- Article
Construction of an Educational Prototype of a Differential Wheeled Mobile Robot
- Celso Márquez-Sánchez,
- Jacobo Sandoval-Gutiérrez and
- Daniel Librado Martínez-Vázquez
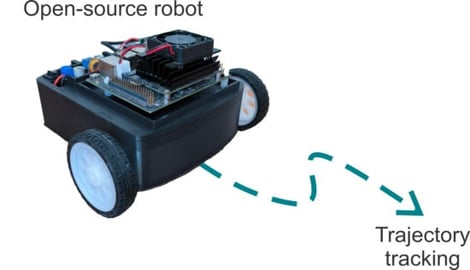
This work presents the development of a differential-drive wheeled mobile robot educational prototype, manufactured using 3D additive techniques. The robot is powered by an embedded ARM-based computing system and uses open-source software. To validate the prototype, a trajectory-tracking task was successfully implemented. The aim of this contribution is to provide an easily replicable prototype for teaching automatic control and related engineering topics in academic settings.
23 January 2026