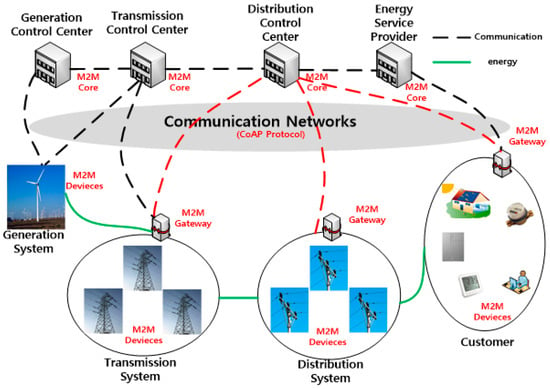
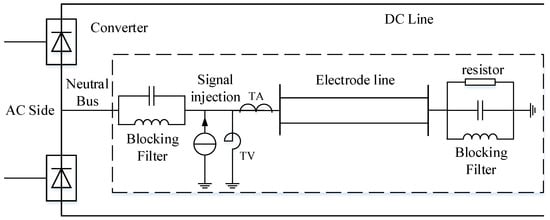
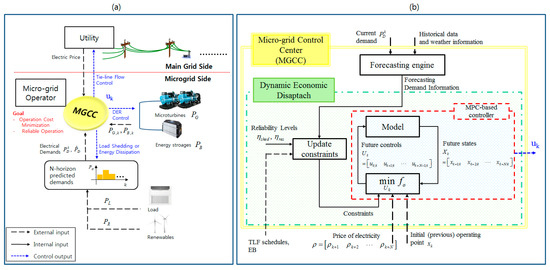
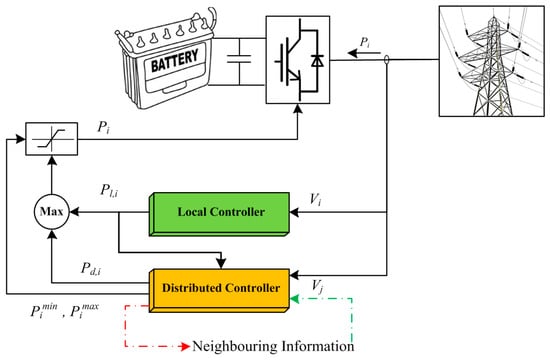
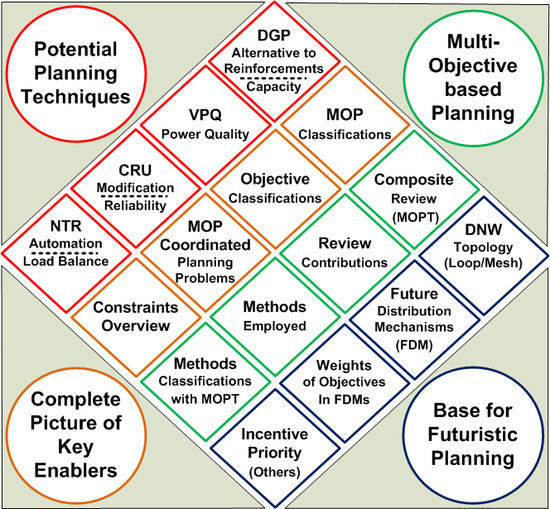
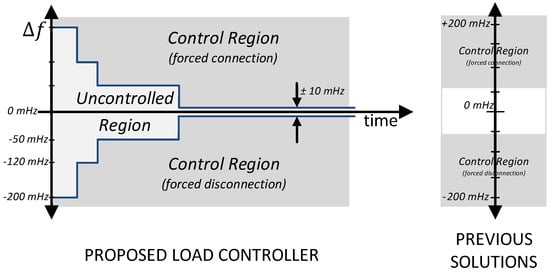
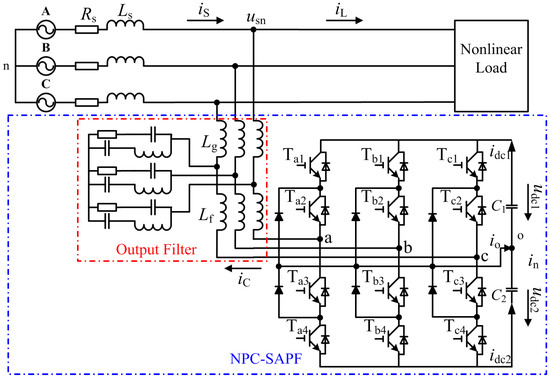
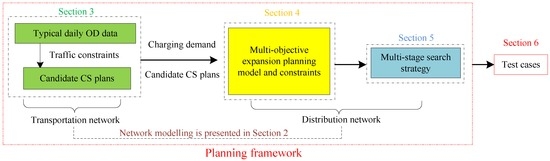
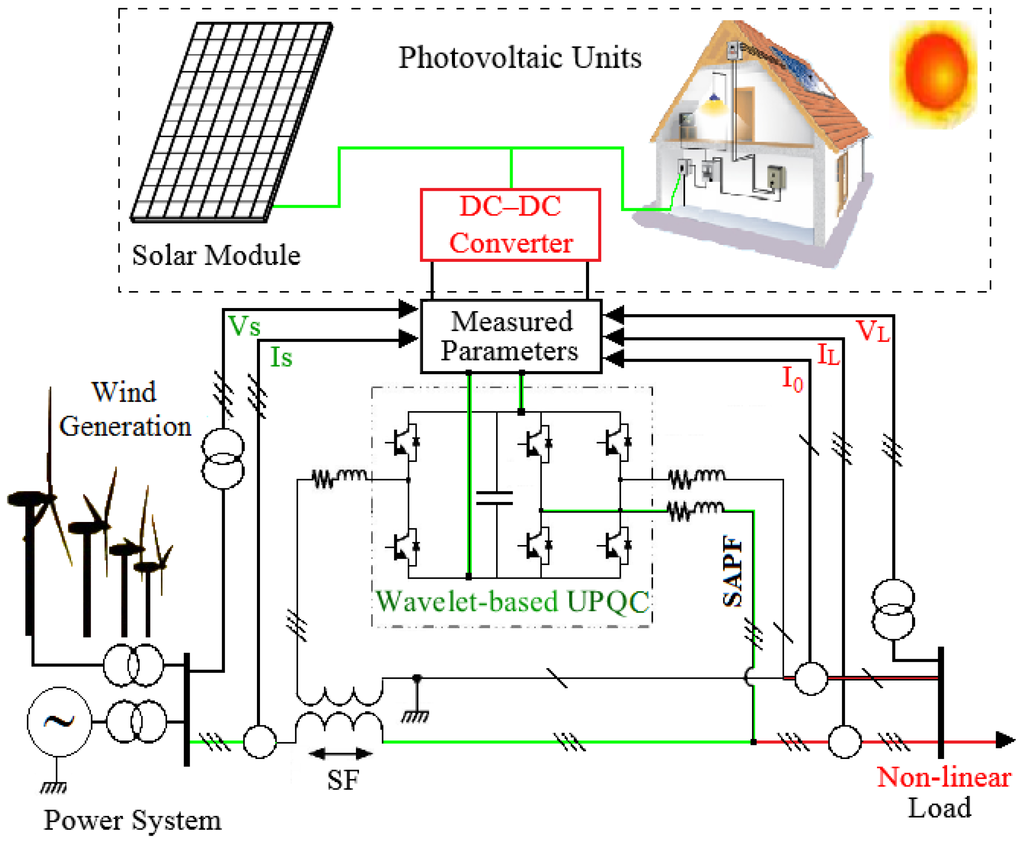
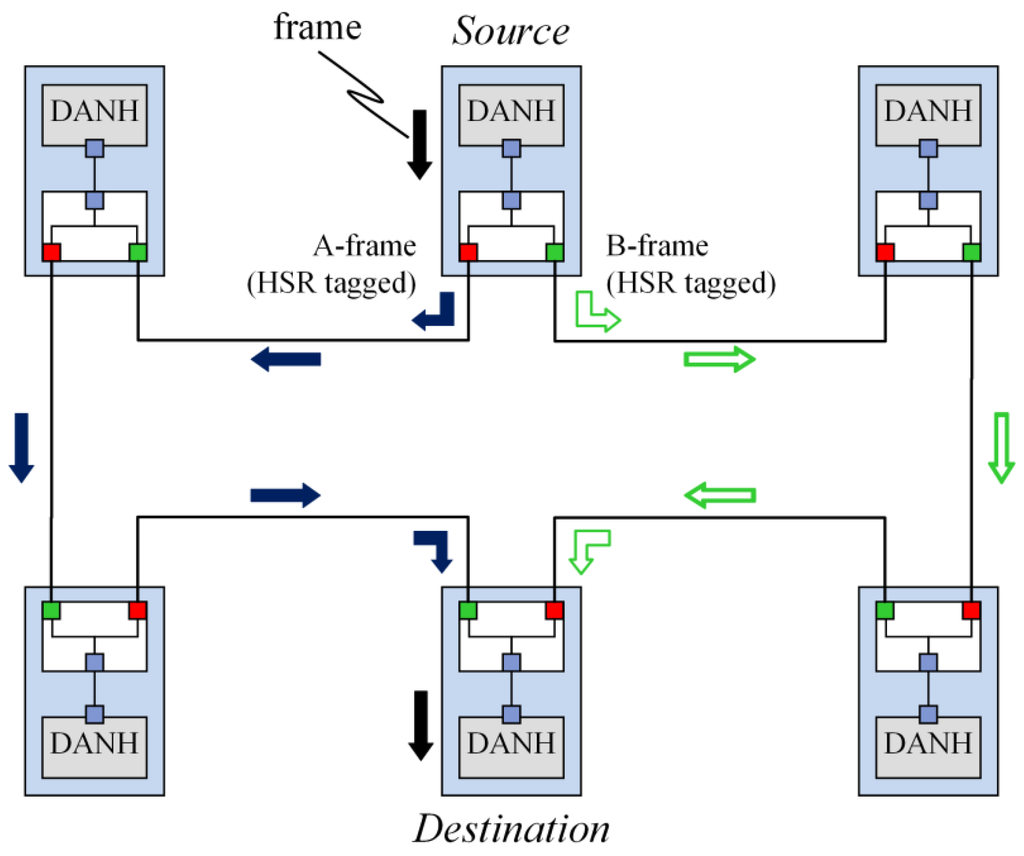
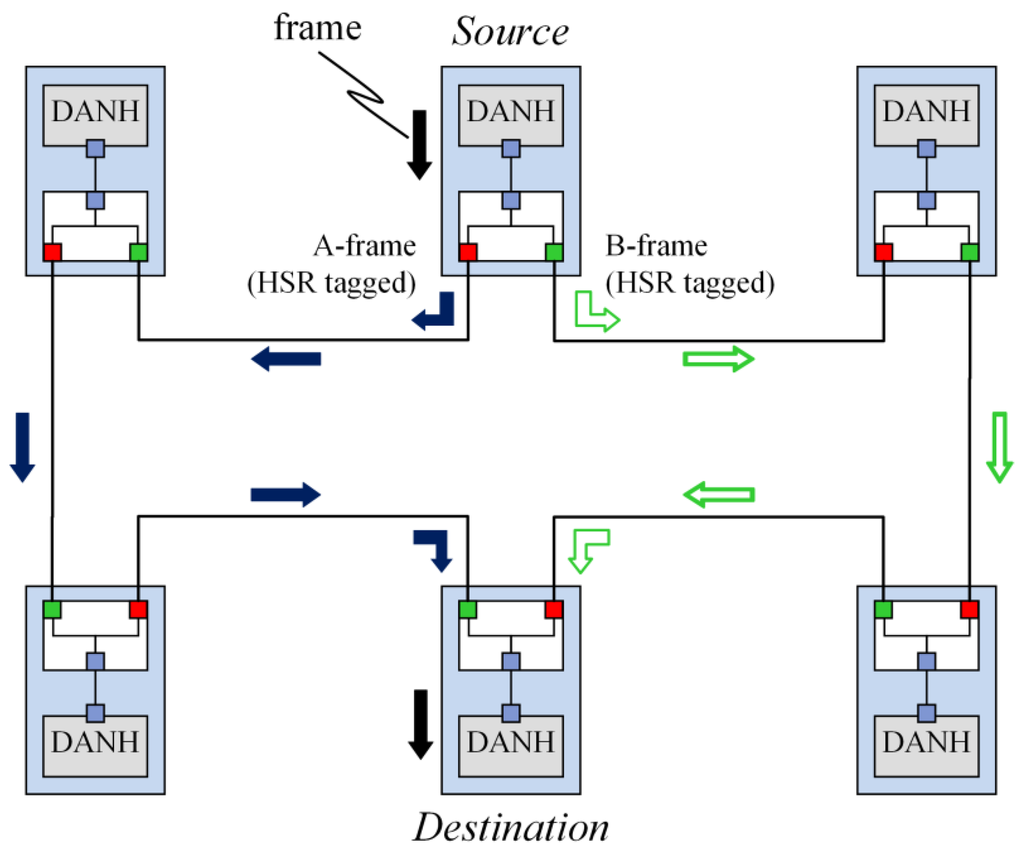
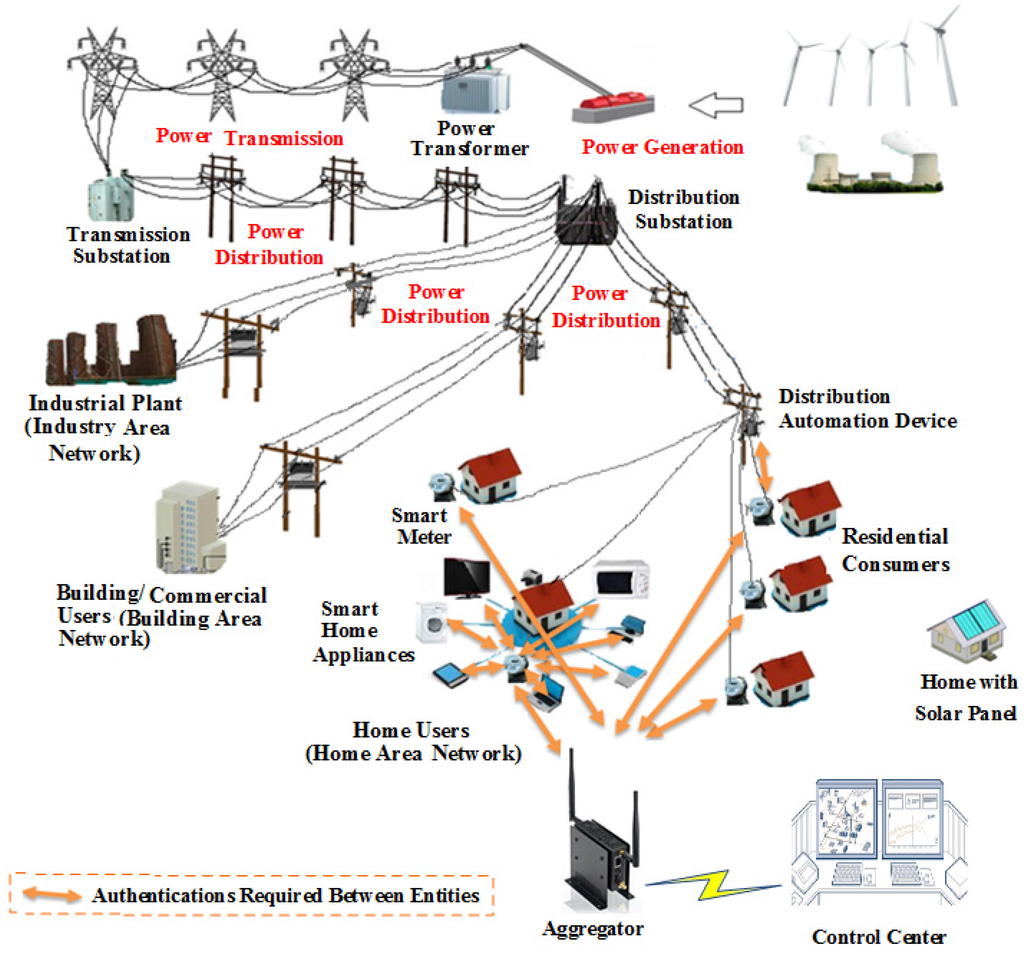
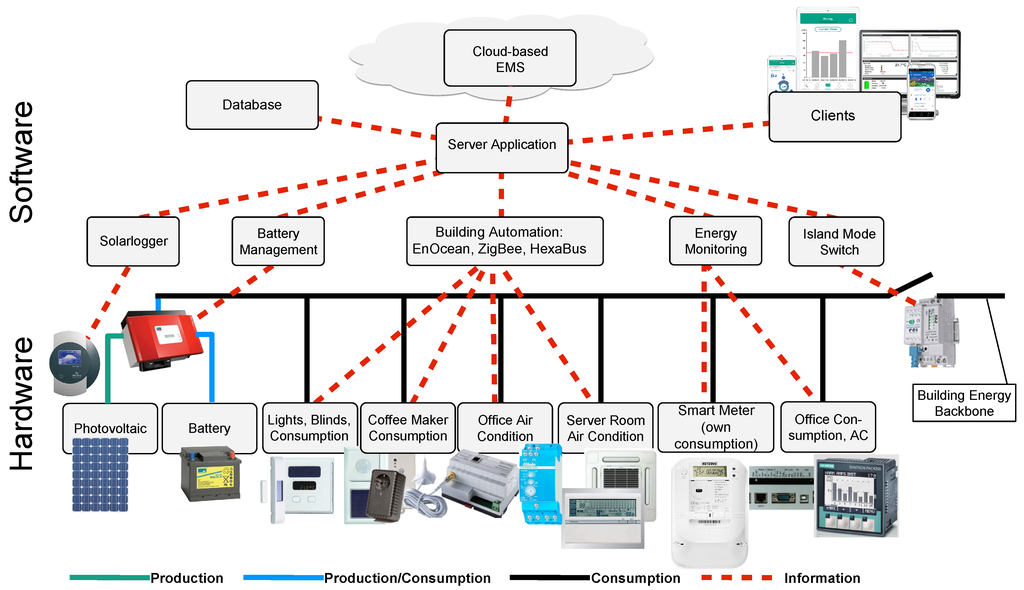
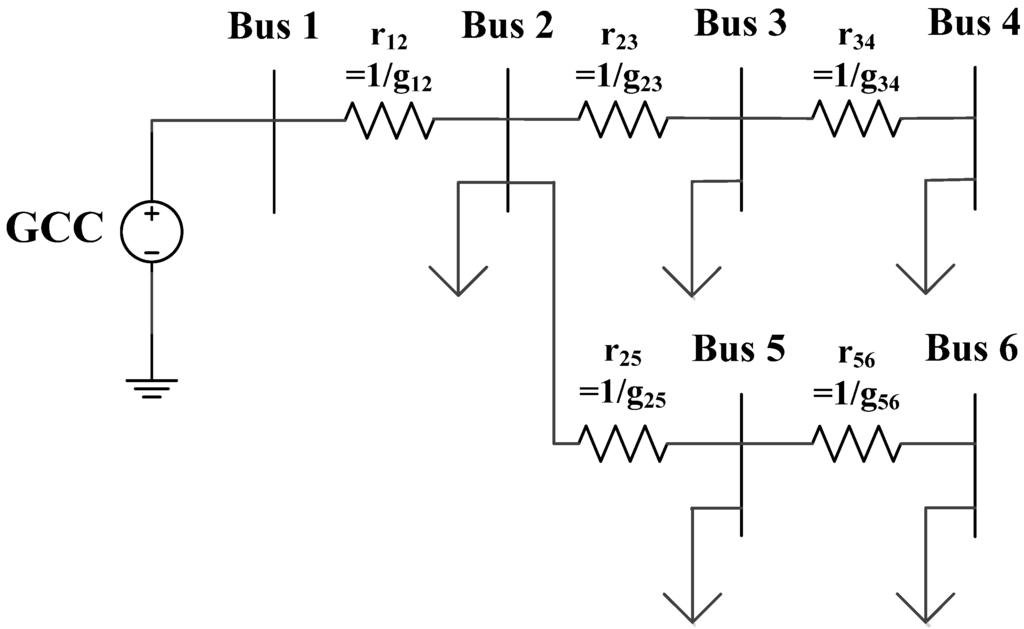
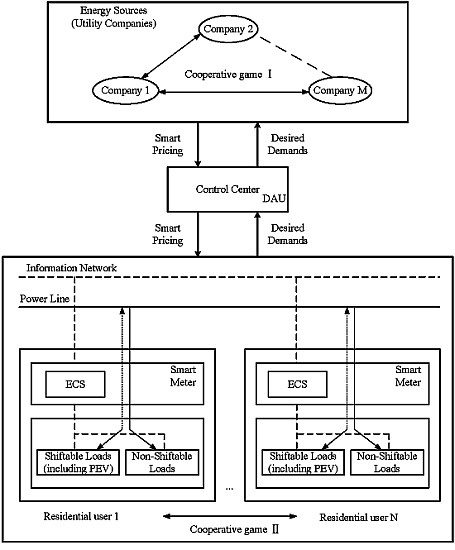
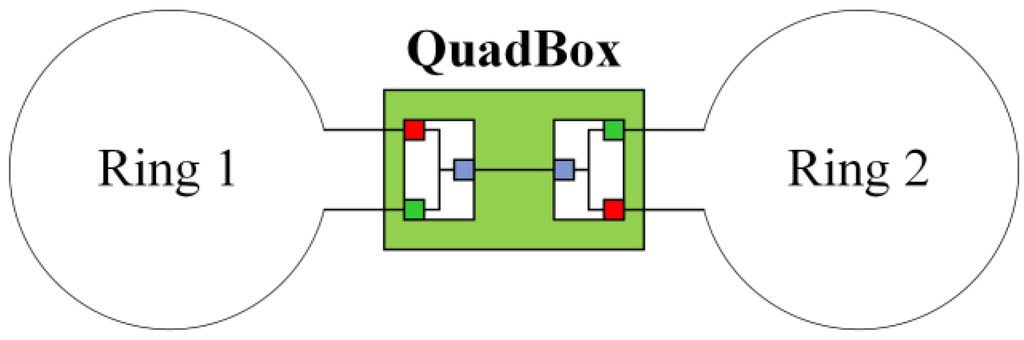
Smart Grid
A topical collection in Energies (ISSN 1996-1073).
Viewed by 571947
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Prof. Dr. Neville R. Watson
Prof. Dr. Neville R. Watson
 Prof. Dr. Neville R. Watson
Prof. Dr. Neville R. Watson
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, University of Canterbury, Private Bag 4800, Christchurch 8140, New Zealand
Interests: power quality; harmonics; electromagnetic transients; HVDC transmission; computer modelling of electrical power systems
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
The need to deliver electricity to customers: reliably, safely and cost effectively and in a sustainable manner, is always with us. To do this given the multiplicity of constraints means the electrical power system must be carefully engineered, not only to meet today's needs, but for the foreseeable future. The Smart Grid initiative is really about making the grid smarter than it is already (as in many cases the grid is already "smart") so as to achieve these objectives. Many countries are devoting time and resources to this initiative due to the immense potential benefits. The perceived benefits are:
- Improved reliability and resilience
- Better operational efficiency
- Better utilization of resources
- Better utilization of assets
- Adequate Power Quality
The term Smart Grid means different things to different people as the perceived benefits, and hence drivers, are different in different countries. Regardless of one's concept of a Smart Grid, the need for a reliable two-way communication system is central. Because of the entwining of both the electrical power system and communication system to form a Smart Grid the two streams to this collection are Smart Grid communications and Smart Grid electrical power system.
Papers in the relevant area of Smart Grid communications, including but not limited to the following, are invited:
- Architectures and Models for Smart Grid
- Smart Grid Sensors, Communications, Computing and Control
- Cyber-Physical Wide-Area Monitoring, Protection & Control (Cyber-Physical WAMPAC)
- Local-Area and Wide-Area networks for Smart Grids and Smart Metering
- Demand Side Management, Demand Response, Dynamic Pricing
- Communications support for Storage, Renewable Resources and Micro-Grids
- Smart Grid Cyber Security and Privacy
- Smart Grid Services and Management Models
- Smart Grid Standards, Test-Beds and Field Trials
Papers in the relevant area of Smart Grid electrical power system, including but not limited to the following, are invited:
- Resilience in the face of faults and disasters
- Load management and Load Balancing
- Customer participation
- Integration of renewable technology
- Security & Reliability of the electricity network
- Smart Algorithms and Devices
- Smart Grid Modelling
- Application of Smart Grid concept to Homes, Distribution or Transmission Systems
- Architectures for Smart Grids
- Power Quality
- Power Transmission in a Smart Grid
Prof. Dr. Neville R. Watson
Emeritus Professor Harsha Sirisena
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts for the topical collection can be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. All papers will be peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on this website. The topical collection considers regular research articles, short communications and review articles. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The article processing charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss francs).
Related Special Issues
Published Papers (130 papers)
Open AccessArticle
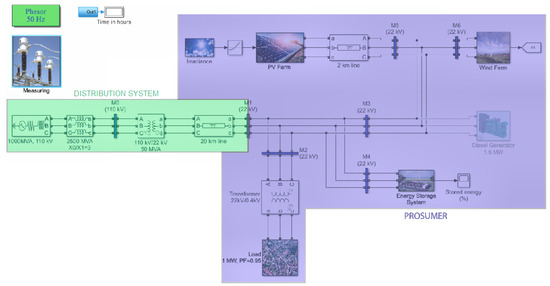
Analysis of Prosumer Behavior in the Electrical Network
by
Dušan Medveď, Michal Kolcun, Marek Pavlík, Ľubomír Beňa and Marián Mešter
Cited by 19 | Viewed by 3151
Abstract
This article deals with the prosumer behavior, specifically on an on-grid electrical network that is connected to a larger synchronous electrical network, as well as an off-grid system. In the Simulink (Matlab) application, two models were constructed for this purpose. The modeling of
[...] Read more.
This article deals with the prosumer behavior, specifically on an on-grid electrical network that is connected to a larger synchronous electrical network, as well as an off-grid system. In the Simulink (Matlab) application, two models were constructed for this purpose. The modeling of the operation of the electrical network’s on-grid system takes place in one of the models. The simulation of the operation of the electrical network’s off-grid system takes place in the other. We examined the model’s behavior in the provided simulated period from the standpoint of transient states and qualitative indicators of electrical energy under various connection configurations in both systems. The simulations resulted in the possibility of incorporating new sources of energy accumulation, such as pumped storage hydropower plants based on energy storage systems (ESSs), and modifying the model to the user’s needs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
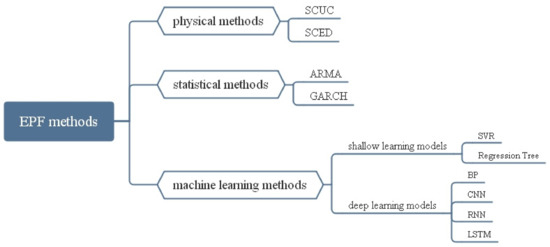
A Multiscale Electricity Price Forecasting Model Based on Tensor Fusion and Deep Learning
by
Xiaoming Xie, Meiping Li and Du Zhang
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 2566
Abstract
The price of electricity is an important factor in the electricity market. Accurate electricity price forecasting (EPF) is very important to all competing electricity market parties. Decision-making in the electricity market is highly dependent on electricity prices, making an EPF model an important
[...] Read more.
The price of electricity is an important factor in the electricity market. Accurate electricity price forecasting (EPF) is very important to all competing electricity market parties. Decision-making in the electricity market is highly dependent on electricity prices, making an EPF model an important part of the orderly and efficient operation of the electricity market. Especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, the prices of raw materials for electricity production, such as coal, have risen sharply. Forecasting electricity prices has become particularly important. Currently, existing EPF prediction models face two main challenges: First, how to integrate multiscale electricity price data to obtain a higher prediction accuracy. Second, how to solve the problem of data noise caused by the fusion of EPF samples and multiscale data. To solve the above problems, we innovatively propose a tensor decomposition method to integrate multiscale electricity price data and use
regularization and wavelet transform to remove data noise. In general, this paper proposes a deep learning EPF prediction model, named the WT_TDLSTM model, based on tensor decomposition, a wavelet transform, and long short-term memory (LSTM). Among them, the LSTM method is used to predict electricity prices. We conducted experiments on three datasets. The experimental results of three data prove that the WT_TDLSTM model is better than the compared EPF model. The indicators of MSE and RMSE are 33.65–99.97% better than the comparison model. We believe that the WT_TDLSTM model is a good supplement to the EPF model.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
A Review of DC Microgrid Energy Management Systems Dedicated to Residential Applications
by
Sadaqat Ali, Zhixue Zheng, Michel Aillerie, Jean-Paul Sawicki, Marie-Cécile Péra and Daniel Hissel
Cited by 189 | Viewed by 11998
Abstract
The fast depletion of fossil fuels and the growing awareness of the need for environmental protection have led us to the energy crisis. Positive development has been achieved since the last decade by the collective effort of scientists. In this regard, renewable energy
[...] Read more.
The fast depletion of fossil fuels and the growing awareness of the need for environmental protection have led us to the energy crisis. Positive development has been achieved since the last decade by the collective effort of scientists. In this regard, renewable energy sources (RES) are being deployed in the power system to meet the energy demand. The microgrid concept (AC, DC) is introduced, in which distributed energy resources (DERs), the energy storage system (ESS) and loads are interconnected. DC microgrids are appreciated due to their high efficiency and reliability performance. Despite its significant growth, the DC microgrid is still relatively novel in terms of grid architecture and control systems. In this context, an energy management system (EMS) is essential for the optimal use of DERs in secure, reliable, and intelligent ways. Therefore, this paper strives to shed light on DC microgrid architecture, control structure, and EMS. With an extensive literature survey on EMSs’ role, different methods and strategies related to microgrid energy management are covered in this article. More attention is centered on the EMS for DC microgrids in terms of size and cost optimization. A very concise analysis of multiple optimization methods and techniques has been presented exclusively for residential applications.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
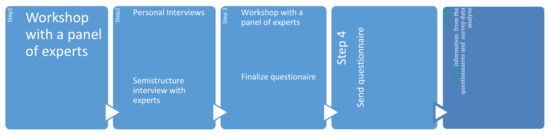
Acceptance of Demand Response and Aggregators as a Solution to Optimize the Relation between Energy Producers and Consumers in order to Increase the Amount of Renewable Energy in the Grid
by
Adrian Tantau, András Puskás-Tompos, Laurentiu Fratila and Costel Stanciu
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 4036
Abstract
Demand response plays a very important role in balancing the intermittent production of an increasing share of renewable energy sources on the energy market. This article analyses the importance of demand response and the role of aggregators for the new development of the
[...] Read more.
Demand response plays a very important role in balancing the intermittent production of an increasing share of renewable energy sources on the energy market. This article analyses the importance of demand response and the role of aggregators for the new development of the electricity market, where the renewables will play a more important role. The main objective of this research is to determine the acceptance level of demand response and its implementation on the energy consumer side. This acceptance should include a professional actor, the aggregator which is assuming the role of optimizing the relation between energy producers and consumers, and to monitor the implementation and use of demand response. The research is based on semi-structured interviews with experts in energy from Hungary, Romania and Serbia, on workshops with experts and a wider online survey with end customers for electricity. The results indicate that there is a willingness potential to implement demand response programs with aggregators as intermediaries between energy providers and end consumers of electrical energy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
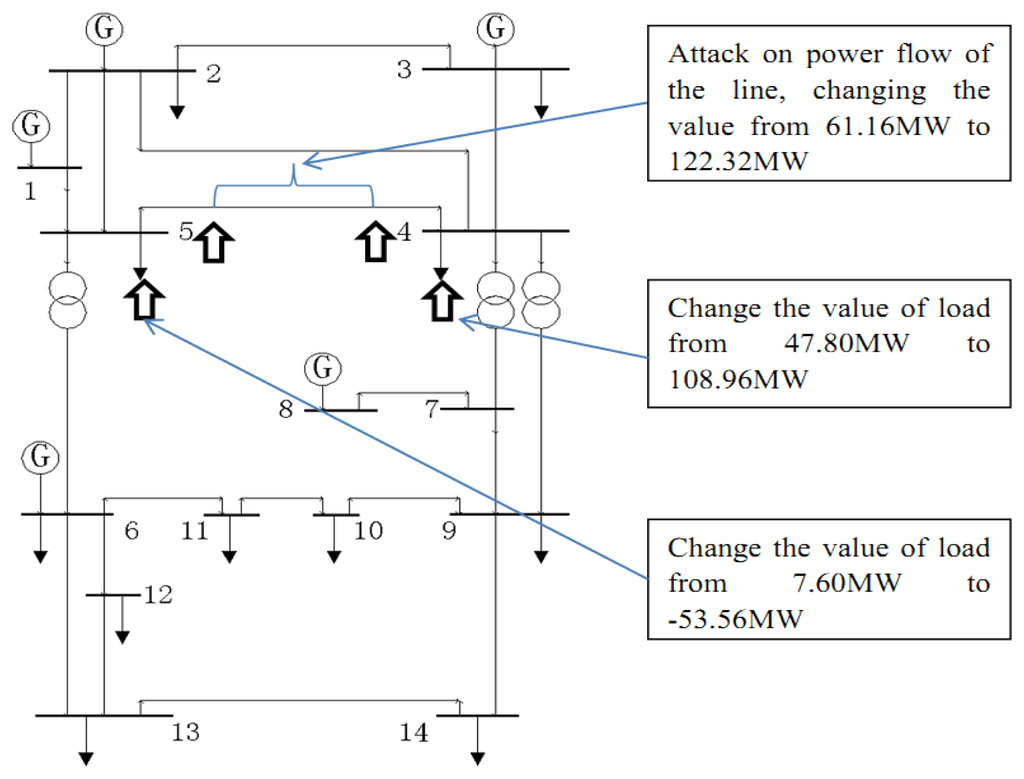
A Practical GERI-Based Method for Identifying Multiple Erroneous Parameters and Measurements Simultaneously
by
Ruipeng Guo, Lilan Dong, Hao Wu, Fangdi Hou and Chen Fang
Viewed by 2259
Abstract
Even with modern smart metering systems, erroneous measurements of the real and reactive power in the power system are unavoidable. Multiple erroneous parameters and measurements may occur simultaneously in the state estimation of a bulk power system. This paper proposes a gross error
[...] Read more.
Even with modern smart metering systems, erroneous measurements of the real and reactive power in the power system are unavoidable. Multiple erroneous parameters and measurements may occur simultaneously in the state estimation of a bulk power system. This paper proposes a gross error reduction index (GERI)-based method as an additional module for existing state estimators in order to identify multiple erroneous parameters and measurements simultaneously. The measurements are acquired from a supervisory control and data acquisition system and mainly include voltage amplitudes, branch current amplitudes, active power flow, and reactive power flow. This method uses a structure consisting of nested two loops. First, gross errors and the GERI indexes are calculated in the inner loop. Second, the GERI indexes are compared and the maximum GERI in each inner loop is associated with the most suspicious parameter or measurement. Third, when the maximum GERI is less than a given threshold in the outer loop, its corresponding erroneous parameter or measurement is identified. Multiple measurement scans are also adopted in order to increase the redundancy of measurements and the observability of parameters. It should be noted that the proposed algorithm can be directly integrated into the Weighted Least Square estimator. Furthermore, using a faster simplified calculation technique with Givens rotations reduces the required computer memory and increases the computation speed. This method has been demonstrated in the IEEE 14-bus test system and several matpower cases. Due to its outstanding practical performance, it is now used at six provincial power control centers in the Eastern Grid of China.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
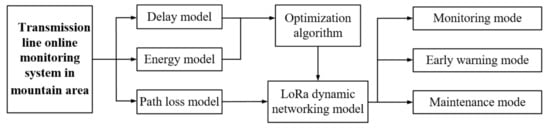
Monitoring System of Transmission Line in Mountainous Area Based on LPWAN
by
Han Zeng, Pengqi Zuo, Fangming Deng and Pei Zhang
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 3501
Abstract
In light of the difficulty of the inspection and maintenance of a transmission line condition monitoring system in remote mountainous areas, this paper proposes a long-term online monitoring scheme based on a low power wide area network (LPWAN). Considering different failure rates, three
[...] Read more.
In light of the difficulty of the inspection and maintenance of a transmission line condition monitoring system in remote mountainous areas, this paper proposes a long-term online monitoring scheme based on a low power wide area network (LPWAN). Considering different failure rates, three monitoring periods of transmission lines in mountainous areas are proposed. An online monitoring framework of transmission lines in mountainous areas was designed based on long range radio (LoRa) and a cellular mobile network, and a dynamic group network model of LoRa was established. The multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm can be used to optimize the energy and delay of the system, and then the suitable working mode for the three monitoring periods can be obtained. The simulation results showed that the minimum packet loss rate of the system could be less than 1%, the energy consumption of the system was 80% lower than the existing monitoring system, and the service life of the system can reach 15.13 years under the normal failure rate. Compared with the existing schemes, the proposed work shows the advantages of high reliability transmission, low cost and long-term monitoring, which is especially for transmission line monitoring in mountainous areas.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
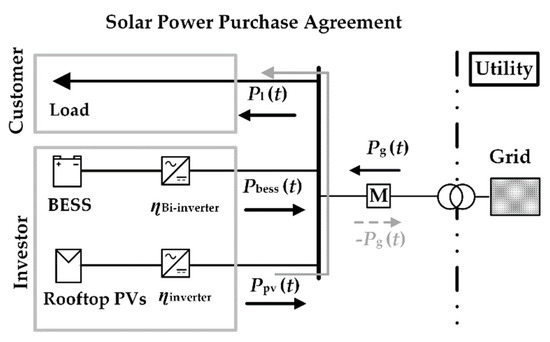
Designing Solar Power Purchase Agreement of Rooftop PVs with Battery Energy Storage Systems under the Behind-the-Meter Scheme
by
Chawin Prapanukool and Surachai Chaitusaney
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 3585
Abstract
With a significant growth of rooftop photovoltaic systems (PVs) with battery energy storage systems (BESS) under the behind-the-meter scheme (BTMS), the solar power purchase agreement (SPPA) has been developed into one of the most attractive models. The SPPA is a scheme where the
[...] Read more.
With a significant growth of rooftop photovoltaic systems (PVs) with battery energy storage systems (BESS) under the behind-the-meter scheme (BTMS), the solar power purchase agreement (SPPA) has been developed into one of the most attractive models. The SPPA is a scheme where the investors propose to directly sell electricity from rooftop PVs to the customers. The proposed rates are typically performed in terms of the discount rates on the time-of-use (TOU) tariff with demand charges. The operation modes of the BESS should also be designed in accordance with the proposed rates. Therefore, this paper proposes a methodology to design the discount rates and operation modes of the BESS which will minimize the electricity charges of the customers while maintaining the revenue of the investors under the SPPA and BTMS. The reverse power flow is considered as additional revenue to the investors. This paper also implements the proposed methodology with tariff structure in Thailand. The result showed that the installed capacity of rooftop PVs and battery capacity directly affect the discount rates and operation modes of the BESS. The rate of excess energy also has a significant impact on the discount rates but not affect the operation modes.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
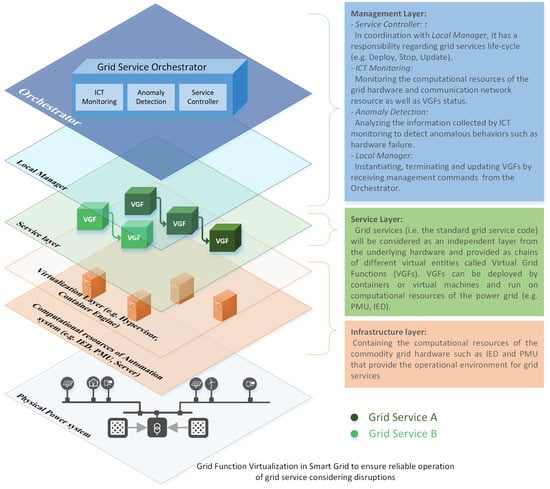
Virtualization Management Concept for Flexible and Fault-Tolerant Smart Grid Service Provision
by
Shadi Attarha, Anand Narayan, Batoul Hage Hassan, Carsten Krüger, Felipe Castro, Davood Babazadeh and Sebastian Lehnhoff
Cited by 22 | Viewed by 4921
Abstract
In modern power systems, reliable provision of grid services (e.g., primary and ancillary services) are highly dependent on automation systems in order to have monitoring, processing, decision making and communication capabilities. The operational flexibility of automation systems is essential for the reliable operation
[...] Read more.
In modern power systems, reliable provision of grid services (e.g., primary and ancillary services) are highly dependent on automation systems in order to have monitoring, processing, decision making and communication capabilities. The operational flexibility of automation systems is essential for the reliable operation of power systems during and after disruptive events. However, this is restricted by integrated hardware-software platforms. Therefore, it will be difficult to reconfigure control strategies during run time. This paper presents the concept of Grid Function Virtualization (GFV) as a potential approach to improve the operational flexibility of grid automation systems. GFV has been proposed to offer a new way to deploy and manage grid services by leveraging virtualization technology. The main idea of GFV is to run grid services (i.e., software implementation of services) independently from underlying hardware. To realize the important design considerations, the GFV architecture and its building blocks is elaborated in details. To this end, an exhaustive review of applications of virtualization in several domains is provided to show the importance of virtualization in improving flexibility and resource utilization. Finally, the advantages of the proposed concept to deal with disruptions in power systems is demonstrated in a proof of concept based on a CIGRE MV benchmark grid.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Intelligent Fault Detection System for Microgrids
by
Cristian Cepeda, Cesar Orozco-Henao, Winston Percybrooks, Juan Diego Pulgarín-Rivera, Oscar Danilo Montoya, Walter Gil-González and Juan Carlos Vélez
Cited by 51 | Viewed by 5068
Abstract
The dynamic features of microgrid operation, such as on-grid/off-grid operation mode, the intermittency of distributed generators, and its dynamic topology due to its ability to reconfigure itself, cause misfiring of conventional protection schemes. To solve this issue, adaptive protection schemes that use robust
[...] Read more.
The dynamic features of microgrid operation, such as on-grid/off-grid operation mode, the intermittency of distributed generators, and its dynamic topology due to its ability to reconfigure itself, cause misfiring of conventional protection schemes. To solve this issue, adaptive protection schemes that use robust communication systems have been proposed for the protection of microgrids. However, the cost of this solution is significantly high. This paper presented an intelligent fault detection (FD) system for microgrids on the basis of local measurements and machine learning (ML) techniques. This proposed FD system provided a smart level to intelligent electronic devices (IED) installed on the microgrid through the integration of ML models. This allowed each IED to autonomously determine if a fault occurred on the microgrid, eliminating the requirement of robust communication infrastructure between IEDs for microgrid protection. Additionally, the proposed system presented a methodology composed of four stages, which allowed its implementation in any microgrid. In addition, each stage provided important recommendations for the proper use of ML techniques on the protection problem. The proposed FD system was validated on the modified IEEE 13-nodes test feeder. This took into consideration typical features of microgrids such as the load imbalance, reconfiguration, and off-grid/on-grid operation modes. The results demonstrated the flexibility and simplicity of the FD system in determining the best accuracy performance among several ML models. The ease of design’s implementation, formulation of parameters, and promising test results indicated the potential for real-life applications.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
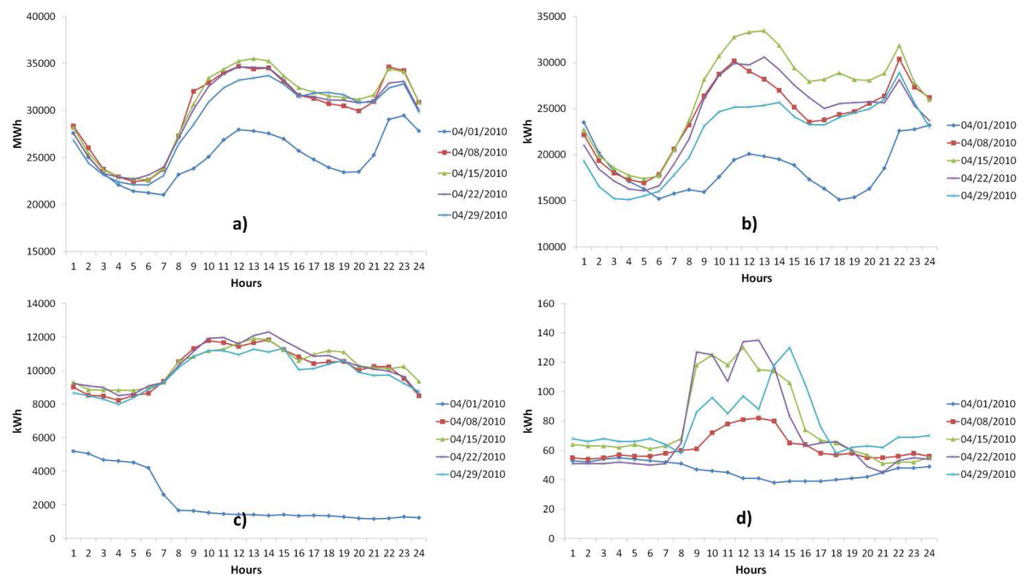
Influence and Impact of Data Averaging and Temporal Resolution on the Assessment of Energetic, Economic and Technical Issues of Hybrid Photovoltaic-Battery Systems
by
Alessandro Burgio, Daniele Menniti, Nicola Sorrentino, Anna Pinnarelli and Zbigniew Leonowicz
Cited by 25 | Viewed by 3527
Abstract
The temporal resolution of the demand and generation profiles may have a significant impact on the estimation of self-sufficiency and self-consumption for consumers and prosumers. As an example, measuring the load profile, with a low temporal resolution, may lead to the under-estimation of
[...] Read more.
The temporal resolution of the demand and generation profiles may have a significant impact on the estimation of self-sufficiency and self-consumption for consumers and prosumers. As an example, measuring the load profile, with a low temporal resolution, may lead to the under-estimation of energy consumption, while measuring solar irradiation with a low temporal resolution may lead to the over-estimation of on-site energy generation. Storage systems may reduce errors due to the lower temporal resolution by 8–10 times or even more, depending on the capacity of the batteries. Besides self-generation and self-consumption, there are other indicators that can be influenced by temporal resolution that deserve to be investigated. This is a detailed study of the influence of temporal resolution and the time averaging on a hybrid photovoltaic-battery system; this study encompasses both economic and technical aspects, from the calculation of savings on the electricity bill to the estimation of the equivalent cycles of battery storage system. To this end, the three-minute load profile of a real case study is used to obtain other three load profiles with temporal resolution equal to 15, 30, and 60 min via data averaging. Therefore, the authors analyze the influence and the impact of temporal resolution and data averaging in terms of: The size of the photovoltaic generator and the capacity of the storage system; the savings in the electricity bill and the balance between costs and savings; the peak values and the average values of power flows during high generation and low generation; the profile of the storage system over the year; the utilization rate of the storage system and the rated power of the electronic converter that regulates the charge and the discharge; the profile of the state of charge of the storage system and the life-time estimation of batteries through the calculation of the equivalent number of cycles.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
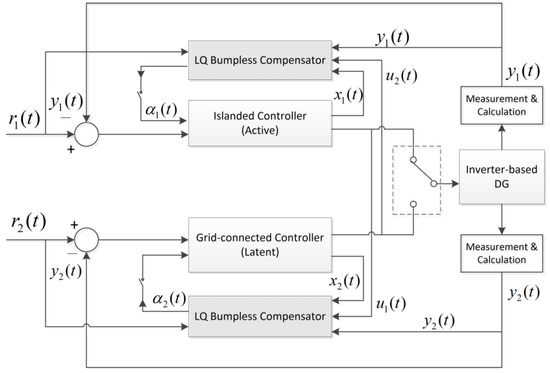
Bumpless Optimal Control over Multi-Objective Microgrids with Mode-Dependent Controllers
by
Ying Wu, Josep M. Guerrero, Juan C. Vasquez and Yanpeng Wu
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 3196
Abstract
To avoid transient jumps at the switching time between two operating modes in microgrids, this paper proposes a linear quadratic-based optimal bumpless controller with two degrees of freedom (DOF) to suppress the transient disturbance and realize seamless switching between mode-dependent controllers. By minimizing
[...] Read more.
To avoid transient jumps at the switching time between two operating modes in microgrids, this paper proposes a linear quadratic-based optimal bumpless controller with two degrees of freedom (DOF) to suppress the transient disturbance and realize seamless switching between mode-dependent controllers. By minimizing the transient performance criteria, which contains both the reference tracking error and the controller tracking error, this bumpless algorithm not only effectively forces the latent controller to track the active controller, but also guarantees the plant output track the reference as close as possible. For the different control objectives of the two modes, a current-based networked PI controller is proposed in islanded mode to achieve power sharing, as well as suppressing circulating current, and a power-based PI controller is designed in grid connected mode to supply required P and Q, as well as effectively synchronize f and v safely with the main grid. A microgrid test system with two operation modes was built in Matlab/Simulink. Several operating cases were executed to verity the feasibility and effectiveness of this optimal bumpless control strategy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
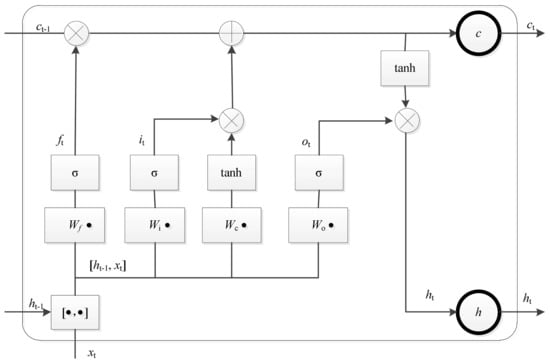
Recurrent Neural Networks Based Photovoltaic Power Forecasting Approach
by
Gangqiang Li, Huaizhi Wang, Shengli Zhang, Jiantao Xin and Huichuan Liu
Cited by 155 | Viewed by 7795
Abstract
The intermittency of solar energy resources has brought a big challenge for the optimization and planning of a future smart grid. To reduce the intermittency, an accurate prediction of photovoltaic (PV) power generation is very important. Therefore, this paper proposes a new forecasting
[...] Read more.
The intermittency of solar energy resources has brought a big challenge for the optimization and planning of a future smart grid. To reduce the intermittency, an accurate prediction of photovoltaic (PV) power generation is very important. Therefore, this paper proposes a new forecasting method based on the recurrent neural network (RNN). At first, the entire solar power time series data is divided into inter-day data and intra-day data. Then, we apply RNN to discover the nonlinear features and invariant structures exhibited in the adjacent days and intra-day data. After that, a new point prediction model is proposed, only by taking the previous PV power data as input without weather information. The forecasting horizons are set from 15 to 90 min. The proposed forecasting method is tested by using real solar power in Flanders, Belgium. The classical persistence method (Persistence), back propagation neural network (BPNN), radial basis function (RBF) neural network and support vector machine (SVM), and long short-term memory (LSTM) networks are adopted as benchmarks. Extensive results show that the proposed forecasting method exhibits a good forecasting quality on very short-term forecasting, which demonstrates the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed forecasting model.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Aggregating Large-Scale Generalized Energy Storages to Participate in the Energy and Regulation Market
by
Yao Yao, Peichao Zhang and Sijie Chen
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 3523
Abstract
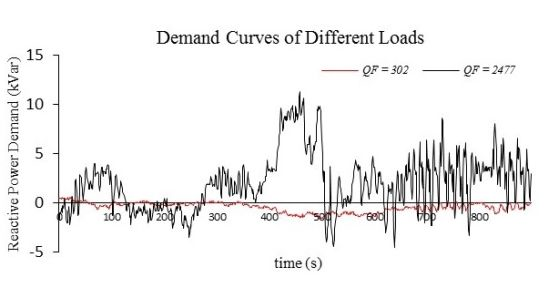
This paper proposes a concept of generalized energy storage (GES) to facilitate the integration of large-scale heterogeneous flexible resources with electric/thermal energy storage capacity, in order to participate in multiple markets. First, a general state variable, referred to as the degree of satisfaction
[...] Read more.
This paper proposes a concept of generalized energy storage (GES) to facilitate the integration of large-scale heterogeneous flexible resources with electric/thermal energy storage capacity, in order to participate in multiple markets. First, a general state variable, referred to as the degree of satisfaction (DoS), is defined, and dynamic models with a unified form are derived for different types of GESs. Then, a real-time market-based coordination framework is proposed to facilitate control, as well as to ensure user privacy and device security. Demand curves of different GESs are then developed, based on DoS, to express their demand urgencies as well as flexibilities. Furthermore, a low-dimensional aggregate dynamic model of a GES cluster is derived, thanks to the DoS-equality control feature provided by the design of the demand curve. Finally, an optimization model for large-scale GESs to participate in both the energy market and regulation market is established, based on the aggregate model. Simulation results demonstrate that the optimization algorithm could effectively reduce the total cost of an aggregator. Additionally, the proposed coordination method has a high tracking accuracy and could well satisfy a diversified power demand.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Economic Multiple Model Predictive Control for HVAC Systems—A Case Study for a Food Manufacturer in Germany
by
Tobias Heidrich, Jonathan Grobe, Henning Meschede and Jens Hesselbach
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 5192
Abstract
The following paper describes an economical, multiple model predictive control (EMMPC) for an air conditioning system of a confectionery manufacturer in Germany. The application consists of a packaging hall for chocolate bars, in which a new local conveyor belt air conditioning system is
[...] Read more.
The following paper describes an economical, multiple model predictive control (EMMPC) for an air conditioning system of a confectionery manufacturer in Germany. The application consists of a packaging hall for chocolate bars, in which a new local conveyor belt air conditioning system is used and thus the temperature and humidity limits in the hall can be significantly extended. The EMMPC calculates the optimum energy or cost humidity and temperature set points in the hall. For this purpose, time-discrete state space models and an economic objective function with which it is possible to react to flexible electricity prices in a cost-optimised manner are created. A possible future electricity price model for Germany with a flexible Renewable Energies levy (EEG levy) was used as a flexible electricity price. The flexibility potential is determined by variable temperature and humidity limits in the hall, which are oriented towards the comfort field for easily working persons, and the building mass. The building mass of the created room model is used as a thermal energy store. Considering the electricity price and weather forecasts as well as an internal, production plan-dependent load forecasts, the model predictive controller directly controls the heating and cooling register and the humidifier of the air conditioning system.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Efficient Economic and Resilience-Based Optimization for Disaster Recovery Management of Critical Infrastructures
by
Eng Tseng Lau, Kok Keong Chai, Yue Chen and Jonathan Loo
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 4173
Abstract
The traditional grid operation is unfortunately lacking the resilience and responsiveness in reacting to contingency events due to the poor utilization of available resources in mitigating the shortfalls. Such an unaddressed issue may affect the grid stability and the ultimate grid blackout. Therefore,
[...] Read more.
The traditional grid operation is unfortunately lacking the resilience and responsiveness in reacting to contingency events due to the poor utilization of available resources in mitigating the shortfalls. Such an unaddressed issue may affect the grid stability and the ultimate grid blackout. Therefore, this paper models a grid optimization module consisting of a mid and low (microgrid) voltage level grid component of an urban grid network for a disaster recovery. The model minimizes the cost of generation required to meet the demand through the economic dispatch in combination with the unit commitment. Two optimization problems are formulated that resemble the grid operation: normal (grid-connected) and islanded. A constrained-based linear programming optimization problem is used to solve the formulated problems, where the dual-simplex algorithm is used as the linear solver. The model ensures sufficient demand to be met during the outages through the
N-1 contingency criterion for critical infrastructures. The simulation length is limited to 24 h and is solved using the MATLAB
® R2017b software. Three different cases are established to evaluated the modelled grid resilience during the grid-connected or the islanding of operations subject to adversed events. The simulated results provide the economical outage recovery that will maintain the grid resilience across the grid.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Role of Charging Infrastructure in Electric Vehicle Implementation within Smart Grids
by
Qing Kong, Michael Fowler, Evgueniy Entchev, Hajo Ribberink and Robert McCallum
Cited by 22 | Viewed by 5748
Abstract
In the integration of electric vehicle (EV) fleets into the smart grid context, charging infrastructure serves as the interlinkage between EV fleets and the power grid and, as such, affects the impacts of EV operation on the smart grid. In this study, the
[...] Read more.
In the integration of electric vehicle (EV) fleets into the smart grid context, charging infrastructure serves as the interlinkage between EV fleets and the power grid and, as such, affects the impacts of EV operation on the smart grid. In this study, the impacts of charging infrastructure on the effectiveness of different EV operational modes were simulated using a multi-component modelling approach, which accounts for both stochastic EV fleet charging behaviors as well as optimal energy vector dispatch operation. Moreover, a campus microgrid case study was presented to demonstrate the various design factors and impacts of charging infrastructure implementation affecting EV fleet adoption and operation. Based on results from the study, it was shown that charging infrastructure should be adopted in excess of the minimum required to satisfy EV charging for driving needs. In addressing uncontrolled charging behaviors, additional charging infrastructure improves EV owner convenience and reduces queuing duration. Meanwhile, controlled charging strategies benefit from increased resilience against uncertain charging behavior and operate more optimally in systems subject to time-of-use (TOU) electricity pricing. Lastly, it was demonstrated that successful vehicle-to-grid (V2G) implementation requires charging infrastructure to emulate the availability and fast response characteristics of stationary energy storage systems, which translates to excess charging port availability, long EV plug-in durations, and bi-directional power flow capabilities well beyond the level 2 charging standard.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
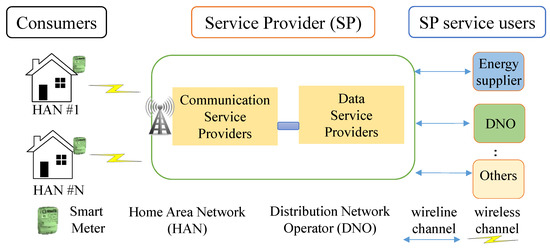
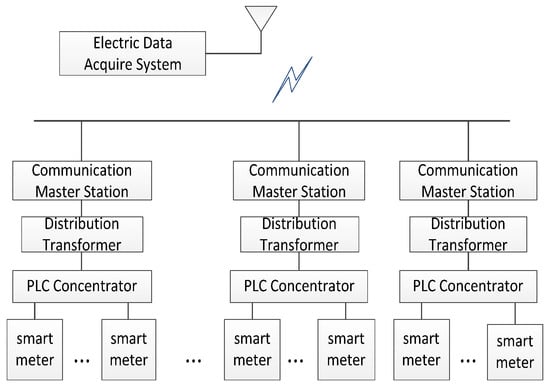
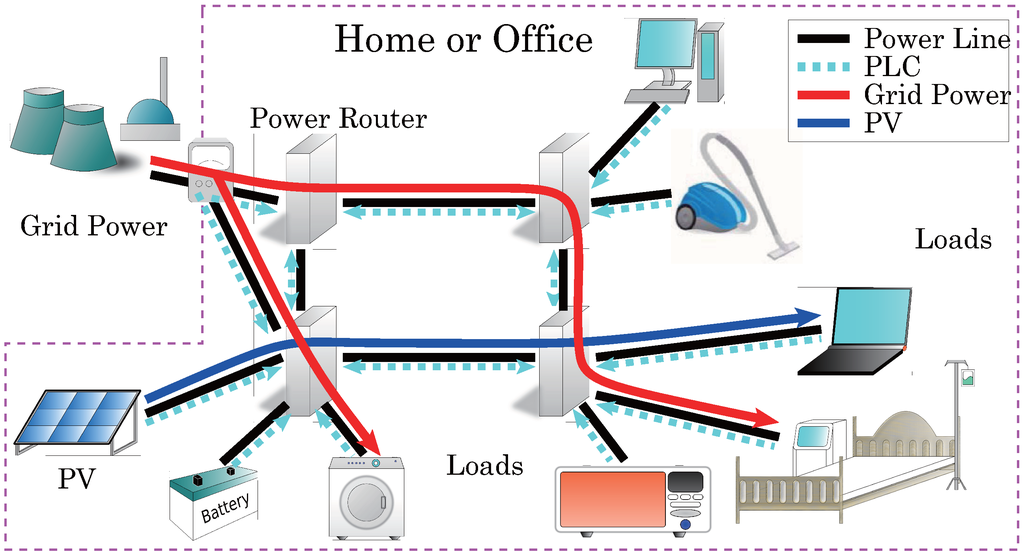
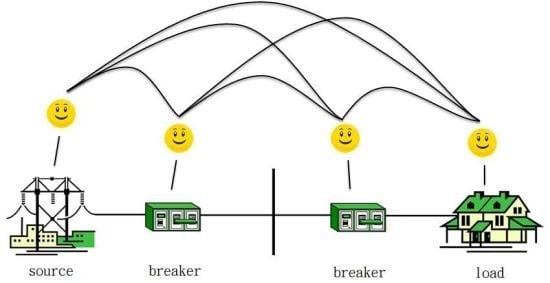
A PLC Channel Model for Home Area Networks
by
Xinyu Fang, Ning Wang and Thomas Aaron Gulliver
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 4162
Abstract
Smart meters (SMs) are key components of the smart grid (SG) which gather electricity usage data from residences and businesses. Home area networks (HANs) are used to support two-way communications between SMs and devices within a building such as appliances. This can be
[...] Read more.
Smart meters (SMs) are key components of the smart grid (SG) which gather electricity usage data from residences and businesses. Home area networks (HANs) are used to support two-way communications between SMs and devices within a building such as appliances. This can be implemented using power line communications (PLCs) via home wiring topologies. In this paper, a bottom-up approach is designed and a HAN-PLC channel model is obtained for a split-phase power system which includes branch circuits, an electric panel with circuit breakers and bars, a secondary transformer and the wiring of neighboring residences. A cell division (CD) method is proposed to construct the channel model. Furthermore, arc fault circuit interrupter (AFCI) and ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) circuit breaker models are developed. Several HAN-PLC channels are presented and compared with those obtained using existing models.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Privacy-Preserving Noise Addition Data Aggregation Scheme for Smart Grid
by
Yuwen Chen, José-Fernán Martínez, Pedro Castillejo and Lourdes López
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 3652
Abstract
Smart meters are applied to the smart grid to report instant electricity consumption to servers periodically; these data enable a fine-grained energy supply. However, these regularly reported data may cause some privacy problems. For example, they can reveal whether the house owner is
[...] Read more.
Smart meters are applied to the smart grid to report instant electricity consumption to servers periodically; these data enable a fine-grained energy supply. However, these regularly reported data may cause some privacy problems. For example, they can reveal whether the house owner is at home, if the television is working, etc. As privacy is becoming a big issue, people are reluctant to disclose this kind of personal information. In this study, we analyzed past studies and found that the traditional method suffers from a meter failure problem and a meter replacement problem, thus we propose a smart meter aggregation scheme based on a noise addition method and the homomorphic encryption algorithm, which can avoid the aforementioned problems. After simulation, the experimental results show that the computation cost on both the aggregator and smart meter side is reduced. A formal security analysis shows that the proposed scheme has semantic security.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
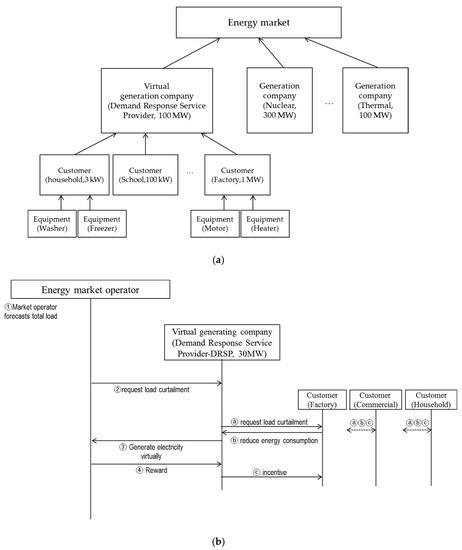
Data-Driven Prediction of Load Curtailment in Incentive-Based Demand Response System
by
Jimyung Kang and Soonwoo Lee
Cited by 16 | Viewed by 3516
Abstract
Demand response, in which energy customers reduce their energy consumption at the request of service providers, is spreading as a new technology. However, the amount of load curtailment from each customer is uncertain. This is because an energy customer can freely decide to
[...] Read more.
Demand response, in which energy customers reduce their energy consumption at the request of service providers, is spreading as a new technology. However, the amount of load curtailment from each customer is uncertain. This is because an energy customer can freely decide to reduce his energy consumption or not in the current liberalized energy market. Because this uncertainty can cause serious problems in a demand response system, it is clear that the amount of energy reduction should be predicted and managed. In this paper, a data-driven prediction method of load curtailment is proposed, considering two difficulties in the prediction. The first problem is that the data is very sparse. Each customer receives a request for load curtailment only a few times a year. Therefore, the
k-nearest neighbor method, which requires a relatively small amount of data, is mainly used in our proposed method. The second difficulty is that the characteristic of each customer is so different that a single prediction method cannot cover all the customers. A prediction method that provides remarkable prediction performance for one customer may provide a poor performance for other customers. As a result, the proposed prediction method adopts a weighted ensemble model to apply different models for different customers. The confidence of each sub-model is defined and used as a weight in the ensemble. The prediction is fully based on the electricity consumption data and the history of demand response events without demanding any other additional internal information from each customer. In the experiment, real data obtained from demand response service providers verifies that the proposed framework is suitable for the prediction of each customer’s load curtailment.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Random Violation Risk Degree Based Service Channel Routing Mechanism in Smart Grid
by
Sujie Shao, Qingtao Zeng, Shaoyong Guo and Xuesong Qiu
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2923
Abstract
Smart gird, integrated power network with communication network, has brought an innovation of traditional power for future green energy. Optical fiber technology and synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) technology is widely used in smart grid communication transmission network. It is a challenge to reduce
[...] Read more.
Smart gird, integrated power network with communication network, has brought an innovation of traditional power for future green energy. Optical fiber technology and synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) technology is widely used in smart grid communication transmission network. It is a challenge to reduce impact of the availability of smart grid communication services caused by random failures and random time to repair. Firstly, we create a service channel violation risk degree (
SCVRD) model to precisely track the violation risk change of communication service channel. It is denoted by the probability of service channel cumulative failure duration exceeding the prescribed duration. Secondly, a service channel violation risk degree routing mechanism is proposed to improve the availability of communication service. At last, the simulation is implemented with MATLAB and network data in one province are used as data instance. The simulation results show that the average service channel failure rate of availability-aware routing based on statistics (AAR-OS) algorithm and risk-aware provisioning algorithm are reduced by 15% and 6%, respectively.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Efficient and Provably Secure Key Agreement for Modern Smart Metering Communications
by
An Braeken, Pardeep Kumar and Andrew Martin
Cited by 64 | Viewed by 4745
Abstract
Security in modern smart metering communications and in smart grid networks has been an area of interest recently. In this field, identity-based mutual authentication including credential privacy without active involvement of a trusted third party is an important building block for smart grid
[...] Read more.
Security in modern smart metering communications and in smart grid networks has been an area of interest recently. In this field, identity-based mutual authentication including credential privacy without active involvement of a trusted third party is an important building block for smart grid technology. Recently, several schemes have been proposed for the smart grid with various security features (e.g., mutual authentication and key agreement). Moreover, these schemes are said to offer session key security under the widely accepted Canetti-Krawczyk (CK) security model. Instead, we argue that all of them are still vulnerable under the CK model. To remedy the problem, we present a new provably secure key agreement model for smart metering communications. The proposed model preserves the security features and provides more resistance against a denial of service attack. Moreover, our scheme is pairing-free, resulting in highly efficient computational and communication efforts.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
An Adaptive Weighted Pearson Similarity Measurement Method for Load Curve Clustering
by
Rongheng Lin, Budan Wu and Yun Su
Cited by 20 | Viewed by 4494
Abstract
Load curve data from advanced metering infrastructure record the consumers’ behavior. User consumption models help one understand a more intelligent power provisioning and clustering the load data is one of the popular approaches for building these models. Similarity measurements are important in the
[...] Read more.
Load curve data from advanced metering infrastructure record the consumers’ behavior. User consumption models help one understand a more intelligent power provisioning and clustering the load data is one of the popular approaches for building these models. Similarity measurements are important in the clustering model, but, load curve data is a time series style data, and traditional measurement methods are not suitable for load curve data. To cluster the load curve data more accurately, this paper applied an enhanced Pearson similarity for load curve data clustering. Our method introduces the ‘trend alteration point’ concept and integrates it with the Pearson similarity. By introducing a weight for Pearson distance, this method helps to keep the whole contour of the load data and the partial similarity. Based on the weighed Pearson distance, a weighed Pearson-based hierarchy clustering algorithm is proposed. Years of load curve data are used for evaluation. Several user consumption models are found and analyzed. Results show that the proposed method improves the accuracy of load data clustering.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Matching of Local Load with On-Site PV Production in a Grid-Connected Residential Building
by
Arslan Ahmad Bashir, Mahdi Pourakbari Kasmaei, Amir Safdarian and Matti Lehtonen
Cited by 25 | Viewed by 4753
Abstract
Efficient utilization of renewable generation inside microgrids remains challenging. In most existing studies, the goal is to optimize the energy cost of microgrids by working in synergy with the main grid. This work aimed at maximizing the self-consumption of on-site photovoltaic (PV) generation
[...] Read more.
Efficient utilization of renewable generation inside microgrids remains challenging. In most existing studies, the goal is to optimize the energy cost of microgrids by working in synergy with the main grid. This work aimed at maximizing the self-consumption of on-site photovoltaic (PV) generation using an electrical storage, as well as demand response solutions, in a building that was also capable of interacting with the main grid. Ten-minute resolution data were used to capture the temporal behavior of the weather. Extensive mathematical models were employed to estimate the demand for hot-water consumption, space cooling, and heating loads. The proposed framework is cast as mixed-integer linear programming model while minimizing the interaction with the grid. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed framework, it was applied to a typical Finnish household. Matching indices were used to evaluate the degree of overlap between generation and demand under different PV penetrations and storage capacities. Despite negative correlation of PV generation with Finnish seasonal consumption, a significant portion of demand can be satisfied solely with on-site PV generation during the spring and summer seasons.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Hybrid Machine Learning Model for Electricity Consumer Categorization Using Smart Meter Data
by
Zigui Jiang, Rongheng Lin and Fangchun Yang
Cited by 39 | Viewed by 5900
Abstract
Time-series smart meter data can record precisely electricity consumption behaviors of every consumer in the smart grid system. A better understanding of consumption behaviors and an effective consumer categorization based on the similarity of these behaviors can be helpful for flexible demand management
[...] Read more.
Time-series smart meter data can record precisely electricity consumption behaviors of every consumer in the smart grid system. A better understanding of consumption behaviors and an effective consumer categorization based on the similarity of these behaviors can be helpful for flexible demand management and effective energy control. In this paper, we propose a hybrid machine learning model including both unsupervised clustering and supervised classification for categorizing consumers based on the similarity of their typical electricity consumption behaviors. Unsupervised clustering algorithm is used to extract the typical electricity consumption behaviors and perform fuzzy consumer categorization, followed by a proposed novel algorithm to identify distinct consumer categories and their consumption characteristics. Supervised classification algorithm is used to classify new consumers and evaluate the validity of the identified categories. The proposed model is applied to a real dataset of U.S. non-residential consumers collected by smart meters over one year. The results indicate that large or special institutions usually have their distinct consumption characteristics while others such as some medium and small institutions or similar building types may have the same characteristics. Moreover, the comparison results with other methods show the improved performance of the proposed model in terms of category identification and classifying accuracy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Online Coordination of Plug-In Electric Vehicles Considering Grid Congestion and Smart Grid Power Quality
by
Sara Deilami
Cited by 22 | Viewed by 4855
Abstract
This paper first introduces the impacts of battery charger and nonlinear load harmonics on smart grids considering random plug-in of electric vehicles (PEVs) without any coordination. Then, a new centralized nonlinear online maximum sensitivity selection-based charging algorithm (NOL-MSSCA) is proposed for coordinating PEVs
[...] Read more.
This paper first introduces the impacts of battery charger and nonlinear load harmonics on smart grids considering random plug-in of electric vehicles (PEVs) without any coordination. Then, a new centralized nonlinear online maximum sensitivity selection-based charging algorithm (NOL-MSSCA) is proposed for coordinating PEVs that minimizes the costs associated with generation and losses considering network and bus total harmonic distortion (THD). The aim is to first attend the high priority customers and charge their vehicles as quickly as possible while postponing the service to medium and low priority consumers to the off-peak hours, considering network, battery and power quality constraints and harmonics. The vehicles were randomly plugged at different locations during a period of 24 h. The proposed PEV coordination is based on the maximum sensitivity selection (MSS), which is the sensitivity of losses (including fundamental and harmonic losses) with respect to the PEV location (PEV bus). The proposed algorithm uses the decoupled harmonic power flow (DHPF) to model the nonlinear loads (including the PEV chargers) as current harmonic sources and computes the harmonic power losses, harmonic voltages and THD of the smart grid. The MSS vectors are easily determined using the entries of the Jacobian matrix of the DHPF program, which includes the spectrums of all injected harmonics by nonlinear electric vehicle (EV) chargers and nonlinear industrial loads. The sensitivity of the objective function (fundamental and harmonic power losses) to the PEVs were then used to schedule PEVs accordingly. The algorithm successfully controls the network THDv level within the standard limit of 5% for low and moderate PEV penetrations by delaying PEV charging activities. For high PEV penetrations, the installation of passive power filters (PPFs) is suggested to reduce the THDv and manage to fully charge the PEVs. Detailed simulations considering random and coordinated charging were performed on the modified IEEE 23 kV distribution system with 22 low voltage residential networks populated with PEVs that have nonlinear battery chargers. Simulation results are provided without/with filters for different penetration levels of PEVs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Internet of Energy Approach for Sustainable Use of Electric Vehicles as Energy Storage of Prosumer Buildings
by
Evgeny Nefedov, Seppo Sierla and Valeriy Vyatkin
Cited by 32 | Viewed by 6061
Abstract
Vehicle-to-building (V2B) technology permits bypassing the power grid in order to supply power to a building from electric vehicle (EV) batteries in the parking lot. This paper investigates the hypothesis stating that the increasing number of EVs on our roads can be also
[...] Read more.
Vehicle-to-building (V2B) technology permits bypassing the power grid in order to supply power to a building from electric vehicle (EV) batteries in the parking lot. This paper investigates the hypothesis stating that the increasing number of EVs on our roads can be also beneficial for making buildings sustainably greener on account of using V2B technology in conjunction with local photovoltaic (PV) generation. It is assumed that there is no local battery storage other than EVs and that the EV batteries are fully available for driving, so that the EVs batteries must be at the intended state of charge at the departure time announced by the EV driver. Our goal is to exploit the potential of the EV batteries capacity as much as possible in order to permit a large area of solar panels, so that even on sunny days all PV power can be used to supply the building needs or the EV charging at the parking lot. A system architecture and collaboration protocols that account for uncertainties in EV behaviour are proposed. The proposed approach is proven in simulation covering one year period for three locations in different climatic regions of the US, resulting in the electricity bill reductions of 15.8%, 9.1% and 4.9% for California, New Jersey and Alaska, respectively. These results are compared to state-of-the-art research in combining V2B with PV or wind power generation. It is concluded that the achieved electricity bill reductions are superior to the state-of-the-art, because previous work is based on problem formulations that exploit only a part of the potential EV battery capacity.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Efficient and Privacy-Preserving Data Aggregation and Dynamic Billing in Smart Grid Metering Networks
by
An Braeken, Pardeep Kumar and Andrew Martin
Cited by 17 | Viewed by 5059
Abstract
The smart grid enables convenient data collection between smart meters and operation centers via data concentrators. However, it presents security and privacy issues for the customer. For instance, a malicious data concentrator cannot only use consumption data for malicious purposes but also can
[...] Read more.
The smart grid enables convenient data collection between smart meters and operation centers via data concentrators. However, it presents security and privacy issues for the customer. For instance, a malicious data concentrator cannot only use consumption data for malicious purposes but also can reveal life patterns of the customers. Recently, several methods in different groups (e.g., secure data aggregation, etc.) have been proposed to collect the consumption usage in a privacy-preserving manner. Nevertheless, most of the schemes either introduce computational complexities in data aggregation or fail to support privacy-preserving billing against the internal adversaries (e.g., malicious data concentrators). In this paper, we propose an efficient and privacy-preserving data aggregation scheme that supports dynamic billing and provides security against internal adversaries in the smart grid. The proposed scheme actively includes the customer in the registration process, leading to end-to-end secure data aggregation, together with accurate and dynamic billing offering privacy protection. Compared with the related work, the scheme provides a balanced trade-off between security and efficacy (i.e., low communication and computation overhead while providing robust security).
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
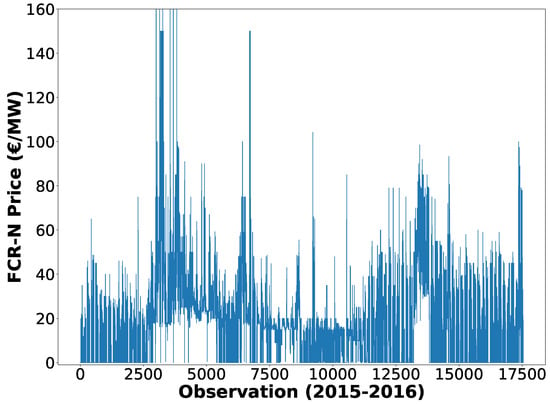
Exploiting Artificial Neural Networks for the Prediction of Ancillary Energy Market Prices
by
Christian Giovanelli, Seppo Sierla, Ryutaro Ichise and Valeriy Vyatkin
Cited by 24 | Viewed by 6613
Abstract
The increase of distributed energy resources in the smart grid calls for new ways to profitably exploit these resources, which can participate in day-ahead ancillary energy markets by providing flexibility. Higher profits are available for resource owners that are able to anticipate price
[...] Read more.
The increase of distributed energy resources in the smart grid calls for new ways to profitably exploit these resources, which can participate in day-ahead ancillary energy markets by providing flexibility. Higher profits are available for resource owners that are able to anticipate price peaks and hours of low prices or zero prices, as well as to control the resource in such a way that exploits the price fluctuations. Thus, this study presents a solution in which artificial neural networks are exploited to predict the day-ahead ancillary energy market prices. The study employs the frequency containment reserve for the normal operations market as a case study and presents the methodology utilized for the prediction of the case study ancillary market prices. The relevant data sources for predicting the market prices are identified, then the frequency containment reserve market prices are analyzed and compared with the spot market prices. In addition, the methodology describes the choices behind the definition of the model validation method and the performance evaluation coefficient utilized in the study. Moreover, the empirical processes for designing an artificial neural network model are presented. The performance of the artificial neural network model is evaluated in detail by means of several experiments, showing robustness and adaptiveness to the fast-changing price behaviors. Finally, the developed artificial neural network model is shown to have better performance than two state of the art models, support vector regression and ARIMA, respectively.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceReview
Peer to Peer Distributed Energy Trading in Smart Grids: A Survey
by
Juhar Abdella and Khaled Shuaib
Cited by 207 | Viewed by 15665
Abstract
Due to the expansion of distributed renewable energy resources, peer to peer energy trading (P2P DET) is expected to be one of the key elements of next generation power systems. P2P DET can provide various benefits such as creating a competitive energy market,
[...] Read more.
Due to the expansion of distributed renewable energy resources, peer to peer energy trading (P2P DET) is expected to be one of the key elements of next generation power systems. P2P DET can provide various benefits such as creating a competitive energy market, reducing power outages, increasing overall efficiency of power systems and supplementing alternative sources of energy according to user preferences. Because of these promising advantages, P2P DET has attracted the attention of several researchers. Current research related to P2P DET include demand response optimization, power routing, network communication, security and privacy. This paper presents a review of the main research topics revolving around P2P DET. Particularly, we present a comprehensive survey of existing demand response optimization models, power routing devices and power routing algorithms. We also identify some key challenges faced in realizing P2P DET. Furthermore, we discuss state of the art enabling technologies such as Energy Internet, Blockchain and Software Defined Networking (SDN) and we provide insights into future research directions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Static and Dynamic Networking of Smart Meters Based on the Characteristics of the Electricity Usage Information
by
Yaxin Huang, Yunlian Sun and Shimin Yi
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 3633
Abstract
The normal communication between smart meter and concentrator is a key factor influencing the normal function of users’ power consumption systems. To solve the communication failure of the smart meter caused by the signal conflict as well as the collected consecutive information abnormality
[...] Read more.
The normal communication between smart meter and concentrator is a key factor influencing the normal function of users’ power consumption systems. To solve the communication failure of the smart meter caused by the signal conflict as well as the collected consecutive information abnormality from the same smart meter, according to the chain optimization index, the networking method of static and dynamic combination proposed in this paper is first used to picked out the optimal relay for a smart meter belonging to multiple relay communication ranges. Meanwhile, the communication with other secondary relays is closed to avoid signal conflict. Then the paper forms different combinations of collected data and these combinations are trained in the extreme learning machine (ELM) to find the characteristics value of power consumption information. Finally, in MATLAB simulation, if ELM detects the abnormal information, new communication path could be promptly found through dynamic adjustment of chain optimization weighted coefficient and the weighted coefficient of the number of the relayed smart meters. It solves the problem of consecutive information abnormality from the same smart meter and raises the reliability of smart meter’s communication, having a significantly meaning to guarantee the normal function of users’ power consumption system.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Applications of Complex Network Analysis in Electric Power Systems
by
Mahmoud Saleh, Yusef Esa and Ahmed Mohamed
Cited by 78 | Viewed by 16519
Abstract
This paper provides a review of the research conducted on complex network analysis (CAN) in electric power systems. Moreover, a new approach is presented to find optimal locations for microgrids (MGs) in electric distribution systems (EDS) utilizing complex network analysis. The optimal placement
[...] Read more.
This paper provides a review of the research conducted on complex network analysis (CAN) in electric power systems. Moreover, a new approach is presented to find optimal locations for microgrids (MGs) in electric distribution systems (EDS) utilizing complex network analysis. The optimal placement in this paper points to the location that will result in enhanced grid resilience, reduced power losses and line loading, better voltage stability, and a supply to critical loads during a blackout. The criteria used to point out the optimal placement of the MGs were predicated on the centrality analysis selected from the complex network theory, the center of mass (COM) concept from physics, and the recently developed controlled delivery grid (CDG) model. An IEEE 30 bus network was utilized as a case study. Results using MATLAB (MathWorks, Inc., Nattick, MA, USA) and PowerWorld (PowerWorld Corporation, Champaign, IL, USA) demonstrate the usefulness of the proposed approach for MGs placement.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Achieving Cost Minimization and Fairness in Multi-Supplier Smart Grid Environment
by
Amna Malik, Zain Ali, Ahmed Bilal Awan, Ahmed G. Abo-Khalil and Guftaar Ahmad Sardar Sidhu
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 3877
Abstract
In this paper, we study the energy management techniques in the smart grid with multiple energy providers. We seek to minimize the electricity cost. In this paper, the desired objectives are achieved through scheduling of different consumers to different utilities at different time
[...] Read more.
In this paper, we study the energy management techniques in the smart grid with multiple energy providers. We seek to minimize the electricity cost. In this paper, the desired objectives are achieved through scheduling of different consumers to different utilities at different time slots. We consider a practical system where multiple users can be allocated to a single utility, but, a user cannot be assigned to more than one utility. As a first goal, we formulate a sum cost minimization problem subject to independent generation capacity of each utility. A dual decomposition approach is exploited to find an efficient solution where the sub-gradient approach is adopted to update the dual variables. Later, a min-max based optimization framework is adopted to achieve the fairness among different customers. Moreover, suboptimal schemes are also designed to reduce the computational complexity. Simulation results are presented to validate the performance of the proposed solutions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Value of Residential Investment in Photovoltaics and Batteries in Networks: A Techno-Economic Analysis
by
Damian Shaw-Williams, Connie Susilawati and Geoffrey Walker
Cited by 32 | Viewed by 6640
Abstract
Australia has one of the highest rates of residential photovoltaics penetration in the world. The willingness of households to privately invest in energy infrastructure, and the maturing of battery technology, provides significant scope for more efficient energy networks. The purpose of this paper
[...] Read more.
Australia has one of the highest rates of residential photovoltaics penetration in the world. The willingness of households to privately invest in energy infrastructure, and the maturing of battery technology, provides significant scope for more efficient energy networks. The purpose of this paper is to evaluate the scope for promoting distributed generation and storage from within existing network spending. In this paper, a techno-economic analysis is conducted to evaluate the economic impacts on networks of private investment in energy infrastructure. A highly granular probabilistic model of households within a test area was developed and an economic evaluation of both household and network sectors performed. Results of this paper show that PV only installations carry the greatest private return and, at current battery prices, the economics of combined PV and battery systems is marginal. However, when network benefits arising from reducing residential evening peaks, improved reliability, and losses avoided are considered, this can more than compensate for private economic losses. The main conclusion of this paper is that there is significant scope for network benefits in retrofitting existing housing stock through the incentivization of a policy of a more rapid adoption of distributed generation and residential battery storage.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
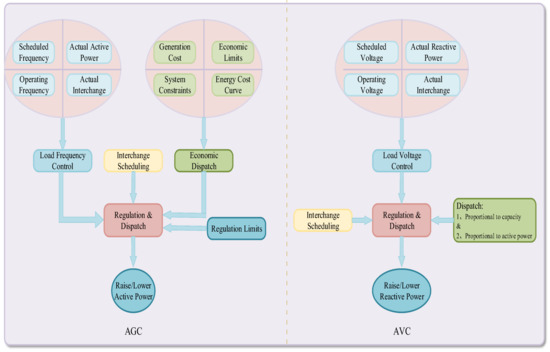
A Distributed Secondary Control Algorithm for Automatic Generation Control Considering EDP and Automatic Voltage Control in an AC Microgrid
by
Mi Dong, Li Li, Lina Wang, Dongran Song, Zhangjie Liu, Xiaoyu Tian, Zhengguo Li and Yinghua Wang
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 4715
Abstract
This paper introduces a distributed secondary control algorithm for automatic generation control (AGC) and automatic voltage control (AVC), which aims at matching area generation to area load and minimizing the total generation cost in an alternating current (AC) microgrids. Firstly, the control algorithm
[...] Read more.
This paper introduces a distributed secondary control algorithm for automatic generation control (AGC) and automatic voltage control (AVC), which aims at matching area generation to area load and minimizing the total generation cost in an alternating current (AC) microgrids. Firstly, the control algorithm utilizes a continuous-time distributed algorithm to generate additional control variables to achieve frequency-voltage recovery for all distributed generators (DGs). Secondary, it solves the economic dispatch problem (EDP) by a distributed economic incremental algorithm in the secondary control level, which avoids the problem caused by communication speed inconsistency between secondary and tertiary control levels. This study also utilizes a fully distributed strategy based on secondary communication network to estimate the total load demand. In addition, the proposed algorithm can be used to realize a seamless handover from the islanded mode to the grid-connected mode, run under the condition of short time communication system out of action, and help to realize the plug and play function. Lastly, the stability of the proposed control algorithm is analyzed and proved, and the effectiveness of the method is verified in some case studies.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Probabilistic Steady-State Operation and Interaction Analysis of Integrated Electricity, Gas and Heating Systems
by
Lun Yang, Xia Zhao, Xinyi Li and Wei Yan
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 5082
Abstract
The existing studies on probabilistic steady-state analysis of integrated energy systems (IES) are limited to integrated electricity and gas networks or integrated electricity and heating networks. This paper proposes a probabilistic steady-state analysis of integrated electricity, gas and heating networks (EGH-IES). Four typical
[...] Read more.
The existing studies on probabilistic steady-state analysis of integrated energy systems (IES) are limited to integrated electricity and gas networks or integrated electricity and heating networks. This paper proposes a probabilistic steady-state analysis of integrated electricity, gas and heating networks (EGH-IES). Four typical operation modes of an EGH-IES are presented at first. The probabilistic energy flow problem of the EGS-IES considering its operation modes and correlated uncertainties in wind/solar power and electricity/gas/heat loads is then formulated and solved by the Monte Carlo method based on Latin hypercube sampling and Nataf transformation. Numerical simulations are conducted on a sample EGH-IES working in the “electricity/gas following heat” mode to verify the probabilistic analysis proposed in this paper and to study the effects of uncertainties and correlations on the operation of the EGH-IES, especially uncertainty transmissions among the subnetworks.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Power Transformer Operating State Prediction Method Based on an LSTM Network
by
Hui Song, Jiejie Dai, Lingen Luo, Gehao Sheng and Xiuchen Jiang
Cited by 41 | Viewed by 6709
Abstract
The state of transformer equipment is usually manifested through a variety of information. The characteristic information will change with different types of equipment defects/faults, location, severity, and other factors. For transformer operating state prediction and fault warning, the key influencing factors of the
[...] Read more.
The state of transformer equipment is usually manifested through a variety of information. The characteristic information will change with different types of equipment defects/faults, location, severity, and other factors. For transformer operating state prediction and fault warning, the key influencing factors of the transformer panorama information are analyzed. The degree of relative deterioration is used to characterize the deterioration of the transformer state. The membership relationship between the relative deterioration degree of each indicator and the transformer state is obtained through fuzzy processing. Through the long short-term memory (LSTM) network, the evolution of the transformer status is extracted, and a data-driven state prediction model is constructed to realize preliminary warning of a potential fault of the equipment. Through the LSTM network, the quantitative index and qualitative index are organically combined in order to perceive the corresponding relationship between the characteristic parameters and the operating state of the transformer. The results of different time-scale prediction cases show that the proposed method can effectively predict the operation status of power transformers and accurately reflect their status.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Computational Intelligence Approaches for Energy Load Forecasting in Smart Energy Management Grids: State of the Art, Future Challenges, and Research Directions
by
Seyedeh Narjes Fallah, Ravinesh Chand Deo, Mohammad Shojafar, Mauro Conti and Shahaboddin Shamshirband
Cited by 223 | Viewed by 14413
Abstract
Energy management systems are designed to monitor, optimize, and control the smart grid energy market. Demand-side management, considered as an essential part of the energy management system, can enable utility market operators to make better management decisions for energy trading between consumers and
[...] Read more.
Energy management systems are designed to monitor, optimize, and control the smart grid energy market. Demand-side management, considered as an essential part of the energy management system, can enable utility market operators to make better management decisions for energy trading between consumers and the operator. In this system, a priori knowledge about the energy load pattern can help reshape the load and cut the energy demand curve, thus allowing a better management and distribution of the energy in smart grid energy systems. Designing a computationally intelligent load forecasting (ILF) system is often a primary goal of energy demand management. This study explores the state of the art of computationally intelligent (i.e., machine learning) methods that are applied in load forecasting in terms of their classification and evaluation for sustainable operation of the overall energy management system. More than 50 research papers related to the subject identified in existing literature are classified into two categories: namely the single and the hybrid computational intelligence (CI)-based load forecasting technique. The advantages and disadvantages of each individual techniques also discussed to encapsulate them into the perspective into the energy management research. The identified methods have been further investigated by a qualitative analysis based on the accuracy of the prediction, which confirms the dominance of hybrid forecasting methods, which are often applied as metaheurstic algorithms considering the different optimization techniques over single model approaches. Based on extensive surveys, the review paper predicts a continuous future expansion of such literature on different CI approaches and their optimizations with both heuristic and metaheuristic methods used for energy load forecasting and their potential utilization in real-time smart energy management grids to address future challenges in energy demand management.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Secure Protocol and IP Core for Configuration of Networking Hardware IPs in the Smart Grid
by
Marcelo Urbina, Naiara Moreira, Mikel Rodriguez, Tatiana Acosta, Jesús Lázaro and Armando Astarloa
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 5769
Abstract
Nowadays, the incorporation and constant evolution of communication networks in the electricity sector have given rise to the so-called Smart Grid, which is why it is necessary to have devices that are capable of managing new communication protocols, guaranteeing the strict requirements of
[...] Read more.
Nowadays, the incorporation and constant evolution of communication networks in the electricity sector have given rise to the so-called Smart Grid, which is why it is necessary to have devices that are capable of managing new communication protocols, guaranteeing the strict requirements of processing required by the electricity sector. In this context, intelligent electronic devices (IEDs) with network architectures are currently available to meet the communication, real-time processing and interoperability requirements of the Smart Grid. The new generation IEDs include an Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA), to support specialized networking switching architectures for the electric sector, as the IEEE 1588-aware High-availability Seamless Redundancy/Parallel Redundancy Protocol (HSR/PRP). Another advantage to using an FPGA is the ability to update or reconfigure the design to support new requirements that are being raised to the standards (IEC 61850). The update of the architecture implemented in the FPGA can be done remotely, but it is necessary to establish a cyber security mechanism since the communication link generates vulnerability in the case the attacker gains physical access to the network. The research presented in this paper proposes a secure protocol and Intellectual Property (IP) core for configuring and monitoring the networking IPs implemented in a Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA). The FPGA based implementation proposed overcomes this issue using a light Layer-2 protocol fully implemented on hardware and protected by strong cryptographic algorithms (AES-GCM), defined in the IEC 61850-90-5 standard. The proposed secure protocol and IP core are applicable in any field where remote configuration over Ethernet is required for IP cores in FPGAs. In this paper, the proposal is validated in communications hardware for Smart Grids.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Improving Control Efficiency of Dynamic Street Lighting by Utilizing the Dual Graph Grammar Concept
by
Igor Wojnicki and Leszek Kotulski
Cited by 24 | Viewed by 5079
Abstract
The paper introduces a definition of
dual graph grammar. It enables two graphs to share information in a synchronized way. A smart city example application, which is an outdoor lighting control system utilizing the
dual graph grammar, is also demonstrated. The
[...] Read more.
The paper introduces a definition of
dual graph grammar. It enables two graphs to share information in a synchronized way. A smart city example application, which is an outdoor lighting control system utilizing the
dual graph grammar, is also demonstrated. The system controls dimming of street lights which is based on traffic intensity. Each luminaire’s light level is adjusted individually to comply with the lighting norms to ensure safety. Benefits of applying the
dual graph grammar are twofold. First, it increases expressive power of the mathematical model that the system uses. It becomes possible to take into account complex geographical distribution of sensors and logical dependencies among them. Second, it increases the system’s efficiency by reducing the problem size during run-time. Experimental results show a reduction of the computation time by a factor of 2.8. The approach has been verified in practice.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Smart Grid Applications for a Practical Implementation of IP over Narrowband Power Line Communications
by
Noelia Uribe-Pérez, Itziar Angulo, David De la Vega, Txetxu Arzuaga, Igor Fernández and Amaia Arrinda
Cited by 30 | Viewed by 6633
Abstract
Currently, Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) systems have equipped the low voltage section with a communication system that is being used mainly for metering purposes, but it can be further employed for additional applications related to the Smart Grid (SG) concept. This paper explores
[...] Read more.
Currently, Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) systems have equipped the low voltage section with a communication system that is being used mainly for metering purposes, but it can be further employed for additional applications related to the Smart Grid (SG) concept. This paper explores the potential applications beyond metering of the available channel in a Power Line Communication-based AMI system. To that end, IP has been implemented over Narrow Band-Power Line Communication (NB-PLC) in a real microgrid, which includes an AMI system. A thorough review of potential applications for the SG that might be implemented for this representative case is included in order to provide a realistic analysis of the potentiality of NB-PLC beyond smart metering. The results demonstrate that existing AMI systems based on NB-PLC have the capacity to implement additional applications such as remote commands or status signals, which entails an added value for deployed AMI systems.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Data-Driven Optimization of Incentive-based Demand Response System with Uncertain Responses of Customers
by
Jimyung Kang and Jee-Hyong Lee
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 5055
Abstract
Demand response is nowadays considered as another type of generator, beyond just a simple peak reduction mechanism. A demand response service provider (DRSP) can, through its subcontracts with many energy customers, virtually generate electricity with actual load reduction. However, in this type of
[...] Read more.
Demand response is nowadays considered as another type of generator, beyond just a simple peak reduction mechanism. A demand response service provider (DRSP) can, through its subcontracts with many energy customers, virtually generate electricity with actual load reduction. However, in this type of virtual generator, the amount of load reduction includes inevitable uncertainty, because it consists of a very large number of independent energy customers. While they may reduce energy today, they might not tomorrow. In this circumstance, a DSRP must choose a proper set of these uncertain customers to achieve the exact preferred amount of load curtailment. In this paper, the customer selection problem for a service provider that consists of uncertain responses of customers is defined and solved. The uncertainty of energy reduction is fully considered in the formulation with data-driven probability distribution modeling and stochastic programming technique. The proposed optimization method that utilizes only the observed load data provides a realistic and applicable solution to a demand response system. The performance of the proposed optimization is verified with real demand response event data in Korea, and the results show increased and stabilized performance from the service provider’s perspective.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Data Analysis Technique to Estimate the Thermal Characteristics of a House
by
Seyed Amin Tabatabaei, Wim Van der Ham, Michel C. A. Klein and Jan Treur
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 5666
Abstract
Almost one third of the energy is used in the residential sector, and space heating is the largest part of energy consumption in our houses. Knowledge about the thermal characteristics of a house can increase the awareness of homeowners about the options to
[...] Read more.
Almost one third of the energy is used in the residential sector, and space heating is the largest part of energy consumption in our houses. Knowledge about the thermal characteristics of a house can increase the awareness of homeowners about the options to save energy, for example by showing that there is room for improvement of the insulation level. However, calculating the exact value of these characteristics is not possible without precise thermal experiments. In this paper, we propose a method to automatically estimate two of the most important thermal characteristics of a house, i.e., the loss rate and the heat capacity, based on collected data about the temperature and gas usage. The method is evaluated with a data set that has been collected in a real-life case study. Although a ground truth is lacking, the analyses show that there is evidence that this method could provide a feasible way to estimate those values from the thermostat data. More detailed data about the houses in which the data was collected is required to draw stronger conclusions. We conclude that the proposed method is a promising way to add energy saving advice to smart thermostats.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A PMU-Based Method for Smart Transmission Grid Voltage Security Visualization and Monitoring
by
Heng-Yi Su and Tzu-Yi Liu
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 8401
Abstract
With the rapid growth of usage of phasor measurement units (PMUs) for modern power grids, the application of synchronized phasors (synchrophasors) to real-time voltage security monitoring has become an active research area. This paper presents a novel approach for fast determination of loading
[...] Read more.
With the rapid growth of usage of phasor measurement units (PMUs) for modern power grids, the application of synchronized phasors (synchrophasors) to real-time voltage security monitoring has become an active research area. This paper presents a novel approach for fast determination of loading margin using PMU data from a wide-area monitoring system (WAMS) to construct the voltage stability boundary (VSB) of a transmission grid. Specifically, a new approach for online loading margin estimation that considers system load trends is proposed based on the Thevenin equivalent (TE) technique and the Mobius transformation (MT) technique. A VSB is then computed by means of real-time PMU measurements and is presented in a complex load power space. VSB can be utilized as a visualization tool that is able to provide real-time visualization of the current voltage stability situation. The proposed method is fast and adequate for online voltage security assessment. Furthermore, it enables us to significantly increase a system operator’s situational awareness for operational decision making. Simulation studies were carried out using different sized power grid models under various operating conditions. The simulation results are shown to validate the capability of the proposed method.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Comparison Study of Short-Term Prediction Methods to Enhance the Model Predictive Controller Applied to Microgrid Energy Management
by
César Hernández-Hernández, Francisco Rodríguez, José Carlos Moreno, Paulo Renato Da Costa Mendes, Julio Elias Normey-Rico and José Luis Guzmán
Cited by 17 | Viewed by 6258
Abstract
Electricity load forecasting, optimal power system operation and energy management play key roles that can bring significant operational advantages to microgrids. This paper studies how methods based on time series and neural networks can be used to predict energy demand and production, allowing
[...] Read more.
Electricity load forecasting, optimal power system operation and energy management play key roles that can bring significant operational advantages to microgrids. This paper studies how methods based on time series and neural networks can be used to predict energy demand and production, allowing them to be combined with model predictive control. Comparisons of different prediction methods and different optimum energy distribution scenarios are provided, permitting us to determine when short-term energy prediction models should be used. The proposed prediction models in addition to the model predictive control strategy appear as a promising solution to energy management in microgrids. The controller has the task of performing the management of electricity purchase and sale to the power grid, maximizing the use of renewable energy sources and managing the use of the energy storage system. Simulations were performed with different weather conditions of solar irradiation. The obtained results are encouraging for future practical implementation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Multiconductor Model of Power Line Communication in Medium-Voltage Lines
by
Lesek Franek and Petr Fiedler
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 6151
Abstract
Most power line communication (PLC) models are designed to date simulate power lines as two-wire lines. However, in alternating current (AC) electrical distribution, the two-wire option is seldom applied, and medium-voltage lines are most often based on the three-phase configuration. In this context,
[...] Read more.
Most power line communication (PLC) models are designed to date simulate power lines as two-wire lines. However, in alternating current (AC) electrical distribution, the two-wire option is seldom applied, and medium-voltage lines are most often based on the three-phase configuration. In this context, the influence of the ground, which constitutes another conductor with specific parameters, cannot be neglected. Two-wire models are characterized by limited accuracy, not allowing us to simulate certain major phenomena affecting PLC. This, for example, could embody the answer to the question of whether it is more advantageous to transmit a signal independently through each phase, reference the signal with respect to another phase or to use the ground as a reference. This paper discusses a multi-conductor model that eliminates the disadvantages outlined above; the proposed model exploits the multi-conductor telegrapher’s equations. In order to be able to include medium-voltage (MV)/ low-voltage (LV) transformers in medium-voltage network models, we constituted a transformer model. The designed models were validated on a real medium-voltage network. To be able to evaluate the suitability of the PLC, the noise in the medium voltage network was measured in order to determine the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR).
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Dual Half-Bridge Converter with Adaptive Energy Storage to Achieve ZVS over Full Range of Operation Conditions
by
Lei Zhao, Chuangyu Xu, Xuemei Zheng and Haoyu Li
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 6594
Abstract
The phase-shifted full-bridge (PSFB) converter is widely employed in high-power applications. However, circulating current, duty-cycle loss, secondary voltage oscillation, and narrow zero-voltage-switching (ZVS) range are the main drawbacks of the conventional PSFB converter. This paper proposes a novel full-bridge converter to improve the
[...] Read more.
The phase-shifted full-bridge (PSFB) converter is widely employed in high-power applications. However, circulating current, duty-cycle loss, secondary voltage oscillation, and narrow zero-voltage-switching (ZVS) range are the main drawbacks of the conventional PSFB converter. This paper proposes a novel full-bridge converter to improve the performance of the conventional PSFB converter. The proposed converter contains two paralleled half-bridge inverters and an auxiliary inductor on the primary side. The rectifier stage is composed of six diodes connected with the form of full-bridge rectification. This structure allows the stored energy for ZVS operation to change adaptively with duty-cycle. The power can be transferred from the primary side to the secondary side during the whole period. Therefore, the requirement of output filter inductance is reduced and the circulating current is removed. The proposed converter is a good candidate for high power, high voltage and variable input voltage applications. The operation principle and performance are verified on a laboratory prototype.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Power Controlling, Monitoring and Routing Center Enabled by a DC-Transformer †
by
Syed Ashad Mustufa Younus, Matteo Nardello, Pietro Tosato and Davide Brunelli
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 6038
Abstract
The penetration of various types of renewable sources and on-site storage devices have recently focused attention towards DC power distribution in consumer grids to achieve the target of zero/positive energy buildings and communities. To achieve this target, the most important component is the
[...] Read more.
The penetration of various types of renewable sources and on-site storage devices have recently focused attention towards DC power distribution in consumer grids to achieve the target of zero/positive energy buildings and communities. To achieve this target, the most important component is the DC consumer grid architecture which can integrate not only renewable sources and storage, but also enable the implementation in any conventional AC distribution network without any significant upgrade. To this end, a unique DC Transformer enabled DC microgrid architecture is presented in this paper. The architecture, called PCmRC (power controlling monitoring routing center) is proposed to manage distributed energy sources and storage at any stage and also directly interconnects the DC consumer grid with the conventional AC power grid. This paper also investigates detailed control algorithms of each component and the DC Transformer topology in addition to proposing four unique stages of grid operational modes to enhance the overall grid stability in any operational condition. The main objectives are to maximize the exploitation of renewable sources, to decrease reliance on fossil fuels, to boost the overall efficiency of the grid by reducing the power conversion losses and demand side management in all possible forms. The simulation platform is designed in MATLAB/Simulink. Simulation results of several types of case studies show the effectiveness of the proposed power distribution and management model.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
International Electronical Committee (IEC) 61850 Mapping with Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP) in Smart Grids Based European Telecommunications Standard Institute Machine-to-Machine (M2M) Environment
by
In-Jae Shin, Byung-Kwen Song and Doo-Seop Eom
Cited by 23 | Viewed by 12959
Abstract
As power systems develop rapidly into smarter and more flexible configurations, so too must the communication technologies that support them. Machine-to-machine (M2M) communication in power systems enables information collection by combining sensors and communication protocols. In doing so, M2M technology supports communication between
[...] Read more.
As power systems develop rapidly into smarter and more flexible configurations, so too must the communication technologies that support them. Machine-to-machine (M2M) communication in power systems enables information collection by combining sensors and communication protocols. In doing so, M2M technology supports communication between machines to improve power quality and protection coordination. When functioning in a “smart grid” environment, M2M has been labelled by the European Telecommunications Standard Institute (ETSI). International Electronical Committee (IEC) 61850 as the most important standard in power network systems. As evidence, this communication platform has been used for device data collection/control in substation automation systems and distribution automation systems. If the IEC 61850 information model were to be combined with a set of contemporary web protocols, the potential benefits would be enormous. Therefore, a constrained application protocol (CoAP) has been adopted to create an ETSI M2M communication architecture. CoAP is compared with other protocols (MQTT, SOAP) to demonstrate the validity of using it. This M2M communication technology is applied in an IEC61850, and use the OPNET Modeler 17.1 to demonstrate intercompatibility of CoAP Gateway. The proposed IEC 61850 and CoAP mapping scheme reduces the mapping time and improves throughput. CoAP is useful in the ETSI M2M environment where device capability is able to be limited.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Electric Field Simulations and Analysis for High Voltage High Power Medium Frequency Transformer
by
Pei Huang, Chengxiong Mao and Dan Wang
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 8450
Abstract
The electronic power transformer (EPT) raises concerns for its notable size and volume reduction compared with traditional line frequency transformers. Medium frequency transformers (MFTs) are important components in high voltage and high power energy conversion systems such as EPTs. High voltage and high
[...] Read more.
The electronic power transformer (EPT) raises concerns for its notable size and volume reduction compared with traditional line frequency transformers. Medium frequency transformers (MFTs) are important components in high voltage and high power energy conversion systems such as EPTs. High voltage and high power make the reliable insulation design of MFT more difficult. In this paper, the influence of wire type and interleaved winding structure on the electric field distribution of MFT is discussed in detail. The electric field distributions for six kinds of typical non-interleaved windings with different wire types are researched using a 2-D finite element method (FEM). The electric field distributions for one non-interleaved winding and two interleaved windings are also studied using 2-D FEM. Furthermore, the maximum electric field intensities are obtained and compared. The results show that, in this case study, compared with foil conductor, smaller maximum electric field intensity can be achieved using litz wire in secondary winding. Besides, interleaving can increase the maximum electric field intensity when insulation distance is constant. The proposed method of studying the electric field distribution and analysis results are expected to make a contribution to the improvement of electric field distribution in transformers.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Novel High-Frequency Voltage Standing-Wave Ratio-Based Grounding Electrode Line Fault Supervision in Ultra-High Voltage DC Transmission Systems
by
Yufei Teng, Xiaopeng Li, Qi Huang, Yifei Wang, Shi Jing, Zhenchao Jiang and Wei Zhen
Cited by 16 | Viewed by 5705
Abstract
In order to improve the fault monitoring performance of grounding electrode lines in ultra-high voltage DC (UHVDC) transmission systems, a novel fault monitoring approach based on the high-frequency voltage standing-wave ratio (VSWR) is proposed in this paper. The VSWR is defined considering a
[...] Read more.
In order to improve the fault monitoring performance of grounding electrode lines in ultra-high voltage DC (UHVDC) transmission systems, a novel fault monitoring approach based on the high-frequency voltage standing-wave ratio (VSWR) is proposed in this paper. The VSWR is defined considering a lossless transmission line, and the characteristics of the VSWR under different conditions are analyzed. It is shown that the VSWR equals 1 when the terminal resistance completely matches the characteristic impedance of the line, and when a short circuit fault occurs on the grounding electrode line, the VSWR will be greater than 1. The VSWR will approach positive infinity under metallic earth fault conditions, whereas the VSWR in non-metallic earth faults will be smaller. Based on these analytical results, a fault supervision criterion is formulated. The effectiveness of the proposed VSWR-based fault supervision technique is verified with a typical UHVDC project established in Power Systems Computer Aided Design/Electromagnetic Transients including DC(PSCAD/EMTDC). Simulation results indicate that the proposed strategy can reliably identify the grounding electrode line fault and has strong anti-fault resistance capability.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Dynamic Economic Dispatch Model for Uncertain Power Demands in an Interconnected Microgrid
by
Young-Sik Jang and Mun-Kyeom Kim
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 6264
Abstract
In this paper, we propose a dynamic economic dispatch (DED) model with sharing of responsibility for supply–demand balance under uncertain demands in a microgrid (MG). For developing the proposed model, an energy band operation scheme, including a tie-line flow (TLF) contraction between the
[...] Read more.
In this paper, we propose a dynamic economic dispatch (DED) model with sharing of responsibility for supply–demand balance under uncertain demands in a microgrid (MG). For developing the proposed model, an energy band operation scheme, including a tie-line flow (TLF) contraction between the main grid and the microgrid (MG), is constructed for preventing considerable changes in the TLFs caused by DED optimization. The proposed scheme generalizes the relationship between TLF contractions and MG operational costs. Moreover, a chance-constrained approach is applied to prevent short- and over-supply risks caused by unpredictable demands in the MG. Based on this approach, it is possible to determine the reasonable ramping capability versus operational cost under uncertain power demands in the MG.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Optimal Cooperative Management of Energy Storage Systems to Deal with Over- and Under-Voltages
by
Ghassem Mokhtari, Ghavameddin Nourbakhsh, Amjad Anvari-Moghadam, Negareh Ghasemi and Aminmohammad Saberian
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 4451
Abstract
This paper presents an optimal cooperative voltage control approach, which coordinates storage units in a distribution network. This technique is developed for storage systems’ active power management with a local strategy to provide robust voltage control and a distributed strategy to deliver optimal
[...] Read more.
This paper presents an optimal cooperative voltage control approach, which coordinates storage units in a distribution network. This technique is developed for storage systems’ active power management with a local strategy to provide robust voltage control and a distributed strategy to deliver optimal storage utilization. Accordingly, three control criteria based on predefined node voltage limits are used for network operation including normal, over-voltage, and under-voltage control modes. The contribution of storage units for voltage support is determined using the control modes and the coordination strategies proposed in this paper. This technique is evaluated in two case studies to assess its capability.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Multi-Objective Planning Techniques in Distribution Networks: A Composite Review
by
Syed Ali Abbas Kazmi, Muhammad Khuram Shahzad and Dong Ryeol Shin
Cited by 43 | Viewed by 7537
Abstract
Distribution networks (DNWs) are facing numerous challenges, notably growing load demands, environmental concerns, operational constraints and expansion limitations with the current infrastructure. These challenges serve as a motivation factor for various distribution network planning (DP) strategies, such as timely addressing load growth aiming
[...] Read more.
Distribution networks (DNWs) are facing numerous challenges, notably growing load demands, environmental concerns, operational constraints and expansion limitations with the current infrastructure. These challenges serve as a motivation factor for various distribution network planning (DP) strategies, such as timely addressing load growth aiming at prominent objectives such as reliability, power quality, economic viability, system stability and deferring costly reinforcements. The continuous transformation of passive to active distribution networks (ADN) needs to consider choices, primarily distributed generation (DG), network topology change, installation of new protection devices and key enablers as planning options in addition to traditional grid reinforcements. Since modern DP (MDP) in deregulated market environments includes multiple stakeholders, primarily owners, regulators, operators and consumers, one solution fit for all planning scenarios may not satisfy all these stakeholders. Hence, this paper presents a review of several planning techniques (PTs) based on mult-objective optimizations (MOOs) in DNWs, aiming at better trade-off solutions among conflicting objectives and satisfying multiple stakeholders. The PTs in the paper spread across four distinct planning classifications including DG units as an alternative to costly reinforcements, capacitors and power electronic devices for ensuring power quality aspects, grid reinforcements, expansions, and upgrades as a separate category and network topology alteration and reconfiguration as a viable planning option. Several research works associated with multi-objective planning techniques (MOPT) have been reviewed with relevant models, methods and achieved objectives, abiding with system constraints. The paper also provides a composite review of current research accounts and interdependence of associated components in the respective classifications. The potential future planning areas, aiming at the multi-objective-based frameworks, are also presented in this paper.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Implementation and Assessment of a Decentralized Load Frequency Control: Application to Power Systems with High Wind Energy Penetration
by
Irene Muñoz-Benavente, Emilio Gómez-Lázaro, Tania García-Sánchez, Antonio Vigueras-Rodríguez and Angel Molina-García
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 5628
Abstract
This paper describes and assesses a decentralized solution based on a wireless sensor-actuator network to provide primary frequency control from demand response in power systems with high wind energy penetration and, subsequently, with relevant frequency excursions. The proposed system is able to modify
[...] Read more.
This paper describes and assesses a decentralized solution based on a wireless sensor-actuator network to provide primary frequency control from demand response in power systems with high wind energy penetration and, subsequently, with relevant frequency excursions. The proposed system is able to modify the electrical power demand of a variety of thermostatically-controlled loads, maintaining minimum comfort levels and minimizing both infrastructure requirements and primary reserves from the supply side. This low-cost hardware solution avoids any additional wiring, extending the wireless sensor-actuator network technology towards small customers, which account for over a 30% share of the current power demand. Frequency excursions are collected by each individual load controller, considering not only the magnitude of the frequency deviation, but also their evolution over time. Based on these time-frequency excursion characteristics, controllers are capable of modifying the power consumption of thermostatically-controlled loads by switching them off and on, thus contributing to primary frequency control in power systems with higher generation unit oscillations as a consequence of relevant wind power integration. Field tests have been carried out in a laboratory environment to assess the load controller performance, as well as to evaluate the electrical and thermal response of individual loads under frequency deviations. These frequency deviations are estimated from power systems with a high penetration of wind energy, which are more sensitive to frequency oscillations and where demand response can significantly contribute to mitigate these frequency excursions. The results, also included in the paper, evaluate the suitability of the proposed load controllers and their suitability to decrease frequency excursions from the demand side in a decentralized manner.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Lyapunov Stability Theory-Based Control Strategy for Three-Level Shunt Active Power Filter
by
Yijia Cao, Yong Xu, Yong Li, Jiaqi Yu and Jingrong Yu
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 6666
Abstract
The three-phase three-wire neutral-point-clamped shunt active power filter (NPC-SAPF), which most adopts classical closed-loop feedback control methods such as proportional-integral (PI), proportional-resonant (PR) and repetitive control, can only output 1st–25th harmonic currents with 10–20 kHz switching frequency. The reason for this is that
[...] Read more.
The three-phase three-wire neutral-point-clamped shunt active power filter (NPC-SAPF), which most adopts classical closed-loop feedback control methods such as proportional-integral (PI), proportional-resonant (PR) and repetitive control, can only output 1st–25th harmonic currents with 10–20 kHz switching frequency. The reason for this is that the controller design must make a compromise between system stability and harmonic current compensation ability under the condition of less than 20 kHz switching frequency. To broaden the bandwidth of the compensation current, a Lyapunov stability theory-based control strategy is presented in this paper for NPC-SAPF. The proposed control law is obtained by constructing the switching function on the basis of the mathematical model and the Lyapunov candidate function, which can avoid introducing closed-loop feedback control and keep the system globally asymptotically stable. By means of the proposed method, the NPC-SAPF has compensation ability for the 1st–50th harmonic currents, the total harmonic distortion (
THD) and each harmonic content of grid currents satisfy the requirements of IEEE Standard 519-2014. In order to verify the superiority of the proposed control strategy, stability conditions of the proposed strategy and the representative PR controllers are compared. The simulation results in MATLAB/Simulink (MathWorks, Natick, MA, USA) and the experimental results obtained on a 6.6 kVA NPC-SAPF laboratory prototype validate the proposed control strategy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Robustness Area Technique Developing Guidelines for Power System Restoration
by
Paulo Murinelli Pesoti, Eliane Valença De Lorenci, Antonio Carlos Zambroni de Souza, Kwok Lun Lo and Benedito Isaias Lima Lopes
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 6688
Abstract
This paper proposes a novel energy based technique called the Robustness Area (RA) technique that measures power system robustness levels, as a helper for planning Power System Restorations (PSRs). The motivation is on account of the latest blackouts in Brazil, where the local
[...] Read more.
This paper proposes a novel energy based technique called the Robustness Area (RA) technique that measures power system robustness levels, as a helper for planning Power System Restorations (PSRs). The motivation is on account of the latest blackouts in Brazil, where the local Independent System Operator (ISO) encountered difficulties related to circuit disconnections during the restoration. The technique identifies vulnerable and robust buses, pointing out system areas that should be firstly reinforced during PSR, in order to enhance system stability. A Brazilian power system restoration area is used to compare the guidelines adopted by the ISO with a more suitable new plan indicated by the RA tool. Active power and reactive power load margin and standing phase angle show the method efficiency as a result of a well balanced system configuration, enhancing the restoration performance. Time domain simulations for loop closures and severe events also show the positive impact that the proposed tool brings to PSRs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Feedback Passivation Design for DC Microgrid and Its DC/DC Converters
by
Feifan Ji, Ji Xiang, Wuhua Li and Quanming Yue
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 9971
Abstract
There are difficulties in analyzing the stability of microgrids since they are located on various network structures. However, considering that the network often consists of passive elements, the passivity theory is applied in this paper to solve the above-mentioned problem. It has been
[...] Read more.
There are difficulties in analyzing the stability of microgrids since they are located on various network structures. However, considering that the network often consists of passive elements, the passivity theory is applied in this paper to solve the above-mentioned problem. It has been formerly shown that when the network is weakly strictly positive real (WSPR), the DC microgrid is stable if all interfaces between the microgrid and converters are made to be passive, which is called interface passivity. Then, the feedback passivation method is proposed for the controller design of various DC–DC converters to achieve the interface passivity. The interface passivity is different from the passivity of closed-loop systems on which the passivity based control (PBC) concentrates. The feedback passivation design is detailed for typical buck converters and boost converters in terms of conditions that the controller parameters should satisfy. The theoretical results are verified by a hardware-in-loop real-time labotray (RTLab) simulation of a DC microgrid with four generators.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Improved Direct Deadbeat Voltage Control with an Actively Damped Inductor-Capacitor Plant Model in an Islanded AC Microgrid
by
Jaehong Kim, Jitae Hong and Hongju Kim
Cited by 26 | Viewed by 6847
Abstract
A direct deadbeat voltage control design method for inverter-based microgrid applications is proposed in this paper. When the inductor-capacitor (LC) filter output voltage is directly controlled using voltage source inverters (VSIs), the plant dynamics exhibit second-order resonant characteristics with a load current disturbance.
[...] Read more.
A direct deadbeat voltage control design method for inverter-based microgrid applications is proposed in this paper. When the inductor-capacitor (LC) filter output voltage is directly controlled using voltage source inverters (VSIs), the plant dynamics exhibit second-order resonant characteristics with a load current disturbance. To effectively damp the resonance caused by the output LC filter, an active damping strategy that does not cause additional energy loss is utilized. The proposed direct deadbeat voltage control law is devised from a detailed, actively damped LC plant model. The proposed deadbeat control method enhances voltage control performance owing to its better disturbance rejection capability than the conventional deadbeat or proportional-integral-based control methods. The most important advantage of the proposed deadbeat control method is that it makes the deadbeat control more robust by bringing discrete closed-loop poles closer to the origin. Simulation and experimental results are shown to verify the enhanced voltage control performance and stability of the proposed voltage control method.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Multi-Objective Distribution Network Expansion Incorporating Electric Vehicle Charging Stations
by
Yue Xiang, Wei Yang, Junyong Liu and Furong Li
Cited by 31 | Viewed by 6525
Abstract
The paper develops a multi-objective planning framework for distribution network expansion with electric vehicle charging stations. Charging loads are modeled in the first place, and then integrated into the optimal distribution network expansion planning. The formulation is extended from the single objective of
[...] Read more.
The paper develops a multi-objective planning framework for distribution network expansion with electric vehicle charging stations. Charging loads are modeled in the first place, and then integrated into the optimal distribution network expansion planning. The formulation is extended from the single objective of the economic cost minimization into three objectives with the additional maximization of the charging station utilization, and maximization of the reliability level. Compared with the existing models, it captures the interactive impacts between charging infrastructures planning and distribution network planning from the aspects of economy, utilization, and reliability. A multi-stage search strategy is designed to solve the multi-objective problem. The models and the strategy are demonstrated by the test case. The results show that the proposed planning framework can make a trade-off among the three objectives, and offer a perspective to effectively integrate the network constraints from both the transportation network and distribution network.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Enhanced Multi-Objective Energy Optimization by a Signaling Method
by
João Soares, Nuno Borges, Zita Vale and P.B. De Moura Oliveira
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 5727
Abstract
In this paper three metaheuristics are used to solve a smart grid multi-objective energy management problem with conflictive design: how to maximize profits and minimize carbon dioxide (CO
2) emissions, and the results compared. The metaheuristics implemented are: weighted particle swarm optimization
[...] Read more.
In this paper three metaheuristics are used to solve a smart grid multi-objective energy management problem with conflictive design: how to maximize profits and minimize carbon dioxide (CO
2) emissions, and the results compared. The metaheuristics implemented are: weighted particle swarm optimization (W-PSO), multi-objective particle swarm optimization (MOPSO) and non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm II (NSGA-II). The performance of these methods with the use of multi-dimensional signaling is also compared with this technique, which has previously been shown to boost metaheuristics performance for single-objective problems. Hence, multi-dimensional signaling is adapted and implemented here for the proposed multi-objective problem. In addition, parallel computing is used to mitigate the methods’ computational execution time. To validate the proposed techniques, a realistic case study for a chosen area of the northern region of Portugal is considered, namely part of Vila Real distribution grid (233-bus). It is assumed that this grid is managed by an energy aggregator entity, with reasonable amount of electric vehicles (EVs), several distributed generation (DG), customers with demand response (DR) contracts and energy storage systems (ESS). The considered case study characteristics took into account several reported research works with projections for 2020 and 2050. The findings strongly suggest that the signaling method clearly improves the results and the Pareto front region quality.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Hierarchical Method for Transient Stability Prediction of Power Systems Using the Confidence of a SVM-Based Ensemble Classifier
by
Yanzhen Zhou, Junyong Wu, Zhihong Yu, Luyu Ji and Liangliang Hao
Cited by 66 | Viewed by 7195
Abstract
Machine learning techniques have been widely used in transient stability prediction of power systems. When using the post-fault dynamic responses, it is difficult to draw a definite conclusion about how long the duration of response data used should be in order to balance
[...] Read more.
Machine learning techniques have been widely used in transient stability prediction of power systems. When using the post-fault dynamic responses, it is difficult to draw a definite conclusion about how long the duration of response data used should be in order to balance the accuracy and speed. Besides, previous studies have the problem of lacking consideration for the confidence level. To solve these problems, a hierarchical method for transient stability prediction based on the confidence of ensemble classifier using multiple support vector machines (SVMs) is proposed. Firstly, multiple datasets are generated by bootstrap sampling, then features are randomly picked up to compress the datasets. Secondly, the confidence indices are defined and multiple SVMs are built based on these generated datasets. By synthesizing the probabilistic outputs of multiple SVMs, the prediction results and confidence of the ensemble classifier will be obtained. Finally, different ensemble classifiers with different response times are built to construct different layers of the proposed hierarchical scheme. The simulation results show that the proposed hierarchical method can balance the accuracy and rapidity of the transient stability prediction. Moreover, the hierarchical method can reduce the misjudgments of unstable instances and cooperate with the time domain simulation to insure the security and stability of power systems.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Operation Cost Minimization of Droop-Controlled AC Microgrids Using Multiagent-Based Distributed Control
by
Chendan Li, Mehdi Savaghebi, Josep M. Guerrero, Ernane A. A. Coelho and Juan C. Vasquez
Cited by 22 | Viewed by 8967
Abstract
Recently, microgrids are attracting increasing research interest as promising technologies to integrate renewable energy resources into the distribution system. Although many works have been done on droop control applied to microgrids, they mainly focus on achieving proportional power sharing based on the power
[...] Read more.
Recently, microgrids are attracting increasing research interest as promising technologies to integrate renewable energy resources into the distribution system. Although many works have been done on droop control applied to microgrids, they mainly focus on achieving proportional power sharing based on the power rating of the power converters. With various primary source for the distributed generator (DG), factors that are closely related to the operation cost, such as fuel cost of the generators and losses should be taken into account in order to improve the efficiency of the whole system. In this paper, a multiagent-based distributed method is proposed to minimize the operation cost in AC microgrids. In the microgrid, each DG is acting as an agent which regulates the power individually using a novel power regulation method based on frequency scheduling. An optimal power command is obtained through carefully designed consensus algorithm by using sparse communication links only among neighbouring agents. Experimental results for different cases verified that the proposed control strategy can effectively reduce the operation cost.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
A Conservation Voltage Reduction Scheme for a Distribution Systems with Intermittent Distributed Generators
by
Pyeong-Ik Hwang, Seung-Il Moon and Seon-Ju Ahn
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 5338
Abstract
In this paper, a conservation voltage reduction (CVR) scheme is proposed for a distribution system with intermittent distributed generators (DGs), such as photovoltaics and wind turbines. The CVR is a scheme designed to reduce energy consumption by lowering the voltages supplied to customers.
[...] Read more.
In this paper, a conservation voltage reduction (CVR) scheme is proposed for a distribution system with intermittent distributed generators (DGs), such as photovoltaics and wind turbines. The CVR is a scheme designed to reduce energy consumption by lowering the voltages supplied to customers. Therefore, an unexpected under-voltage violation can occur due to the variation of active power output from the intermittent DGs. In order to prevent the under-voltage violation and improve the CVR effect, a new reactive power controller which complies with the IEEE Std. 1547
TM, and a parameter determination method for the controller are proposed. In addition, an optimal power flow (OPF) problem to determine references for the resources of CVR is formulated with consideration of the intermittent DGs. The proposed method is validated using a modified IEEE 123-node test feeder. With the proposed method, the voltages of the test system are maintained to be greater than the lower bound, even though the active power outputs of the DGs are varied. Moreover, the CVR effect is improved compared to that used with the conventional reactive power control methods.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Statistical Framework for Automatic Leakage Detection in Smart Water and Gas Grids
by
Marco Fagiani, Stefano Squartini, Leonardo Gabrielli, Marco Severini and Francesco Piazza
Cited by 19 | Viewed by 6581
Abstract
In the last few years, due to the technological improvement of advanced metering infrastructures, water and natural gas grids can be regarded as smart-grids, similarly to power ones. However, considering the number of studies related to the application of computational intelligence to distribution
[...] Read more.
In the last few years, due to the technological improvement of advanced metering infrastructures, water and natural gas grids can be regarded as smart-grids, similarly to power ones. However, considering the number of studies related to the application of computational intelligence to distribution grids, the gap between power grids and water/gas grids is notably wide. For this purpose, in this paper, a framework for leakage identification is presented. The framework is composed of three sections aimed at the extraction and the selection of features and at the detection of leakages. A variation of the Sequential Feature Selection (SFS) algorithm is used to select the best performing features within a set, including, also, innovative temporal ones. The leakage identification is based on novelty detection and exploits the characterization of a normality model. Three statistical approaches, The Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM), Hidden Markov Model (HMM) and One-Class Support Vector Machine (OC-SVM), are adopted, under a comparative perspective. Both residential and office building environments are investigated by means of two datasets. One is the Almanac of Minutely Power dataset (AMPds), and it provides water and gas data consumption at 1, 10 and 30 min of time resolution; the other is the Department of International Development (DFID) dataset, and it provides water and gas data consumption at 30 min of time resolution. The achieved performance, computed by means of the Area Under the Curve (AUC), reaches
in the office building case study, thus confirming the suitability of the proposed approach for applications in smart water and gas grids.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
An Algorithmic Game Approach for Demand Side Management in Smart Grid with Distributed Renewable Power Generation and Storage
by
Ren-Shiou Liu
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 6001
Abstract
In this paper, the problem of minimizing electricity cost and the peak system load in smart grids with distributed renewable energy resources is studied. Unlike prior research works that either assume all of the jobs are interruptible or power-shiftable, this paper focuses on
[...] Read more.
In this paper, the problem of minimizing electricity cost and the peak system load in smart grids with distributed renewable energy resources is studied. Unlike prior research works that either assume all of the jobs are interruptible or power-shiftable, this paper focuses on more challenging scenarios in which jobs are non-interruptible and non-power-shiftable. In addition, as more and more newly-built homes have rooftop solar arrays, it is assumed that all users are equipped with a solar-plus-battery system in this paper. Thus, power can be drawn from the battery as needed to reduce the cost of electricity or to lower the overall system load. With a quadratic load-dependent cost function, this paper first shows that the electricity cost minimization problem in such a setting is NP-hard and presents a distributed demand-side management algorithm, called DDSM, to solve this. Experimental results show that the proposed DDSM algorithm is effective, scalable and converges to a Nash equilibrium in finite rounds.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Broadband PLC for Clustered Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) Architecture
by
Augustine Ikpehai, Bamidele Adebisi and Khaled M. Rabie
Cited by 56 | Viewed by 11702
Abstract
Advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) subsystems monitor and control energy distribution through exchange of information between smart meters and utility networks. A key challenge is how to select a cost-effective communication system without compromising the performance of the applications. Current communication technologies were developed
[...] Read more.
Advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) subsystems monitor and control energy distribution through exchange of information between smart meters and utility networks. A key challenge is how to select a cost-effective communication system without compromising the performance of the applications. Current communication technologies were developed for conventional data networks with different requirements. It is therefore necessary to investigate how much of existing communication technologies can be retrofitted into the new energy infrastructure to cost-effectively deliver acceptable level of service. This paper investigates broadband power line communications (BPLC) as a backhaul solution in AMI. By applying the disparate traffic characteristics of selected AMI applications, the network performance is evaluated. This study also examines the communication network response to changes in application configurations in terms of packet sizes. In each case, the network is stress-tested and performance is assessed against acceptable thresholds documented in the literature. Results show that, like every other communication technology, BPLC has certain limitations; however, with some modifications in the network topology, it indeed can fulfill most AMI traffic requirements for flexible and time-bounded applications. These opportunities, if tapped, can significantly improve fiscal and operational efficiencies in AMI services. Simulation results also reveal that BPLC as a backhaul can support flat and clustered AMI structures with cluster size ranging from 1 to 150 smart meters.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
New Scheme for Seamless Operation for Stand-Alone Power Systems
by
Hyun-Jun Kim, Yoon-Seok Lee, Byung-Moon Han and Young-Doo Yoon
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 5796
Abstract
On remote islands photovoltaic (PV) panels with battery energy storage systems (BESSs) supply electric power to customers in parallel operation with engine generators (EGs) to reduce fuel consumption and environmental burden. A BESS operates in voltage control mode when it supplies power to
[...] Read more.
On remote islands photovoltaic (PV) panels with battery energy storage systems (BESSs) supply electric power to customers in parallel operation with engine generators (EGs) to reduce fuel consumption and environmental burden. A BESS operates in voltage control mode when it supplies power to loads alone, while it operates in current control mode when it supplies power to loads in parallel with the EG. This paper proposes a smooth mode change of the BESS from current control to voltage control by using initial value at the output of integral part in the voltage controller, and a smooth mode change from voltage control to current control by tracking the EG output voltage to the BESS output voltage using a phase-locked loop (PLL). The feasibility of the proposed scheme was verified through computer simulations and experiments with a scaled prototype.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Wavelet-Based Unified Power Quality Conditioner to Eliminate Wind Turbine Non-Ideality Consequences on Grid-Connected Photovoltaic Systems
by
Bijan Rahmani, Weixing Li and Guihua Liu
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 8111
Abstract
The integration of renewable power sources with power grids presents many challenges, such as synchronization with the grid, power quality problems and so on. The shunt active power filter (SAPF) can be a solution to address the issue while suppressing the grid-end current
[...] Read more.
The integration of renewable power sources with power grids presents many challenges, such as synchronization with the grid, power quality problems and so on. The shunt active power filter (SAPF) can be a solution to address the issue while suppressing the grid-end current harmonics and distortions. Nonetheless, available SAPFs work somewhat unpredictably in practice. This is attributed to the dependency of the SAPF controller on nonlinear complicated equations and two distorted variables, such as load current and voltage, to produce the current reference. This condition will worsen when the plant includes wind turbines which inherently produce 3rd, 5th, 7th and 11th voltage harmonics. Moreover, the inability of the typical phase locked loop (PLL) used to synchronize the SAPF reference with the power grid also disrupts SAPF operation. This paper proposes an improved synchronous reference frame (SRF) which is equipped with a wavelet-based PLL to control the SAPF, using one variable such as load current. Firstly the fundamental positive sequence of the source voltage, obtained using a wavelet, is used as the input signal of the PLL through an orthogonal signal generator process. Then, the generated orthogonal signals are applied through the SRF-based compensation algorithm to synchronize the SAPF’s reference with power grid. To further force the remained uncompensated grid current harmonics to pass through the SAPF, an improved series filter (SF) equipped with a current harmonic suppression loop is proposed. Concurrent operation of the improved SAPF and SF is coordinated through a unified power quality conditioner (UPQC). The DC-link capacitor of the proposed UPQC, used to interconnect a photovoltaic (PV) system to the power grid, is regulated by an adaptive controller. Matlab/Simulink results confirm that the proposed wavelet-based UPQC results in purely sinusoidal grid-end currents with total harmonic distortion (THD) = 1.29%, which leads to high electrical efficiency of a grid-connected PV system.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Developing a New HSR Switching Node (SwitchBox) for Improving Traffic Performance in HSR Networks
by
Nguyen Xuan Tien and Jong Myung Rhee
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 7399
Abstract
High availability is crucial for industrial Ethernet networks as well as Ethernet-based control systems such as automation networks and substation automation systems (SAS). Since standard Ethernet does not support fault tolerance capability, the high availability of Ethernet networks can be increased by using
[...] Read more.
High availability is crucial for industrial Ethernet networks as well as Ethernet-based control systems such as automation networks and substation automation systems (SAS). Since standard Ethernet does not support fault tolerance capability, the high availability of Ethernet networks can be increased by using redundancy protocols. Various redundancy protocols for Ethernet networks have been developed and standardized, such as rapid spanning tree protocol (RSTP), media redundancy protocol (MRP), parallel redundancy protocol (PRP), high-availability seamless redundancy (HSR) and others. RSTP and MRP have switchover delay drawbacks. PRP provides zero recovery time, but requires a duplicate network infrastructure. HSR operation is similar to PRP, but HSR uses a single network. However, the standard HSR protocol is mainly applied to ring-based topologies and generates excessively unnecessary redundant traffic in the network. In this paper, we develop a new switching node for the HSR protocol, called SwitchBox, which is used in HSR networks in order to support any network topology and significantly reduce redundant network traffic, including unicast, multicast and broadcast traffic, compared with standard HSR. By using the SwitchBox, HSR not only provides seamless communications with zero switchover time in case of failure, but it is also easily applied to any network topology and significantly reduces unnecessary redundant traffic in HSR networks.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Electricity Customer Clustering Following Experts’ Principle for Demand Response Applications
by
Jimyung Kang and Jee-Hyong Lee
Cited by 20 | Viewed by 6204
Abstract
The clustering of electricity customers might have an effective meaning if, and only if, it is verified by domain experts. Most of the previous studies on customer clustering, however, do not consider real applications, but only the structure of clusters. Therefore, there is
[...] Read more.
The clustering of electricity customers might have an effective meaning if, and only if, it is verified by domain experts. Most of the previous studies on customer clustering, however, do not consider real applications, but only the structure of clusters. Therefore, there is no guarantee that the clustering results are applicable to real domains. In other words, the results might not coincide with those of domain experts. In this paper, we focus on formulating clusters that are applicable to real applications based on domain expert knowledge. More specifically, we try to define a distance between customers that generates clusters that are applicable to demand response applications. First, the
k-sliding distance, which is a new distance between two electricity customers, is proposed for customer clustering. The effect of
k-sliding distance is verified by expert knowledge. Second, a genetic programming framework is proposed to automatically determine a more improved distance measure. The distance measure generated by our framework can be considered as a reflection of the clustering principles of domain experts. The results of the genetic programming demonstrate the possibility of deriving clustering principles.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Comparison of Techniques for Reducing Unicast Traffic in HSR Networks
by
Nguyen Xuan Tien, Saad Allawi Nsaif and Jong Myung Rhee
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 6660
Abstract
This paper investigates several existing techniques for reducing high-availability seamless redundancy (HSR) unicast traffic in HSR networks for substation automation systems (SAS). HSR is a redundancy protocol for Ethernet networks that provides duplicate frames for separate physical paths with zero recovery time. This
[...] Read more.
This paper investigates several existing techniques for reducing high-availability seamless redundancy (HSR) unicast traffic in HSR networks for substation automation systems (SAS). HSR is a redundancy protocol for Ethernet networks that provides duplicate frames for separate physical paths with zero recovery time. This feature of HSR makes it very suited for real-time and mission-critical applications such as SAS systems. HSR is one of the redundancy protocols selected for SAS systems. However, the standard HSR protocol generates too much unnecessary redundant unicast traffic in connected-ring networks. This drawback degrades network performance and may cause congestion and delay. Several techniques have been proposed to reduce the redundant unicast traffic, resulting in the improvement of network performance in HSR networks. These HSR traffic reduction techniques are broadly classified into two categories based on their traffic reduction manner, including traffic filtering-based techniques and predefined path-based techniques. In this paper, we provide an overview and comparison of these HSR traffic reduction techniques found in the literature. The concepts, operational principles, network performance, advantages, and disadvantages of these techniques are investigated, summarized. We also provide a comparison of the traffic performance of these HSR traffic reduction techniques.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
State of the Art Authentication, Access Control, and Secure Integration in Smart Grid
by
Neetesh Saxena and Bong Jun Choi
Cited by 67 | Viewed by 13432
Abstract
The smart grid (SG) is a promising platform for providing more reliable, efficient, and cost effective electricity to the consumers in a secure manner. Numerous initiatives across the globe are taken by both industry and academia in order to compile various security issues
[...] Read more.
The smart grid (SG) is a promising platform for providing more reliable, efficient, and cost effective electricity to the consumers in a secure manner. Numerous initiatives across the globe are taken by both industry and academia in order to compile various security issues in the smart grid network. Unfortunately, there is no impactful survey paper available in the literature on authentications in the smart grid network. Therefore, this paper addresses the required objectives of an authentication protocol in the smart grid network along with the focus on mutual authentication, access control, and secure integration among different SG components. We review the existing authentication protocols, and analyze mutual authentication, privacy, trust, integrity, and confidentiality of communicating information in the smart grid network. We review authentications between the communicated entities in the smart grid, such as smart appliance, smart meter, energy provider, control center (CC), and home/building/neighborhood area network gateways (GW). We also review the existing authentication schemes for the vehicle-to-grid (V2G) communication network along with various available secure integration and access control schemes. We also discuss the importance of the mutual authentication among SG entities while providing confidentiality and privacy preservation, seamless integration, and required access control with lower overhead, cost, and delay. This paper will help to provide a better understanding of current authentication, authorization, and secure integration issues in the smart grid network and directions to create interest among researchers to further explore these promising areas.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
An Energy Management Service for the Smart Office
by
Cristina Rottondi, Markus Duchon, Dagmar Koss, Andrei Palamarciuc, Alessandro Pití, Giacomo Verticale and Bernhard Schätz
Cited by 19 | Viewed by 9715
Abstract
The evolution of the electricity grid towards the smart grid paradigm is fostering the integration of distributed renewable energy sources in smart buildings: a combination of local power generation, battery storage and controllable loads can greatly increase the energetic self-sufficiency of a smart
[...] Read more.
The evolution of the electricity grid towards the smart grid paradigm is fostering the integration of distributed renewable energy sources in smart buildings: a combination of local power generation, battery storage and controllable loads can greatly increase the energetic self-sufficiency of a smart building, enabling it to maximize the self-consumption of photovoltaic electricity and to participate in the energy market, thus taking advantage of time-variable tariffs to achieve economic savings. This paper proposes an energy management infrastructure specifically tailored for a smart office building, which relies on measured data and on forecasting algorithms to predict the future patterns of both local energy generation and power loads. The performance is compared to the optimal energy usage scheduling, which would be obtained assuming the exact knowledge of the future energy production and consumption trends, showing gaps below 10% with respect to the optimum.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Formulation and Analysis of an Approximate Expression for Voltage Sensitivity in Radial DC Distribution Systems
by
Ho-Yong Jeong, Jong-Chan Choi, Dong-Jun Won, Seon-Ju Ahn and Seung-il Moon
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 5966
Abstract
Voltage is an important variable that reflects system conditions in DC distribution systems and affects many characteristics of a system. In a DC distribution system, there is a close relationship between the real power and the voltage magnitude, and this is one of
[...] Read more.
Voltage is an important variable that reflects system conditions in DC distribution systems and affects many characteristics of a system. In a DC distribution system, there is a close relationship between the real power and the voltage magnitude, and this is one of major differences from the characteristics of AC distribution systems. One such relationship is expressed as the voltage sensitivity, and an understanding of voltage sensitivity is very useful to describe DC distribution systems. In this paper, a formulation for a novel approximate expression for the voltage sensitivity in a radial DC distribution system is presented. The approximate expression is derived from the power flow equation with some additional assumptions. The results of approximate expression is compared with an exact calculation, and relations between the voltage sensitivity and electrical quantities are analyzed analytically using both the exact form and the approximate voltage sensitivity equation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Power System Optimal Dispatch Strategy Considering the Flow of Carbon Emissions and Large Consumers
by
Jun Yang, Xin Feng, Yufei Tang, Jun Yan, Haibo He and Chao Luo
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 6074
Abstract
The carbon emissions trading market and direct power purchases by large consumers are two promising directions of power system development. To trace the carbon emission flow in the power grid, the theory of carbon emission flow is improved by allocating power loss to
[...] Read more.
The carbon emissions trading market and direct power purchases by large consumers are two promising directions of power system development. To trace the carbon emission flow in the power grid, the theory of carbon emission flow is improved by allocating power loss to the load side. Based on the improved carbon emission flow theory, an optimal dispatch model is proposed to optimize the cost of both large consumers and the power grid, which will benefit from the carbon emissions trading market. Moreover, to better simulate reality, the direct purchase of power by large consumers is also considered in this paper. The OPF (optimal power flow) method is applied to solve the problem. To evaluate our proposed optimal dispatch strategy, an IEEE 30-bus system is used to test the performance. The effects of the price of carbon emissions and the price of electricity from normal generators and low-carbon generators with regards to the optimal dispatch are analyzed. The simulation results indicate that the proposed strategy can significantly reduce both the operation cost of the power grid and the power utilization cost of large consumers.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Real-Time Recognition Non-Intrusive Electrical Appliance Monitoring Algorithm for a Residential Building Energy Management System
by
Kofi Afrifa Agyeman, Sekyung Han and Soohee Han
Cited by 37 | Viewed by 7606
Abstract
The concern of energy price hikes and the impact of climate change because of energy generation and usage forms the basis for residential building energy conservation. Existing energy meters do not provide much information about the energy usage of the individual appliance apart
[...] Read more.
The concern of energy price hikes and the impact of climate change because of energy generation and usage forms the basis for residential building energy conservation. Existing energy meters do not provide much information about the energy usage of the individual appliance apart from its power rating. The detection of the appliance energy usage will not only help in energy conservation, but also facilitate the demand response (DR) market participation as well as being one way of building energy conservation. However, energy usage by individual appliance is quite difficult to estimate. This paper proposes a novel approach: an unsupervised disaggregation method, which is a variant of the hidden Markov model (HMM), to detect an appliance and its operation state based on practicable measurable parameters from the household energy meter. Performing experiments in a practical environment validates our proposed method. Our results show that our model can provide appliance detection and power usage information in a non-intrusive manner, which is ideal for enabling power conservation efforts and participation in the demand response market.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Optimal Energy Management of Multi-Microgrids with Sequentially Coordinated Operations
by
Nah-Oak Song, Ji-Hye Lee, Hak-Man Kim, Yong Hoon Im and Jae Yong Lee
Cited by 67 | Viewed by 7646
Abstract
We propose an optimal electric energy management of a cooperative multi-microgrid community with sequentially coordinated operations. The sequentially coordinated operations are suggested to distribute computational burden and yet to make the optimal 24 energy management of multi-microgrids possible. The sequential operations are mathematically
[...] Read more.
We propose an optimal electric energy management of a cooperative multi-microgrid community with sequentially coordinated operations. The sequentially coordinated operations are suggested to distribute computational burden and yet to make the optimal 24 energy management of multi-microgrids possible. The sequential operations are mathematically modeled to find the optimal operation conditions and illustrated with physical interpretation of how to achieve optimal energy management in the cooperative multi-microgrid community. This global electric energy optimization of the cooperative community is realized by the ancillary internal trading between the microgrids in the cooperative community which reduces the extra cost from unnecessary external trading by adjusting the electric energy production amounts of combined heat and power (CHP) generators and amounts of both internal and external electric energy trading of the cooperative community. A simulation study is also conducted to validate the proposed mathematical energy management models.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Learning Agent for a Heat-Pump Thermostat with a Set-Back Strategy Using Model-Free Reinforcement Learning
by
Frederik Ruelens, Sandro Iacovella, Bert J. Claessens and Ronnie Belmans
Cited by 64 | Viewed by 8162
Abstract
The conventional control paradigm for a heat pump with a less efficient auxiliary heating element is to keep its temperature set point constant during the day. This constant temperature set point ensures that the heat pump operates in its more efficient heat-pump mode
[...] Read more.
The conventional control paradigm for a heat pump with a less efficient auxiliary heating element is to keep its temperature set point constant during the day. This constant temperature set point ensures that the heat pump operates in its more efficient heat-pump mode and minimizes the risk of activating the less efficient auxiliary heating element. As an alternative to a constant set-point strategy, this paper proposes a learning agent for a thermostat with a set-back strategy. This set-back strategy relaxes the set-point temperature during convenient moments, e.g., when the occupants are not at home. Finding an optimal set-back strategy requires solving a sequential decision-making process under uncertainty, which presents two challenges. The first challenge is that for most residential buildings, a description of the thermal characteristics of the building is unavailable and challenging to obtain. The second challenge is that the relevant information on the state, i.e., the building envelope, cannot be measured by the learning agent. In order to overcome these two challenges, our paper proposes an auto-encoder coupled with a batch reinforcement learning technique. The proposed approach is validated for two building types with different thermal characteristics for heating in the winter and cooling in the summer. The simulation results indicate that the proposed learning agent can reduce the energy consumption by 4%–9% during 100 winter days and by 9%–11% during 80 summer days compared to the conventional constant set-point strategy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Automated Linear Function Submission-Based Double Auction as Bottom-up Real-Time Pricing in a Regional Prosumers’ Electricity Network
by
Tadahiro Taniguchi, Koki Kawasaki, Yoshiro Fukui, Tomohiro Takata and Shiro Yano
Cited by 16 | Viewed by 8460
Abstract
A linear function submission-based double auction (LFS-DA) mechanism for a regional electricity network is proposed in this paper. Each agent in the network is equipped with a battery and a generator. Each agent simultaneously becomes a producer and consumer of electricity, i.e., a
[...] Read more.
A linear function submission-based double auction (LFS-DA) mechanism for a regional electricity network is proposed in this paper. Each agent in the network is equipped with a battery and a generator. Each agent simultaneously becomes a producer and consumer of electricity, i.e., a prosumer, and trades electricity in the regional market at a variable price. In the LFS-DA, each agent uses linear demand and supply functions when they submit bids and asks to an auctioneer in the regional market. The LFS-DA can achieve an exact balance between electricity demand and supply for each time slot throughout the learning phase and was shown capable of solving the primal problem of maximizing the social welfare of the network without any central price setter, e.g., a utility or a large electricity company, in contrast with conventional real-time pricing (RTP). This paper presents a clarification of the relationship between the RTP algorithm derived on the basis of a dual decomposition framework and LFS-DA. Specifically, we proved that the changes in the price profile of the LFS-DA mechanism are equal to those achieved by the RTP mechanism derived from the dual decomposition framework, except for a constant factor.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Autonomous Household Energy Management Based on a Double Cooperative Game Approach in the Smart Grid
by
Bingtuan Gao, Xiaofeng Liu, Wenhu Zhang and Yi Tang
Cited by 33 | Viewed by 6557
Abstract
Taking advantage of two-way communication infrastructure and bidirectional energy trading between utility companies and customers in the future smart grid (SG), autonomous energy management programs become crucial to the demand-side management (DSM). Most of the existing autonomous energy management schemes are for the
[...] Read more.
Taking advantage of two-way communication infrastructure and bidirectional energy trading between utility companies and customers in the future smart grid (SG), autonomous energy management programs become crucial to the demand-side management (DSM). Most of the existing autonomous energy management schemes are for the scenario with a single utility company or the scenario with one-way energy trading. In this paper, an autonomous household energy management system with multiple utility companies and multiple residential customers is studied by considering the bidirectional energy trading. To minimize the overall costs of both the utility companies and the residential customers, the energy management system is formulated as a double cooperative game. That is, the interaction among the residential users is formulated as a cooperative game, where the players are the customers and the strategies are the daily schedules of their household appliances; and the interaction among the utility companies is also formulated as a cooperative game, where the players are the suppliers and the strategies are the proportions of the daily total energy they provide for the customers. Without loss of generality, the bidirectional energy trading in the double cooperative game is formulated by allowing plug-in electric vehicles (PEVs) to discharge and sell energy back. Two distributed algorithms will be provided to realize the global optimal performance in terms of minimizing the energy costs, which can be guaranteed at the Nash equilibriums of the formulated cooperative games. Finally, simulation results illustrated that the proposed double cooperative game can benefit both the utility companies and residential users significantly.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
FHT: A Novel Approach for Filtering High-Availability Seamless Redundancy (HSR) Traffic
by
Nguyen Xuan Tien and Jong Myung Rhee
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 6745
Abstract
High-availability seamless redundancy (HSR) is a protocol for Ethernet networks that provides duplicated frames with zero recovery time in the event of any network component’s failure. It is suited for applications that demand high availability and a very short time-outs such as substation
[...] Read more.
High-availability seamless redundancy (HSR) is a protocol for Ethernet networks that provides duplicated frames with zero recovery time in the event of any network component’s failure. It is suited for applications that demand high availability and a very short time-outs such as substation automation systems (SAS). However, HSR generates excessive unnecessary unicast frames and spreads them throughout connected-ring networks, whether or not the destination node exists in network’s rings. This unnecessary redundant traffic causes high bandwidth consumption, resulting in degradation of network performance. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach for filtering and reducing HSR unicast traffic in connected-ring networks, called “filtering HSR traffic” (FHT). The purpose of FHT is to filter HSR unicast traffic and remove circulated traffic for all rings in connected-ring networks. Therefore, FHT significantly reduces network unicast traffic in connected-ring networks. The traffic performance of FHT has been analyzed, evaluated, and compared to that of standard HSR protocol and the port locking (PL) approach. Various simulations were conducted to validate the traffic performance analysis. Analytical and simulation results showed that, for our sample network, FHT reduced network unicast traffic by about 82% compared with standard HSR and by about 56% compared with the PL approach, thus freeing up network bandwidth and improving network traffic performance.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Locational Pricing to Mitigate Voltage Problems Caused by High PV Penetration
by
Sam Weckx, Reinhilde D'hulst and Johan Driesen
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 5574
Abstract
In this paper, a locational marginal pricing algorithm is proposed to control the voltage in unbalanced distribution grids. The increasing amount of photovoltaic (PV) generation installed in the grid may cause the voltage to rise to unacceptable levels during periods of low consumption.
[...] Read more.
In this paper, a locational marginal pricing algorithm is proposed to control the voltage in unbalanced distribution grids. The increasing amount of photovoltaic (PV) generation installed in the grid may cause the voltage to rise to unacceptable levels during periods of low consumption. With locational prices, the distribution system operator can steer the reactive power consumption and active power curtailment of PV panels to guarantee a safe network operation. Flexible loads also respond to these prices. A distributed gradient algorithm automatically defines the locational prices that avoid voltage problems. Using these locational prices results in a minimum cost for the distribution operator to control the voltage. Locational prices can differ between the three phases in unbalanced grids. This is caused by a higher consumption or production in one of the phases compared to the other phases and provides the opportunity for arbitrage, where power is transferred from a phase with a low price to a phase with a high price. The effect of arbitrage is analyzed. The proposed algorithm is applied to an existing three-phase four-wire radial grid. Several simulations with realistic data are performed.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
RETRACTED: A Robust WLS Power System State Estimation Method Integrating a Wide-Area Measurement System and SCADA Technology
by
Tao Jin, Fuliang Chu, Cong Ling and Daniel Legrand Mon Nzongo
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 8583
|
Retraction
Abstract
With the development of modern society, the scale of the power system is rapidly increased accordingly, and the framework and mode of running of power systems are trending towards more complexity. It is nowadays much more important for the dispatchers to know exactly
[...] Read more.
With the development of modern society, the scale of the power system is rapidly increased accordingly, and the framework and mode of running of power systems are trending towards more complexity. It is nowadays much more important for the dispatchers to know exactly the state parameters of the power network through state estimation. This paper proposes a robust power system WLS state estimation method integrating a wide-area measurement system (WAMS) and SCADA technology, incorporating phasor measurements and the results of the traditional state estimator in a post-processing estimator, which greatly reduces the scale of the non-linear estimation problem as well as the number of iterations and the processing time per iteration. This paper firstly analyzes the wide-area state estimation model in detail, then according to the issue that least squares does not account for bad data and outliers, the paper proposes a robust weighted least squares (WLS) method that combines a robust estimation principle with least squares by equivalent weight. The performance assessment is discussed through setting up mathematical models of the distribution network. The effectiveness of the proposed method was proved to be accurate and reliable by simulations and experiments.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
High Efficiency Variable-Frequency Full-Bridge Converter with a Load Adaptive Control Method Based on the Loss Model
by
Lei Zhao, Haoyu Li, Yuan Liu and Zhenwei Li
Cited by 27 | Viewed by 10133
Abstract
In this paper, a load adaptive control method to improve the efficiency and dynamic performance of the Phase-Shifted Full-Bridge (PSFB) converter which works under a wide range of load conditions is presented. The proposed control method can be used as a battery charger
[...] Read more.
In this paper, a load adaptive control method to improve the efficiency and dynamic performance of the Phase-Shifted Full-Bridge (PSFB) converter which works under a wide range of load conditions is presented. The proposed control method can be used as a battery charger since this application demands a wide range of load conditions. The composition of the PSFB converter’s losses and the loss analysis model are both discussed. According to this model, the optimum switching frequency which results in minimum power loss is adopted to improve the efficiency. The relationship between switching frequency and power loss is formulated over a wide load range. Indicated by this kind of relationship, the proposed controller adjusts the switching frequency at different load currents. Moreover, an adaptive gain adjustment controller is applied to replace the traditional controller, with the aim to improve the dynamic performance which is influenced by the changes of the switching frequency and load current. In addition, the experimental results show that the maximum improvement of efficiency is up to 20%. These results confirm the effectiveness of the proposed load adaptive control method.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Research on Shaft Subsynchronous Oscillation Characteristics of Parallel Generators and SSDC Application in Mitigating SSO of Multi-Generators
by
Shen Wang and Zheng Xu
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 5864
Abstract
Subsynchronous oscillation (SSO) of generators caused by high voltage direct current (HVDC) systems can be solved by applying supplemental subsynchronous damping controller (SSDC). SSDC application in mitigating SSO of single-generator systems has been studied intensively. This paper focuses on SSDC application in mitigating
[...] Read more.
Subsynchronous oscillation (SSO) of generators caused by high voltage direct current (HVDC) systems can be solved by applying supplemental subsynchronous damping controller (SSDC). SSDC application in mitigating SSO of single-generator systems has been studied intensively. This paper focuses on SSDC application in mitigating SSO of multi-generator systems. The phase relationship of the speed signals of the generators under their common mechanical natural frequencies is a key consideration in SSDC design. The paper studies in detail the phase relationship of the speed signals of two generators in parallel under their shared mechanical natural frequency, revealing regardless of whether the two generators are identical or not, there always exists a common-mode and an anti-mode under their common natural frequency, and the phase relationship of the speed signals of the generators depends on the extent to which the anti-mode is stimulated. The paper further demonstrates that to guarantee the effectiveness of SSDC, the anti-phase mode component of its input signal should be eliminated. Based on the above analysis, the paper introduces the design process of SSDC for multi-generator systems and verifies its effectiveness through simulation in Power Systems Computer Aided Design/Electromagnetic Transients including Direct Current (PSCAD/EMTDC).
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Optimal Real-Time Scheduling of Wind Integrated Power System Presented with Storage and Wind Forecast Uncertainties
by
Yuchong Huo, Ping Jiang, Yuan Zhu, Shuang Feng and Xi Wu
Cited by 19 | Viewed by 6355
Abstract
The volatility of wind power poses great challenges to the operation of power systems. This paper deals with the economic dispatch problems presented by energy storage in wind integrated systems. A policy iteration algorithm for deriving the cost optimal policy of real-time scheduling
[...] Read more.
The volatility of wind power poses great challenges to the operation of power systems. This paper deals with the economic dispatch problems presented by energy storage in wind integrated systems. A policy iteration algorithm for deriving the cost optimal policy of real-time scheduling is proposed, taking the effect of wind forecast uncertainties into account. First, energy loss and use of fast-ramping generation are selected as the performance metrics. Then, a policy iteration algorithm is developed using the Perturbed Markov decision process. This algorithm has a two-level optimization structure in which both the long-term and short-term behaviors of real-time scheduling policy are optimized. In addition, a unified optimal storage control strategy is presented. The feasibility of the proposed methodology is demonstrated via the wind power archive of Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT). Through comparative numerical experiments, both the performance of the policy iteration algorithm in the short-term and long-term are verified and the consistency, robustness, good convergence and high computational efficiency of the proposed algorithm are also corroborated.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Control Strategies to Smooth Short-Term Power Fluctuations in Large Photovoltaic Plants Using Battery Storage Systems
by
Javier Marcos, Iñigo De la Parra, Miguel García and Luis Marroyo
Cited by 120 | Viewed by 12058
Abstract
The variations in irradiance produced by changes in cloud cover can cause rapid fluctuations in the power generated by large photovoltaic (PV) plants. As the PV power share in the grid increases, such fluctuations may adversely affect power quality and reliability. Thus, energy
[...] Read more.
The variations in irradiance produced by changes in cloud cover can cause rapid fluctuations in the power generated by large photovoltaic (PV) plants. As the PV power share in the grid increases, such fluctuations may adversely affect power quality and reliability. Thus, energy storage systems (ESS) are necessary in order to smooth power fluctuations below the maximum allowable. This article first proposes a new control strategy (step-control), to improve the results in relation to two state-of-the-art strategies, ramp-rate control and moving average. It also presents a method to quantify the storage capacity requirements according to the three different smoothing strategies and for different PV plant sizes. Finally, simulations shows that, although the moving-average (MA) strategy requires the smallest capacity, it presents more losses (2–3 times more) and produces a much higher number of cycles over the ESS (around 10 times more), making it unsuitable with storage technologies as lithium-ion. The step-control shown as a better option in scenery with exigent ramp restrictions (around 2%/min) and distributed generation against the ramp-rate control in all ESS key aspects: 20% less of capacity, up to 30% less of losses and a 40% less of ageing. All the simulations were based on real PV production data, taken every 5 s in the course of one year (2012) from a number of systems with power outputs ranging from 550 kW to 40 MW.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Multi-Objective Planning of Multi-Type Distributed Generation Considering Timing Characteristics and Environmental Benefits
by
Yajing Gao, Jianpeng Liu, Jin Yang, Haifeng Liang and Jiancheng Zhang
Cited by 33 | Viewed by 6982
Abstract
This paper presents a novel approach to multi-type distributed generation (DG) planning based on the analysis of investment and income brought by grid-connected DG. Firstly, the timing characteristics of loads and DG outputs, as well as the environmental benefits of DG are analyzed.
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a novel approach to multi-type distributed generation (DG) planning based on the analysis of investment and income brought by grid-connected DG. Firstly, the timing characteristics of loads and DG outputs, as well as the environmental benefits of DG are analyzed. Then, on the basis of the classification of daily load sequences, the typical daily load sequence and the typical daily output sequence of DG per unit capacity can be computed. The proposed planning model takes the location, capacity and types of DG into account as optimization variables. An improved adaptive genetic algorithm is proposed to solve the model. Case studies have been carried out on the IEEE 14-node distribution system to verify the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed method and model.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Multi-Faceted Assessment of a Wireless Communications Infrastructure for the Green Neighborhoods of the Smart Grid
by
Gregorio López, Pedro Moura, José Ignacio Moreno and José Manuel Camacho
Cited by 25 | Viewed by 10653
Abstract
Reducing electricity consumption and integrating renewable power generation sources represent two of the main drivers of the so-called Smart Grid. Machine-to-Machine (M2M) communications will play a key role on making such a Smart Grid a reality, since they will enable the required bidirectional
[...] Read more.
Reducing electricity consumption and integrating renewable power generation sources represent two of the main drivers of the so-called Smart Grid. Machine-to-Machine (M2M) communications will play a key role on making such a Smart Grid a reality, since they will enable the required bidirectional real-time bulk information exchange. However, communications for the Smart Grid present specific requirements from both technical and economic perspectives, so it is crucial to evaluate how existing communication architectures and technologies meet them before undertaking the important investments needed to deploy this kind of infrastructure on a large scale. The main goal of this paper is to evaluate, from different perspectives, the core M2M communications infrastructure of a platform designed to reduce electricity consumption and integrate renewable generation at residential level. Such a communications infrastructure is fully based on widely deployed wireless communications technologies such as IEEE 802.11 and General Packet Radio Service (GPRS). Notably, the paper assesses the operational costs of using different security solutions in the GPRS segment and the performance of the selected communications technologies based on different metrics (goodput, in the case of IEEE 802.11, and transmission time, in the case of GPRS).
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Reviewing Microgrids from a Multi-Agent Systems Perspective
by
Jorge J. Gomez-Sanz, Sandra Garcia-Rodriguez, Nuria Cuartero-Soler and Luis Hernandez-Callejo
Cited by 52 | Viewed by 8915
Abstract
The construction of Smart Grids leads to the main question of what kind of intelligence such grids require and how to build it. Some authors choose an agent based solution to realize this intelligence. However, there may be some misunderstandings in the way
[...] Read more.
The construction of Smart Grids leads to the main question of what kind of intelligence such grids require and how to build it. Some authors choose an agent based solution to realize this intelligence. However, there may be some misunderstandings in the way this technology is being applied. This paper exposes some considerations of this subject, focusing on the Microgrid level, and shows a practical example through INGENIAS methodology, which is a methodology for the development of Agent Oriented systems that applies Model Driven Development techniques to produce fully functional Multi-Agent Systems.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Valuation of Wind Energy Projects: A Real Options Approach
by
Luis M. Abadie and José M. Chamorro
Cited by 45 | Viewed by 10249
Abstract
We address the valuation of an operating wind farm and the finite-lived option to invest in it under different reward/support schemes: a constant feed-in tariff, a premium on top of the electricity market price (either a fixed premium or a variable subsidy such
[...] Read more.
We address the valuation of an operating wind farm and the finite-lived option to invest in it under different reward/support schemes: a constant feed-in tariff, a premium on top of the electricity market price (either a fixed premium or a variable subsidy such as a renewable obligation certificate or ROC), and a transitory subsidy, among others. Futures contracts on electricity with ever longer maturities enable market-based valuations to be undertaken. The model considers up to three sources of uncertainty: the electricity price, the level of wind generation, and the certificate (ROC) price where appropriate. When analytical solutions are lacking, we resort to a trinomial lattice combined with Monte Carlo simulation; we also use a two-dimensional binomial lattice when uncertainty in the ROC price is considered. Our data set refers to the UK. The numerical results show the impact of several factors involved in the decision to invest: the subsidy per MWh generated, the initial lump-sum subsidy, the maturity of the investment option, and electricity price volatility. Different combinations of variables can help bring forward investments in wind generation. One-off policies, e.g., a transitory initial subsidy, seem to have a stronger effect than a fixed premium per MWh produced.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Autoregressive with Exogenous Variables and Neural Network Short-Term Load Forecast Models for Residential Low Voltage Distribution Networks
by
Christopher Bennett, Rodney A. Stewart and Junwei Lu
Cited by 69 | Viewed by 10354
Abstract
This paper set out to identify the significant variables which affect residential low voltage (LV) network demand and develop next day total energy use (NDTEU) and next day peak demand (NDPD) forecast models for each phase. The models were developed using both autoregressive
[...] Read more.
This paper set out to identify the significant variables which affect residential low voltage (LV) network demand and develop next day total energy use (NDTEU) and next day peak demand (NDPD) forecast models for each phase. The models were developed using both autoregressive integrated moving average with exogenous variables (ARIMAX) and neural network (NN) techniques. The data used for this research was collected from a LV transformer serving 128 residential customers. It was observed that temperature accounted for half of the residential LV network demand. The inclusion of the double exponential smoothing algorithm, autoregressive terms, relative humidity and day of the week dummy variables increased model accuracy. In terms of
R2 and for each modelling technique and phase, NDTEU hindcast accuracy ranged from 0.77 to 0.87 and forecast accuracy ranged from 0.74 to 0.84. NDPD hindcast accuracy ranged from 0.68 to 0.74 and forecast accuracy ranged from 0.56 to 0.67. The NDTEU models were more accurate than the NDPD models due to the peak demand time series being more variable in nature. The NN models had slight accuracy gains over the ARIMAX models. A hybrid model was developed which combined the best traits of the ARIMAX and NN techniques, resulting in improved hindcast and forecast fits across the all three phases.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Enabling Privacy in Vehicle-to-Grid Interactions for Battery Recharging
by
Cristina Rottondi, Simone Fontana and Giacomo Verticale
Cited by 31 | Viewed by 8537
Abstract
The diffusion of Electric Vehicles (EV) fostered by the evolution of the power system towards the new concept of Smart Grid introduces several technological challenges related to the synergy among electricity-propelled vehicle fleets and the energy grid ecosystem. EVs promise to reduce carbon
[...] Read more.
The diffusion of Electric Vehicles (EV) fostered by the evolution of the power system towards the new concept of Smart Grid introduces several technological challenges related to the synergy among electricity-propelled vehicle fleets and the energy grid ecosystem. EVs promise to reduce carbon emissions by exploiting Renewable Energy Sources (RESes) for battery recharge, and could potentially serve as storage bank to flatten the fluctuations of power generation caused by the intermittent nature of RESes by relying on a load aggregator, which intelligently schedules the battery charge/discharge of a fleet of vehicles according to the users’ requests and grid’s needs. However, the introduction of such vehicle-to-grid (V2G) infrastructure rises also privacy concerns: plugging the vehicles in the recharging infrastructures may expose private information regarding the user’s locations and travelling habits. Therefore, this paper proposes a privacy-preserving V2G infrastructure which does not disclose to the aggregator the current battery charge level, the amount of refilled energy, nor the time periods in which the vehicles are actually plugged in. The communication protocol relies on the Shamir Secret Sharing threshold cryptosystem. We evaluate the security properties of our solution and compare its performance to the optimal scheduling achievable by means of an Integer Linear Program (ILP) aimed at maximizing the ratio of the amount of charged/discharged energy to/from the EV’s batteries to the grid power availability/request. This way, we quantify the reduction in the effectiveness of the scheduling strategy due to the preservation of data privacy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Fast Cut Back Thermal Power Plant Load Rejection and Black Start Field Test Analysis
by
Kaiwen Zeng, Jinyu Wen, Longpeng Ma, Shijie Cheng, En Lu and Ning Wang
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 13281
Abstract
Fast and reliable black start plays a key role in improving the ability of the power system to resist the risk of large-scale blackouts. For a black start with high voltage and long-distance transmission lines, it is much easier to cause phenomena such
[...] Read more.
Fast and reliable black start plays a key role in improving the ability of the power system to resist the risk of large-scale blackouts. For a black start with high voltage and long-distance transmission lines, it is much easier to cause phenomena such as self-excitation and power frequency/operating overvoltage, which may lead to black start failure and impact the reliability of the system’s restoration. Meanwhile, the long time needed to crank up the non-black start units will impact the speed of the restoration. This paper addresses the advantages of using a thermal power unit with a fast cut back (FCB) function as a black start unit, and studies the transient process of the FCB unit during the restoration. Firstly, key problems in the power system black start process are analyzed and a practical engineering criterion of self-excitation is proposed. Secondly, the dynamic model of the FCB unit is presented. Thirdly, the field test of the FCB unit load rejection and black start is introduced, which is the first successful field test of black start with 500 kV long-distance lines in China Southern Power Grid (CSG). Finally, the transient process of this test is simulated using the PSCAD/EMTDC software, and the simulation results accord well with the field test results, which verifies the correctness of the FCB model and the self-excitation engineering criterion proposed.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Fault Detection and Location by Static Switches in Microgrids Using Wavelet Transform and Adaptive Network-Based Fuzzy Inference System
by
Ying-Yi Hong, Yan-Hung Wei, Yung-Ruei Chang, Yih-Der Lee and Pang-Wei Liu
Cited by 45 | Viewed by 10993
Abstract
Microgrids are a highly efficient means of embedding distributed generation sources in a power system. However, if a fault occurs inside or outside the microgrid, the microgrid should be immediately disconnected from the main grid using a static switch installed at the secondary
[...] Read more.
Microgrids are a highly efficient means of embedding distributed generation sources in a power system. However, if a fault occurs inside or outside the microgrid, the microgrid should be immediately disconnected from the main grid using a static switch installed at the secondary side of the main transformer near the point of common coupling (PCC). The static switch should have a reliable module implemented in a chip to detect/locate the fault and activate the breaker to open the circuit immediately. This paper proposes a novel approach to design this module in a static switch using the discrete wavelet transform (DWT) and adaptive network-based fuzzy inference system (ANFIS). The wavelet coefficient of the fault voltage and the inference results of ANFIS with the wavelet energy of the fault current at the secondary side of the main transformer determine the control action (open or close) of a static switch. The ANFIS identifies the faulty zones inside or outside the microgrid. The proposed method is applied to the first outdoor microgrid test bed in Taiwan, with a generation capacity of 360.5 kW. This microgrid test bed is studied using the real-time simulator eMegaSim developed by Opal-RT Technology Inc. (Montreal, QC, Canada). The proposed method based on DWT and ANFIS is implemented in a field programmable gate array (FPGA) by using the Xilinx System Generator. Simulation results reveal that the proposed method is efficient and applicable in the real-time control environment of a power system.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Wide-Area Measurement Systems-Based Adaptive Strategy for Controlled Islanding in Bulk Power Systems
by
Honglei Song, Junyong Wu and Kui Wu
Cited by 19 | Viewed by 9278
Abstract
Controlled islanding is the last countermeasure for a bulk power system when it suffers from severe cascading contingencies. The objective of controlled islanding is to maintain the stability of each island and to keep the total loss of loads of the whole system
[...] Read more.
Controlled islanding is the last countermeasure for a bulk power system when it suffers from severe cascading contingencies. The objective of controlled islanding is to maintain the stability of each island and to keep the total loss of loads of the whole system to a minimum. This paper presents a novel integrated wide-area measurement systems (WAMS)-based adaptive controlled islanding strategy, which depends on the dynamic post-fault trajectories under different failure modes. We first utilize an improved Laplacian eigenmap algorithm (ILEA) to identify the coherent generators and use the slow coherency grouping algorithm to guarantee coherent stability within an island. Using the identification result, we then define the minimum coherent generator virtual nodes to reduce the searching space in a graph and utilize the k-way partitioning (KWP) algorithm to obtain a preliminary partition of the simplified graph. Based on the preliminary partition, we consider the direction of power flow and propose a variable neighborhood heuristic searching algorithm to search the optimal separation surfaces so that the net imbalanced power of islands is minimized. Finally, the bidirectional power flow tracing algorithm and PQ decomposition power flow analysis are utilized to determine the corrective controls within each island. The test results with the New England 39-bus system and the IEEE 118-bus system show that the proposed integrated controlled islanding strategy can automatically adapt to different fault modes through generator coherency identification and effectively group the different coherent generators into different islands.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Design of a Control Scheme for Distribution Static Synchronous Compensators with Power-Quality Improvement Capability
by
Pedro Roncero-Sànchez and Enrique Acha
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 9809
Abstract
Electric power systems are among the greatest achievements of the last century. Today, important issues, such as an ever-increasing demand, the flexible and reliable integration of distributed generation or a growth in disturbing loads, must be borne in mind. In this context, smart
[...] Read more.
Electric power systems are among the greatest achievements of the last century. Today, important issues, such as an ever-increasing demand, the flexible and reliable integration of distributed generation or a growth in disturbing loads, must be borne in mind. In this context, smart grids play a key role, allowing better efficiency of power systems. Power electronics provides solutions to the aforementioned matters, since it allows various energy sources to be integrated into smart grids. Nevertheless, the design of the various control schemes that are necessary for the correct operation of the power-electronic interface is a very important issue that must always be taken into consideration. This paper deals with the design of the control system of a distribution static synchronous compensator (DSTATCOM) based on flying-capacitor multilevel converters. The control system is tailored to compensate for both voltage sags by means of reactive-power injection and voltage imbalances caused by unbalanced loads. The design of the overall control is carried out by using the root-locus and frequency-response techniques, improving both the transient response and the steady-state error of the closed-loop system. Simulation results obtained using PSCADTM/EMTDCTM (Manitoba Hydro International Ltd., Commerce Drive, Winnipeg, MB, Canada) show the resultant voltage regulation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Strategies for Power Line Communications Smart Metering Network Deployment
by
Alberto Sendin, Ivan Peña and Pablo Angueira
Cited by 67 | Viewed by 17573
Abstract
Smart Grids are becoming a reality all over the world. Nowadays, the research efforts for the introduction and deployment of these grids are mainly focused on the development of the field of Smart Metering. This emerging application requires the use of technologies to
[...] Read more.
Smart Grids are becoming a reality all over the world. Nowadays, the research efforts for the introduction and deployment of these grids are mainly focused on the development of the field of Smart Metering. This emerging application requires the use of technologies to access the significant number of points of supply (PoS) existing in the grid, covering the Low Voltage (LV) segment with the lowest possible costs. Power Line Communications (PLC) have been extensively used in electricity grids for a variety of purposes and, of late, have been the focus of renewed interest. PLC are really well suited for quick and inexpensive pervasive deployments. However, no LV grid is the same in any electricity company (utility), and the particularities of each grid evolution, architecture, circumstances and materials, makes it a challenge to deploy Smart Metering networks with PLC technologies, with the Smart Grid as an ultimate goal. This paper covers the evolution of Smart Metering networks, together with the evolution of PLC technologies until both worlds have converged to project PLC-enabled Smart Metering networks towards Smart Grid. This paper develops guidelines over a set of strategic aspects of PLC Smart Metering network deployment based on the knowledge gathered on real field; and introduces the future challenges of these networks in their evolution towards the Smart Grid.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Priority-Based Hierarchical Operational Management for Multiagent-Based Microgrids
by
Takumi Kato, Hideyuki Takahashi, Kazuto Sasai, Gen Kitagata, Hak-Man Kim and Tetsuo Kinoshita
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 8978
Abstract
Electricity consumption in the world is constantly increasing, making our lives become more and more dependent on electricity. There are several new paradigms proposed in the field of power grids. In Japan, especially after the Great East Japan Earthquake in March 2011, the
[...] Read more.
Electricity consumption in the world is constantly increasing, making our lives become more and more dependent on electricity. There are several new paradigms proposed in the field of power grids. In Japan, especially after the Great East Japan Earthquake in March 2011, the new power grid paradigms are expected to be more resilient to survive several difficulties during disasters. In this paper, we focus on microgrids and propose priority-based hierarchical operational management for multiagent-based microgrids. The proposed management is a new multiagent-based load shedding scheme and multiagent-based hierarchical architecture to realize such resilient microgrids. We developed a prototype system and performed an evaluation of the proposed management using the developed system. The result of the evaluation shows the effectiveness of our proposal in power shortage situations, such as disasters.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Stochastic Modeling and Optimization in a Microgrid: A Survey
by
Hao Liang and Weihua Zhuang
Cited by 179 | Viewed by 16578
Abstract
The future smart grid is expected to be an interconnected network of small-scale and self-contained microgrids, in addition to a large-scale electric power backbone. By utilizing microsources, such as renewable energy sources and combined heat and power plants, microgrids can supply electrical and
[...] Read more.
The future smart grid is expected to be an interconnected network of small-scale and self-contained microgrids, in addition to a large-scale electric power backbone. By utilizing microsources, such as renewable energy sources and combined heat and power plants, microgrids can supply electrical and heat loads in local areas in an economic and environment friendly way. To better adopt the intermittent and weather-dependent renewable power generation, energy storage devices, such as batteries, heat buffers and plug-in electric vehicles (PEVs) with vehicle-to-grid systems can be integrated in microgrids. However, significant technical challenges arise in the planning, operation and control of microgrids, due to the randomness in renewable power generation, the buffering effect of energy storage devices and the high mobility of PEVs. The two-way communication functionalities of the future smart grid provide an opportunity to address these challenges, by offering the communication links for microgrid status information collection. However, how to utilize stochastic modeling and optimization tools for efficient, reliable and economic planning, operation and control of microgrids remains an open issue. In this paper, we investigate the key features of microgrids and provide a comprehensive literature survey on the stochastic modeling and optimization tools for a microgrid. Future research directions are also identified.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Economic Scheduling of Residential Plug-In (Hybrid) Electric Vehicle (PHEV) Charging
by
Maigha and Mariesa L. Crow
Cited by 27 | Viewed by 8150
Abstract
In the past decade, plug-in (hybrid) electric vehicles (PHEVs) have been widely proposed as a viable alternative to internal combustion vehicles to reduce fossil fuel emissions and dependence on petroleum. Off-peak vehicle charging is frequently proposed to reduce the stress on the electric
[...] Read more.
In the past decade, plug-in (hybrid) electric vehicles (PHEVs) have been widely proposed as a viable alternative to internal combustion vehicles to reduce fossil fuel emissions and dependence on petroleum. Off-peak vehicle charging is frequently proposed to reduce the stress on the electric power grid by shaping the load curve. Time of use (TOU) rates have been recommended to incentivize PHEV owners to shift their charging patterns. Many utilities are not currently equipped to provide real-time use rates to their customers, but can provide two or three staggered rate levels. To date, an analysis of the optimal number of levels and rate-duration of TOU rates for a given consumer demographic versus utility generation mix has not been performed. In this paper, we propose to use the U.S. National Household Travel Survey (NHTS) database as a basis to analyze typical PHEV energy requirements. We use Monte Carlo methods to model the uncertainty inherent in battery state-of-charge and trip duration. We conclude the paper with an analysis of a different TOU rate schedule proposed by a mix of U.S. utilities. We introduce a centralized scheduling strategy for PHEV charging using a genetic algorithm to accommodate the size and complexity of the optimization.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Development and Field Test of a Real-Time Database in the Korean Smart Distribution Management System
by
Sang-Yun Yun and Joon-Ho Choi
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 8036
Abstract
Recently, a distribution management system (DMS) that can conduct periodical system analysis and control by mounting various applications programs has been actively developed. In this paper, we summarize the development and demonstration of a database structure that can perform real-time system analysis and
[...] Read more.
Recently, a distribution management system (DMS) that can conduct periodical system analysis and control by mounting various applications programs has been actively developed. In this paper, we summarize the development and demonstration of a database structure that can perform real-time system analysis and control of the Korean smart distribution management system (KSDMS). The developed database structure consists of a common information model (CIM)-based off-line database (DB), a physical DB (PDB) for DB establishment of the operating server, a real-time DB (RTDB) for real-time server operation and remote terminal unit data interconnection, and an application common model (ACM) DB for running application programs. The ACM DB for real-time system analysis and control of the application programs was developed by using a parallel table structure and a link list model, thereby providing fast input and output as well as high execution speed of application programs. Furthermore, the ACM DB was configured with hierarchical and non-hierarchical data models to reflect the system models that increase the DB size and operation speed through the reduction of the system, of which elements were unnecessary for analysis and control. The proposed database model was implemented and tested at the Gochaing and Jeju offices using a real system. Through data measurement of the remote terminal units, and through the operation and control of the application programs using the measurement, the performance, speed, and integrity of the proposed database model were validated, thereby demonstrating that this model can be applied to real systems.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
DVP: A Novel High-Availability Seamless Redundancy (HSR) Protocol Traffic-Reduction Algorithm for a Substation Automation System Network
by
Saad Nsaif and Jong-Myung Rhee
Cited by 22 | Viewed by 8272
Abstract
The high-availability seamless redundancy (HSR) protocol, a potential candidate for substation automation system (SAS) networks, provides duplicated frame copies of each sent frame, with zero fault-recovery time. This means that even in the case of node or link failure, the destination node will
[...] Read more.
The high-availability seamless redundancy (HSR) protocol, a potential candidate for substation automation system (SAS) networks, provides duplicated frame copies of each sent frame, with zero fault-recovery time. This means that even in the case of node or link failure, the destination node will receive at least one copy of the sent frame. Consequently, there is no network operation down time. However, the forwarding process of the QuadBox node in HSR is not smart and relies solely on duplication and random forwarding of all received frames. Thus, if a unicast frame is sent in any closed-loop network, the frame copies will be spread through most of all the links in both directions until they reach the destination node, which inevitably results in significant, unnecessary network traffic. In this paper, we present an algorithm called the dual virtual paths (DVP) algorithm to solve such an HSR excessive traffic issue. The idea behind our DVP algorithm is to establish automatic DVP between each HSR node and all the other nodes in the network, except for the QuadBox node. These virtual paths will be used for DVP unicast traffic transmission, rather than using the standard HSR transmission process. Therefore, the DVP algorithm results in less traffic, because there is no duplication or random forwarding, contrary to standard HSR. For the sample networks selected in this paper, the DVP algorithm shows more than a 70% reduction in network traffic and about an 80% reduction in the discarded traffic compared to the standard HSR protocol.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Comparison between Underground Cable and Overhead Line for a Low-Voltage Direct Current Distribution Network Serving Communication Repeater
by
Jae-Han Kim, Ju-Yong Kim, Jin-Tae Cho, Il-Keun Song, Bo-Min Kweon, Il-Yop Chung and Joon-Ho Choi
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 13007
Abstract
This paper compares the differences in economic feasibility and dynamic characteristics between underground (U/G) cable and overhead (O/H) line for low-voltage direct current (LVDC) distribution. Numerous low loaded long-distance distribution networks served by medium-voltage alternative current (MVAC) distribution lines exist in the Korean
[...] Read more.
This paper compares the differences in economic feasibility and dynamic characteristics between underground (U/G) cable and overhead (O/H) line for low-voltage direct current (LVDC) distribution. Numerous low loaded long-distance distribution networks served by medium-voltage alternative current (MVAC) distribution lines exist in the Korean distribution network. This is an unavoidable choice to compensate voltage drop, therefore, excessive cost is expended for the amount of electrical power load. The Korean Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO) is consequently seeking a solution to replace the MVAC distribution line with a LVDC distribution line, reducing costs and providing better quality direct current (DC) electricity. A LVDC distribution network can be installed with U/G cables or O/H lines. In this paper, a realistic MVAC distribution network in a mountainous area was selected as the target model to replace with LVDC. A 30 year net present value (NPV) analysis of the economic feasibility was conducted to compare the cost of the two types of distribution line. A simulation study compared the results of the DC line fault with the power system computer aided design/electro-magnetic transient direct current (PSCAD/EMTDC). The economic feasibility evaluation and simulation study results will be used to select the applicable type of LVDC distribution network.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Coordinated Control of Distributed and Bulk Energy Storage for Alleviation of Post-Contingency Overloads
by
Yunfeng Wen, Chuangxin Guo and Shufeng Dong
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 8035
Abstract
This paper presents a novel corrective control strategy that can effectively coordinate distributed and bulk energy storage to relieve post-contingency overloads. Immediately following a contingency, distributed batteries are implemented to provide fast corrective actions to reduce power flows below their short-term emergency ratings.
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a novel corrective control strategy that can effectively coordinate distributed and bulk energy storage to relieve post-contingency overloads. Immediately following a contingency, distributed batteries are implemented to provide fast corrective actions to reduce power flows below their short-term emergency ratings. During the long-term period, Pumped Hydro Storage units work in pumping or generation mode to aid conventional generating units keep line flows below the normal ratings. This problem is formulated as a multi-stage Corrective Security-constrained OPF (CSCOPF). An algorithm based on Benders decomposition was proposed to find the optimal base case solution and seek feasible corrective actions to handle all contingencies. Case studies based on a modified RTS-96 system demonstrate the performance and effectiveness of the proposed control strategy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Artificial Neural Network for Short-Term Load Forecasting in Distribution Systems
by
Luis Hernández, Carlos Baladrón, Javier M. Aguiar, Lorena Calavia, Belén Carro, Antonio Sánchez-Esguevillas, Francisco Pérez, Ángel Fernández and Jaime Lloret
Cited by 109 | Viewed by 11974
Abstract
The new paradigms and latest developments in the Electrical Grid are based on the introduction of distributed intelligence at several stages of its physical layer, giving birth to concepts such as
Smart Grids,
Virtual Power Plants,
microgrids,
Smart Buildings and
[...] Read more.
The new paradigms and latest developments in the Electrical Grid are based on the introduction of distributed intelligence at several stages of its physical layer, giving birth to concepts such as
Smart Grids,
Virtual Power Plants,
microgrids,
Smart Buildings and
Smart Environments.
Distributed Generation (
DG) is a philosophy in which energy is no longer produced exclusively in huge centralized plants, but also in smaller premises which take advantage of local conditions in order to minimize transmission losses and optimize production and consumption. This represents a new opportunity for renewable energy, because small elements such as solar panels and wind turbines are expected to be scattered along the grid, feeding local installations or selling energy to the grid depending on their local generation/consumption conditions. The introduction of these highly dynamic elements will lead to a substantial change in the curves of demanded energy. The aim of this paper is to apply
Short-Term Load Forecasting (
STLF) in
microgrid environments with curves and similar behaviours, using two different data sets: the first one packing electricity consumption information during four years and six months in a
microgrid along with calendar data, while the second one will be just four months of the previous parameters along with the solar radiation from the site. For the first set of data different
STLF models will be discussed, studying the effect of each variable, in order to identify the best one. That model will be employed with the second set of data, in order to make a comparison with a new model that takes into account the solar radiation, since the photovoltaic installations of the
microgrid will cause the power demand to fluctuate depending on the solar radiation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Extended Distributed State Estimation: A Detection Method against Tolerable False Data Injection Attacks in Smart Grids
by
Dai Wang, Xiaohong Guan, Ting Liu, Yun Gu, Chao Shen and Zhanbo Xu
Cited by 78 | Viewed by 11078
Abstract
False data injection (FDI) is considered to be one of the most dangerous cyber-attacks in smart grids, as it may lead to energy theft from end users, false dispatch in the distribution process, and device breakdown during power generation. In this paper, a
[...] Read more.
False data injection (FDI) is considered to be one of the most dangerous cyber-attacks in smart grids, as it may lead to energy theft from end users, false dispatch in the distribution process, and device breakdown during power generation. In this paper, a novel kind of FDI attack, named tolerable false data injection (TFDI), is constructed. Such attacks exploit the traditional detector’s tolerance of observation errors to bypass the traditional bad data detection. Then, a method based on extended distributed state estimation (EDSE) is proposed to detect TFDI in smart grids. The smart grid is decomposed into several subsystems, exploiting graph partition algorithms. Each subsystem is extended outward to include the adjacent buses and tie lines, and generate the extended subsystem. The Chi-squares test is applied to detect the false data in each extended subsystem. Through decomposition, the false data stands out distinctively from normal observation errors and the detection sensitivity is increased. Extensive TFDI attack cases are simulated in the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 14-, 39-, 118- and 300-bus systems. Simulation results show that the detection precision of the EDSE-based method is much higher than that of the traditional method, while the proposed method significantly reduces the associated computational costs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Development and Empirical Evaluation of the Korean Smart Distribution Management System
by
Sang-Yun Yun, Chul-Min Chu, Seong-Chul Kwon, Il-Keun Song and Joon-Ho Choi
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 9091
Abstract
This paper introduces the development and actual test results of the Korean Smart Distribution Management System (KSDMS). The KSDMS has been designed and developed to cope with the lack of interconnection capability of the Dispersed Energy Resource (DER), to provide standardization and compatibility,
[...] Read more.
This paper introduces the development and actual test results of the Korean Smart Distribution Management System (KSDMS). The KSDMS has been designed and developed to cope with the lack of interconnection capability of the Dispersed Energy Resource (DER), to provide standardization and compatibility, and to implement automatic processing of service restoration, in the existing Distribution Automation System (DAS) in Korea. First, real-time system analysis and control application programs were developed, to solve the problems of the existing DAS; and the Distribution Management System (DMS) platform was developed, to run the developed application programs. Second, international standard-based communication, platform, and database structures were adopted, for standardization and compatibility. Third, a platform and application program functions were developed to process faults automatically; and a communication device and an intelligent electronic device (IED) were developed to automate fault restoration, through communication between devices. The KSDMS was evaluated by three tests: unit function test, platform and application program integration test, and empirical test. The first two were conducted on both small and large demonstration systems. The empirical test was performed at the Power Testing Center (PTC) in Gochang, and on a real system, at the Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO), on Jeju Island. The test results verified that the KSDMS can actively resolve the problems of the existing DAS.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Development and Improvement of an Intelligent Cable Monitoring System for Underground Distribution Networks Using Distributed Temperature Sensing
by
Jintae Cho, Jae-Han Kim, Hak-Ju Lee, Ju-Yong Kim, Il-Keun Song and Joon-Ho Choi
Cited by 27 | Viewed by 10397
Abstract
With power systems switching to smart grids, real-time and on-line monitoring technologies for underground distribution power cables have become a priority. Most distribution components have been developed with self-diagnostic sensors to realize self-healing, one of the smart grid functions in a distribution network.
[...] Read more.
With power systems switching to smart grids, real-time and on-line monitoring technologies for underground distribution power cables have become a priority. Most distribution components have been developed with self-diagnostic sensors to realize self-healing, one of the smart grid functions in a distribution network. Nonetheless, implementing a real-time and on-line monitoring system for underground distribution cables has been difficult because of high cost and low sensitivity. Nowadays, optical fiber composite power cables (OFCPCs) are being considered for communication and power delivery to cope with the increasing communication load in a distribution network. Therefore, the application of distributed temperature sensing (DTS) technology on OFCPCs used as underground distribution lines is studied for the real-time and on-line monitoring of the underground distribution power cables. Faults can be reduced and operating ampacity of the underground distribution system can be increased. This paper presents the development and improvement of an intelligent cable monitoring system for the underground distribution power system, using DTS technology and OFCPCs as the underground distribution lines in the field.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Voltage Support Provided by STATCOM in Unbalanced Power Systems
by
Ana Rodríguez, Emilio J. Bueno, Álvar Mayor, Francisco J. Rodríguez and Aurelio García-Cerrada
Cited by 20 | Viewed by 10080
Abstract
The presence of an unbalanced voltage at the point of common coupling (PCC) results in the appearance of a negative sequence current component that deteriorates the control performance. Static synchronous compensators (STATCOMs) are well-known to be a power application capable of carrying out
[...] Read more.
The presence of an unbalanced voltage at the point of common coupling (PCC) results in the appearance of a negative sequence current component that deteriorates the control performance. Static synchronous compensators (STATCOMs) are well-known to be a power application capable of carrying out the regulation of the PCC voltage in distribution lines that can suffer from grid disturbances. This article proposes a novel PCC voltage controller in synchronous reference frame to compensate an unbalanced PCC voltage by means of a STATCOM, allowing an independent control of both positive and negative voltage sequences. Several works have been proposed in this line but they were not able to compensate an unbalance in the PCC voltage. Furthermore, this controller includes aspects as antiwindup and droop control to improve the control system performance.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Development and Field Test of Voltage VAR Optimization in the Korean Smart Distribution Management System
by
Sang-Yun Yun, Pyeong-Ik Hwang, Seung-Il Moon, Seong-Chul Kwon, Il-Keun Song and Joon-Ho Choi
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 8109
Abstract
This paper is a summary of the development and demonstration of an optimization program, voltage VAR optimization (VVO), in the Korean Smart Distribution Management System (KSDMS). KSDMS was developed to address the lack of receptivity of distributed generators (DGs), standardization and compatibility, and
[...] Read more.
This paper is a summary of the development and demonstration of an optimization program, voltage VAR optimization (VVO), in the Korean Smart Distribution Management System (KSDMS). KSDMS was developed to address the lack of receptivity of distributed generators (DGs), standardization and compatibility, and manual failure recovery in the existing Korean automated distribution system. Focusing on the lack of receptivity of DGs, we developed a real-time system analysis and control program. The KSDMS VVO enhances manual system operation of the existing distribution system and provides a solution with all control equipment operated at a system level. The developed VVO is an optimal power flow (OPF) method that resolves violations, minimizes switching costs, and minimizes loss, and its function can vary depending on the operator’s command. The sequential mixed integer linear programming (SMILP) method was adopted to find the solution of the OPF. We tested the precision of the proposed VVO on selected simulated systems and its applicability to actual systems at two substations on the Jeju Island. Running the KSDMS VVO on a regular basis improved system stability, and it also raised no issues regarding its applicability to actual systems.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Distributed Load-Shedding System for Agent-Based Autonomous Microgrid Operations
by
Yujin Lim, Hak-Man Kim and Tetsuo Kinoshita
Cited by 38 | Viewed by 8715
Abstract
A microgrid is an eco-friendly power system because renewable sources are used as main power sources. In the islanded operation mode of a microgrid, maintaining the balance between power supply and power demand is a very important problem. In the case of surplus
[...] Read more.
A microgrid is an eco-friendly power system because renewable sources are used as main power sources. In the islanded operation mode of a microgrid, maintaining the balance between power supply and power demand is a very important problem. In the case of surplus supply, decreased generation output and/or charge of distributed storages can be applied to solve the imbalance between power supply and demand. In the case of supply shortages, increased generation output and/or discharge of distributed storages can be applied. Especially in the case of critical supply shortages, load shedding should be applied. In a distributed load-shedding approach, microgrid components need to make decisions autonomously. For autonomous microgrid operation, a multi-agent system has been investigated. In this paper, a distributed load-shedding system for agent-based autonomous operation of a microgrid is designed. The designed system is implemented and tested to show the functionality and feasibility of the proposed system.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of the Dynamic Performance of Self-Excited Induction Generators Employed in Renewable Energy Generation
by
Mohamed E. A. Farrag and Ghanim A. Putrus
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 7480
Abstract
Incentives, such as the Feed-in-tariff are expected to lead to continuous increase in the deployment of Small Scale Embedded Generation (SSEG) in the distribution network. Self-Excited Induction Generators (SEIG) represent a significant segment of potential SSEG. The quality of SEIG output voltage magnitude
[...] Read more.
Incentives, such as the Feed-in-tariff are expected to lead to continuous increase in the deployment of Small Scale Embedded Generation (SSEG) in the distribution network. Self-Excited Induction Generators (SEIG) represent a significant segment of potential SSEG. The quality of SEIG output voltage magnitude and frequency is investigated in this paper to support the SEIG operation for different network operating conditions. The dynamic behaviour of the SEIG resulting from disconnection, reconnection from/to the grid and potential operation in islanding mode is studied in detail. The local load and reactive power supply are the key factors that determine the SEIG performance, as they have significant influence on the voltage and frequency change after disconnection from the grid. Hence, the aim of this work is to identify the optimum combination of the reactive power supply (essential for self excitation of the SEIG) and the active load (essential for balancing power generation and demand). This is required in order to support the SEIG operation after disconnection from the grid, during islanding and reconnection to the grid. The results show that the generator voltage and speed (frequency) can be controlled and maintained within the statuary limits. This will enable safe disconnection and reconnection of the SEIG from/to the grid and makes it easier to operate in islanding mode.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Implementation and Control of a Residential Electrothermal Microgrid Based on Renewable Energies, a Hybrid Storage System and Demand Side Management
by
Julio Pascual, Pablo Sanchis and Luis Marroyo
Cited by 55 | Viewed by 10149
Abstract
This paper proposes an energy management strategy for a residential electrothermal microgrid, based on renewable energy sources. While grid connected, it makes use of a hybrid electrothermal storage system, formed by a battery and a hot water tank along with an electrical water
[...] Read more.
This paper proposes an energy management strategy for a residential electrothermal microgrid, based on renewable energy sources. While grid connected, it makes use of a hybrid electrothermal storage system, formed by a battery and a hot water tank along with an electrical water heater as a controllable load, which make possible the energy management within the microgrid. The microgrid emulates the operation of a single family home with domestic hot water (DHW) consumption, a heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) system as well as the typical electric loads. An energy management strategy has been designed which optimizes the power exchanged with the grid profile in terms of peaks and fluctuations, in applications with high penetration levels of renewables. The proposed energy management strategy has been evaluated and validated experimentally in a full scale residential microgrid built in our Renewable Energy Laboratory, by means of continuous operation under real conditions. The results show that the combination of electric and thermal storage systems with controllable loads is a promising technology that could maximize the penetration level of renewable energies in the electric system.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Optimal Sizing of Battery Storage Systems for Industrial Applications when Uncertainties Exist
by
Guido Carpinelli, Anna Rita Di Fazio, Shahab Khormali and Fabio Mottola
Cited by 34 | Viewed by 8206
Abstract
Demand response (DR) can be very useful for an industrial facility, since it allows noticeable reductions in the electricity bill due to the significant value of energy demand. Although most industrial processes have stringent constraints in terms of hourly active power, DR only
[...] Read more.
Demand response (DR) can be very useful for an industrial facility, since it allows noticeable reductions in the electricity bill due to the significant value of energy demand. Although most industrial processes have stringent constraints in terms of hourly active power, DR only becomes attractive when performed with the contemporaneous use of battery energy storage systems (BESSs). When this option is used, an optimal sizing of BESSs is desirable, because the investment costs can be significant. This paper deals with the optimal sizing of a BESS installed in an industrial facility to reduce electricity costs. A four-step procedure, based on Decision Theory, was used to obtain a good solution for the sizing problem, even when facing uncertainties; in fact, we think that the sizing procedure must properly take into account the unavoidable uncertainties introduced by the cost of electricity and the load demands of industrial facilities. Three approaches provided by Decision Theory were applied, and they were based on: (1) the minimization of expected cost; (2) the regret felt by the sizing engineer; and (3) a mix of (1) and (2). The numerical applications performed on an actual industrial facility provided evidence of the effectiveness of the proposed procedure.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Load Fluctuation Characteristic Index and Its Application to Pilot Node Selection
by
Huaichang Ge, Qinglai Guo, Hongbin Sun, Bin Wang, Boming Zhang and Wenchuan Wu
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 7807
Abstract
The operation of power systems has been complicated by the rapid diversification of loads. Analyzing load characteristics becomes necessary to different utilities in energy management systems to ensure the reliability of power systems. Here, we describe a method of analyzing and quantifying the
[...] Read more.
The operation of power systems has been complicated by the rapid diversification of loads. Analyzing load characteristics becomes necessary to different utilities in energy management systems to ensure the reliability of power systems. Here, we describe a method of analyzing and quantifying the load characteristics and introduce its application to pilot nodes selection for zone based voltage control. We propose a new index, the Q-fluctuation (QF), to quantify the load characteristic of reactive power based on an analysis of historical data. A second index, the V-fluctuation (VF), which is a combination of the QF and the
Q–V sensitivity that reflects structural information for the grid describes the voltage deviation at each node. These indices are used to construct the voltage fluctuation space, which is then used to select the pilot node for each zone. Simulation studies using IEEE 14-bus and 118-bus systems are described, and used to demonstrate the advantages of the proposed method. The method was able to improve the secondary voltage control and enhance the grid reliability in response to structural changes.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Impact of Scheduling Flexibility on Demand Profile Flatness and User Inconvenience in Residential Smart Grid System
by
Naveed Ul Hassan, Muhammad Adeel Pasha, Chau Yuen, Shisheng Huang and Xiumin Wang
Cited by 48 | Viewed by 7968
Abstract
The objective of this paper is to study the impact of scheduling flexibility on both demand profile flatness and user inconvenience in residential smart grid systems. Temporal variations in energy consumption by end users result in peaks and troughs in the aggregated demand
[...] Read more.
The objective of this paper is to study the impact of scheduling flexibility on both demand profile flatness and user inconvenience in residential smart grid systems. Temporal variations in energy consumption by end users result in peaks and troughs in the aggregated demand profile. In a residential smart grid, some of these peaks and troughs can be eliminated through appropriate load balancing algorithms. However, load balancing requires user participation by allowing the grid to re-schedule some of their loads. In general, more scheduling flexibility can result in more demand profile flatness, however the resulting inconvenience to users would also increase. In this paper, our objective is to help the grid determine an appropriate amount of scheduling flexibility that it should demand from users, based on which, proper incentives can be designed. We consider three different types of scheduling flexibility (delay, advance scheduling and flexible re-scheduling) in flexible loads and develop both optimal and sub-optimal scheduling algorithms. We discuss their implementation in centralized and distributed manners. We also identify the existence of a saturation point. Beyond this saturation point, any increase in scheduling flexibility does not significantly affect the flatness of the demand profile while user inconvenience continues to increase. Moreover, full participation of all the households is not required since increasing user participation only marginally increases demand profile flatness.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Optimal Scheduling for the Complementary Energy Storage System Operation Based on Smart Metering Data in the DC Distribution System
by
Bokyung Ko, Nugroho Prananto Utomo, Gilsoo Jang, Jaehan Kim and Jintae Cho
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 6511
Abstract
The increasing penetration of distributed generation (DG) sources in low-voltage grid feeders causes problems concerning voltage regulation. The penetration of DG sources such as photovoltaics (PVs) in the distribution system can significantly impact the power flow and voltage conditions on the customer side.
[...] Read more.
The increasing penetration of distributed generation (DG) sources in low-voltage grid feeders causes problems concerning voltage regulation. The penetration of DG sources such as photovoltaics (PVs) in the distribution system can significantly impact the power flow and voltage conditions on the customer side. As the DG sources are more commonly connected to low-voltage distribution systems, voltage fluctuations in the distribution system are experienced because of the DG fluctuation and uncertainty. Therefore, the penetration of DGs in distribution systems is often limited by the required operating voltage ranges. By using an energy storage system (ESS), voltage fluctuation can be compensated for, thus satisfying the voltage regulation requirements. This paper presents an ESS scheduling algorithm based on the power injection data obtained from a smart metering system. The proposed ESS scheduling algorithm is designed for use within a direct current (DC) distribution grid, which comprises customers, each with a PV and an ESS system. The purpose of this ESS scheduling algorithm is to optimize the ESS scheduling by considering the complementary operation among all the ESSs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Operation Optimization Based on the Power Supply and Storage Capacity of an Active Distribution Network
by
Wenpeng Yu, Dong Liu and Yuhui Huang
Cited by 30 | Viewed by 7145
Abstract
Due to the interconnection and active management of Distributed Generation (DG) and Energy Storage Systems (ESSs), the traditional electrical distribution network has become an Active Distribution Network (ADN), posing challenges to the operation optimization of the network. The power supply and storage capacity
[...] Read more.
Due to the interconnection and active management of Distributed Generation (DG) and Energy Storage Systems (ESSs), the traditional electrical distribution network has become an Active Distribution Network (ADN), posing challenges to the operation optimization of the network. The power supply and storage capacity indexes of a Local Autonomy Control Region (LACR), which consists of DGs, ESSs and the network, are proposed in this paper to quantify the power regulating range of a LACR. DG/ESS and the network are considered as a whole in the model of the indexes, considering both network constraints and power constraints of the DG/ESS. The index quantifies the maximum LACR power supplied to or received from ADN lines. Similarly, power supply and storage capacity indexes of the ADN line are also proposed to quantify the maximum power exchanged between ADN lines. Then a practical algorithm to calculate the indexes is presented, and an operation optimization model is proposed based on the indexes to maximum the economic benefit of DG/ESS. In the optimization model, the power supply reliability of the ADN line is also considered. Finally, the indexes of power supply and storage capacity and the optimization are demonstrated in a case study.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of the Effects of Nationwide Conservation Voltage Reduction on Peak-Load Shaving Using SOMAS Data
by
Soon-Ryul Nam, Sang-Hee Kang, Joo-Ho Lee, Seon-Ju Ahn and Joon-Ho Choi
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 6274
Abstract
In this paper we propose a new method to evaluate the effects of nationwide conservation voltage reduction (CVR) on peak-load shaving, using substation operating results management system (SOMAS) data. Its evaluation is based on a national CVR factor, which is defined as the
[...] Read more.
In this paper we propose a new method to evaluate the effects of nationwide conservation voltage reduction (CVR) on peak-load shaving, using substation operating results management system (SOMAS) data. Its evaluation is based on a national CVR factor, which is defined as the weighted average of CVR factors associated with all transformer banks and weighting coefficients are determined by the reconstructed loads corresponding to each transformer bank. To make use of the data resulting from nationwide CVR without installing additional measuring devices, we adopt a linearized static-load model with a linearizing parameter. SOMAS data are used to evaluate the effects of nationwide CVR on peak-load shaving in the Korean power system. Evaluation results show that the national CVR factor of the Korean power system has small values in the summer season and large values in the winter season. This means that the effect of nationwide CVR on peak-load shaving in the Korean power system presents stronger benefits during winter months.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
AC Power Local Network with Multiple Power Routers
by
Ryo Takahashi, Yutaro Kitamori and Takashi Hikihara
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 7898
Abstract
Controlling power flow and achieving appropriate matching between power sources and loads according to the quality of energy is expected to be one of the approaches to reduce wasted energy consumption. A power router, proposed recently, has the capability of realizing circuit switching
[...] Read more.
Controlling power flow and achieving appropriate matching between power sources and loads according to the quality of energy is expected to be one of the approaches to reduce wasted energy consumption. A power router, proposed recently, has the capability of realizing circuit switching in a power distribution network. This study focuses on the feasibility of an AC power routing network system composed of multiple power routers. To evaluate the feasibility, we experimentally confirm the circuit switching operation of the parallel and series configurations of the power routers, so that the network system can be designed by the combination of parallel and series configurations.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Design and Implementation of Real-Time Intelligent Control and Structure Based on Multi-Agent Systems in Microgrids
by
Ming-Tse Kuo and Shiue-Der Lu
Cited by 32 | Viewed by 10232
Abstract
By consulting various worldwide definitions of microgrids and distributed energy, this study presents a microgrid-structured multi-agent system and uses Matlab/Simulink to construct a circuit with microgrid features, which enables the changes in each electrical source and load in the microgrid to be monitored
[...] Read more.
By consulting various worldwide definitions of microgrids and distributed energy, this study presents a microgrid-structured multi-agent system and uses Matlab/Simulink to construct a circuit with microgrid features, which enables the changes in each electrical source and load in the microgrid to be monitored and controlled. This multi-agent system adheres to the Java Agent Development Framework (JADE) platform specifications of the Foundation for Intelligent Physical Agents (FIPA), facilitating communication, information transfers, and the receipt of real-time information regarding the microgrid and each component in the microgrid. Furthermore, the real-time state in the microgrid can be correspondingly controlled, achieving the most efficient real-time monitoring and control for electrical sources and load management in the microgrid.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Price Forecasting in the Day-Ahead Energy Market by an Iterative Method with Separate Normal Price and Price Spike Frameworks
by
Sergey Voronin and Jarmo Partanen
Cited by 55 | Viewed by 9101
Abstract
A forecasting methodology for prediction of both normal prices and price spikes in the day-ahead energy market is proposed. The method is based on an iterative strategy implemented as a combination of two modules separately applied for normal price and price spike predictions.
[...] Read more.
A forecasting methodology for prediction of both normal prices and price spikes in the day-ahead energy market is proposed. The method is based on an iterative strategy implemented as a combination of two modules separately applied for normal price and price spike predictions. The normal price module is a mixture of wavelet transform, linear AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) and nonlinear neural network models. The probability of a price spike occurrence is produced by a compound classifier in which three single classification techniques are used jointly to make a decision. Combined with the spike value prediction technique, the output from the price spike module aims to provide a comprehensive price spike forecast. The overall electricity price forecast is formed as combined normal price and price spike forecasts. The forecast accuracy of the proposed method is evaluated with real data from the Finnish Nord Pool Spot day-ahead energy market. The proposed method provides significant improvement in both normal price and price spike prediction accuracy compared with some of the most popular forecast techniques applied for case studies of energy markets.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Output Current Ripple Reduction Algorithms for Home Energy Storage Systems
by
Jin-Hyuk Park, Hae-Gwang Jeong and Kyo-Beum Lee
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 8453
Abstract
This paper proposes an output current ripple reduction algorithm using a proportional-integral (PI) controller for an energy storage system (ESS). In single-phase systems, the DC/AC inverter has a second-order harmonic at twice the grid frequency of a DC-link voltage caused by pulsation of
[...] Read more.
This paper proposes an output current ripple reduction algorithm using a proportional-integral (PI) controller for an energy storage system (ESS). In single-phase systems, the DC/AC inverter has a second-order harmonic at twice the grid frequency of a DC-link voltage caused by pulsation of the DC-link voltage. The output current of a DC/DC converter has a ripple component because of the ripple of the DC-link voltage. The second-order harmonic adversely affects the battery lifetime. The proposed algorithm has an advantage of reducing the second-order harmonic of the output current in the variable frequency system. The proposed algorithm is verified from the PSIM simulation and experiment with the 3 kW ESS model.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Design and Implementation of a High Quality Power Supply Scheme for Distributed Generation in a Micro-Grid
by
Mingchao Xia and Xiaoliang Li
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 7359
Abstract
A low carbon, high efficiency and high quality power supply scheme for Distributed Generation (DG) in a micro-grid is presented. A three-phase, four-leg DG grid-interfacing converter based on the improved structure of a Unified Power Quality Conditioner (UPQC, including a series converter and
[...] Read more.
A low carbon, high efficiency and high quality power supply scheme for Distributed Generation (DG) in a micro-grid is presented. A three-phase, four-leg DG grid-interfacing converter based on the improved structure of a Unified Power Quality Conditioner (UPQC, including a series converter and a parallel converter) is adopted, and improved indirect and direct control strategies are proposed. It can be observed that these strategies effectively compensate for voltage sags, voltage swells and voltage distortion, as well as voltage power quality problems resulting from the nonlinear and unbalanced loads in a micro-grid. While solving the coupling interference from series–parallel, the grid-interfacing converter can achieve proper load power sharing in a micro-grid. In particular, an improved minimum-energy compensation method is proposed that can overcome the conventional compensation algorithm defects, ensure the load voltage’s phase angle stability, improve the voltage compensating ability and range, reduce the capacity and cost of converters, and reduce the shock of micro-grid switching between grid-connected mode and islanded mode. Moreover, the advantages/disadvantages and application situation of the two improved control strategies are analyzed. Finally, the performance of the proposed control strategies has been verified through a MATLAB/Simulink simulation under various operating conditions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Adaptive Wide-Area Damping Control Scheme for Smart Grids with Consideration of Signal Time Delay
by
Guowei Cai, Deyou Yang and Cheng Liu
Cited by 16 | Viewed by 7940
Abstract
As an important part of the smart grid, a wide-area measurement system (WAMS) provides the key technical support for power system monitoring, protection and control. But 20 uncertainties in system parameters and signal transmission time delay could worsen the damping effect and deteriorate
[...] Read more.
As an important part of the smart grid, a wide-area measurement system (WAMS) provides the key technical support for power system monitoring, protection and control. But 20 uncertainties in system parameters and signal transmission time delay could worsen the damping effect and deteriorate the system stability. In the presented study, the subspace system identification technique (SIT) is used to firstly derive a low-order linear model of a power system from the measurements. Then, a novel adaptive wide-area damping control scheme for online tuning of the wide-area damping controller (WADC) parameters using the residue method is proposed. In order to eliminate the effects of the time delay to the signal transmission, a simple and practical time delay compensation algorithm is proposed to compensate the time delay in each wide-area control signal. Detailed examples, inspired by the IEEE test system under various disturbance scenarios, have been used to verify the effectiveness of the proposed adaptive wide-area damping control scheme.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
General and Simple Decision Method for DG Penetration Level in View of Voltage Regulation at Distribution Substation Transformers
by
Il-Keun Song, Won-Wook Jung, Chul-Min Chu, Seong-Soo Cho, Hyun-Koo Kang and Joon-Ho Choi
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 8568
Abstract
A distribution system was designed and operated by considering unidirectional power flow from a utility source to end-use loads. The large penetrations of distributed generation (DG) into the existing distribution system causes a variety of technical problems, such as frequent tap changing problems
[...] Read more.
A distribution system was designed and operated by considering unidirectional power flow from a utility source to end-use loads. The large penetrations of distributed generation (DG) into the existing distribution system causes a variety of technical problems, such as frequent tap changing problems of the on-load tap changer (OLTC) transformer, local voltage rise, protection coordination, exceeding short-circuit capacity, and harmonic distortion. In view of voltage regulation, the intermittent fluctuation of the DG output power results in frequent tap changing operations of the OLTC transformer. Thus, many utilities limit the penetration level of DG and are eager to find the reasonable penetration limits of DG in the distribution system. To overcome this technical problem, utilities have developed a new voltage regulation method in the distribution system with a large DG penetration level. In this paper, the impact of DG on the OLTC operations controlled by the line drop compensation (LDC) method is analyzed. In addition, a generalized determination methodology for the DG penetration limits in a distribution substation transformer is proposed. The proposed DG penetration limits could be adopted for a simplified interconnection process in DG interconnection guidelines.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Recursive Pyramid Algorithm-Based Discrete Wavelet Transform for Reactive Power Measurement in Smart Meters
by
Najam Ul Hasan, Waleed Ejaz, Mahin K. Atiq and Hyung Seok Kim
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 8448
Abstract
Measurement of the active, reactive, and apparent power is one of the most fundamental tasks of smart meters in energy systems. Recently, a number of studies have employed the discrete wavelet transform (DWT) for power measurement in smart meters. The most common way
[...] Read more.
Measurement of the active, reactive, and apparent power is one of the most fundamental tasks of smart meters in energy systems. Recently, a number of studies have employed the discrete wavelet transform (DWT) for power measurement in smart meters. The most common way to implement DWT is the pyramid algorithm; however, this is not feasible for practical DWT computation because it requires either a log N cascaded filter or O (N) word size memory storage for an input signal of the N-point. Both solutions are too expensive for practical applications of smart meters. It is proposed that the recursive pyramid algorithm is more suitable for smart meter implementation because it requires only word size storage of L × Log (N-L), where L is the length of filter. We also investigated the effect of varying different system parameters, such as the sampling rate, dc offset, phase offset, linearity error in current and voltage sensors, analog to digital converter resolution, and number of harmonics in a non-sinusoidal system, on the reactive energy measurement using DWT. The error analysis is depicted in the form of the absolute difference between the measured and the true value of the reactive energy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Improved Short-Term Load Forecasting Based on Two-Stage Predictions with Artificial Neural Networks in a Microgrid Environment
by
Luis Hernández, Carlos Baladrón, Javier M. Aguiar, Lorena Calavia, Belén Carro, Antonio Sánchez-Esguevillas, Javier Sanjuán, Álvaro González and Jaime Lloret
Cited by 43 | Viewed by 8397
Abstract
Short-Term Load Forecasting plays a significant role in energy generation planning, and is specially gaining momentum in the emerging Smart Grids environment, which usually presents highly disaggregated scenarios where detailed real-time information is available thanks to Communications and Information Technologies, as it happens
[...] Read more.
Short-Term Load Forecasting plays a significant role in energy generation planning, and is specially gaining momentum in the emerging Smart Grids environment, which usually presents highly disaggregated scenarios where detailed real-time information is available thanks to Communications and Information Technologies, as it happens for example in the case of
microgrids. This paper presents a two stage prediction model based on an Artificial Neural Network in order to allow Short-Term Load Forecasting of the following day in
microgrid environment, which first estimates peak and valley values of the demand curve of the day to be forecasted. Those, together with other variables, will make the second stage, forecast of the entire demand curve, more precise than a direct, single-stage forecast. The whole architecture of the model will be presented and the results compared with recent work on the same set of data, and on the same location, obtaining a Mean Absolute Percentage Error of 1.62% against the original 2.47% of the single stage model.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Analysis and Simulation of Fault Characteristics of Power Switch Failures in Distribution Electronic Power Transformers
by
Zixia Sang, Chengxiong Mao, Jiming Lu and Dan Wang
Cited by 33 | Viewed by 8363
Abstract
This paper presents research on the voltage and current distortion in the input stage, isolation stage and output stage of Distribution Electronic Power transformer (D-EPT) after the open-circuit and short-circuit faults of its power switches. In this paper, the operational principles and the
[...] Read more.
This paper presents research on the voltage and current distortion in the input stage, isolation stage and output stage of Distribution Electronic Power transformer (D-EPT) after the open-circuit and short-circuit faults of its power switches. In this paper, the operational principles and the control methods for input stage, isolation stage and output stage of D-EPT, which work as a cascaded H-bridge rectifier, DC-DC converter and inverter, respectively, are introduced. Based on conclusions derived from the performance analysis of D-EPT after the faults, this paper comes up with the effects from its topology design and control scheme on the current and voltage distortion. According to the EPT fault characteristics, since the waveforms of relevant components heavily depend on the location of the faulty switch, it is very easy to locate the exact position of the faulty switch. Finally, the fault characteristics peculiar to D-EPT are analyzed, and further discussed with simulation on the Saber platform, as well as a fault location diagnosis algorithm.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures