-
 Progress in Gliotoxin Research
Progress in Gliotoxin Research -
 Fluorimetric Determination of Eosin Y in Water Samples and Drinks Using Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Liquid-Phase Microextraction
Fluorimetric Determination of Eosin Y in Water Samples and Drinks Using Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Liquid-Phase Microextraction -
 Synthesis, Structures and Corrosion Inhibition Properties of 4-Nitrophenylacetato-Rare-Earth(III) 1D Coordination Polymers
Synthesis, Structures and Corrosion Inhibition Properties of 4-Nitrophenylacetato-Rare-Earth(III) 1D Coordination Polymers -
 Catechins and Human Health: Breakthroughs from Clinical Trials
Catechins and Human Health: Breakthroughs from Clinical Trials
Journal Description
Molecules
Molecules
is a leading international, peer-reviewed, open access journal of chemistry, and is published semimonthly online by MDPI. The International Society of Nucleosides, Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids (IS3NA), Spanish Society of Medicinal Chemistry (SEQT) and International Society of Heterocyclic Chemistry (ISHC) are affiliated with Molecules and their members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, MEDLINE, PMC, Reaxys, CaPlus / SciFinder, MarinLit, AGRIS, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Biochemistry and Molecular Biology) / CiteScore - Q1 (Organic Chemistry)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 16.1 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Sections: published in 25 topical sections.
- Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about Molecules.
- Companion journal: Foundations.
- Journal Cluster of Chemical Reactions and Catalysis: Catalysts, Chemistry, Electrochem, Inorganics, Molecules, Organics, Oxygen, Photochem, Reactions, Sustainable Chemistry.
Impact Factor:
4.6 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
5.0 (2024)
Latest Articles
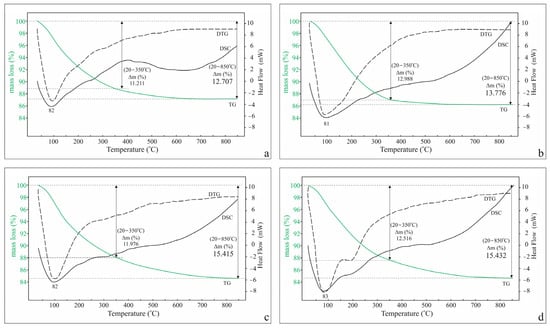
Comparative Multi-Stage TG-DSC Study of K+, Na+, Ca2+ and Mg2+-Exchanged Clinoptilolite Forms
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4770; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244770 (registering DOI) - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
A multi-stage TG-DSC approach consisting of five heating/holding and five cooling/holding stages within one experiment in the temperature range 20–320 °C was applied to investigate the dehydration/hydration processes in K+, Na+, Ca2+, and Mg2+ clinoptilolite forms.
[...] Read more.
A multi-stage TG-DSC approach consisting of five heating/holding and five cooling/holding stages within one experiment in the temperature range 20–320 °C was applied to investigate the dehydration/hydration processes in K+, Na+, Ca2+, and Mg2+ clinoptilolite forms. The influence of extra-framework cations on the parameters characterizing these processes (such as mass changes, dehydration and hydration heats calculated per gram zeolite, amounts of water molecules leaving and entering the structure, and enthalpy values calculated per mol water) was established. The values of molar enthalpy of dehydration for different cationic clinoptilolite forms increase in different ways with temperature increasing (within the framework of 50–120 kJ mol−1). The data on the molar enthalpy are in good agreement with the distributions of the two types of water molecules—weakly bound to cations and water molecules coordinating cations in the applied crystal chemical models of the cationic exchange samples. The data obtained for water molecules and their molar enthalpies of dehydration for the various cationic forms are useful in studying the sorption of water vapor and other sorbates, in choosing a desiccant and an object to dry at room conditions, etc. The first data on the hydration energy of sequentially added water molecules in a dynamic cooling mode in the temperature range 320–20 °C were obtained.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Design, Synthesis, and Application of Zeolite Materials)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Aqueous Biphasic Systems Based on Tetrabutylammonium Bromide for Extraction and Determination of Azorubine, Allura Red, Sunset Yellow, Tartrazine and Fast Green in Food Samples
by
Svetlana V. Smirnova, Anastasia V. Gorbovskaia, Yulia S. Vershinina, Vladimir V. Apyari and Mikhail A. Proskurnin
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4769; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244769 (registering DOI) - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
Aqueous biphasic systems (ABSs) based on tetrabutylammonium bromide (TBABr) and potassium thiocyanate or citrate (K3Cit) were proposed as “green” tools for liquid–liquid microextraction of Azorubine, Allura Red, Sunset Yellow, Tartrazine and Fast Green followed by spectrophotometric determination. The dye extraction into
[...] Read more.
Aqueous biphasic systems (ABSs) based on tetrabutylammonium bromide (TBABr) and potassium thiocyanate or citrate (K3Cit) were proposed as “green” tools for liquid–liquid microextraction of Azorubine, Allura Red, Sunset Yellow, Tartrazine and Fast Green followed by spectrophotometric determination. The dye extraction into the water-saturated tetrabutylammonium thiocyanate phase, which separates from water when mixing aqueous solutions of TBABr and KSCN, depends on the hydrophobicity of dyes. Only Azorubine is extracted quantitatively at HCl concentration ≥ 0.05 mol L−1, with an equimolar TBABr/KSCN ratio and total concentration of 0.4 mol L−1 in less than 1 min. To estimate the hydrophobicity and identify factors affecting the distribution of dyes in ABSs, the experimental 1-octanol-water distribution coefficients of the dyes were determined. In contrast, all the dyes studied are quantitatively extracted into the TBABr–K3Cit–H2O ABS regardless of their hydrophobicity. The effects of pH, concentration of phase-forming components, extraction/centrifugation time and other factors were investigated for both ABSs. The linearity ranges and detection limits were 0.05–2.60 mg L−1 and 0.006–0.02 mg L−1, respectively. The proposed procedures were applied for the determination of dyes in food samples.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Food Analytical Methods)
►▼
Show Figures
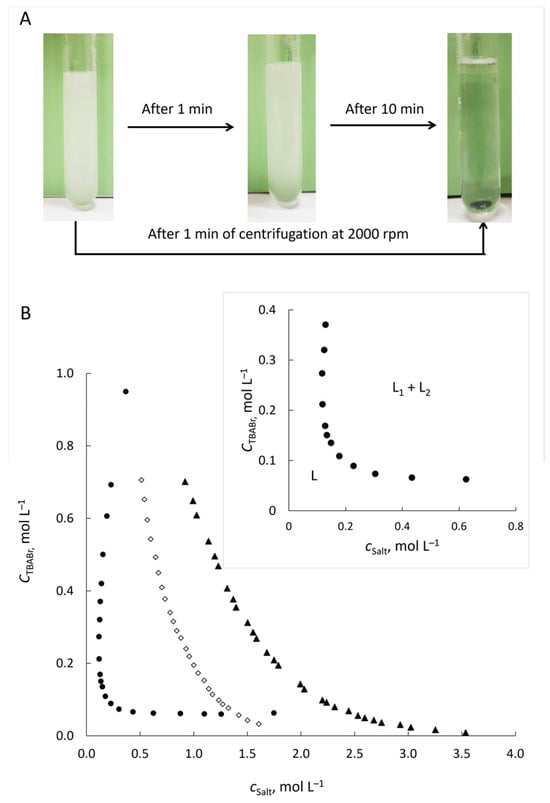
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Alteration in Photosynthetic and Yield Parameters, Content of Metabolites, and Antioxidant Activity of Pepper (Capsicum annuum): Effect of Bio-Organic Substrate and Depolymerized Chitosan
by
Piotr Salachna, Agnieszka Zawadzińska, Rafał Piechocki, Małgorzata Mikiciuk, Julita Rabiza-Świder, Ewa Skutnik and Łukasz Łopusiewicz
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4768; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244768 (registering DOI) - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
Peppers are of substantial economic importance and hold a prominent position among vegetables rich in health-promoting compounds, which drives continuous efforts to develop improved cultivation strategies. The study aimed to determine the effects of substrate type and depolymerized chitosan on the physiological parameters,
[...] Read more.
Peppers are of substantial economic importance and hold a prominent position among vegetables rich in health-promoting compounds, which drives continuous efforts to develop improved cultivation strategies. The study aimed to determine the effects of substrate type and depolymerized chitosan on the physiological parameters, the chemical composition of leaves and fruits, and the yield of two bell pepper cultivars: ‘Marta Polka’ and ‘Oda’. The plants were grown in a 100% peat substrate and in a mixture of peat, wood fiber (Pinus sylvestris), and green compost (2:1:1 v/v/v), with or without drenching with a solution of depolymerized chitosan. Results indicated that the growing medium, chitosan application, cultivar type, and their interactions altered several physiological, morphological, and biochemical traits. The highest total fruit weight fresh (471.23 g plant−1) was obtained for the ‘Marta Polka’ cultivar grown in peat drenched with chitosan, whereas the lowest (192.02 g plant−1) was recorded for ‘Oda’ grown in a substrate mix without the biostimulant. Net CO2 assimilation rate, stomatal conductance, fresh weight of fruit, and antioxidant activity (ABTS and FRAP assays) were improved in the ‘Oda’ cultivar grown in the substrate mix and treated with depolymerized chitosan compared with plants grown in 100% peat without chitosan. The ‘Marta Polka’ plants grown in the substrate mix and treated with chitosan had a higher net CO2 assimilation rate, photosynthetic water-use efficiency, total free amino acid content, and antioxidant activity (FRAP assay) than those grown in peat alone and not treated with the biostimulant. The results demonstrate that both substrate composition and the response to depolymerized chitosan are cultivar-specific, and that wood fiber and compost can serve as ecological alternatives to peat, enhancing overall pepper fruit quality.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Green Chemistry and Molecular Tools in Agriculture)
Open AccessArticle
Neuroprotective Effect of Fresh Gac Fruit Parts Against β-Amyloid-Induced Toxicity and Its Influence on Synaptic Gene Expression in HT-22 Cell Model
by
Asif Ali, Chih-Li Lin and Chin-Kun Wang
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4767; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244767 (registering DOI) - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
Neurodegenerative diseases (NDs) have emerged as a significant global health crisis, disproportionately affecting the aging population. As longevity increases, the incidence, healthcare costs, and caregiver burden associated with NDs are escalating at an alarming rate. As of recent data, NDs such as Alzheimer’s
[...] Read more.
Neurodegenerative diseases (NDs) have emerged as a significant global health crisis, disproportionately affecting the aging population. As longevity increases, the incidence, healthcare costs, and caregiver burden associated with NDs are escalating at an alarming rate. As of recent data, NDs such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD) are not only significant health burdens but also reflect a complex interplay between socio-economic factors and healthcare systems worldwide. Gac fruit (Momordica cochinchinensis) is a rich source of bioactive compounds that has been used as food and traditional medicine. Gac fruit ameliorates memory deficits, enhances beta amyloid (Aβ)1–42 clearance, and induces neurite outgrowth. In this study, we examined the anti-neurodegenerative and synaptic improvement effect of fresh gac fruit parts extracts (FGPEs) produced from different solvents. Results showed that the 80% ethanol extract of peel (PE-EtOH) and ethyl acetate extract of seed (SE-EtOAc) significantly protected HT-22 cells by attenuating Aβ-induced cell death, intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, mitochondrial dysfunction, and synaptic dysfunction. PE-EtOH protected synaptic functions by significantly increasing the postsynaptic density protein-95 (PSD-95) and reducing the neurexin 2 mRNA expression. In contrast, SE-EtOAc increased the PSD-95 and neurexin 3 and reduced the neurexin 2 expressions. These findings indicate that PE-EtOH and SE-EtOAc could have great potential in ameliorating Aβ-induced toxicity in an HT-22 cell model.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Recent Updates on Molecular and Physical Therapies for Organ Fibrosis
by
Michał Filipski, Natalia Libergal, Maksymilian Mikołajczyk, Daria Sznajderowicz, Vitalij Novickij, Augustinas Želvys, Paulina Malakauskaitė, Olga Michel, Julita Kulbacka and Anna Choromańska
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4766; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244766 (registering DOI) - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Organ fibrosis is a progressive and often irreversible pathological process characterized by excessive deposition of extracellular matrix, leading to tissue dysfunction and failure. Despite its significant impact on various organ systems, available antifibrotic therapies remain limited. This review focuses on novel therapeutic approaches
[...] Read more.
Organ fibrosis is a progressive and often irreversible pathological process characterized by excessive deposition of extracellular matrix, leading to tissue dysfunction and failure. Despite its significant impact on various organ systems, available antifibrotic therapies remain limited. This review focuses on novel therapeutic approaches to inhibit fibrosis and improve clinical outcomes. Current strategies include small molecule inhibitors, monoclonal antibodies targeting fibrosis mediators, gene therapies, and cell-based approaches, including mesenchymal stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells. In addition, the development of innovative drug delivery systems and combination therapies involving pulsed magnetic fields (PMFs) opens new possibilities for increasing the precision and efficacy of treatment. In recent years, multiomic approaches have enabled a better understanding of fibrosis mechanisms, facilitating the personalization of therapy. The role of artificial intelligence in drug discovery has also increased, as exemplified by models that support the design of small-molecule inhibitors currently undergoing clinical evaluation. This review discusses key signaling pathways involved in fibrosis progression, such as TGF-β, p38 MAPK, and fibroblast activation, as well as novel therapeutic targets. Although clinical trial results indicate promising potential for new therapies, challenges remain in optimizing drug delivery, considering patient heterogeneity, and ensuring long-term safety. The future of fibrosis therapy relies on integrating precision medicine, combination therapies, and molecularly targeted strategies to inhibit or even reverse the fibrosis process. Further intensive interdisciplinary collaboration is required to successfully implement these innovative solutions in clinical practice.
Full article
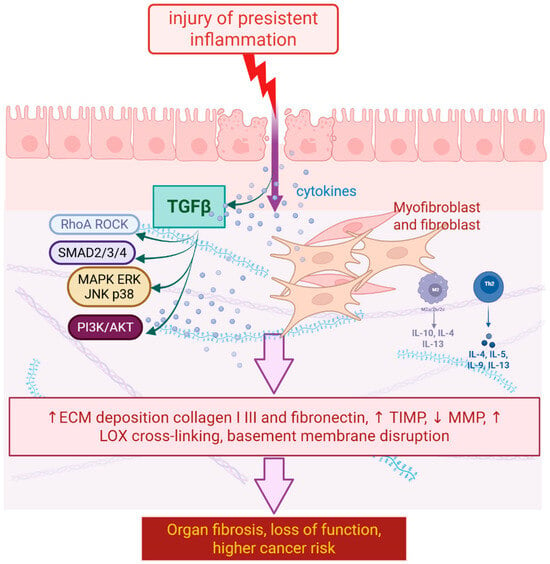
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Wheat Pasta Enriched with Green Coffee Flour: Physicochemical, Antioxidant and Sensory Properties
by
Dariusz Dziki, Grażyna Cacak-Pietrzak, Julia Kopyto-Krzepicka, Agata Marzec, Sylwia Stępniewska, Anna Krajewska, Wioleta Dołomisiewicz, Renata Nowak and Sebastian Kanak
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4765; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244765 (registering DOI) - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
This study aimed to evaluate the impact of green coffee flour (GCF) addition (2–8%) and drying method (convective versus microwave-vacuum drying) on the physicochemical, textural, and bioactive properties of pasta. Both factors were found to significantly influence the assessed parameters. Green coffee had
[...] Read more.
This study aimed to evaluate the impact of green coffee flour (GCF) addition (2–8%) and drying method (convective versus microwave-vacuum drying) on the physicochemical, textural, and bioactive properties of pasta. Both factors were found to significantly influence the assessed parameters. Green coffee had no observable effect on the microstructure of convectively dried pasta, whereas microwave-vacuum drying caused visible cracks and a heterogeneous starch-protein matrix even at a 2% supplementation level. Microwave-vacuum-dried pasta exhibited a shorter optimal cooking time and higher water absorption compared with convectively dried samples, while increasing the level of GCF prolonged cooking time and increased cooking losses. Texture analysis revealed that convectively dried pasta showed decreased elasticity and cohesiveness with increasing GCF content, whereas microwave -vacuum-dried pasta maintained a relatively uniform texture regardless of supplementation. The incorporation of GCF enhanced the antioxidant capacity of pasta, with the most pronounced effect at 2% addition, while higher levels showed reduced benefits. Similarly, fortification increased the content of phenolic acids, particularly chlorogenic acid and its isomers, with convectively dried samples exhibiting higher levels than microwave-vacuum-dried pasta. Consumer acceptance was highest for convectively dried pasta without GCF and for samples containing 2%, while pasta with higher GCF levels or microwave-vacuum-dried samples received lower scores.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nutritional Properties, Sensory Profile and Bioactive Components of Food, 3rd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
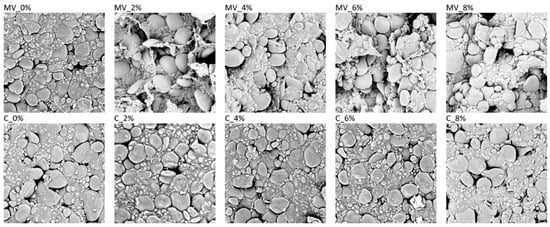
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Sustainable Activation of Persulfate Using Corn Cob Biochar for Pesticide Degradation in Wastewater Treatment
by
Tijana Marjanović Srebro, Nina Đukanović, Tajana Simetić, Tamara Apostolović, Jasmina Anojčić, Sanja Mutić and Jelena Beljin
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4764; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244764 (registering DOI) - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
This study investigates the potential of corn cob-derived biochars produced at 400 °C (BC400) and 700 °C (BC700) as heterogeneous catalysts for the degradation of organochlorine pesticides, lindane and β-endosulfan, through persulfate-based advanced oxidation processes (AOPs). BC700 exhibited enhanced degradation performance compared to
[...] Read more.
This study investigates the potential of corn cob-derived biochars produced at 400 °C (BC400) and 700 °C (BC700) as heterogeneous catalysts for the degradation of organochlorine pesticides, lindane and β-endosulfan, through persulfate-based advanced oxidation processes (AOPs). BC700 exhibited enhanced degradation performance compared to BC400, likely due to its greater surface area, higher aromaticity, and lower surface polarity. Under optimized conditions (3.0 mM persulfate, pH 7.02, 0.2 g/L biochar), BC700 enabled the removal of up to 94% of β-endosulfan and 82% of lindane within four hours. Quenching experiments suggested different dominant degradation pathways: singlet oxygen (1O2) appeared to play a key role in lindane degradation, while β-endosulfan degradation likely involved both radical (SO4•−, HO•) and non-radical mechanisms. Reusability tests indicated that BC700 retained catalytic activity for β-endosulfan across multiple cycles, whereas lindane degradation efficiency decreased, possibly due to surface fouling or catalyst deactivation. Experiments conducted in real surface water highlighted the influence of matrix components, with partial inhibition observed for β-endosulfan and an unexpected improvement in lindane removal. These results point to the promise of high-temperature corn cob biochar as a selective and potentially reusable catalyst for AOPs in water treatment, warranting further investigation into regeneration strategies and matrix-specific effects.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Chemical Approaches for Wastewater Treatment and Resource Utilization)
►▼
Show Figures
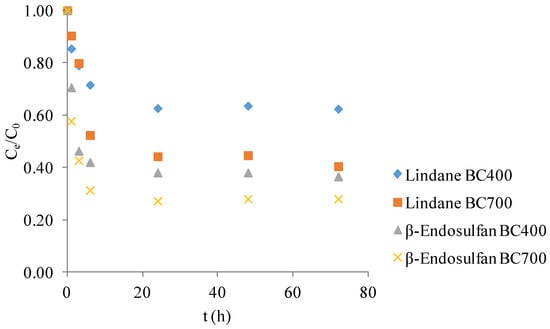
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Isolation, Total Synthesis and Anti-Diabetic Activity of Filiforidine from Cassytha filiformis
by
Caiyun Zhang, Hong Zhu, Fang Zhang, Yuexia Jiang, Zibao Huang, Dong Lin, Niangen Chen, Xiaopo Zhang and Yanhui Fu
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4763; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244763 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
Cassytha filiformis is a folkloric herbal medicine used to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). In this study, an oxidized aporphine alkaloid, designated as Filiforidine (3,10,11-trimethoxy-1,2-methylenedioxy-7-oxoaporphine), was isolated from C. filiformis, and its structure was elucidated through comprehensive spectroscopic analysis. Owing to
[...] Read more.
Cassytha filiformis is a folkloric herbal medicine used to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). In this study, an oxidized aporphine alkaloid, designated as Filiforidine (3,10,11-trimethoxy-1,2-methylenedioxy-7-oxoaporphine), was isolated from C. filiformis, and its structure was elucidated through comprehensive spectroscopic analysis. Owing to its novel structure and significant glucose consumption activity, the total synthesis of Filiforidine was achieved for the first time. The key steps featured an electrophilic addition reaction, involving the reduction of a nitro group to an amino group with lithium tetrahydroaluminum, and a copper bromide-catalyzed oxidative aromatization reaction as well as a photocyclization reaction. Several experimental steps were optimized. Furthermore, a complex post-treatment method was developed, which reduced the column chromatography separation steps. Specifically, 2-(4-methoxybenzo[d][1,3]dioxol -5-yl) ethan-1-amine is salted with dilute hydrochloric acid. Cytotoxicity assay and glucose oxidase assay showed that Filiforidine had significant glucose consumption-promoting effects on HL-7702 cells at 0.625 μM, 1.25 μM, and 2.5 μM but without cytotoxicity. Therefore, Filiforidine might be a promising drug candidate for the treatment of diabetes.
Full article
Open AccessReview
In2O3: An Oxide Semiconductor for Thin-Film Transistors, a Short Review
by
Christophe Avis and Jin Jang
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4762; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244762 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
With the discovery of amorphous oxide semiconductors, a new era of electronics opened. Indium gallium zinc oxide (IGZO) overcame the problems of amorphous and poly-silicon by reaching mobilities of ~10 cm2/Vs and demonstrating thin-film transistors (TFTs) are easy to manufacture on
[...] Read more.
With the discovery of amorphous oxide semiconductors, a new era of electronics opened. Indium gallium zinc oxide (IGZO) overcame the problems of amorphous and poly-silicon by reaching mobilities of ~10 cm2/Vs and demonstrating thin-film transistors (TFTs) are easy to manufacture on transparent and flexible substrates. However, mobilities over 30 cm2/Vs have been difficult to reach and other materials have been introduced. Recently, polycrystalline In2O3 has demonstrated breakthroughs in the field. In2O3 TFTs have attracted attention because of their high mobility of over 100 cm2/Vs, which has been achieved multiple times, and because of their use in scaled devices with channel lengths down to 10 nm for high integration in back-end-of-the-line (BEOL) applications and others. The present review focuses first on the material properties with the understanding of the bandgap value, the importance of the position of the charge neutrality level (CNL), the doping effect of various atoms (Zr, Ge, Mo, Ti, Sn, or H) on the carrier concentration, the optical properties, the effective mass, and the mobility. We introduce the effects of the non-parabolicity of the conduction band and how to assess them. We also introduce ways to evaluate the CNL position (usually at ~EC + 0.4 eV). Then, we describe TFTs’ general properties and parameters, like the field effect mobility, the subthreshold swing, the measurements necessary to assess the TFT stability through positive and negative bias temperature stress, and the negative bias illumination stress (NBIS), to finally introduce In2O3 TFTs. Then, we will introduce vacuum and non-vacuum processes like spin-coating and liquid metal printing. We will introduce the various dopants and their applications, from mobility and crystal size improvements with H to NBIS improvements with lanthanides. We will also discuss the importance of device engineering, introducing how to choose the passivation layer, the source and drain, the gate insulator, the substrate, but also the possibility of advanced engineering by introducing the use of dual gate and 2 DEG devices on the mobility improvement. Finally, we will introduce the recent breakthroughs where In2O3 TFTs are integrated in neuromorphic applications and 3D integration.
Full article
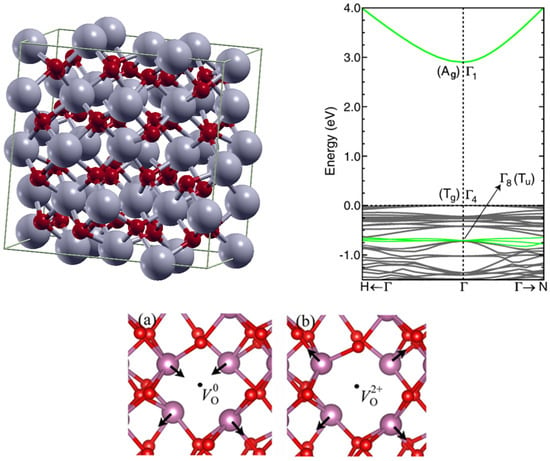
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Orientational Structure and Electro-Optical Properties of Chiral Nematic Droplets with Conical Anchoring
by
Kristina A. Feizer, Mikhail N. Krakhalev, Vladimir Yu. Rudyak and Victor Ya. Zyryanov
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4761; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244761 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
The polymer dispersed liquid crystals (PDLCs) with conical boundary conditions are considered. PDLC films with different values of the relative chirality parameter
The polymer dispersed liquid crystals (PDLCs) with conical boundary conditions are considered. PDLC films with different values of the relative chirality parameter
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Liquid Crystals, 3rd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
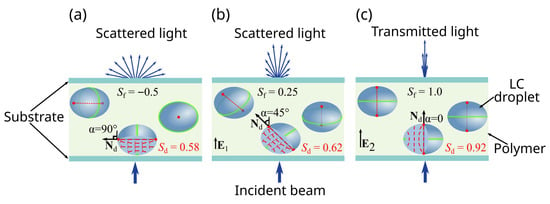
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Recent Advances in Synthetic Isoquinoline-Based Derivatives in Drug Design
by
Łukasz Balewski and Anita Kornicka
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4760; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244760 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
Compounds based on an isoquinoline scaffold (benzo[c]pyridine) display a broad spectrum of biological activities. In recent years, studies have focused mainly on their anticancer properties. Their antiproliferative effects are associated with diverse mechanisms that include targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways and reactive
[...] Read more.
Compounds based on an isoquinoline scaffold (benzo[c]pyridine) display a broad spectrum of biological activities. In recent years, studies have focused mainly on their anticancer properties. Their antiproliferative effects are associated with diverse mechanisms that include targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways and reactive oxygen species or inducing apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Furthermore, isoquinolines may inhibit microtubule polymerization, topoisomerase, or tumor multidrug resistance. Recent studies have also shown that these compounds may act as effective antimicrobial, antifungal, antiviral, and antiprotozoal agents. Moreover, it has also been demonstrated that isoquinoline derivatives exhibit potent anti-Alzheimer effects, alleviating central nervous system functions. Additionally, they possess anti-inflammatory and antidiabetic properties. Due to the presence of donor nitrogen, the isoquinoline core constitutes an appropriate ligand that may be employed for the development of metal complexes with improved pharmacological properties. A number of chelates containing copper, iridium, or platinum were found to exhibit prominent biological activity, which places them in a leading position for the development of effective medications. This review summarizes the recent development of synthetic isoquinoline-based compounds with proven pharmacological properties in the period of 2020–2025. Also, other biomedical applications for synthetic isoquinoline derivatives are provided.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Heterocycles: Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation, 4th Edition)
Open AccessArticle
Antileukemic Potential of Sodium Caseinate in Cytarabine-Resistant HL60-CR50 Human Leukemia Cells
by
Edelmiro Santiago-Osorio, Daniel Romero-Trejo, Víctor Manuel Macías-Zaragoza, Katia Michell Rodríguez-Terán, Víctor Manuel Mendoza-Núñez, Edith Sierra-Mondragón, Ernesto Romero-López, Lorena Shira, David Hernández-Álvarez and Itzen Aguiñiga-Sánchez
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4759; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244759 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
Chemoresistance is the leading cause of mortality in cancer patients. The poor clinical prognosis and limited therapeutic options for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients demand the development of new therapeutic strategies capable of overcoming chemoresistance and avoiding toxic side effects in normal cells.
[...] Read more.
Chemoresistance is the leading cause of mortality in cancer patients. The poor clinical prognosis and limited therapeutic options for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients demand the development of new therapeutic strategies capable of overcoming chemoresistance and avoiding toxic side effects in normal cells. Sodium caseinate (SC), a derivative of casein protein found in milk, has demonstrated a dual role: it inhibits the proliferation of several murine AML cell lines while promoting the proliferation of normal hematopoietic cells. Furthermore, we previously showed that SC can modulate the expression of genes associated with chemoresistance in mouse cells. However, its biological effects on cytarabine-resistant human leukemia cells remain unclear. Here, we developed the HL60-CR50 subline, resistant to cytarabine, and investigated the effects of SC. We demonstrated that SC significantly reduced cell proliferation, decreased SIRT1 levels, increased acetylated p53, activated cleaved caspase-3, and enhanced apoptosis in cytarabine-resistant cells. These findings suggest that SC might have potential as a therapeutic adjuvant for AML, providing efficacy in chemoresistant cases compared with cytarabine treatment alone.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Antitumor Bioactive Compounds: Synthesis, Extraction and Evaluation)
►▼
Show Figures
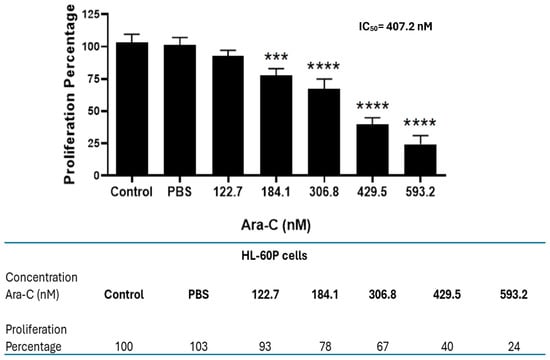
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Superior Oxidase-Mimetic Activity of Co-MOF Nanozyme for Smartphone-Based Visually Colorimetric Assay of Mancozeb
by
Shuyue Pang, Lina Chen, Yangyuxin Liu, Xiuting Lu, Hongfei Liu, Yuting Shu, Helong Bai, Jing Wang and Dongfang Shi
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4758; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244758 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Mancozeb (MCZ), a widely used fungicide in agricultural production, has been reported as an environmental endocrine disruptor, posing serious risks to ecosystems and human health. In this work, multivalent Co-MOF nanozymes (MVCM) with excellent oxidase-like activity were synthesized, which can promote the oxidation
[...] Read more.
Mancozeb (MCZ), a widely used fungicide in agricultural production, has been reported as an environmental endocrine disruptor, posing serious risks to ecosystems and human health. In this work, multivalent Co-MOF nanozymes (MVCM) with excellent oxidase-like activity were synthesized, which can promote the oxidation of 2,2′-azino-bis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) into a blue oxidative product (ABTS•+), with an obvious absorption peak at 415 nm. With the addition of MCZ, the ABTS•+ was reduced to colorless ABTS through the REDOX reactions between MCZ and ABTS•+. Based on the unique reducing behavior of MCZ, a nanozyme-based colorimetric detection platform was proposed for the detection of MCZ, with a linear range of 3–27 μM and a detection limit (LOD) of 0.15 μM. Furthermore, the sensor was integrated with smartphones and test strips, establishing a portable smartphone-based platform for the real-time, on-site, and visual quantitative detection of MCZ. The detection concentration range was 15–90 μM, with LOD as low as 15 μM. The assay exhibited high adaptability in practical applications. In summary, this work provided a simple, accurate, and low-cost approach for visual determination of MCZ without complicated instruments and procedures.
Full article
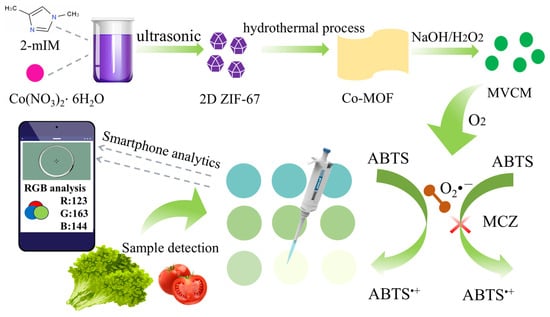
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Visible Light-Driven BiVO4 Nanoparticles: Effects of Eu3+ Ions on the Luminescent, Structural, and Photocatalytic Properties
by
Dragana Marinković, Bojana Vasiljević, Nataša Tot, Tanja Barudžija, Sudha Maria Lis Scaria, Stefano Varas, Rossana Dell’Anna, Alessandro Chiasera, Bernhard Fickl, Bernhard C. Bayer, Giancarlo C. Righini and Maurizio Ferrari
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4757; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244757 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
The optimization of BiVO4-based structures significantly contributes to the development of a global system towards clean, renewable, and sustainable energies. Enhanced photocatalytic performance has been reported for numerous doped BiVO4 materials. Bi3+-based compounds can be easily doped with
[...] Read more.
The optimization of BiVO4-based structures significantly contributes to the development of a global system towards clean, renewable, and sustainable energies. Enhanced photocatalytic performance has been reported for numerous doped BiVO4 materials. Bi3+-based compounds can be easily doped with rare earth (RE3+) ions due to their equal valence and similar ionic radius. This means that RE3+ ions could be regarded as active co-catalysts and dopants to enhance the photocatalytic activity of BiVO4. In this study, a simple microwave-assisted approach was used for preparing nanostructured Bi1−xEuxVO4 (x = 0, 0.03, 0.06, 0.09, and 0.12) samples. Microwave heating at 170 °C yields a bright yellow powder after 10 min of radiation. The materials are characterized through X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), ultraviolet–visible–near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (UV-Vis-NIR DRS), photoluminescence spectroscopy (PL), and micro-Raman techniques. The effects of the different Eu3+ ion concentrations incorporated into the BiVO4 matrix on the formation of the monoclinic scheelite (ms-) or tetragonal zircon-type (tz-) BiVO4 structure, on the photoluminescent intensity, on the decay dynamics of europium emission, and on photocatalytic efficiency in the degradation of Rhodamine B (RhB) were studied in detail. Additionally, microwave chemistry proved to be beneficial in the synthesis of the tz-BiVO4 nanostructure and Eu3+ ion doping, leading to an enhanced luminescent and photocatalytic performance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Chemiluminescence and Photoluminescence of Advanced Compounds)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Novel Adamantane–Sclareol Hybrids Exploit ROS Vulnerability to Overcome Multidrug-Resistance in Glioblastoma Cells
by
Ema Lupšić, Pavle Stojković, Marija Grozdanić, Nataša Terzić-Jovanović, Milica Pajović, Fani Koutsougianni, Dimitra Alexopoulou, Igor M. Opsenica, Milica Pešić and Ana Podolski-Renić
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4756; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244756 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
Multidrug resistance (MDR) presents a significant challenge in the treatment of glioblastoma. We evaluated six novel adamantane–sclareol hybrids that integrate a natural labdane diterpene scaffold with an adamantane moiety to address this issue. Compounds 2, 5, and 6 demonstrated the ability
[...] Read more.
Multidrug resistance (MDR) presents a significant challenge in the treatment of glioblastoma. We evaluated six novel adamantane–sclareol hybrids that integrate a natural labdane diterpene scaffold with an adamantane moiety to address this issue. Compounds 2, 5, and 6 demonstrated the ability to bypass P-glycoprotein (P-gp)-mediated resistance in resistant U87-TxR cells and induced collateral sensitivity, with compound 2 exhibiting the highest selectivity for glioblastoma compared to normal glial cells. Mechanistic studies revealed that compounds 2 and 5 selectively triggered early apoptosis in MDR cells, significantly elevated levels of H2O2 and peroxynitrite, and disrupted mitochondrial membrane potential. Additionally, these compounds altered the expression of key genes involved in glutathione (GSH) and thioredoxin (Trx) antioxidant defense systems and increased ASK1 protein levels, indicating the activation of ROS-driven apoptotic signaling. Both compounds inhibited P-gp function, leading to enhanced intracellular accumulation of rhodamine 123 (Rho 123) and synergistically sensitized U87-TxR cells to paclitaxel (PTX). A preliminary Rag1 xenograft study demonstrated that compound 5 effectively suppressed tumor growth without causing significant weight loss. Collectively, these findings position adamantane–sclareol hybrids, particularly compounds 2 and 5, as promising strategies that exploit an MDR-associated reactive oxygen species (ROS) vulnerability, combining selective cytotoxicity, redox disruption, and P-gp modulation to eliminate resistant glioblastoma cells and enhance the efficacy of chemotherapeutics.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Natural Bioactive Compounds as a Promising Approach to Mitigating Oxidative Stress)
►▼
Show Figures
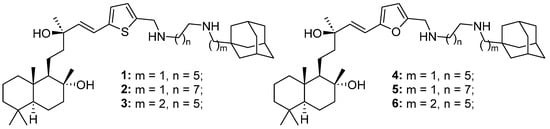
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Constructing High-Performance Solar Cells by Incorporating an A1-A2-Type Polymer Donor as a Guest Material
by
Min Li, Guo Chen, Ai Lan, Sein Chung, Mingming Que, Yongjoon Cho and Bin Huang
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4755; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244755 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
Owing to the intramolecular push-pull electron effect between the electron donor (D) unit and electron acceptor (A) unit, the D-A type based polymer donors display outstanding device performance. However, the imperfect energy levels lead to the D-A-type-based polymer device exhibiting high voltage loss.
[...] Read more.
Owing to the intramolecular push-pull electron effect between the electron donor (D) unit and electron acceptor (A) unit, the D-A type based polymer donors display outstanding device performance. However, the imperfect energy levels lead to the D-A-type-based polymer device exhibiting high voltage loss. In this study, an A1-A2-type copolymer M1 was developed with 1,3-bis(2-ethylhexyl)-5,7-di(thiophen-2-yl)benzo[1,2-c:4,5-c’]dithiophene-4,8-dione (BDD) as the A1 unit and dithieno[3′,2′:3,4;2″,3″:5,6]benzo[1,2-c][1,2,5]thiadiazole (DTBT) as the A2 unit. Compared with D-A-type-based polymer donor PM6, the A1-A2 type based M1 possesses lower energy levels, broader absorption, and stronger crystallinity. After introducing M1 to the PM6:L8-BO-based system as the guest material, the ternary blend films exhibited exceptional face-on molecular orientation and favorable active-layer morphology, which promotes exciton dissociation and suppresses charge recombination. Consequently, the PM6:M1(5%):L8-BO-based ternary device exhibited an impressive power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 19.70% with simultaneously enhanced photostability, which is superior to the PM6:L8-BO-based binary system. Our work offers an efficient approach to developing high-performance ternary devices by introducing a novel A1-A2 type polymer donors as the guest material.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Emerging Photovoltaic: From Materials and Devices to Modules)
►▼
Show Figures
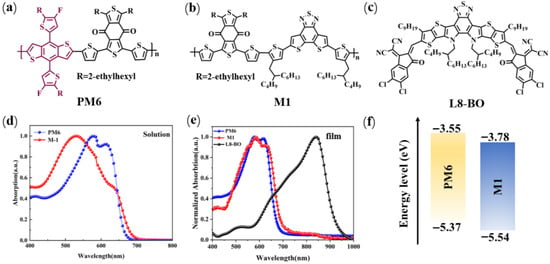
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comparison of Extraction, Isolation, Purification, Structural Characterization and Immunomodulatory Activity of Polysaccharides from Two Species of Cistanche
by
Jingya Ruan, Juan Zhang, Lequan Yu, Ping Zhang, Anxin Chen, Dongmei Wang, Yi Zhang and Tao Wang
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4754; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244754 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
This study focuses on polysaccharides from Cistanche deserticola and Cistanche tubulosa, medicinal plants renowned for their health benefits. The “water extraction and alcohol precipitation” method was used to obtain the crude polysaccharides of the wine-making residues of C. deserticola (CDP) and C.
[...] Read more.
This study focuses on polysaccharides from Cistanche deserticola and Cistanche tubulosa, medicinal plants renowned for their health benefits. The “water extraction and alcohol precipitation” method was used to obtain the crude polysaccharides of the wine-making residues of C. deserticola (CDP) and C. tubulosa (CTP), respectively. Then, ultrafiltration membrane (UFM), DEAE-52, and Sephadex-G75 or Smartdex-G100 gel chromatography were used to separate and purify the crude polysaccharides, yielding the homogeneous fractions CDP1-5-1, CDP2-2-2, CDP2-3-2, CTP1-5-1, and CTP1-5-3. Structural analysis was conducted by using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), high-performance anion-exchange chromatography coupled with multi-angle laser light scattering and refractive index detection (HPAEC-MALLS-RID), gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), congo red, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). CDP1-5-1 was found to be an arabinan, while CDP2-2-2 and CDP2-3-2 were agavin-like fructans with different molecular weights. CTP1-5-1 and CTP1-5-3 were identified as a heteropolysaccharide and a galacturonan, respectively. Immunological evaluation using RAW264.7 macrophages showed that they all significantly enhanced nitric oxide (NO) production, with CDP1-5-1 exhibiting the most potent activity. The structural–activity relationship is summarized as follows: the arabinose was a key active unit with NO stimulatory effects. This research provides foundational data on the structure and immune-enhancing potential of Cistanche polysaccharides, supporting their further development and application.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Food Chemistry)
►▼
Show Figures
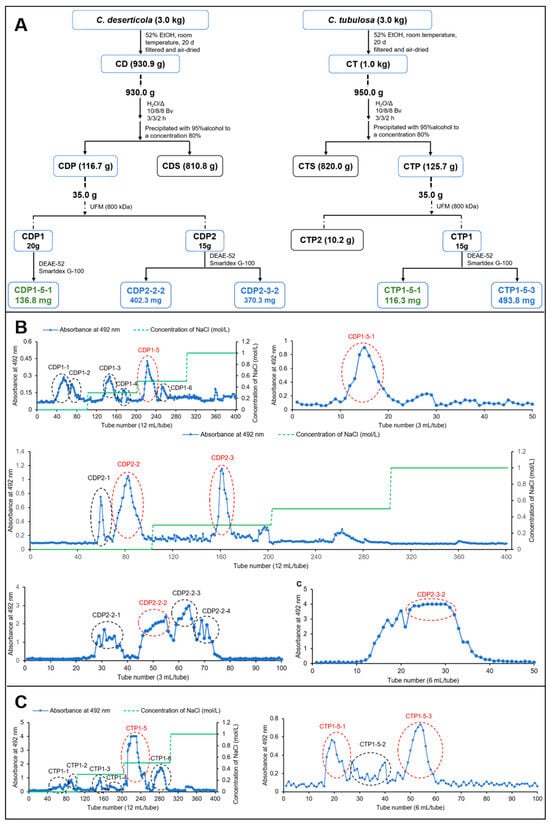
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Catalytic Transformation of Ginsenoside Re over Mesoporous Silica-Supported Heteropoly Acids: Generation of Diverse Rare Ginsenosides in Aqueous Ethanol Revealed by HPLC-HRMSn
by
Qi Wang, Yanyan Chang, Bing Li, Zhenxuan Zhang, Mengya Zhao, Huanxi Zhao and Yang Xiu
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4753; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244753 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
The efficient generation of structurally diverse rare ginsenosides from abundant precursors remains a significant challenge. In this study, a heterogeneous catalyst, 12-tungstosilicic acid supported on mesoporous silica (HSiW@mSiO2), was developed for the transformation of ginsenoside Re in aqueous ethanol solution. The
[...] Read more.
The efficient generation of structurally diverse rare ginsenosides from abundant precursors remains a significant challenge. In this study, a heterogeneous catalyst, 12-tungstosilicic acid supported on mesoporous silica (HSiW@mSiO2), was developed for the transformation of ginsenoside Re in aqueous ethanol solution. The reaction was conducted under mild conditions, and the products were systematically analyzed using high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with multistage tandem mass spectrometry and high-resolution mass spectrometry. A total of 24 transformation products were identified, arising from deglycosylation, epimerization, dehydration, cyclization, and nucleophilic addition reactions. Structural elucidation revealed the formation of deglycosylated, hydrated and dehydrated derivatives, C-20 epimers, and novel ethoxylated protopanaxatriol-type ginsenosides resulting from solvent incorporation at the C-24(25) or C-20 position. Product distribution varied with reaction parameters, including solvent composition, reaction time, temperature, and catalyst dosage. The synthesized HSiW@mSiO2 catalyst could be readily recovered by centrifugation and reused for five consecutive cycles, with complete conversion of ginsenoside Re maintained in the first two runs and a gradual decline in conversion to approximately 50% by the fifth cycle. This work demonstrates the efficacy of solid acid catalysts in enabling the structural diversification of ginsenosides through solvent-involved pathways.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Natural Products Chemistry)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Acetylenic Fatty Acids and Stilbene Glycosides Isolated from Santalum yasi Collected from the Fiji Islands
by
Khalid Al Maqbali, Miriama Vuiyasawa, Mercy Ayinya Gube-Ibrahim, Shubham Sewariya, Clément Balat, Kirsti Helland, Tamar Garcia-Sorribes, Mercedes de la Cruz, Bastien Cautain, Jeanette Hammer Andersen, Fernando Reyes and Jioji N. Tabudravu
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4752; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244752 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
In our continuing search for new anticancer and/or antimicrobial compounds from natural products, we screened for these activities in bark and leaf extracts of sandalwood plants collected from the Fiji Islands and found Santalum yasi to be the most active. Resulting chemical workup
[...] Read more.
In our continuing search for new anticancer and/or antimicrobial compounds from natural products, we screened for these activities in bark and leaf extracts of sandalwood plants collected from the Fiji Islands and found Santalum yasi to be the most active. Resulting chemical workup enabled the isolation and structural characterization of a new acetylenic acid, methyl (E)-octadec-6-en-8-ynoate (1), and an atropisomeric stilbene glycoside (4) (Yasibeneoside) together with six known compounds: 11,13-octadecadien-9-ynoic acid (2), methyl octadeca-9,11-diynoate (3), gaylussacin (5) chrysin-7-beta-monoglucoside (6), neoschaftoside (7), and chrysin-6-C-glucoside-8-C-arabinoside (8). Compound 1 (18:2 (6t, 8a) is an example of a Δ6, Δ8 acetylenic system containing the trans double bond at C-6 and the triple bond at C-8, which is reported here for the first time. All molecular structure elucidations and dereplications were performed using spectroscopic techniques, including 2D NMR and HRMS-MS/MS spectrometry. Methyl (E)-octadec-6-en-8-ynoate showed moderate activity activity with an IC50 of 91.2 ug/mL against the human breast adenocarcinoma cell line MCF-7.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Harnessing Nature’s Chemical Diversity: Innovations in Isolation, Identification, and Synthesis)
►▼
Show Figures
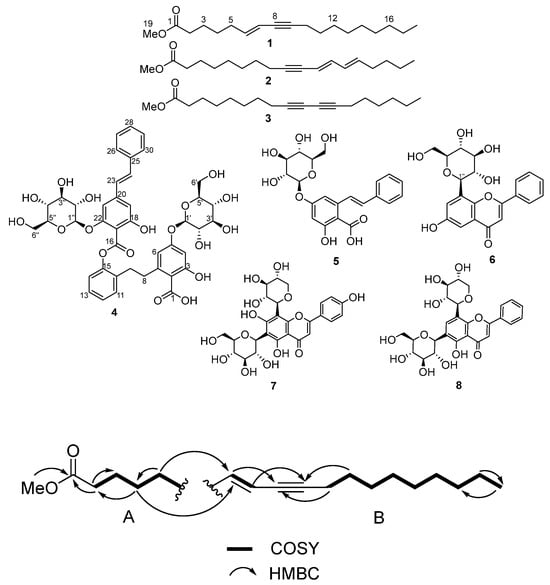
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
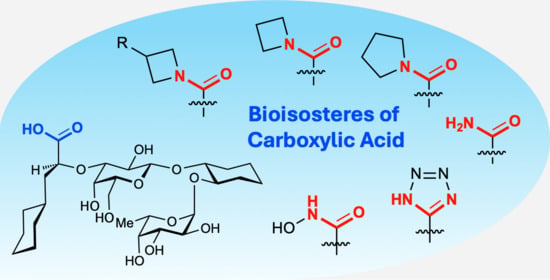
Acid Versus Amide—Facts and Fallacies: A Case Study in Glycomimetic Ligand Design
by
Martin Smieško, Roman P. Jakob, Tobias Mühlethaler, Roland C. Preston, Timm Maier and Beat Ernst
Molecules 2025, 30(24), 4751; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30244751 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The replacement of ionizable functional groups that are predominantly charged at physiological pH with neutral bioisosteres is a common strategy in medicinal chemistry; however, its impact on binding affinity is often context-dependent. Here, we investigated a series of amide derivatives of a glycomimetic
[...] Read more.
The replacement of ionizable functional groups that are predominantly charged at physiological pH with neutral bioisosteres is a common strategy in medicinal chemistry; however, its impact on binding affinity is often context-dependent. Here, we investigated a series of amide derivatives of a glycomimetic E-selectin ligand, in which the carboxylate group of the lead compound is substituted with a range of amide and isosteric analogs. Despite the expected loss of the salt-bridge interaction with Arg97, several amides retained or even improved the binding affinity. Co-crystal structures revealed conserved binding poses across the series, with consistent interactions involving the carbonyl oxygen of the amide and the key residues Tyr48 and Arg97. High-level quantum chemical calculations ruled out a direct correlation between carbonyl partial charges and affinity. Instead, a moderate correlation was observed between ligand binding and the out-of-plane pyramidality of the amide nitrogen, suggesting a favorable steric adaptation within the binding site. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations revealed that high-affinity ligands exhibit enhanced solution-phase pre-organization toward the bioactive conformation, likely reducing the entropic penalty upon binding. Further analysis of protein–ligand complexes using Molecular mechanics/Generalized born surface area (MM-GB/SA) decomposition suggested minor lipophilic contributions from amide substituents. Taken together, this work underscores the importance of geometric and conformational descriptors, beyond classical electrostatics, in driving affinity in glycomimetic ligand design and provides new insights into the nuanced role of amides as carboxylate isosteres in protein–ligand recognition.
Full article
Graphical abstract

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Molecules Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal Browser-
arrow_forward_ios
Forthcoming issue
arrow_forward_ios Current issue - Vol. 30 (2025)
- Vol. 29 (2024)
- Vol. 28 (2023)
- Vol. 27 (2022)
- Vol. 26 (2021)
- Vol. 25 (2020)
- Vol. 24 (2019)
- Vol. 23 (2018)
- Vol. 22 (2017)
- Vol. 21 (2016)
- Vol. 20 (2015)
- Vol. 19 (2014)
- Vol. 18 (2013)
- Vol. 17 (2012)
- Vol. 16 (2011)
- Vol. 15 (2010)
- Vol. 14 (2009)
- Vol. 13 (2008)
- Vol. 12 (2007)
- Vol. 11 (2006)
- Vol. 10 (2005)
- Vol. 9 (2004)
- Vol. 8 (2003)
- Vol. 7 (2002)
- Vol. 6 (2001)
- Vol. 5 (2000)
- Vol. 4 (1999)
- Vol. 3 (1998)
- Vol. 2 (1997)
- Volumes not published by MDPI
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Biomass, Energies, Materials, Molecules, Nanomaterials, Polymers
Biomass for Energy, Chemicals and Materials
Topic Editors: Shaohua Jiang, Changlei Xia, Shifeng Zhang, Xiaoshuai HanDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topic in
J. Compos. Sci., Materials, Molecules, Nanomaterials, Polymers, Processes, Recycling
Science and Technology of Polymeric Blends, Composites, and Nanocomposites
Topic Editors: Roberto Scaffaro, Emmanuel Fortunato GulinoDeadline: 28 February 2026
Topic in
Cancers, IJMS, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Sci. Pharm., Current Oncology, Molecules
Recent Advances in Anticancer Strategies, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Hassan Bousbaa, Zhiwei HuDeadline: 31 March 2026
Topic in
Applied Nano, Catalysts, Materials, Nanomaterials, Polymers, Molecules
Application of Nanomaterials in Environmental Analysis
Topic Editors: Yonggang Zhao, Yun ZhangDeadline: 13 April 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Molecules
Recent Advances in Development of Small Molecules to Fight Cancer—2nd Edition
Guest Editors: Giulia Bononi, Carlotta GranchiDeadline: 15 December 2025
Special Issue in
Molecules
Nano-Functional Materials for Sensor Applications—2nd Edition
Guest Editors: Li Fu, Aiwu WangDeadline: 15 December 2025
Special Issue in
Molecules
Computational Studies and Drug Design
Guest Editor: Elena CicheroDeadline: 15 December 2025
Special Issue in
Molecules
Heterocycles: Synthesis, Biological Activity, Pharmacokinetic Profiles, and Mechanism of Actions
Guest Editors: Guang Huang, Lucjan Strekowski, Xin LiDeadline: 15 December 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Molecules
Recent Advances in Flavors and Fragrances
Collection Editor: Luca Forti
Topical Collection in
Molecules
Natural Products as Leads or Drugs against Neglected Tropical Diseases
Collection Editors: Thomas J. Schmidt, Valeria Sülsen, Josphat Matasyoh
Topical Collection in
Molecules
Featured Reviews in Natural Products Chemistry
Collection Editors: Enrique Barrajón-Catalán, Vicente Micol, María Herranz-López
Topical Collection in
Molecules
Preanalytical Methods for Natural Products Production
Collection Editors: Young Hae Choi, Farid Chemat, Giancarlo Cravotto, Erica G. Wilson