Analysis of Vibrations in Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Considering Air-Gap Deformation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Analysis of Radial Magnetic Force Density Considering Air-Gap Deformation
2.1. Air-Gap Permeance
- (1)
- The air-gap of the IPMSM is assumed to be smooth and uniform, with magnetic saturation and slot opening being neglected;
- (2)
- The radial air-gap length is much smaller than the stator and rotor radii;
- (3)
- The air-gap deformation is so small that the value of stator deformation at the maximum air-gap length is assumed to be the same as that at minimum air-gap length;
- (4)
- The three-phase IPMSM is fed with a sinusoidal and balanced current system.
2.2. Magnetic Flux Density
2.3. Radial Magnetic Force Density
- (1)
- the product (b1(α,t))2 of the stator harmonics of the same number v;
- (2)
- the product (b2(α,t))2 of the rotor harmonics of the same number μ;
- (3)
- the product 2b1(α,t)b2(α,t) of the stator v and rotor μ harmonics.
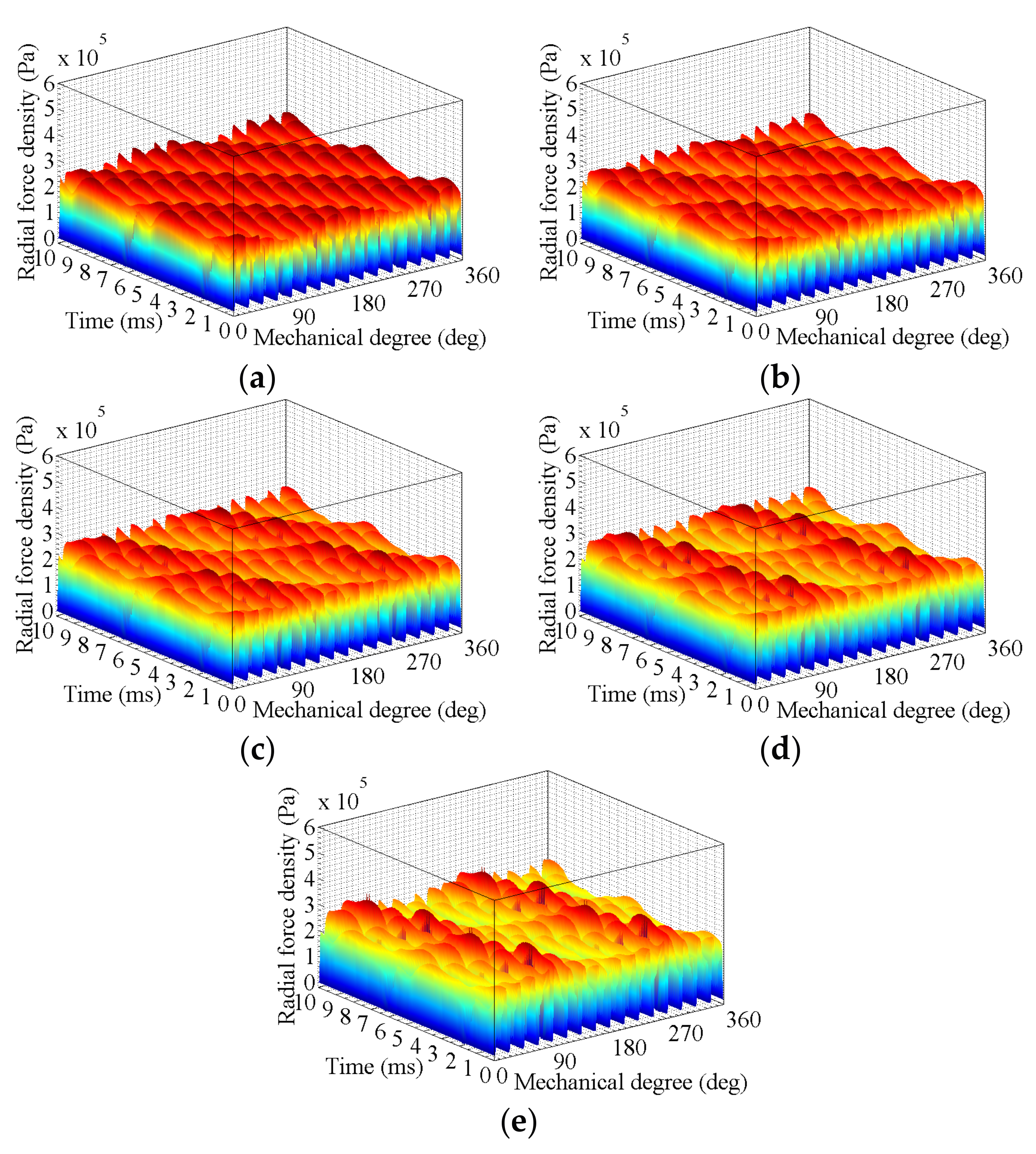
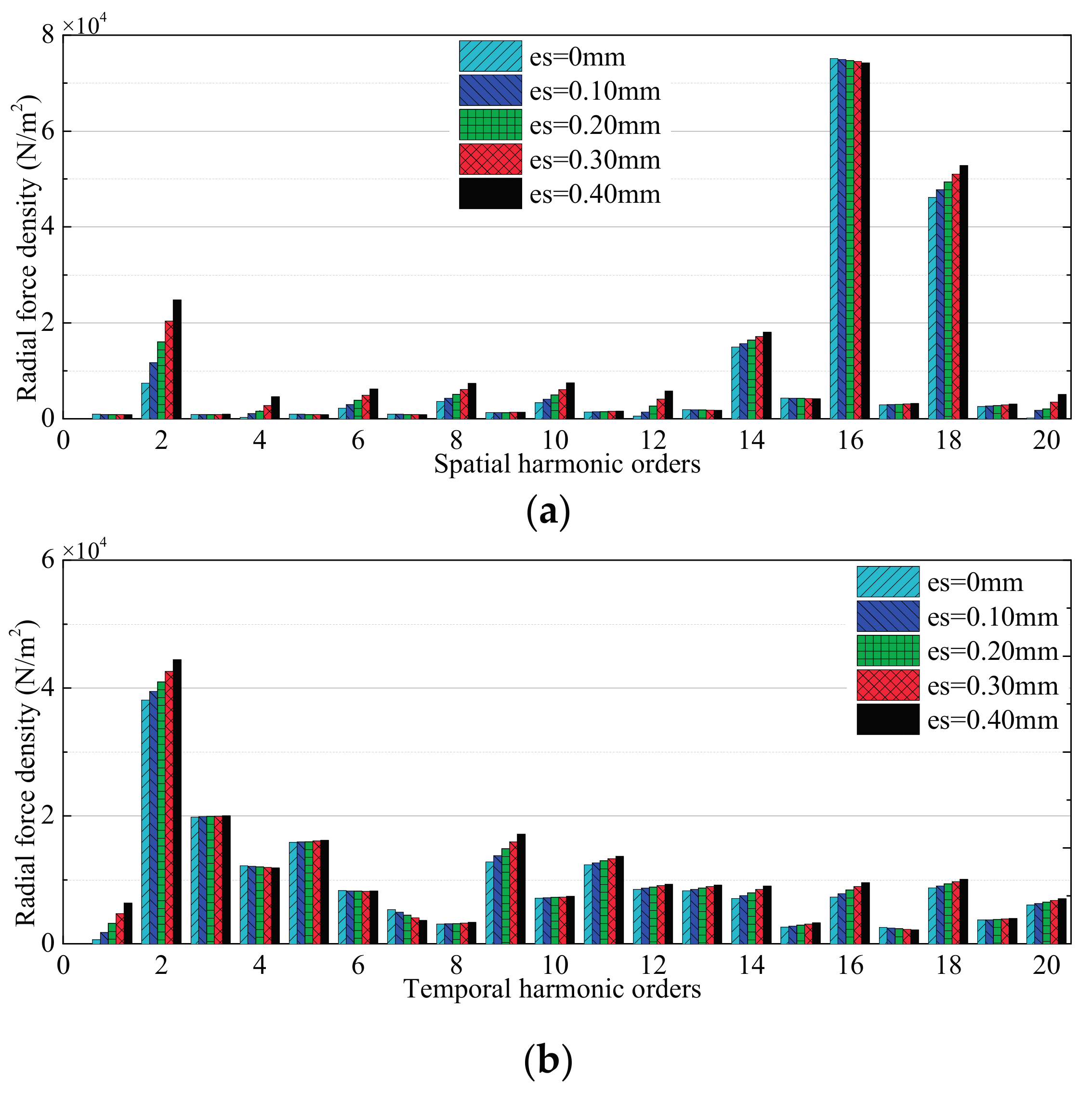
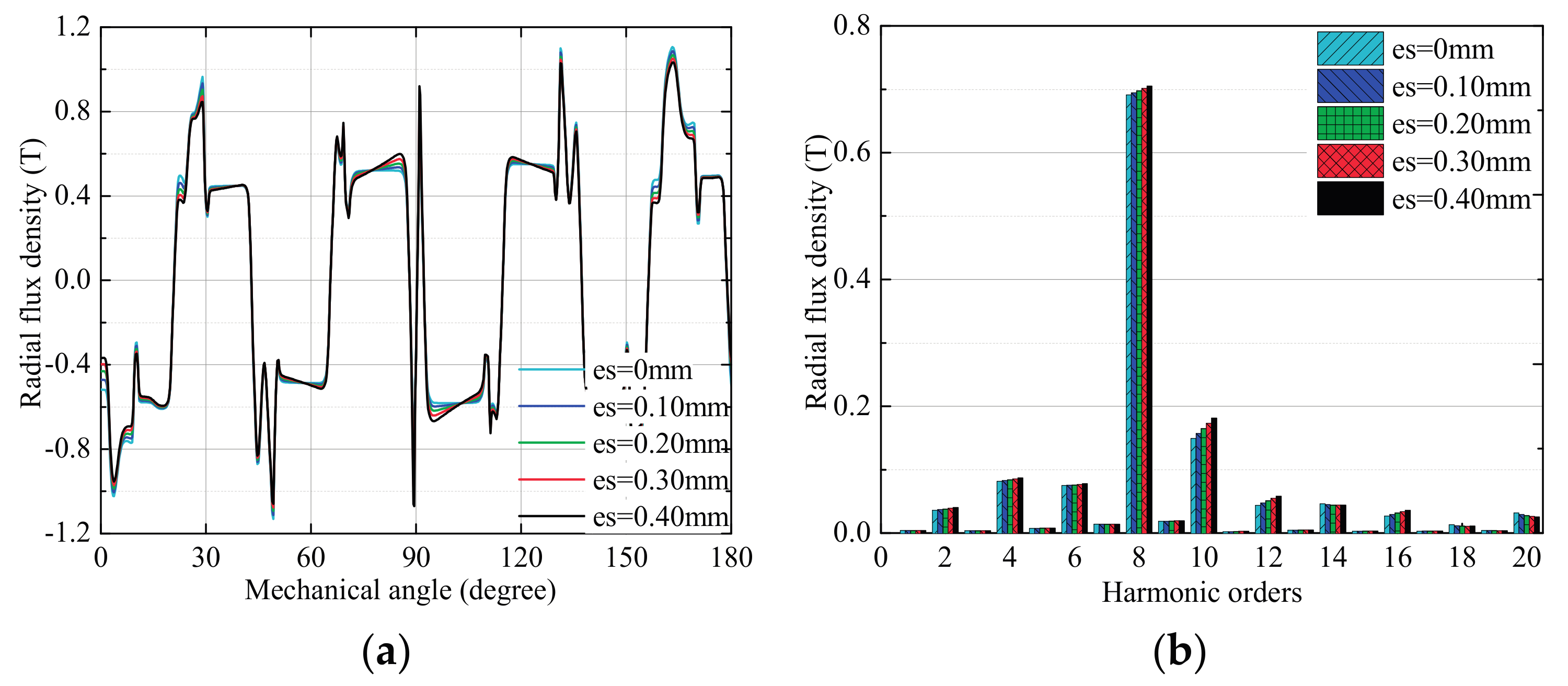
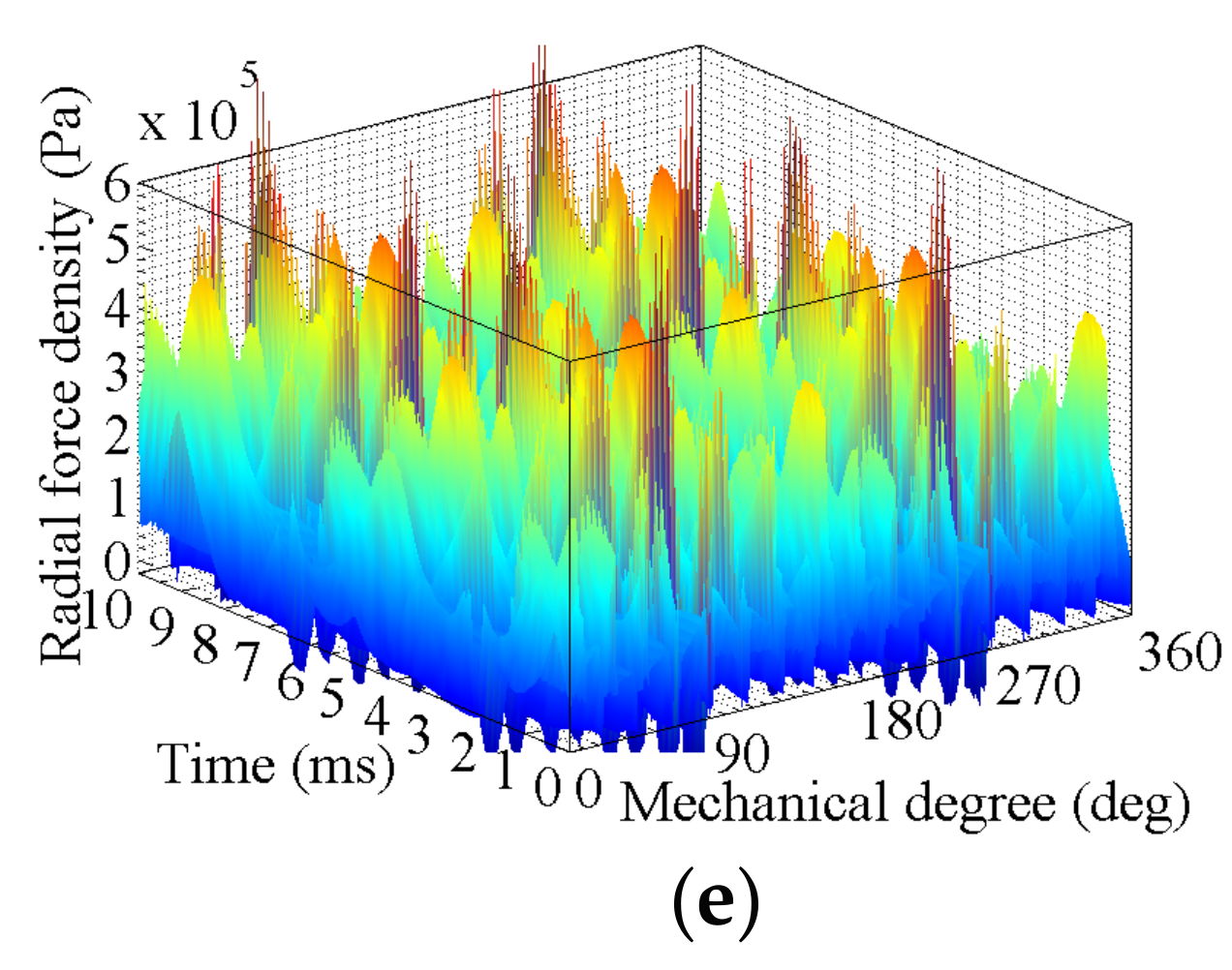
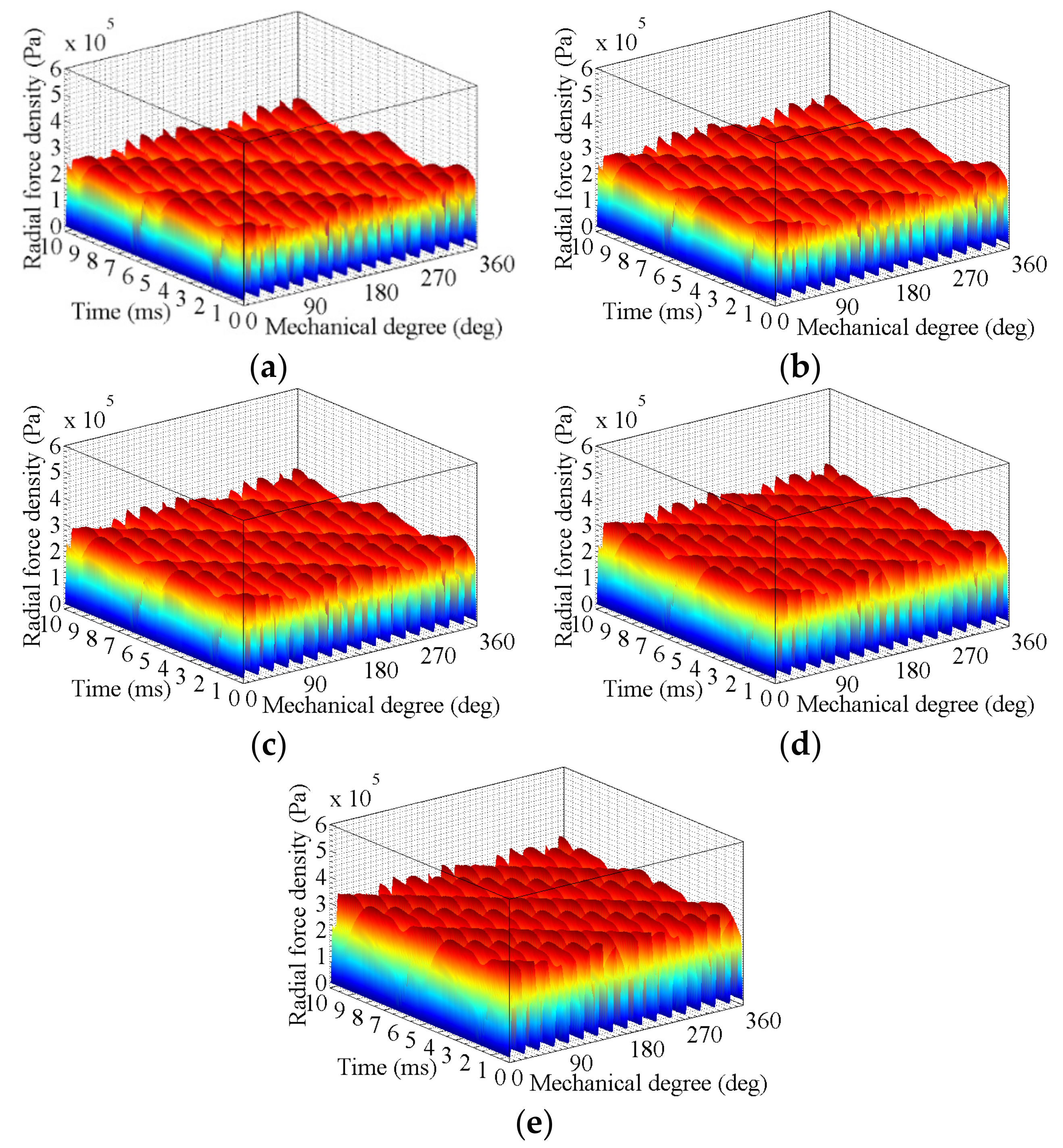
3. FEA of Air-Gap Deformation Effects
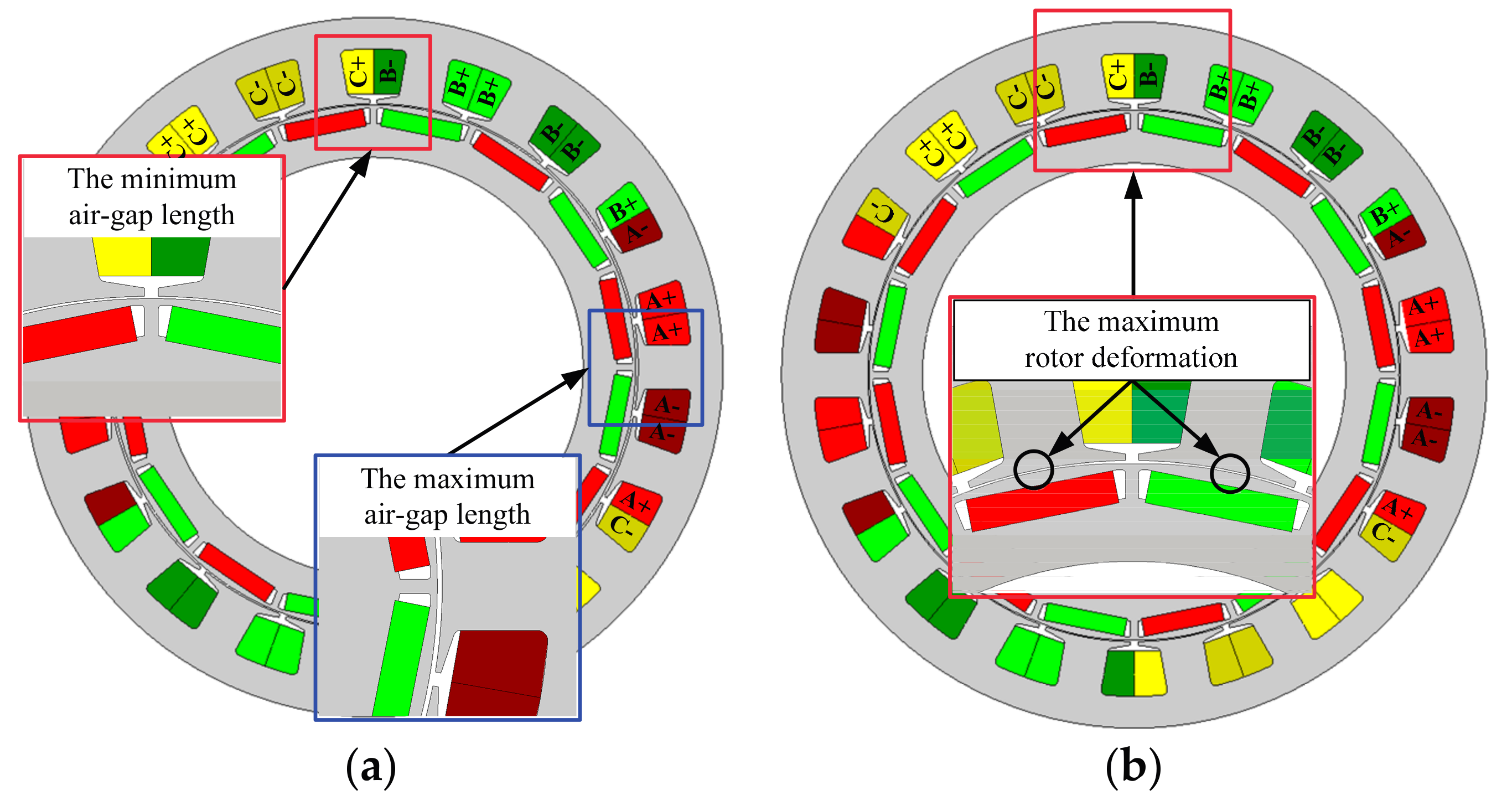
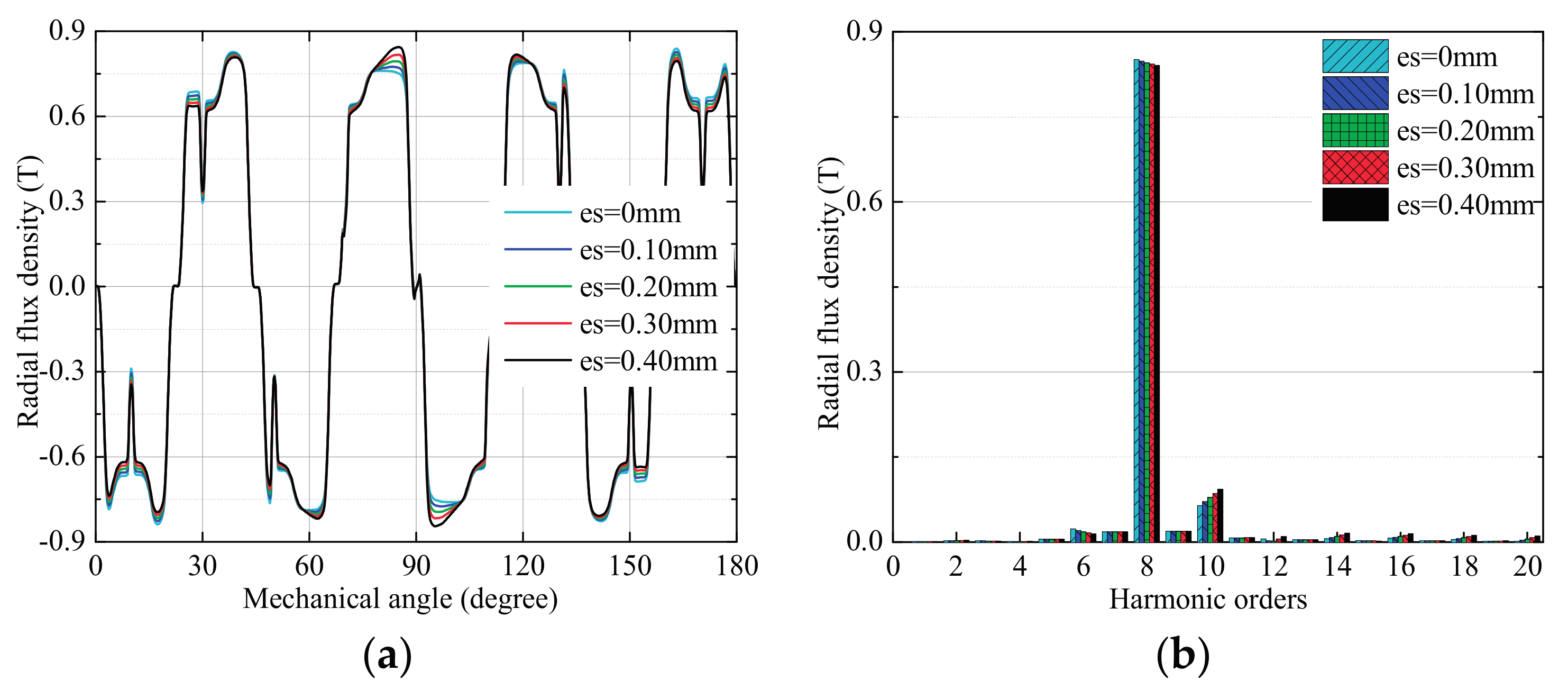
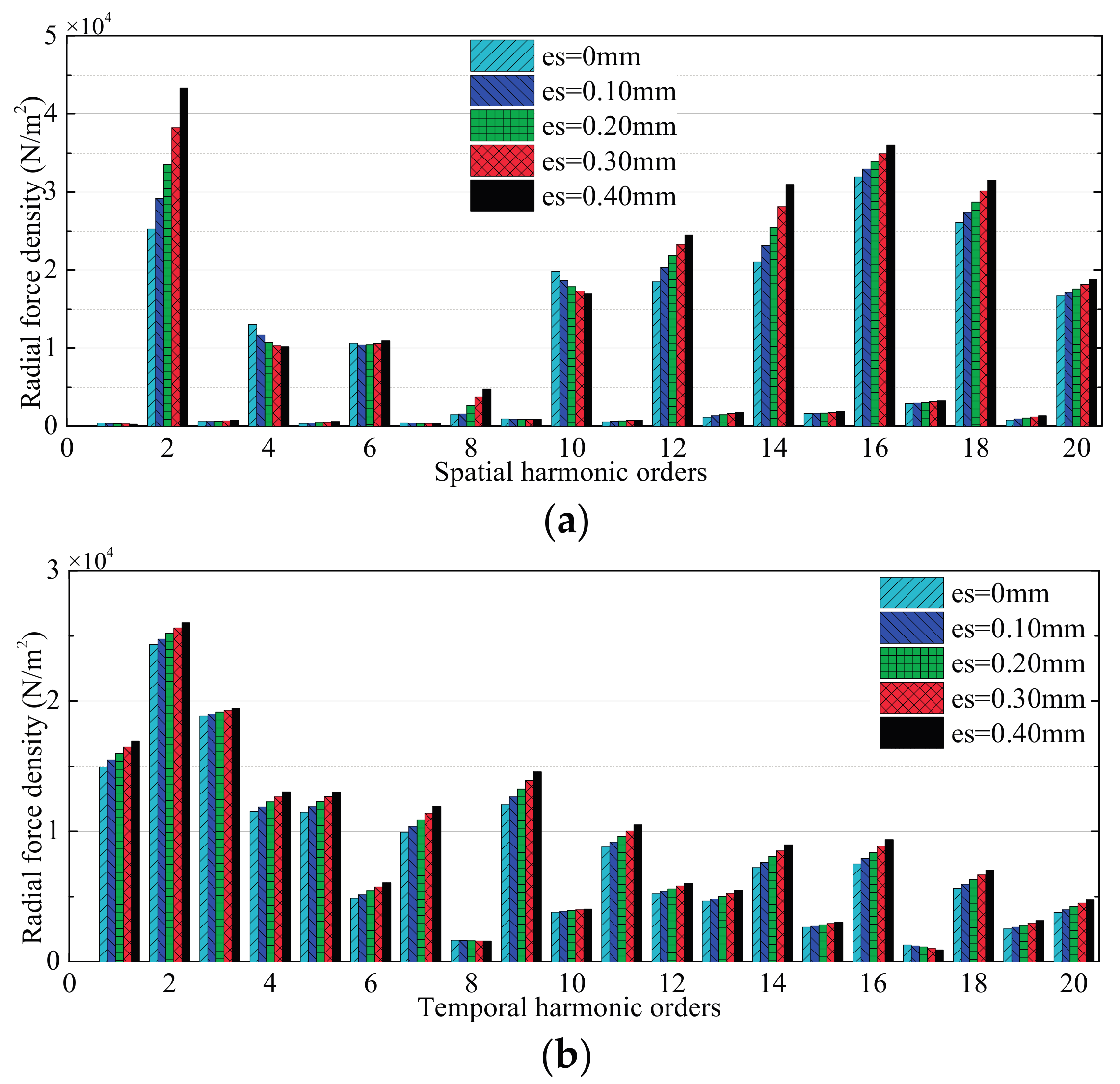
3.1. Effects of Stator Deformation
3.1.1. No-Load Condition
3.1.2. High-Speed Load Condition
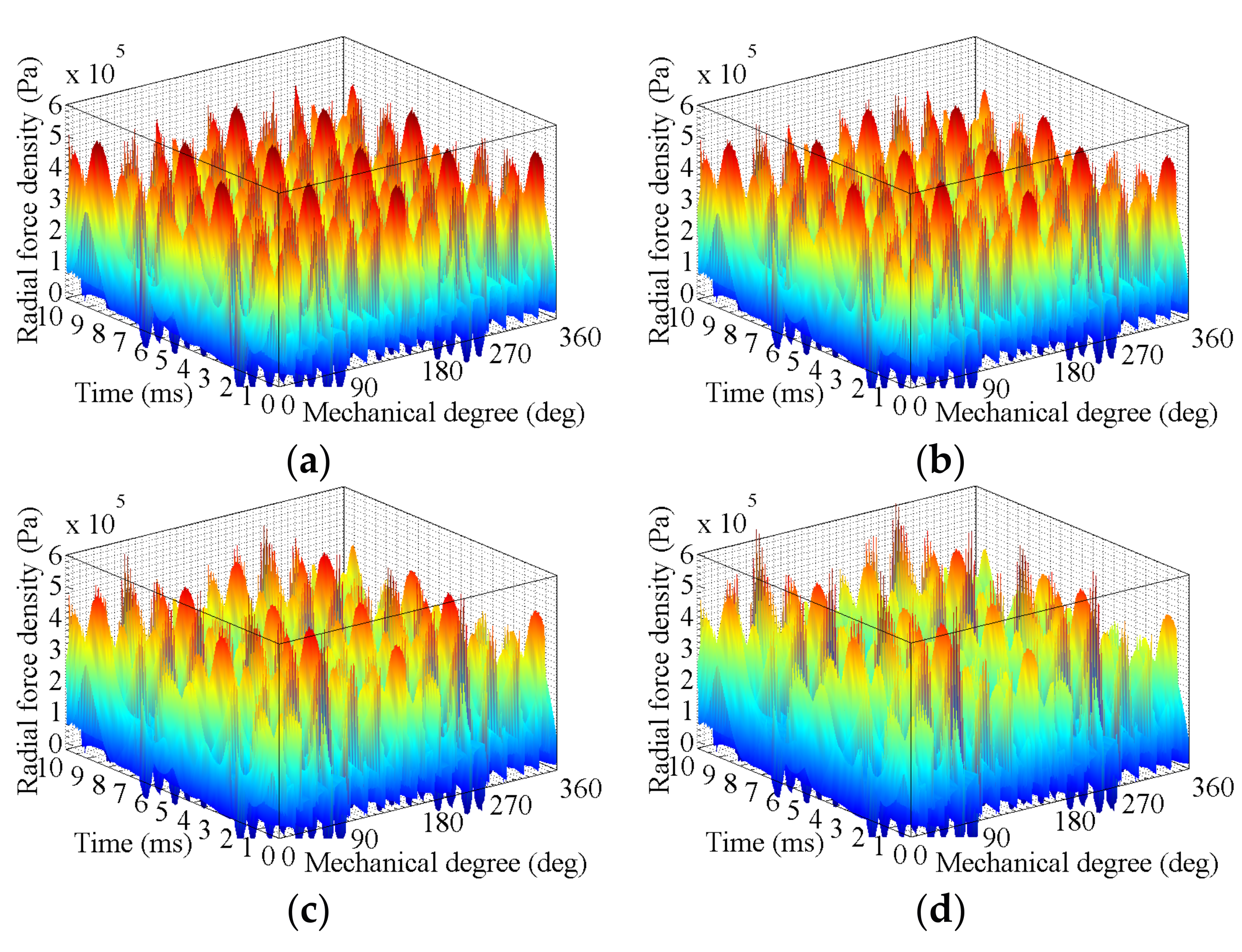
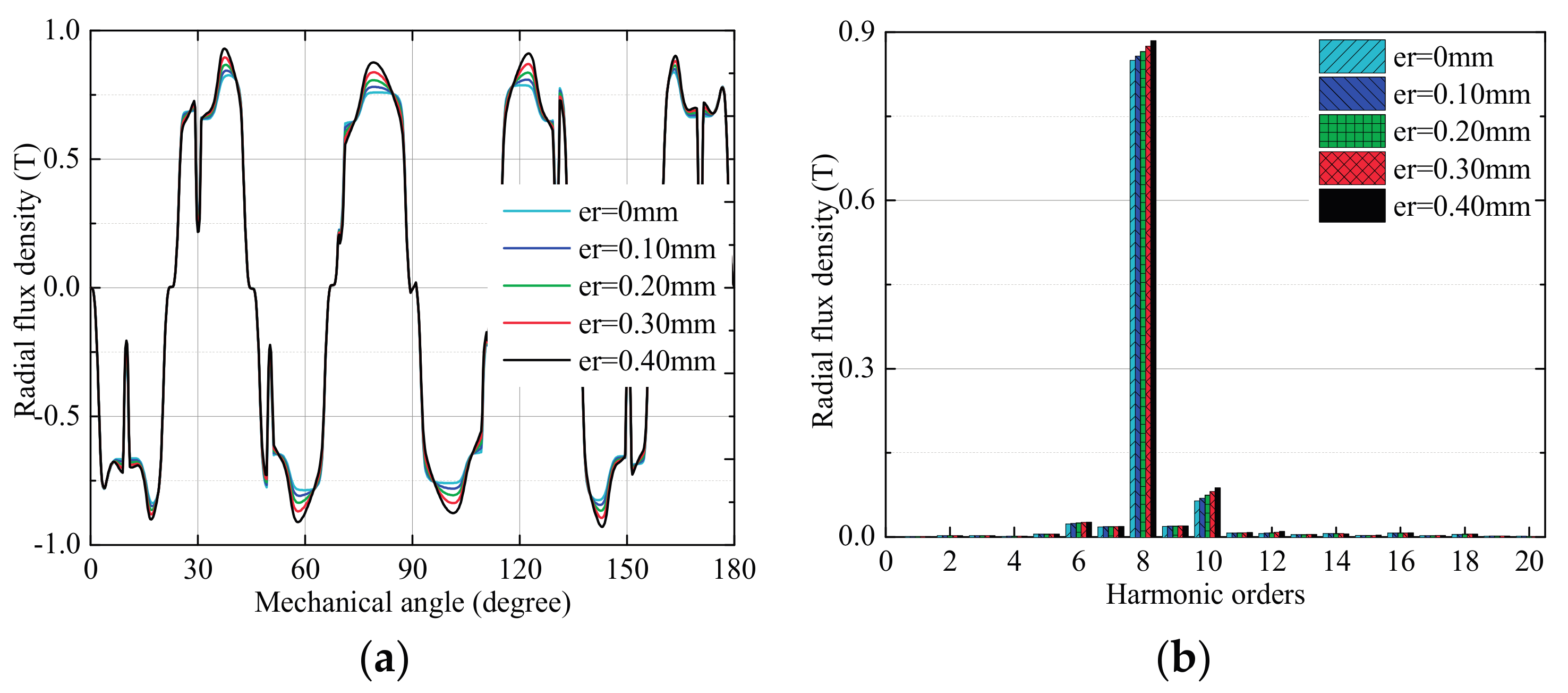
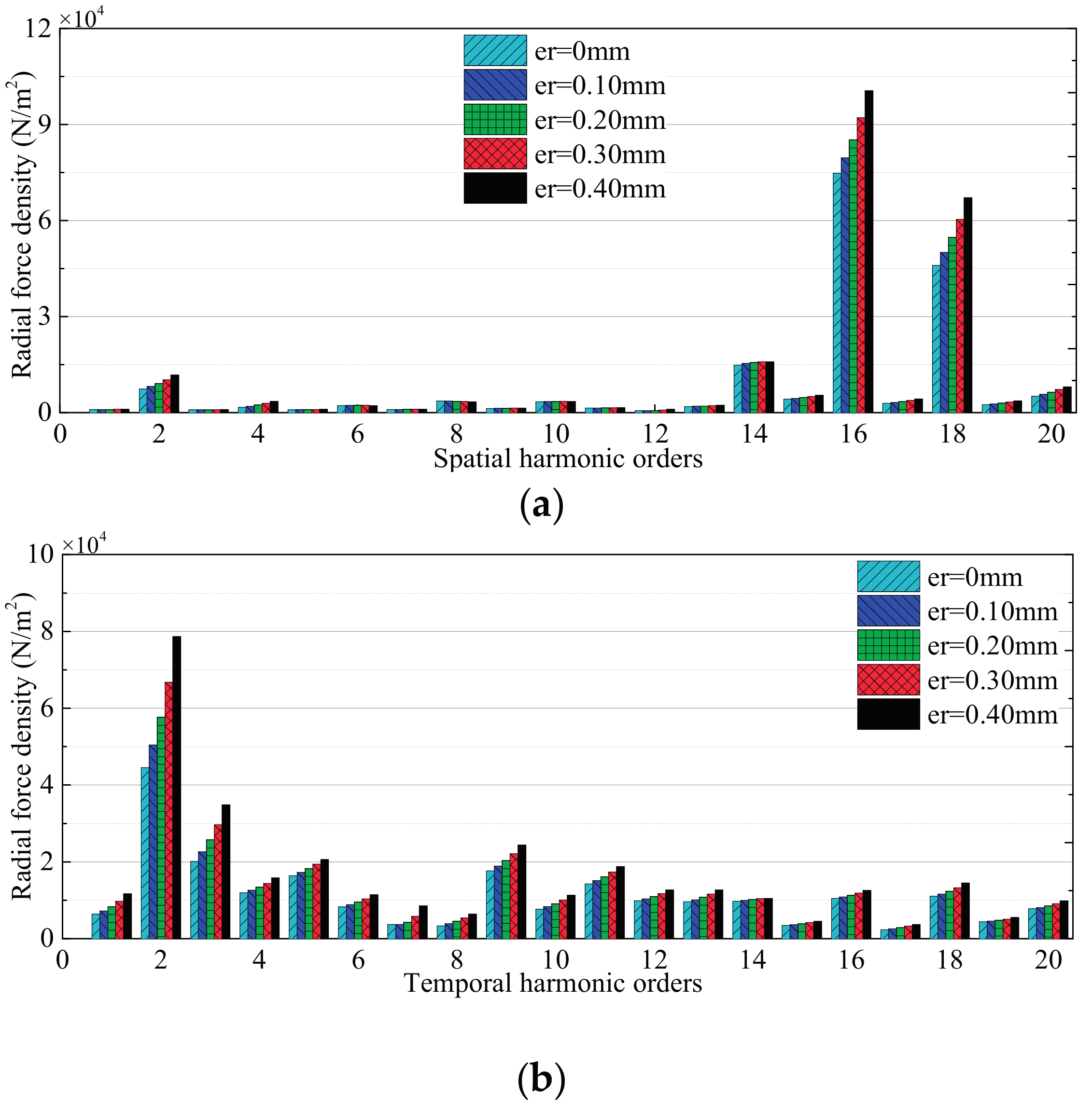
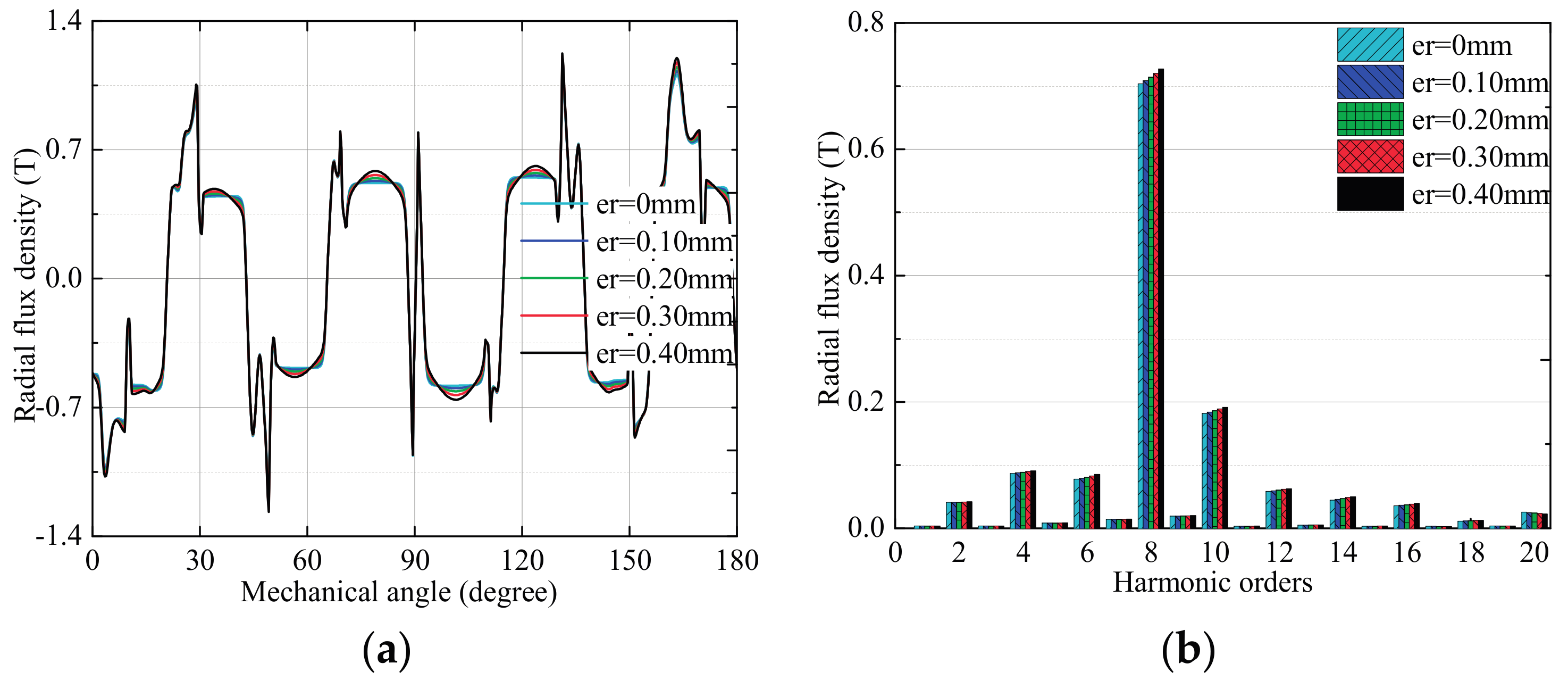
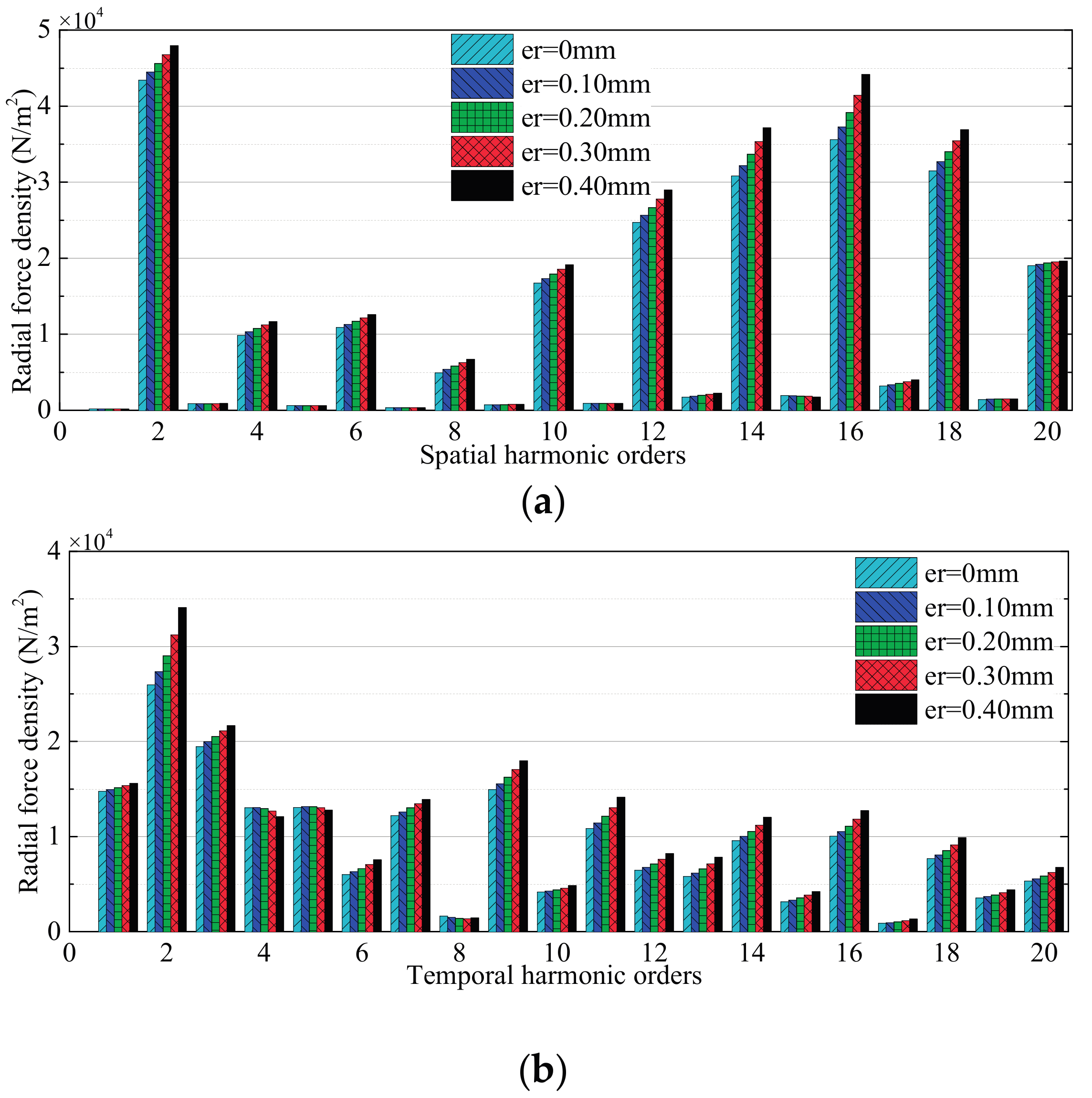
3.2. Effects of Rotor Deformation
3.2.1. No-Load Condition
3.2.2. High-Speed Load Condition
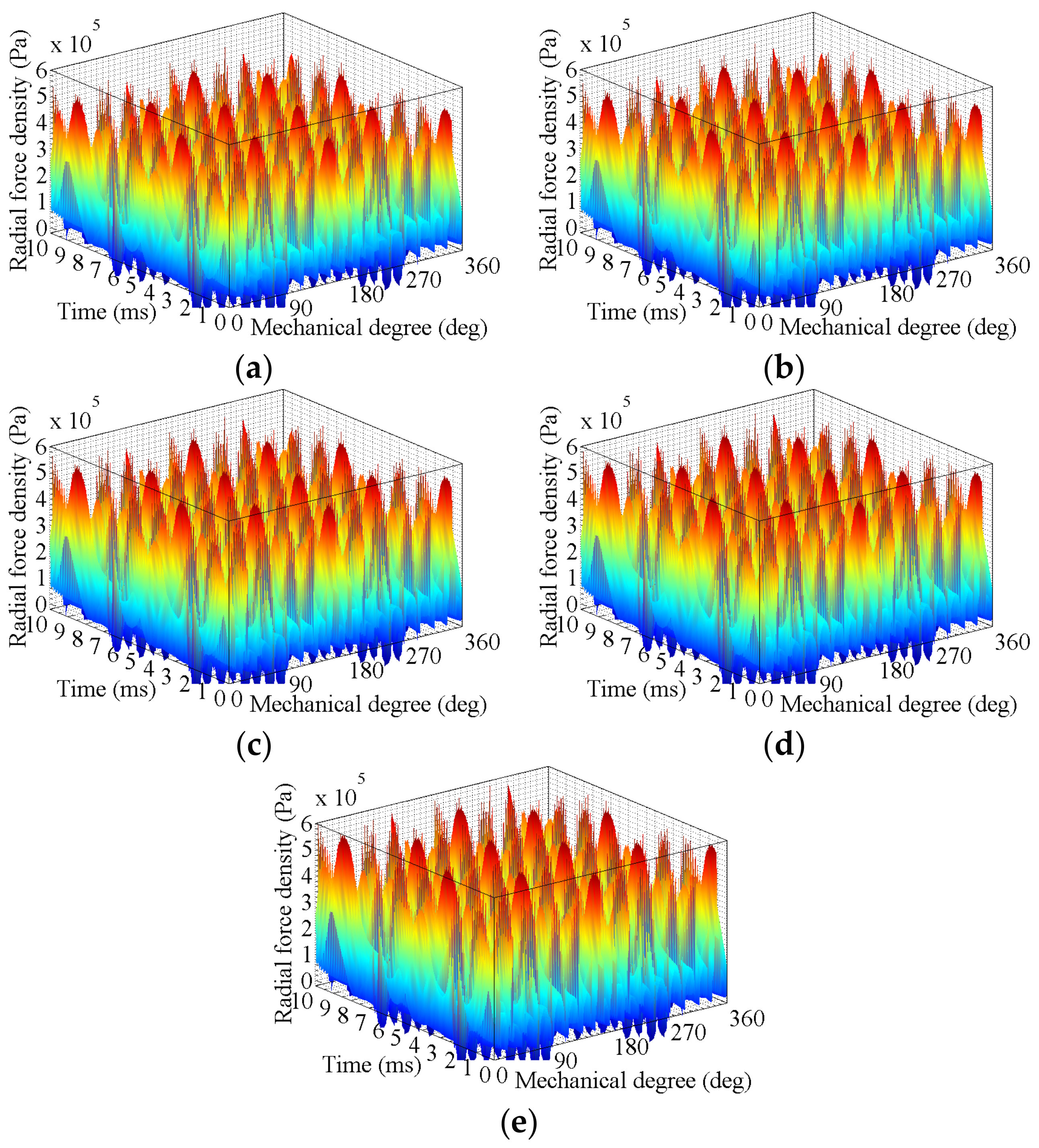
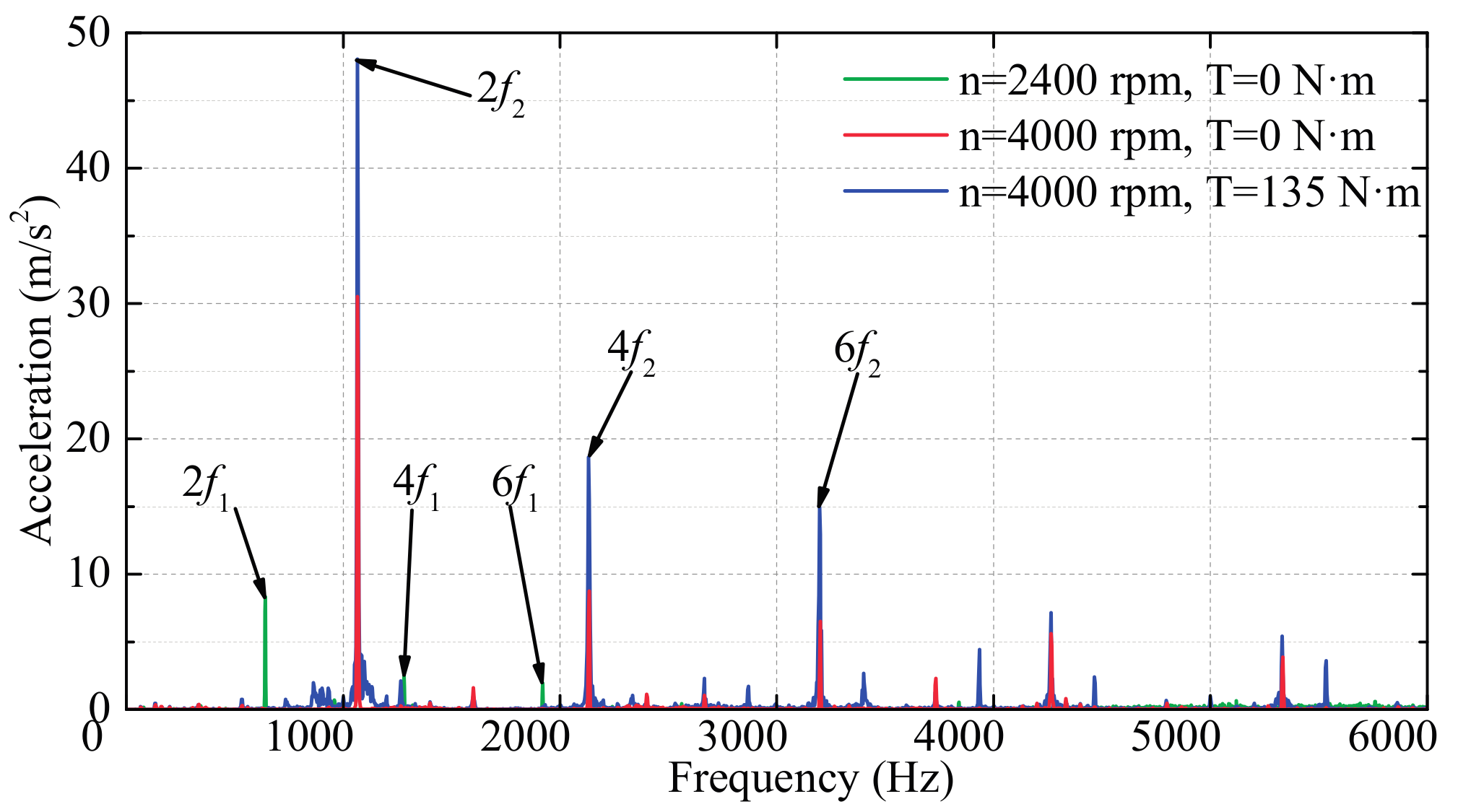
4. Vibration Experiments
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Rso, Rsi | Outer and inner radii of the stator core |
| Rro, Rri | Outer and inner radii of the rotor core |
| lm, hm | Length and height of the PM |
| hmb | Thickness of magnetic bridge |
| hmr | Thickness of magnetic rib |
| μ0 | Magnetic permeability of free space |
| g0 | Average air-gap length in a healthy IPMSM |
| Λ0 | Relative permeance of the smooth air-gap |
| α | Mechanical angle of the rotor position |
| p | Number of pole-pairs |
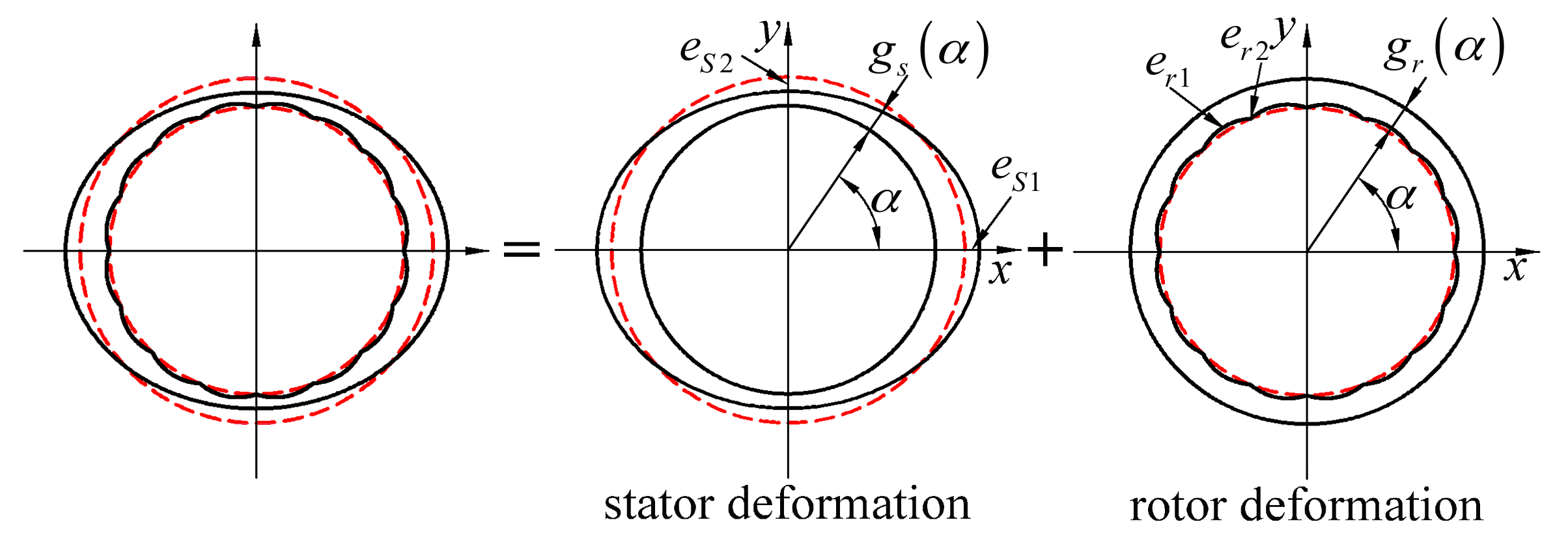
| es1, es2 | Values of maximum and minimum stator deformations |
| er1, er2 | Values of maximum and minimum rotor deformations |
| δs1, δs2 | Values of maximum and minimum relative stator deformations |
| δr1, δr2 | Values of maximum and minimum relative rotor deformations |
| Λg(α, t) | Relative permeance of the deformed air-gap |
| λg(α, t) | Relative specific permeance of the deformed air-gap |
| gs(α) | Radial air-gap length of the stator oval deformation |
| gr(α, t) | Radial air-gap length of the rotor centrifugal distortion |
| λgs(α) | Relative specific permeance of the air-gap with stator deformation (dimensionless) |
| λgr(α, t) | Relative specific permeance of the air-gap with rotor deformation (dimensionless) |
| αs1 | Cofficient, which is defined as αs1 = (δs1 + δs2)/2 |
| αr0 | Cofficient, which is defined as αr0 = (δr1 + δr2)/2 |
| αr1 | Cofficient, which is defined as αr1 = (δr1 − δr2)/2 |
| v | Number of stator MMF harmonics |
| μ | Number of rotor MMF harmonics |
| ωr | Rotor mechanical angular frequency |
| ω | Current angular frequency |
| Fmv | Magnitude of the v-th harmonic of stator MMF |
| Fmμ | Magnitude of the μ-th harmonic of rotor MMF |
| ωμ | Electrical angular frequency of rotor harmonics |
| ϕμ | Angle between vectors of the stator and rotor harmonics of equal order |
References
- Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Zhao, J.; Belahcen, A. Research on the performances and parameters of interior PMSM used for electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 3533–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Pei, Y.; Chai, F.; Zhao, K. Analytical calculation of d-and q-axis inductance for interior permanent magnet motors based on winding function theory. Energies 2016, 9, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Wu, F.; Lei, Y.; Sui, Y.; Yu, B. Investigation of a Novel 24-Slot/14-Pole Six-Phase Fault-Tolerant Modular Permanent-Magnet In-Wheel Motor for Electric Vehicles. Energies 2013, 6, 4980–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, F.; Liang, P.; Pei, Y.; Cheng, S. Analytical Method for Iron Losses Reduction in Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Zhu, X.; Quan, L.; Du, Y. Design and Optimization of Permanent Magnet Brushless Machines for Electric Vehicle Applications. Energies 2015, 8, 13996–14008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, W.; Li, B.; Liu, X.; Gao, C.; Gu, Z. Investigation of Electromagnetic, Thermal and Mechanical Characteristics of a Five-Phase Dual-Rotor Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor. Energies 2015, 8, 9688–9718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Zuo, S.; Deng, W.; Wu, S. Modeling and analysis of electromagnetic force, vibration, and noise in permanent-magnet synchronous motor considering current harmonics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 7455–7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieras, J.F.; Wang, C.; Lai, J.C. Noise of Polyphase Electric Motors, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, F.; Li, Y.; Liang, P.; Pei, Y. Calculation of the maximum mechanical stress on the rotor of interior permanent-magnet synchronous motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 3420–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, S.; Lin, F.; Wu, X. Noise analysis, calculation, and reduction of external rotor permanent-magnet synchronous motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 6204–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urresty, J.C.; Atashkhooei, R.; Riba, J.R.; Romeral, L.; Royo, S. Shaft trajectory analysis in a partially demagnetized permanent-magnet synchronous motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 3454–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, C.; Bao, X.; Wang, H.; Lv, Q.; He, Y. Modeling and analysis of unbalanced magnetic pull in cage induction motors with curved dynamic eccentricity. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 8106507. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimi, B.M.; Faiz, J.; Roshtkhari, M.J. Static-, dynamic-, and mixed-eccentricity fault diagnoses in permanent-magnet synchronous motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 4727–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.K.; Hur, J. Detection of inter-turn and dynamic eccentricity faults using stator current frequency pattern in IPM-type BLDC motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 1771–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, B.M.; Roshtkhari, M.J.; Faiz, J.; Khatami, S.V. Advanced eccentricity fault recognition in permanent magnet synchronous motors using stator current signature analysis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 2041–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Torres, C.; Riba, J.R.; Garcia, A.; Romeral, L. Detection of Eccentricity Faults in Five-Phase Ferrite-PM Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machines. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, Q.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Wu, L.J.; Li, G.J.; Wu, D. Analytical synthesis of air-gap field distribution in permanent magnet machines with rotor eccentricity by superposition method. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 8110404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, M.; Faiz, J.; Ebrahimi, B.M.; Amini, S.; Nazarzadeh, J. A detailed analytical model of a salient-pole synchronous generator under dynamic eccentricity fault. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wu, J.; Hao, L. Fast Calculation Model and Theoretical Analysis of Rotor Unbalanced Magnetic Pull for Inter-Turn Short Circuit of Field Windings of Non-Salient Pole Generators. Energies 2017, 10, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.W.; Bilgin, B.; Sathyan, A.; Dadkhah, H.; Emadi, A. Analysis of unbalanced magnetic pull in eccentric interior permanent magnet machines with series and parallel windings. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2016, 10, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelli, L.; Coia, Y.; Marignetti, F.; Zhu, Z.Q. Analysis of eccentricity in permanent-magnet tubular machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 2208–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, B.M.; Faiz, J. Magnetic field and vibration monitoring in permanent magnet synchronous motors under eccentricity fault. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2012, 6, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biček, M.; Gotovac, G.; Miljavec, D.; Zupan, S. Mechanical Failure Mode Causes of In-Wheel Motors. J. Mech. Eng. 2015, 61, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuler, P.; Klätschke, H. Generation and use of standardised load spectra and load–time histories. Int. J. Fatigue 2005, 27, 974–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuler, P.; Bruder, T.; Klätschke, H. Standardised load-time histories—A contribution to durability issues under spectrum loading. Materwiss Werksttech 2005, 36, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valavi, M.; Nysveen, A.; Nilssen, R.; Rølvåg, T. Slot harmonic effect on magnetic forces and vibration in low-speed permanent-magnet machine with concentrated windings. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 3304–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan-Kim, A.; Hagen, N.; Lanfranchi, V.; Clénet, S.; Coorevits, T.; Mipo, J.C.; Palleschi, F. Influence of the manufacturing process of a claw-pole alternator on its stator shape and acoustic noise. In Proceedings of the 2016 XXII International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Lausanne, Switzerland, 4–7 September 2016; pp. 2273–2279. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Q.; Fang, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Bao, X. Finite element analysis of a squirrel cage induction motor with an oval stator under eccentricity conditions. In Proceedings of the 2013 5th International Conference on Power Electronics Systems and Applications (PESA), Hong Kong, China, 11–13 December 2013; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Putri, A.K.; Rick, S.; Franck, D.; Hameyer, K. Application of Sinusoidal Field Pole in a Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machine to Improve the NVH Behavior Considering the MTPA and MTPV Operation Area. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 2280–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
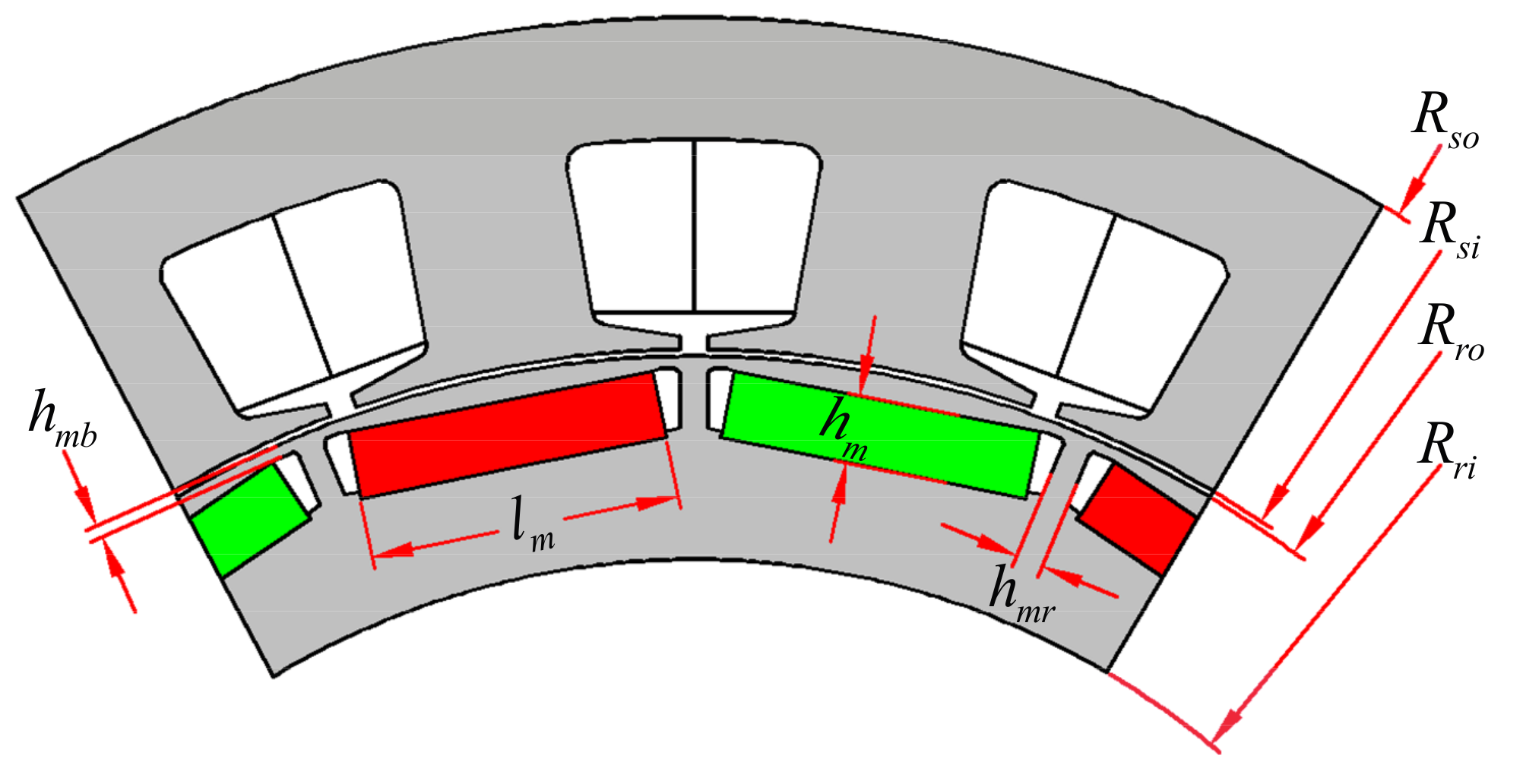
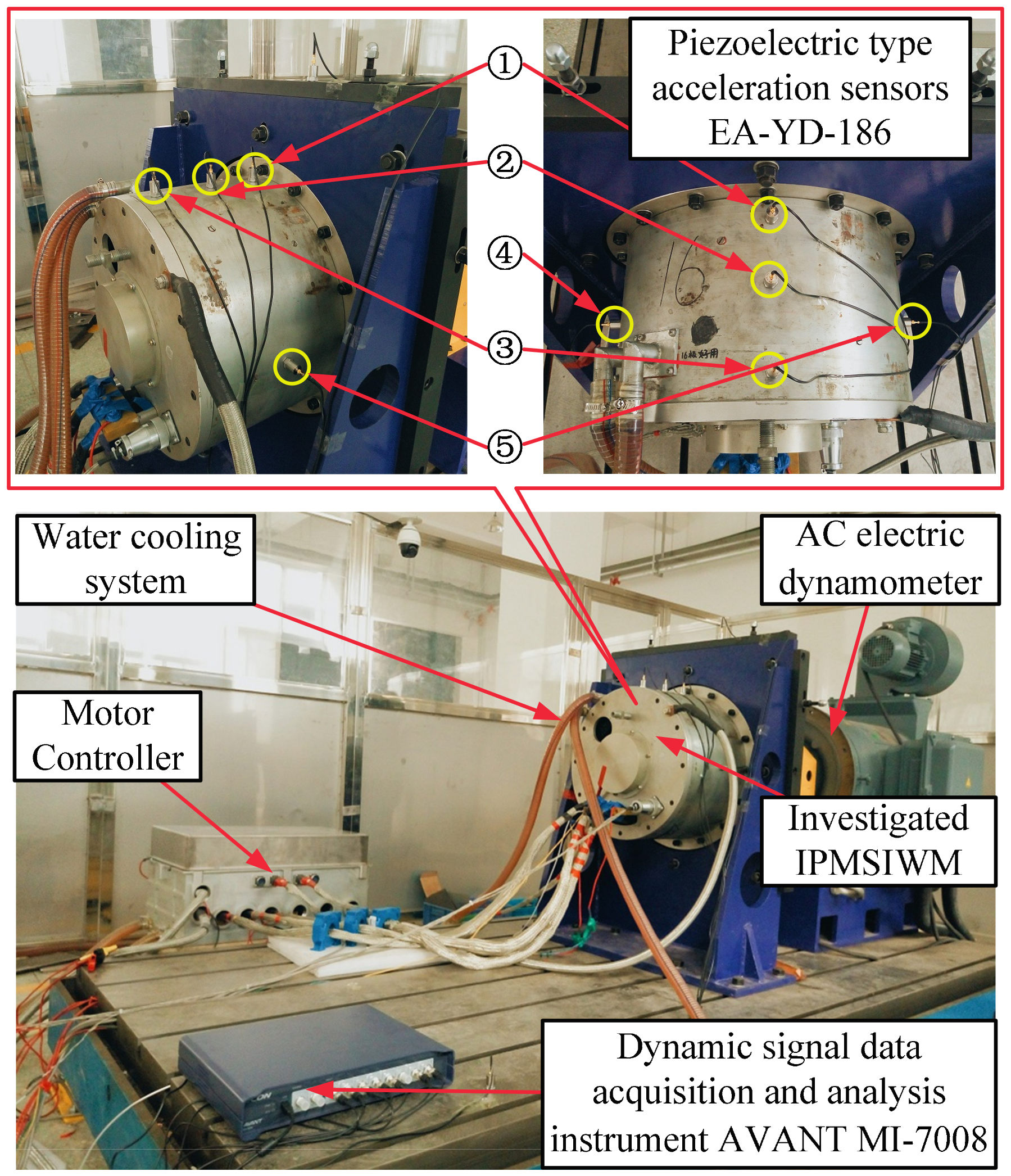
| Items | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Peak rotating speed | 4000 | rpm |
| Rated rotating speed | 2400 | rpm |
| Number of poles/slots | 16/18 | - |
| Outer radius of rotor | 150 | mm |
| Stack length of rotor | 165 | mm |
| Air-gap length | 1 | mm |
| Height of PM | 10 | mm |
| Length of PM | 46 | mm |
| Thickness of magnetic bridge | 1.8 | mm |
| Thickness of magnetic rib | 4 | mm |
| Source | Order | Frequency (Hz) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stator deformation | No-load condition | ||
| On-load condition | |||
| Rotor deformation | No-load condition | ||
| On-load condition | |||
| Order | Order (Circumferential Mode) | Frequency (Hz) |
|---|---|---|
| Stator deformation | ||
| Rotor deformation | ||
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Chai, F.; Song, Z.; Li, Z. Analysis of Vibrations in Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Considering Air-Gap Deformation. Energies 2017, 10, 1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10091259
Li Y, Chai F, Song Z, Li Z. Analysis of Vibrations in Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Considering Air-Gap Deformation. Energies. 2017; 10(9):1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10091259
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yi, Feng Chai, Zaixin Song, and Zongyang Li. 2017. "Analysis of Vibrations in Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Considering Air-Gap Deformation" Energies 10, no. 9: 1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10091259
APA StyleLi, Y., Chai, F., Song, Z., & Li, Z. (2017). Analysis of Vibrations in Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Considering Air-Gap Deformation. Energies, 10(9), 1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10091259







