- Article
Generation of Novel Natural Products by Disrupting Azaphilone Synthesis in Penicillum sclerotiorum E23Y-1A
- Wenjun Chang,
- Yanhua Yang and
- Yanbo Zeng
- + 3 authors
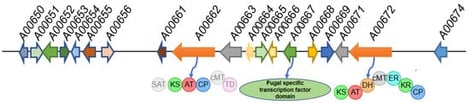
Marine-derived filamentous fungi are a rich source of structurally diverse and biologically active natural products. However, many biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) in fungi remain silent under standard conditions. In this study, we employed a metabolic shunting strategy to disrupt azaphilone biosynthesis in the marine-derived fungus Penicillium sclerotiorum E23Y-1A by deleting the pathway-specific regulator gene A00667. HPLC analysis revealed the emergence of new metabolite peaks in the mutant strain Δ667 compared to the wild type. Subsequent purification yielded seven compounds: the mutant produced two novel meroterpenoids sclerotilins A and B (1 and 2) along with the known steroids ergosta-5,7,22-trien-3β-ol (3) and cerevisterol (4), while the wild type yielded the known steroid (22E)-5α,8α-epidioxyergosta-6,22-dien-3β-ol (5) and two azaphilones geumsanol G (6) and 5-chloro-3-[(1E,3R,4R,5S)-3,4-dihydroxy-3,5-dimethyl-1-hepten-1-yl]-1,7,8,8a-tetrahydro-7,8-dihydroxy-7-methyl-(7R,8R,8aS)-6H-2-benzopyran-6-one (7). Bioactivity assays showed that compound 6 exhibited moderate antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus, and compound 3 displayed moderate cytotoxicity against five human cancer cell lines. These results demonstrate that A00667 is essential for azaphilone biosynthesis and that its disruption leads to the production of structurally distinct natural products, highlighting the potential of pathway engineering to redirect fungal metabolism to yield novel natural products.
27 February 2026