Journal Description
Software
Software
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on all aspects of software engineering published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 28.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Software is a companion journal of Electronics.
Latest Articles
Assessing the Generalizability of Mobile Software Engineering Research Through Combined Systematic Methods
Software 2026, 5(1), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/software5010012 - 3 Mar 2026
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Mobile Software Engineering has emerged as a distinct subfield, raising questions about the transferability of its research findings to general software engineering. This paper addresses the challenge of evaluating the generalizability of mobile-specific research, using Green Computing as a representative case. We propose
[...] Read more.
Mobile Software Engineering has emerged as a distinct subfield, raising questions about the transferability of its research findings to general software engineering. This paper addresses the challenge of evaluating the generalizability of mobile-specific research, using Green Computing as a representative case. We propose a combination of systematic methods to identify potentially overlooked mobile-specific papers with a focused literature review to assess their broader relevance. Applying this approach, we find that several mobile-specific studies offer insights applicable beyond their original context, particularly in areas such as energy efficiency guidelines, measurement, and trade-offs. The results demonstrate that systematic identification and evaluation can reveal valuable contributions for the wider software engineering community. The proposed method provides a structured framework for future research to assess the generalizability of findings from specialized domains, fostering greater integration and knowledge transfer across software engineering disciplines.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Is Code Co-Committal an Indicator of Evolutionary Coupling in Software Repositories?
by
Niall Price, David Cutting and Vahid Garousi
Software 2026, 5(1), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/software5010011 - 1 Mar 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Software repositories such as Git are significant sources of metadata about software projects, containing information such as modified files, change authors, and often commentary describing the change. An emerging approach to support software change impact analysis is to exploit this metadata to determine
[...] Read more.
Software repositories such as Git are significant sources of metadata about software projects, containing information such as modified files, change authors, and often commentary describing the change. An emerging approach to support software change impact analysis is to exploit this metadata to determine which files are linked by co-committal, i.e., when two files are frequently updated together within the same Git commit. Such information can serve as an indicator for identifying potential change-impact sets in future development activities. The aim of this study is to determine whether co-committal is a reliable indicator of links between software artifacts stored in Git and, if so, whether these links persist as the artifacts evolve—thereby offering a potentially valuable dimension for change impact analysis. To investigate this, we mined the metadata of five large Git repositories comprising over 14K commits and extracted co-change sets from the resulting data. The results show that: (1) co-committal links between artifacts vary widely in both strength and frequency, with these variations strongly influenced by the development style and activity levels of the contributing developers, and (2) although co-committal can serve as an indicator of evolutionary coupling in certain scenarios, its usefulness depends on project-specific development practices and observable patterns of developer behavior.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
CONSENT: A Software Architecture for Dynamic and Secure Consent Management
by
Christina Zoi, Ioannis Zozas and Stamatia Bibi
Software 2026, 5(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/software5010010 - 26 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Current research in consent management techniques focuses on isolated aspects of data security, privacy, or auditability, but important issues like (i) dynamically integrating regulatory updates into form generation, (ii) support in content generation with verifiable audit trails, and (iii) tools that make compliance
[...] Read more.
Current research in consent management techniques focuses on isolated aspects of data security, privacy, or auditability, but important issues like (i) dynamically integrating regulatory updates into form generation, (ii) support in content generation with verifiable audit trails, and (iii) tools that make compliance reasoning transparent for non-legal users are not yet addressed. This paper introduces CONSENT, an architecture that integrates AI-based consent reasoning using Large Language Models (LLMs) for automated consent-form drafting and compliance evaluation, alongside blockchain technology for secure and auditable storage. The architecture builds on prior work to address the aforementioned issues by introducing three supporting mechanisms: (a) Specialized AI models coordinated through expert routing which coordinate subtasks such as automation in form generation and regulatory compliance, (b) Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) that supports the integration of regulatory updates into forms, and (c) Explainable AI (XAI) for the reasoning behind form content and compliance assessments. CONSENT architecture is evaluated through 250 test cases and a pilot case study for clinical trial consent management involving 20 engineers and attorneys, who evaluated the prototype on form quality (i.e., coherence, conciseness, factuality, fluency, and relevance) as well as time and effort efficiency. Results show that CONSENT substantially reduces the manual effort in consent-form creation while providing transparent, audit-ready compliance assessments, highlighting its potential for dynamic, user-centric consent management.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Verifying Machine Learning Interpretability and Explainability Requirements Through Provenance
by
Lynn Vonderhaar, Juan Couder, Tyler Thomas Procko, Eva Lueddeke, Daryela Cisneros and Omar Ochoa
Software 2026, 5(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/software5010009 - 14 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Machine learning (ML) engineering increasingly incorporates principles from software and requirements engineering to improve development rigor; however, key non-functional requirements (NFRs) such as interpretability and explainability remain difficult to specify and verify using traditional requirements practices. Although prior work defines these qualities conceptually,
[...] Read more.
Machine learning (ML) engineering increasingly incorporates principles from software and requirements engineering to improve development rigor; however, key non-functional requirements (NFRs) such as interpretability and explainability remain difficult to specify and verify using traditional requirements practices. Although prior work defines these qualities conceptually, their lack of measurable criteria prevents systematic verification. This paper presents a novel provenance-driven approach that decomposes ML interpretability and explainability NFRs into verifiable functional requirements (FRs) by leveraging model and data provenance to make model behavior transparent. The approach identifies the specific provenance artifacts required to validate each FR and demonstrates how their verification collectively establishes compliance with interpretability and explainability NFRs. The results show that ML provenance can operationalize otherwise abstract NFRs, transforming interpretability and explainability into quantifiable, testable properties and enabling more rigorous, requirements-based ML engineering.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Towards Service-Oriented Knowledge-Based Process Planning Supporting Service-Based Smart Production Environments
by
Kathrin Gorgs, Heiko Friedrich, Tobias Vogel and Matthias L. Hemmje
Software 2026, 5(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/software5010008 - 12 Feb 2026
Abstract
The increasing decentralization of industrial processes in Industry 4.0 necessitates the distribution and coordination of resources such as machines, materials, expertise, and knowledge across organizations in a value chain. To facilitate effective operations in such distributed environments, it is essential to digitize processes
[...] Read more.
The increasing decentralization of industrial processes in Industry 4.0 necessitates the distribution and coordination of resources such as machines, materials, expertise, and knowledge across organizations in a value chain. To facilitate effective operations in such distributed environments, it is essential to digitize processes and resources, establish interconnectedness, and implement a scalable management approach. The present paper addresses these challenges through the knowledge-based production planning (KPP) system, which was originally developed as a monolithic prototype. It is argued that the KPP-System must evolve towards a service-oriented architecture (SOA) in order to align with distributed and interoperable Industry 4.0 requirements. The paper provides a comprehensive overview of the motivation and background of KPP, identifies the key research questions that are to be addressed, and presents a conceptual design for transitioning KPP into an SOA. The approach under discussion is notable for its consideration of compatibility with the Arrowhead Framework (AF), a consideration that is intended to ensure interoperability with smart production environments. The contribution of this work is the first architectural concept that demonstrates how KPP components can be encapsulated as services and integrated into local cloud environments, thus laying the foundation for adaptive, ontology-based process planning in distributed manufacturing. In addition to the conceptual architecture, the first implementation phase has been conducted to validate the proposed approach. This includes the realization and evaluation of the mediator-based service layer, which operationalizes the transformation of planning data into semantic function blocks (FBs) and enables the interaction of distributed services within the envisioned SO-KPP architecture. The implementation demonstrates the feasibility of the service-oriented transformation and provides a functional proof of concept for ontology-based integration in future adaptive production planning systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Software Engineering and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Functional Yield-Based Traversal Pattern for Concise, Composable, and Efficient Stream Pipelines
by
Fernando Miguel Carvalho
Software 2026, 5(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/software5010007 - 10 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The stream pipeline idiom provides a fluent and composable way to express computations over collections. It gained widespread popularity after its introduction in .NET in 2005, later influencing many platforms, including Java in 2014 with the introduction of Java Streams, and continues to
[...] Read more.
The stream pipeline idiom provides a fluent and composable way to express computations over collections. It gained widespread popularity after its introduction in .NET in 2005, later influencing many platforms, including Java in 2014 with the introduction of Java Streams, and continues to be adopted in contemporary languages such as Kotlin. However, the set of operations available in standard libraries is limited, and developers often need to introduce operations that are not provided out of the box. Two options typically arise: implementing custom operations using the standard API or adopting a third-party collections library that offers a richer suite of operations. In this article, we show that both approaches may incur performance overhead, and that the former can also suffer from verbosity and reduced readability. We propose an alternative approach that remains faithful to the stream-pipeline pattern: developers implement the unit operations of the pipeline from scratch using a functional yield-based traversal pattern. We demonstrate that this approach requires low programming effort, eliminates the performance overheads of existing alternatives, and preserves the key qualities of a stream pipeline. Our experimental results show up to a 3× speedup over the use of native yield in custom extensions.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Integrating Continuous Compliance into DevSecOps Pipelines: A Data Engineering Perspective
by
Aleksandr Zakharchenko
Software 2026, 5(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/software5010006 - 10 Feb 2026
Abstract
Modern DevSecOps environments face a persistent tension between accelerating deployment velocity and maintaining verifiable compliance with regulatory, security, and internal governance standards. Traditional snapshot-in-time audits and fragmented compliance tooling struggle to capture the dynamic nature of containerized, continuous delivery, often resulting in compliance
[...] Read more.
Modern DevSecOps environments face a persistent tension between accelerating deployment velocity and maintaining verifiable compliance with regulatory, security, and internal governance standards. Traditional snapshot-in-time audits and fragmented compliance tooling struggle to capture the dynamic nature of containerized, continuous delivery, often resulting in compliance drift and delayed remediation. This paper introduces the Continuous Compliance Framework (CCF), a data-centric reference architecture that embeds compliance validation directly into CI/CD pipelines. The framework treats compliance as a first-class, computable system property by combining declarative policies-as-code, standardized evidence collection, and cryptographically verifiable attestations. Central to the approach is a Compliance Data Lakehouse that transforms heterogeneous pipeline artifacts into a queryable, time-indexed compliance data product, enabling audit-ready evidence generation and continuous assurance. The proposed architecture is validated through an end-to-end synthetic microservice implementation. Experimental results demonstrate full policy lifecycle enforcement with a minimal pipeline overhead and sub-second policy evaluation latency. These findings indicate that compliance can be shifted from a post hoc audit activity to an intrinsic, verifiable property of the software delivery process without materially degrading deployment velocity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Software Reliability, Security and Quality Assurance)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Data-Centric Serverless Computing with LambdaStore
by
Kai Mast, Suyan Qu, Aditya Jain, Andrea Arpaci-Dusseau and Remzi Arpaci-Dusseau
Software 2026, 5(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/software5010005 - 21 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
LambdaStore is a data-centric serverless platform that breaks the split between stateless functions and external storage in classic cloud computing platforms. By scheduling serverless invocations near data instead of pulling data to compute, LambdaStore substantially reduces the state access cost that dominates today’s
[...] Read more.
LambdaStore is a data-centric serverless platform that breaks the split between stateless functions and external storage in classic cloud computing platforms. By scheduling serverless invocations near data instead of pulling data to compute, LambdaStore substantially reduces the state access cost that dominates today’s serverless workloads. Leveraging its transactional storage engine, LambdaStore delivers serializable guarantees and exactly-once semantics across chains of lambda invocations—a capability missing in current Function-as-a-Service offerings. We make three key contributions: (1) an object-oriented programming model that ties function invocations with its data; (2) a transaction layer with adaptive lock granularity and an optimistic concurrency control protocol designed for serverless workloads to keep contention low while preserving serializability; and (3) an elastic storage system that preserves the elasticity of the serverless paradigm while lambda functions run close to their data. Under read-heavy workloads, LambdaStore lifts throughput by orders of magnitude over existing serverless platforms while holding end-to-end latency below 20 ms.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Mitigating Prompt Dependency in Large Language Models: A Retrieval-Augmented Framework for Intelligent Code Assistance
by
Saja Abufarha, Ahmed Al Marouf, Jon George Rokne and Reda Alhajj
Software 2026, 5(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/software5010004 - 21 Jan 2026
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: The implementation of Large Language Models (LLMs) in software engineering has provided new and improved approaches to code synthesis, testing, and refactoring. However, even with these new approaches, the practical efficacy of LLMs is restricted due to their reliance on user-given
[...] Read more.
Background: The implementation of Large Language Models (LLMs) in software engineering has provided new and improved approaches to code synthesis, testing, and refactoring. However, even with these new approaches, the practical efficacy of LLMs is restricted due to their reliance on user-given prompts. The problem is that these prompts can vary a lot in quality and specificity, which results in inconsistent or suboptimal results for the LLM application. Methods: This research therefore aims to alleviate these issues by developing an LLM-based code assistance prototype with a framework based on Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) that automates the prompt-generation process and improves the outputs of LLMs using contextually relevant external knowledge. Results: The tool aims to reduce dependence on the manual preparation of prompts and enhance accessibility and usability for developers of all experience levels. The tool achieved a Code Correctness Score (CCS) of 162.0 and an Average Code Correctness (ACC) score of 98.8% in the refactoring task. These results can be compared to those of the generated tests, which scored CCS 139.0 and ACC 85.3%, respectively. Conclusions: This research contributes to the growing list of Artificial Intelligence (AI)-powered development tools and offers new opportunities for boosting the productivity of developers.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessRetraction
RETRACTED: Stephenson, M.J. A Differential Datalog Interpreter. Software 2023, 2, 427–446
by
Matthew James Stephenson
Software 2026, 5(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/software5010003 - 21 Jan 2026
Abstract
The Journal retracts the article titled, “A Differential Datalog Interpreter” [...]
Full article
Open AccessArticle
rUnit—A Framework for Test Analysis of C Programs
by
Peter Backeman
Software 2026, 5(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/software5010002 - 2 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Asserting program correctness is a longstanding challenge in software development that consumes lots of resources and manpower. It is often accomplished through software testing at various levels. One such level is unit testing, where the behaviour of individual components is tested. In this
[...] Read more.
Asserting program correctness is a longstanding challenge in software development that consumes lots of resources and manpower. It is often accomplished through software testing at various levels. One such level is unit testing, where the behaviour of individual components is tested. In this paper, we introduce the concept of test analysis, which instead of executing unit tests, analyses them to establish their outcome. This is line with previous approaches towards using formal methods for program verification; however, we introduce a middle layer called the test analysis framework, which allows for the introduction of new capabilities. We (briefly) formalize ordinary testing and test analysis to define the relation between the two. We introduce the notion of rich tests with a syntax and semantic instantiated for C. A prototype framework is implemented and extended to handle property-based stubbing and non-deterministic string variables. A few select examples are presented to demonstrate the capabilities of the framework.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
RoboDeploy: A Metamodel-Driven Framework for Automated Multi-Host Docker Deployment of ROS 2 Systems in IoRT Environments
by
Miguel Ángel Barcelona, Laura García-Borgoñón, Pablo Torner and Ariadna Belén Ruiz
Software 2026, 5(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/software5010001 - 19 Dec 2025
Abstract
Robotic systems increasingly operate in complex and distributed environments, where software deployment and orchestration pose major challenges. This paper presents a model-driven approach that automates the containerized deployment of robotic systems in Internet of Robotic Things (IoRT) environments. Our solution integrates Model-Driven Engineering
[...] Read more.
Robotic systems increasingly operate in complex and distributed environments, where software deployment and orchestration pose major challenges. This paper presents a model-driven approach that automates the containerized deployment of robotic systems in Internet of Robotic Things (IoRT) environments. Our solution integrates Model-Driven Engineering (MDE) with containerization technologies to improve scalability, reproducibility, and maintainability. A dedicated metamodel introduces high-level abstractions for describing deployment architectures, repositories, and container configurations. A web-based tool enables collaborative model editing, while an external deployment automator generates validated Docker and Compose artifacts to support seamless multi-host orchestration. We validated the approach through real-world experiments, which show that the method effectively automates deployment workflows, ensures consistency across development and production environments, and significantly reduces configuration effort. These results demonstrate that model-driven automation can bridge the gap between Software Engineering (SE) and robotics, enabling Software-Defined Robotics (SDR) and supporting scalable IoRT applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Software Engineering and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Graph Generalization for Software Engineering
by
Mohammad Reza Kianifar and Robert J. Walker
Software 2025, 4(4), 33; https://doi.org/10.3390/software4040033 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Graph generalization is a powerful concept with a wide range of potential applications, while established algorithms exist for generalizing simple graphs, practical approaches for more complex graphs remain elusive. We introduce a novel formal model and algorithm (GGA) that generalizes labeled directed graphs
[...] Read more.
Graph generalization is a powerful concept with a wide range of potential applications, while established algorithms exist for generalizing simple graphs, practical approaches for more complex graphs remain elusive. We introduce a novel formal model and algorithm (GGA) that generalizes labeled directed graphs without assuming label identity. We evaluate GGA by focusing on its information preservation relative to its input graphs, its scalability in execution, and its utility for three applications: abstract syntax trees, class graphs, and call graphs. Our findings reveal the superiority of GGA over alternative tools. GGA outperforms ASGard by an average of 5–18% on metrics related to information preservation; GGA matches 100% with diffsitter, indicating the correctness of the output. For class graphs, GGA achieves 77.1% in precision at 5, while for call graphs, it exhibits 60% in precision at 5 for a specific application problem. We also test performance for the first two applications: GGA’s execution time scales linearly with respect to the product of vertex count and edge count. Our research demonstrates the ability of GGA to preserve information in diverse applications while performing efficiently, signaling its potential to advance the field.
Full article
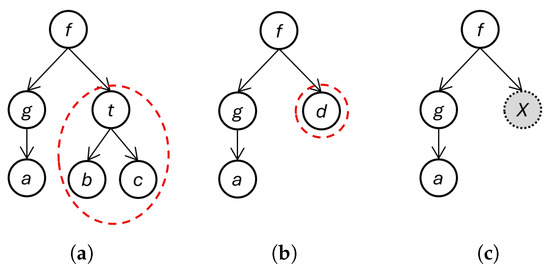
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Dynamic Frontend Architecture for Runtime Component Versioning and Feature Flag Resolution in Regulated Applications
by
Roman Fedytskyi
Software 2025, 4(4), 32; https://doi.org/10.3390/software4040032 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
Regulated web systems require traceable, rollback-safe UI delivery, yet conventional static deployments and Boolean flagging struggle to provide per-user versioning, deterministic fallbacks, and audit-grade observability. The objective of this research is to develop and validate a runtime frontend architecture that enables per-session component
[...] Read more.
Regulated web systems require traceable, rollback-safe UI delivery, yet conventional static deployments and Boolean flagging struggle to provide per-user versioning, deterministic fallbacks, and audit-grade observability. The objective of this research is to develop and validate a runtime frontend architecture that enables per-session component versioning with deterministic fallbacks and audit-grade traceability for regulated systems. We present a dynamic frontend architecture that integrates typed GraphQL flag schemas, runtime module federation, and structured observability to enable per-session and per-route component versioning with deterministic fallbacks. We formalize a version-resolution function v = f(u, r, t) and implement a production system that achieved a 96% reduction in MTTR, a P90 fallback rate below 0.7%, and over 280 k session-level logs across 45 days. Compared to static delivery and standard flag evaluators, our approach adds schema-driven targeting, component-level isolation, and audit-ready render traces suitable for compliance. Limitations include cold-start overhead and governance complexity; we provide mitigation strategies and discuss portability beyond fintech.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Software Engineering and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Building Shared Alignment for Agile at Scale: A Tool-Supported Method for Cross-Stakeholder Process Synthesis
by
Giulio Serra and Antonio De Nicola
Software 2025, 4(4), 31; https://doi.org/10.3390/software4040031 - 3 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Organizations increasingly rely on Agile software development to navigate the complexities of digital transformation. Agile emphasizes flexibility, empowerment, and emergent design, yet large-scale initiatives often extend beyond single teams to include multiple subsidiaries, business units, and regulatory stakeholders. In such contexts, team-level mechanisms
[...] Read more.
Organizations increasingly rely on Agile software development to navigate the complexities of digital transformation. Agile emphasizes flexibility, empowerment, and emergent design, yet large-scale initiatives often extend beyond single teams to include multiple subsidiaries, business units, and regulatory stakeholders. In such contexts, team-level mechanisms such as retrospectives, backlog refinement, and planning events may prove insufficient to achieve alignment across diverse perspectives, organizational boundaries, and compliance requirements. To address this limitation, this paper introduces a complementary framework and a supporting software tool that enable systematic cross-stakeholder alignment. Rather than replacing Agile practices, the framework enhances them by capturing heterogeneous stakeholder views, surfacing tacit knowledge, and systematically reconciling differences into a shared alignment artifact. The methodology combines individual Functional Resonance Analysis Method (FRAM)-based process modeling, iterative harmonization, and an evidence-supported selection mechanism driven by quantifiable performance indicators, all operationalized through a prototype tool. The approach was evaluated in a real industrial case study within the regulated gaming sector, involving practitioners from both a parent company and a subsidiary. The results show that the methodology effectively revealed misalignments among stakeholders’ respective views of the development process, supported structured negotiation to reconcile these differences, and produced a consolidated process model that improved transparency and alignment across organizational boundaries. The study demonstrates the practical viability of the methodology and its value as a complementary mechanism that strengthens Agile ways of working in complex, multi-stakeholder environments.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Software Quality Assurance and AI: A Systems-Theoretic Approach to Reliability, Safety, and Security
by
Joseph R. Laracy, Ziyuan Meng, Vassilka D. Kirova, Cyril S. Ku and Thomas J. Marlowe
Software 2025, 4(4), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/software4040030 - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The integration of modern artificial intelligence into software systems presents transformative opportunities and novel challenges for software quality assurance (SQA). While AI enables powerful enhancements in testing, monitoring, and defect prediction, it also introduces non-determinism, continuous learning, and opaque behavior that challenge traditional
[...] Read more.
The integration of modern artificial intelligence into software systems presents transformative opportunities and novel challenges for software quality assurance (SQA). While AI enables powerful enhancements in testing, monitoring, and defect prediction, it also introduces non-determinism, continuous learning, and opaque behavior that challenge traditional quality and reliability paradigms. This paper proposes a framework for addressing these issues, drawing on concepts from systems theory. We argue that AI-enabled software systems should be understood as dynamical systems, i.e., stateful adaptive systems whose behavior depends on prior inputs, feedback, and environmental interaction, as well as components embedded within broader socio-technical ecosystems. From this perspective, quality assurance becomes a matter of maintaining stability by enforcing constraints as well as designing robust feedback and control mechanisms that account for interactions across the full ecosystem of stakeholders, infrastructure, and operational environments. This paper outlines how the systems-theoretic perspective can inform the development of modern SQA processes. This ecosystem-aware approach repositions software quality as an ongoing, systemic responsibility, especially important in mission-critical AI applications.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
RCEGen: A Generative Approach for Automated Root Cause Analysis Using Large Language Models (LLMs)
by
Rubel Hassan Mollik, Arup Datta, Anamul Haque Mollah and Wajdi Aljedaani
Software 2025, 4(4), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/software4040029 - 7 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Root cause analysis (RCA) identifies the faults and vulnerabilities underlying software failures, informing better design and maintenance decisions. Earlier approaches typically framed RCA as a classification task, predicting coarse categories of root causes. With recent advances in large language models (LLMs), RCA can
[...] Read more.
Root cause analysis (RCA) identifies the faults and vulnerabilities underlying software failures, informing better design and maintenance decisions. Earlier approaches typically framed RCA as a classification task, predicting coarse categories of root causes. With recent advances in large language models (LLMs), RCA can be treated as a generative task that produces natural language explanations of faults. We introduce RCEGen, a framework that leverages state-of-the-art open-source LLMs to generate root cause explanations (RCEs) directly from bug reports. Using 298 reports, we evaluated five LLMs in conjunction with human developers and LLM judges across three key aspects: correctness, clarity, and reasoning depth. Qwen2.5-Coder-Instruct achieved the strongest performance (correctness ≈ 0.89, clarity ≈ 0.88, reasoning ≈ 0.65, overall ≈ 0.79), and RCEs exhibited high semantic fidelity (CodeBERTScore ≈ 0.98) to developer-written references despite low lexical overlap. The results demonstrated that LLMs achieve high accuracy in root cause identification from bug report titles and descriptions, particularly when reports contained error logs and reproduction steps.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Software Engineering Aspects of Federated Learning Libraries: A Comparative Survey
by
Hiba Alsghaier and Tian Zhao
Software 2025, 4(4), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/software4040028 - 5 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Federated Learning (FL) has emerged as a pivotal paradigm for privacy-preserving machine learning. While numerous FL libraries have been developed to operationalize this paradigm, their rapid proliferation has created a significant challenge for practitioners and researchers: selecting the right tool requires a deep
[...] Read more.
Federated Learning (FL) has emerged as a pivotal paradigm for privacy-preserving machine learning. While numerous FL libraries have been developed to operationalize this paradigm, their rapid proliferation has created a significant challenge for practitioners and researchers: selecting the right tool requires a deep understanding of their often undocumented software architectures and extensibility, aspects that are largely overlooked by existing algorithm-focused surveys. This paper addresses this gap by conducting the first comprehensive survey of FL libraries from a software engineering perspective. We systematically analyze ten popular open-source FL libraries, dissecting their architectural designs, support for core and advanced FL features, and most importantly, their extension mechanisms for customization. Our analysis produces a novel taxonomy of FL concepts grounded in software implementation, a practical decision framework for library selection, and an in-depth discussion of architectural limitations and pathways for future development. The findings provide developers with actionable guidance for selecting and extending FL tools and offer researchers a clear roadmap for advancing FL infrastructure.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Evolution of Software Usability in Developer Communities: An Empirical Study on Stack Overflow
by
Hans Djalali, Wajdi Aljedaani and Stephanie Ludi
Software 2025, 4(4), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/software4040027 - 31 Oct 2025
Abstract
This study investigates how software developers discuss usability on Stack Overflow through an analysis of posts from 2008 to 2024. Despite recognizing the importance of usability for software success, there is a limited amount of research on developer engagement with usability topics. Using
[...] Read more.
This study investigates how software developers discuss usability on Stack Overflow through an analysis of posts from 2008 to 2024. Despite recognizing the importance of usability for software success, there is a limited amount of research on developer engagement with usability topics. Using mixed methods that combine quantitative metric analysis and qualitative content review, we examine temporal trends, comparative engagement patterns across eight non-functional requirements, and programming context-specific usability issues. Our findings show a significant decrease in usability posts since 2010, contrasting with other non-functional requirements, such as performance and security. Despite this decline, usability posts exhibit high resolution efficiency, achieving the highest answer and acceptance rates among all topics, suggesting that the community is highly effective at resolving these specialized questions. We identify distinctive platform-specific usability concerns: web development prioritizes responsive layouts and form design; desktop applications emphasize keyboard navigation and complex controls; and mobile development focuses on touch interactions and screen constraints. These patterns indicate a transformation in the sharing of usability knowledge, reflecting the maturation of the field, its integration into frameworks, and the migration to specialized communities. This first longitudinal analysis of usability discussions on Stack Overflow provides insights into developer engagement with usability and highlights opportunities for integrating usability guidance into technical contexts.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Software Engineering and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Using Genetic Algorithms for Research Software Structure Optimization
by
Henning Schnoor, Wilhelm Hasselbring and Reiner Jung
Software 2025, 4(4), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/software4040026 - 28 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Our goal is to generate restructuring recommendations for research software systems based on software architecture descriptions that were obtained via reverse engineering. We reconstructed these software architectures via static and dynamic analysis methods in the reverse engineering process. To do this, we combined
[...] Read more.
Our goal is to generate restructuring recommendations for research software systems based on software architecture descriptions that were obtained via reverse engineering. We reconstructed these software architectures via static and dynamic analysis methods in the reverse engineering process. To do this, we combined static and dynamic analysis for call relationships and dataflow into a hierarchy of six analysis methods. For generating optimal restructuring recommendations, we use genetic algorithms, which optimize the module structure. For optimizing the modularization, we use coupling and cohesion metrics as fitness functions. We applied these methods to Earth System Models to test their efficacy. In general, our results confirm the applicability of genetic algorithms for optimizing the module structure of research software. Our experiments show that the analysis methods have a significant impact on the optimization results. A specific observation from our experiments is that the pure dynamic analysis produces significantly better modularizations than the optimizations based on the other analysis methods that we used for reverse engineering. Furthermore, a guided, interactive optimization with a domain expert’s feedback improves the modularization recommendations considerably. For instance, cohesion is improved by 57% with guided optimization.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Applied Sciences, ASI, Blockchains, Computers, MAKE, Software
Recent Advances in AI-Enhanced Software Engineering and Web Services
Topic Editors: Hai Wang, Zhe HouDeadline: 31 May 2026
Topic in
Algorithms, Applied Sciences, Electronics, MAKE, AI, Software
Applications of NLP, AI, and ML in Software Engineering
Topic Editors: Affan Yasin, Javed Ali Khan, Lijie WenDeadline: 30 August 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Software
Software Reliability, Security and Quality Assurance
Guest Editors: Tadashi Dohi, Junjun Zheng, Xiao-Yi ZhangDeadline: 31 December 2026








