Abstract
In this paper, by considering and establishing the relationship between the maximum operating speed and d-axis inductance, a new design and optimization method is proposed. Thus, a more extended constant power speed range, as well as reduced losses and increased efficiency, especially in the high-speed region, can be obtained, which is essential for electric vehicles (EVs). In the first step, the initial permanent magnet (PM) brushless machine is designed based on the consideration of the maximum speed and performance specifications in the entire operation region. Then, on the basis of increasing d-axis inductance, and meanwhile maintaining constant permanent magnet flux linkage, the PM brushless machine is optimized. The corresponding performance of the initial and optimal PM brushless machines are analyzed and compared by the finite-element method (FEM). Several tests are carried out in an EV simulation model based on the urban dynamometer driving schedule (UDDS) for evaluation. Both theoretical analysis and simulation results verify the validity of the proposed design and optimization method.
1. Introduction
In recent decades, interior permanent magnet (PM) brushless machines have achieved considerable attention due to the high power density, high efficiency, and excellent dynamic performances [1]. Compared with the surface-mounted PM brushless machines, the improved torque production, enhanced flux-weakening capability, and robust rotor structure promote the application of interior PM brushless machines in modern electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), such as the Toyota Pruis [2,3,4].
To meet the requirements of various driving conditions of frequent acceleration or deceleration, climbing under heavy load and high-speed cruise, the extended constant power speed range, as well as high power and high efficiency over the torque-speed envelope, are also essential for the interior PM brushless machines [5,6]. However, the old design method, which is based on the single operation condition of the rated speed, will bring obvious constraints to the extended operating speed range [7,8]. Such a mismatch of the single operation design method and multiple driving conditions may result in a narrow constant power speed range and low overall efficiency in the entire operation region [9,10,11,12,13]. Thus, the vector control method is introduced to adjust the d-axis current, hence realizing different magnetization states of a variable-flux flux-intensifying interior PM machine to obtain increased efficiency over a driving cycle [14]. However, requirements of precision control are relatively enhanced and the speed range is limited by the inverter capability. In [15], a hybrid excitation machine with additional DC excitation windings is proposed to improve the flux-weakening ability. Yet, the copper loss of DC excitation windings is added and control difficulty is increased in coordinating the armature and excitation current to achieve high torque and efficiency.
In this paper, an interior PM brushless machine with fractional-slot concentrated modular windings is investigated and a new design and optimization method is proposed. In Section 2, the machine geometric topology and relationship between the stator slots and rotor pole numbers are introduced. In order to satisfy multiple driving condition requirements of EV traction machines, the maximum speed and performances requirements in the entire operation region are taken into consideration to determine the initial design of the PM brushless machine. In Section 3, effects of the d-axis inductance and PM flux linkage on the constant power speed range and efficiency are analyzed in details. On this basis, the PM brushless machine is optimized to obtain a more extended constant power speed range, as well as reduced losses and increased efficiency over the torque-speed envelope, especially in the high-speed region. In Section 4, simulation results of the PM brushless machine and EV tests are presented and analyzed in detail to confirm the validity of the proposed method. Section 5 provides the concluding remarks.
2. Machine Design Specifications
The configuration of the investigated interior PM brushless machine is shown in Figure 1, where a V-type flux-focusing rotor structure, which is similar to the rotor structure of the Toyota Pruis, is adopted. However, different from the distributed winding structure of the motor in the Toyota Pruis, fractional-slot concentrated modular windings are newly-employed in the investigated interior PM brushless machine. The coils which belong to each phase are wound on consecutive teeth, which are conducive to a high copper packing factor and to reducing the copper loss due to relatively short end windings [16]. Additionally, the cogging torque can be significantly reduced without the use of skew [17]. Such a modular machine can exhibit a high inductance, since the energy that is associated with fundamental magnetomotive force (MMF) and other lower-order space harmonics is stored in the magnetic field rather than being converted into mechanical energy [18]. Thus, constant power operation can be achieved for this investigated PM brushless machine over an extended speed range.
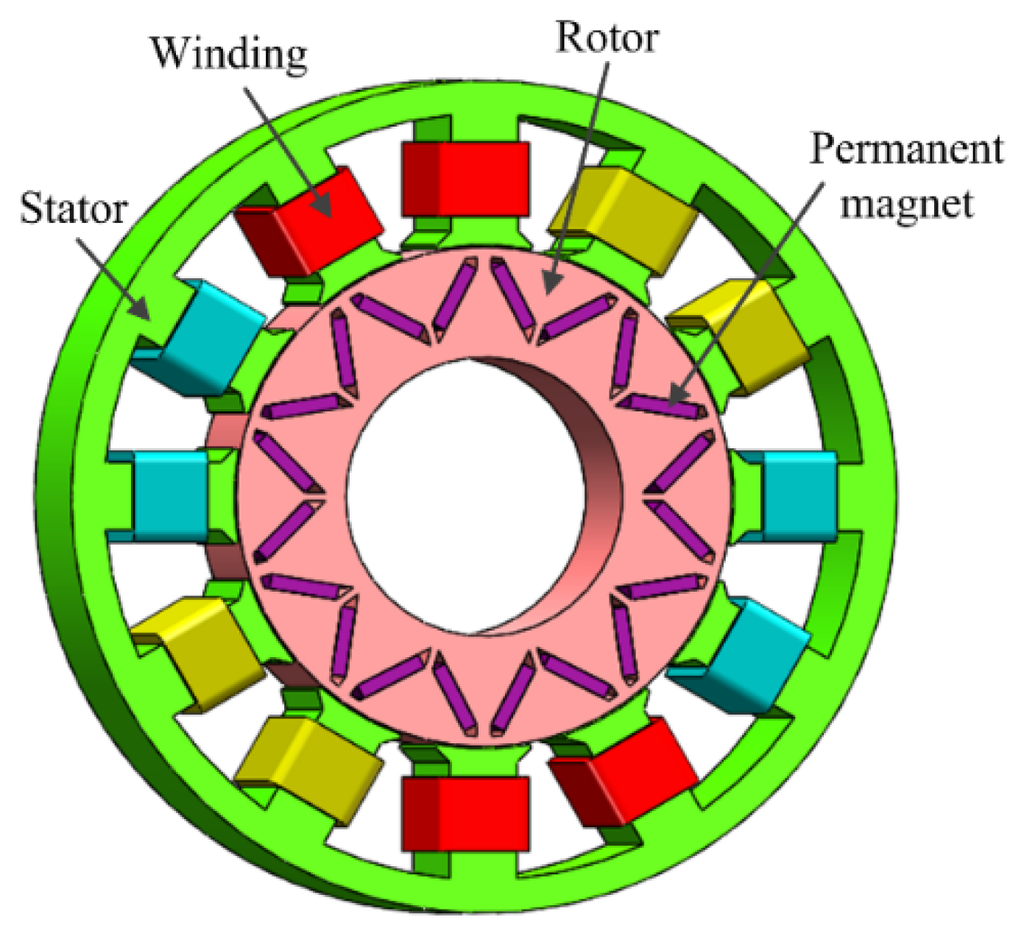
Figure 1.
Configuration of the interior permanent magnet (PM) brushless machine.
Though a similar rotor structure as the motor in the Toyota Pruis is adopted in this investigated PM brushless machine, electromagnetic performances, such as the distribution of the magnetic field and inductances, are obviously changed due to the variation of the winding structure. Moreover, due to the multiple operating conditions of the PM brushless machine in EVs, a new design method should be developed and proposed. Firstly, in order to improve the valid flux linked by armature windings and output torque density, the coil pitch of the motor is designed to be close to the pole pitch [19,20]. Therefore, appropriate numbers of slots and poles should be related by:
where Ns is the slot number, and p is the number of pole pairs. Machines applying a Ns = 2p ± 1 combination have asymmetric stator and rotor structure [21], which may result in relatively high unbalanced magnetic force, excessive noise, and vibration, hence reducing the bearing life. Thus, an Ns = 2p ± 2 combination is preferred, and a 12-slot/10-pole PM brushless machine is selected in this paper.
Since this proposed PM brushless machine is designed to operate over an extended speed range, the maximum operating speed, as well as a speed correction factor, is introduced to the initial dimension equation. Based on the conventional design method [22], it can be deduced as:
where Di1 is the inner diameter of stator, L is the stack length, Pc is the continuous power, η is the efficiency, αi is the calculating pole-arc coefficient, kB is the waveform factor of air-gap flux, kdp is the winding factor, kn is the speed correction factor related to the maximum operating speed nmax, A is the electrical load, and Bδ is the maximum value of air-gap flux density.
In this paper, a 5 KW PM brushless machine is designed. At the base speed of 1200 rpm, the torque can be deduced as 40 Nm. Considering the EV application, the maximum speed of 5000 rpm is required, and the constant power speed range should be 3−4 times the base speed [5]. Moreover, within the speed range from the base speed to the maximum speed, the efficiency is expected to be 80%−93%. The detailed design specifications are listed in Table 1, based on which, the rated speed and maximum speed operating points are calculated. From the rated speed to the maximum speed, the efficiency decreases within the given range. Thus, the dimension range can be obtained as:
In the constraints of structure reasonability and machine manufacture, initial values of some key parameters are also determined and listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Design specifications and initial design.
| Parameters | Values | |
|---|---|---|
| Design specifications | Continuous power Pc (kW) | 5 |
| Continuous torque below and at base speed Tc (Nm) | 40 | |
| Efficiency η (%) | 80–93 | |
| Base speed ωb (rpm) | 1200 | |
| Maximum speed ωmax (rpm) | 5000 | |
| Constant power speed range | 3–4 | |
| Maximum phase voltage Ulim (V) | 74 | |
| Maximum phase current Ilim (A) | 28 | |
| Initial design | Number of slots Ns | 12 |
| Number of pole pairs p | 5 | |
| Stator outer diameter D1 (mm) | 200 | |
| Stator inner diameter Di1 (mm) | 121 | |
| Stack length L (mm) | 79.2 | |
| Number of turns N | 20 | |
3. Optimization of the Constant Power Speed Range
The PM brushless machine applied in EVs needs to provide extended constant power speed range which is always 3–4 times the base speed, where a relatively large inductance is preferred to provide a better flux-weakening capability and lower energy consumption [23,24]. In order to maximize the constant power speed range, the corresponding optimization model is defined as follows:
where the current is assumed to be entirely used for flux weakening, ωmax_c is the maximum speed in the constant power region, ωb is the base speed, ψf is the PM flux linkage, Ilim is the maximum phase current, and, Lq and Ld are q-axis and d-axis inductance, respectively, and, ψf and Ld are expressed as:
where N is the number of turns, BM is the PM magnetic field intensity, bM is the effective width of the PM, L is the stack length, μ0 is the air permeability, αi is the calculating pole-arc coefficient, τ is the pole pitch, δ is the air-gap length, kδ is the air-gap coefficient, and ks is the saturation coefficient of the magnetic circuit.
In order to make little influence on the torque output ability, decreasing ψf is not suitable to extend the constant power speed range. Thus, under the condition of maintaining constant ψf, increasing Ld is more effective. There are a variety of ways to increase the machine inductance [25,26,27], such as reducing the air-gap length or the PM thickness to increase the permeance. However, since permeability of NdFeB is quite close to air, the machine inductance will lack the sensitivity to variation of the air-gap length or the PM thickness. Reducing the slot opening width or increasing the tooth-tip height is also be an effective method in increasing the inductance. However, great flux leakage and high level saturation may occur in the tooth-tip region, resulting in increased iron loss. It can be concluded from Equations (5) and (6) that ψf is proportional to N and L, whereas Ld is proportional to the square of N and L. In order to increase the machine inductance with little effects on other performances, N should be increased, and L should be proportionally decreased to realize constant ψf.
In addition to the more extended constant power speed range, the losses are often decreased over the torque-speed envelope due to the increased d-axis inductance. The corresponding iron loss is calculated as a function of flux density and frequency [28], which is given by:
where kh, ke, α and β are coefficients of the silicon steels, and G is the weight of the PM brushless machine. Due to the higher inductance, the flux-weakening capability is improved, hence reducing the flux density B. Meanwhile, the decreased L is contributed to lighter G. Thus, the higher the d-axis inductance is, the lower the iron loss will be.
Additionally, the copper loss is given by:
where m is the phase number, I is the phase current, R is the phase resistance, lD, τy, αc are parameters of the coils, s is the slot number, α1 is the number of branches in parallel, Nt is the number of wires in parallel, and qa is the cross section of the wire. Since N is increased and L is decreased proportionally, R is increased. In the region of low speed operation, due to the little-changed I, the copper loss is increased while, in the region of high speed operation, the increased d-inductance yields a lower d-axis current to weaken the PM flux field, hence, resulting in a much lower copper loss.
In general, by increasing the d-axis inductance, the constant power speed range is extended. The copper loss is increased at low speed and decreased at high speed, whereas the iron loss is reduced consistently.
However, with the increase of the d-axis inductance, the voltage is increased. Considering the limitations of the PM brushless machine itself and the inverter capacity, a limit maximum value of d-axis inductance should be selected. Theoretically, when the d-axis flux linkage can fully weaken the PM flux linkage, the PM brushless machine can operate within a limitless constant power speed range [29] and this d-axis inductance is the desired value.
Thus, aimed at realizing a similar ideal operation condition, the optimal values of N and L, as well as some key machine parameters are listed and compared with the initial values in Table 2. As expected, the PM flux linkage is unchanged, while the d-axis inductance is increased by a factor of 6/5, which agrees well with the increase ratio of N.

Table 2.
Comparison of machine parameters of the initial and optimal permanent magnet (PM) brushless machines.
| Design variants | Initial Values | Optimal Values |
|---|---|---|
| Number of turns N | 20 | 24 |
| Stack length L (mm) | 79.2 | 66 |
| d-axis inductance Ld (mH) | 4.26 | 5.11 |
| Permanent magnet flux linkage ψf (wb) | 0.14 | 0.14 |
4. Performance Analysis
Based on the optimization results, the optimal PM brushless machine is established and the corresponding electromagnetic performance of the optimal PM brushless machine is analyzed in detail by the finite element method (FEM). Meanwhile, an EV simulation model involving the PM brushless machine is built and tested based on the urban dynamometer driving schedule (UDDS) for evaluation.
4.1. Performance Analysis at the Rated Operating Point
The flux linkage, back electromotive force (EMF), and torque characteristics of the proposed PM brushless machine are given in Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4. As expected, both the initial and optimal PM brushless machines based on the proposed design method can provide good electromagnetic performance. Moreover, it can be observed from Figure 2a that the amplitude of PM flux linkage is unchanged after optimization and Phase A of the initial PM brushless machine shows 120 degree ahead of Phase B of the optimal one, indicating the consistency of PM flux linkage of the initial and optimal PM brushless machines. As shown in Figure 2b, the d-axis inductance is indeed increased from 4.26 mH to 5.11 mH, verifying the validity of the proposed optimization method. Furthermore, the no-load back EMF of the optimal PM brushless machine at the base speed of 1200 rpm is given in Figure 3a, which exhibits a sinusoidal waveform. Meanwhile, the relevant harmonic spectrum is calculated. The total harmonic distortion (THD) is only 2.57%, as shown in Figure 3b.
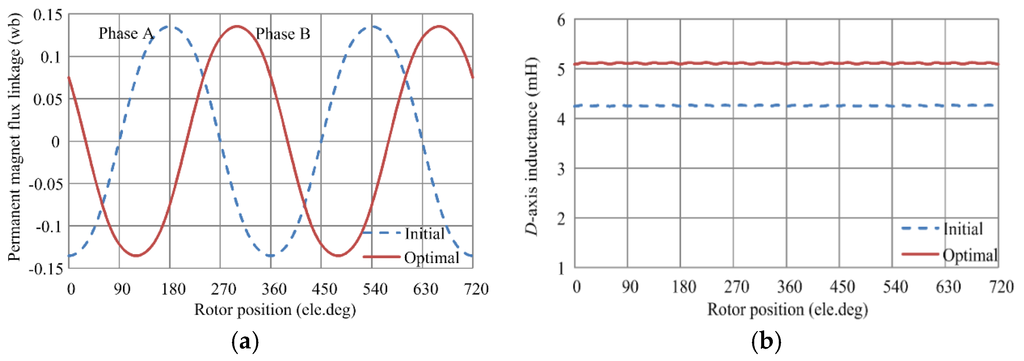
Figure 2.
PM flux linkage and d-axis inductance curves of the initial and optimal PM brushless machines. (a) PM flux linkage; and (b) d-axis inductance.
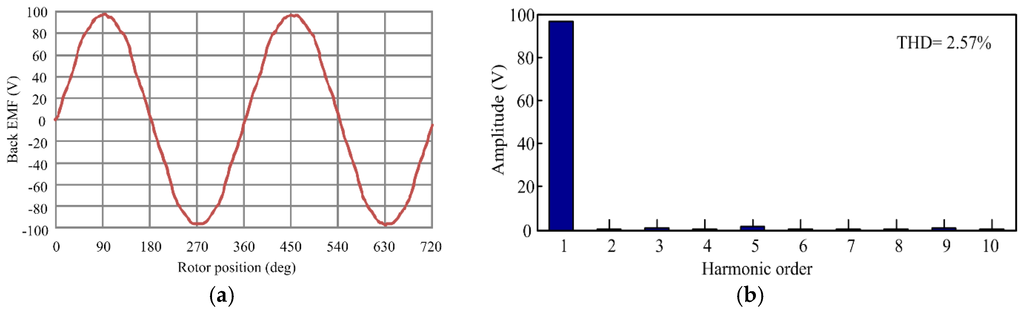
Figure 3.
No-load back electromotive force (EMF) of the optimal PM brushless machine. (a) Waveform; and (b) harmonic spectrum.
The cogging torque of the initial and optimal PM brushless machines at the rated operating point within a cycle are compared in Figure 4a. It can be seen that the peak-to-peak value of the cogging torque is decreased by 16.7% after optimization. When the same sinusoidal current of 40 A is injected in the armature windings, torque performances of the both PM brushless machines are shown in Figure 4b. The output torque is decreased slightly due to the reduced stack length and the torque ripple is increased with the increase of the reluctance torque.
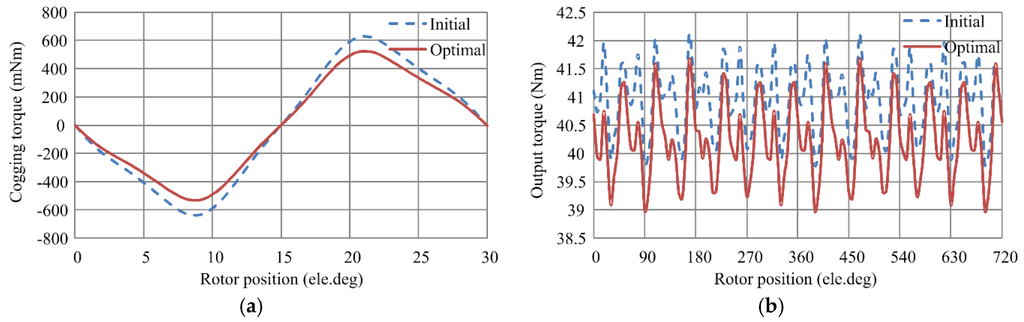
Figure 4.
Cogging torque and output torque curves of the initial and optimal PM brushless machines. (a) Cogging torque; and (b) output torque.
Detailed torque and losses characteristics of the initial and optimal PM brushless machines are listed and compared in Table 3 at the base speed of 1200 rpm. It can be concluded that, due to the increased N and decreased L, the output torque of the optimal machine is slightly decreased. Meanwhile, the copper loss and total loss of the optimal machine is increased by a few percent. However, a relatively high efficiency 93.84% can still be obtained at the rated operation point. Moreover, the optimal machine exhibits 15.2% higher torque density and 17.9% higher torque production per unit PM than that of the optimal machine. The iron loss is decreased by about 11%. In general, even under the rated operation condition, the optimal machine can provide high efficiency and high torque density while ensuring a relatively high inductance, which establishes the foundation for improved wide-speed-range operation performances of the PM brushless machine.

Table 3.
Comparison of output torque and losses of the initial and optimal PM brushless machines.
| Performances | Initial Machine | Optimal Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Torque (Nm) | 40.8 | 40.1 |
| Torque density (kNm/m3) | 18.47 | 21.78 |
| Torque production per unit PM (kNm/mm3) | 4.46 | 5.26 |
| Power (kW) | 5.1 | 5.0 |
| Iron loss (W) | 43.8 | 38.5 |
| Eddy loss (W) | 13.9 | 17.0 |
| Copper loss (W) | 163.2 | 175.2 |
| Total loss (W) | 320.9 | 330.8 |
| Efficiency (%) | 94.12 | 93.84 |
4.2. Performances Analysis over the Speed Range
Since the PM brushless machine serves as a traction machine in EVs, the performances analysis over the speed range is inevitable. The constant power operation curve is given in Figure 5a. It can be seen that the optimal machine shows a more extended constant power speed range, which is about 3.7 times the base speed, satisfying the requirement of 3–4 times the base speed for EV traction machines. Figure 5b gives the torque-speed envelopes, in which the optimal PM brushless machine provides lower torque in the low-speed region, but higher torque in the high-speed region, compared with the initial PM brushless machine.
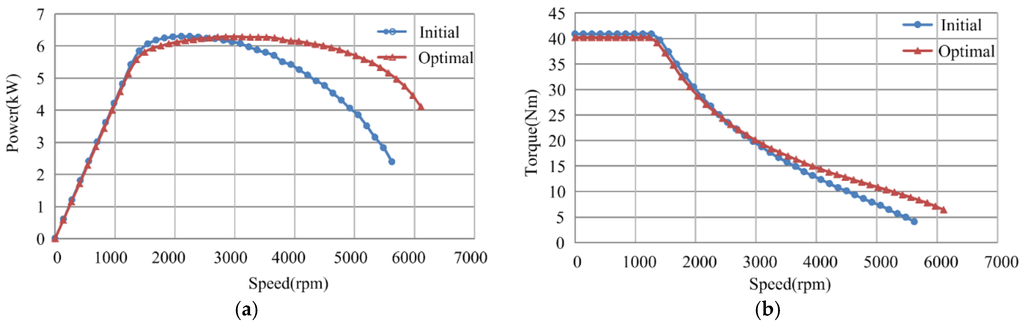
Figure 5.
Power-speed and torque-speed curves of the initial and optimal PM brushless machines. (a) Power-speed; and (b) torque-speed.
In order to make a fair comparison between the initial and optimal machines, iron loss per unit torque, copper loss per unit torque, total loss per unit torque, and efficiency are given in Figure 6, respectively. As shown, under the speed of 3000 rpm, both the initial and optimal PM brushless machines exhibit similar performance. However, with the increase of speed above 3000 rpm, obvious performance improvement is obtained by the optimal PM brushless machine. It is observed from Figure 6a that the iron loss of the optimal PM brushless machine is lower than that of the initial one due to the reduced flux density and shorter stack length. In Figure 6b, the increased d-axis inductance reduces the current to weaken the flux field, hence decreasing the copper loss greatly in the high speed region. Consequently, the total loss of the optimal PM brushless machine is much lower at high speed, as shown in Figure 6c. Thus, the efficiency is improved, especially in the high speed region, as shown in Figure 6d. Meanwhile, the reduced losses are conducive to a lower temperature rise, hence ensuring the safe operation at high speed with low torque. In general, the optimal machine maintains high efficiency in the entire operation region when possessing an extended constant power speed range.
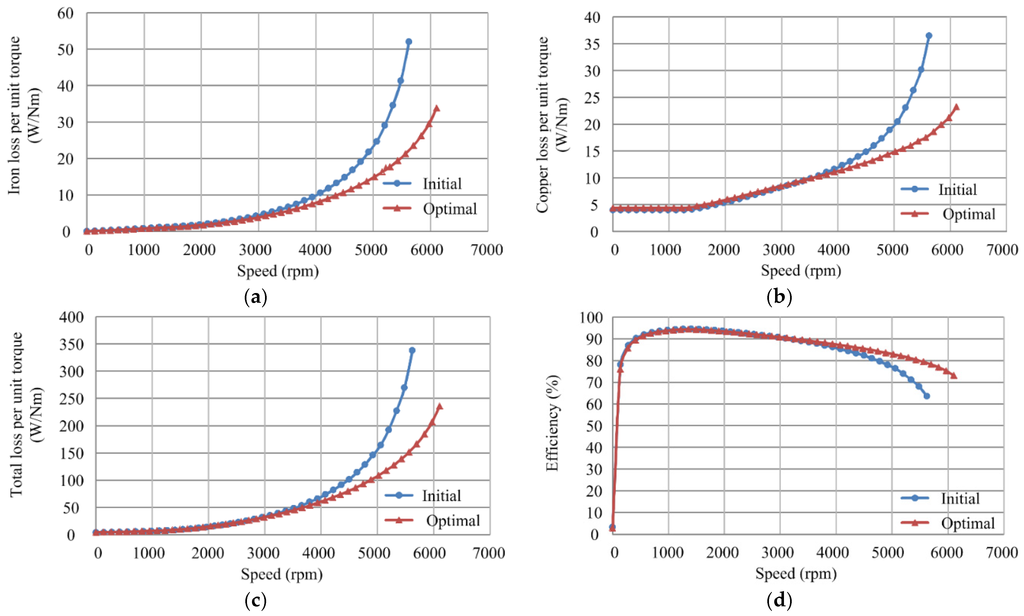
Figure 6.
Losses and efficiency curves of the initial and optimal PM brushless machines. (a) Iron loss; (b) copper loss; (c) total loss; and (d) efficiency.
The detailed efficiency and loss characteristics over a certain torque speed range of the optimal PM brushless machine are summarized in Figure 7. It can be observed from Figure 7a that, the optimal PM brushless machine exhibits efficiency greater than or equal to 80% over a wide torque speed range, where the speed reaches up to 5000 rpm. As shown in Figure 7b, with the increase of operating speed, the frequency of the machine increases, thus the iron loss grows up. However, at the same speed, the iron loss changes a little with the torque variation. The copper loss map is shown in Figure 7c. Under a certain load, with the increase of the operating speed, the current remains unchanged below the base speed and increases above the base speed, so the copper loss exhibits a similar tendency. At a certain speed, the copper loss increases with the increase of the load torque. Thus, the highest copper loss concentrates on the upper region of the torque speed range. The total loss distortion is given in Figure 7d, where with the increase of the operating speed, the total loss increases. Thus, it is of vital importance to reduce losses at high speed to improve the performance of traction machines for EVs.
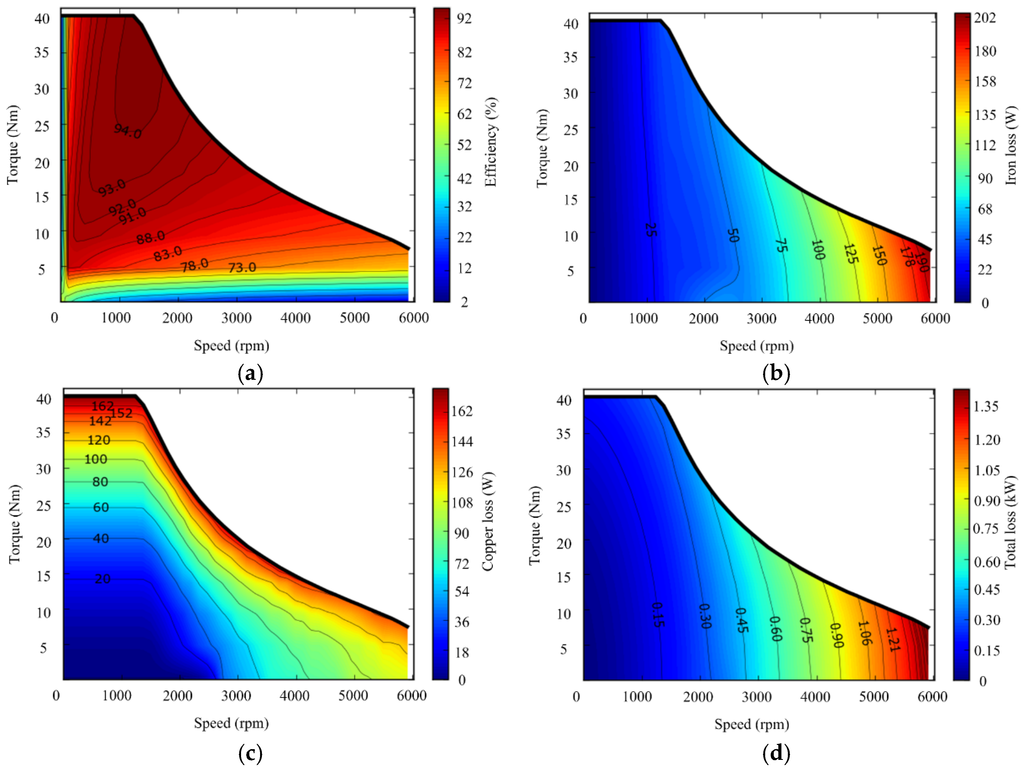
Figure 7.
Efficiency and loss maps of the optimal PM brushless machine. (a) Efficiency; (b) iron loss; (c) copper loss; and (d) total loss.
4.3. Performances Comparison over the Urban Dynamometer Driving Schedule
To further verify the validity of the proposed design and optimization method, an integrated EV model, which consists of wheel/axle, transmission, motor, and energy storage, is built. As shown in Figure 8, the motor is connected to the front axle, where the transmission and differential are assembled in a shell, thus reducing the transmission losses and improving the transmission efficiency. By the secondary development, the initial and optimal PM brushless machine is applied to the EV model respectively so that the simulation model based on Simulink can be obtained, as shown in Figure 9, where, the backward and forward simulation models are combined. That is, the driving schedule claims specific torque and speed from the vehicle, and each module demands required torque and speed from its superior module in the direction of the backward simulation data flow. When the data flow arrives at the final energy storage, the battery will supply available energy according to the requirements. Then, available torque and speed are transmitted to the junior module in the direction of the forward simulation data flow, meanwhile, the real torque and speed can also be calculated.
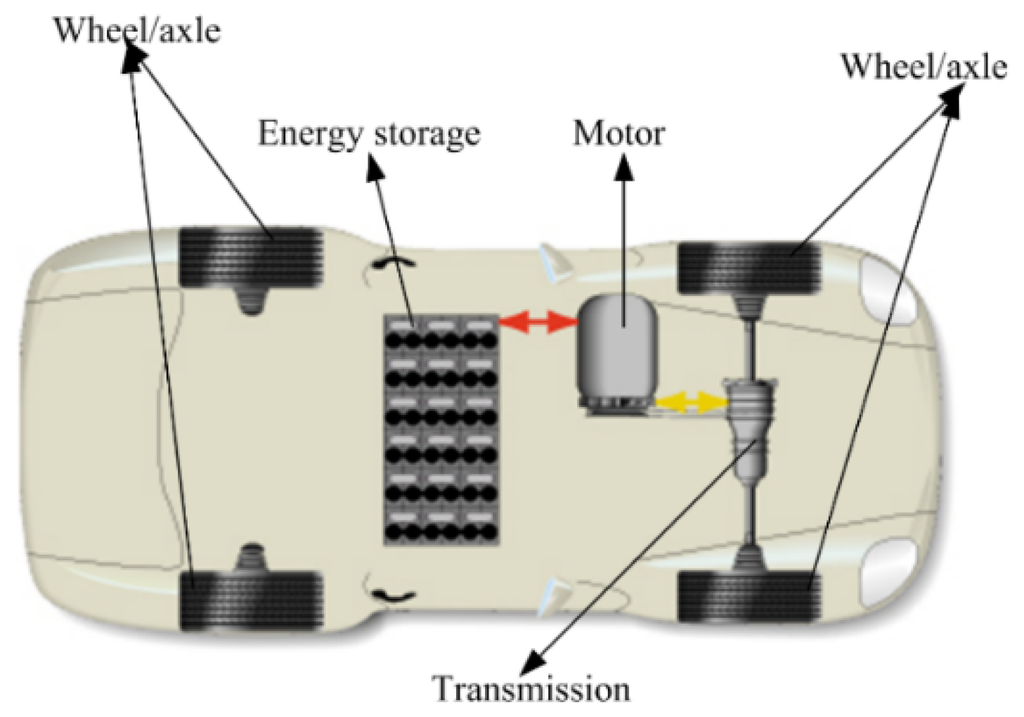
Figure 8.
Integrated electric vehicle (EV) model.
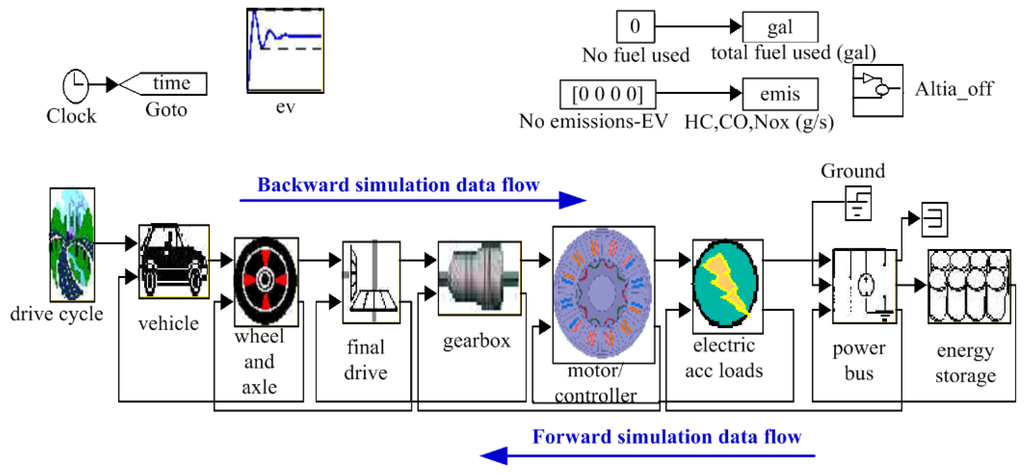
Figure 9.
Simulation model of the EV involving the PM brushless machine.
Based on the efficiency map, the integrated EV models involving the initial and optimal machines are simulated and compared over the UDDS. By employing the proposed design and optimization method, the optimal PM brushless machine obtains a wider constant power speed range. Thus, compared to the EV employing the initial PM brushless machine, the EV employing the optimal one exhibits better torque and speed production abilities, which is shown in Figure 10a. It can also be observed from Figure 10b that, the state of charge (SOC) of the energy storage decreases during the acceleration process, while the SOC increases when decelerating. Additionally, the SOC of the energy storage of the EV adopting the initial PM brushless machine shows a higher rate of change, which may bring higher requirements on the power electronic devices. Moreover, owing to the higher efficiency at high speed with low torque, the energy storage in the EV employing the optimal PM brushless machine exhibits higher SOC. As a result, the utilization ratio of the energy storage is improved, hence saving the energy.
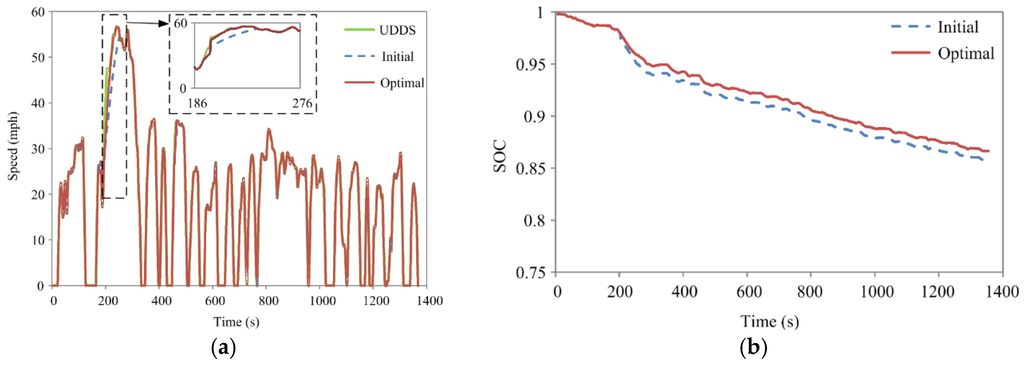
Figure 10.
Simulation results of the initial and optimal PM brushless machines. (a) Speed; and (b) state of charge (SOC).
Meanwhile, the acceleration ability and equivalent fuel economy of both EVs applying the initial and optimal PM brushless machines are listed and compared in Table 4. It is obvious that the time for EV using the optimal machine to accelerate from 0 mph to 30 mph, 20 mph to 55 mph and 0 mph to 55 mph is much less than that for EV using the initial machine. The EV using the optimal machine exhibits higher maximum acceleration and higher maximum speed. Since the fuel economy is unique for vehicles consuming fuels, gasoline equivalent is put forward to evaluate the energy consumption of EVs. The miles per gallon of EV using optimal machine is higher than that of EV using initial machine, hence consuming less energy within the same distance.

Table 4.
Comparison of acceleration ability and equivalent fuel economy of EVs applying initial and optimal PM brushless machines.
| Performances | Initial Machine | Optimal Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Acceleration time of 0–30 mph (s) | 6.2 | 6.1 |
| Acceleration time of 20–55 mph (s) | 12.7 | 10.6 |
| Acceleration time of 0–55 mph (s) | 34.1 | 24 |
| Maximum acceleration (ft/s2) | 7.2 | 7.9 |
| Maximum speed (mph) | 59.9 | 65.2 |
| Gasoline equivalent (mpg) | 102.9 | 106.7 |
Furthermore, the detailed operation condition of the optimal PM brushless machine is researched over the UDDS. And torque speed trajectory is given in Figure 11. It can be observed that, when the PM brushless machine serves as a motor, the torque and speed are positive to provide tractive effort. On the other hand, when the EV is braking, the PM brushless machine serves as a generator, whose torque is negative and speed is positive to realize energy recovery. The majority of the operating points are between the maximum continuous motoring torque and the maximum continuous generating torque envelopes. Thus, the EV can operate under the UDDS without reaching the thermal limit. Moreover, the operating points concentrate on the region where the efficiency is in the range of 80%–94%, which reveals good performances of the optimal PM brushless machine applied in the EV.
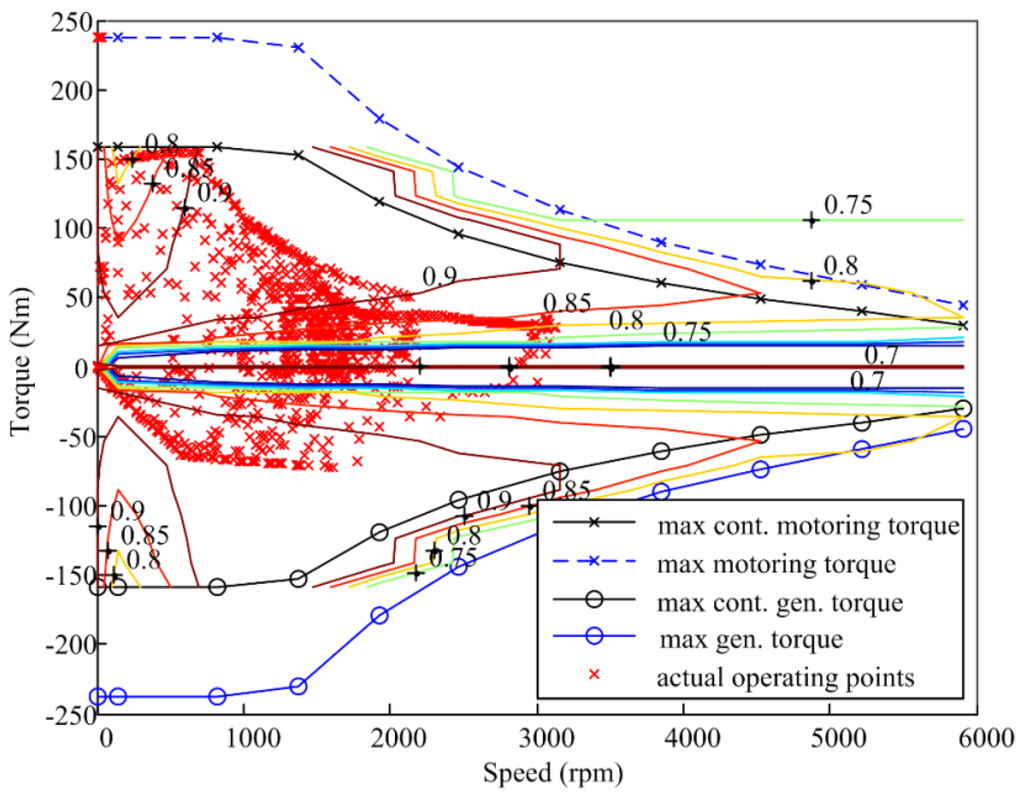
Figure 11.
Operation conditions of the optimal PM brushless machine over the urban dynamometer driving schedule (UDDS).
5. Conclusions
In this paper, a new design and optimization method is proposed for PM brushless machines to satisfy requirements of the multiple driving conditions in EVs. It has been shown that the proposed design method considering the maximum operating speed and performances specifications over the entire speed range is effective to give an initial PM brushless machine with well performances. Moreover, based on increasing d-axis inductance and meanwhile maintaining constant PM flux linkage, the proposed optimization method can achieve a wider constant power speed range, as well as reduced the losses and improved efficiency over the torque-speed envelope, especially in the high-speed region. Consequently, the SOC of the energy storage is increased, thus improving the energy utilization ratio. Both the analysis and simulation results reveal the feasibility of the optimal PM brushless machine to be applied in the EV, hence verifying the validity of the proposed design and optimization method for EV traction machines.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51177065, 51377073 and 51477069) and partly supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant Nos. 2013T60504 and 2012M521010).
Author Contributions
Xiaoyong Zhu conceived of the idea of the research and provided guidance and supervision. Weiwei Gu is the main author of this manuscript who implemented the research and performed the analysis. Li Quan and Yi Du provided some useful suggestions in the construction of this paper. All the authors have contributed significantly to this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- De Santiago, J.; Bernhoff, H.; Ekergard, B.; Eriksson, S.; Ferhatovic, S.; Waters, R.; Leijon, M. Electrical motor drivelines in commercial all-electric vehicles: A review. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2012, 61, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Sun, L.; Buja, G.; Song, L. Advanced electrical machines and machine-based systems for electric and hybrid vehicles. Energies 2015, 8, 9541–9564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.Y.; Ritchie, E. Torque analysis with saturation effects for non-salient single-phase permanent-magnet machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 1732–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyukdegirmenci, V.T.; Bazzi, A.M.; Krein, P.T. Evaluation of induction and permanent magnet synchronous machines using drive-cycle energy and loss minimization in traction applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Q.; Howe, D. Electrical machine and drives for electric, hybrid, and fuel cell vehicles. Proc. IEEE 2007, 95, 746–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Kim, M.S.; Lim, J.Y.; Kim, K.C. Study on design and control strategy of interior permanent magnet synchronous motor for high efficiency and wide constant-power operation. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Busan, Korea, 26–29 October 2013; pp. 1157–1159.
- Kreuawan, S.; Gillon, F.; Brochet, P. Comparative study of design approach for electric machine in traction application. Int. Rev. Electr. Eng. 2008, 3, 455–465. [Google Scholar]
- Sulaiman, E.; Kosaka, T.; Matsui, N. Design and performance of 6-slot 5-pole PMFSM with hybrid excitation for hybrid electric vehicle applications. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Power Electronics Conference (IPEC), Sapporo, Japan, 21–24 June 2010; pp. 1962–1968.
- Wang, J.; Yuan, X.; Atallah, K. Design optimization of a surface-mounted permanent-magnet with concentrated windings for electric vehicle applications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2013, 62, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Wang, J. Torque distribution strategy for a front- and rear-wheel-driven electric vehicle. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2012, 61, 3365–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Wu, F.; Lei, Y.; Sui, Y.; Yu, B. Investigation of a novel 24-slot/14-pole six-phase fault-tolerant modular permanent-magnet in-wheel motor for electric vehicles. Energies 2013, 6, 4980–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerling, D.; Dajaku, G.; Muhlbauer, K. Cost-effective electric traction drive with high efficiency at low-load operation. In Proceedings of the 2010 Emobility-Electrical Power Train, Leipzig, Germany, 8–9 November 2010; pp. 1–6.
- Lazari, P.; Wang, J.; Chen, L. A computationally efficient design technique for electric-vehicle traction machines. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Marseille, France, 2–5 September 2012; pp. 2596–2602.
- Fukushige, T.; Limsuwan, N.; Kato, T.; Akatsu, K.; Lorenz, R.D. Efficiency contours and loss minimization over a driving cycle of a variable flux-intensifying machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 2984–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lin, H.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Fang, S.; Huang, Y. A winding-switching concept for flux weakening in consequent magnet pole switched flux memory machine. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xia, Z.P.; Howe, D. Three-phase modular permanent magnet brushless machines for torque boosting on a downsized ICE vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2005, 54, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xia, Z.P.; Howe, D.; Long, S.A. Comparative study of 3-phase permanent magnet brushless machines with concentrated, distributed and modular windings. In Proceedings of the 2006 IET International Conference on Power Electronics, Machines and Drives, Dublin, Ireland, 4–6 April 2006; pp. 489–493.
- Wang, J.; Atallah, K.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Howe, D. Modular three-phase permanent-magnet brushless machines for in-wheel applications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2008, 57, 2714–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germishuizen, J.; Kamper, M. IPM traction machine with single layer non-overlapping concentrated windings. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2009, 45, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.B.; Patel, V.I.; Wang, W. Fractional-slot permanent magnet brushless machines with low space harmonic contents. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, G.; Zhao, W.; Shao, M.; Liu, Z. Design and analysis of the new high-reliability motors with hybrid permanent magnet material. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Niu, S. Electromagnetic design and analysis of a novel fault-tolerant flux-modulated memory machine. Energies 2015, 8, 8069–8085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Refaie, A.M.; Jahns, T.M. Optimal flux-weakening in surface PM machines using concentrated windings. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2005, 41, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soong, W.L.; Ertugrul, N. Field weakening performance of interior permanent magnet motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2002, 38, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Lin, S.K. Analytical prediction of the incremental inductance of the permanent magnet synchronous motors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 40, 2044–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.Y.; Reigosa, D.D.; Lorenz, R.D. Position self-sensing evaluation of a FI-IPMSM based on high-frequency signal injection methods. IEEE Trans. Ind. 2013, 49, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Zhu, X.Y.; Chen, L. Design and evaluation of a new flux-intensifying permanent magnet brushless motor. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Hangzhou, China, 22–25 October 2014; pp. 673–677.
- Pellegrino, G.; Vagati, A.; Boazzo, B.; Gualielmi, P. Comparison of induction and PM synchronous motor drives for EV application including design examples. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2012, 48, 2322–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.H.; Seok, J.K.; Lorenz, R.D. Wide-speed direct torque and flux control for interior PM synchronous motors operating at voltage and current limits. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2013, 49, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).