- Article
Distance-Invariant Constant-Power DC-to-DC Wireless Power Transfer Using Nonlinear Resonance
- Abdullah Alothman,
- Andrew DeVries and
- Amir Mortazawi
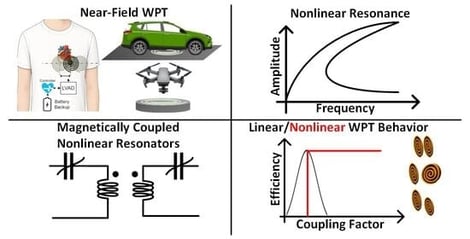
Wireless power transfer (WPT) systems are generally sensitive to variations in separation distance and coil alignment, which result in reduced power transfer efficiency and delivered power. Various approaches based on control system and active matching circuits have resulted in more complex implementations. This work, by contrast, presents a full DC–DC inductively coupled WPT system employing coupled nonlinear resonators to automatically adapt the system for variations in transfer coil separation and orientation, maintaining high transfer efficiency at a constant output power level. With entirely passive circuit components, the nonlinear resonators suppress the frequency-splitting phenomenon typical of WPT systems that leads to efficiency degradation. A class-EF power amplifier used in the transmitter experiences an approximately constant impedance, providing a constant output power while maintaining high efficiency. On the receive side, a class-E rectifier operates at a constant input power, achieving high overall efficiency without active control. An experimental demonstration delivers 5 W with a 6.12% power variation over a 1 to 9 cm distance variation and achieves a peak DC–DC efficiency of 71.6%. The response of the system to changes in coil separation is compared with a conventional linear WPT circuit, showing a constant-power and high-efficiency operation.
26 February 2026



![Self-injection-locked magnetron from reference [55].](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/microwave/microwave-02-00003/article_deploy/html/images/microwave-02-00003-g001-550.jpg)