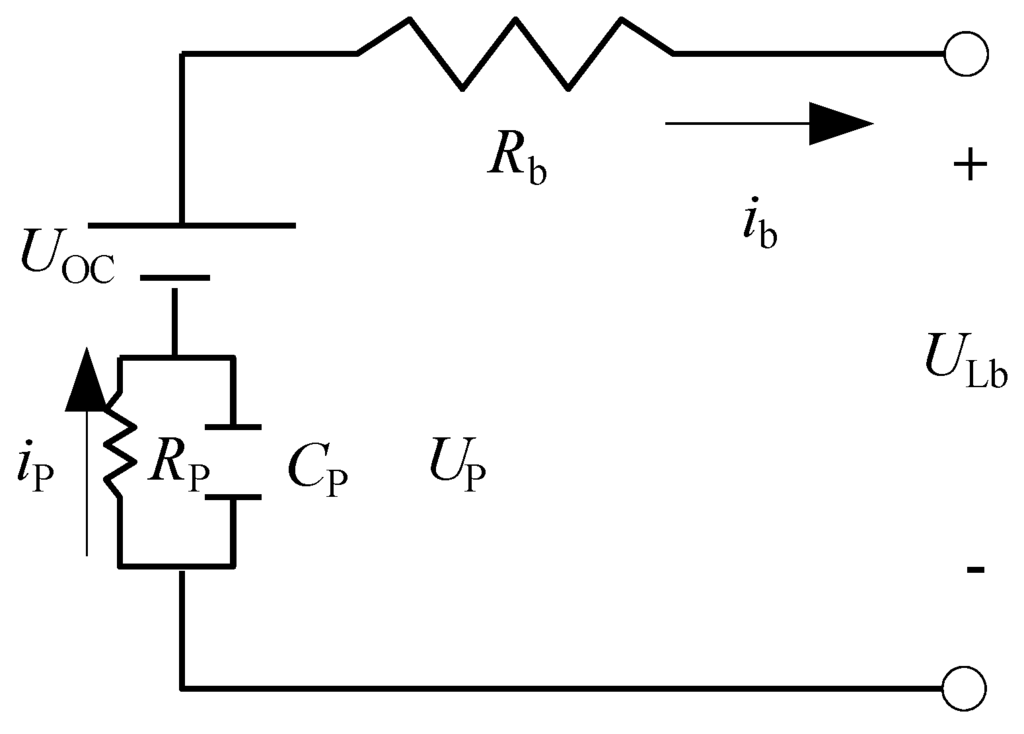
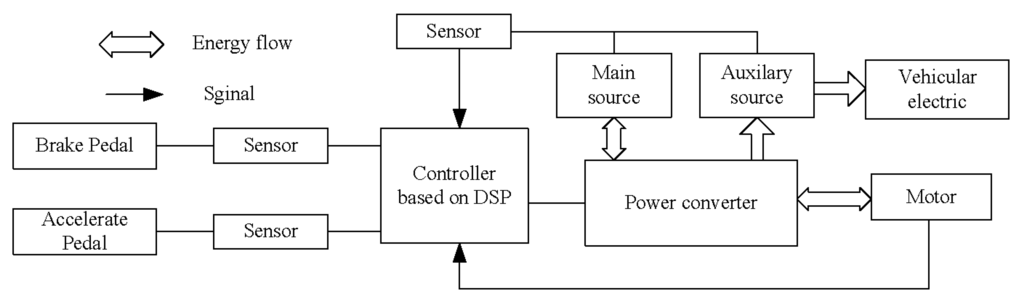
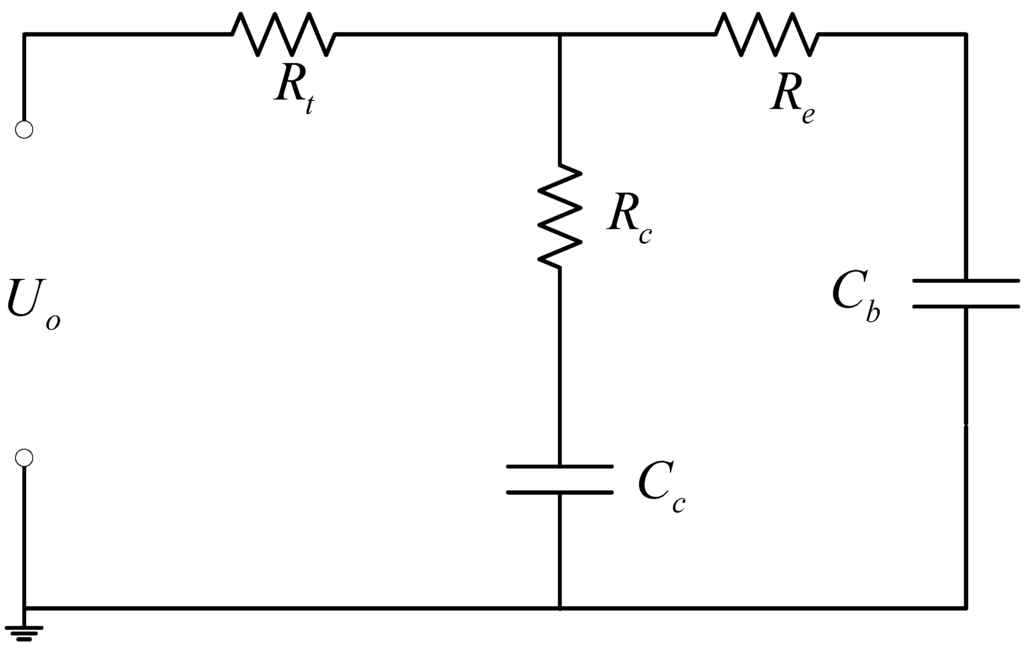
Electric and Hybrid Vehicles Collection
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Prof. Dr. Kwok Tong Chau
Prof. Dr. Kwok Tong Chau
 Prof. Dr. Kwok Tong Chau
Prof. Dr. Kwok Tong Chau
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, China
Interests: electric vehicle technologies; renewable energy systems; machines and drives; power electronics
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
In a world where energy conservation, environmental protection and sustainable development are growing concerns, the development of electric vehicle (EV) and hybrid EV (HEV) technologies has taken on an accelerated pace. This collection entitled “Electric and Hybrid Vehicles” invites articles that address the state-of-the-art technologies and new developments for EVs and HEVs, including but not limited to energy sources, electric powertrains, hybrid powertrains, energy management systems, energy refueling systems, regenerative braking systems, system integration, system optimization and infrastructure. Articles which deal with the latest hot topics for EVs and HEVs are particularly encouraged such as advanced lithium-ion batteries, ultracapacitors, energy-efficient motor drives, bidirectional power converters, integrated-starter-generator systems, electric variable transmission systems, on-board renewable energy, inductive or wireless charging technology, and vehicle-to-grid technology. As the impact of the use of EVs and HEVs on our daily lives is utmost important, articles which deal with the relationships between the use of EVs or HEVs and the energy, environment and economy would be of particular interest.
Prof. Dr. K.T. Chau
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts for the topical collection can be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. All papers will be peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on this website. The topical collection considers regular research articles, short communications and review articles. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The article processing charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss francs).
Related Special Issues
Published Papers (168 papers)
Open AccessArticle
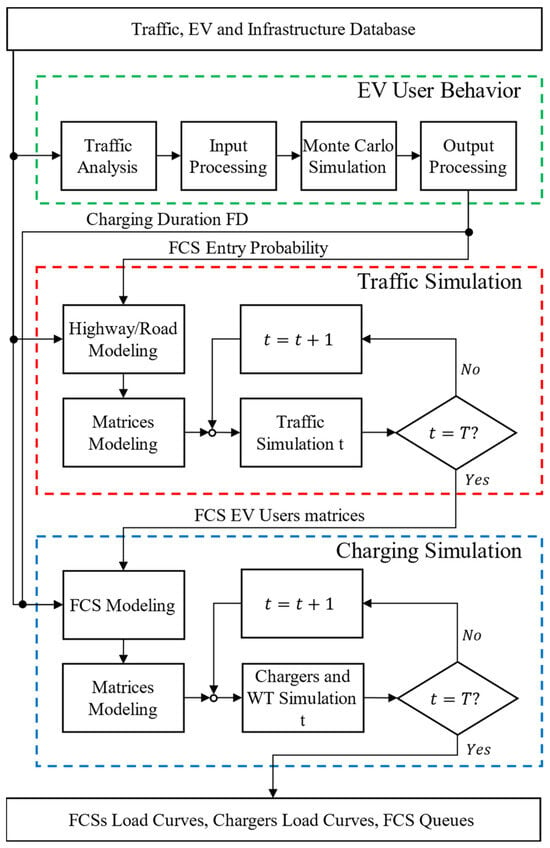
A Stochastic Methodology for EV Fast-Charging Load Curve Estimation Considering the Highway Traffic and User Behavior
by
Leonardo Nogueira Fontoura da Silva, Marcelo Bruno Capeletti, Alzenira da Rosa Abaide and Luciano Lopes Pfitscher
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 2179
Abstract
The theoretical impact of the electric vehicle (EV) market share growth has been widely discussed with regards to technical and socioeconomic aspects in recent years. However, the prospection of EV scenarios is a challenge, and the difficulty increases with the granularity of the
[...] Read more.
The theoretical impact of the electric vehicle (EV) market share growth has been widely discussed with regards to technical and socioeconomic aspects in recent years. However, the prospection of EV scenarios is a challenge, and the difficulty increases with the granularity of the study and the set of variables affected by user behavior and regional aspects. Moreover, the lack of a robust database to estimate fast-charging stations’ load curves, for example, affects the quality of planning, allocation, or grid impact studies. When this problem is evaluated on highways, the challenge increases due to the reduced number of trips related to the reduced number of charger units installed and the limited EVs range, which influence user anxiety. This paper presents a methodology to estimate the highway fast-charging station operation condition, considering regional and EV user aspects. The process is based in a block of traffic simulation, considering the traffic information and highway patterns composing the matrix solution model. Also, the output block estimates charging stations’ operational conditions, considering infrastructure scenarios and simulated traffic. A Monte Carlo simulation is presented to model entrance rates and charging times, considering the PDF of stochastic inputs. The results are shown for the aspects of load curve and queue length for one case study, and a sensibility study was conducted to evaluate the impact of model inputs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Substation Placement for Electric Road Systems
by
Niklas Jakobsson, Elias Hartvigsson, Maria Taljegard and Filip Johnsson
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2827
Abstract
One option to avoid range issues for electrified heavy vehicles, and the large individual batteries for each such vehicle, is to construct electric road systems (ERS), where vehicles are supplied with electricity while driving. In this article, a model has been developed that
[...] Read more.
One option to avoid range issues for electrified heavy vehicles, and the large individual batteries for each such vehicle, is to construct electric road systems (ERS), where vehicles are supplied with electricity while driving. In this article, a model has been developed that calculates the cost for supplying an ERS with electricity from a regional grid to a road in the form of cables and substations, considering the power demand profile for heavy transport. The modeling accounts for electric losses and voltage drop in cables and transformers. We have used the model to exhaustively compute and compared the cost of different combinations of substation sizes and locations along the road, using a European highway in West Sweden as a case study. Our results show that the costs for building an electricity distribution system for an ERS vary only to a minor extent with the location of substations (10% difference between the cheapest cost and the average cost of all configurations). Furthermore, we have varied the peak and average power demand profile for the investigated highway to investigate the impact of a specific demand profile on the results. The results from this variation show that the sum of the peak power demand is the most important factor in system cost. Specifically, a 30% change in the peak power demand for the road has a significant impact on the electricity supply system cost. A reduction in the geographical variation of power demand along the road has no significant impact on the electricity distribution system cost as long as the aggregated peak power demand for all road segments is held constant. The results of the work are relevant as input to future work on comparing the cost–benefit of ERS with other alternatives when reducing CO
2 from road traffic—in particular from heavy road traffic.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Research on Oil Mist Leakage of Bearing in Hydropower Station: A Review
by
Jie Sun, Yuquan Zhang, Bin Liu, Xinfeng Ge, Yuan Zheng and Emmanuel Fernandez-Rodriguez
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 7408
Abstract
Hydropower is a clean and renewable energy, fundamental to the attainment of a sustainable society. Despite its efficacy and success, there is a need to address the hydroelectric stations’ oil throwing and mist leakage, resulting in the deterioration of the generating units, water,
[...] Read more.
Hydropower is a clean and renewable energy, fundamental to the attainment of a sustainable society. Despite its efficacy and success, there is a need to address the hydroelectric stations’ oil throwing and mist leakage, resulting in the deterioration of the generating units, water, and biodiversity. The conventional engineering measures to deal with oil mist leakage include: the reduction in the operating pad and oil temperature, optimization of the oil circulation loop in the oil tank, improvement of the sealing performance, and design of the oil mist emission device. However, the problem of oil mist leakage of bearings is complex, intractable, and cannot be solved by only one method. Numerical simulation can help to solve the oil mist problem and make up for the shortage of engineering measures. Yet, the mass transfer, involving multi-component and multi-phase flow, becomes a limitation for many numerical studies. As a result, this paper seeks to integrate the solutions by reviewing two influences: the global measures of oil mist leakage proof in the oil tank of bearings in the past 40 years, and the views and experiences of engineering practices. These findings offer some relevant insights into the effectiveness of the applied methods and solving of the oil mist leakage problem.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Real-Time Optimal Car-Following Power Management Strategy for Hybrid Electric Vehicles with ACC Systems
by
Xiaobo Sun, Weirong Liu, Mengfei Wen, Yue Wu, Heng Li, Jiahao Huang, Chao Hu and Zhiwu Huang
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 3316
Abstract
This paper develops a model predictive multi-objective control framework based on an adaptive cruise control (ACC) system to solve the energy allocation and battery state of charge (SOC) maintenance problems of hybrid electric vehicles in the car-following scenario. The proposed control framework is
[...] Read more.
This paper develops a model predictive multi-objective control framework based on an adaptive cruise control (ACC) system to solve the energy allocation and battery state of charge (SOC) maintenance problems of hybrid electric vehicles in the car-following scenario. The proposed control framework is composed of a car-following layer and an energy allocation layer. In the car-following layer, a multi-objective problem is solved to maintain safety and comfort, and the generated speed sequence in the prediction time domain is put forward to the energy allocation layer. In the energy allocation layer, an adaptive equivalent-factor-based consumption minimization strategy with the predicted velocity sequences is adopted to improve the engine efficiency and fuel economy. The equivalent factor reflects the extent of SOC variation, which is used to maintain the battery SOC level when optimizing the energy. The proposed controller is evaluated in the New York City Cycle (NYCC) driving cycle and the Urban Dynamometer Driving Schedule (UDDS) driving cycle, and the comparison results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed controller.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
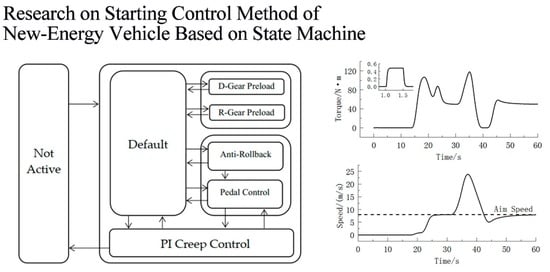
Research on Starting Control Method of New-Energy Vehicle Based on State Machine
by
Yezhen Wu, Yuliang Xu, Jianwei Zhou, Zhen Wang and Haopeng Wang
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2668
Abstract
In order to improve the starting smoothness of new-energy vehicles under multiple working conditions and meet the driving intention better, and to make the control strategy have high portability and integration, a starting control method for vehicle based on state machine is designed.
[...] Read more.
In order to improve the starting smoothness of new-energy vehicles under multiple working conditions and meet the driving intention better, and to make the control strategy have high portability and integration, a starting control method for vehicle based on state machine is designed. Based on inclination, starting of vehicle is divided into three working conditions: flat road, slight slope and steep slope. The method of vehicle starting control is designed, which includes five control states: default state control, torque pre-loading control, anti-rollback control, pedal control and PI (Proportion-Intergral) creep control. The simulation is carried out under the conditions of flat road, slight slope and steep slope. In terms of flat road and light slope, the vehicle travels below 3 km/h according to the driver’s intention, the speed is stable at 8 km/h during the creeping control phase and the jerk is lower than 5 m/s
3. In terms of steep slope, the speed is controlled at 0 km/h basically and the 10 s-rollback distance is less than 0.04 m. The results show that the strategy can fully meet the driver’s intention with lower jerk, better dynamic and stability, and the method can achieve the demand of new-energy vehicle starting control.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of a Parallel Hybrid Electric Tractor for Agricultural Applications
by
Francesco Mocera and Aurelio Somà
Cited by 85 | Viewed by 8055
Abstract
The field of Non-Road Mobile Machineries (NRMM) is now more than ever considering the adoption of electric systems to reduce the amount of pollutant emissions per unit of work. However, the intensity and complexity of the tasks performed by a working machine during
[...] Read more.
The field of Non-Road Mobile Machineries (NRMM) is now more than ever considering the adoption of electric systems to reduce the amount of pollutant emissions per unit of work. However, the intensity and complexity of the tasks performed by a working machine during its life is an obstacle to the widespread adoption of electric systems. Specific design solutions are required to properly split the power output of the hybrid powertrain among the different loads (wheel, power take off, hydraulic tools, etc.). In this work, a performance analysis between a traditional agricultural tractor and a proposed hybrid electric architecture of the same vehicle is shown. The comparison was performed on a set of tasks characterized on a real orchard tractor which were used to build the input signals of two different numerical models: one for the traditional diesel architecture and the other for the hybrid electric solution. The two models were tested with the same operating tasks to have a one to one comparison of the two architectures. Peak power capabilities of the hybrid solution and performance of the Load Observer energy management strategy were investigated to validate the feasibility of the proposed solution.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Operational Aspects of Electric Vehicles from Car-Sharing Systems
by
Katarzyna Turoń, Andrzej Kubik and Feng Chen
Cited by 26 | Viewed by 5851
Abstract
The article was dedicated to the topic of energy consumption of driving cars equipped with an electric motor. Due to the emerging demands for the excessive use of energy by vehicles (including car-sharing system vehicles), the authors carried out research to determine factors
[...] Read more.
The article was dedicated to the topic of energy consumption of driving cars equipped with an electric motor. Due to the emerging demands for the excessive use of energy by vehicles (including car-sharing system vehicles), the authors carried out research to determine factors that affect the energy consumption. Due to the occurrence of a research gap related to the lack of reliable scientific information regarding real electricity consumption by vehicles used in car-sharing systems, the authors attempted to determine these values based on the proposed research experiment. The purpose of the research was to identify factors that increase energy consumption while driving in the case of car-sharing systems and developing recommendations for users of car-sharing systems and system operators in relation to energy consumption. Based on data received from car-sharing system operators and to their demands that users move cars uneconomically and use too much energy, the authors performed a scientific experiment based on Hartley’s plan. The authors made journeys with electric cars from car-sharing (measurements) in order to compare real consumption with data obtained from operators. As a result, the authors developed a list of factors that negatively affect the energy consumption of electric vehicles from car-sharing systems. As conclusion, a number of recommendations were developed for car-sharing system operators on how to manage their systems to reduce excessive energy consumption in electric vehicles.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Adaptive Rule-Based Energy Management Strategy for a Parallel HEV
by
Rishikesh Mahesh Bagwe, Andy Byerly, Euzeli Cipriano dos Santos, Jr. and Zina Ben-Miled
Cited by 42 | Viewed by 4579
Abstract
This paper proposes an Adaptive Rule-Based Energy Management Strategy (ARBS EMS) for a parallel hybrid electric vehicle (HEV). The aim of the strategy is to facilitate the aftermarket hybridization of medium- and heavy-duty vehicles. ARBS can be deployed online to optimize fuel consumption
[...] Read more.
This paper proposes an Adaptive Rule-Based Energy Management Strategy (ARBS EMS) for a parallel hybrid electric vehicle (HEV). The aim of the strategy is to facilitate the aftermarket hybridization of medium- and heavy-duty vehicles. ARBS can be deployed online to optimize fuel consumption without any detailed knowledge of the engine efficiency map of the vehicle or the entire duty cycle. The proposed strategy improves upon the established Preliminary Rule-Based Strategy (PRBS), which has been adopted in commercial vehicles, by dynamically adjusting the regions of operations of the engine and the motor. It prevents the engine from operating in highly inefficient regions while reducing the total equivalent fuel consumption of the vehicle. Using an HEV model developed in Simulink
®, both the proposed ARBS and the established PRBS strategies are compared over an extended duty cycle consisting of both urban and highway segments. The results show that ARBS can achieve high MPGe with different thresholds for the boundary between the motor region and the engine region. In contrast, PRBS can achieve high MPGe only if this boundary is carefully established from the engine efficiency map. This difference between the two strategies makes the ARBS particularly suitable for aftermarket hybridization where full knowledge of the engine efficiency map may not be available.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Segmental Track Analysis in Dynamic Wireless Power Transfer
by
Shi-Chun Yang, Hong He, Xiao-Yu Yan, Yu-Hang Chen, Yang Hua, Yao-Guang Cao, Jun Li, Hong-Hai Li and Sheng Yin
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 3291
Abstract
Electric vehicles have gained more and more attention because of the serious oil crisis and environmental problems. However, the disadvantages of the electric vehicle, such as short driving range, high battery cost, and inconvenient charging, are hindering its market development and expansion. The
[...] Read more.
Electric vehicles have gained more and more attention because of the serious oil crisis and environmental problems. However, the disadvantages of the electric vehicle, such as short driving range, high battery cost, and inconvenient charging, are hindering its market development and expansion. The realization of on-road wireless power transfer technology can effectively solve the problems of short driving range, prevent the battery from being completely discharged to prolong its service life, and reduce requirement of on-board battery. In this paper, the charging mode and the compensation topology of wireless power transfer technology are discussed and then the equivalent circuit model of segmental wireless power transfer system is built. We carried out some magnetic field simulation to analyze how the track shape and length influence coupling coefficient, which is later verified by experiments.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Prediction of Electric Vehicle Range: A Comprehensive Review of Current Issues and Challenges
by
Bogdan Ovidiu Varga, Arsen Sagoian and Florin Mariasiu
Cited by 173 | Viewed by 21227
Abstract
Electric vehicles (EV) are the immediate solution to drastically reducing pollutant emissions from the transport sector. There is a continuing increase in the number of EVs in use, but their widespread and massive acceptance by automotive consumers is related to the performance they
[...] Read more.
Electric vehicles (EV) are the immediate solution to drastically reducing pollutant emissions from the transport sector. There is a continuing increase in the number of EVs in use, but their widespread and massive acceptance by automotive consumers is related to the performance they can deliver. The most important feature here (a hot topic at present in EV research) is related to the possibility of providing a more accurate prediction of range. Range prediction is a complex problem because it depends on a lot of influence factors (internal, external, constant, variables) and the present paper aims to investigate the effect of these factors on the range of EVs. The results and aspects of current worldwide research on this theme are presented through the analysis of the main classes of influence factors: Vehicle design, the driver and the environment. Further, the weight and effect of each potential factor which influences EV range was analyzed by presenting current issues. An exhaustive and comprehensive analysis has made it possible to identify future research and development directions in the EV research field, resulting in massive future and immediate EV penetration in the automotive market.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Direct Driven Hydraulic Drive: Effect of Oil on Efficiency in Sub-Zero Conditions
by
Tatiana Minav, Jani Heikkinen, Thomas Schimmel and Matti Pietola
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 5356
Abstract
Direct driven hydraulic drives (DDH) have the advantages of compact high power density in hydraulic systems and flexible control of electric motors. These advantages can benefit non-road mobile machinery (NRMM) applications. However, maintaining high efficiency while working in sub-zero conditions with NRMM is
[...] Read more.
Direct driven hydraulic drives (DDH) have the advantages of compact high power density in hydraulic systems and flexible control of electric motors. These advantages can benefit non-road mobile machinery (NRMM) applications. However, maintaining high efficiency while working in sub-zero conditions with NRMM is challenging. Therefore, this paper investigates the effect of hydraulic oil on the efficiency of a DDH in a cold environment for an NRMM application. In the DDH setup, the speed and position control of a double-acting cylinder was implemented directly with an electric motor drive in a closed-loop system without the conventional control valves. Efficiency measurements of the DDH setup with two oils (conventional multi-grade and high-performance) were conducted under different operating conditions (speed and payload) and environmental conditions (temperature in °C). The paper provides an evaluation of the electro-hydraulic system and a discussion on the usage of hydraulic oil by non-road mobile working machines in sub-zero conditions. An experimental investigation demonstrated an improvement in efficiency of 5%-unit at 22 °C, from 2%-unit to 5%-unit at 3 °C, and of almost a 10%-unit at temperatures below zero (−10 °C) by changing oil.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Research into an Efficient Energy Equalizer for Lithium-Ion Battery Packs
by
Hongrui Liu, Bo Li, Yixuan Guo, Chunfeng Du, Shilong Chen and Sizhao Lu
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 3444
Abstract
An efficient multi-mode energy equalizer for lithium-ion battery packs is proposed and energy balance strategies are studied in this paper. The energy balance strategies include the selection of the controlled object in the battery’s different working states and the current form of the
[...] Read more.
An efficient multi-mode energy equalizer for lithium-ion battery packs is proposed and energy balance strategies are studied in this paper. The energy balance strategies include the selection of the controlled object in the battery’s different working states and the current form of the controlled object. During the energy balancing process, the strongest single cell or the weakest single cell is selected as the controlled object according to the different working states of the battery, and the balanced current of the controlled object is continuous. Therefore, the energy equalizer proposed in this paper has a fast balancing speed, an improved balancing effect, and an excellent balancing reliability. According to the energy equalizer, the relevant experimental platform was built, and balance experiments in the battery’s different working states using a battery pack composed of four serially-connected lithium iron phosphate batteries were completed. Finally, the experimental results proved the effectiveness of the energy equalizer.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Advanced Methodology for the Optimal Sizing of the Energy Storage System in a Hybrid Electric Refuse Collector Vehicle Using Real Routes
by
Ernest Cortez, Manuel Moreno-Eguilaz and Francisco Soriano
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 5190
Abstract
This paper presents a new methodology for optimal sizing of the energy storage system (
), with the aim of being used in the design process of a hybrid electric (HE) refuse collector vehicle (
). This
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a new methodology for optimal sizing of the energy storage system (
), with the aim of being used in the design process of a hybrid electric (HE) refuse collector vehicle (
). This methodology has, as the main element, to model a multi-objective optimisation problem that considers the specific energy of a basic cell of lithium polymer (
–
) battery and the cost of manufacture. Furthermore, optimal space solutions are determined from a multi-objective genetic algorithm that considers linear inequalities and limits in the decision variables. Subsequently, it is proposed to employ optimal space solutions for sizing the energy storage system, based on the energy required by the drive cycle of a conventional refuse collector vehicle. In addition, it is proposed to discard elements of optimal space solutions for sizing the energy storage system so as to achieve the highest fuel economy in the hybrid electric refuse collector vehicle design phase.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
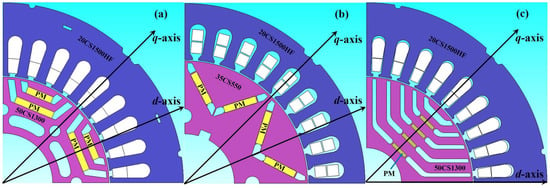
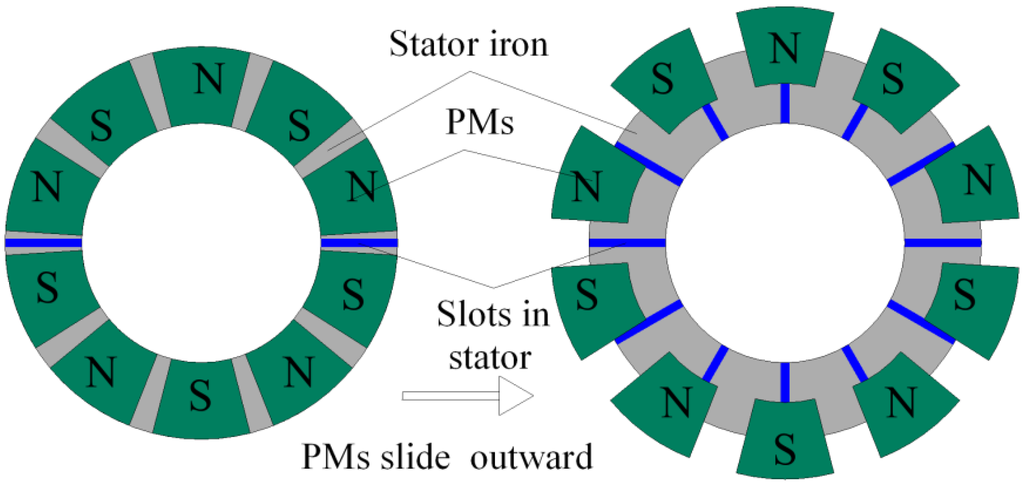
Quantitative Comparison of Vernier Permanent-Magnet Motors with Interior Permanent-Magnet Motor for Hybrid Electric Vehicles
by
Christopher H. T. Lee, Matthew Angle, Krishan Kant Bhalla, Mohammad Qasim, Jie Mei, Sajjad Mohammadi, K. Lakshmi Varaha Iyer, Jasmin Jijina Sinkular and James L. Kirtley
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 6041
Abstract
In this paper, three Vernier permanent-magnet (VPM) motor, namely the inner-rotor VPM (IR-VPM) motor, the outer-rotor VPM (OR-VPM) motor and the OR consequent-pole VPM (OR-CP-VPM) motor are proposed for the hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) applications. Owing to employment of toroidal-winding arrangement, the OR-VPM
[...] Read more.
In this paper, three Vernier permanent-magnet (VPM) motor, namely the inner-rotor VPM (IR-VPM) motor, the outer-rotor VPM (OR-VPM) motor and the OR consequent-pole VPM (OR-CP-VPM) motor are proposed for the hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) applications. Owing to employment of toroidal-winding arrangement, the OR-VPM and the OR-CP-VPM motors can enjoy better material utilization and easier manufacturing process than its IR-VPM counterpart. Meanwhile the OR-CP-VPM motor can utilize the consequent-pole topology to minimize flux leakage that exists in conventional design. With the support of finite element method (FEM), the motor performances among the VPM motors and the profound interior permanent-magnet (IPM) motor can be compared quantitatively.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Simulation of the Oxygen Reduction Reaction (ORR) Inside the Cathode Catalyst Layer (CCL) of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells Using the Kinetic Monte Carlo Method
by
Baosheng Bai and Yi-Tung Chen
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 6123
Abstract
In this paper, a numerical model of the kinetic Monte Carlo (KMC) method has been developed to study the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) that occurs inside the cathode catalyst layer (CCL). Firstly, a 3-D model of the CCL that consists of Pt and
[...] Read more.
In this paper, a numerical model of the kinetic Monte Carlo (KMC) method has been developed to study the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) that occurs inside the cathode catalyst layer (CCL). Firstly, a 3-D model of the CCL that consists of Pt and carbon spheres is built using the sphere packing method; secondly, an efficient procedure of the proton-oxygen reaction process is developed and simulated. In the proton-oxygen reaction process, all of the continuous movements of protons and oxygen are considered. The maximum reaction distance is determined to be 8 Å. The input pressures of protons and oxygen are represented by the number of spheres of the species. The value of the current density is calculated based on the amount of reaction during the interval time. Indications are that the results of the present model match reasonably well with the published results. A new way to apply the KMC method in the proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) research field is developed in this paper.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
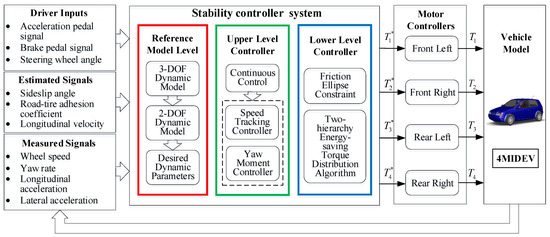
Steering Stability Control for a Four Hub-Motor Independent-Drive Electric Vehicle with Varying Adhesion Coefficient
by
Rufei Hou, Li Zhai and Tianmin Sun
Cited by 17 | Viewed by 4920
Abstract
In order to enhance the steering stability of a four hub-motor independent-drive electric vehicle (4MIDEV) on a road with varying adhesion coefficient, for example on a joint road, this paper proposes a hierarchical steering stability control strategy adapted to the road adhesion. The
[...] Read more.
In order to enhance the steering stability of a four hub-motor independent-drive electric vehicle (4MIDEV) on a road with varying adhesion coefficient, for example on a joint road, this paper proposes a hierarchical steering stability control strategy adapted to the road adhesion. The upper control level of the proposed strategy realizes the integrated control of the sideslip angle and yaw rate in the direct yaw moment control (DYC), where the influences of the road adhesion and sideslip angle are both studied by the fuzzy control. The lower control level employs a weight-based optimal torque distribution algorithm in which weight factors for each motor torque are designed to accommodate different adhesion of each wheel. The proposed stability control strategy was validated in a co-simulation of the Carsim and Matlab/Simulink platforms. The results of double-lane-change maneuver simulations under different conditions indicate that the proposed strategy can effectively achieve robustness to changes in the adhesion coefficient and improve the steering stability of the 4MIDEV.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Analytical Calculation of Armature Reaction Field of the Interior Permanent Magnet Motor
by
Fangwu Ma, Hongbin Yin, Lulu Wei, Liang Wu and Cansong Gu
Cited by 22 | Viewed by 5018
Abstract
The energy crisis and environmental concerns worldwide have helped usher in the age of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid EVs (HEVs). The interior permanent magnet motors (IPMMs) are widely used in these vehicles. The analysis of the armature reaction field is the most
[...] Read more.
The energy crisis and environmental concerns worldwide have helped usher in the age of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid EVs (HEVs). The interior permanent magnet motors (IPMMs) are widely used in these vehicles. The analysis of the armature reaction field is the most critical issue in the study of IPMMs since it determines the characters of torque, efficiency, vibration, and the radiated acoustic noise. This paper provides a calculation method of the armature reaction magnetic field (ARMF) of an IPMM. First, the formulas of ARMF without magnetic barrier are derived. Second, the relative permeance function of an IPMM is calculated. Third, the analytical solution of the ARMF of an IPMM is derived by applying the armature reaction magnetic field with unsaturated rotor multiplied by relative permeance function. Finally, several results of comparisons between the calculation method proposed in this paper and the finite element method are presented. Based on the calculation method proposed in this paper, the magnetic barrier’s influence on the ARMF is studied. The spatial harmonic orders and time harmonic orders of the ARMF of IPMM are revealed respectively.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
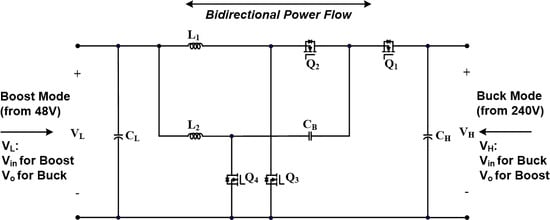
Digital Control of an Interleaving Operated Buck-Boost Synchronous Converter Used in a Low-Cost Testing System for an Automotive Powertrain
by
Miran Rodič, Miro Milanovič and Mitja Truntič
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 4645
Abstract
Based on the standardization in the automotive industry, systems require extensive testing, which represents significant costs regarding personnel and equipment. The testing systems must be built in such a way that a bidirectional power flow is possible between the power source and the
[...] Read more.
Based on the standardization in the automotive industry, systems require extensive testing, which represents significant costs regarding personnel and equipment. The testing systems must be built in such a way that a bidirectional power flow is possible between the power source and the tested system. Additionally, applied testing systems have to possess high disturbance immunity. Classical current programmed control performed using an analogue approach suffers from low disturbance rejection during switching operation. The digital control of DC–DC converter can solve this problem with the use of digital integration in a measurement chain. The integrals of values are obtained by using a Voltage Control Oscillator (VCO) and appropriate counters. Digital control of an interleaving operated bidirectional buck-boost synchronous converter can be applied in the testing system for automotive powertrains. The voltage and current measurements with the application of an integral-measurement principle act as low-pass filters, which remove the disturbances from the measured values. The digital implementation of a compensation ramp (current mode control) and method for choice of control parameters are described. All the tasks for measurements, as well as current and voltage control, were implemented within the FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array). The presented converter can operate as a close to ideal voltage or current source, and satisfies the requirements of testing electric motor drive-trains with bidirectional DC–AC converters that are applied in automotive applications. The proposed system was verified by simulation and experiments.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
In Operando Neutron Radiography Analysis of a High-Temperature Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell Based on a Phosphoric Acid-Doped Polybenzimidazole Membrane Using the Hydrogen-Deuterium Contrast Method
by
Yu Lin, Tobias Arlt, Nikolay Kardjilov, Ingo Manke and Werner Lehnert
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 4742
Abstract
In order to characterize high temperature polymer electrolyte fuel cells (HT-PEFCs) in operando, neutron radiography imaging, in combination with the deuterium contrast method, was used to analyze the hydrogen distribution and proton exchange processes in operando. These measurements were then combined with the
[...] Read more.
In order to characterize high temperature polymer electrolyte fuel cells (HT-PEFCs) in operando, neutron radiography imaging, in combination with the deuterium contrast method, was used to analyze the hydrogen distribution and proton exchange processes in operando. These measurements were then combined with the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy measurements. The cell was operated under different current densities and stoichiometries. Neutron images of the active area of the cell were captured in order to study the changeover times when the fuel supply was switched between hydrogen and deuterium, as well as to analyze the cell during steady state conditions. This work demonstrates that the changeover from proton to deuteron (and vice versa) leads to local varying media distributions in the electrolyte, independent of the overall exchange dynamics. A faster proton-to-deuteron exchange was re-discovered when switching the gas supply from H
2 to D
2 than that from D
2 to H
2. Furthermore, the D
2 uptake and discharge were faster at a higher current density. Specifically, the changeover from H to D takes 5–6 min at 200 mA cm
−2, 2–3 min at 400 mA cm
−2 and 1–2 min at 600 mA cm
−2. An effect on the transmittance changes is apparent when the stoichiometry changes.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Integrated Sizing and Energy Management for Four-Wheel-Independently-Actuated Electric Vehicles Considering Realistic Constructed Driving Cycles
by
Zhenpo Wang, Changhui Qu, Lei Zhang, Jin Zhang and Wen Yu
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 4701
Abstract
This paper presents an integrated optimization framework of sizing and energy management for four-wheel-independently-actuated electric vehicles. The optimization framework consists of an inner and an outer layer that are responsible for energy management, i.e., torque allocation, and powertrain parameter optimizations. The optimal torque
[...] Read more.
This paper presents an integrated optimization framework of sizing and energy management for four-wheel-independently-actuated electric vehicles. The optimization framework consists of an inner and an outer layer that are responsible for energy management, i.e., torque allocation, and powertrain parameter optimizations. The optimal torque allocation in the inner layer is achieved via the dynamic programming (DP) method while the desirable powertrain parameters in the outer layer are pursued based on the exhaustive method. In order to verify the proposed optimization framework, two driving cycles are constructed to represent the comprehensive and realistic driving conditions. One cycle is built by combining six typical driving cycles, which cover urban, high-way and rural driving styles to enhance representativeness. The other one is synthesized using the Markov chain method based on a vast quantity of real-time operating data of electric vehicles in Beijing. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed strategy decreases the power consumption by 15.1% and 13.3%, respectively, in the two driving cycles, compared to the non-optimal, even-torque-allocation strategy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Performance Analysis of Permanent Magnet Motors for Electric Vehicles (EV) Traction Considering Driving Cycles
by
Thanh Anh Huynh and Min-Fu Hsieh
Cited by 107 | Viewed by 18902
Abstract
This paper evaluates the electromagnetic and thermal performance of several traction motors for electric vehicles (EVs). Two different driving cycles are employed for the evaluation of the motors, one for urban and the other for highway driving. The electromagnetic performance to be assessed
[...] Read more.
This paper evaluates the electromagnetic and thermal performance of several traction motors for electric vehicles (EVs). Two different driving cycles are employed for the evaluation of the motors, one for urban and the other for highway driving. The electromagnetic performance to be assessed includes maximum motor torque output for vehicle acceleration and the flux weakening capability for wide operating range under current and voltage limits. Thermal analysis is performed to evaluate the health status of the magnets and windings for the prescribed driving cycles. Two types of traction motors are investigated: two interior permanent magnet motors and one permanent magnet-assisted synchronous reluctance motor. The analysis results demonstrate the benefits and disadvantages of these motors for EV traction and provide suggestions for traction motor design. Finally, experiments are conducted to validate the analysis.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Gear Ratio Optimization of a Multi-Speed Transmission for Electric Dump Truck Operating on the Structure Route
by
Senqi Tan, Jue Yang, Xinxin Zhao, Tingting Hai and Wenming Zhang
Cited by 33 | Viewed by 8902
Abstract
Research demonstrated that the application of a multi-speed transmission could improve the dynamic and economic performance of electric vehicles. This paper deals with a novel multi-speed transmission for the electric dump truck (EDT) operating on the structure route (SR), which has a definite
[...] Read more.
Research demonstrated that the application of a multi-speed transmission could improve the dynamic and economic performance of electric vehicles. This paper deals with a novel multi-speed transmission for the electric dump truck (EDT) operating on the structure route (SR), which has a definite starting point and end point without complex traffic conditions. To optimize the gear ratio and shift schedule to reduce energy consumption in such conditions, the mathematical model of the transmission and the dynamic model of the EDT are initially required. Following this, the shift schedule is presented according to the motor efficiency map. After that, the gear ratio optimization is carried out by a particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm. Moreover, the proposed EDT is compared with an EDT with a single-speed transmission. The simulation results show that the energy consumption is reduced by 6.1%.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
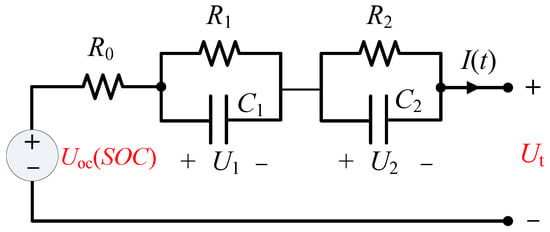
Experimental Data-Driven Parameter Identification and State of Charge Estimation for a Li-Ion Battery Equivalent Circuit Model
by
Hui Pang and Fengqi Zhang
Cited by 19 | Viewed by 7465
Abstract
It is well known that accurate identification of the key state parameters and State of Charge (SOC) estimation method for a Li-ion battery cell is of great significance for advanced battery management system (BMS) of electric vehicles (EVs), which further facilitates the commercialization
[...] Read more.
It is well known that accurate identification of the key state parameters and State of Charge (SOC) estimation method for a Li-ion battery cell is of great significance for advanced battery management system (BMS) of electric vehicles (EVs), which further facilitates the commercialization of EVs. This study proposed a systematic experimental data-driven parameter identification scheme and an adaptive extended Kalman Filter (AEKF)-based SOC estimation algorithm for a Li-Ion battery equivalent circuit model in EV applications. The key state parameters of Li-ion battery cell were identified based on the second-order resistor capacitor (RC) equivalent circuit model and the experimental battery test data using genetic algorithm (GA). Meanwhile, the proposed parameter identification procedure was validated by carrying out a comparative study of the simulated and experimental output voltage under the same input current profile. Then, SOC estimation was performed based on the AEKF algorithm. Finally, the effectiveness and feasibility of the proposed SOC estimator was verified by loading different operating profiles.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
An Enhanced Hybrid Switching-Frequency Modulation Strategy for Fuel Cell Vehicle Three-Level DC-DC Converters with Quasi-Z Source
by
Yun Zhang, Jilong Shi, Chuanzhi Fu, Wei Zhang, Ping Wang, Jing Li and Mark Sumner
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 4916
Abstract
For fuel cell vehicles, the fuel cell stack has a soft output characteristic whereby the output voltage drops quickly with the increasing output current. In order to interface the dynamic low voltage of the fuel cell stack with the required constant high voltage
[...] Read more.
For fuel cell vehicles, the fuel cell stack has a soft output characteristic whereby the output voltage drops quickly with the increasing output current. In order to interface the dynamic low voltage of the fuel cell stack with the required constant high voltage (400 V) of the inverter DC link bus for fuel cell vehicles, an enhanced hybrid switching-frequency modulation strategy that can improve the voltage-gain range is proposed in this paper for the boost three-level DC-DC converter with a quasi-Z source (BTL-qZ) employed in fuel-cell vehicles. The proposed modulation strategy retains the same advantages of the original modulation strategy with more suitable duty cycles [1/3, 2/3) which avoids extreme duty cycles. Finally, the experimental results validate the feasibility of the proposed modulation strategy and the correctness of its operating principles. Therefore, the BTL-qZ converter is beneficial to interface the fuel cell stack and the DC bus for fuel cell vehicles by using the proposed modulation strategy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Exploring the Potential of Camber Control to Improve Vehicles’ Energy Efficiency during Cornering
by
Peikun Sun, Annika Stensson Trigell, Lars Drugge, Jenny Jerrelind and Mats Jonasson
Cited by 16 | Viewed by 6080
Abstract
Actively controlling the camber angle to improve energy efficiency has recently gained interest due to the importance of reducing energy consumption and the driveline electrification trend that makes cost-efficient implementation of actuators possible. To analyse how much energy that can be saved with
[...] Read more.
Actively controlling the camber angle to improve energy efficiency has recently gained interest due to the importance of reducing energy consumption and the driveline electrification trend that makes cost-efficient implementation of actuators possible. To analyse how much energy that can be saved with camber control, the effect of changing the camber angles on the forces and moments of the tyre under different driving conditions should be considered. In this paper, Magic Formula tyre models for combined slip and camber are used for simulation of energy analysis. The components of power loss during cornering are formulated and used to explain the influence that camber angles have on the power loss. For the studied driving paths and the assumed driver model, the simulation results show that active camber control can have considerable influence on power loss during cornering. Different combinations of camber angles are simulated, and a camber control algorithm is proposed and verified in simulation. The results show that the camber controller has very promising application prospects for energy-efficient cornering.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Thermal Characteristics of an Oscillating Heat Pipe Cooling System for Electric Vehicle Li-Ion Batteries
by
Ri-Guang Chi, Won-Sik Chung and Seok-Ho Rhi
Cited by 59 | Viewed by 11076
Abstract
The heat generation of lithium ion batteries in electric vehicles (EVs) leads to a degradation of energy capacity and lifetime. To solve this problem, a new cooling concept using an oscillating heat pipe (OHP) is proposed. In the present study, an OHP has
[...] Read more.
The heat generation of lithium ion batteries in electric vehicles (EVs) leads to a degradation of energy capacity and lifetime. To solve this problem, a new cooling concept using an oscillating heat pipe (OHP) is proposed. In the present study, an OHP has been adopted for Li-ion battery cooling. Due to the limited space in EVs, the cooling channel is installed on the bottom of the battery module. In the bottom cooling method with an OHP, generated heat can be dissipated easily and conveniently. However, most studies on heat pipes have used bottom heating and top or side cooling methods, so we investigate the various effects of parameters with a top heating/bottom cooling mode with the OHP, i.e., the inclination angle of the system, amount of working fluid charged, the heating amount, and the cold plate temperature with ethanol as a working fluid. The experimental results show that the thermal resistance (0.6 °C/W) and uneven pulsating features influence the heat transfer performance. A heater used as a simulated battery was sustained under 60 °C under 10 W and 14 W heating conditions. This indicates that the proposed cooling system with the bottom cooling is feasible for use as an EV’s battery cooling system.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
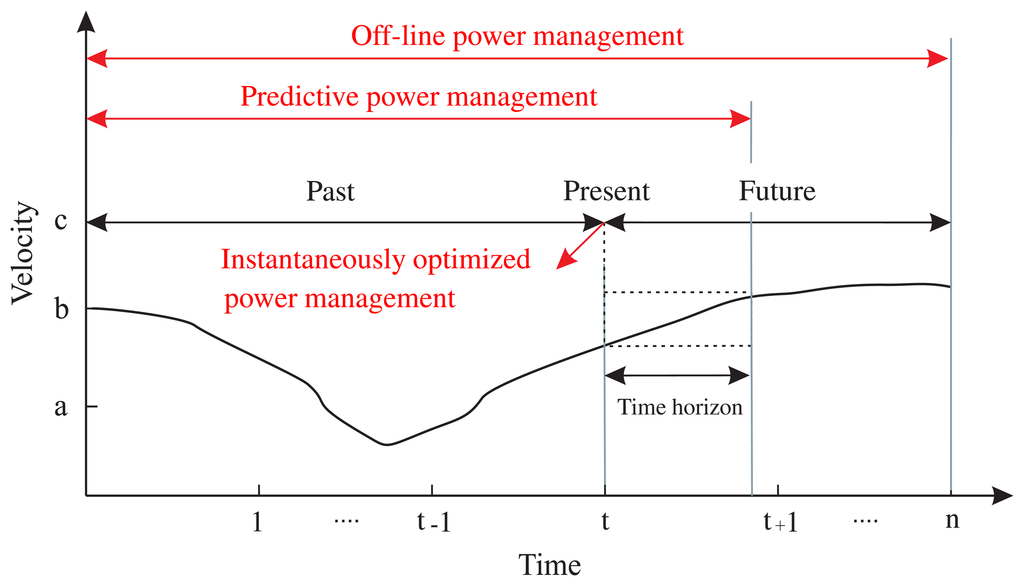
Towards Optimal Power Management of Hybrid Electric Vehicles in Real-Time: A Review on Methods, Challenges, and State-Of-The-Art Solutions
by
Ahmed M. Ali and Dirk Söffker
Cited by 124 | Viewed by 12109
Abstract
In light of increasing alerts about limited energy sources and environment degradation, it has become essential to search for alternatives to thermal engine-based vehicles which are a major source of air pollution and fossil fuel depletion. Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), encompassing multiple energy
[...] Read more.
In light of increasing alerts about limited energy sources and environment degradation, it has become essential to search for alternatives to thermal engine-based vehicles which are a major source of air pollution and fossil fuel depletion. Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), encompassing multiple energy sources, are a short-term solution that meets the performance requirements and contributes to fuel saving and emission reduction aims. Power management methods such as regulating efficient energy flow to the vehicle propulsion, are core technologies of HEVs. Intelligent power management methods, capable of acquiring optimal power handling, accommodating system inaccuracies, and suiting real-time applications can significantly improve the powertrain efficiency at different operating conditions. Rule-based methods are simply structured and easily implementable in real-time; however, a limited optimality in power handling decisions can be achieved. Optimization-based methods are more capable of achieving this optimality at the price of augmented computational load. In the last few years, these optimization-based methods have been under development to suit real-time application using more predictive, recognitive, and artificial intelligence tools. This paper presents a review-based discussion about these new trends in real-time optimal power management methods. More focus is given to the adaptation tools used to boost methods optimality in real-time. The contribution of this work can be identified in two points: First, to provide researchers and scholars with an overview of different power management methods. Second, to point out the state-of-the-art trends in real-time optimal methods and to highlight promising approaches for future development.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Continuous Steering Stability Control Based on an Energy-Saving Torque Distribution Algorithm for a Four in-Wheel-Motor Independent-Drive Electric Vehicle
by
Li Zhai, Rufei Hou, Tianmin Sun and Steven Kavuma
Cited by 57 | Viewed by 7619
Abstract
In this paper, a continuous steering stability controller based on an energy-saving torque distribution algorithm is proposed for a four in-wheel-motor independent-drive electric vehicle (4MIDEV) to improve the energy consumption efficiency while maintaining the stability in steering maneuvers. The controller is designed as
[...] Read more.
In this paper, a continuous steering stability controller based on an energy-saving torque distribution algorithm is proposed for a four in-wheel-motor independent-drive electric vehicle (4MIDEV) to improve the energy consumption efficiency while maintaining the stability in steering maneuvers. The controller is designed as a hierarchical structure, including the reference model level, the upper-level controller, and the lower-level controller. The upper-level controller adopts the direct yaw moment control (DYC), which is designed to work continuously during the steering maneuver to better ensure steering stability in extreme situations, rather than working only after the vehicle is judged to be unstable. An adaptive two-hierarchy energy-saving torque distribution algorithm is developed in the lower-level controller with the friction ellipse constraint as a basis for judging whether the algorithm needs to be switched, so as to achieve a more stable and energy-efficient steering operation. The proposed stability controller was validated in a co-simulation of CarSim and Matlab/Simulink. The simulation results under different steering maneuvers indicate that the proposed controller, compared with the conventional servo controller and the ordinary continuous controller, can reduce energy consumption up to 23.68% and improve the vehicle steering stability.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Study of the Energy Conversion Process in the Electro-Hydrostatic Drive of a Vehicle
by
Wiesław Grzesikiewicz, Lech Knap, Michał Makowski and Janusz Pokorski
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 5026
Abstract
In the paper, we describe a study of an electro-hydrostatic hybrid drive of a utility van intended for city traffic. In this hybrid drive, the electric drive is periodically accompanied by hydrostatic drive, especially during acceleration and regenerative braking of the vehicle. We
[...] Read more.
In the paper, we describe a study of an electro-hydrostatic hybrid drive of a utility van intended for city traffic. In this hybrid drive, the electric drive is periodically accompanied by hydrostatic drive, especially during acceleration and regenerative braking of the vehicle. We present a mathematical model of the hybrid drive as a set of dynamics and regulation equations of the van traveling at a given speed. On this basis, we construct a computer program which we use to simulate the processes of energy conversion in the electro-hydrostatic drive. The main goal of the numerical simulation is to assess the possibility of reducing energy intensity of the electric drive through such a support of the hydrostatic drive. The obtained results indicate that it is possible to reduce the load on elements of the electric system and, therefore, improve energy conversion.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
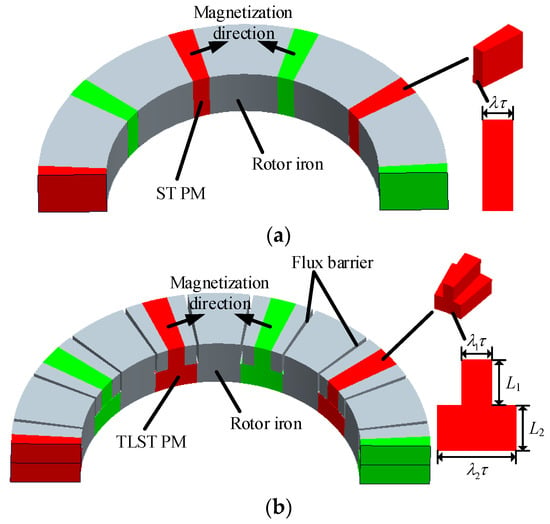
Magnet Shape Optimization of Two-Layer Spoke-Type Axial Flux Interior Permanent Magnet Machines
by
Feng Chai, Yunlong Bi and Yulong Pei
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 7516
Abstract
In this paper, the two-layer spoke-type (TLST) axial flux interior permanent magnet (AFIPM) machine is proposed. Simple flux barriers are added to optimize the air gap flux density, in which way there is no need to change the surface of the rotor. The
[...] Read more.
In this paper, the two-layer spoke-type (TLST) axial flux interior permanent magnet (AFIPM) machine is proposed. Simple flux barriers are added to optimize the air gap flux density, in which way there is no need to change the surface of the rotor. The optimization principle is revealed and the advantages of the TLST AFIPM machine compared with the spoke-type (ST) AFIPM machine are clarified. An optimization design process based on magnetic equivalent circuit combined with idealized and improved air gap flux density waveform is proposed, in which way the calculation time is saved by avoiding an excess of finite element method (FEM) simulations. Finally, 3D FEM simulation is adopted to verify the optimization results.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Impact of Different Driving Cycles and Operating Conditions on CO2 Emissions and Energy Management Strategies of a Euro-6 Hybrid Electric Vehicle
by
Claudio Cubito, Federico Millo, Giulio Boccardo, Giuseppe Di Pierro, Biagio Ciuffo, Georgios Fontaras, Simone Serra, Marcos Otura Garcia and Germana Trentadue
Cited by 57 | Viewed by 8543
Abstract
Although Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) represent one of the key technologies to reduce CO
2 emissions, their effective potential in real world driving conditions strongly depends on the performance of their Energy Management System (EMS) and on its capability to maximize the efficiency
[...] Read more.
Although Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) represent one of the key technologies to reduce CO
2 emissions, their effective potential in real world driving conditions strongly depends on the performance of their Energy Management System (EMS) and on its capability to maximize the efficiency of the powertrain in real life as well as during Type Approval (TA) tests. Attempting to close the gap between TA and real world CO
2 emissions, the European Commission has decided to introduce from September 2017 the Worldwide Harmonized Light duty Test Procedure (WLTP), replacing the previous procedure based on the New European Driving Cycle (NEDC). The aim of this work is the analysis of the impact of different driving cycles and operating conditions on CO
2 emissions and on energy management strategies of a Euro-6 HEV through the limited number of information available from the chassis dyno tests. The vehicle was tested considering different initial battery State of Charge (SOC), ranging from 40% to 65%, and engine coolant temperatures, from −7 °C to 70 °C. The change of test conditions from NEDC to WLTP was shown to lead to a significant reduction of the electric drive and to about a 30% increase of CO
2 emissions. However, since the specific energy demand of WLTP is about 50% higher than that of NEDC, these results demonstrate that the EMS strategies of the tested vehicle can achieve, in test conditions closer to real life, even higher efficiency levels than those that are currently evaluated on the NEDC, and prove the effectiveness of HEV technology to reduce CO
2 emissions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
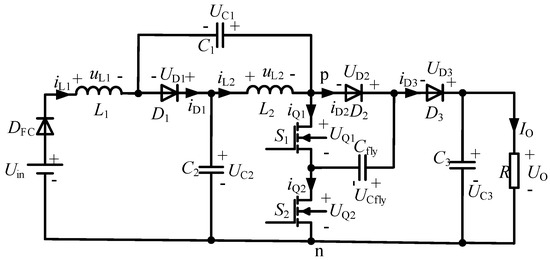
A High-Frequency Isolation (HFI) Charging DC Port Combining a Front-End Three-Level Converter with a Back-End LLC Resonant Converter
by
Guowei Cai, Duolun Liu, Chuang Liu, Wei Li and Jiajun Sun
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 10790
Abstract
The high-frequency isolation (HFI) charging DC port can serve as the interface between unipolar/bipolar DC buses and electric vehicles (EVs) through the two-power-stage system structure that combines the front-end three-level converter with the back-end logical link control (LLC) resonant converter. The DC output
[...] Read more.
The high-frequency isolation (HFI) charging DC port can serve as the interface between unipolar/bipolar DC buses and electric vehicles (EVs) through the two-power-stage system structure that combines the front-end three-level converter with the back-end logical link control (LLC) resonant converter. The DC output voltage can be maintained within the desired voltage range by the front-end converter. The electrical isolation can be realized by the back-end LLC converter, which has the bus converter function. According to the three-level topology, the low-voltage rating power devices can be adapted for half-voltage stress of the total DC grid, and the PWM phase-shift control can double the equivalent switching frequency to greatly reduce the filter volume. LLC resonant converters have advance characteristics of inverter-side zero-voltage-switching (ZVS) and rectifier-side zero-current switching (ZCS). In particular, it can achieve better performance under quasi-resonant frequency mode. Additionally, the magnetizing current can be modified following different DC output voltages, which have the self-adaptation ZVS condition for decreasing the circulating current. Here, the principles of the proposed topology are analyzed in detail, and the design conditions of the three-level output filter and high-frequency isolation transformer are explored. Finally, a 20 kW prototype with the 760 V input and 200–500 V output are designed and tested. The experimental results are demonstrated to verify the validity and performance of this charging DC port system structure.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
An Adaptive Square Root Unscented Kalman Filter Approach for State of Charge Estimation of Lithium-Ion Batteries
by
Shulin Liu, Naxin Cui and Chenghui Zhang
Cited by 42 | Viewed by 7056
Abstract
An accurate state of charge (SOC) estimation is of great importance for the battery management systems of electric vehicles. To improve the accuracy and robustness of SOC estimation, lithium-ion battery SOC is estimated using an adaptive square root unscented Kalman filter (ASRUKF) method.
[...] Read more.
An accurate state of charge (SOC) estimation is of great importance for the battery management systems of electric vehicles. To improve the accuracy and robustness of SOC estimation, lithium-ion battery SOC is estimated using an adaptive square root unscented Kalman filter (ASRUKF) method. The square roots of the variance matrices of the SOC and noise can be calculated directly by the ASRUKF algorithm, which ensures the symmetry and nonnegative definiteness of the matrices. The process values and measurement noise covariance can be adaptively adjusted, which greatly improves the accuracy, stability, and self-adaptability of the filter. The effectiveness of the proposed method has been verified through experiments under different operating conditions. The obtained results were compared with those of extended Kalman filter (EKF) and unscented Kalman filter (UKF) , which indicates that the ASRUKF method provides better accuracy, robustness and convergence in the estimation of battery SOC for electric vehicles. The proposed method has a mean SOC estimation error of 0.5% and a maximum SOC estimation error of 0.8%. These errors are lower than those of other methods.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Online Lithium-Ion Battery Internal Resistance Measurement Application in State-of-Charge Estimation Using the Extended Kalman Filter
by
Dian Wang, Yun Bao and Jianjun Shi
Cited by 101 | Viewed by 18285
Abstract
The lithium-ion battery is a viable power source for hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) and, more recently, electric vehicles (EVs). Its performance, especially in terms of state of charge (SOC), plays a significant role in the energy management of these vehicles. The extended Kalman
[...] Read more.
The lithium-ion battery is a viable power source for hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) and, more recently, electric vehicles (EVs). Its performance, especially in terms of state of charge (SOC), plays a significant role in the energy management of these vehicles. The extended Kalman filter (EKF) is widely used to estimate online SOC as an efficient estimation algorithm. However, conventional EKF algorithms cannot accurately estimate the difference between individual batteries, which should not be ignored. However, the internal resistance of a battery can represent this difference. Therefore, this work proposes using an EKF with internal resistance measurement based on the conventional algorithm. Lithium-ion battery real-time resistances can help the Kalman filter overcome defects from simplistic battery models. In addition, experimental results show that it is useful to introduce online internal resistance to the estimation of SOC.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of Vibrations in Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Considering Air-Gap Deformation
by
Yi Li, Feng Chai, Zaixin Song and Zongyang Li
Cited by 30 | Viewed by 7399
Abstract
This paper studies the non-uniform air-gap caused by stator and rotor deformations, together with its effects on the spatial and temporal spectrum of the radial magnetic force density in an interior permanent magnet synchronous motor (IPMSM). According to the mathematical model of the
[...] Read more.
This paper studies the non-uniform air-gap caused by stator and rotor deformations, together with its effects on the spatial and temporal spectrum of the radial magnetic force density in an interior permanent magnet synchronous motor (IPMSM). According to the mathematical model of the deformed air-gap length, the superposition method is adopted to derive the air-gap permeance. Then, the formulas of the magnetic flux field and radial force density of the IPMSM considering air-gap deformation are obtained. Considering the stator oval deformation and the rotor centrifugal distortion in the electromagnetic finite element models (FEMs), the finite element analysis (FEA) and experiments of the investigated IPMSM are carried out to verify the results obtained by the theoretical analysis at different operations. Finally, the mathematical correlation between air-gap deformation and electromagnetic vibration is obtained. The result is helpful in solving problems of mutual influence between electromagnetic and mechanical characteristics during the optimization design of IPMSM.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of Cooling Effectiveness and Temperature Uniformity in a Battery Pack for Cylindrical Batteries
by
Seham Shahid and Martin Agelin-Chaab
Cited by 89 | Viewed by 8833
Abstract
In this paper, techniques to improve cooling and temperature uniformity in a simple battery pack are examined. Four battery pack configurations are developed. In the first configuration, an inlet plenum is added to a simple battery pack. In the second configuration, jet inlets
[...] Read more.
In this paper, techniques to improve cooling and temperature uniformity in a simple battery pack are examined. Four battery pack configurations are developed. In the first configuration, an inlet plenum is added to a simple battery pack. In the second configuration, jet inlets are incorporated along with the inlet plenum, and in the third configuration, multiple vortex generators are added in addition to the inlet plenum. Finally, in the fourth configuration, an inlet plenum, jet inlets, and multiple vortex generators are incorporated into the battery pack. The results conclude that by adding inlet plenum, multiple vortex generators, and jet inlets in the same configuration, significant improvements are observed. The results also show that the maximum temperature of the battery pack is reduced by ~5%, and the temperature difference between the maximum temperature and the minimum temperature exhibited by the battery pack is reduced by 21.5%. Moreover, there is a ~16% improvement in the temperature uniformity of a single cell.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of On-Board Photovoltaics for a Battery Electric Bus and Their Impact on Battery Lifespan
by
Kevin R. Mallon, Francis Assadian and Bo Fu
Cited by 83 | Viewed by 9862
Abstract
Heavy-duty electric powertrains provide a potential solution to the high emissions and low fuel economy of trucks, buses, and other heavy-duty vehicles. However, the cost, weight, and lifespan of electric vehicle batteries limit the implementation of such vehicles. This paper proposes supplementing the
[...] Read more.
Heavy-duty electric powertrains provide a potential solution to the high emissions and low fuel economy of trucks, buses, and other heavy-duty vehicles. However, the cost, weight, and lifespan of electric vehicle batteries limit the implementation of such vehicles. This paper proposes supplementing the battery with on-board photovoltaic modules. In this paper, a bus model is created to analyze the impact of on-board photovoltaics on electric bus range and battery lifespan. Photovoltaic systems that cover the bus roof and bus sides are considered. The bus model is simulated on a suburban bus drive cycle on a bus route in Davis, CA, USA for a representative sample of yearly weather conditions. Roof-mounted panels increased vehicle driving range by 4.7% on average annually, while roof and side modules together increased driving range by 8.9%. However, variations in weather conditions meant that this additional range was not reliably available. For constant vehicle range, rooftop photovoltaic modules extended battery cycle life by up to 10% while modules on both the roof and sides extended battery cycle life by up to 19%. Although side-mounted photovoltaics increased cycle life and range, they were less weight- and cost-effective compared to the roof-mounted panels.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Research on the Optimal Charging Strategy for Li-Ion Batteries Based on Multi-Objective Optimization
by
Haitao Min, Weiyi Sun, Xinyong Li, Dongni Guo, Yuanbin Yu, Tao Zhu and Zhongmin Zhao
Cited by 49 | Viewed by 7797
Abstract
Charging performance affects the commercial application of electric vehicles (EVs) significantly. This paper presents an optimal charging strategy for Li-ion batteries based on the voltage-based multistage constant current (VMCC) charging strategy. In order to satisfy the different charging demands of the EV users
[...] Read more.
Charging performance affects the commercial application of electric vehicles (EVs) significantly. This paper presents an optimal charging strategy for Li-ion batteries based on the voltage-based multistage constant current (VMCC) charging strategy. In order to satisfy the different charging demands of the EV users for charging time, charged capacity and energy loss, the multi-objective particle swarm optimization (MOPSO) algorithm is employed and the influences of charging stage number, charging cut-off voltage and weight factors of different charging goals are analyzed. Comparison experiments of the proposed charging strategy and the traditional normal and fast charging strategies are carried out. The experimental results demonstrate that the traditional normal and fast charging strategies can only satisfy a small range of EV users’ charging demand well while the proposed charging strategy can satisfy the whole range of the charging demand well. The relative increase in charging performance of the proposed charging strategy can reach more than 80% when compared to the normal and fast charging dependently.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Fast-Acting Diagnostic Algorithm of Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor Open Circuit Faults for Power Inverters in Electric Vehicles
by
Lei Yu, Youtong Zhang, Wenqing Huang and Khaled Teffah
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 7275
Abstract
To improve the diagnostic detection speed in electric vehicles, a novel diagnostic algorithm of insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) open circuit faults for power inverters is proposed in this paper. The average of the difference between the actual three-phase current and referential three-phase
[...] Read more.
To improve the diagnostic detection speed in electric vehicles, a novel diagnostic algorithm of insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) open circuit faults for power inverters is proposed in this paper. The average of the difference between the actual three-phase current and referential three-phase current values over one electrical period is used as the diagnostic variable. The normalization method based on the amplitude of the
d-q axis referential current is applied to the diagnostic variables to improve the response speed of diagnosis, and to avoid the noise and the delay caused by signal acquisition. In the parameter discretization process, the variable parameter moving average method (VPMAM) is adopted to solve the variation of the average value over a period with the speed of the motor; hence, the diagnostic reliability of the system is improved. This algorithm is robust, independent of load variations, and has a high resistivity against false alarms. Since only the three-phase current of the motor is utilized for calculations in the time domain, a fast diagnostic detection speed can be achieved, which is significantly essential for real-time control in electric vehicles. The effectiveness of the proposed algorithm is verified by both simulation and experimental results.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Analytical Calculation of Magnetic Field Distribution and Stator Iron Losses for Surface-Mounted Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines
by
Zhen Tian, Chengning Zhang and Shuo Zhang
Cited by 29 | Viewed by 8110
Abstract
Permanent-magnet synchronous machines (PMSMs) are widely used in electric vehicles owing to many advantages, such as high power density, high efficiency, etc. Iron losses can account for a significant component of the total loss in permanent-magnet (PM) machines. Consequently, these losses should be
[...] Read more.
Permanent-magnet synchronous machines (PMSMs) are widely used in electric vehicles owing to many advantages, such as high power density, high efficiency, etc. Iron losses can account for a significant component of the total loss in permanent-magnet (PM) machines. Consequently, these losses should be carefully considered during the PMSM design. In this paper, an analytical calculation method has been proposed to predict the magnetic field distribution and stator iron losses in the surface-mounted permanent magnet (SPM) synchronous machines. The method introduces the notion of complex relative air-gap permeance to take into account the effect of slotting. The imaginary part of the relative air-gap permeance is neglected to simplify the calculation of the magnetic field distribution in the slotted air gap for the surface-mounted permanent-magnet (SPM) machine. Based on the armature reaction magnetic field analysis, the stator iron losses can be estimated by the modified Steinmetz equation. The stator iron losses under load conditions are calculated according to the varying d-q-axis currents of different control methods. In order to verify the analysis method, finite element simulation results are compared with analytical calculations. The comparisons show good performance of the proposed analytical method.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Comparison Study of Two Semi-Active Hybrid Energy Storage Systems for Hybrid Electric Vehicle Applications and Their Experimental Validation
by
Haitao Min, Changlu Lai, Yuanbin Yu, Tao Zhu and Cong Zhang
Cited by 31 | Viewed by 9500
Abstract
Both the battery/supercapacitor (SC) and SC/battery are two common semi-active configurations of hybrid energy storage systems (HESSs) in hybrid electric vehicles, which can take advantage of the battery’s and supercapacitor’s respective characteristics, including the energy ability, power ability and the long lifetime. To
[...] Read more.
Both the battery/supercapacitor (SC) and SC/battery are two common semi-active configurations of hybrid energy storage systems (HESSs) in hybrid electric vehicles, which can take advantage of the battery’s and supercapacitor’s respective characteristics, including the energy ability, power ability and the long lifetime. To explore in depth the characteristics and applicability of the two kinds of HESS, an analysis and comparison study is proposed in this paper. Based on the data collected from public transit hybrid electric bus (PTHEB) with battery-only on-board energy storage, the range and distribution probability of electric power/energy demand is comprehensively statistically analyzed with the decomposing and normalizing methods. Accordingly, the performance of each topology under different parameter matching conditions but same mass, volume and cost values with battery-only energy storage, are presented and compared quantitatively. The results show that both HESS configurations can meet the electric power demand of the hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) through reasonable design. In particular, the SC/battery can make better use of the SC features resulting in high efficiency and long life cycles compared with the battery/SC. Equally, it proves that the SC/battery topology is a better choice for the HEV. Finally, an experimental validation of a real HEV is carried out, which indicated that a 7% fuel economy improvement can be achieved by a SC/battery system compared with battery-only topology.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
An Optimized Energy Management Strategy for Preheating Vehicle-Mounted Li-ion Batteries at Subzero Temperatures
by
Tao Zhu, Haitao Min, Yuanbin Yu, Zhongmin Zhao, Tao Xu, Yang Chen, Xinyong Li and Cong Zhang
Cited by 68 | Viewed by 9493
Abstract
This paper presents an optimized energy management strategy for Li-ion power batteries used on electric vehicles (EVs) at low temperatures. In low-temperature environments, EVs suffer a sharp driving range loss resulting from the energy and power capability reduction of the battery. Simultaneously, because
[...] Read more.
This paper presents an optimized energy management strategy for Li-ion power batteries used on electric vehicles (EVs) at low temperatures. In low-temperature environments, EVs suffer a sharp driving range loss resulting from the energy and power capability reduction of the battery. Simultaneously, because of Li plating, battery degradation becomes an increasing concern as the temperature drops. All these factors could greatly increase the total vehicle operation cost. Prior to battery charging and vehicle operating, preheating the battery to a battery-friendly temperature is an approach to promote energy utilization and reduce total cost. Based on the proposed LiFePO
4 battery model, the total vehicle operation cost under certain driving cycles is quantified in the present paper. Then, given a certain ambient temperature, a target preheating temperature is optimized under the principle of minimizing total cost. As for the preheating method, a liquid heating system is also implemented on an electric bus. Simulation results show that the preheating process becomes increasingly necessary with decreasing ambient temperature, however, the preheating demand declines as driving range grows. Vehicle tests verify that the preheating management strategy proposed in this paper is able to save on total vehicle operation costs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Hybrid System Modeling and Full Cycle Operation Analysis of a Two-Stroke Free-Piston Linear Generator
by
Peng Sun, Chi Zhang, Jinhua Chen, Fei Zhao, Youyong Liao, Guilin Yang and Chinyin Chen
Cited by 26 | Viewed by 7261
Abstract
Free-piston linear generators (FPLGs) have attractive application prospects for hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) owing to their high-efficiency, low-emissions and multi-fuel flexibility. In order to achieve long-term stable operation, the hybrid system design and full-cycle operation strategy are essential factors that should be considered.
[...] Read more.
Free-piston linear generators (FPLGs) have attractive application prospects for hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) owing to their high-efficiency, low-emissions and multi-fuel flexibility. In order to achieve long-term stable operation, the hybrid system design and full-cycle operation strategy are essential factors that should be considered. A 25 kW FPLG consisting of an internal combustion engine (ICE), a linear electric machine (LEM) and a gas spring (GS) is designed. To improve the power density and generating efficiency, the LEM is assembled with two modular flat-type double-sided PM LEM units, which sandwich a common moving-magnet plate supported by a middle keel beam and bilateral slide guide rails to enhance the stiffness of the moving plate. For the convenience of operation processes analysis, the coupling hybrid system is modeled mathematically and a full cycle simulation model is established. Top-level systemic control strategies including the starting, stable operating, fault recovering and stopping strategies are analyzed and discussed. The analysis results validate that the system can run stably and robustly with the proposed full cycle operation strategy. The effective electric output power can reach 26.36 kW with an overall system efficiency of 36.32%.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
State of Charge and State of Health Estimation of AGM VRLA Batteries by Employing a Dual Extended Kalman Filter and an ARX Model for Online Parameter Estimation
by
Ngoc-Tham Tran, Abdul Basit Khan and Woojin Choi
Cited by 54 | Viewed by 10755
Abstract
State of charge (SOC) and state of health (SOH) are key issues for the application of batteries, especially the absorbent glass mat valve regulated lead-acid (AGM VRLA) type batteries used in the idle stop start systems (ISSs) that are popularly integrated into conventional
[...] Read more.
State of charge (SOC) and state of health (SOH) are key issues for the application of batteries, especially the absorbent glass mat valve regulated lead-acid (AGM VRLA) type batteries used in the idle stop start systems (ISSs) that are popularly integrated into conventional engine-based vehicles. This is due to the fact that SOC and SOH estimation accuracy is crucial for optimizing battery energy utilization, ensuring safety and extending battery life cycles. The dual extended Kalman filter (DEKF), which provides an elegant and powerful solution, is widely applied in SOC and SOH estimation based on a battery parameter model. However, the battery parameters are strongly dependent on operation conditions such as the SOC, current rate and temperature. In addition, battery parameters change significantly over the life cycle of a battery. As a result, many experimental pretests investigating the effects of the internal and external conditions of a battery on its parameters are required, since the accuracy of state estimation depends on the quality of the information regarding battery parameter changes. In this paper, a novel method for SOC and SOH estimation that combines a DEKF algorithm, which considers hysteresis and diffusion effects, and an auto regressive exogenous (ARX) model for online parameters estimation is proposed. The DEKF provides precise information concerning the battery open circuit voltage (OCV) to the ARX model. Meanwhile, the ARX model continues monitoring parameter variations and supplies information on them to the DEKF. In this way, the estimation accuracy can be maintained despite the changing parameters of a battery. Moreover, online parameter estimation from the ARX model can save the time and effort used for parameter pretests. The validation of the proposed algorithm is given by simulation and experimental results.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Integrated Traction Control Strategy for Distributed Drive Electric Vehicles with Improvement of Economy and Longitudinal Driving Stability
by
Xudong Zhang and Dietmar Göhlich
Cited by 39 | Viewed by 11990
Abstract
This paper presents an integrated traction control strategy (ITCS) for distributed drive electric vehicles. The purpose of the proposed strategy is to improve vehicle economy and longitudinal driving stability. On high adhesion roads, economy optimization algorithm is applied to maximize motors efficiency by
[...] Read more.
This paper presents an integrated traction control strategy (ITCS) for distributed drive electric vehicles. The purpose of the proposed strategy is to improve vehicle economy and longitudinal driving stability. On high adhesion roads, economy optimization algorithm is applied to maximize motors efficiency by means of the optimized torque distribution. On low adhesion roads, a sliding mode control (SMC) algorithm is implemented to guarantee the wheel slip ratio around the optimal slip ratio point to make full use of road adhesion capacity. In order to avoid the disturbance on slip ratio calculation due to the low vehicle speed, wheel rotational speed is taken as the control variable. Since the optimal slip ratio varies according to different road conditions, Bayesian hypothesis selection is utilized to estimate the road friction coefficient. Additionally, the ITCS is designed for combining the vehicle economy and stability control through three traction allocation cases: economy-based traction allocation, pedal self-correcting traction allocation and inter-axles traction allocation. Finally, simulations are conducted in CarSim and Matlab/Simulink environment. The results show that the proposed strategy effectively reduces vehicle energy consumption, suppresses wheels-skid and enhances the vehicle longitudinal stability and dynamic performance.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Structural Identifiability of Equivalent Circuit Models for Li-Ion Batteries
by
Thomas R. B. Grandjean, Andrew McGordon and Paul A. Jennings
Cited by 33 | Viewed by 8423
Abstract
Structural identifiability is a critical aspect of modelling that has been overlooked in the vast majority of Li-ion battery modelling studies. It considers whether it is possible to obtain a unique solution for the unknown model parameters from experimental data. This is a
[...] Read more.
Structural identifiability is a critical aspect of modelling that has been overlooked in the vast majority of Li-ion battery modelling studies. It considers whether it is possible to obtain a unique solution for the unknown model parameters from experimental data. This is a fundamental prerequisite of the modelling process, especially when the parameters represent physical battery attributes and the proposed model is utilised to estimate them. Numerical estimates for unidentifiable parameters are effectively meaningless since unidentifiable parameters have an infinite number of possible numerical solutions. It is demonstrated that the physical phenomena assignment to a two-RC (resistor–capacitor) network equivalent circuit model (ECM) is not possible without additional information. Established methods to ascertain structural identifiability are applied to 12 ECMs covering the majority of model templates used previously. Seven ECMs are shown not to be uniquely identifiable, reducing the confidence in the accuracy of the parameter values obtained and highlighting the relevance of structural identifiability even for relatively simple models. Suggestions are proposed to make the models identifiable and, therefore, more valuable in battery management system applications. The detailed analyses illustrate the importance of structural identifiability prior to performing parameter estimation experiments, and the algebraic complications encountered even for simple models.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Field Synergy Analysis and Optimization of the Thermal Behavior of Lithium Ion Battery Packs
by
Hongwen He, Hui Jia, Weiwei Huo and Fengchun Sun
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 6679
Abstract
In this study, a three dimensional (3D) modeling has been built for a lithium ion battery pack using the field synergy principle to obtain a better thermal distribution. In the model, the thermal behavior of the battery pack was studied by reducing the
[...] Read more.
In this study, a three dimensional (3D) modeling has been built for a lithium ion battery pack using the field synergy principle to obtain a better thermal distribution. In the model, the thermal behavior of the battery pack was studied by reducing the maximum temperature, improving the temperature uniformity and considering the difference between the maximum and maximum temperature of the battery pack. The method is further verified by simulation results based on different environmental temperatures and discharge rates. The thermal behavior model demonstrates that the design and cooling policy of the battery pack is crucial for optimizing the air-outlet patterns of electric vehicle power cabins.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Detection of Internal Short Circuit in Lithium Ion Battery Using Model-Based Switching Model Method
by
Minhwan Seo, Taedong Goh, Minjun Park, Gyogwon Koo and Sang Woo Kim
Cited by 64 | Viewed by 10848
Abstract
Early detection of an internal short circuit (ISCr) in a Li-ion battery can prevent it from undergoing thermal runaway, and thereby ensure battery safety. In this paper, a model-based switching model method (SMM) is proposed to detect the ISCr in the Li-ion battery.
[...] Read more.
Early detection of an internal short circuit (ISCr) in a Li-ion battery can prevent it from undergoing thermal runaway, and thereby ensure battery safety. In this paper, a model-based switching model method (SMM) is proposed to detect the ISCr in the Li-ion battery. The SMM updates the model of the Li-ion battery with ISCr to improve the accuracy of ISCr resistance
estimates. The open circuit voltage (OCV) and the state of charge (SOC) are estimated by applying the equivalent circuit model, and by using the recursive least squares algorithm and the relation between OCV and SOC. As a fault index, the
is estimated from the estimated OCVs and SOCs to detect the ISCr, and used to update the model; this process yields accurate estimates of OCV and
. Then the next
is estimated and used to update the model iteratively. Simulation data from a MATLAB/Simulink model and experimental data verify that this algorithm shows high accuracy of
estimates to detect the ISCr, thereby helping the battery management system to fulfill early detection of the ISCr.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Real-Time Velocity Optimization to Minimize Energy Use in Passenger Vehicles
by
Thomas Levermore, M. Necip Sahinkaya, Yahya Zweiri and Ben Neaves
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 5679
Abstract
Energy use in internal combustion engine passenger vehicles contributes directly to
emissions and fuel consumption, as well as producing a number of air pollutants. Optimizing the vehicle velocity by utilising upcoming road information is an opportunity to minimize vehicle energy use
[...] Read more.
Energy use in internal combustion engine passenger vehicles contributes directly to
emissions and fuel consumption, as well as producing a number of air pollutants. Optimizing the vehicle velocity by utilising upcoming road information is an opportunity to minimize vehicle energy use without requiring mechanical design changes. Dynamic programming is capable of such an optimization task and is shown in simulation to produce fuel savings, on average 12%, compared to real driving data; however, in this paper it is also applied in real time on a Raspberry Pi, a low cost miniature computer, in situ in a vehicle. A test drive was undertaken with driver feedback being provided by a dynamic programming algorithm, and the results are compared to a simulated intelligent cruise control system that can follow the algorithm results precisely. An 8% reduction in fuel with no loss in time is reported compared to the test driver.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Decoupling Design and Verification of a Free-Piston Linear Generator
by
Peng Sun, Chi Zhang, Jinhua Chen, Fei Zhao, Youyong Liao, Guilin Yang and Chinyin Chen
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 6991
Abstract
This paper proposes a decoupling design approach for a free-piston linear generator (FPLG) constituted of three key components, including a combustion chamber, a linear generator and a gas spring serving as rebounding device. The approach is based on the distribution of the system
[...] Read more.
This paper proposes a decoupling design approach for a free-piston linear generator (FPLG) constituted of three key components, including a combustion chamber, a linear generator and a gas spring serving as rebounding device. The approach is based on the distribution of the system power and efficiency, which provides a theoretical design method from the viewpoint of the overall power and efficiency demands. The energy flow and conversion processes of the FPLG are analyzed, and the power and efficiency demands of the thermal-mechanical and mechanical-electrical energy conversion are confirmed. The energy and efficiency distributions of the expansion and compression strokes within a single stable operation cycle are analyzed and determined. Detailed design methodologies of crucial geometric dimensions and operational parameters of each key component are described. The feasibility of the proposed decoupling design approach is validated through several design examples with different output power.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Comparison of Optimized Control Strategies of a High-Speed Traction Machine with Five Phases and Bi-Harmonic Electromotive Force
by
Hussein Zahr, Jinlin Gong, Eric Semail and Franck Scuiller
Cited by 16 | Viewed by 6181
Abstract
The purpose of the paper is to present the potentialities in terms of the control of a new kind of PM synchronous machine. With five phases and electromotive forces whose first (
) and third (
) harmonics are
[...] Read more.
The purpose of the paper is to present the potentialities in terms of the control of a new kind of PM synchronous machine. With five phases and electromotive forces whose first (
) and third (
) harmonics are of similar amplitude, the studied machine, so-called bi-harmonic, has properties that are interesting for traction machine payload. With three-phase machines, supplied by a mono-harmonic sinusoidal current, the weak number of freedom degrees limits the strategy of control for traction machines especially when voltage saturation occurs at high speeds. As the torque is managed for three-phase machines by a current with only one harmonic, flux weakening is necessary to increase speed when the voltage limitation is reached. The studied five-phase machine, thanks to the increase in the number of freedom degrees for control, aims to alleviate this fact. In this paper, three optimized control strategies are compared in terms of efficiency and associated torque/speed characteristics. These strategies take into account numerous constraints either from the supply (with limited voltage) or from the machine (with limited current densities and maximum acceptable copper, iron and permanent magnet losses). The obtained results prove the wide potentialities of such a kind of five-phase bi-harmonic machine in terms of control under constraints. It is thus shown that the classical Maximum Torque Per Ampere (MTPA) strategy developed for the three-phase machine is clearly not satisfying on the whole range of speed because of the presence of iron losses whose values can no more be neglected at high speeds. Two other strategies have been then proposed to be able to manage the compromises, at high speeds, between the high values of torque and efficiency under the constraints of admissible total losses either in the rotor or in the stator.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Coil Design for High Misalignment Tolerant Inductive Power Transfer System for EV Charging
by
Kafeel Ahmed Kalwar, Saad Mekhilef, Mehdi Seyedmahmoudian and Ben Horan
Cited by 72 | Viewed by 12867
Abstract
The inductive power transfer (IPT) system for electric vehicle (EV) charging has acquired more research interest in its different facets. However, the misalignment tolerance between the charging coil (installed in the ground) and pick-up coil (mounted on the car chassis), has been a
[...] Read more.
The inductive power transfer (IPT) system for electric vehicle (EV) charging has acquired more research interest in its different facets. However, the misalignment tolerance between the charging coil (installed in the ground) and pick-up coil (mounted on the car chassis), has been a challenge and fundamental interest in the future market of EVs. This paper proposes a new coil design QDQ (Quad D Quadrature) that maintains the high coupling coefficient and efficient power transfer during reasonable misalignment. The QDQ design makes the use of four adjacent circular coils and one square coil, for both charging and pick-up side, to capture the maximum flux at any position. The coil design has been modeled in JMAG software for calculation of inductive parameters using the finite element method (FEM), and its hardware has been tested experimentally at various misaligned positions. The QDQ coils are shown to be capable of achieving good coupling coefficient and high efficiency of the system until the misalignment displacement reaches 50% of the employed coil size.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Analytical Modeling of Static Eccentricities in Axial Flux Permanent-Magnet Machines with Concentrated Windings
by
Yunkai Huang, Baocheng Guo, Ahmed Hemeida and Peter Sergeant
Cited by 28 | Viewed by 10638
Abstract
The aim of this paper is to calculate the static eccentricity (SE) of a double rotor axial flux permanent magnet (AFPM) machine by using a general analytical model. The flux density in the air gap under healthy conditions is calculated firstly, where the
[...] Read more.
The aim of this paper is to calculate the static eccentricity (SE) of a double rotor axial flux permanent magnet (AFPM) machine by using a general analytical model. The flux density in the air gap under healthy conditions is calculated firstly, where the axial and circumferential magnetic flux densities are obtained using a coupled solution of Maxwell’s equations and Schwarz-Christoffel (SC) mapping. The magnetic flux densities under SE conditions are calculated afterwards using a novel bilinear mapping. Some important electromagnetic parameters, e.g., back electromotive force (EMF), cogging torque and electromagnetic (EM) torque, are calculated for both SE and healthy conditions, and compared with the finite element (FE) model. As for the double rotor AFPM, SE does not contribute much effect on the back EMF and EM torque, while the cogging torque is increased. At each calculated section, FE models were built to validate the analytical model. The results show that the analytical predictions agree well with the FE results. Finally, the results of analytical model are verified via experimental results.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
A Review of Frequency Response Analysis Methods for Power Transformer Diagnostics
by
Saleh Alsuhaibani, Yasin Khan, Abderrahmane Beroual and Nazar Hussain Malik
Cited by 78 | Viewed by 11263
Abstract
Power transformers play a critical role in electric power networks. Such transformers can suffer failures due to multiple stresses and aging. Thus, assessment of condition and diagnostic techniques are of great importance for improving power network reliability and service continuity. Several techniques are
[...] Read more.
Power transformers play a critical role in electric power networks. Such transformers can suffer failures due to multiple stresses and aging. Thus, assessment of condition and diagnostic techniques are of great importance for improving power network reliability and service continuity. Several techniques are available to diagnose the faults within the power transformer. Frequency response analysis (FRA) method is a powerful technique for diagnosing transformer winding deformation and several other types of problems that are caused during manufacture, transportation, installation and/or service life. This paper provides a comprehensive review on FRA methods and their applications in diagnostics and fault identification for power transformers. The paper discusses theory and applications of FRA methods as well as various issues and challenges faced in the application of this method.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
State-of-Charge Estimation for Li-Ion Power Batteries Based on a Tuning Free Observer
by
Xiaopeng Tang, Boyang Liu, Furong Gao and Zhou Lv
Cited by 27 | Viewed by 6100
Abstract
A battery’s state-of-charge (
SOC) can be used to estimate the mileage an electric vehicle (EV) can travel. It is desirable to make such an estimation not only accurate, but also economical in computation, so that the battery management system (BMS) can
[...] Read more.
A battery’s state-of-charge (
SOC) can be used to estimate the mileage an electric vehicle (EV) can travel. It is desirable to make such an estimation not only accurate, but also economical in computation, so that the battery management system (BMS) can be cost-effective in its implementation. Existing computationally-efficient
SOC estimation algorithms, such as the Luenberger observer, suffer from low accuracy and require tuning of the feedback gain by trial-and-error. In this study, an algorithm named lazy-extended Kalman filter (LEKF) is proposed, to allow the Luenberger observer to learn periodically from the extended Kalman filter (EKF) and solve the problems, while maintaining computational efficiency. We demonstrated the effectiveness and high performance of LEKF by both numerical simulation and experiments under different load conditions. The results show that LEKF can have 50% less computational complexity than the conventional EKF and a near-optimal estimation error of less than 2%.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessCorrection
Correction: Juan, A.A.; Mendez, C.A.; Faulin, J.; de Armas, J.; Grasman, S.E. Electric Vehicles in Logistics and Transportation: A Survey on Emerging Environmental, Strategic, and Operational Challenges. Energies 2016, 9, 86
by
Angel Alejandro Juan, Carlos Alberto Mendez, Javier Faulin, Jesica De Armas and Scott Erwin Grasman
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 5905
Abstract
The authors wish to make the following changes to the published paper [1].[...]
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Online Identification with Reliability Criterion and State of Charge Estimation Based on a Fuzzy Adaptive Extended Kalman Filter for Lithium-Ion Batteries
by
Zhongwei Deng, Lin Yang, Yishan Cai and Hao Deng
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 8524
Abstract
In the field of state of charge (SOC) estimation, the Kalman filter has been widely used for many years, although its performance strongly depends on the accuracy of the battery model as well as the noise covariance. The Kalman gain determines the confidence
[...] Read more.
In the field of state of charge (SOC) estimation, the Kalman filter has been widely used for many years, although its performance strongly depends on the accuracy of the battery model as well as the noise covariance. The Kalman gain determines the confidence coefficient of the battery model by adjusting the weight of open circuit voltage (OCV) correction, and has a strong correlation with the measurement noise covariance (
R). In this paper, the online identification method is applied to acquire the real model parameters under different operation conditions. A criterion based on the OCV error is proposed to evaluate the reliability of online parameters. Besides, the equivalent circuit model produces an intrinsic model error which is dependent on the load current, and the property that a high battery current or a large current change induces a large model error can be observed. Based on the above prior knowledge, a fuzzy model is established to compensate the model error through updating
R. Combining the positive strategy (
i.e., online identification) and negative strategy (
i.e., fuzzy model), a more reliable and robust SOC estimation algorithm is proposed. The experiment results verify the proposed reliability criterion and SOC estimation method under various conditions for LiFePO
4 batteries.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Mitigation Emission Strategy Based on Resonances from a Power Inverter System in Electric Vehicles
by
Li Zhai, Xinyu Zhang, Natalia Bondarenko, David Loken, Thomas P. Van Doren and Daryl G. Beetner
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 8083
Abstract
Large d
v/d
t and d
i/d
t outputs of power devices in the DC-fed motor power inverter can generate conducted and/or radiated emissions through parasitics that interfere with low voltage electric systems in electric vehicles (EVs) and nearby vehicles. The
[...] Read more.
Large d
v/d
t and d
i/d
t outputs of power devices in the DC-fed motor power inverter can generate conducted and/or radiated emissions through parasitics that interfere with low voltage electric systems in electric vehicles (EVs) and nearby vehicles. The electromagnetic interference (EMI) filters, ferrite chokes, and shielding added in the product process based on the “black box” approach can reduce the emission levels in a specific frequency range. However, these countermeasures may also introduce an unexpected increase in EMI noises in other frequency ranges due to added capacitances and inductances in filters resonating with elements of the power inverter, and even increase the weight and dimension of the power inverter system in EVs with limited space. In order to predict the interaction between the mitigation techniques and power inverter geometry, an accurate model of the system is needed. A power inverter system was modeled based on series of two-port network measurements to study the impact of EMI generated by power devices on radiated emission of AC cables. Parallel resonances within the circuit can cause peaks in the S21 (transmission coefficient between the phase-node-to-chassis voltage and the center-conductor-to-shield voltage of the AC cable connecting to the motor) and Z11 (input impedance at Port 1 between the Insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) phase node and chassis) at those resonance frequencies and result in enlarged noise voltage peaks at Port 1. The magnitude of S21 between two ports was reduced to decrease the amount of energy coupled from the noise source between the phase node and chassis to the end of the AC cable by lowering the corresponding quality factor. The equivalent circuits were built by analyzing current-following paths at three critical resonance frequencies. Interference voltage peaks can be suppressed by mitigating the resonances. The capacitances and inductances generating the parallel resonances and responsible elements were determined by the calculation through the equivalent circuits. A combination of mitigation strategies including adding common-mode (CM) ferrite chokes through the Y-caps and the AC bus bar was designed to mitigate the resonances at 6 MHz, 11 MHz, and 26 MHz related to the CM conducted emission by IGBT switching and the radiated emission of the AC cable. The values of Z11 decreased respectively by 15 dB at 6 MHz, 0.4 dB at 11 MHz, and 11.5 dB at 26 MHz and the values of S21 decreased respectively by 8.6 dB at 6 MHz, 7 dB at 11 MHz, and 6.3 dB at 26 MHz. An equivalent model of the power inverter system for real-time simulation in time domain was built to validate the mitigation strategy in simulation software PSPICE.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Design and Application of a Power Unit to Use Plug-In Electric Vehicles as an Uninterruptible Power Supply
by
Gorkem Sen, Ali Rifat Boynuegri, Mehmet Uzunoglu, Ozan Erdinc and João P. S. Catalão
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 9630
Abstract
Grid-enabled vehicles (GEVs) such as plug-in electric vehicles present environmental and energy sustainability advantages compared to conventional vehicles. GEV runs solely on power generated by its own battery group, which supplies power to its electric motor. This battery group can be charged from
[...] Read more.
Grid-enabled vehicles (GEVs) such as plug-in electric vehicles present environmental and energy sustainability advantages compared to conventional vehicles. GEV runs solely on power generated by its own battery group, which supplies power to its electric motor. This battery group can be charged from external electric sources. Nowadays, the interaction of GEV with the power grid is unidirectional by the charging process. However, GEV can be operated bi-directionally by modifying its power unit. In such operating conditions, GEV can operate as an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) and satisfy a portion or the total energy demand of the consumption center independent from utility grid, which is known as vehicle-to-home (V2H). In this paper, a power unit is developed for GEVs in the laboratory to conduct simulation and experimental studies to test the performance of GEVs as a UPS unit in V2H mode at the time of need. The activation and deactivation of the power unit and islanding protection unit are examined when energy is interrupted.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Development and Simulation of a Type of Four-Shaft ECVT for a Hybrid Electric Vehicle
by
Yong Zhang, Xuerui Ma, Chengliang Yin and Shifei Yuan
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 9099
Abstract
In hybrid electric vehicles with power-split configurations, the engine can be decoupled from the wheel and operated with improved fuel economy, while the entire efficiency of the powertrain is affected by the circular electric power flow. Two planetary gear (2-PG) sets with adding
[...] Read more.
In hybrid electric vehicles with power-split configurations, the engine can be decoupled from the wheel and operated with improved fuel economy, while the entire efficiency of the powertrain is affected by the circular electric power flow. Two planetary gear (2-PG) sets with adding brakes/clutches, namely a type of four shaft elelctric continuously variable transmission (ECVT) can provide multi-mode operation for the powertrain and extend the efficient area. First, a conventional 2-PG AT (Automatic Transmission) architecture is investigated. By analyzing and comparing the connection and operating modes based on the kinematic relationship and lever analogy, a feasible four-shaft ECVT architecture with two brakes and two simplified versions are picked. To make a trade-off between fuel economy and configuration complexity, an instantaneous optimal control strategy based on the equivalent consumption minimization strategy (ECMS) concept is then developed and employed as the unified optimization method in the simulations of three different configurations. Finally, the simulation results show that the simplified versions are suboptimal sets and the fuel economy is sacrificed by the limits of different modes. From the viewpoint of concept design, a multi-mode power-split configuration is more suitable for hybrid electric vehicles. This research applied a systematic methodology from concept design to energy management optimization, which can provide the guidelines for researchers to select a suitable multi-mode power-split hybrid powertrain.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Influence of Electrode Density on the Performance of Li-Ion Batteries: Experimental and Simulation Results
by
Jelle Smekens, Rahul Gopalakrishnan, Nils Van den Steen, Noshin Omar, Omar Hegazy, Annick Hubin and Joeri Van Mierlo
Cited by 57 | Viewed by 18462
Abstract
Lithium-ion battery (LIB) technology further enabled the information revolution by powering smartphones and tablets, allowing these devices an unprecedented performance against reasonable cost. Currently, this battery technology is on the verge of carrying the revolution in road transport and energy storage of renewable
[...] Read more.
Lithium-ion battery (LIB) technology further enabled the information revolution by powering smartphones and tablets, allowing these devices an unprecedented performance against reasonable cost. Currently, this battery technology is on the verge of carrying the revolution in road transport and energy storage of renewable energy. However, to fully succeed in the latter, a number of hurdles still need to be taken. Battery performance and lifetime constitute a bottleneck for electric vehicles as well as stationary electric energy storage systems to penetrate the market. Electrochemical battery models are one of the engineering tools which could be used to enhance their performance. These models can help us optimize the cell design and the battery management system. In this study, we evaluate the ability of the Porous Electrode Theory (PET) to predict the effect of changing positive electrode density in the overall performance of Li-ion battery cells. It can be concluded that Porous Electrode Theory (PET) is capable of predicting the difference in cell performance due to a changing positive electrode density.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Optimization of Fuel Consumption and Emissions for Auxiliary Power Unit Based on Multi-Objective Optimization Model
by
Yongpeng Shen, Zhendong He, Dongqi Liu and Binjie Xu
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 9616
Abstract
Auxiliary power units (APUs) are widely used for electric power generation in various types of electric vehicles, improvements in fuel economy and emissions of these vehicles directly depend on the operating point of the APUs. In order to balance the conflicting goals of
[...] Read more.
Auxiliary power units (APUs) are widely used for electric power generation in various types of electric vehicles, improvements in fuel economy and emissions of these vehicles directly depend on the operating point of the APUs. In order to balance the conflicting goals of fuel consumption and emissions reduction in the process of operating point choice, the APU operating point optimization problem is formulated as a constrained multi-objective optimization problem (CMOP) firstly. The four competing objectives of this CMOP are fuel-electricity conversion cost, hydrocarbon (HC) emissions, carbon monoxide (CO) emissions and nitric oxide (NO x ) emissions. Then, the multi-objective particle swarm optimization (MOPSO) algorithm and weighted metric decision making method are employed to solve the APU operating point multi-objective optimization model. Finally, bench experiments under New European driving cycle (NEDC), Federal test procedure (FTP) and high way fuel economy test (HWFET) driving cycles show that, compared with the results of the traditional fuel consumption single-objective optimization approach, the proposed multi-objective optimization approach shows significant improvements in emissions performance, at the expense of a slight drop in fuel efficiency.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Environmental Analysis of Petrol, Diesel and Electric Passenger Cars in a Belgian Urban Setting
by
Nils Hooftman, Luis Oliveira, Maarten Messagie, Thierry Coosemans and Joeri Van Mierlo
Cited by 124 | Viewed by 33331
Abstract
The combustion of fossil fuels in the transport sector leads to an aggravation of the air quality along city roads and highways. Urban air quality is a serious problem nowadays as the number of vehicles increases on a yearly basis. With stricter Euro
[...] Read more.
The combustion of fossil fuels in the transport sector leads to an aggravation of the air quality along city roads and highways. Urban air quality is a serious problem nowadays as the number of vehicles increases on a yearly basis. With stricter Euro emission regulations, vehicle manufacturers are not meeting the imposed limits and are also disregarding the non-exhaust emissions. This paper highlights the relevance of non-exhaust emissions of passenger vehicles, both conventional (diesel and petrol) or electric vehicles (EV), on air quality levels in an urban environment in Belgium. An environmental life cycle assessment was carried out based on a real-world emission model for passenger cars and fuel refinery data. A cut-off was applied to the models to highlight what emissions, both from the refinery to the exhaust and electricity production for EV, do actually occur within Belgium’s borders. Results show that not much progress has been made from Euro 4 to 6 for conventional vehicles. Electric vehicles pose the best alternative solution as a more environmentally friendly means of transportation. The analysis results target policy makers with the intention that regulations and policies would be developed in the future and target the characterization of non-exhaust emissions from vehicles. These results indicate that EVs offer a valid solution for addressing the urban air quality issue and that non-exhaust emissions should be addressed in future regulatory steps as they dominate the impact spectrum.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Chaotic-Based Control of Three-Port Isolated Bidirectional DC/DC Converters for Electric and Hybrid Vehicles
by
Zheng Wang, Bochen Liu, Yue Zhang, Ming Cheng, Kai Chu and Liang Xu
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 10513
Abstract
Three-port isolated (TPI) bidirectional DC/DC converters have three energy ports and offer advantages of large voltage gain, galvanic isolation ability and high power density. For this reason this kind of converters are suitable to connect different energy sources and loads in electric and
[...] Read more.
Three-port isolated (TPI) bidirectional DC/DC converters have three energy ports and offer advantages of large voltage gain, galvanic isolation ability and high power density. For this reason this kind of converters are suitable to connect different energy sources and loads in electric and hybrid vehicles. The purpose of this paper is to propose chaotic modulation and the related control scheme for TPI bidirectional DC/DC converters, in such a way that the switching harmonic peaks can be suppressed in spectrum and the conducted electromagnetic interference (EMI) is reduced. Two chaotic modulation strategies, namely the continuously chaotic modulation and the discretely chaotic modulation are presented. These two chaotic modulation strategies are applied for TPI bidirectional DC/DC converters with shifted-phase angle based control and phase-shifted PWM control. Both simulation and experiments are given to verify the validity of the proposed chaotic modulation-based control schemes.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Vibration Durability Testing of Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC) Lithium-Ion 18,650 Battery Cells
by
James Michael Hooper, James Marco, Gael Henri Chouchelamane and Christopher Lyness
Cited by 57 | Viewed by 16619
Abstract
Electric vehicle (EV) manufacturers are employing cylindrical format cells in the construction of the vehicles’ battery systems. There is evidence to suggest that both the academic and industrial communities have evaluated cell degradation due to vibration and other forms of mechanical loading. The
[...] Read more.
Electric vehicle (EV) manufacturers are employing cylindrical format cells in the construction of the vehicles’ battery systems. There is evidence to suggest that both the academic and industrial communities have evaluated cell degradation due to vibration and other forms of mechanical loading. The primary motivation is often the need to satisfy the minimum requirements for safety certification. However, there is limited research that quantifies the durability of the battery and in particular, how the cells will be affected by vibration that is representative of a typical automotive service life (e.g., 100,000 miles). This paper presents a study to determine the durability of commercially available 18,650 cells and quantifies both the electrical and mechanical vibration-induced degradation through measuring changes in cell capacity, impedance and natural frequency. The impact of the cell state of charge (SOC) and in-pack orientation is also evaluated. Experimental results are presented which clearly show that the performance of 18,650 cells can be affected by vibration profiles which are representative of a typical vehicle life. Consequently, it is recommended that EV manufacturers undertake vibration testing, as part of their technology selection and development activities to enhance the quality of EVs and to minimize the risk of in-service warranty claims.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Investigation of a Co-Axial Dual-Mechanical Ports Flux-Switching Permanent Magnet Machine for Hybrid Electric Vehicles
by
Wei Hua and Ling Kang Zhou
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 7372
Abstract
In this paper, a co-axial dual-mechanical ports flux-switching permanent magnet (CADMP-FSPM) machine for hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) is proposed and investigated, which is comprised of two conventional co-axial FSPM machines, namely one high-speed inner rotor machine and one low-speed outer rotor machine and
[...] Read more.
In this paper, a co-axial dual-mechanical ports flux-switching permanent magnet (CADMP-FSPM) machine for hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) is proposed and investigated, which is comprised of two conventional co-axial FSPM machines, namely one high-speed inner rotor machine and one low-speed outer rotor machine and a non-magnetic ring sandwiched in between. Firstly, the topology and operation principle of the CADMP-FSPM machine are introduced; secondly, the control system of the proposed electronically-controlled continuously-variable transmission (E-CVT) system is given; thirdly, the key design specifications of the CADMP-FSPM machine are determined based on a conventional dual-mechanical ports (DMP) machine with a wound inner rotor. Fourthly, the performances of the CADMP-FSPM machine and the normal DMP machine under the same overall volume are compared, and the results indicate that the CADMP-FSPM machine has advantages over the conventional DMP machine in the elimination of brushes and slip rings, improved thermal dissipation conditions for the inner rotor, direct-driven operation, more flexible modes, lower cogging torque and torque ripple, lower total harmonic distortion (THD) values of phase PM flux linkage and phase electro-motive force (EMF), higher torque output capability and is suitable for the E-CVT systems. Finally, the pros and cons of the CADMP-FSPM machine are highlighted. This paper lays a theoretical foundation for further research on CADMP-FSPM machines used for HEVs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Design and Optimization of Permanent Magnet Brushless Machines for Electric Vehicle Applications
by
Weiwei Gu, Xiaoyong Zhu, Li Quan and Yi Du
Cited by 38 | Viewed by 11769
Abstract
In this paper, by considering and establishing the relationship between the maximum operating speed and
d-axis inductance, a new design and optimization method is proposed. Thus, a more extended constant power speed range, as well as reduced losses and increased efficiency, especially
[...] Read more.
In this paper, by considering and establishing the relationship between the maximum operating speed and
d-axis inductance, a new design and optimization method is proposed. Thus, a more extended constant power speed range, as well as reduced losses and increased efficiency, especially in the high-speed region, can be obtained, which is essential for electric vehicles (EVs). In the first step, the initial permanent magnet (PM) brushless machine is designed based on the consideration of the maximum speed and performance specifications in the entire operation region. Then, on the basis of increasing
d-axis inductance, and meanwhile maintaining constant permanent magnet flux linkage, the PM brushless machine is optimized. The corresponding performance of the initial and optimal PM brushless machines are analyzed and compared by the finite-element method (FEM). Several tests are carried out in an EV simulation model based on the urban dynamometer driving schedule (UDDS) for evaluation. Both theoretical analysis and simulation results verify the validity of the proposed design and optimization method.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Lossy Counting-Based State of Charge Estimation Method and Its Application to Electric Vehicles
by
Hong Zhang, Li Zhao and Yong Chen
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 7069
Abstract
Estimating the residual capacity or state-of-charge (SoC) of commercial batteries on-line without destroying them or interrupting the power supply, is quite a challenging task for electric vehicle (EV) designers. Many Coulomb counting-based methods have been used to calculate the remaining capacity in EV
[...] Read more.
Estimating the residual capacity or state-of-charge (SoC) of commercial batteries on-line without destroying them or interrupting the power supply, is quite a challenging task for electric vehicle (EV) designers. Many Coulomb counting-based methods have been used to calculate the remaining capacity in EV batteries or other portable devices. The main disadvantages of these methods are the cumulative error and the time-varying Coulombic efficiency, which are greatly influenced by the operating state (SoC, temperature and current). To deal with this problem, we propose a lossy counting-based Coulomb counting method for estimating the available capacity or SoC. The initial capacity of the tested battery is obtained from the open circuit voltage (OCV). The charging/discharging efficiencies, used for compensating the Coulombic losses, are calculated by the lossy counting-based method. The measurement drift, resulting from the current sensor, is amended with the distorted Coulombic efficiency matrix. Simulations and experimental results show that the proposed method is both effective and convenient.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A New Method for State of Charge Estimation of Lithium-Ion Battery Based on Strong Tracking Cubature Kalman Filter
by
Bizhong Xia, Haiqing Wang, Mingwang Wang, Wei Sun, Zhihui Xu and Yongzhi Lai
Cited by 44 | Viewed by 7486
Abstract
The estimation of state of charge (SOC) is a crucial evaluation index in a battery management system (BMS). The value of SOC indicates the remaining capacity of a battery, which provides a good guarantee of safety and reliability of battery operation. It is
[...] Read more.
The estimation of state of charge (SOC) is a crucial evaluation index in a battery management system (BMS). The value of SOC indicates the remaining capacity of a battery, which provides a good guarantee of safety and reliability of battery operation. It is difficult to get an accurate value of the SOC, being one of the inner states. In this paper, a strong tracking cubature Kalman filter (STCKF) based on the cubature Kalman filter is presented to perform accurate and reliable SOC estimation. The STCKF algorithm can adjust gain matrix online by introducing fading factor to the state estimation covariance matrix. The typical second-order resistor-capacitor model is used as the battery’s equivalent circuit model to dynamically simulate characteristics of the battery. The exponential-function fitting method accomplishes the task of relevant parameters identification. Then, the developed STCKF algorithm has been introduced in detail and verified under different operation current profiles such as Dynamic Stress Test (DST) and New European Driving Cycle (NEDC). Making a comparison with extended Kalman filter (EKF) and CKF algorithm, the experimental results show the merits of the STCKF algorithm in SOC estimation accuracy and robustness.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Steady-State Characteristics Analysis of Hybrid-Excited Flux-Switching Machines with Identical Iron Laminations
by
Gan Zhang, Wei Hua and Ming Cheng
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 8121
Abstract
Since the air-gap field of flux-switching permanent magnet (FSPM) machines is difficult to regulate as it is produced by the stator-magnets alone, a type of hybrid-excited flux-switching (HEFS) machine is obtained by reducing the magnet length of an original FSPM machine and introducing
[...] Read more.
Since the air-gap field of flux-switching permanent magnet (FSPM) machines is difficult to regulate as it is produced by the stator-magnets alone, a type of hybrid-excited flux-switching (HEFS) machine is obtained by reducing the magnet length of an original FSPM machine and introducing a set of field windings into the saved space. In this paper, the steady-state characteristics, especially for the loaded performances of four prototyped HEFS machines, namely, PM-top, PM-middle-1, PM-middle-2, and PM-bottom, are comprehensively compared and evaluated based on both 2D and 3D finite element analysis. Also, the influences of PM materials including ferrite and NdFeB, respectively, on the characteristics of HEFS machines are covered. Particularly, the impacts of magnet movement in the corresponding slot on flux-regulating performances are studied in depth. The best overall performances employing NdFeB can be obtained when magnets are located near the air-gap. The FEA predictions are validated by experimental measurements on corresponding machine prototypes.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Open-Phase Fault Tolerance Techniques of Five-Phase Dual-Rotor Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor
by
Jing Zhao, Xu Gao, Bin Li, Xiangdong Liu and Xing Guan
Cited by 19 | Viewed by 8994
Abstract
Multi-phase motors are gaining more attention due to the advantages of good fault tolerance capability and high power density,
etc. By applying dual-rotor technology to multi-phase machines, a five-phase dual-rotor permanent magnet synchronous motor (DRPMSM) is researched in this paper to further promote
[...] Read more.
Multi-phase motors are gaining more attention due to the advantages of good fault tolerance capability and high power density,
etc. By applying dual-rotor technology to multi-phase machines, a five-phase dual-rotor permanent magnet synchronous motor (DRPMSM) is researched in this paper to further promote their torque density and fault tolerance capability. It has two rotors and two sets of stator windings, and it can adopt a series drive mode or parallel drive mode. The fault-tolerance capability of the five-phase DRPMSM is researched. All open circuit fault types and corresponding fault tolerance techniques in different drive modes are analyzed. A fault-tolerance control strategy of injecting currents containing a certain third harmonic component is proposed for five-phase DRPMSM to ensure performance after faults in the motor or drive circuit. For adjacent double-phase faults in the motor, based on where the additional degrees of freedom are used, two different fault-tolerance current calculation schemes are adopted and the torque results are compared. Decoupling of the inner motor and outer motor is investigated under fault-tolerant conditions in parallel drive mode. The finite element analysis (FMA) results and co-simulation results based on Simulink-Simplorer-Maxwell verify the effectiveness of the techniques.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
An Online Learning Control Strategy for Hybrid Electric Vehicle Based on Fuzzy Q-Learning
by
Yue Hu, Weimin Li, Hui Xu and Guoqing Xu
Cited by 31 | Viewed by 8438
Abstract
In order to realize the online learning of a hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) control strategy, a fuzzy Q-learning (FQL) method is proposed in this paper. FQL control strategies consists of two parts: The optimal action-value function
Q*(
x,
u) estimator
[...] Read more.
In order to realize the online learning of a hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) control strategy, a fuzzy Q-learning (FQL) method is proposed in this paper. FQL control strategies consists of two parts: The optimal action-value function
Q*(
x,
u) estimator network (QEN) and the fuzzy parameters tuning (FPT). A back propagation (BP) neural network is applied to estimate
Q*(
x,
u) as QEN. For the fuzzy controller, we choose a Sugeno-type fuzzy inference system (FIS) and the parameters of the FIS are tuned online based on
Q*(
x,
u). The action exploration modifier (AEM) is introduced to guarantee all actions are tried. The main advantage of a FQL control strategy is that it does not rely on prior information related to future driving conditions and can self-tune the parameters of the fuzzy controller online. The FQL control strategy has been applied to a HEV and simulation tests have been done. Simulation results indicate that the parameters of the fuzzy controller are tuned online and that a FQL control strategy achieves good performance in fuel economy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Flywheel Energy Storage for Automotive Applications
by
Magnus Hedlund, Johan Lundin, Juan De Santiago, Johan Abrahamsson and Hans Bernhoff
Cited by 116 | Viewed by 34473
Abstract
A review of flywheel energy storage technology was made, with a special focus on the progress in automotive applications. We found that there are at least 26 university research groups and 27 companies contributing to flywheel technology development. Flywheels are seen to excel
[...] Read more.
A review of flywheel energy storage technology was made, with a special focus on the progress in automotive applications. We found that there are at least 26 university research groups and 27 companies contributing to flywheel technology development. Flywheels are seen to excel in high-power applications, placing them closer in functionality to supercapacitors than to batteries. Examples of flywheels optimized for vehicular applications were found with a specific power of 5.5 kW/kg and a specific energy of 3.5 Wh/kg. Another flywheel system had 3.15 kW/kg and 6.4 Wh/kg, which can be compared to a state-of-the-art supercapacitor vehicular system with 1.7 kW/kg and 2.3 Wh/kg, respectively. Flywheel energy storage is reaching maturity, with 500 flywheel power buffer systems being deployed for London buses (resulting in fuel savings of over 20%), 400 flywheels in operation for grid frequency regulation and many hundreds more installed for uninterruptible power supply (UPS) applications. The industry estimates the mass-production cost of a specific consumer-car flywheel system to be 2000 USD. For regular cars, this system has been shown to save 35% fuel in the U.S. Federal Test Procedure (FTP) drive cycle.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Control and Performance Evaluation of Multiphase FSPM Motor in Low-Speed Region for Hybrid Electric Vehicles
by
Feng Yu, Ming Cheng, Kwok Tong Chau and Feng Li
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 8619
Abstract
The flux-switching permanent-magnet (FSPM) motor has been viewed as a highly reliable machine with both armature windings and magnets on the stator. Owing to the high torque-production capability with low torque ripple, FSPM motors with a higher number of phases are potential candidates
[...] Read more.
The flux-switching permanent-magnet (FSPM) motor has been viewed as a highly reliable machine with both armature windings and magnets on the stator. Owing to the high torque-production capability with low torque ripple, FSPM motors with a higher number of phases are potential candidates for traction applications in hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs). However, existing research has mostly focused on the principles and static performance of multiphase FSPM motors, and little attention has been paid to advanced control strategies. In this paper, the fully decoupled current control of a 36/34-pole nine-phase FSPM (NP-FSPM) motor is developed and the performance under different operating conditions is investigated. The aim of the design is to alleviate cross coupling effects and unwanted low-order stator harmonic currents, to guarantee fast transient response and small steady-state error. In addition, its fault-tolerance is further elaborated. These features are very important in automotive applications where low torque pulsation, high fault-tolerant capability and high dynamic performance are of major importance. Firstly, the research status of multiphase FSPM motors is briefly reviewed. Secondly, the mathematical model in the
dq reference frames and control strategies are presented. Then, the control and performance of the NP-FSPM motor are evaluated by using MATLAB/Simulink. Finally, experiments on an NP-FSPM motor prototype are carried out to validate the study.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Study of Fuel Economy Improvement in a Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle using Engine on/off and Battery Charging Power Control Based on Driver Characteristics
by
Seulgi Lee, Jingyu Choi, Kiyun Jeong and Hyunsoo Kim
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 8020
Abstract
In this study, driving data for various types of drivers are collected using a VIDE (virtual integrated driving environment), and a driver model is developed. To represent the driver tendencies quantitatively, the DDA (degree of driver aggression) is proposed based on fuzzy logic.
[...] Read more.
In this study, driving data for various types of drivers are collected using a VIDE (virtual integrated driving environment), and a driver model is developed. To represent the driver tendencies quantitatively, the DDA (degree of driver aggression) is proposed based on fuzzy logic. DDA has a 0-1 value; the closer the DDA is to one, the more aggressive the driver. Using the DDA, an engine on/off and battery charging power control algorithm are developed to improve the fuel economy of a power-split-type plug-in hybrid electric vehicle. The engine on/off control reduces the frequent engine on/off caused by aggressive driving, whereas the battery charging power control maintains the battery state of charge (SOC) by operating the engine according to the DDA. It is found that the proposed control algorithm improves fuel economy by 17.3% compared to the existing control for an aggressive driver.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Study and Implementation of a Two-Phase Interleaved Bidirectional DC/DC Converter for Vehicle and DC-Microgrid Systems
by
Ching-Ming Lai, Yuan-Chih Lin and Dasheng Lee
Cited by 72 | Viewed by 13994
Abstract
The objective of this paper is to implement a two-phase, interleaved, bidirectional DC/DC converter topology with an improved voltage conversion ratio for electric vehicle (EV) and DC-microgrid systems. In this study, a two-phase interleaved charge-pump topology is introduced to achieve a high voltage
[...] Read more.
The objective of this paper is to implement a two-phase, interleaved, bidirectional DC/DC converter topology with an improved voltage conversion ratio for electric vehicle (EV) and DC-microgrid systems. In this study, a two-phase interleaved charge-pump topology is introduced to achieve a high voltage conversion ratio with very simple control circuits. In discharge mode, the circuit topology acts as a voltage-multiplier boost converter to achieve a high step-up conversion ratio (48 V to 240 V). In charge mode, the circuit topology acts as a voltage-divider buck converter to achieve a high voltage step-down conversion ratio (240 V to 48 V). The circuit configuration, operating principle, steady-state analysis and the closed-loop control of the proposed converter are presented. Experiments conducted on a laboratory prototype with 500 W power-rating are presented to verify the effectiveness. The maximum efficiency levels in discharge and charge modes are about 97.7% and 98.4% respectively.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Investigation of Electromagnetic, Thermal and Mechanical Characteristics of a Five-Phase Dual-Rotor Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor
by
Jing Zhao, Wei Liu, Bin Li, Xiangdong Liu, Congzhe Gao and Zhongxin Gu
Cited by 19 | Viewed by 12314
Abstract
This paper investigates of a kind of five-phase dual-rotor permanent-magnet synchronous motor (DRPMSM), which contains dual rotors and a single stator. This kind of motor has the potential advantages of high power density, high reliability and high efficiency, which make it more appropriate
[...] Read more.
This paper investigates of a kind of five-phase dual-rotor permanent-magnet synchronous motor (DRPMSM), which contains dual rotors and a single stator. This kind of motor has the potential advantages of high power density, high reliability and high efficiency, which make it more appropriate for using in electric vehicles (EVs). In order to evaluate the most suitable power level for this kind of structure, the electromagnetic, the thermal and the mechanical characteristics are investigated in this paper. The length to diameter ratio of motors is researched to obtain the highest power density and then the optimum ratio is obtained. Based on the optimum ratio, the thermal characteristics are researched under natural condition and forced-air cooling condition with different wind speeds. In addition, the mechanical characteristics are analyzed under no-load and different loads conditions, respectively. All of the results are analyzed by two-dimension (2-D) and three-dimension (3-D) finite element method (FEM) simulation, which provide a good reference to select suitable power level for this kind of motor structure. Finally, a DRPMSM prototype is manufactured and tested. The experimental results effectively verify the FEM results.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Advanced Electrical Machines and Machine-Based Systems for Electric and Hybrid Vehicles
by
Ming Cheng, Le Sun, Giuseppe Buja and Lihua Song
Cited by 123 | Viewed by 17827
Abstract
The paper presents a number of advanced solutions on electric machines and machine-based systems for the powertrain of electric vehicles (EVs). Two types of systems are considered, namely the drive systems designated to the EV propulsion and the power split devices utilized in
[...] Read more.
The paper presents a number of advanced solutions on electric machines and machine-based systems for the powertrain of electric vehicles (EVs). Two types of systems are considered, namely the drive systems designated to the EV propulsion and the power split devices utilized in the popular series-parallel hybrid electric vehicle architecture. After reviewing the main requirements for the electric drive systems, the paper illustrates advanced electric machine topologies, including a stator permanent magnet (stator-PM) motor, a hybrid-excitation motor, a flux memory motor and a redundant motor structure. Then, it illustrates advanced electric drive systems, such as the magnetic-geared in-wheel drive and the integrated starter generator (ISG). Finally, three machine-based implementations of the power split devices are expounded, built up around the dual-rotor PM machine, the dual-stator PM brushless machine and the magnetic-geared dual-rotor machine. As a conclusion, the development trends in the field of electric machines and machine-based systems for EVs are summarized.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Taxi Fleet Renewal in Cities with Improved Hybrid Powertrains: Life Cycle and Sensitivity Analysis in Lisbon Case Study
by
António P. Castel-Branco, João P. Ribau and Carla M. Silva
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 8245
Abstract
Stringent emissions regulations in cities and the high amount of daily miles driven by taxi vehicles enforce the need to renew these fleets with more efficient and cleaner technologies. Hybrid vehicles are potential candidates due to their enhanced powertrain, and slower battery depletion
[...] Read more.
Stringent emissions regulations in cities and the high amount of daily miles driven by taxi vehicles enforce the need to renew these fleets with more efficient and cleaner technologies. Hybrid vehicles are potential candidates due to their enhanced powertrain, and slower battery depletion and fewer lifetime issues, relative to full electric vehicles. This paper proposes a methodology to analyze the best theoretical hybrid powertrain candidate with maximum in-use efficiency, minimum life cycle greenhouse gas emissions, and minimum additional cost, for a Lisbon taxi fleet case study. A multi-objective genetic algorithm integrated with a vehicle simulator is used to achieve several trade-off optimal solutions for different driving patterns. Potential improvements in taxi carbon footprint are discussed as a function of its lifetime, urban/extra-urban driving and maintenance/fuel life cycle uncertainty. Hybrid powertrains reveal to be advantageous comparatively to the conventional vehicle, especially in urban conditions. Specifically optimized solutions could reduce in-use energy consumption by 43%–47% in urban driving, and 27%–34% in extra-urban driving conditions, and reduce life cycle emissions by 47%–49% and 34%–36% respectively, relative to the conventional taxi. A financial gain of 50 $/km/fleet in extra-urban and 226 $/km/fleet in urban routes could be achieved by replacing the taxi fleet with the optimal solutions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Detuning Minimization of Induction Motor Drive System for Alternative Energy Vehicles
by
Habibur Rehman
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 6873
Abstract
This paper evaluates different types of AC machines and various control techniques for their suitability for the drive system of Alternative Energy Vehicles (AEV). An Indirect Field Oriented (IFO) drive system for the AEV application is chosen and its major problem of detuning
[...] Read more.
This paper evaluates different types of AC machines and various control techniques for their suitability for the drive system of Alternative Energy Vehicles (AEV). An Indirect Field Oriented (IFO) drive system for the AEV application is chosen and its major problem of detuning is addressed by designing an offline and an online rotor resistance adaptation technique. The offline scheme sets the slip gain at various operating conditions based on the fact that if the rotor resistance is set correctly and field orientation is achieved, then there should be a linear relationship between the torque current and the output torque. The online technique is designed using Model Reference Adaptive System (MRAS) for the rotor resistance adaptation. For an ideal field oriented machine, the rotor flux along the q-axis should be zero. This condition acts as a reference model for the proposed MRAS scheme. The current model flux observer in the synchronous frame of reference is selected as an adjustable model and its rotor resistance is tuned so that the flux along the q-axis becomes zero. The effectiveness of the offline tuning scheme is evident through performance validation of the drive system, which is implemented in a real Ford vehicle. The experimental results obtained while driving the test vehicle are included in the paper while the proposed online scheme is validated on a 3.75 kW prototype induction motor.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of the Effect of Operating Parameters on Thermal Performance of an Integrated Starter Generator in Hybrid Electric Vehicles
by
Moo-Yeon Lee, Dong Hyun Lim and Sung Chul Kim
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 9494
Abstract
The belt-driven-type integrated starter generator motor in a hybrid electric vehicle is vulnerable to thermal problems owing to its high output power and proximity to the engine. These problems may cause demagnetization and insulation breakdown, reducing the performance and durability of the motor.
[...] Read more.
The belt-driven-type integrated starter generator motor in a hybrid electric vehicle is vulnerable to thermal problems owing to its high output power and proximity to the engine. These problems may cause demagnetization and insulation breakdown, reducing the performance and durability of the motor. Hence, it is necessary to evaluate the thermal performance and enhance the cooling capacity of the belt-driven type Integrated Starter Generator. In this study, the internal temperature variations of the motor were investigated with respect to the operating parameters, particularly the rotation speed and environment temperature. At a maximum ambient temperature of 105 °C and rotation speed (motor design point) of 4500 rpm, the coil of the motor was heated to approximately 189 °C in generating mode. The harsh conditions of the starting mode were analyzed by assuming that the motor operates during the start-up time at a maximum ambient temperature of 105 °C and rotation speed (motor design point) of 800 rpm; the coil was heated to approximately 200 °C, which is close to the insulation temperature limit. The model for analyzing the thermal performance of the ISG was verified by comparing its results with those obtained through a generating-mode-based experiment
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Real-Time Joint Estimator for Model Parameters and State of Charge of Lithium-Ion Batteries in Electric Vehicles
by
Jianping Gao, Yongzhi Zhang and Hongwen He
Cited by 30 | Viewed by 9595
Abstract
Accurate state of charge (SoC) estimation of batteries plays an important role in promoting the commercialization of electric vehicles. The main work to be done in accurately determining battery SoC can be summarized in three parts. (1) In view of the model-based SoC
[...] Read more.
Accurate state of charge (SoC) estimation of batteries plays an important role in promoting the commercialization of electric vehicles. The main work to be done in accurately determining battery SoC can be summarized in three parts. (1) In view of the model-based SoC estimation flow diagram, the
n-order resistance-capacitance (RC) battery model is proposed and expected to accurately simulate the battery’s major time-variable, nonlinear characteristics. Then, the mathematical equations for model parameter identification and SoC estimation of this model are constructed. (2) The Akaike information criterion is used to determine an optimal tradeoff between battery model complexity and prediction precision for the
n-order RC battery model. Results from a comparative analysis show that the first-order RC battery model is thought to be the best based on the Akaike information criterion (AIC) values. (3) The real-time joint estimator for the model parameter and SoC is constructed, and the application based on two battery types indicates that the proposed SoC estimator is a closed-loop identification system where the model parameter identification and SoC estimation are corrected mutually, adaptively and simultaneously according to the observer values. The maximum SoC estimation error is less than 1% for both battery types, even against the inaccurate initial SoC.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Torque Distribution Algorithm for an Independently Driven Electric Vehicle Using a Fuzzy Control Method
by
Jinhyun Park, Houn Jeong, In Gyu Jang and Sung-Ho Hwang
Cited by 48 | Viewed by 11284
Abstract
The in-wheel electric vehicle is expected to be a popular next-generation vehicle because an in-wheel system can simplify the powertrain and improve driving performance. In addition, it also has an advantage in that it maximizes driving efficiency through independent torque control considering the
[...] Read more.
The in-wheel electric vehicle is expected to be a popular next-generation vehicle because an in-wheel system can simplify the powertrain and improve driving performance. In addition, it also has an advantage in that it maximizes driving efficiency through independent torque control considering the motor efficiency. However, there is an instability problem if only the driving torque is controlled in consideration of only the motor efficiency. In this paper, integrated torque distribution strategies are proposed to overcome these problems. The control algorithm consists of various strategies for optimizing driving efficiency, satisfying driver demands, and considering tire slip and vehicle cornering. Fuzzy logic is used to determine the appropriate timing of intervention for each distribution strategy. A performance simulator for in-wheel electric vehicles was developed by using MATLAB/Simulink and CarSim to validate the control strategies. From simulation results under complex driving conditions, the proposed algorithm was verified to improve both the driving stability and fuel economy of the in-wheel vehicle.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Cell-in-the-Loop Approach to Systems Modelling and Simulation of Energy Storage Systems
by
James Marco, Neelu Kumari, W. Dhammika Widanage and Peter Jones
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 6227
Abstract
This research is aligned with the engineering challenge of scaling-up individual battery cells into a complete energy storage system (ESS). Manufacturing tolerances, coupled with thermal gradients and the differential electrical loading of adjacent cells, can result in significant variations in the rate of
[...] Read more.
This research is aligned with the engineering challenge of scaling-up individual battery cells into a complete energy storage system (ESS). Manufacturing tolerances, coupled with thermal gradients and the differential electrical loading of adjacent cells, can result in significant variations in the rate of cell degradation, energy distribution and ESS performance. The uncertain transition from cell to system often manifests itself in over-engineered, non-optimal ESS designs within both the transport and energy sectors. To alleviate these issues, the authors propose a novel model-based framework for cell-in-the-loop simulation (CILS) in which a physical cell may be integrated within a complete model of an ESS and exercised against realistic electrical and thermal loads in real-time. This paper focuses on the electrical integration of both real and simulated cells within the CILS test environment. Validation of the CILS approach using real-world electric vehicle data is presented for an 18650 cell. The cell is integrated within a real-time simulation model of a series string of similar cells in a 4sp1 configuration. Results are presented that highlight the impact of cell variability (
i.e., capacity and impedance) on the energy available from the multi-cell system and the useable capacity of the physical cell.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Thermal Analysis of a Novel Cylindrical Transverse-Flux Permanent-Magnet Linear Machine
by
Bin Yu, Shukuan Zhang, Jidong Yan, Luming Cheng and Ping Zheng
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 8716
Abstract
This paper presents a novel staggered-teeth cylindrical transverse-flux permanent-magnet linear machine (TFPMLM), which aims to improve the power factor and force density. Due to the compact structure and high performance requirement, thermal problems should be seriously considered. The three-dimensional (3-D) temperature field model
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a novel staggered-teeth cylindrical transverse-flux permanent-magnet linear machine (TFPMLM), which aims to improve the power factor and force density. Due to the compact structure and high performance requirement, thermal problems should be seriously considered. The three-dimensional (3-D) temperature field model is established. The determination of convection heat transfer coefficients is discussed. Equivalent thermal conductivities of stator core and winding are given to simplify the analysis. With the thermal effect of the adhesive coatings among permanent magnets (PMs) and mover yoke taken into account, the temperature field distribution and variation rules of the TFPMLM are obtained using the finite volume method (FVM). The influences of slot filling factor and air flow velocity on the temperature field distribution are analyzed. It is found that the hottest spot of the TFPMLM appears in the middle of the end winding; and there is no risk of demagnetization for PMs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Multi-Function Conversion Technique for Vehicle-to-Grid Applications
by
Ying Fan, Weixia Zhu, Zhongbing Xue, Li Zhang and Zhixiang Zou
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 8437
Abstract
This paper presents a new multi-function conversion technique for vehicle-to-grid (V2G) applications. The proposed bi-directional charger can achieve three functions, including EV battery charging, grid-connection and reactive compensation, which are keys for energy management of the grid. With the proposed multi-function technology, the
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a new multi-function conversion technique for vehicle-to-grid (V2G) applications. The proposed bi-directional charger can achieve three functions, including EV battery charging, grid-connection and reactive compensation, which are keys for energy management of the grid. With the proposed multi-function technology, the bi-directional charger will benefit both the grid and electricity customers. A hybrid regulation of energy bi-directional transfer for V2G systems is proposed in this paper, which consists of the battery-side controller and the grid-side controller. This proposed multi-function conversion technique improves the whole system performance with proportional-resonant (PR) control and achieves reactive power compensation with instantaneous reactive theory and a deadbeat control scheme. Simulation and experimental results demonstrate the validity of this new multi-function technique in a V2G system.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Reinforcement Learning–Based Energy Management Strategy for a Hybrid Electric Tracked Vehicle
by
Teng Liu, Yuan Zou, Dexing Liu and Fengchun Sun
Cited by 96 | Viewed by 10236
Abstract
This paper presents a reinforcement learning (RL)–based energy management strategy for a hybrid electric tracked vehicle. A control-oriented model of the powertrain and vehicle dynamics is first established. According to the sample information of the experimental driving schedule, statistical characteristics at various velocities
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a reinforcement learning (RL)–based energy management strategy for a hybrid electric tracked vehicle. A control-oriented model of the powertrain and vehicle dynamics is first established. According to the sample information of the experimental driving schedule, statistical characteristics at various velocities are determined by extracting the transition probability matrix of the power request. Two RL-based algorithms, namely
Q-learning and
Dyna algorithms, are applied to generate optimal control solutions. The two algorithms are simulated on the same driving schedule, and the simulation results are compared to clarify the merits and demerits of these algorithms. Although the
Q-learning algorithm is faster (3 h) than the
Dyna algorithm (7 h), its fuel consumption is 1.7% higher than that of the
Dyna algorithm. Furthermore, the
Dyna algorithm registers approximately the same fuel consumption as the dynamic programming–based global optimal solution. The computational cost of the
Dyna algorithm is substantially lower than that of the stochastic dynamic programming.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Wheel Slip Control for Improving Traction-Ability and Energy Efficiency of a Personal Electric Vehicle
by
Kanghyun Nam, Yoichi Hori and Choonyoung Lee
Cited by 77 | Viewed by 16719
Abstract
In this paper, a robust wheel slip control system based on a sliding mode controller is proposed for improving traction-ability and reducing energy consumption during sudden acceleration for a personal electric vehicle. Sliding mode control techniques have been employed widely in the development
[...] Read more.
In this paper, a robust wheel slip control system based on a sliding mode controller is proposed for improving traction-ability and reducing energy consumption during sudden acceleration for a personal electric vehicle. Sliding mode control techniques have been employed widely in the development of a robust wheel slip controller of conventional internal combustion engine vehicles due to their application effectiveness in nonlinear systems and robustness against model uncertainties and disturbances. A practical slip control system which takes advantage of the features of electric motors is proposed and an algorithm for vehicle velocity estimation is also introduced. The vehicle velocity estimator was designed based on rotational wheel dynamics, measurable motor torque, and wheel velocity as well as rule-based logic. The simulations and experiments were carried out using both CarSim software and an experimental electric vehicle equipped with in-wheel-motors. Through field tests, traction performance and effectiveness in terms of energy saving were all verified. Comparative experiments with variations of control variables proved the effectiveness and practicality of the proposed control design.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
An Electric Bus with a Battery Exchange System
by
Jeongyong Kim, Inho Song and Woongchul Choi
Cited by 35 | Viewed by 11322
Abstract
As part of the ongoing effort to be independent of petroleum resources and to be free from pollutant emission issues, various electric vehicles have been developed and tested through their integration with real world systems. In the current paper, yet another application specific
[...] Read more.
As part of the ongoing effort to be independent of petroleum resources and to be free from pollutant emission issues, various electric vehicles have been developed and tested through their integration with real world systems. In the current paper, yet another application specific EV for public transportation, an electric bus, is introduced and explained with results from the pilot test program which was carried out under real traffic conditions. The main feature of the current system is a battery exchanging mechanism mounted on the roof of the bus. The current configuration certainly requires an externally fabricated battery exchanging robot system that would complement the electric bus for a fully automated battery exchanging process. The major advantage of the current system is the quick re-charging of the electric energy through the physical battery exchange and the possible utilization of the battery exchange station as a mini scale energy storage system for grid system peak power shaving. With the total system solution approach for the public transportation system, it is fully expected to create outstanding business opportunities in number of areas such as battery suppliers, battery exchanging station management, battery leasing and many more.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Three-Phase High-Power and Zero-Current-Switching OBC for Plug-In Electric Vehicles
by
Cheng-Shan Wang, Wei Li, Zhun Meng, Yi-Feng Wang and Jie-Gui Zhou
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 8921
Abstract
In this paper, an interleaved high-power zero-current-switching (ZCS) onboard charger (OBC) based on the three-phase single-switch buck rectifier is proposed for application to plug-in electric vehicles (EVs). The multi-resonant structure is used to achieve high efficiency and high power density, which are necessary
[...] Read more.
In this paper, an interleaved high-power zero-current-switching (ZCS) onboard charger (OBC) based on the three-phase single-switch buck rectifier is proposed for application to plug-in electric vehicles (EVs). The multi-resonant structure is used to achieve high efficiency and high power density, which are necessary to reduce the volume and weight of the OBC. This study focuses on the border conditions of ZCS converting with a battery load, which means the variation ranges of the output voltage and current are very large. Furthermore, a novel hybrid control method combining pulse frequency modulation (PFM) and pulse width modulation (PWM) together is presented to ensure a driving frequency higher than 10 kHz, and this will reduce the unexpected inner resonant power flow and decrease the total harmonic distortion (THD) of the input current under a light load at the end of the charging process. Finally, a prototype is established, and experiments are carried out. According to the experimental results, the conversion efficiency is higher than 93.5%, the THD about 4.3% and power factor (PF) 0.98 under the maximum power output condition. Besides, a three-stage charging process is also carried out the experimental platform.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Model-based Sensor Fault Diagnosis of a Lithium-ion Battery in Electric Vehicles
by
Zhentong Liu and Hongwen He
Cited by 96 | Viewed by 11102
Abstract
The battery critical functions such as State-of-Charge (SoC) and State-of-Health (SoH) estimations, over-current, and over-/under-voltage protections mainly depend on current and voltage sensor measurements. Therefore, it is imperative to develop a reliable sensor fault diagnosis scheme to guarantee the battery performance, safety and
[...] Read more.
The battery critical functions such as State-of-Charge (SoC) and State-of-Health (SoH) estimations, over-current, and over-/under-voltage protections mainly depend on current and voltage sensor measurements. Therefore, it is imperative to develop a reliable sensor fault diagnosis scheme to guarantee the battery performance, safety and life. This paper presents a systematic model-based fault diagnosis scheme for a battery cell to detect current or voltage sensor faults. The battery model is developed based on the equivalent circuit technique. For the diagnostic scheme implementation, the extended Kalman filter (EKF) is used to estimate the terminal voltage of battery cell, and the residual carrying fault information is then generated by comparing the measured and estimated voltage. Further, the residual is evaluated by a statistical inference method that determines the presence of a fault. To highlight the importance of battery sensor fault diagnosis, the effects of sensors faults on battery SoC estimation and possible influences are analyzed. Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed diagnostic scheme is experimentally validated, and the results show that the current or voltage sensor fault can be accurately detected.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Four-Phase High Voltage Conversion Ratio Bidirectional DC-DC Converter for Battery Applications
by
Li-Kun Xue, Ping Wang, Yi-Feng Wang, Tai-Zhou Bei and Hai-Yun Yan
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 9977
Abstract
This study presents a four-phase interleaved high voltage conversion ratio bidirectional DC-DC converter circuit based on coupled inductors and switched capacitors, which can eliminate the defects of conventional high voltage conversion ratio bidirectional DC-DC converters in terms of high-voltage/current stress, less efficiency and
[...] Read more.
This study presents a four-phase interleaved high voltage conversion ratio bidirectional DC-DC converter circuit based on coupled inductors and switched capacitors, which can eliminate the defects of conventional high voltage conversion ratio bidirectional DC-DC converters in terms of high-voltage/current stress, less efficiency and low-power limitation. Parallel channels are used to reduce current stress at the low-voltage side and series connected switched capacitors are used to enlarge voltage conversion ratio, reduce voltage stress and achieve auto current sharing. This paper proposes the operation principle, feature analysis and optimization design considerations. On this basis the objectives of high voltage conversion ratio, low voltage/current stress, high power density, high efficiency and high-power applications can be achieved. Some experimental results based on a 500 W prototype converter (24 V to 48 V at low-voltage side, 400 V at high-voltage side) are given to verify the theoretical analysis and the effectiveness of the proposed converter.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Power Management Optimization of an Experimental Fuel Cell/Battery/Supercapacitor Hybrid System
by
Farouk Odeim, Jürgen Roes and Angelika Heinzel
Cited by 106 | Viewed by 11076
Abstract
In this paper, an experimental fuel cell/battery/supercapacitor hybrid system is investigated in terms of modeling and power management design and optimization. The power management strategy is designed based on the role that should be played by each component of the hybrid power source.
[...] Read more.
In this paper, an experimental fuel cell/battery/supercapacitor hybrid system is investigated in terms of modeling and power management design and optimization. The power management strategy is designed based on the role that should be played by each component of the hybrid power source. The supercapacitor is responsible for the peak power demands. The battery assists the supercapacitor in fulfilling the transient power demand by controlling its state-of-energy, whereas the fuel cell system, with its slow dynamics, controls the state-of-charge of the battery. The parameters of the power management strategy are optimized by a genetic algorithm and Pareto front analysis in a framework of multi-objective optimization, taking into account the hydrogen consumption, the battery loading and the acceleration performance. The optimization results are validated on a test bench composed of a fuel cell system (1.2 kW, 26 V), lithium polymer battery (30 Ah, 37 V), and a supercapacitor (167 F, 48 V).
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Research on a Novel Power Inductor-Based Bidirectional Lossless Equalization Circuit for Series-Connected Battery Packs
by
Xiangwei Guo, Longyun Kang, Zhizhen Huang, Yuan Yao and Huizhou Yang
Cited by 37 | Viewed by 7371
Abstract
Cell balancing plays an important role in preserving the life of series-connected battery packs; without a suitable balancing system, the individual cell voltages will differ over time, and the battery pack capacity will decrease quickly. This paper presents a novel power inductor-based bidirectional
[...] Read more.
Cell balancing plays an important role in preserving the life of series-connected battery packs; without a suitable balancing system, the individual cell voltages will differ over time, and the battery pack capacity will decrease quickly. This paper presents a novel power inductor-based bidirectional lossless equalization circuit. This circuit consists of several balancing sub-circuits, which allow the dynamic adjustment of the equalization path and equalization threshold. The simulation and experiment results demonstrate that the proposed circuit, which features a simple control method, fast balancing, and a large equalization current, exhibits outstanding equalization performance.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Extended Kalman Filter with a Fuzzy Method for Accurate Battery Pack State of Charge Estimation
by
Saeed Sepasi, Leon R. Roose and Marc M. Matsuura
Cited by 71 | Viewed by 10824
Abstract
As the world moves toward greenhouse gas reduction, there is increasingly active work around Li-ion chemistry-based batteries as an energy source for electric vehicles (EVs), hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) and smart grids. In these applications, the battery management system (BMS) requires an accurate
[...] Read more.
As the world moves toward greenhouse gas reduction, there is increasingly active work around Li-ion chemistry-based batteries as an energy source for electric vehicles (EVs), hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) and smart grids. In these applications, the battery management system (BMS) requires an accurate online estimation of the state of charge (SOC) in a battery pack. This estimation is difficult, especially after substantial battery aging. In order to address this problem, this paper utilizes SOC estimation of Li-ion battery packs using a fuzzy-improved extended Kalman filter (fuzzy-IEKF) for Li-ion cells, regardless of their age. The proposed approach introduces a fuzzy method with a new class and associated membership function that determines an approximate initial value applied to SOC estimation. Subsequently, the EKF method is used by considering the single unit model for the battery pack to estimate the SOC for following periods of battery use. This approach uses an adaptive model algorithm to update the model for each single cell in the battery pack. To verify the accuracy of the estimation method, tests are done on a LiFePO
4 aged battery pack consisting of 120 cells connected in series with a nominal voltage of 432 V.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Rule-Based Energy Management Strategy for a Plug-in Hybrid School Bus Based on a Controller Area Network Bus
by
Jiankun Peng, Hao Fan, Hongwen He and Deng Pan
Cited by 64 | Viewed by 10449
Abstract
This paper presents a rule-based energy management strategy for a plug-in hybrid school bus (PHSB). In order to verify the effectiveness and rationality of the proposed energy management strategy, the powertrain and control models were built with MATLAB/Simulink. The PHSB powertrain model includes
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a rule-based energy management strategy for a plug-in hybrid school bus (PHSB). In order to verify the effectiveness and rationality of the proposed energy management strategy, the powertrain and control models were built with MATLAB/Simulink. The PHSB powertrain model includes an engine model, ISG (integrated started and generator) model, drive motor model, power battery packs model, driver model, and vehicle longitudinal dynamics model. To evaluate the controller area network (CAN) bus performance features such as the bus load, signal hysteresis, and to verify the reliability and real-time performance of the CAN bus multi-node control method, a co-simulation platform was built with CANoe and MATLAB/Simulink. The co-simulation results show that the control strategy can meet the requirements of the PHSB’s dynamic performance. Meanwhile, the charge-depleting mode (CD) and charge-sustaining mode (CS) can switch between each other and maintain a state-of-charge (SoC) of around 30%, indicating that the energy management strategy effectively extends the working period of the CD mode and improves the fuel economy further. The energy consumption per 100 km includes 13.7 L diesel and 10.5 kW·h electricity with an initial SoC of 75%. The CANoe simulation results show that the bus communication performs well without error frames.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Energy Efficiency Comparison between Hydraulic Hybrid and Hybrid Electric Vehicles
by
Jia-Shiun Chen
Cited by 69 | Viewed by 19013
Abstract
Conventional vehicles tend to consume considerable amounts of fuel, which generates exhaust gases and environmental pollution during intermittent driving cycles. Therefore, prospective vehicle designs favor improved exhaust emissions and energy consumption without compromising vehicle performance. Although pure electric vehicles feature high performance and
[...] Read more.
Conventional vehicles tend to consume considerable amounts of fuel, which generates exhaust gases and environmental pollution during intermittent driving cycles. Therefore, prospective vehicle designs favor improved exhaust emissions and energy consumption without compromising vehicle performance. Although pure electric vehicles feature high performance and low pollution characteristics, their limitations are their short driving range and high battery costs. Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) are comparatively environmentally friendly and energy efficient, but cost substantially more compared with conventional vehicles. Hydraulic hybrid vehicles (HHVs) are mainly operated using engines, or using alternate combinations of engine and hydraulic power sources while vehicles accelerate. When the hydraulic system accumulator is depleted, the conventional engine reengages; concurrently, brake-regenerated power is recycled and reused by employing hydraulic motor–pump modules in circulation patterns to conserve fuel and recycle brake energy. This study adopted MATLAB Simulink to construct complete HHV and HEV models for backward simulations. New European Driving Cycles were used to determine the changes in fuel economy. The output of power components and the state-of-charge of energy could be retrieved. Varying power component models, energy storage component models, and series or parallel configurations were combined into seven different vehicle configurations: the conventional manual transmission vehicle, series hybrid electric vehicle, series hydraulic hybrid vehicle, parallel hybrid electric vehicle, parallel hydraulic hybrid vehicle, purely electric vehicle, and hydraulic-electric hybrid vehicle. The simulation results show that fuel consumption was 21.80% lower in the series hydraulic hybrid vehicle compared to the series hybrid electric vehicle; additionally, fuel consumption was 3.80% lower in the parallel hybrid electric vehicle compared to the parallel hydraulic hybrid vehicle. Furthermore, the hydraulic–electric hybrid vehicles consumed 11.4% less electricity than the purely electric vehicle did. The simulations indicated that hydraulic-electric hybrid vehicle could provide the best energy cost among all the configurations studied.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Lithium-Ion Battery Cell Cycling and Usage Analysis in a Heavy-Duty Truck Field Study
by
Pontus Svens, Mårten Behm and Göran Lindbergh
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 8152
Abstract
This paper presents results from a field test performed on commercial power-optimized lithium-ion battery cells cycled on three heavy-duty trucks. The goal with this study was to age battery cells in a hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) environment and find suitable methods for identifying
[...] Read more.
This paper presents results from a field test performed on commercial power-optimized lithium-ion battery cells cycled on three heavy-duty trucks. The goal with this study was to age battery cells in a hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) environment and find suitable methods for identifying cell ageing. The battery cells were cycled on in-house developed equipment intended for testing on conventional vehicles by emulating an HEV environment. A hybrid strategy that allows battery usage to vary within certain limits depending on driving patterns was used. This concept allows unobtrusive and low-cost testing of battery cells under realistic conditions. Each truck was equipped with one cell cycling equipment and two battery cells. One cell per vehicle was cycled during the test period while a reference cell on each vehicle experienced the same environmental conditions without being cycled. Differential voltage analysis and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy were used to identify ageing of the tested battery cells. Analysis of driving patterns and battery usage was performed from collected vehicle data and battery cell data.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Concept of EV’s Intelligent Integrated Station and Its Energy Flow
by
Da Xie, Haoxiang Chu, Yupu Lu, Chenghong Gu, Furong Li and Yu Zhang
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 7716
Abstract
The increasing number of electric vehicles (EVs) connected to existing distribution networks as time-variant loads cause significant distortions in line current and voltage. A novel EV’s intelligent integrated station (IIS) making full use of retired batteries is introduced in this paper to offer
[...] Read more.
The increasing number of electric vehicles (EVs) connected to existing distribution networks as time-variant loads cause significant distortions in line current and voltage. A novel EV’s intelligent integrated station (IIS) making full use of retired batteries is introduced in this paper to offer a potential solution for accommodating the charging demand of EVs. It proposes the concept of generalized energy in IIS, based on the energy/power flow between IIS and EVs, and between IIS and the power grid, to systematically evaluate the energy capacity of IIS. In order to derive a unique and satisfactory operation mode, information from both the grid (in terms of load level) and IIS (in terms of its energy capacity and EVs battery charging/exchanging requests) is merged. Then, based on the generalized energy of different systems, a novel charging/discharging control strategy is presented and whereby the operating status of the grid and energy capacity of IIS are monitored to make reasonable operation plans for IIS. Simulation results suggest that the proposed IIS offers peak load shifting when EV battery charging/exchanging requests are satisfied compared to existing charging stations.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Acceleration Slip Regulation Strategy for Distributed Drive Electric Vehicles with Independent Front Axle Drive Motors
by
Lingfei Wu, Jinfang Gou, Lifang Wang and Junzhi Zhang
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 8593
Abstract
This paper presents an acceleration slip regulation strategy for distributed drive electric vehicles with two motors on the front axle. The tasks of the strategy include controlling the slip ratio to make full use of the road grip and controlling the yaw rate
[...] Read more.
This paper presents an acceleration slip regulation strategy for distributed drive electric vehicles with two motors on the front axle. The tasks of the strategy include controlling the slip ratio to make full use of the road grip and controlling the yaw rate to eliminate the lateral movement due to the difference between motor torques. The rate of the slip ratio change can be controlled by controlling the motor torque, so that the slip ratio can be controlled by applying a proportional-integral control strategy to control the rate of the slip ratio change. The yaw rate can be controlled to almost zero by applying torque compensation based on yaw rate feedback. A coordination control strategy for the slip ratio control and yaw rate control is proposed based on analysis of the priorities and features of the two control processes. Simulations were carried out using MATLAB/Simulink, and experiments were performed on a hardware-in-loop test bench with actual motors. The results of the simulations and experiments showed that the proposed strategy could improve the longitudinal driving performance and straight line driving stability of the vehicle.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Multi-Period Optimization Model for Electricity Generation Planning Considering Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle Penetration
by
Lena Ahmadi, Ali Elkamel, Sabah A. Abdul-Wahab, Michael Pan, Eric Croiset, Peter L. Douglas and Evgueniy Entchev
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 7669
Abstract
One of the main challenges for widespread penetration of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) is their impact on the electricity grid. The energy sector must anticipate and prepare for this extra demand and implement long-term planning for electricity production. In this paper, the
[...] Read more.
One of the main challenges for widespread penetration of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) is their impact on the electricity grid. The energy sector must anticipate and prepare for this extra demand and implement long-term planning for electricity production. In this paper, the additional electricity demand on the Ontario electricity grid from charging PHEVs is incorporated into an electricity production planning model. A case study pertaining to Ontario energy planning is considered to optimize the value of the cost of the electricity over sixteen years (2014–2030). The objective function consists of the fuel costs, fixed and variable operating and maintenance costs, capital costs for new power plants, and the retrofit costs of existing power plants. Five different case studies are performed with different PHEVs penetration rates, types of new power plants, and CO
2 emission constraints. Among all the cases studied, the one requiring the most new capacity, (~8748 MW), is assuming the base case with 6% reduction in CO
2 in year 2018 and high PHEV penetration. The next highest one is the base case, plus considering doubled NG prices, PHEV medium penetration rate and no CO
2 emissions reduction target with an increase of 34.78% in the total installed capacity in 2030. Furthermore, optimization results indicate that by not utilizing coal power stations the CO
2 emissions are the lowest: ~500 tonnes compared to ~900 tonnes when coal is permitted.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Indirect Matrix Converter for Hybrid Electric Vehicle Application with Three-Phase and Single-Phase Outputs
by
Yeongsu Bak, Eunsil Lee and Kyo-Beum Lee
Cited by 43 | Viewed by 10725
Abstract
This paper presents an indirect matrix converter (IMC) topology for hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) application with three-phase and single-phase outputs. The HEV includes mechanical, electrical, control, and electrochemical systems among others. In the mechanical system, a traction motor and a compressor motor are
[...] Read more.
This paper presents an indirect matrix converter (IMC) topology for hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) application with three-phase and single-phase outputs. The HEV includes mechanical, electrical, control, and electrochemical systems among others. In the mechanical system, a traction motor and a compressor motor are used to drive the HEV. The traction motor and the compressor motor are usually operated as three-phase and single-phase motors, respectively. In this respect, a dual AC-drive system can operate the traction and the compressor motor simultaneously. Furthermore, compared to a conventional dual matrix converter system, the proposed topology can reduce the number of switches that the dual outputs share with a DC-link. The application of this system for HEV has advantages, like long lifetime and reduced volume due to the lack of a DC-link. The proposed control strategy and modulation schemes ensure the sinusoidal input and output waveforms and bidirectional power transmission. The proposed system for the HEV application is verified by simulation and experiments.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Comparison of Output Current Ripple in Single and Dual Three-Phase Inverters for Electric Vehicle Motor Drives
by
Jelena Loncarski, Mats Leijon, Milan Srndovic, Claudio Rossi and Gabriele Grandi
Cited by 25 | Viewed by 11617
Abstract
The standard solution for the traction system in battery powered electric vehicles (EVs) is a two-level (2L) inverter feeding a three-phase motor. A simple and effective way to achieve a three-level (3L) inverter in battery-supplied electric vehicles consists of using two standard three-phase
[...] Read more.
The standard solution for the traction system in battery powered electric vehicles (EVs) is a two-level (2L) inverter feeding a three-phase motor. A simple and effective way to achieve a three-level (3L) inverter in battery-supplied electric vehicles consists of using two standard three-phase 2L inverters with the open-end winding connection of standard three-phase ac motors. The 3L inverter solution can be usefully adopted in EVs since it combines several benefits such as current ripple reduction, increment of phase motor voltage with limited voltage ratings of the two battery banks, improvement in system reliability,
etc. The reduction in current ripple amplitude is particularly relevant since it is a source of electromagnetic interference and audio noise from the inverter-motor power connection cables and from the motor itself. By increasing the inverter switching frequency the ripple amplitude is reduced, but the drive efficiency decreases due to the proportionally increased switching losses. In this paper the peak-to-peak ripple amplitude of the dual-2L inverter is evaluated and compared with the corresponding ripple of the single-2L inverter, considering the same voltage and power motor ratings. The ripple analysis is carried out as a function of the modulation index to cover the whole modulation range of the inverter, and the theoretical results are verified with experimental tests carried out by an inverter-motor drive prototype.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Wheel Torque Distribution of Four-Wheel-Drive Electric Vehicles Based on Multi-Objective Optimization
by
Cheng Lin and Zhifeng Xu
Cited by 84 | Viewed by 10984
Abstract
The wheel driving torque on four-wheel-drive electric vehicles (4WDEVs) can be modulated precisely and continuously, therefore maneuverability and energy-saving control can be carried out at the same time. In this paper, a wheel torque distribution strategy is developed based on multi-objective optimization to
[...] Read more.
The wheel driving torque on four-wheel-drive electric vehicles (4WDEVs) can be modulated precisely and continuously, therefore maneuverability and energy-saving control can be carried out at the same time. In this paper, a wheel torque distribution strategy is developed based on multi-objective optimization to improve vehicle maneuverability and reduce energy consumption. In the high-layer of the presented method, sliding mode control is used to calculate the desired yaw moment due to the model inaccuracy and parameter error. In the low-layer, mathematical programming with the penalty function consisting of the yaw moment control offset, the drive system energy loss and the slip ratio constraint is used for wheel torque control allocation. The programming is solved with the combination of off-line and on-line optimization to reduce the calculation cost, and the optimization results are sent to motor controllers as torque commands. Co-simulation based on MATLAB
® and Carsim
® proves that the developed strategy can both improve the vehicle maneuverability and reduce energy consumption.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Optimal Energy Management Strategy of a Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle Based on a Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm
by
Zeyu Chen, Rui Xiong, Kunyu Wang and Bin Jiao
Cited by 148 | Viewed by 14844
Abstract
Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) have been recognized as one of the most promising vehicle categories nowadays due to their low fuel consumption and reduced emissions. Energy management is critical for improving the performance of PHEVs. This paper proposes an energy management approach
[...] Read more.
Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) have been recognized as one of the most promising vehicle categories nowadays due to their low fuel consumption and reduced emissions. Energy management is critical for improving the performance of PHEVs. This paper proposes an energy management approach based on a particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm. The optimization objective is to minimize total energy cost (summation of oil and electricity) from vehicle utilization. A main drawback of optimal strategies is that they can hardly be used in real-time control. In order to solve this problem, a rule-based strategy containing three operation modes is proposed first, and then the PSO algorithm is implemented on four threshold values in the presented rule-based strategy. The proposed strategy has been verified by the US06 driving cycle under the MATLAB/Simulink software environment. Two different driving cycles are adopted to evaluate the generalization ability of the proposed strategy. Simulation results indicate that the proposed PSO-based energy management method can achieve better energy efficiency compared with traditional blended strategies. Online control performance of the proposed approach has been demonstrated through a driver-in-the-loop real-time experiment.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Application Study on the Dynamic Programming Algorithm for Energy Management of Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles
by
Ximing Wang, Hongwen He, Fengchun Sun and Jieli Zhang
Cited by 174 | Viewed by 12579
Abstract
To explore the problems associated with applying dynamic programming (DP) in the energy management strategies of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), a plug-in hybrid bus powertrain is introduced and its dynamic control model is constructed. The numerical issues, including the discretization resolution of
[...] Read more.
To explore the problems associated with applying dynamic programming (DP) in the energy management strategies of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), a plug-in hybrid bus powertrain is introduced and its dynamic control model is constructed. The numerical issues, including the discretization resolution of the relevant variables and the boundary issue of their feasible regions, were considered when implementing DP to solve the optimal control problem of PHEVs. The tradeoff between the optimization accuracy when using the DP algorithm and the computational burden was systematically investigated. As a result of overcoming the numerical issues, the DP-based approach has the potential to improve the fuel-savings potential of PHEVs. The results from comparing the DP-based strategy and the traditional control strategy indicate that there is an approximately 20% improvement in fuel economy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Research on an Axial Flux PMSM with Radially Sliding Permanent Magnets
by
Jing Zhao, Bin Li and Zhongxin Gu
Cited by 19 | Viewed by 15789
Abstract
Axial flux permanent-magnet synchronous machines (PMSMs) are very suitable candidates for the power train of electric vehicles (EVs) due to high power density and high efficiency. This paper researches an axial flux PMSM with radially sliding permanent magnets (PMs) to fulfill field-weakening control.
[...] Read more.
Axial flux permanent-magnet synchronous machines (PMSMs) are very suitable candidates for the power train of electric vehicles (EVs) due to high power density and high efficiency. This paper researches an axial flux PMSM with radially sliding permanent magnets (PMs) to fulfill field-weakening control. The field weakening principle and the structure of this kind of axial flux PMSM by mechanical method of sliding PMs are proposed and analyzed. The influences of radially sliding PMs on magnetic flux density distribution, inductance, flux linkage and torque are analyzed and discussed based on 3D finite element method (FEM). The field weakening capabilities by mechanical method and electrical method are compared. The field weakening capability of the machine can be much improved by the optimized combination of the two methods, which is very satisfying for EV drive application. The forces on the PMs are analyzed and calculated. The hysteretic characteristics caused by the friction of the PMs are investigated, which provide useful reference for designing this kind of machine.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Towards a Friendly Energy Management Strategy for Hybrid Electric Vehicles with Respect to Pollution, Battery and Drivability
by
Guillaume Colin, Yann Chamaillard, Alain Charlet and Dominique Nelson-Gruel
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 8313
Abstract
The paper proposes a generic methodology to incorporate constraints (pollutant emission, battery health, drivability) into on-line energy management strategies (EMSs) for hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs). The integration of each constraint into the EMS, made with the Pontryagin
[...] Read more.
The paper proposes a generic methodology to incorporate constraints (pollutant emission, battery health, drivability) into on-line energy management strategies (EMSs) for hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs). The integration of each constraint into the EMS, made with the Pontryagin maximum principle, shows a tradeoff between the fuel consumption and the constraint introduced. As state dynamics come into play (catalyst temperature, battery cell temperature, etc.), the optimization problem becomes more complex. Simulation results are presented to highlight the contribution of this generic strategy, including constraints compared to the standard approach. These results show that it is possible to find an energy management strategy that takes into account an increasing number of constraints (drivability, pollution, aging, environment, etc.). However, taking these constraints into account increases fuel consumption (the existence of a trade-off curve). This trade-off can be sometimes difficult to find, and the tools developed in this paper should help to find an acceptable solution quickly
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Battery Sizing for Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles in Beijing: A TCO Model Based Analysis
by
Cong Hou, Hewu Wang and Minggao Ouyang
Cited by 29 | Viewed by 10048
Abstract
This paper proposes a total cost of ownership (TCO) model for battery sizing of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs). The proposed systematic TCO model innovatively integrates the Beijing driving database and optimal PHEV energy management strategies developed earlier. The TCO, including battery, fuel,
[...] Read more.
This paper proposes a total cost of ownership (TCO) model for battery sizing of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs). The proposed systematic TCO model innovatively integrates the Beijing driving database and optimal PHEV energy management strategies developed earlier. The TCO, including battery, fuel, electricity, and salvage costs, is calculated in yearly cash flows. The salvage cost, based on battery degradation model, is proposed for the first time. The results show that the optimal battery size for PHEVs in Beijing is 6–8 kWh. Several additional scenarios are also analyzed: (1) 10% increase in battery price or discount rate leads to an optimal battery size of 6 kWh, and 10% increase in fuel price shifts the optimal battery size to 8 kWh; (2) the longer and more dispersive daily range distribution in the U.S. increases the optimal battery size to 14 kWh; (3) the subsidy in China results in an optimal battery size of 13 kWh, while that in the U.S. results in 17 kWh, and a fuel savings rate based subsidy policy is innovatively proposed; (4) the optimal battery size with Li
4Ti
5O
12 batteries is 2 kWh, but the TCO of Li
4Ti
5O
12 batteries is higher than that of LiFePO
4 batteries.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Topology of a Bidirectional Converter for Energy Interaction between Electric Vehicles and the Grid
by
Jiuchun Jiang, Yan Bao and Le Yi Wang
Cited by 60 | Viewed by 20054
Abstract
In vehicle-to-grid (V2G) systems, electric vehicles interact with the grid as distributed energy storage systems that offer many potential benefits. As an energy interface between a vehicle and the grid, the bidirectional converter plays a crucial role in their interaction. Its reliability, safety,
[...] Read more.
In vehicle-to-grid (V2G) systems, electric vehicles interact with the grid as distributed energy storage systems that offer many potential benefits. As an energy interface between a vehicle and the grid, the bidirectional converter plays a crucial role in their interaction. Its reliability, safety, cost, efficiency, weight, size, harmonics, and other factors are of essential importance for V2G realization, especially for on-board operations. Beyond the common existing topologies for bidirectional chargers, this paper introduces a novel high-power-factor bidirectional single-stage full-bridge (BSS-FBC) topology, which offers advantages in power density, size, weight, cost, efficiency, power quality, dynamic characteristic, reliability, and complexity. Its operational principles and control strategies are presented. Harmonic analysis on the basis of double-Fourier integral is performed with detailed comparison of line current harmonic characteristics between the BSS-FBC topology and unipolar/bipolar controlled single-phase pulse width modulation (PWM) converters. A dynamic model of the topology is derived, its dynamic behavior analyzed, and its compensator design method developed. Simulation and experimental results are employed to verify the design and analysis. Design considerations for the key parameters are discussed. A 3.3 kW prototype is developed for this topology and validated in its vehicle applications. The results demonstrate clearly the benefits and advantages of the new topology.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
SDP Policy Iteration-Based Energy Management Strategy Using Traffic Information for Commuter Hybrid Electric Vehicles
by
Xiaohong Jiao and Tielong Shen
Cited by 34 | Viewed by 9115
Abstract
This paper demonstrates an energy management method using traffic information for commuter hybrid electric vehicles. A control strategy based on stochastic dynamic programming (SDP) is developed, which minimizes on average the equivalent fuel consumption, while satisfying the battery charge-sustaining constraints and the overall
[...] Read more.
This paper demonstrates an energy management method using traffic information for commuter hybrid electric vehicles. A control strategy based on stochastic dynamic programming (SDP) is developed, which minimizes on average the equivalent fuel consumption, while satisfying the battery charge-sustaining constraints and the overall vehicle power demand for drivability. First, according to the sample information of the traffic speed profiles, the regular route is divided into several segments and the statistic characteristics in the different segments are constructed from gathered data on the averaged vehicle speeds. And then, the energy management problem is formulated as a stochastic nonlinear and constrained optimal control problem and a modified policy iteration algorithm is utilized to generate a time-invariant state-dependent power split strategy. Finally, simulation results over some driving cycles are presented to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed energy management strategy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Neural Network Combined Inverse Controller for a Two-Rear-Wheel Independently Driven Electric Vehicle
by
Duo Zhang, Guohai Liu, Wenxiang Zhao, Penghu Miao, Yan Jiang and Huawei Zhou
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 8420
Abstract
Vehicle active safety control is attracting ever increasing attention in the attempt to improve the stability and the maneuverability of electric vehicles. In this paper, a neural network combined inverse (NNCI) controller is proposed, incorporating the merits of left-inversion and right-inversion. As the
[...] Read more.
Vehicle active safety control is attracting ever increasing attention in the attempt to improve the stability and the maneuverability of electric vehicles. In this paper, a neural network combined inverse (NNCI) controller is proposed, incorporating the merits of left-inversion and right-inversion. As the left-inversion soft-sensor can estimate the sideslip angle, while the right-inversion is utilized to decouple control. Then, the proposed NNCI controller not only linearizes and decouples the original nonlinear system, but also directly obtains immeasurable state feedback in constructing the right-inversion. Hence, the proposed controller is very practical in engineering applications. The proposed system is co-simulated based on the vehicle simulation package CarSim in connection with Matlab/Simulink. The results verify the effectiveness of the proposed control strategy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Real World Operation of a Complex Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle: Analysis of Its CO2 Emissions and Operating Costs
by
Federico Millo, Luciano Rolando and Rocco Fuso
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 9587
Abstract
Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (pHEVs) could represent the stepping stone to move towards a more sustainable mobility and combine the benefits of electric powertrains with the high range capability of conventional vehicles. Nevertheless, despite the huge potential in terms of CO
2 emissions
[...] Read more.
Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (pHEVs) could represent the stepping stone to move towards a more sustainable mobility and combine the benefits of electric powertrains with the high range capability of conventional vehicles. Nevertheless, despite the huge potential in terms of CO
2 emissions reduction, the performance of such vehicles has to be deeply investigated in real world driving conditions considering also the CO
2 production related to battery recharge which, on the contrary, is currently only partially considered by the European regulation to foster the diffusion of pHEVs. Therefore, this paper aims to assess, through numerical simulation, the real performance of a test case pHEV, the energy management system (EMS) of which is targeted to the minimization of its overall CO
2 emissions. The paper highlights, at the same time, the relevance of the CO
2 production related to the battery recharge from the power grid. Different technologies mixes used to produce the electricity required for the battery recharge are also taken into account in order to assess the influence of this parameter on the vehicle CO
2 emissions. Finally, since the operating cost still represents the main driver in orienting the customer’s choice, an alternative approach for the EMS, targeted to the minimization of this variable, is also analyzed.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Energy Management and Control of Electric Vehicles, Using Hybrid Power Source in Regenerative Braking Operation
by
Bo Long, Shin Teak Lim, Zhi Feng Bai, Ji Hyoung Ryu and Kil To Chong
Cited by 45 | Viewed by 16496
Abstract
Today’s battery powered electric vehicles still face many issues: (1) Ways of improving the regenerative braking energy; (2) how to maximally extend the driving-range of electric vehicles (EVs) and prolong the service life of batteries; (3) how to satisfy the energy requirements of
[...] Read more.
Today’s battery powered electric vehicles still face many issues: (1) Ways of improving the regenerative braking energy; (2) how to maximally extend the driving-range of electric vehicles (EVs) and prolong the service life of batteries; (3) how to satisfy the energy requirements of the EVs both in steady and dynamic state. The electrochemical double-layer capacitors, also called ultra-capacitors (UCs), have the merits of high energy density and instantaneous power output capability, and are usually combined with power battery packs to form a hybrid power supply system (HPSS). The power circuit topology of the HPSS has been illustrated in this paper. In the proposed HPSS, all the UCs are in series, which may cause an imbalanced voltage distribution of each unit, moreover, the energy allocation between the batteries and UCs should also be considered. An energy-management scheme to solve this problem has been presented. Moreover, due to the parameter variations caused by temperature changes and produced errors, the modelling procedure of the HPSS becomes very difficult, so an H
∞ current controller is presented. The proposed hybrid power source circuit is implemented on a laboratory hardware setup using a digital signal processor (DSP). Simulation and experimental results have been put forward to demonstrate the feasibility and validity of the approach.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Fuel Economy of Hybrid Buses: The Role of Ancillaries in Real Urban Driving
by
Francesco Bottiglione, Tommaso Contursi, Angelo Gentile and Giacomo Mantriota
Cited by 25 | Viewed by 13685
Abstract
In the present context of the global economic crisis and environmental emergency, transport science is asked to find innovative solutions to turn traditional vehicles into fuel-saving and eco-friendly devices. In the last few years, hybrid vehicles have been shown to have potential benefits
[...] Read more.
In the present context of the global economic crisis and environmental emergency, transport science is asked to find innovative solutions to turn traditional vehicles into fuel-saving and eco-friendly devices. In the last few years, hybrid vehicles have been shown to have potential benefits in this sense. In this paper, the fuel economy of series hybrid-electric and hybrid-mechanical buses is simulated in two real driving situations: cold and hot weather driving in the city of Taranto, in Southern Italy. The numerical analysis is carried out by an inverse dynamic approach, where the bus speed is given as a velocity pattern measured in the field tests performed on one of the city bus routes. The city of Taranto drive schedule is simulated in a typical tempered climate condition and with a hot temperature, when the air conditioning system must be switched on for passenger comfort. The fuel consumptions of hybrid-electric and hybrid-mechanical buses are compared to each other and with a traditional bus powered by a diesel engine. It is shown that the series hybrid-electric vehicle outperforms both the traditional and the mechanical hybrid vehicles in the cold weather driving simulation, reducing the fuel consumption by about 35% with respect to the traditional diesel bus. However, it is also shown that the performance of the hybrid-electric bus gets dramatically worse when the air-cooling system is continuously turned on. In this situation, the fuel consumption of the three different technologies for city buses under investigation is comparable.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Investigation of a Five-Phase Dual-Rotor Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Used for Electric Vehicles
by
Yumeng Li, Jing Zhao, Zhen Chen and Xiangdong Liu
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 14913
Abstract
This paper presents a novel five-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM), which contains dual rotors and a single stator, equivalent to two five-phase motors working together. Thus, this kind of motor has the potential of good fault tolerant capability and high torque density,
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a novel five-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM), which contains dual rotors and a single stator, equivalent to two five-phase motors working together. Thus, this kind of motor has the potential of good fault tolerant capability and high torque density, which makes it appropriate for use in electric vehicles. In view of the different connection types, the inside and outside stator windings can be driven in series or parallel, which results in the different performances of the magnetomotive force (MMF) and torque under open-circuit fault conditions. By decomposing the MMF, the reason that torque ripple increases after open-circuit faults is explained, and the relationship between MMF and torque is revealed. Then, the current control strategy is applied to adjust the open-circuit faults, and the electromagnetic analysis and MMF harmonics analysis are performed to interpret the phenomenon that the torque ripple is still larger than in the normal situation. The investigations are verified by finite element analysis results.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
An Acceleration Slip Regulation Strategy for Four-Wheel Drive Electric Vehicles Based on Sliding Mode Control
by
Hongwen He, Jiankun Peng, Rui Xiong and Hao Fan
Cited by 66 | Viewed by 15148
Abstract
This paper presents an acceleration slip regulation (ASR) system for four-wheel drive (4WD) electric vehicles, which are driven by the front and rear axles simultaneously. The ASR control strategy includes three control modes: average distribution of inter-axle torque, optimal distribution of inter-axle torque
[...] Read more.
This paper presents an acceleration slip regulation (ASR) system for four-wheel drive (4WD) electric vehicles, which are driven by the front and rear axles simultaneously. The ASR control strategy includes three control modes: average distribution of inter-axle torque, optimal distribution of inter-axle torque and independent control of optimal slip rate, respectively, which are designed based on the torque adaptive principle of inter-axle differential and sliding mode control theory. Furthermore, in order to accurately describe the longitudinal tyre force characteristic, a slip rate calculation formula in the form of a state equation was used for solving the numerical problem posed by the traditional way. A simulation was carried out with the MATLAB/Simulink software. The simulation results show that the proposed ASR system can fully use the road friction condition, inhibit the drive-wheels from slipping, and improve the vehicle longitudinal driving stability.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Sensitivity Analyses for Cross-Coupled Parameters in Automotive Powertrain Optimization
by
Pongpun Othaganont, Francis Assadian and Daniel Auger
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 8767
Abstract
When vehicle manufacturers are developing new hybrid and electric vehicles, modeling and simulation are frequently used to predict the performance of the new vehicles from an early stage in the product lifecycle. Typically, models are used to predict the range, performance and energy
[...] Read more.
When vehicle manufacturers are developing new hybrid and electric vehicles, modeling and simulation are frequently used to predict the performance of the new vehicles from an early stage in the product lifecycle. Typically, models are used to predict the range, performance and energy consumption of their future planned production vehicle; they also allow the designer to optimize a vehicle’s configuration. Another use for the models is in performing sensitivity analysis, which helps us understand which parameters have the most influence on model predictions and real-world behaviors. There are various techniques for sensitivity analysis, some are numerical, but the greatest insights are obtained analytically with sensitivity defined in terms of partial derivatives. Existing methods in the literature give us a useful, quantified measure of parameter sensitivity, a first-order effect, but they do not consider second-order effects. Second-order effects could give us additional insights: for example, a first order analysis might tell us that a limiting factor is the efficiency of the vehicle’s prime-mover; our new second order analysis will tell us how quickly the efficiency of the powertrain will become of greater significance. In this paper, we develop a method based on formal optimization mathematics for rapid second-order sensitivity analyses and illustrate these through a case study on a C-segment electric vehicle.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Review and Comparison of Power Management Approaches for Hybrid Vehicles with Focus on Hydraulic Drives
by
Mohammad Ali Karbaschian and Dirk Söffker
Cited by 57 | Viewed by 11530
Abstract
The main advantage of hybrid powertrains is based on the efficient transfer of power and torque from power sources to the powertrain as well as recapturing of reversible energies without effecting the vehicle performance. The benefits of hybrid hydraulic powertrains can be better
[...] Read more.
The main advantage of hybrid powertrains is based on the efficient transfer of power and torque from power sources to the powertrain as well as recapturing of reversible energies without effecting the vehicle performance. The benefits of hybrid hydraulic powertrains can be better utilized with an appropriate power management. In this paper, different types of power management algorithms like off-line and on-line methods are briefly reviewed and classified. Finally, the algorithms are evaluated and compared. Therefore, different related criteria are evaluated and applied.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Equivalent Consumption Minimization Strategy for the Control of Real Driving NOx Emissions of a Diesel Hybrid Electric Vehicle
by
Tobias Nüesch, Alberto Cerofolini, Giorgio Mancini, Nicolò Cavina, Christopher Onder and Lino Guzzella
Cited by 104 | Viewed by 14380
Abstract
Motivated by the fact that the real driving NOx emissions (RDE) of conventional diesel vehicles can exceed the legislation norms by far, a concept for the control of RDE with a diesel parallel hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) is proposed. By extending the well-known
[...] Read more.
Motivated by the fact that the real driving NOx emissions (RDE) of conventional diesel vehicles can exceed the legislation norms by far, a concept for the control of RDE with a diesel parallel hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) is proposed. By extending the well-known equivalent consumption minimization strategy (ECMS), the power split degree of freedom is used to control the NOx emissions and the battery state of charge (SOC) simultaneously. Through an appropriate formulation of the problem, the feedback control is shown to be separable into two dependent PI controllers. By hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) experiments, as well as by simulations, the proposed method is shown to minimize the fuel consumption while tracking a given reference trajectory for both the NOx emissions and the battery SOC.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Optimal Charging Scheduling of Electric Vehicles in Smart Grids by Heuristic Algorithms
by
Monica Alonso, Hortensia Amaris, Jean Gardy Germain and Juan Manuel Galan
Cited by 203 | Viewed by 18903
Abstract
Transportation electrification has become an important issue in recent decades and the large scale deployment of electric vehicles (EVs) has yet to be achieved. The smart coordination of EV demand addresses an improvement in the flexibility of power systems and reduces the costs
[...] Read more.
Transportation electrification has become an important issue in recent decades and the large scale deployment of electric vehicles (EVs) has yet to be achieved. The smart coordination of EV demand addresses an improvement in the flexibility of power systems and reduces the costs of power system investment. The uncertainty in EV drivers’ behaviour is one of the main problems to solve to obtain an optimal integration of EVs into power systems. In this paper, an optimisation algorithm to coordinate the charging of EVs has been developed and implemented using a Genetic Algorithm (GA), where thermal line limits, the load on transformers, voltage limits and parking availability patterns are taken into account to establish an optimal load pattern for EV charging-based reliability. This methodology has been applied to an existing residential low-voltage system. The results indicate that a smart charging schedule for EVs leads to a
flattening of the
load profile, peak load shaving and the prevention of the aging of power system elements.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Day-Ahead Energy Planning with 100% Electric Vehicle Penetration in the Nordic Region by 2050
by
Zhaoxi Liu, Qiuwei Wu, Arne Hejde Nielsen and Yun Wang
Cited by 17 | Viewed by 9828
Abstract
This paper presents the day-ahead energy planning of passenger cars with 100% electric vehicle (EV) penetration in the Nordic region by 2050. EVs will play an important role in the future energy systems which can both reduce the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from
[...] Read more.
This paper presents the day-ahead energy planning of passenger cars with 100% electric vehicle (EV) penetration in the Nordic region by 2050. EVs will play an important role in the future energy systems which can both reduce the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from the transport sector and provide the demand side flexibility required by smart grids. On the other hand, the EVs will increase the electricity consumption. In order to quantify the electricity consumption increase due to the 100% EV penetration in the Nordic region to facilitate the power system planning studies, the day-ahead energy planning of EVs has been investigated with different EV charging scenarios. Five EV charging scenarios have been considered in the energy planning analysis which are: uncontrolled charging all day, uncontrolled charging at home, timed charging, spot price based charging all day and spot price based charging at home. The demand profiles of the five charging analysis show that timed charging is the least favorable charging option and the spot priced based EV charging might induce high peak demands. The EV charging demand will have a considerable share of the energy consumption in the future Nordic power system.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Electromagnetic Design of a New Electrically Controlled Magnetic Variable-Speed Gearing Machine
by
Chunhua Liu and K. T. Chau
Cited by 26 | Viewed by 12674
Abstract
This paper proposes a new electrically controlled magnetic variable-speed gearing (EC-MVSG) machine, which is capable of providing controllable gear ratios for hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) applications. The key design feature involves the adoption of a magnetic gearing structure and acceptance of the memory
[...] Read more.
This paper proposes a new electrically controlled magnetic variable-speed gearing (EC-MVSG) machine, which is capable of providing controllable gear ratios for hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) applications. The key design feature involves the adoption of a magnetic gearing structure and acceptance of the memory machine flux-mnemonic concept. Hence, the proposed machine can not only offer a gear-shifting mechanism for torque and speed transmission, but also provide variable gear ratios for torque and speed variation. The electromagnetic design is studied and discussed. The finite-element method is developed with the hysteresis model to verify the validity of the machine design.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Magnetless Axial-Flux Machine for Range-Extended Electric Vehicles
by
Christopher H. T. Lee, Chunhua Liu and K. T. Chau
Cited by 29 | Viewed by 15272
Abstract
A new magnetless axial-flux doubly-salient DC-field (AF-DSDC) machine is proposed and implemented into the application of a range-extended electric vehicle (RE-EV). By employing the radial active part for the torque production, the proposed machine can produce satisfactory torque density to fulfill the requirements
[...] Read more.
A new magnetless axial-flux doubly-salient DC-field (AF-DSDC) machine is proposed and implemented into the application of a range-extended electric vehicle (RE-EV). By employing the radial active part for the torque production, the proposed machine can produce satisfactory torque density to fulfill the requirements of the RE-EV system. With the support of the 3D finite element method (3D-FEM), the performances of the proposed machine are calculated and compared with the requirements of the typical passenger RE-EV applications. To offer a more comprehensive illustration, the common radial-flux (RF) machines are included for comparison.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Range-Based Vehicle Life Cycle Assessment Incorporating Variability in the Environmental Assessment of Different Vehicle Technologies and Fuels
by
Maarten Messagie, Faycal-Siddikou Boureima, Thierry Coosemans, Cathy Macharis and Joeri Van Mierlo
Cited by 170 | Viewed by 27220
Abstract
How to compare the environmental performance of different vehicle technologies? Vehicles with lower tailpipe emissions are perceived as cleaner. However, does it make sense to look only to tailpipe emissions? Limiting the comparison only to these emissions denies the fact that there are
[...] Read more.
How to compare the environmental performance of different vehicle technologies? Vehicles with lower tailpipe emissions are perceived as cleaner. However, does it make sense to look only to tailpipe emissions? Limiting the comparison only to these emissions denies the fact that there are emissions involved during the production of a fuel and this approach gives too much advantage to zero-tailpipe vehicles like battery electric vehicles (BEV) and fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV). Would it be enough to combine fuel production and tailpipe emissions? Especially when comparing the environmental performance of alternative vehicle technologies, the emissions during production of the specific components and their appropriate end-of-life treatment processes should also be taken into account. Therefore, the complete life cycle of the vehicle should be included in order to avoid problem shifting from one life stage to another. In this article, a full life cycle assessment (LCA) of petrol, diesel, fuel cell electric (FCEV), compressed natural gas (CNG), liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), hybrid electric, battery electric (BEV), bio-diesel and bio-ethanol vehicles has been performed. The aim of the manuscript is to investigate the impact of the different vehicle technologies on the environment and to develop a range-based modeling system that enables a more robust interpretation of the LCA results for a group of vehicles. Results are shown for climate change, respiratory effects, acidification and mineral extraction damage of the different vehicle technologies. A broad range of results is obtained due to the variability within the car market. It is concluded that it is essential to take into account the influence of all the vehicle parameters on the LCA results.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Investigation of the Cooling and Thermal-Measuring System of a Compound-Structure Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machine
by
Jingang Bai, Yong Liu, Yi Sui, Chengde Tong, Quanbin Zhao and Jiawei Zhang
Cited by 19 | Viewed by 11023
Abstract
The compound-structure permanent-magnet synchronous machine (CS-PMSM) is a power-split device which can enable the internal combustion engine (ICE) to operate at optimum efficiency during all driving conditions by controlling its torque and speed. However, the CS-PMSM has more serious temperature rise and heat
[...] Read more.
The compound-structure permanent-magnet synchronous machine (CS-PMSM) is a power-split device which can enable the internal combustion engine (ICE) to operate at optimum efficiency during all driving conditions by controlling its torque and speed. However, the CS-PMSM has more serious temperature rise and heat dissipation problems than conventional permanent-magnet (PM) machines, especially when the CS-PMSM is running at low speed and under full load conditions. As the thermal resistance of double-layer air gaps is quite big, the hot spot proves to be in the inner winding rotor. To ensure the safe operation of the CS-PMSM, the use of forced-air and water cooling in the inner winding rotor are investigated. The study shows that the water cooling can provide a better cooling effect, but require a complicated mechanical structure. Considering the complexity of the high efficiency cooling system, a real-time temperature monitoring method is proposed and a temperature measuring system which can accurately measure the real-time temperature of multiple key points in the machine is developed to promptly adjust the operating and cooling conditions based on the measured temperature results. Finally, the temperature rise experiment of the CS-PMSM prototype is done and the simulation results are partly validated by the experimental data.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Design and Control of a Multi-Functional Energy Recovery Power Accumulator Battery Pack Testing System for Electric Vehicles
by
Bo Long, Ji Hyoung Ryu, Shin Teak Lim and Kil To Chong
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 9147
Abstract
In this paper, aiming at the energy loss and harmonic problems in the conventional power accumulator battery pack testing system (PABPTS), an improved multi-functional energy recovery PABPTS (ERPABPTS) for electric vehicles (EVs) was proposed. The improved system has the functions of harmonic detection,
[...] Read more.
In this paper, aiming at the energy loss and harmonic problems in the conventional power accumulator battery pack testing system (PABPTS), an improved multi-functional energy recovery PABPTS (ERPABPTS) for electric vehicles (EVs) was proposed. The improved system has the functions of harmonic detection, suppression, reactive compensation and energy recovery. The ERPABPTS, which contains a bi-directional buck-boost direct current (DC)-DC converter and a bi-directional alternating current (AC)-DC converter with an inductor-capacitor-inductor (LCL) type filter interfacing to the AC-grid, is proposed. System configuration and operation principle of the combined system are discussed first, then, the reactive compensation and harmonic suppression controller under balanced grid-voltage condition are presented. Design of a fourth order band-pass Butterworth filter for current harmonic detection is put forward, and the reactive compensator design procedure considering the non-linear load is also illustrated. The proposed scheme is implemented in a 175-kW prototype in the laboratory. Simulation and experimental results show that the combined configuration can effectively realize energy recovery for high accuracy current test requirement, meanwhile, can effectively achieve reactive compensation and current harmonic suppression.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Research on a 20-Slot/22-Pole Five-Phase Fault-Tolerant PMSM Used for Four-Wheel-Drive Electric Vehicles
by
Yi Sui, Ping Zheng, Fan Wu, Bin Yu, Pengfei Wang and Jiawei Zhang
Cited by 20 | Viewed by 9997
Abstract
This paper presents a five-phase fault-tolerant permanent-magnet synchronous machine (PMSM) used for electric vehicles. In multiphase fault-tolerant PMSMs equipped with fractional-slot concentrated windings, excessive magneto-motive force (MMF) harmonics can lead to thermal demagnetization of the permanent magnets (PMs). In order to reduce the
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a five-phase fault-tolerant permanent-magnet synchronous machine (PMSM) used for electric vehicles. In multiphase fault-tolerant PMSMs equipped with fractional-slot concentrated windings, excessive magneto-motive force (MMF) harmonics can lead to thermal demagnetization of the permanent magnets (PMs). In order to reduce the lower-order harmonics, the origins of the 2-pole harmonic in conventional winding configurations are investigated, and an unequal-turn winding configuration is applied to cancel the lower-order harmonics. The main electromagnetic performances of the unequal-turn winding configuration are investigated and compared with conventional winding topologies. Based on the principle of maintaining constant instantaneous power, the fault-tolerant control strategies for open-circuits of up to two phases are developed. All of the investigations are verified by finite element analysis (FEA) results.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Planning Minimum Interurban Fast Charging Infrastructure for Electric Vehicles: Methodology and Application to Spain
by
Antonio Colmenar-Santos, Carlos De Palacio, David Borge-Diez and Oscar Monzón-Alejandro
Cited by 31 | Viewed by 9426
Abstract
The goal of the research is to assess the minimum requirement of fast charging infrastructure to allow country-wide interurban electric vehicle (EV) mobility. Charging times comparable to fueling times in conventional internal combustion vehicles are nowadays feasible, given the current availability of fast
[...] Read more.
The goal of the research is to assess the minimum requirement of fast charging infrastructure to allow country-wide interurban electric vehicle (EV) mobility. Charging times comparable to fueling times in conventional internal combustion vehicles are nowadays feasible, given the current availability of fast charging technologies. The main contribution of this paper is the analysis of the planning method and the investment requirements for the necessary infrastructure, including the definition of the Maximum Distance between Fast Charge (MDFC) and the Basic Highway Charging Infrastructure (BHCI) concepts. According to the calculations, distance between stations will be region-dependent, influenced primarily by weather conditions. The study considers that the initial investment should be sufficient to promote the EV adoption, proposing an initial state-financed public infrastructure and, once the adoption rate for EVs increases, additional infrastructure will be likely developed through private investment. The Spanish network of state highways is used as a case study to demonstrate the methodology and calculate the investment required. Further, the results are discussed and quantitatively compared to other incentives and policies supporting EV technology adoption in the light-vehicle sector.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Performance Evaluation of an In-Wheel Motor Cooling System in an Electric Vehicle/Hybrid Electric Vehicle
by
Dong Hyun Lim, Moo-Yeon Lee, Ho-Seong Lee and Sung Chul Kim
Cited by 42 | Viewed by 13135
Abstract
High power and miniaturization of motors in an in-wheel drive system, which is installed inside the wheels of a vehicle, are required for directly driving the wheels. In addition, an efficient cooling system is required to ensure high driving performance and durability. This
[...] Read more.
High power and miniaturization of motors in an in-wheel drive system, which is installed inside the wheels of a vehicle, are required for directly driving the wheels. In addition, an efficient cooling system is required to ensure high driving performance and durability. This study experimentally evaluated the heat dissipation performance of a 35-kW-class large-capacity in-wheel motor equipped with an internal-circulation-type oil-cooling system that exhibits high cooling performance and can be easily miniaturized to this motor. Temperatures of the coil and stator core of cooling systems with and without a radiator were measured in real time under in-wheel motor driving conditions. It was found that operating the cooling system at a continuous-rating maximum speed without the radiator was difficult. We confirmed that under continuous-rating base speed and continuous-rating maximum speed driving conditions, the cooling system with the radiator showed thermally stable operation. Furthermore, under maximum-rating base speed and maximum-rating maximum speed driving conditions, the cooling system with the radiator provided additional driving times of approximately 22 s and 2 s, respectively.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Research on the Power Management Strategy of Hybrid Electric Vehicles Based on Electric Variable Transmissions
by
Qiwei Xu, Shumei Cui, Liwei Song and Qianfan Zhang
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 9236
Abstract
Electric variable transmission is a new electromechanical energy conversion device structure, which is especially suitable as the driving force distribution device for hybrid electric vehicles. This paper focuses on the power management strategy of hybrid electric vehicles based on an electric variable transmission,
[...] Read more.
Electric variable transmission is a new electromechanical energy conversion device structure, which is especially suitable as the driving force distribution device for hybrid electric vehicles. This paper focuses on the power management strategy of hybrid electric vehicles based on an electric variable transmission, and a kind of hierarchical control ideology is proposed. The control strategy is composed of four control levels, namely analysis of force requirement, operation mode switching, force distribution and coordinate control, which are designed respectively in this paper. Then a simulation model is built based on the notion of energetic macroscopic representation, and an experimental test bench is built. The simulation and experiment results demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed strategy, and it can be taken as a new theory and method for the study of hybrid electric vehicle based on electric variable transmission.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Convex Optimization for the Energy Management of Hybrid Electric Vehicles Considering Engine Start and Gearshift Costs
by
Tobias Nüesch, Philipp Elbert, Michael Flankl, Christopher Onder and Lino Guzzella
Cited by 154 | Viewed by 14293
Abstract
This paper presents a novel method to solve the energy management problem for hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) with engine start and gearshift costs. The method is based on a combination of deterministic dynamic programming (DP) and convex optimization. As demonstrated in a case
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a novel method to solve the energy management problem for hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) with engine start and gearshift costs. The method is based on a combination of deterministic dynamic programming (DP) and convex optimization. As demonstrated in a case study, the method yields globally optimal results while returning the solution in much less time than the conventional DP method. In addition, the proposed method handles state constraints, which allows for the application to scenarios where the battery state of charge (SOC) reaches its boundaries.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Energy-Regenerative Braking Control of Electric Vehicles Using Three-Phase Brushless Direct-Current Motors
by
Bo Long, Shin Teak Lim, Ji Hyoung Ryu and Kil To Chong
Cited by 57 | Viewed by 25057
Abstract
Regenerative braking provides an effective way of extending the driving range of battery powered electric vehicles (EVs). This paper analyzes the equivalent power circuit and operation principles of an EV using regenerative braking control technology. During the braking period, the switching sequence of
[...] Read more.
Regenerative braking provides an effective way of extending the driving range of battery powered electric vehicles (EVs). This paper analyzes the equivalent power circuit and operation principles of an EV using regenerative braking control technology. During the braking period, the switching sequence of the power converter is controlled to inverse the output torque of the three-phase brushless direct-current (DC) motor, so that the braking energy can be returned to the battery. Compared with the presented methods, this technology can achieve several goals: energy recovery, electric braking, ultra-quiet braking and extending the driving range. Merits and drawbacks of different braking control strategy are further elaborated. State-space model of the EVs under energy-regenerative braking operation is established, considering that parameter variations are unavoidable due to temperature change, measured error, un-modeled dynamics, external disturbance and time-varying system parameters, a sliding mode robust controller (SMRC) is designed and implemented. Phase current and DC-link voltage are selected as the state variables, respectively. The corresponding control law is also provided. The proposed control scheme is compared with a conventional proportional-integral (PI) controller. A laboratory EV for experiment is setup to verify the proposed scheme. Experimental results show that the drive range of EVs can be improved about 17% using the proposed controller with energy-regeneration control.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Analysis and Design of a Transverse-Flux Dual Rotor Machine for Power-Split Hybrid Electric Vehicle Applications
by
Ping Zheng, Quanbin Zhao, Jingang Bai, Bin Yu, Zhiyi Song and Jing Shang
Cited by 22 | Viewed by 9026
Abstract
A novel compound-structure transverse-flux permanent-magnet synchronous machine (CS-TFPMSM) is proposed in this paper, which is used in hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) to fulfill the power-split function. The key component of the CS-TFPMSM is a brushless transverse-flux dual rotor machine (TFDRM). The TFDRM originates
[...] Read more.
A novel compound-structure transverse-flux permanent-magnet synchronous machine (CS-TFPMSM) is proposed in this paper, which is used in hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) to fulfill the power-split function. The key component of the CS-TFPMSM is a brushless transverse-flux dual rotor machine (TFDRM). The TFDRM originates from the transverse-flux machines, and is capable of speed adjustment between the transverse-flux rotor and the permanent-magnet rotor without using any brushes. The structure and principle of the TFDRM are described. The torque equations of the TFDRM are deduced, which are different from those of traditional machines. Based on the investigation, the TFDRM tends to have high leakage and a poor power factor. The method to obtain high power factor is discussed. The back electromotive force (BEMF) and torque of the TFDRM are simulated with the variation of parameters, such as pole-pair number, width of the permanent magnets (PMs), and so on. A prototype of a 10kW TFDRM is designed.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Combined Cooperative Braking Model with a Predictive Control Strategy in an Electric Vehicle
by
Hongqiang Guo, Hongwen He and Fengchun Sun
Cited by 19 | Viewed by 8684
Abstract
Cooperative braking with regenerative braking and mechanical braking plays an important role in electric vehicles for energy-saving control. Based on the parallel and the series cooperative braking models, a combined model with a predictive control strategy to get a better cooperative braking performance
[...] Read more.
Cooperative braking with regenerative braking and mechanical braking plays an important role in electric vehicles for energy-saving control. Based on the parallel and the series cooperative braking models, a combined model with a predictive control strategy to get a better cooperative braking performance is presented. The balance problem between the maximum regenerative energy recovery efficiency and the optimum braking stability is solved through an off-line process optimization stream with the collaborative optimization algorithm (CO). To carry out the process optimization stream, the optimal Latin hypercube design (Opt LHD) is presented to discrete the continuous design space. To solve the poor real-time problem of the optimization, a high-precision predictive model based on the off-line optimization data of the combined model is built, and a predictive control strategy is proposed and verified through simulation. The simulation results demonstrate that the predictive control strategy and the combined model are reasonable and effective.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Thermal Performance of Motor and Inverter in an Integrated Starter Generator System for a Hybrid Electric Vehicle
by
Sung Chul Kim
Cited by 28 | Viewed by 17707
Abstract
If the integrated starter generator (ISG) motor and inverter operate under continuously high loading conditions, the system’s performance and durability will decrease and the heat dissipation requirements will increase. Therefore, in this study, we developed two cooling designs for the ISG motor and
[...] Read more.
If the integrated starter generator (ISG) motor and inverter operate under continuously high loading conditions, the system’s performance and durability will decrease and the heat dissipation requirements will increase. Therefore, in this study, we developed two cooling designs for the ISG motor and inverter, and then carried out both a model analysis and an experiment on the fluid flow and thermal characteristics of the system under various operating conditions. As the outdoor temperature increased from 25 °C to 95 °C, the coil temperature of the air-cooled motor increased by about 82 °C. Under the harsh-air condition of 95 °C, the coil of the air-cooled motor increased to a maximum temperature of about 158.5 °C. We also determined that the temperature of the metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) chip in the liquid-cooled inverter increased to a maximum temperature of about 96.8 °C under a coolant flow rate of 4 L/min and a coolant temperature of 65 °C. The observed thermal performance of the ISG motor and inverter using the proposed cooling structures was found to be sufficient for heat loads under various real driving conditions for a hybrid electric vehicle (HEV).
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Comparative Study on Different Energy Management Strategies for Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles
by
Ximing Wang, Hongwen He, Fengchun Sun, Xiaokun Sun and Henglu Tang
Cited by 77 | Viewed by 11690
Abstract
Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) have a larger battery and can replace a certain amount of conventional fossil fuels with grid electricity, which differs from the traditional hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs). The application of the onboard electrical energy significantly influences the energy utilization
[...] Read more.
Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) have a larger battery and can replace a certain amount of conventional fossil fuels with grid electricity, which differs from the traditional hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs). The application of the onboard electrical energy significantly influences the energy utilization efficiency and thus impacts the fuel economy. In this paper, the basic PHEV operation modes are defined as pure electric driving (PED), hybrid driving charge depleting (HDCD) and hybrid driving charge sustaining (HDCS) based on the battery state of charge (
SoC) profile. For a plug-in hybrid electric bus (PHEB), three different energy management strategies, which are combined with two or three of the basic operation modes, are put forward and comparatively examined based on simulation models. If some trip information can be approximately known in advance such as the trip distance and the mean power demand, the PED + HDCD + HDCS strategy comprised optimally of the PED mode, the HDCD mode and the HDCS mode would be the best energy management strategy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Investigation of a Novel 24-Slot/14-Pole Six-Phase Fault-Tolerant Modular Permanent-Magnet In-Wheel Motor for Electric Vehicles
by
Ping Zheng, Fan Wu, Yu Lei, Yi Sui and Bin Yu
Cited by 72 | Viewed by 14526
Abstract
In this paper, a six-phase fault-tolerant modular permanent magnet synchronous machine (PMSM) with a novel 24-slot/14-pole combination is proposed as a high-performance actuator for wheel-driving electric vehicle (EV) applications. Feasible slot/pole combinations of the fractional-slot concentrated winding six-phase PMSM are elicited and analyzed
[...] Read more.
In this paper, a six-phase fault-tolerant modular permanent magnet synchronous machine (PMSM) with a novel 24-slot/14-pole combination is proposed as a high-performance actuator for wheel-driving electric vehicle (EV) applications. Feasible slot/pole combinations of the fractional-slot concentrated winding six-phase PMSM are elicited and analyzed for scheme selection. The novel 24-slot/14-pole combination is derived from the analysis and suppression of the magnetomotive force (MMF) harmonics. By making use of alternate-teeth-wound concentrated winding configuration, two adjacent coils per phase and unequal teeth widths, the phase windings of the proposed machine is magnetically, thermally isolated, which offers potentials of modular design and fault tolerant capability. Taking advantage of the leakage component of winding inductance, 1.0 per unit short-circuit current is achieved endowing the machine with short-circuit proof capability. Optimal design of essential parameters aiming at low eddy current losses, high winding factor and short-circuit-proof ability are presented to pave the way for a high-quality system implementation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Research on an Axial Magnetic-Field-Modulated Brushless Double Rotor Machine
by
Ping Zheng, Zhiyi Song, Jingang Bai, Chengde Tong and Bin Yu
Cited by 29 | Viewed by 8220
Abstract
Double rotor machine, an electronic continuously variable transmission, has great potential in application of hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), wind power and marine propulsion. In this paper, an axial magnetic-field-modulated brushless double rotor machine (MFM-BDRM), which can realize the speed decoupling between the shaft
[...] Read more.
Double rotor machine, an electronic continuously variable transmission, has great potential in application of hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), wind power and marine propulsion. In this paper, an axial magnetic-field-modulated brushless double rotor machine (MFM-BDRM), which can realize the speed decoupling between the shaft of the modulating ring rotor and that of the permanent magnet rotor is proposed. Without brushes and slip rings, the axial MFM-BDRM offers significant advantages such as excellent reliability and high efficiency. Since the number of pole pairs of the stator is not equal to that of the permanent magnet rotor, which differs from the traditional permanent magnet synchronous machine, the operating principle of the MFM-BDRM is deduced. The relations of corresponding speed and toque transmission are analytically discussed. The cogging toque characteristics, especially the order of the cogging torque are mathematically formulated. Matching principle of the number of pole pairs of the stator, that of the permanent magnet rotor and the number of ferromagnetic pole pieces is inferred since it affects MFM-BDRM’s performance greatly, especially in the respect of the cogging torque and electromagnetic torque ripple. The above analyses are assessed with the three-dimensional (3D) finite-element method (FEM).
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
State of Charge Estimation Using the Extended Kalman Filter for Battery Management Systems Based on the ARX Battery Model
by
Shifei Yuan, Hongjie Wu and Chengliang Yin
Cited by 134 | Viewed by 16894
Abstract
State of charge (SOC) is a critical factor to guarantee that a battery system is operating in a safe and reliable manner. Many uncertainties and noises, such as fluctuating current, sensor measurement accuracy and bias, temperature effects, calibration errors or even sensor failure,
[...] Read more.
State of charge (SOC) is a critical factor to guarantee that a battery system is operating in a safe and reliable manner. Many uncertainties and noises, such as fluctuating current, sensor measurement accuracy and bias, temperature effects, calibration errors or even sensor failure,
etc. pose a challenge to the accurate estimation of SOC in real applications. This paper adds two contributions to the existing literature. First, the auto regressive exogenous (ARX) model is proposed here to simulate the battery nonlinear dynamics. Due to its discrete form and ease of implemention, this straightforward approach could be more suitable for real applications. Second, its order selection principle and parameter identification method is illustrated in detail in this paper. The hybrid pulse power characterization (HPPC) cycles are implemented on the 60AH LiFePO
4 battery module for the model identification and validation. Based on the proposed ARX model, SOC estimation is pursued using the extended Kalman filter. Evaluation of the adaptability of the battery models and robustness of the SOC estimation algorithm are also verified. The results indicate that the SOC estimation method using the Kalman filter based on the ARX model shows great performance. It increases the model output voltage accuracy, thereby having the potential to be used in real applications, such as EVs and HEVs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Impact of PHEVs Penetration on Ontario’s Electricity Grid and Environmental Considerations
by
Lena Ahmadi, Eric Croiset, Ali Elkamel, Peter L. Douglas, Woramon Unbangluang and Evgueniy Entchev
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 7672
Abstract
Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) have a large potential to reduce greenhouse gases emissions and increase fuel economy and fuel flexibility. PHEVs are propelled by the energy from both gasoline and electric power sources. Penetration of PHEVs into the automobile market affects the
[...] Read more.
Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) have a large potential to reduce greenhouse gases emissions and increase fuel economy and fuel flexibility. PHEVs are propelled by the energy from both gasoline and electric power sources. Penetration of PHEVs into the automobile market affects the electrical grid through an increase in electricity demand. This paper studies effects of the wide spread adoption of PHEVs on peak and base load demands in Ontario, Canada. Long-term forecasting models of peak and base load demands and the number of light-duty vehicles sold were developed. To create proper forecasting models, both linear regression (LR) and non-linear regression (NLR) techniques were employed, considering different ranges in the demographic, climate and economic variables. The results from the LR and NLR models were compared and the most accurate one was selected. Furthermore, forecasting the effects of PHEVs penetration is done through consideration of various scenarios of penetration levels, such as mild, normal and aggressive ones. Finally, the additional electricity demand on the Ontario electricity grid from charging PHEVs is incorporated for electricity production planning purposes.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Novel Speed Bumps Design and Optimization for Vehicles' Energy Recovery in Smart Cities
by
Andrea Pirisi, Francesco Grimaccia, Marco Mussetta and Riccardo E. Zich
Cited by 36 | Viewed by 11502
Abstract
Recently the technology development and increasing amounts of investment in renewables has led to a growing interest towards design and optimization of green energy systems. In this context, advanced Computational Intelligence (CI) techniques can be applied by engineers to several technical problems in
[...] Read more.
Recently the technology development and increasing amounts of investment in renewables has led to a growing interest towards design and optimization of green energy systems. In this context, advanced Computational Intelligence (CI) techniques can be applied by engineers to several technical problems in order to find out the best structure and to improve efficiency in energy recovery. This research promises to give new impulse to using innovative unconventional renewable sources and to develop the so-called Energy Harvesting Devices (EHDs). In this paper, the optimization of a Tubular Permanent Magnet-Linear Generator for energy harvesting from vehicles to grid is presented. The optimization process is developed by means of hybrid evolutionary algorithms to reach the best overall system efficiency and the impact on the environment and transportation systems. Finally, an experimental validation of the designed EHD prototype is presented.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Vehicle to Grid Services: Potential and Applications
by
Mehrdad Ehsani, Milad Falahi and Saeed Lotfifard
Cited by 113 | Viewed by 12123
Abstract
Electric Vehicle (EV) technology is expected to take a major share in the light-vehicle market in the coming decades
. Charging of EVs will put an extra burden on the distribution grid and in some cases adjustments will need to be made. On
[...] Read more.
Electric Vehicle (EV) technology is expected to take a major share in the light-vehicle market in the coming decades
. Charging of EVs will put an extra burden on the distribution grid and in some cases adjustments will need to be made. On the other hand, EVs have the potential to support the grid under various conditions. This paper studies possible potential and applications of Vehicle to Grid (V2G) services, including active power services, which discharge the EV batteries, and power quality services, which do not engage the battery or require only small amounts of battery charge. The advantages and disadvantages of each service and the likelihood that a given service will be effective and beneficial for the grid in the future are discussed. Further, the infrastructure cost, duration, and value of V2G services are compared qualitatively.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Dynamic Coordinated Shifting Control of Automated Mechanical Transmissions without a Clutch in a Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle
by
Hongwen He, Zhentong Liu, Liming Zhu and Xinlei Liu
Cited by 49 | Viewed by 11991
Abstract
On the basis of
the
shifting process of automated mechanical transmissions (AMTs) for traditional hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), and by combining the features of electric machines with fast response speed, the dynamic model of the hybrid electric AMT vehicle powertrain is built up,
[...] Read more.
On the basis of
the
shifting process of automated mechanical transmissions (AMTs) for traditional hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), and by combining the features of electric machines with fast response speed, the dynamic model of the hybrid electric AMT vehicle powertrain is built up, the dynamic characteristics of each phase of shifting process are analyzed, and a control strategy in which torque and speed of the engine and electric machine are coordinatively controlled to achieve AMT shifting control for a plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) without clutch is proposed. In the shifting process, the engine and electric machine are well controlled, and the shift jerk and power interruption and restoration time are reduced. Simulation and real car test results show that the proposed control strategy can more efficiently improve the shift quality for PHEVs equipped with AMTs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Rechargeable Energy Storage Systems for Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles—Assessment of Electrical Characteristics
by
Noshin Omar, Mohamed Daowd, Peter van den Bossche, Omar Hegazy, Jelle Smekens, Thierry Coosemans and Joeri van Mierlo
Cited by 160 | Viewed by 20065
Abstract
In this paper, the performances of various lithium-ion chemistries for use in plug-in hybrid electric vehicles have been investigated and compared to several other rechargeable energy storage systems technologies such as lead-acid, nickel-metal hydride and electrical-double layer capacitors. The analysis has shown the
[...] Read more.
In this paper, the performances of various lithium-ion chemistries for use in plug-in hybrid electric vehicles have been investigated and compared to several other rechargeable energy storage systems technologies such as lead-acid, nickel-metal hydride and electrical-double layer capacitors. The analysis has shown the beneficial properties of lithium-ion in the terms of energy density, power density and rate capabilities. Particularly, the nickel manganese cobalt oxide cathode stands out with the high energy density up to 160 Wh/kg, compared to 70–110, 90 and 71 Wh/kg for lithium iron phosphate cathode, lithium nickel cobalt aluminum cathode and, lithium titanate oxide anode battery cells, respectively. These values are considerably higher than the lead-acid (23–28 Wh/kg) and nickel-metal hydride (44–53 Wh/kg) battery technologies. The dynamic discharge performance test shows that the energy efficiency of the lithium-ion batteries is significantly higher than the lead-acid and nickel-metal hydride technologies. The efficiency varies between 86% and 98%, with the best values obtained by pouch battery cells, ahead of cylindrical and prismatic battery design concepts. Also the power capacity of lithium-ion technology is superior compared to other technologies. The power density is in the range of 300–2400 W/kg against 200–400 and 90–120 W/kg for lead-acid and nickel-metal hydride, respectively. However, considering the influence of energy efficiency, the power density is in the range of 100–1150 W/kg. Lithium-ion batteries optimized for high energy are at the lower end of this range and are challenged to meet the United States Advanced Battery Consortium, SuperLIB and Massachusetts Institute of Technology goals. Their association with electric-double layer capacitors, which have low energy density (4–6 Wh/kg) but outstanding power capabilities, could be very interesting. The study of the rate capability of the lithium-ion batteries has allowed for a new state of charge estimation, encompassing all essential performance parameters. The rate capabilities tests are reflected by Peukert constants, which are significantly lower for lithium-ion batteries than for nickel-metal hydride and lead-acid. Furthermore, rate capabilities during charging have been investigated. Lithium-ion batteries are able to store about 80% of the capacity at current rate 2I
t, with high power cells accepting over 90%. At higher charging rates of 5I
t or more, the internal resistance impedes charge acceptance by high energy cells. The lithium titanate anode, due to its high surface area (100 m
2/g compared to 3 m
2/g for the graphite based anode) performs much better in this respect. The behavior of lithium-ion batteries has been investigated at different conditions. The analysis has leaded us to a new lithium ion battery model. This model will be compared to existing battery models in future research contributions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Electric Vehicle Scenario Simulator Tool for Smart Grid Operators
by
João Soares, Bruno Canizes, Cristina Lobo, Zita Vale and Hugo Morais
Cited by 95 | Viewed by 13547
Abstract
This paper presents a simulator for electric vehicles in the context of smart grids and distribution networks. It aims to support network operators’ planning and operations but can be used by other entities for related studies. The paper describes the parameters supported by
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a simulator for electric vehicles in the context of smart grids and distribution networks. It aims to support network operators’ planning and operations but can be used by other entities for related studies. The paper describes the parameters supported by the current version of the Electric Vehicle Scenario Simulator (EVeSSi) tool and its current algorithm. EVeSSi enables the definition of electric vehicles scenarios on distribution networks using a built-in movement engine. The scenarios created with EVeSSi can be used by external tools (e.g., power flow) for specific analysis, for instance grid impacts. Two scenarios are briefly presented for illustration of the simulator capabilities.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Online Estimation of Peak Power Capability of Li-Ion Batteries in Electric Vehicles by a Hardware-in-Loop Approach
by
Rui Xiong, Hongwen He, Fengchun Sun and Kai Zhao
Cited by 128 | Viewed by 14077
Abstract
Battery peak power capability estimations play an important theoretical role for the proper use of the battery in electric vehicles. To address the failures in relaxation effects and real-time ability performance, neglecting the battery’s design limits and other issues of the traditional peak
[...] Read more.
Battery peak power capability estimations play an important theoretical role for the proper use of the battery in electric vehicles. To address the failures in relaxation effects and real-time ability performance, neglecting the battery’s design limits and other issues of the traditional peak power capability calculation methods, a new approach based on the dynamic electrochemical-polarization (EP) battery model, taking into consideration constraints of current, voltage, state of charge (SoC) and power is proposed. A hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) system is built for validating the online model-based peak power capability estimation approach of batteries used in hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) and a HIL test based on the Federal Urban Driving Schedules (FUDS) is used to verify and evaluate its real-time computation performance, reliability and robustness. The results show the proposed approach gives a more accurate estimate compared with the hybrid pulse power characterization (HPPC) method, avoiding over-charging or over-discharging and providing a powerful guarantee for the optimization of HEVs power systems. Furthermore, the HIL test provides valuable data and critical guidance to evaluate the accuracy of the developed battery algorithms.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Estimation of State of Charge of Lithium-Ion Batteries Used in HEV Using Robust Extended Kalman Filtering
by
Caiping Zhang, Jiuchun Jiang, Weige Zhang and Suleiman M. Sharkh
Cited by 68 | Viewed by 10260
Abstract
A robust extended Kalman filter (EKF) is proposed as a method for estimation of the state of charge (SOC) of lithium-ion batteries used in hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs). An equivalent circuit model of the battery, including its electromotive force (EMF) hysteresis characteristics and
[...] Read more.
A robust extended Kalman filter (EKF) is proposed as a method for estimation of the state of charge (SOC) of lithium-ion batteries used in hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs). An equivalent circuit model of the battery, including its electromotive force (EMF) hysteresis characteristics and polarization characteristics is used. The effect of the robust EKF gain coefficient on SOC estimation is analyzed, and an optimized gain coefficient is determined to restrain battery terminal voltage from fluctuating. Experimental and simulation results are presented. SOC estimates using the standard EKF are compared with the proposed robust EKF algorithm to demonstrate the accuracy and precision of the latter for SOC estimation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Standardization Work for BEV and HEV Applications: Critical Appraisal of Recent Traction Battery Documents
by
Noshin Omar, Mohamed Daowd, Omar Hegazy, Grietus Mulder, Jean-Marc Timmermans, Thierry Coosemans, Peter Van den Bossche and Joeri Van Mierlo
Cited by 74 | Viewed by 14178
Abstract
The increased activity in the field of Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) and Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) have led to an increase in standardization work, performed by both world-wide organizations like the IEC or the ISO, as by regional and national bodies such as
[...] Read more.
The increased activity in the field of Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) and Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) have led to an increase in standardization work, performed by both world-wide organizations like the IEC or the ISO, as by regional and national bodies such as CEN, CENELEC, SAE or JEVA. The issues of these standards cover several topics: safety, performance and operational/dimension issues. This paper reports a brief overview of current standardization activities of lithium batteries based on IEC 62660-1/2 and ISO 12405-1/2. Furthermore, in this paper, a series of innovative test procedures for lithium-ion batteries are presented. Thanks to these tests, the general characteristics of a battery such as charge and discharge capabilities, power performances and life cycle can be determined. Then, a new approach for extracting the life cycle of a battery in function of depth of discharge has been developed.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Performance Analysis and Simulation of a Novel Brushless Double Rotor Machine for Power-Split HEV Applications
by
Ping Zheng, Qian Wu, Jing Zhao, Chengde Tong, Jingang Bai and Quanbin Zhao
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 8384
Abstract
A new type of brushless double rotor machine (BDRM) is proposed in this paper. The BDRM is an important component in compound-structure permanent-magnet synchronous machine (CS-PMSM) systems, which are promising for power-split hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) applications. The BDRM can realize the speed
[...] Read more.
A new type of brushless double rotor machine (BDRM) is proposed in this paper. The BDRM is an important component in compound-structure permanent-magnet synchronous machine (CS-PMSM) systems, which are promising for power-split hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) applications. The BDRM can realize the speed adjustment between claw-pole rotor and permanent-magnet rotor without brushes and slip rings. The structural characteristics of the BDRM are described and its magnetic circuit model is built. Reactance parameters of the BDRM are deduced by an analytical method. It is found that the size characteristics of the BDRM are different from those of conventional machines. The new sizing and torque equations are analyzed and the theoretical results are used in the optimization process. Studies of the analytical magnetic circuit and finite element method (FEM) model show that the BDRM tends to have high leakage flux and low power factor, and then the method to obtain high power factor is discussed. Furthermore, a practical methodology of the BDRM design is developed, which includes an analytical tool, 2D field calculation and performance evaluation by 3D field calculation. Finally, different topologies of the BDRM are compared and an optimum prototype is designed.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Is the Electric Vehicle an Attractive Option for Customers?
by
Israel García and Luis Javier Miguel
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 9380
Abstract
As a new technology, electric mobility has the potential to achieve a reduction in CO
2 emissions and contribute to the transition from the current transportation system to a better one, environmentally speaking. The objective of the paper is to aid the necessary
[...] Read more.
As a new technology, electric mobility has the potential to achieve a reduction in CO
2 emissions and contribute to the transition from the current transportation system to a better one, environmentally speaking. The objective of the paper is to aid the necessary decision-making for the adoption and development of electric vehicles in Spain, taking the time horizon of 2020. This will be achieved by building a System Dynamics model for various scenarios that will be used for the analysis and comparison of various dynamic variables, as well as to determine how, and to what extent, they will influence the number of electric vehicles that will run on Spanish roads in the coming years, focusing on the cost variable.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Modeling and Control of a Flux-Modulated Compound-Structure Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machine for Hybrid Electric Vehicles
by
Ping Zheng, Chengde Tong, Jingang Bai, Jing Zhao, Yi Sui and Zhiyi Song
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 10681
Abstract
The compound-structure permanent-magnet synchronous machine (CS-PMSM), comprising a double rotor machine (DRM) and a permanent-magnet (PM) motor, is a promising electronic-continuously variable transmission (e-CVT) concept for hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs). By CS-PMSM, independent speed and torque control of the vehicle engine is realized
[...] Read more.
The compound-structure permanent-magnet synchronous machine (CS-PMSM), comprising a double rotor machine (DRM) and a permanent-magnet (PM) motor, is a promising electronic-continuously variable transmission (e-CVT) concept for hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs). By CS-PMSM, independent speed and torque control of the vehicle engine is realized without a planetary gear unit. However, the slip rings and brushes of the conventional CS-PMSM are considered a major drawback for vehicle application. In this paper, a brushless flux-modulated CS-PMSM is investigated. The operating principle and basic working modes of the CS-PMSM are discussed. Mathematical models of the CS-PMSM system are given, and joint control of the two integrated machines is proposed. As one rotor of the DRM is mechanically connected with the rotor of the PM motor, special rotor position detection and torque allocation methods are required. Simulation is carried out by Matlab/Simulink, and the feasibility of the control system is proven. Considering the complexity of the controller, a single digital signal processor (DSP) is used to perform the interconnected control of dual machines instead of two separate ones, and a typical hardware implementation is proposed.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of a Single-Phase Z-Source Inverter for Battery Discharging in Vehicle to Grid Applications
by
Yifan Yu, Qianfan Zhang, Bin Liang, Xiaofei Liu and Shumei Cui
Cited by 23 | Viewed by 8893
Abstract
Vehicle to Grid technology allows the batteries of electric vehicles to operate as energy storage elements for renewable energy power systems. The Z-Source inverter is a new and attractive topology for the power electronics interface. In this paper, the equivalent DC-link voltage ripple
[...] Read more.
Vehicle to Grid technology allows the batteries of electric vehicles to operate as energy storage elements for renewable energy power systems. The Z-Source inverter is a new and attractive topology for the power electronics interface. In this paper, the equivalent DC-link voltage ripple of a single-phase Z-Source inverter for Vehicle to Grid applications is analyzed in this paper before deriving a general design approach for the Z-Source network. These theoretical findings, and design rule for a Z-Source network have been confirmed by computer simulations and a laboratory-implemented prototype.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Battery Management Systems in Electric and Hybrid Vehicles
by
Yinjiao Xing, Eden W. M. Ma, Kwok L. Tsui and Michael Pecht
Cited by 478 | Viewed by 53156
Abstract
The battery management system (BMS) is a critical component of electric and hybrid electric vehicles. The purpose of the BMS is to guarantee safe and reliable battery operation. To maintain the safety and reliability of the battery, state monitoring and evaluation, charge control,
[...] Read more.
The battery management system (BMS) is a critical component of electric and hybrid electric vehicles. The purpose of the BMS is to guarantee safe and reliable battery operation. To maintain the safety and reliability of the battery, state monitoring and evaluation, charge control, and cell balancing are functionalities that have been implemented in BMS. As an electrochemical product, a battery acts differently under different operational and environmental conditions. The uncertainty of a battery’s performance poses a challenge to the implementation of these functions. This paper addresses concerns for current BMSs. State evaluation of a battery, including state of charge, state of health, and state of life, is a critical task for a BMS. Through reviewing the latest methodologies for the state evaluation of batteries, the future challenges for BMSs are presented and possible solutions are proposed as well.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
An Intelligent Regenerative Braking Strategy for Electric Vehicles
by
Guoqing Xu, Weimin Li, Kun Xu and Zhibin Song
Cited by 170 | Viewed by 27066
Abstract
Regenerative braking is an effective approach for electric vehicles (EVs) to extend their driving range. A fuzzy-logic-based regenerative braking strategy (RBS) integrated with series regenerative braking is developed in this paper to advance the level of energy-savings. From the viewpoint of securing car
[...] Read more.
Regenerative braking is an effective approach for electric vehicles (EVs) to extend their driving range. A fuzzy-logic-based regenerative braking strategy (RBS) integrated with series regenerative braking is developed in this paper to advance the level of energy-savings. From the viewpoint of securing car stability in braking operations, the braking force distribution between the front and rear wheels so as to accord with the ideal distribution curve are considered to prevent vehicles from experiencing wheel lock and slip phenomena during braking. Then, a fuzzy RBS using the driver’s braking force command, vehicle speed, battery SOC, battery temperature are designed to determine the distribution between friction braking force and regenerative braking force to improve the energy recuperation efficiency. The experimental results on an “LF620” prototype EV validated the feasibility and effectiveness of regenerative braking and showed that the proposed fuzzy RBS was endowed with good control performance. The maximum driving range of LF620 EV was improved by 25.7% compared with non-RBS conditions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Model Predictive Control-Based Fast Charging for Vehicular Batteries
by
Jingyu Yan, Guoqing Xu, Huihuan Qian, Yangsheng Xu and Zhibin Song
Cited by 52 | Viewed by 11354
Abstract
Battery fast charging is one of the most significant and difficult techniques affecting the commercialization of electric vehicles (EVs). In this paper, we propose a fast charge framework based on model predictive control, with the aim of simultaneously reducing the charge duration, which
[...] Read more.
Battery fast charging is one of the most significant and difficult techniques affecting the commercialization of electric vehicles (EVs). In this paper, we propose a fast charge framework based on model predictive control, with the aim of simultaneously reducing the charge duration, which represents the out-of-service time of vehicles, and the increase in temperature, which represents safety and energy efficiency during the charge process. The RC model is employed to predict the future State of Charge (SOC). A single mode lumped-parameter thermal model and a neural network trained by real experimental data are also applied to predict the future temperature in simulations and experiments respectively. A genetic algorithm is then applied to find the best charge sequence under a specified fitness function, which consists of two objectives: minimizing the charging duration and minimizing the increase in temperature. Both simulation and experiment demonstrate that the Pareto front of the proposed method dominates that of the most popular constant current constant voltage (CCCV) charge method.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Large-Scale Battery System Development and User-Specific
Driving Behavior Analysis for Emerging Electric-Drive Vehicles
by
Jie Wu, Kun Li, Yifei Jiang, Qin Lv, Li Shang and Yihe Sun
Cited by 24 | Viewed by 10800
Abstract
Emerging green-energy transportation, such as hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs)
and plug-in HEVs (PHEVs), has a great potential for reduction of fuel consumption and
greenhouse emissions. The lithium-ion battery system used in these vehicles, however,
is bulky, expensive and unreliable, and has been the primary roadblock for
[...] Read more.
Emerging green-energy transportation, such as hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs)
and plug-in HEVs (PHEVs), has a great potential for reduction of fuel consumption and
greenhouse emissions. The lithium-ion battery system used in these vehicles, however,
is bulky, expensive and unreliable, and has been the primary roadblock for transportation
electrification. Meanwhile, few studies have considered user-specific driving behavior
and its significant impact on (P)HEV fuel efficiency, battery system lifetime, and the
environment. This paper presents a detailed investigation of battery system modeling and
real-world user-specific driving behavior analysis for emerging electric-drive vehicles. The
proposed model is fast to compute and accurate for analyzing battery system run-time
and long-term cycle life with a focus on temperature dependent battery system capacity
fading and variation. The proposed solution is validated against physical measurement using
real-world user driving studies, and has been adopted to facilitate battery system design and
optimization. Using the collected real-world hybrid vehicle and run-time driving data, we
have also conducted detailed analytical studies of users’ specific driving patterns and their
impacts on hybrid vehicle electric energy and fuel efficiency. This work provides a solid
foundation for future energy control with emerging electric-drive applications.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Novel Field Test Equipment for Lithium-Ion Batteries in Hybrid Electrical Vehicle Applications
by
Pontus Svens, Johan Lindstrom, Olle Gelin, Marten Behm and Goran Lindbergh
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 10265
Abstract
Lifetime testing of batteries for hybrid-electrical vehicles (HEV) is usually performed in the lab, either at the cell, module or battery pack level. Complementary field tests of battery packs in vehicles are also often performed. There are, however, difficulties related to field testing
[...] Read more.
Lifetime testing of batteries for hybrid-electrical vehicles (HEV) is usually performed in the lab, either at the cell, module or battery pack level. Complementary field tests of battery packs in vehicles are also often performed. There are, however, difficulties related to field testing of battery-packs. Some examples are cost issues and the complexity of continuously collecting battery performance data, such as capacity fade and impedance increase. In this paper, a novel field test equipment designed primarily for lithium-ion battery cell testing is presented. This equipment is intended to be used on conventional vehicles, not hybrid vehicles, as a cheaper and faster field testing method for batteries, compared to full scale HEV testing. The equipment emulates an HEV environment for the tested battery cell by using real time vehicle sensor information and the existing starter battery as load and source. In addition to the emulated battery cycling, periodical capacity and pulse testing capability are implemented as well. This paper begins with presenting some background information about hybrid electrical vehicles and describing the limitations with today’s HEV battery testing. Furthermore, the functionality of the test equipment is described in detail and, finally, results from verification of the equipment are presented and discussed.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of Lithium-Ion Battery Equivalent Circuit Models for State of Charge Estimation by an Experimental Approach
by
Hongwen He, Rui Xiong and Jinxin Fan
Cited by 1005 | Viewed by 55345
Abstract
To improve the use of lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicle (EV) applications, evaluations and comparisons of different equivalent circuit models are presented in this paper. Based on an analysis of the traditional lithium-ion battery equivalent circuit models such as the Rint, RC, Thevenin
[...] Read more.
To improve the use of lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicle (EV) applications, evaluations and comparisons of different equivalent circuit models are presented in this paper. Based on an analysis of the traditional lithium-ion battery equivalent circuit models such as the Rint, RC, Thevenin and PNGV models, an improved Thevenin model, named dual polarization (DP) model, is put forward by adding an extra RC to simulate the electrochemical polarization and concentration polarization separately. The model parameters are identified with a genetic algorithm, which is used to find the optimal time constant of the model, and the experimental data from a Hybrid Pulse Power Characterization (HPPC) test on a LiMn
2O
4 battery module. Evaluations on the five models are carried out from the point of view of the dynamic performance and the state of charge (SoC) estimation. The dynamic performances of the five models are obtained by conducting the Dynamic Stress Test (DST) and the accuracy of SoC estimation with the Robust Extended Kalman Filter (REKF) approach is determined by performing a Federal Urban Driving Schedules (FUDS) experiment. By comparison, the DP model has the best dynamic performance and provides the most accurate SoC estimation. Finally, sensitivity of the different SoC initial values is investigated based on the accuracy of SoC estimation with the REKF approach based on the DP model. It is clear that the errors resulting from the SoC initial value are significantly reduced and the true SoC is convergent within an acceptable error.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Simultaneous Optimization for Hybrid Electric Vehicle Parameters Based on Multi-Objective Genetic Algorithms
by
Lincun Fang, Shiyin Qin, Gang Xu, Tianli Li and Kemin Zhu
Cited by 75 | Viewed by 11913
Abstract
Compared to conventional vehicles Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) provide fairly high fuel economy with lower emissions. To enhance HEV performance in terms of fuel economy and emissions, and ensure user satisfaction with driving performance, the need for simultaneous optimization for the main parameters
[...] Read more.
Compared to conventional vehicles Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) provide fairly high fuel economy with lower emissions. To enhance HEV performance in terms of fuel economy and emissions, and ensure user satisfaction with driving performance, the need for simultaneous optimization for the main parameters of powertrain components and control system is inevitable. However, this problem is challenging due to the large amount of coupling design parameters, conflicting design objectives and nonlinear constraints. Considering the defect of the methods which convert multi-objective optimization problems into single-objective ones, a comprehensive methodology based on the non-dominated sorting genetic algorithms II (NSGA II) to achieve parameter optimization for powertrain components and control system simultaneously and successfully find the Pareto-optimal solutions set is presented in this paper. A case simulation is carried out and simulated by ADVISOR, The simulation results show that this method can produce many Pareto-optimal solutions and a satisfactory solution can be selected by decision-makers according to their requirements. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of the algorithms proposed in this paper.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Proposal for CO2 Abatement in Urban Areas: The UDR1–Lethe© Turbo-Hybrid Vehicle
by
Roberto Capata, Antonio Coccia and Max Lora
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 10231
Abstract
For years the interest of the University of Roma 1 (UDR1) research group has been focused on the development of a Hybrid Series vehicle (called Lethe
©), different from standard ones, thanks to the use of a Gas Turbine (GT) set as
[...] Read more.
For years the interest of the University of Roma 1 (UDR1) research group has been focused on the development of a Hybrid Series vehicle (called Lethe
©), different from standard ones, thanks to the use of a Gas Turbine (GT) set as a thermal engine. The reason for this choice resides in the opportunity to reduce weight and dimensions, in comparison to a traditional Internal Combustion Engine. It’s currently not possible to use the GT engine set directly for the vehicle traction, so the UDR1 HS configuration only shows the GT set connected with the electric generator. The result is that the traction is purely electric. The resulting engine configuration is commonly described as a Hybrid Series Plug In. Several previous studies have been carried out, and this research has allowed us to define the correct ratio (Degree of Hybridization) between the installed power of the battery pack and that of the GT electric generator which simultaneously guarantee the main life for the battery package and the capacity of the vehicle to complete a common mission without lack of energy or stopping. This article reports the final step of the research: once all data has been calculated, how to “hybridize” a commercial city car, passenger sedan or any other vehicle.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Experiment and Simulation of Medium-Duty Tactical Truck for Fuel Economy Improvement
by
Yeau-Jian Gene Liao and Allen M. Quail, Jr.
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 12036
Abstract
Fuel economy improvement on medium-duty tactical truck has and continues to be a significant initiative for the U.S. Army. The focus of this study is the investigation of Automated Manual Transmissions (AMT) and mild hybridization powertrain that have potential to improve the fuel
[...] Read more.
Fuel economy improvement on medium-duty tactical truck has and continues to be a significant initiative for the U.S. Army. The focus of this study is the investigation of Automated Manual Transmissions (AMT) and mild hybridization powertrain that have potential to improve the fuel economy of the 2.5-ton cargo trucks. The current platform uses a seven-speed automatic transmission. This study utilized a combination of on-road experimental vehicle data and analytical vehicle modeling and simulation. This paper presents the results of (1) establishment of a validated, high fidelity baseline analytical vehicle model, (2) modeling and simulation of two AMTs and their control strategy, (3) optimization of transmissions shift schedules, and (4) modeling and simulation of engine idle stop/start and Belt-Integrated-Starter-Generator (B-ISG) systems to improve the fuel economy. The fuel economy discrepancy between experimental average and the baseline simulation result was 2.87%. The simulation results indicated a 14.5% and 12.2% fuel economy improvement for the 10-speed and 12-speed AMT respectively. A stop/start system followed by a B-ISG mild hybrid system incorporating regenerative braking was estimated to improve fuel economy 3.39% and 10.2% respectively.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Dynamic Modeling and Simulation on a Hybrid Power System for Electric Vehicle Applications
by
Hong-Wen He, Rui Xiong and Yu-Hua Chang
Cited by 69 | Viewed by 15641
Abstract
Hybrid power systems, formed by combining high-energy-density batteries and high-power-density ultracapacitors in appropriate ways, provide high-performance and high-efficiency power systems for electric vehicle applications. This paper first establishes dynamic models for the ultracapacitor, the battery and a passive hybrid power system, and then
[...] Read more.
Hybrid power systems, formed by combining high-energy-density batteries and high-power-density ultracapacitors in appropriate ways, provide high-performance and high-efficiency power systems for electric vehicle applications. This paper first establishes dynamic models for the ultracapacitor, the battery and a passive hybrid power system, and then based on the dynamic models a comparative simulation between a battery only power system and the proposed hybrid power system was done under the UDDS (Urban Dynamometer Driving Schedule). The simulation results showed that the hybrid power system could greatly optimize and improve the efficiency of the batteries and their dynamic current was also decreased due to the participation of the ultracapacitors, which would have a good influence on batteries’ cycle life. Finally, the parameter matching for the passive hybrid power system was studied by simulation and comparisons.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Energy Recovery for the Main and Auxiliary Sources of Electric Vehicles
by
Min Ye, Shengjie Jiao and Binggang Cao
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 11833
Abstract
Based on the traditional regenerative braking electrical circuit, a novel energy recovery system for the main and auxiliary sources of electric vehicles (EVs) has been developed to improve their energy efficiency. The electrical circuit topology is presented in detail. During regenerative braking, the
[...] Read more.
Based on the traditional regenerative braking electrical circuit, a novel energy recovery system for the main and auxiliary sources of electric vehicles (EVs) has been developed to improve their energy efficiency. The electrical circuit topology is presented in detail. During regenerative braking, the recovered mechanical energy is stored in both the main source and the auxiliary source at the same time. The mathematical model of the proposed system is derived step by step. Combining the merits and defects of H
2 optimal control and H
∞ robust control, a H
2/H
∞ controller is designed to guarantee both the system performance and robust stability. The perfect match between the simulated and experimental results validates the notion that the proposed novel energy recovery system is both feasible and effective, as more energy is recovered than that with the traditional energy recovery systems, in which recovered energy is stored only in the main source.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Robust State of Charge Estimation for Hybrid Electric Vehicles: Framework and Algorithms
by
Jingyu Yan, Guoqing Xu, Huihuan Qian and Yangsheng Xu
Cited by 49 | Viewed by 13458
Abstract
State of Charge (SoC) estimation is one of the most significant and difficult techniques to promote the commercialization of electric vehicles (EVs). Suffering from various interference in vehicle driving environment and model uncertainties due to the strong time-variant property and inconsistency of batteries,
[...] Read more.
State of Charge (SoC) estimation is one of the most significant and difficult techniques to promote the commercialization of electric vehicles (EVs). Suffering from various interference in vehicle driving environment and model uncertainties due to the strong time-variant property and inconsistency of batteries, the existing typical SoC estimators such as coulomb counting and extended Kalman filter cannot perform their theoretically optimal efficacy in practical applications. Aiming at enhancing the robustness of SoC estimation and improving accuracy under the real driving conditions with noises and uncertainties, this paper proposes a framework consisting of (1) an adaptive-κ nonlinear diffusion filter to reduce the noise in current measurement, (2) a self-learning strategy to estimate and remove the zero-drift, (3) a coulomb counting algorithm to realize open-loop SoC estimation, (4) an H
∞ filter to implement closed-loop robust estimation, and (5) a data fusion unite to achieve the final estimation by integrating the advantages of the two SoC estimators. The availability and efficacy of each component have been demonstrated based on comparative studiesin simulation with the conventional approaches respectively, under the testing conditions of noises with various signal-noise-ratios, varying zero-drifts, and different model errors. The overall framework has also been verified to rationally and efficiently combine these components and achieve robust estimation results in the presence of kinds of noises and uncertainties.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Estimation of State of Charge of a Lithium-Ion Battery Pack for Electric Vehicles Using an Adaptive Luenberger Observer
by
Xiaosong Hu, Fengchun Sun and Yuan Zou
Cited by 264 | Viewed by 19714
|
Correction
Abstract
In order to safely and efficiently use the power as well as to extend the lifetime of the traction battery pack, accurate estimation of State of Charge (SoC) is very important and necessary. This paper presents an adaptive observer-based technique for estimating SoC
[...] Read more.
In order to safely and efficiently use the power as well as to extend the lifetime of the traction battery pack, accurate estimation of State of Charge (SoC) is very important and necessary. This paper presents an adaptive observer-based technique for estimating SoC of a lithium-ion battery pack used in an electric vehicle (EV). The RC equivalent circuit model in ADVISOR is applied to simulate the lithium-ion battery pack. The parameters of the battery model as a function of SoC, are identified and optimized using the numerically nonlinear least squares algorithm, based on an experimental data set. By means of the optimized model, an adaptive Luenberger observer is built to estimate online the SoC of the lithium-ion battery pack. The observer gain is adaptively adjusted using a stochastic gradient approach so as to reduce the error between the estimated battery output voltage and the filtered battery terminal voltage measurement. Validation results show that the proposed technique can accurately estimate SoC of the lithium-ion battery pack without a heavy computational load.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures