Journal Description
Journal of Clinical Medicine
Journal of Clinical Medicine
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal of clinical medicine, published semimonthly online by MDPI. The International Bone Research Association (IBRA), Spanish Society of Hematology and Hemotherapy (SEHH), Japan Association for Clinical Engineers (JACE), European Independent Foundation in Angiology/ Vascular Medicine (VAS) and others are all affiliated with JCM, and their members receive a discount on article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, Embase, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Medicine, General and Internal) / CiteScore - Q1 (General Medicine)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 17.7 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Companion journals for JCM include: Epidemiologia, Transplantology, Uro, Sinusitis, Rheumato, Journal of Clinical & Translational Ophthalmology, Journal of Vascular Diseases, Osteology, Complications, Therapeutics, Sclerosis, Pharmacoepidemiology and Journal of CardioRenal Medicine.
- Journal Clusters of Hematology: Hemato, Hematology Reports, Thalassemia Reports and Journal of Clinical Medicine.
Impact Factor:
2.9 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.3 (2024)
Latest Articles
Ten-Year Outcomes of Patients with Left Main Coronary Artery Disease and Diabetes Mellitus Treated with Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14(24), 8851; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248851 (registering DOI) - 14 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Long-term outcomes of patients with left main coronary artery (LMCA) disease and diabetes mellitus (DM) undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) are incompletely investigated. The aim of this study was to assess the 10-year clinical outcomes after PCI according to diabetic status and
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Long-term outcomes of patients with left main coronary artery (LMCA) disease and diabetes mellitus (DM) undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) are incompletely investigated. The aim of this study was to assess the 10-year clinical outcomes after PCI according to diabetic status and antidiabetic therapy in patients with LMCA. Methods: This study represents a pooled analysis of two randomized trials (n = 1257 patients) on LMCA PCI focused on the prespecified subgroups of diabetic patients. Patients were categorized in groups according to the diabetic status and antidiabetic therapy (oral drugs or insulin therapy). The primary endpoint was 10-year all-cause mortality. Results: Overall, 361 patients had DM (246 patients on oral antidiabetic drugs and 115 patients on insulin therapy) and 896 patients had no DM. At 10 years, 477 patients died: 291 nondiabetic patients (35.7%), 111 diabetic patients (49.5%) on oral antidiabetic drugs and 75 diabetic patients (70.0%) on insulin therapy (hazard ratio [HR] = 1.57, 95% confidence interval [1.26–1.96]; p < 0.001 for diabetic patients on oral antidiabetic drugs vs. nondiabetic patients; HR = 2.80 [2.17–3.61]; p < 0.001 for diabetic patients on insulin therapy vs. nondiabetic patients; HR = 1.78 [1.33–2.39]; p <0.001 for diabetic patients on insulin therapy vs. diabetic patients on oral antidiabetic drugs). The 10-year incidence of myocardial infarction was higher in diabetic patients on insulin therapy (10.0%) versus diabetic patients on oral antidiabetic drugs (3.0%). There were no significant differences between the groups regarding the 10-year incidence of definite stent thrombosis, coronary artery bypass graft surgery, repeat PCI or stroke. Conclusions: In patients with LMCA disease undergoing PCI, DM was associated with a higher 10-year incidence of all-cause mortality than patients without DM with the worst outcomes observed in diabetic patients on insulin therapy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cardiology)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Scintigraphic Assessment of Lung Perfusion and Ventilation in Patients After Pneumonectomy
by
Karina Witkiewicz, Małgorzata Edyta Wojtyś, Norbert Wójcik, Krzysztof Safranow, Jarosław Pieróg, Jacek Szulc, Tadeusz Sulikowski, Konrad Jarosz, Tomasz Grodzki and Janusz Wójcik
J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14(24), 8849; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248849 (registering DOI) - 14 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: The physiological ventilation–perfusion ratio (V/Q) in the upper pulmonary field is >3 and in the lower pulmonary field it is <1 due to the effect of gravity when the body is in an upright position. Pneumonectomy leads to significant changes in ventilation
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The physiological ventilation–perfusion ratio (V/Q) in the upper pulmonary field is >3 and in the lower pulmonary field it is <1 due to the effect of gravity when the body is in an upright position. Pneumonectomy leads to significant changes in ventilation and perfusion conditions. The aim of this study was to evaluate perfusion and ventilation after pneumonectomy complicated by pleural empyema, including the relationship between surgical outcomes, sex, and time from pneumonectomy. Methods: The study group included 30 patients (25 men, 5 women) who underwent pneumonectomy complicated by pleural empyema. Lung function was assessed using ventilation–perfusion scintigraphy. Twenty-one patients were assessed within 5 years after pneumonectomy and nine patients >5 years after pneumonectomy. Results: Average flow was 21.1% in the upper field, 47.8% in the middle field, and 30.35% in the lower field. The mean perfusion value was significantly higher in the lower field of the right lung than in the lower field of the left lung (33.35 vs. 28.05, p = 0.001). Average ventilation was 17.21% in the upper field, 46.73% in the middle field, and 34.28% in the lower field. The mean V/Q in the upper field was in the range of 0.81–0.87, but it reached approximately 1 (0.96–1) in the middle field and exceeded 1 (1.05–1.25) in the lower field. Conclusions: Pneumonectomy led to increased perfusion in the upper pulmonary field and increased ventilation in the lower pulmonary field compared to the literature for patients with the two lungs (the two-lung system), with a reversal of the V/Q between the upper and lower field.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovations in Thoracic Surgery and Disease Management: Integrating Genomics, Technology, and Multidisciplinary Care)
Open AccessArticle
Psychological Pain Measurement in the Context of Suicidal Behavior: Rasch Analysis of the Spanish Psychache Scale Version
by
Jorge L. Ordóñez-Carrasco, Claudia Suárez-Yera, María Sánchez-Castelló and Antonio J. Rojas-Tejada
J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14(24), 8847; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248847 (registering DOI) - 14 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: The Psychache Scale (PS) is the most widely used scale to measure psychological pain due to its ease of application, favorable evidence of predictive validity, and adequate psychometric properties from the CTT (Classical Test Theory) approach. This paper aims to contribute
[...] Read more.
Background: The Psychache Scale (PS) is the most widely used scale to measure psychological pain due to its ease of application, favorable evidence of predictive validity, and adequate psychometric properties from the CTT (Classical Test Theory) approach. This paper aims to contribute to the improvement of the Spanish version of the PS by analyzing its psychometric properties using a Rasch model. Methods: Using quota sampling, 905 young adults completed an online questionnaire with the PS. Results: The items and response categories showed an acceptable fit to the model and good performance. The separation index indicated three strata for persons. The item-person map showed that persons were placed lower on the psychological pain continuum than item, and some item pairs presented small difference in their severity. The study of men-women DIF (differential item functioning) showed a slight differential functioning only for item 6. Conclusions: This study provides new evidence that supports the use of the PS to measure psychological pain.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Psychological Pain and Suicidal Behavior: Clinical Implications)
Open AccessSystematic Review
The Impact of Surgical Approach on Mid-Term Clinical Outcomes Following Hemiarthroplasty for Femoral Neck Fractures: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Postero-Lateral Versus Direct Lateral Approaches
by
Gianmarco Marcello, Francesco Rosario Parisi, Lorenzo Alirio Diaz Balzani, Alessandro Del Monaco, Emanuele Zappalà, Giuseppe Francesco Papalia, Chiara Capperucci, Erika Albo, Augusto Ferrini, Biagio Zampogna and Rocco Papalia
J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14(24), 8846; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248846 (registering DOI) - 14 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Femoral neck fractures in the elderly often necessitate hemiarthroplasty, but the optimal surgical approach remains a highly debated topic. The postero-lateral and direct lateral approaches are commonly employed, each with benefits and drawbacks. Despite their widespread use, robust, long-term comparative studies
[...] Read more.
Background: Femoral neck fractures in the elderly often necessitate hemiarthroplasty, but the optimal surgical approach remains a highly debated topic. The postero-lateral and direct lateral approaches are commonly employed, each with benefits and drawbacks. Despite their widespread use, robust, long-term comparative studies on definitive outcomes, including pain, functional recovery, and complication rates, are notably lacking. This systematic review and meta-analysis aim to address this critical gap by meticulously comparing these approaches with long-term follow-up. Methods: A systematic literature search was performed, including only comparative studies with a minimum 1-year follow-up. A meta-analysis was performed for the primary outcome measures: operative time, dislocations, infections, perioperative fractures and reoperations. Secondary outcomes included a qualitative synthesis of patient-reported outcomes (quality of life, pain, and satisfaction). Methodological quality was assessed using RoB 2.0 for randomized controlled trials and MINORS criteria for cohort studies. Results: Our meta-analysis provides robust quantitative evidence. The direct lateral approach is associated with a significantly lower risk of post-operative dislocations (I2 = 58%; OR = 2.86, 95% CI: 2.53 to 3.22; p < 0.00001) and a significantly lower rate of reoperation (I2 = 0%; OR = 1.25, 95% CI: 1.12 to 1.40; p = 0.0001) compared to postero-lateral approach. Operative time, infection, and perioperative fracture rates were found to be statistically comparable. However, patient-reported outcomes yielded inconsistent results across studies, often becoming non-significant after adjusting for confounders. Conclusions: This meta-analysis shows that the direct lateral approach is associated with lower rates of dislocation and reoperation compared with the postero-lateral approach, while patient-reported outcomes remain variable across studies. Further high-quality comparative trials are needed to confirm these associations and guide surgical decision-making.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Clinical Updates on Knee and Hip Arthroplasty)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessBrief Report
Intraovarian Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy for PCOS: Unanswered Questions and Future Research Directions
by
Zaher Merhi
J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14(24), 8845; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248845 (registering DOI) - 14 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)-related infertility remains a major challenge and the efficacy of conventional treatments is limited in certain patient groups and often fails to address the underlying causes of ovarian dysfunction. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is rich in growth factors and cytokines
[...] Read more.
Background: Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)-related infertility remains a major challenge and the efficacy of conventional treatments is limited in certain patient groups and often fails to address the underlying causes of ovarian dysfunction. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is rich in growth factors and cytokines and has emerged as a potential regenerative therapy for women with a diminished ovarian reserve. Methods: A literature search for studies pertaining to intraovarian PRP administration and PCOS was performed on PubMed. Results: Preclinical studies in PCOS animal models have demonstrated that intraovarian PRP can improve folliculogenesis, enhance antioxidant defenses, normalize steroid hormone levels, and downregulate pro-apoptotic pathways. Early clinical reports suggest that intraovarian PRP may restore ovulation and improve ovarian reserve in women with long-standing amenorrhea and poor responses to standard fertility treatments. The proposed mechanisms of how PRP could improve folliculogenesis include the modulation of local ovarian gene expression, the activation of dormant follicles, angiogenesis, and a reduction in oxidative stress and inflammation. Conclusions: Although preliminary data are promising, larger studies are needed to establish the efficacy, if any, of intraovarian PRP administration as a potential novel therapeutic adjunct in women with PCOS.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Endocrinology & Metabolism)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Fibroblast Growth Factor 21: Their Role in Early Cardiovascular Involvement in Rheumatoid Arthritis
by
Mariusz Ciołkiewicz, Anna Kuryliszyn-Moskal, Ewa Jabłońska, Wioletta Ratajczak-Wrona, Mariusz Wojciuk and Piotr A. Klimiuk
J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14(24), 8844; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248844 (registering DOI) - 14 Dec 2025
Abstract
Introduction: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is associated with increased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) represents an early sign of cardiac involvement in RA. Objectives: This study aimed to evaluate the incidence of LVDD and the association of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is associated with increased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) represents an early sign of cardiac involvement in RA. Objectives: This study aimed to evaluate the incidence of LVDD and the association of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and circulating FGF21 levels with chosen LVDD echocardiographic parameters, as well as to assess their diagnostic utility for LVDD in a cohort of patients with RA. Patients and Methods: A total of 51 RA patients (46 females, 5 males; average age 48.8 ± 8.2 years; median disease duration of 12 years) were enrolled. NLR and serum FGF21 levels were analysed for association with echocardiographic parameters of LVDD using univariate regression models. The diagnostic performance of these markers was evaluated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. Results: LVDD was diagnosed in 10 patients (19.6%). The NLR was associated negatively with E velocity (β = −4.99, p = 0.02), E/A ratio (β = −0.16, p = 0.004), lateral and medial e′ velocities (β = −1.05, p = 0.038 and β = −0.97, p = 0.013, respectively), and positively with left atrial diameter (β = 2.08, p = 0.006). Serum FGF21 levels were negatively associated with the E/A ratio (β = −0.0005, p = 0.009) and lateral e′ velocity (β = −0.003, p = 0.04). ROC analysis demonstrated a greater diagnostic value for NLR (Youden index 0.30, cut-off point 2.26, sensitivity 50%, specificity 80%, and area under curve [AUC] 0.58) compared to FGF21 (Youden index 0.30, cut-off value 852.85 pg/mL, 100% specificity, 30% sensitivity, and AUC 0.48). Conclusions: NLR and FGF21 are associated with the echocardiographic parameters of the left ventricular diastolic dysfunction prior to the fulfilment of LVDD diagnostic criteria. RA patients with elevated NLR and FGF21 serum levels should be considered for LVDD screening.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Immunology & Rheumatology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Increased suPAR Plasma Levels May Indicate Postoperative Sepsis Following Open Thoracoabdominal Aortic Repair
by
Dragos Socol, Cathryn Bassett, Bernhard Hruschka, Jelle Frankort, Moustafa Elfeky, Katja Heller, Florian Kahles, Berkan Kurt, Christian Uhl, Panagiotis Doukas and Alexander Gombert
J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14(24), 8843; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248843 (registering DOI) - 14 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Postoperative organ complications following open thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm (TAAA) repair pose significant challenges during the early postoperative period, where prompt detection is crucial for improving patient outcomes. Sepsis is often a central factor in these complications. This study investigates the perioperative
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Postoperative organ complications following open thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm (TAAA) repair pose significant challenges during the early postoperative period, where prompt detection is crucial for improving patient outcomes. Sepsis is often a central factor in these complications. This study investigates the perioperative dynamics of soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR) plasma levels in TAAA patients undergoing elective surgical repair and evaluates its diagnostic potential for early detection of postoperative sepsis. Methods: In this retrospective, single-center study, 28 patients (mean age 52.6 ± 13.4 years; 67.9% male) underwent elective open TAAA repair between 2022 and 2024. Blood samples were collected at five perioperative time points, and suPAR levels were measured using ELISA. The primary endpoint was the onset of postoperative sepsis, with secondary endpoints including other organ complications. The predictive performance of suPAR levels was evaluated using Receiver Operator Characteristics (ROC) analysis. Results: Postoperative sepsis developed in 7 of 28 patients (25%), with the diagnostic criteria met at a mean of 9.7 ± 6.9 days. Baseline suPAR levels did not differ between groups; however, from 12 h after surgery, the sepsis group exhibited significantly higher serum concentrations (14.43 ng/mL vs. 7.23 ng/mL; p = 0.004), a difference that persisted throughout the first 24 h. At 24 h, suPAR had the highest predictive accuracy for sepsis, with an AUC of 0.90, 90% sensitivity, and 86% specificity at a 9 ng/mL cut-off (p < 0.001). Conclusions: Elevated suPAR levels in the early postoperative period are strongly associated with the later onset of sepsis. Early monitoring may enable timely intervention, potentially improving outcomes in this high-risk patient population.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cardiovascular Medicine)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Associations Between Screen Time, Sleep, and Executive Function in School-Aged Children and Adolescents: The Moderating Role of Digital Content and Age
by
Csongor Toth, Brigitte Osser, Laura Ioana Bondar, Roland Fazakas, Florin Mihai Marcu, Nicoleta Anamaria Pascalau, Ramona Nicoleta Suciu and Bombonica Gabriela Dogaru
J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14(24), 8842; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248842 (registering DOI) - 14 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Increased and unstructured digital exposure has raised growing concerns about its potential impact on children’s cognitive and behavioral development. Executive functions (EFs)—encompassing attention, working memory, inhibition, and cognitive flexibility—are particularly sensitive to environmental influences during development. Beyond its empirical
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Increased and unstructured digital exposure has raised growing concerns about its potential impact on children’s cognitive and behavioral development. Executive functions (EFs)—encompassing attention, working memory, inhibition, and cognitive flexibility—are particularly sensitive to environmental influences during development. Beyond its empirical aim, this study also sought to address a theoretical gap by clarifying how multiple dimensions of digital exposure (quantity, content quality, and sleep-related timing) jointly relate to EF performance, an area insufficiently integrated into current EF frameworks. This study aimed to examine the quantitative and qualitative dimensions of digital exposure in relation to sleep duration and EF performance among Romanian school-aged children and adolescents. Materials and Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted among 142 students aged 5–19 years, using standardized cognitive tasks and structured parent questionnaires to assess screen time, digital content type, and sleep duration. Analyses included correlational tests, group comparisons, regression models, and moderation procedures. Results: Higher daily screen time was associated with poorer attention and working-memory performance and shorter nocturnal sleep. Children and adolescents who exceeded the recommended daily screen-time limits performed worse on executive-function measures than those within recommended limits. Digital content type and sleep duration each contributed uniquely to executive performance, and recreational digital content as well as younger age intensified the negative effects of screen exposure. Conclusions: Excessive daily screen time, especially involving passive or recreational content, is associated with poorer EF performance and shorter sleep in children. Adequate sleep and educational or interactive digital engagement may mitigate these effects. The findings underscore the importance of age-appropriate, structured, and balanced digital habits to support healthy cognitive development.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mind–Body Connection: The Impact of Mental Health on Physical Well-Being)
Open AccessArticle
Retrospective Observational Study on Implant Site Preparation Using Magnetodynamic Surgery vs. Piezoelectric and Traditional Surgery
by
Lorenzo Bevilacqua, Luca De Angelis, Lucio Torelli, Antonio Scarano, Gianmarco Gronelli and Michele Maglione
J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14(24), 8841; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248841 (registering DOI) - 14 Dec 2025
Abstract
Objective: This study compared magnetodynamic surgery, traditional drill-based surgery, and piezoelectric surgery for the preparation of the implant site, focusing on operative time and intra/postoperative discomfort. Methods: A total of 86 patients (69.8% female, 30.2% male) treated at the Oral Surgery Clinic, University
[...] Read more.
Objective: This study compared magnetodynamic surgery, traditional drill-based surgery, and piezoelectric surgery for the preparation of the implant site, focusing on operative time and intra/postoperative discomfort. Methods: A total of 86 patients (69.8% female, 30.2% male) treated at the Oral Surgery Clinic, University of Trieste, were included: 43 underwent implant placement with the Magnetic Mallet (MM); the remaining 43 received preparations with the Piezodevice (IP) on one side and drills (Ds) on the other. All surgeries were performed by the same operator. Data included bone quality, operative time, and postoperative questionnaire responses for pain (VAS) and analgesic use. A statistical analysis was conducted using Mann–Whitney U and Kruskal–Wallis tests. Results: Significant differences emerged in operative times and pain perception, influenced by bone quality. The MM and D had comparable times in D1–D2 and D3–D4 bone, but the D produced higher VAS scores. The MM vs. IP showed significant differences in absolute times (p = 0.00018) and relative times for both D1–D2 (p = 0.01875) and D3–D4 (p = 0.00584), with qualitative VAS differences. The IP vs. D also showed significant absolute (p = 0.000005) and relative time differences for D1–D2 (p = 0.00718) and D3–D4 (p = 0.000145), with VAS variations. In the MM group, higher bone density significantly prolonged times (p = 0.04136). Conclusions: Within the limits of this study, the traditional drill-based technique remains valid and widely used, but the Magnetic Mallet can offer advantages in terms of patient comfort and postoperative recovery. The Piezodevice, while excelling in tissue preservation, is limited by longer operative times.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Novel Developments in Dental and Oral Surgery)
►▼
Show Figures
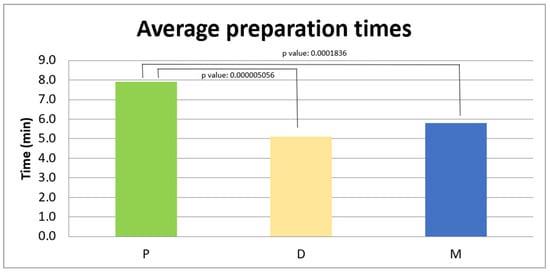
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Association Between Postoperative Pain Intensity and Delirium in Cardiac and Neurosurgical Patients: A Retrospective Pilot Study
by
Mateusz Szczupak, Jacek Kobak, Jakub Wiśniewski, Jolanta Wierzchowska and Sabina Krupa-Nurcek
J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14(24), 8840; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248840 (registering DOI) - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objective: Postoperative pain and delirium are frequent and clinically relevant complications in patients undergoing major cardiac or neurosurgical procedures. The interaction between these conditions remains insufficiently characterized, particularly across heterogeneous surgical populations. This study aimed to investigate the relationship between postoperative pain
[...] Read more.
Background/Objective: Postoperative pain and delirium are frequent and clinically relevant complications in patients undergoing major cardiac or neurosurgical procedures. The interaction between these conditions remains insufficiently characterized, particularly across heterogeneous surgical populations. This study aimed to investigate the relationship between postoperative pain intensity and delirium severity within the first 48 h after surgery in cardiac and neurosurgical patients. Methods: This retrospective observational analysis included 408 individuals—202 following cardiac surgery and 206 after neurosurgical procedures. Pain intensity was measured using the Numerical Rating Scale (NRS), while delirium presence and severity were assessed using the CAM-ICU and CAM-ICU-7 instruments. Associations between NRS scores, delirium severity, demographic characteristics, and ICU length of stay were examined. Results: Cardiac surgery patients experienced higher pain levels on postoperative day 1 compared with neurosurgical patients; this difference was not observed on day 2. In the cardiac cohort, higher NRS scores were positively associated with greater delirium severity on both postoperative days. No such association was detected in the neurosurgical group. Pain scores also differed across procedure types within each specialty, and several demographic variables (age, sex, ICU stay duration) were linked with variations in pain intensity. On postoperative day 1, pain intensity showed a moderate association with delirium severity (Spearman ρ = 0.23; 95% CI 0.14–0.32). Patients who developed delirium had higher pain scores (r = 0.25). In ordinal logistic regression, greater pain on postoperative day 1 independently predicted higher delirium severity (OR 2.24; 95% CI 1.70–2.94). Conclusions: Significant associations between postoperative pain intensity and delirium severity were identified in cardiac surgery patients, whereas no similar pattern emerged among neurosurgical patients. Given the retrospective design and incomplete data on perioperative pharmacotherapy, the findings should be interpreted descriptively and do not support causal conclusions. These results underscore the importance of systematic monitoring of pain and cognitive function in high-risk postoperative populations and highlight the need for prospective studies to elucidate the complex interplay between pain, perioperative factors, and postoperative delirium.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Clinical Management and Long-Term Prognosis in Intensive Care)
Open AccessCase Report
Malignant Syphilis in an Immunocompetent Patient: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
by
Chiara Vincenza Mazzola, Eleonora Bono, Ilenia Giacchino, Cinzia Calà, Luca Pipitò and Antonio Cascio
J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14(24), 8839; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248839 (registering DOI) - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Syphilis can present with diverse clinical manifestations, earning the name “great imitator.” Malignant syphilis (MS) is a rare, severe form of secondary syphilis, typically reported in immunocompromised patients, particularly those living with HIV. However, MS can occasionally occur in immunocompetent individuals,
[...] Read more.
Background: Syphilis can present with diverse clinical manifestations, earning the name “great imitator.” Malignant syphilis (MS) is a rare, severe form of secondary syphilis, typically reported in immunocompromised patients, particularly those living with HIV. However, MS can occasionally occur in immunocompetent individuals, posing diagnostic challenges due to its atypical presentation. Methods: A case report is presented alongside a PubMed literature search using the terms “(malignant syphilis OR lues maligna) AND (immunocompetent) AND (case report OR case series).” No language or temporal restrictions were applied, yielding 18 relevant publications. Results: A 60-year-old HIV-negative man presented with fever, weight loss, papular lesions, and a single ulcer on the sternum. Serology was positive for syphilis, and PCR confirmed T. pallidum DNA in the lesion. Treatment with a single intramuscular dose of benzathine penicillin G led to prompt clinical and serological improvement. Literature review (n = 18) showed that MS in immunocompetent patients affects both sexes (55% male; mean age 37.1 years), often presents with ulceronodular or rupioid crusted lesions, and frequently involves systemic symptoms. Molecular diagnostics were rarely reported, with most diagnoses relying on histopathology and serology. Treatment with benzathine penicillin G was effective in all cases, and full recovery was achieved. Conclusions: MS can occur in immunocompetent, HIV-negative individuals without obvious risk factors. Clinicians should maintain a high index of suspicion in cases of systemic, cutaneous, or ocular manifestations suggestive of MS. Molecular assays can facilitate diagnosis and prevent unnecessary invasive procedures. Benzathine penicillin G remains the treatment of choice, demonstrating high therapeutic effectiveness. MS should be considered in the differential diagnosis of ulcerative or nodular dermatoses, regardless of immune status.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sexually Transmitted Infections as a Challenge of Modern Society: Old Problems and Modern Solutions)
Open AccessArticle
Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Partially Absorbable Transobturator Mid-Urethral Sling in Women Aged 65 Years and Older
by
Réka Fábián-Kovács, Asnat Groutz, Jonatan Neuman, Menahem Neuman, Yoav Baruch and Ronen S. Gold
J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14(24), 8838; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248838 (registering DOI) - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
Objectives: To assess the long-term safety and efficacy of the Serasis® partially absorbable transobturator mid-urethral sling (MUS) in women aged ≥65 years compared to younger women. Methods: A retrospective comparative study of 375 consecutive women who underwent Serasis® MUS for stress
[...] Read more.
Objectives: To assess the long-term safety and efficacy of the Serasis® partially absorbable transobturator mid-urethral sling (MUS) in women aged ≥65 years compared to younger women. Methods: A retrospective comparative study of 375 consecutive women who underwent Serasis® MUS for stress urinary incontinence (SUI). Patients were stratified into two age groups: 45–64 years (N = 118) and ≥65 years (N = 257), with further subdivision of the elderly cohort into 65–74 years (N = 208) and 75–84 years (N = 49). Primary outcomes included perioperative safety and long-term subjective cure rates, assessed via standardized telephone survey at a mean follow-up of 8.5 years (range, 6.8–10.9 years). Results: Perioperative outcomes were comparable across age groups. At 4 months postoperatively, subjective cure was achieved in 82.9% of elderly and 86.4% of younger patients. Long-term subjective cure rates were 79.6% and 85.4%, respectively (p = 0.27). Elderly patients experienced higher rates of postoperative voiding dysfunction and persistent overactive bladder symptoms, though subjective satisfaction remained high. Long-term mesh-related complications were infrequent across age groups. Specifically, vaginal mesh erosion requiring surgical removal occurred in three elderly patients (1.6%) and in only one younger patient (1.1%). A multivariate logistic regression analysis identified preoperative mixed urinary incontinence, BMI >30 kg/m2 and concomitant pelvic organ prolapse repair as independent predictors of surgical failure. Age ≥65 years was not an independent predictor of surgical failure (OR 1.3, 95% CI 0.8–2.1, p = 0.31). Conclusions: The use of a partially absorbable MUS in elderly women with SUI is a safe and effective surgical approach, associated with a significant reduction in long-term mesh-related complications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Obstetrics & Gynecology)
Open AccessReview
Exposure-Based Intervention in Virtual Reality to Address Kinesiophobia in Parkinson’s Disease: A Narrative Review
by
Alice Jeanningros, Stéphane Bouchard and Alexandra Potvin-Desrochers
J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14(24), 8837; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248837 (registering DOI) - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Physical activity alleviates symptoms and may slow Parkinson’s disease (PD) progression, yet many individuals with PD remain sedentary. Kinesiophobia, the fear of movement, may represent a significant but underexplored psychological barrier to physical activity in this population. Virtual reality (VR), already
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Physical activity alleviates symptoms and may slow Parkinson’s disease (PD) progression, yet many individuals with PD remain sedentary. Kinesiophobia, the fear of movement, may represent a significant but underexplored psychological barrier to physical activity in this population. Virtual reality (VR), already effective in phobias, may represent a promising approach to address this challenge. This review initially aimed to systematically examine exposure-based interventions in VR (E-IVR) directly targeting kinesiophobia in PD. Methods: Database searches using keywords such as “kinesiophobia,” “fear of movement,” and “VR” combined with “PD” yielded no eligible studies. Consequently, the scope was broadened to include populations with neurological or musculoskeletal conditions, and a narrative review format was adopted to synthesize the available evidence. Furthermore, relevant studies of interventions in VR applied in PD, although not specifically addressing kinesiophobia, are detailed to provide evidence of efficacy and feasibility of VR interventions in PD. Finally, directions are offered to support the creation of E-IVR targeting kinesiophobia in individuals with PD. Results: Meta-analyses in neurological and musculoskeletal populations demonstrate moderate to large reductions in kinesiophobia following VR interventions, although effects vary depending on assessment tools, degree of immersion, and exposure design. In PD, VR has been applied to rehabilitation, anxiety reduction, and quality of life enhancement. These interventions achieved high adherence (≥90%), were well tolerated, and reported no major adverse events. Conclusions: Kinesiophobia is prevalent in PD and could contribute to physical inactivity. E-IVR appears feasible, safe, and innovative for addressing kinesiophobia in people living with PD.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Clinical Neurology)
Open AccessArticle
Three Decades of Spinal Cord Injury in Saudi Arabia: Trends in Incidence, Prevalence, and Disability Outcomes
by
Ahmad F. Alahmary, Mishal M. Aldaihan, Vishal Vennu and Saad M. Bindawas
J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14(24), 8836; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248836 (registering DOI) - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objective: Spinal cord injury (SCI) is a life-altering condition representing a major cause of long-term disability and substantial health burden worldwide. In the Middle East, including Saudi Arabia, rapid urbanization and evolving injury patterns may have influenced SCI trends; however, national data remain
[...] Read more.
Background/Objective: Spinal cord injury (SCI) is a life-altering condition representing a major cause of long-term disability and substantial health burden worldwide. In the Middle East, including Saudi Arabia, rapid urbanization and evolving injury patterns may have influenced SCI trends; however, national data remain limited. This study aimed to examine age-standardized trends in SCI incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability (YLDs) in Saudi Arabia from 1990 to 2021, comparing transport-related and non-transport unintentional injuries, and describing age- and sex-specific SCI patterns in 2021. Methods: Using data from the Global Burden of Diseases (GBD) 2021 study, we conducted a population-based trend analysis for Saudi Arabia from 1990 to 2021, stratified by age, sex, and injury cause. Outcomes included age-standardized incidence, prevalence, and YLD rates per 100,000 population, along with percentage changes, average annual percentage changes, and rate ratios with 95% uncertainty intervals (UIs). Results: Between 1990 and 2021, age-standardized SCI showed a point estimate increase in incidence (25.0%; 95% UI: −28.3 to 116.8) and prevalence (24.3%; 95% UI: 0.8 to 53.4), while YLDs showed a modest rise (1.4%; 95% UI: −44.5 to 83.9). Males experienced greater increases in incidence (31.9%) and prevalence (32.3%) than females. Non-transport unintentional injuries surpassed transport-related causes, accounting for nearly 75% of SCI-related YLDs in 2021. The highest burden occurred among young adult males (highest incidence) and older adults (peak prevalence). Conclusion: The burden of SCI in Saudi Arabia has increased over the past three decades, with a shift toward non-transport unintentional injuries. Because wide uncertainty intervals limit definitive conclusions on trend direction, strengthening injury prevention, rehabilitation, and surveillance programs is crucial to mitigate this growing burden.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue State of the Art in Spinal Cord Injuries: Clinical Rehabilitation and Management)
Open AccessReview
The Role of Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in Children with Cystic Fibrosis
by
Francesca Galluzzi, Werner Garavello, Gianluca Dalfino, Francesca De Bernardi, Paolo Castelnuovo and Mario Turri-Zanoni
J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14(24), 8835; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248835 (registering DOI) - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to assess the role of functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) in the treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) in children with cystic fibrosis (CF). Methods: We performed a comprehensive review of the literature by searching PubMed/MEDLINE. Results:
[...] Read more.
Objectives: The aim of this study was to assess the role of functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) in the treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) in children with cystic fibrosis (CF). Methods: We performed a comprehensive review of the literature by searching PubMed/MEDLINE. Results: CRS affects most children with CF. Though subjective symptoms are variable, radiological and endoscopic examination demonstrated typical objective findings. FESS is recommended for children with significant nasal symptoms that do not respond to medical treatment. At present, there are no uniform criteria for timing and extension of surgery. Primary surgery includes nasal polypectomy and correction of any bone anatomical variants that reduce ventilation of paranasal sinuses predisposing to recurrent sinusitis and complications. In case of recurrences, revision surgery supports a more expanded surgical approach. Moreover, FESS can relieve symptoms, improve patients’ quality of life, manage complications, ameliorate the delivery of medical therapy, and reduce sinonasal and lung superinfections. Conclusions: FESS has emerged as a safe and effective procedure for the treatment of CRS in children with CF. Since children with CF and CRS are difficult-to-treat patients, a multidisciplinary approach in tertiary-care referral centers is required.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Otolaryngology)
►▼
Show Figures
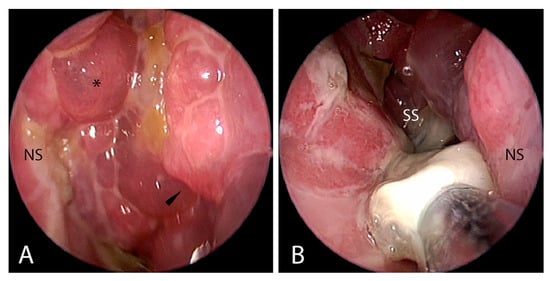
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Prophylactic Noninvasive Ventilation Reduces Complications Following Minimally Invasive Coronary Surgery
by
Janusz Konstanty-Kalandyk, Anna Kędziora, Dominika Batycka-Stachnik, Piotr Śliwiński, Przemysław Ptak, Dorota Sobczyk and Jacek Piątek
J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14(24), 8834; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248834 (registering DOI) - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
Objective: Postoperative pulmonary complications (PPCs) remain a significant source of morbidity and mortality in patients undergoing minimally invasive cardiothoracic procedures. Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) is frequently employed as adjunctive therapy to manage respiratory insufficiency. This study evaluated the implementation of prophylactic NIV immediately following
[...] Read more.
Objective: Postoperative pulmonary complications (PPCs) remain a significant source of morbidity and mortality in patients undergoing minimally invasive cardiothoracic procedures. Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) is frequently employed as adjunctive therapy to manage respiratory insufficiency. This study evaluated the implementation of prophylactic NIV immediately following extubation after minimally invasive direct coronary artery bypass (MIDCAB) surgery. Methods: A total of 454 consecutive patients undergoing MIDCAB were included. In total, 139 patients received prophylactic NIV (P-NIV)—postoperative management, 315 patients formed a historical control group treated according to the previous standard of care. Clinical outcomes assessed postoperative pulmonary complications, in-hospital mortality, and one-year survival. Results: The incidence of PPCs was significantly lower in the P-NIV group compared with the control cohort (6.5% vs. 14.9%; p = 0.012). Unadjusted analyses demonstrated a significant reduction in the odds of PPCs with P-NIV (odds ratio [OR], 0.39; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.17–0.85). Using inverse probability of treatment weighting, prophylactic NIV was associated with an absolute reduction of 8.0 percentage points in PPC risk across the entire cohort (average treatment effect [ATE], −0.080; 95% CI, −0.136 to −0.024; z = −2.80; p = 0.005). Kaplan–Meier analysis demonstrated significantly improved one-year survival in the P-NIV group (log-rank p = 0.047). Conclusions: The implementation of prophylactic NIV following MIDCAB was associated with a greater than 50% reduction in the odds of PPCs in both unadjusted and adjusted analyses and improved one-year survival. These results support the adoption of routine prophylactic NIV in the postoperative management of patients undergoing minimally invasive coronary surgery.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue State-of-the-Art in Cardiac Surgery: Progress, Challenges and Opportunities)
►▼
Show Figures
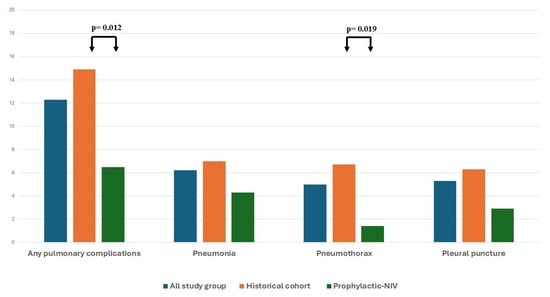
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Ovarian Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: Challenges and Future Perspectives
by
Valentina Di Vito, Gabriele Veroi, Laura Rizza, Francesca Rota, Andrea Baiocchini, Maria Cristina Macciomei, Carla Lubrano, Anna La Salvia, Andrea Lania, Lucia Rosalba Grillo, Silvia Migliaccio, Guido Rindi and Roberto Baldelli
J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14(24), 8833; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248833 (registering DOI) - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Ovarian neuroendocrine neoplasms (O-NENs) are extremely rare, representing less than 1% of all ovarian neoplasms and under 5% of all neuroendocrine tumors (NETs). They encompass two primary histological subtypes: well-differentiated carcinoids and poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinomas, which display distinct biological behaviors
[...] Read more.
Background: Ovarian neuroendocrine neoplasms (O-NENs) are extremely rare, representing less than 1% of all ovarian neoplasms and under 5% of all neuroendocrine tumors (NETs). They encompass two primary histological subtypes: well-differentiated carcinoids and poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinomas, which display distinct biological behaviors and prognoses. The ovary can also be a site of metastasis from extra-ovarian NETs. Owing to their rarity, clinical management lacks standardization, and diagnosis is often incidental following surgery for presumed epithelial ovarian neoplasms. Objectives: This review aims to provide an updated synthesis of current evidence on the epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation, diagnosis, treatment strategies, and prognosis of O-NENs, highlighting unmet clinical needs. Methods: A literature search was performed on PubMed for the years 2014–2024 using the keywords: “ovarian neuroendocrine tumor”, “ovarian neuroendocrine neoplasm”, “ovarian neuroendocrine carcinoma”, and “ovarian carcinoid”. Only articles published in English were considered. Given the rarity of the disease, in addition to meta-analyses and systematic reviews, relevant case reports and case series were also included to provide a comprehensive clinical picture, yielding 32 eligible articles. Results: Evidence indicates that O-NENs remain understudied, with most data derived from case reports and small series. Clinical presentations vary from asymptomatic masses to hormone-related syndromes, often mimicking other ovarian pathologies. Diagnostic work-up typically follows the same protocol as epithelial ovarian cancer, with the neuroendocrine nature only recognized postoperatively. Treatment strategies are empirical and largely extrapolated from extra-ovarian NETs due to the absence of specific guidelines. Prognosis varies widely depending on histotype, stage, and secretory activity. Conclusions: O-NENs pose significant diagnostic and therapeutic challenges due to their rarity and heterogeneity. Greater clinical awareness, multidisciplinary management, and multicenter research are essential to establish evidence-based protocols and improve patient outcomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures
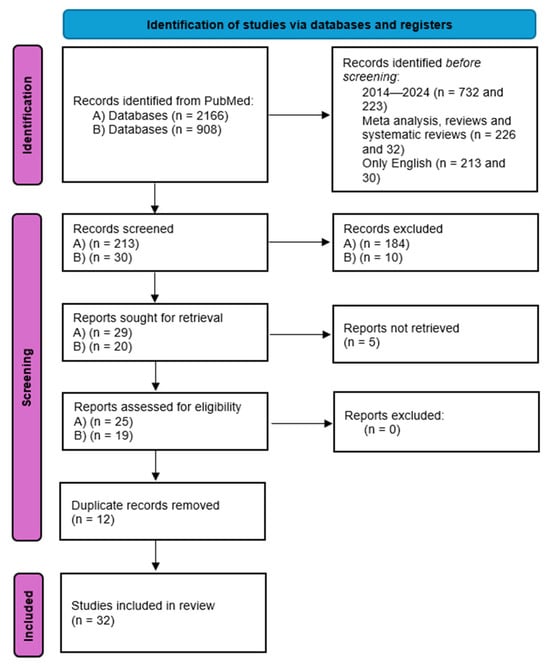
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Multicentre Trial Evaluating the Safety and Tolerability of Estetrol-Drospirenone Combined Oral Contraceptive in Postmenarchal Female Adolescents
by
Angelica Lindén Hirschberg, Lali Pkhaladze, Kristina Gemzell-Danielsson, Kai Haldre, Kateryna Ruban, Nina Flerin, Guillaume Chatel and Dan Apter
J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14(24), 8832; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248832 (registering DOI) - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
Objectives: This study aims to evaluate the safety and tolerability of estetrol/drospirenone in adolescents. Methods: In this Phase 3 open-label study, postmenarchal adolescents (12–17 years) received estetrol (E4)/drospirenone (DRSP) 15 mg/3 mg orally for six cycles (24 active/4 placebo regimen). Safety
[...] Read more.
Objectives: This study aims to evaluate the safety and tolerability of estetrol/drospirenone in adolescents. Methods: In this Phase 3 open-label study, postmenarchal adolescents (12–17 years) received estetrol (E4)/drospirenone (DRSP) 15 mg/3 mg orally for six cycles (24 active/4 placebo regimen). Safety was evaluated through adverse event (AE) reporting. Participants also recorded daily pill intake, bleeding/spotting, dysmenorrhea, and pain medication use in e-diaries. Descriptive statistics were used. Results: Of 112 enrolled participants, 105 received treatment (mean age: 15.2 years), and 84.8% were completers. No serious treatment-related AEs or safety concerns were observed. Nausea and dysmenorrhea (each 1.9%) were the most common treatment-related AEs. Over 71% of participants took all tablets in each cycle. The percentage of participants with unscheduled bleeding and/or spotting decreased from 45.8% (Cycle 1) to 14.5% (Cycle 5), and the number of days with unscheduled bleeding and/or spotting decreased from nine to six days per cycle. The scheduled bleeding and/or spotting rate ranged between 77.4% and 90.5%, with a duration decreasing from six to four days in Cycle 1 to Cycle 5. Absence of scheduled bleeding increased from 9.5% in Cycle 3 to 22.6% in Cycle 5. The proportion of participants reporting dysmenorrhea decreased by 34.8%, with a median visual analogue scale score dropping from 5.0 at baseline to 3.7 at Cycle 6. Pain medication use decreased from 63.9% to 31.6% in Cycle 6. Conclusions: The use of E4/DRSP in adolescents raised no safety concerns, was well tolerated, resulted in a clear and stable cyclic bleeding pattern, and reduced pain associated with dysmenorrhea.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology)
►▼
Show Figures
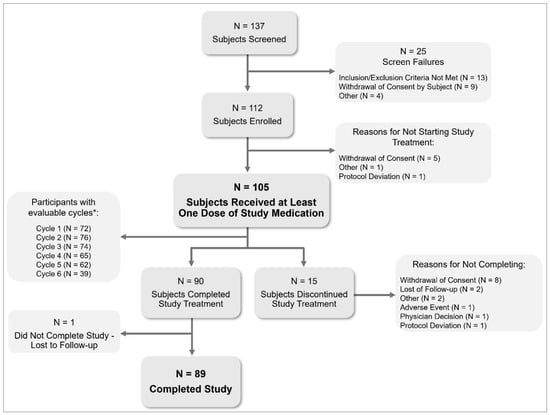
Figure 1
Open AccessBrief Report
Combination Treatment of Persistent SARS-CoV-2 Infection with Dual Antiviral Therapy and Intravenous Immunoglobulin: A Novel Approach
by
Myrto Blizou, Stefanos Lampadakis, Emmanouil Karofylakis, Andromachi Blizou, Konstantinos Thomas, Spyridon Prountzos, Vasileios Papavasileiou, Thomas Raptakis, Effrosyni D. Manali, Spyros A. Papiris, Stelios Loukides and Elvira-Markela Antonogiannaki
J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14(24), 8831; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248831 (registering DOI) - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Immunocompromised patients, particularly those with humoral immune deficiencies or receiving B-cell-targeted therapies, are at increased risk of persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection, a condition often underrecognized and lacking standardized treatment. Methods: We present a case series of patients with persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection and underlying
[...] Read more.
Background: Immunocompromised patients, particularly those with humoral immune deficiencies or receiving B-cell-targeted therapies, are at increased risk of persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection, a condition often underrecognized and lacking standardized treatment. Methods: We present a case series of patients with persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection and underlying humoral immunodeficiency, treated at the General University Hospital “Attikon” from February 2023 to September 2024. Persistent infection was defined by prolonged symptoms, compatible imaging findings, and RT-PCR positivity beyond 21 days. All patients received combination antiviral therapy with remdesivir and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir, and intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), using a structured diagnostic and therapeutic algorithm. Results: Eleven patients (55% male), median age 56 [IQR 50–66] years, were included. Seven (64%) had hematologic malignancy, 10 (91%) received anti-CD20 therapy, and 6 (55%) had both. Median symptom duration before diagnosis was 63 [58–135] days. Ten (91%) experienced recurrent symptoms; one (9%) had progressive symptoms with severe respiratory failure requiring high-flow nasal cannula. Persistent infection was confirmed via bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage in 6 patients (55%). Prior to diagnosis, 5 patients (45%) required one hospitalization, 1 (9%) was hospitalized twice, and 2 (18%) had more than two hospitalizations. Following combination therapy, 10 (91%) achieved complete response at 180-day follow-up. Conclusions: The proposed diagnostic and therapeutic algorithm combining remdesivir, nirmatrelvir/ritonavir, and IVIG enhanced diagnostic value and therapeutic outcomes in this high-risk population.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Coronavirus Disease 2019: Clinical Presentation, Pathogenesis and Treatment)
Open AccessArticle
Immediate Loading of Implants Placed Immediately in Fresh Sockets: A 10-Year Single-Arm Prospective Case Series Follow-Up
by
Eugenio Velasco-Ortega, Ivan Ortiz-Garcia, Loreto Monsalve-Guil, José López-López, Enrique Núñez-Márquez, Nuno Matos-Garrido, José Luis Rondón-Romero, Álvaro Jiménez-Guerra and Jesús Moreno-Muñoz
J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14(24), 8830; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248830 (registering DOI) - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
Implant dentistry is an important treatment option for patients requiring prosthetic rehabilitation after tooth loss. This study reports the evaluation of immediately loaded, immediately placed implants in fresh extraction sockets. Methods. Fifty-two partially edentulous patients (27 females and 25 males with mean
[...] Read more.
Implant dentistry is an important treatment option for patients requiring prosthetic rehabilitation after tooth loss. This study reports the evaluation of immediately loaded, immediately placed implants in fresh extraction sockets. Methods. Fifty-two partially edentulous patients (27 females and 25 males with mean age of 53.6 years), were treated with 112 Galimplant ® implants placed immediately into fresh sockets for prosthodontic rehabilitation. All implants were loaded immediately. Clinical and radiographic parameters related to both the implants and the prosthodontic restorations were followed for 10 years. Results. Nine patients (17.3%) had a history of periodontitis, 26.9% were smokers, and 21.1% presented with chronic systemic conditions. The outcomes demonstrated an implant survival and success rate of 97.1%, indicating that immediately placed implants with immediate loading can achieve and maintain successful osseointegration. Three implants were lost during the healing period. The mean marginal bone loss was 1.09 ± 0.75 mm. Mucositis affected 21.4% of implants, and peri-implantitis was observed in 11.6% of implants. Fourteen implants (7.1%) were associated with technical complications, including screw loosening and ceramic chipping. Conclusions. The clinical findings of this study indicate favorable long-term outcomes for immediately loaded implants placed in fresh extraction sockets. Both implants and prosthetic restorations demonstrated a success rate of over 92.9% during the observation period.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Clinical Updates on Prosthodontics)

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- JCM Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Dentistry Journal, JCM, Materials, Biomedicines, Life
Medical and Dental Care, Photobiomodulation and Photomedicine
Topic Editors: Samir Nammour, Chukuka Samuel Enwemeka, Aldo Brugnera JuniorDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topic in
Applied Sciences, IJERPH, JCM, JPM, Technologies, Healthcare
Smart Healthcare: Technologies and Applications, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Gang Kou, Shuai Ding, Li Luo, Tian Lu, Yogesan KanagasingamDeadline: 20 January 2026
Topic in
JFMK, Medicina, Therapeutics, Healthcare, JCM, Rheumato
New Trends in Physiotherapy Care: Improvements in Functionality, Pain Management, and Quality of Life
Topic Editors: Carlos Bernal-Utrera, Ernesto Anarte-Lazo, Juan José González GerezDeadline: 3 March 2026
Topic in
Biomedicines, Diagnostics, Endocrines, JCM, JPM, IJMS
Development of Diagnosis and Treatment Modalities in Obstetrics and Gynecology
Topic Editors: Osamu Hiraike, Fuminori TaniguchiDeadline: 20 March 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
JCM
Aortic Pathologies: Aneurysm, Atherosclerosis and More
Guest Editors: Alexander Gombert, Panagiotis DoukasDeadline: 15 December 2025
Special Issue in
JCM
Clinical Advancements in Intraocular Lens Power Calculation Methods
Guest Editors: Christoph Martin Lwowski, Thomas KohnenDeadline: 15 December 2025
Special Issue in
JCM
Latest Advances in Pediatric Surgery
Guest Editors: Francesco Macchini, Andrea ZaniniDeadline: 15 December 2025
Special Issue in
JCM
Physical Activity, Exercise and Health: Clinical Management and Research
Guest Editors: Do-yeon Kim, Dae Yun Seo, Ju-yong BaeDeadline: 15 December 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
JCM
Coronavirus Disease 2019: Clinical Presentation, Pathogenesis and Treatment
Collection Editor: Vito Racanelli
Topical Collection in
JCM
Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology
Collection Editor: Panagiotis Christopoulos
Topical Collection in
JCM
New Insights into Hepato-Biliary Diseases: Translating Science into Practice
Collection Editors: Elisa Ceccherini, Antonella Cecchettini











