Journal Description
Future Pharmacology
Future Pharmacology
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on pharmacology, drug discovery, and therapeutics published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), EBSCO, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Pharmacology and Pharmacy)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 25.6 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Future Pharmacology is a companion journal of Pharmaceutics.
- Journal Clusters-Pharmaceutical Science: Scientia Pharmaceutica, Marine Drugs, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Pharmacy, Future Pharmacology, Pharmacoepidemiology, Drugs and Drug Candidates and Journal of Pharmaceutical and BioTech Industry.
Impact Factor:
2.7 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.7 (2024)
Latest Articles
Perampanel-Induced Psychosis and Psychosis-like Symptoms: A Systematic Review
Future Pharmacol. 2026, 6(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol6010010 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: This study aimed to investigate whether therapy with perampanel is associated with the development of psychosis or psychosis-like symptoms in patients with epilepsy. Methods: We conducted systematic electronic searches in PubMed, Google Scholar, ScienceDirect, and Scindex databases. We included articles published as
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: This study aimed to investigate whether therapy with perampanel is associated with the development of psychosis or psychosis-like symptoms in patients with epilepsy. Methods: We conducted systematic electronic searches in PubMed, Google Scholar, ScienceDirect, and Scindex databases. We included articles published as case reports/case series, as well as conference abstracts and letters from the editor, if they contained enough data for analysis and quality assessment. The main inclusion criteria relate to patients who experienced psychosis or psychosis-like symptoms described by the authors during perampanel therapy or during its recent use. Results: Publications (n = 17) describing a total of 33 patients who met the inclusion criteria were included. Patient ages ranged from 11 to 70 years, and the majority of them were female (66.67%). A confirmed personal psychiatric history was identified in 60.61% of patients. The time interval between the initiation of perampanel and the onset of adverse events varied significantly across cases. The most frequently reported symptom was aggression (75.75%), followed by irritability (30.30%), while delusions or hallucinations were observed in 8 patients (24.24%). Conclusions: Clinicians should be aware that psychosis or psychosis-like symptoms may represent dose-dependent adverse effects of perampanel with a satisfactory prognosis. Identified risk factors for these developments were positive personal psychiatric history, antiseizure polytherapy at high doses, women’s gender, and focal epilepsies with secondary generalization, mainly manifested as tonic–clonic seizures. Early recognition of symptoms, followed by drug discontinuation, dose reduction, symptomatic treatment, or a combination of the mentioned strategies, is crucial for achieving better outcomes.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Infection and Treatment Protocols in Galleria mellonella for In Vivo Anti-Candida Drug Screening
by
Letícia Targino Campos, Diego Romário-Silva, Priscilla Vasconcelos, Joanilda Paolla Raimundo e Silva, Vinícius Rocha Lima Santos, Larissa Almeida Sarmento, Eutália Maria Veloso Antonino, Joana de Freitas Santos, Jozinete Pereira, Pedro Luiz Rosalén and Edja Costa
Future Pharmacol. 2026, 6(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol6010009 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Galleria mellonella (G. mellonella) larvae have emerged as a valuable in vivo model for antifungal drug screening. This study aimed to determine the optimal inoculum concentrations of Candida albicans (C. albicans) in G. mellonella, as well as
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Galleria mellonella (G. mellonella) larvae have emerged as a valuable in vivo model for antifungal drug screening. This study aimed to determine the optimal inoculum concentrations of Candida albicans (C. albicans) in G. mellonella, as well as the appropriate fluconazole concentrations, in order to standardize a preliminary screening method for compounds with antifungal activity. Methods: Larvae were infected with four C. albicans strains, including two reference strains (ATCC® 10231 and ATCC® 90028) and two oral isolates (A1 and A2). Fluconazole toxicity was evaluated at doses of 20, 40, and 80 mg/kg over a 72 h period. In the treatment assays, larvae were infected via the left pro-leg and treated with fluconazole, administered as a single or two doses, one hour after infection. Larval viability was monitored over five days based on movement, cocoon formation, and melanization, and survival data were analyzed using Kaplan–Meier curves and the log-rank test. Results: Fluconazole showed no toxicity at the tested concentrations. Infection with up to 2 × 107 cells/mL was non-lethal for most strains, except for A2, which exhibited 50% mortality within 48 h but it was effectively controlled with a single 20 mg/kg dose of fluconazole. Infection with 2 × 108 cells/mL resulted in complete mortality within 48 h; however, a single 80 mg/kg dose significantly improved survival. Conclusions: The G. mellonella model proved to be a suitable and reproducible in vivo system for the preliminary screening of antifungal compounds. The standardized experimental conditions established in this study support its applicability for evaluating antifungal activity in early research stages. Future studies should expand this approach to different fungal species and antifungal agents, as well as explore its applicability in combination therapies.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Intranasally Delivered Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reverses Prodromal Non-Motor Deficits and Nigral Loss in a Parkinson’s Disease Mouse Model
by
Soung Hee Moon, Young Eun Huh and Hyun Jin Choi
Future Pharmacol. 2026, 6(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol6010008 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra (SN). Because current therapeutics have limited efficacy once PD is fully developed, it is crucial to start disease-modifying interventions during the prodromal stage
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra (SN). Because current therapeutics have limited efficacy once PD is fully developed, it is crucial to start disease-modifying interventions during the prodromal stage of PD. In the present study, we aimed to evaluate whether intranasally delivered human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hUC-MSCs) have an efficacy in the rotenone-induced prodromal PD-like phenotype mouse model. Methods: To produce the prodromal PD mouse model, C57BL/6 mice were treated with intraperitoneal (i.p.) rotenone for 1 or 2 weeks. hUC-MSCs or PBS were delivered intranasally for 1 or 2 weeks with rotenone injection. We subsequently performed behavioral assessments to evaluate motor and non-motor features, followed by pathological analyses of the mouse brains. Results: Intranasal administration of hUC-MSCs restored motor performance and protected dopaminergic neurons in the SN of mice treated with rotenone for 2 weeks. In the 1-week rotenone mice, hUC-MSCs treatment ameliorated depressive-like behaviors and attenuated olfactory dysfunction. Furthermore, intranasal hUC-MSC treatment suppressed the accumulation of protein aggregates in the brains of mice, which is associated with enhanced autophagic function, as indicated by increased LC3B and normalization of LAMP2A protein expression. Conclusions: Our data demonstrate that intranasal administration of hUC-MSCs improves non-motor symptoms at early time points and attenuates progression to nigrostriatal loss and motor deficits in the rotenone-induced PD mouse model. These findings support the potential of a non-invasive, prodromal-stage intervention to modulate early pathological progression in PD.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Off-Target Effects of Mirabegron on Muscarinic Receptors
by
Shizuo Yamada, Masaki Mogi, Satomi Kagota and Kazumasa Shinozuka
Future Pharmacol. 2026, 6(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol6010007 - 30 Jan 2026
Abstract
Older adults with multiple diseases are likely to be prescribed multiple medications including anticholinergic agents, which are frequently prescribed to manage conditions such as overactive bladder and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and Parkinson’s disease. Overactive bladder (OAB) has been the subject of increased
[...] Read more.
Older adults with multiple diseases are likely to be prescribed multiple medications including anticholinergic agents, which are frequently prescribed to manage conditions such as overactive bladder and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and Parkinson’s disease. Overactive bladder (OAB) has been the subject of increased disease awareness and is a common and significant cause of reduced quality of life, particularly in the elderly. The selective β3 adrenoceptor agonist, mirabegron was developed for the pharmacological treatment of OAB. Mirabegron has been shown to exert off-target effects on various functional proteins such as muscarinic receptors in rat tissues. This agent may relax the detrusor muscle by activating β3 adrenoceptors and also antagonizing muscarinic receptors. Mirabegron and antimuscarinics exerted additive effects on muscarinic receptor binding and relaxant responses of cholinergic contractions of the detrusor muscle. Mirabegron excreted in human urine appears to directly attenuate muscarinic receptor-mediated functions in the bladder. Combination therapy of mirabegron and solifenacin in patients with OAB may enhance not only their therapeutic effects on OAB, but also increase the risk of anticholinergic adverse effects. Therefore, the safety of concomitant use of mirabegron and other drugs such as antimuscarinics for elderly patients needs to be carefully considered.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Future Pharmacology 2025)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Advanced Liposomal Systems for Cancer Therapy with Focus on Lipid–Polymer Hybrids and Cell Membrane-Coated Liposomes
by
Paraskevi Zagana and Alexandra Paxinou
Future Pharmacol. 2026, 6(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol6010006 - 16 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Since their discovery in the 1960s, liposomes have become a versatile platform for drug delivery in cancer research, capable of carrying both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs. Throughout the past decades, liposomes have evolved to improve stability, blood circulation time, and targeting ability, overcoming
[...] Read more.
Since their discovery in the 1960s, liposomes have become a versatile platform for drug delivery in cancer research, capable of carrying both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs. Throughout the past decades, liposomes have evolved to improve stability, blood circulation time, and targeting ability, overcoming many disadvantages of early formulations. Lipid–polymer hybrid liposomes (LPHLs), a third-generation nanoparticle model, are vesicles where polymers are incorporated in or around the lipid bilayer to increase their stability, to control drug release, and to provide multifunctional capabilities. More recently, cell membrane-coated (CMC) liposomes, which consist of “core” liposomes (preformed liposomes) cloaked in natural cell membranes, have emerged as an even more innovative approach, offering superior immune evasion and highly selective targeting, which are both particularly promising for cancer therapy. Preclinical studies in cancer models demonstrate that these advanced liposomal systems improve pharmacokinetics and therapeutic outcomes. They hold significant potential for developing next-generation, personalized nanomedicines for cancer and other complex diseases. However, challenges related to large-scale production, long-term stability, and safety evaluation remain.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Pharmacogenetics in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
by
Ana Cabetas, Antonio del Bosque, María Sainz-Gil and Zoraida Verde
Future Pharmacol. 2026, 6(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol6010005 - 7 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a highly heritable neurodevelopmental condition, and pharmacogenetic studies aim to clarify interindividual variability in treatment responses and adverse effects. Despite increasing research, the field remains fragmented. This review provides a bibliometric analysis of ADHD pharmacogenetics (2005–2025), identifying
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a highly heritable neurodevelopmental condition, and pharmacogenetic studies aim to clarify interindividual variability in treatment responses and adverse effects. Despite increasing research, the field remains fragmented. This review provides a bibliometric analysis of ADHD pharmacogenetics (2005–2025), identifying its intellectual foundations, thematic structure, and global distribution. Methods: A bibliometric search was conducted in Scopus and Web of Science, retrieving 711 documents published between 2005 and July 2025. Data were analyzed with the Bibliometrix R package and Biblioshiny interface, applying bibliometric mapping, Bradford’s Law, co-word analysis, and thematic mapping. Only peer-reviewed journal articles, books, and book chapters were included to ensure scientific rigor. Results: The dataset shows a modest annual growth rate but strong impact, with an average of 29.6 citations per article. Highly cited works converge into four domains: (i) clinical guidelines and pharmacological treatments; (ii) cognitive heterogeneity and subtypes; (iii) neurodevelopmental and genetic mechanisms; (iv) environmental and health-related influences. Geographically, the United States leads with 24.8% of publications, followed by Brazil, China, and European countries. Keyword analysis reveals two main clusters: a clinical–therapeutic pole (methylphenidate, atomoxetine, child) and a genetic–molecular pole (dopamine transporter, SNPs, genotype). Conclusions: ADHD pharmacogenetics shows consolidation with strong clinical and genetic cores but limited integration of comorbidity, adult populations, and non-stimulant treatments. Future research should prioritize multi-center cohorts, multi-omic designs, and stronger international collaboration to advance precision medicine in ADHD.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Transdiagnostic Psychopharmacology: Bridging Mechanisms Across Mental Disorders)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Preparation, Characterization, and Antibiofilm Activity of Free and Nanoencapsulated Tetradenia riparia (Hochst.) Codd Leaf Essential Oil
by
Regina Yasuko Makimori, Eliana Harue Endo, Julia Watanabe Makimori, Priscila Firmino Ribas, Fernanda Vitória Leimann, Odinei Hess Gonçalves, Zilda Cristiani Gazim, Tânia Ueda-Nakamura, Celso Vataru Nakamura and Benedito Prado Dias Filho
Future Pharmacol. 2026, 6(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol6010004 - 6 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background: Staphylococcus aureus is a clinically relevant pathogen with a strong ability to form biofilms on a wide range of surfaces, which markedly reduces the effectiveness of antimicrobial treatments and contributes to therapeutic failure. Although essential oils (EOs) represent effective and economical
[...] Read more.
Background: Staphylococcus aureus is a clinically relevant pathogen with a strong ability to form biofilms on a wide range of surfaces, which markedly reduces the effectiveness of antimicrobial treatments and contributes to therapeutic failure. Although essential oils (EOs) represent effective and economical antimicrobial alternatives, their clinical application is limited by rapid oxidation, volatility, and potential cytotoxicity. In this context, nanoencapsulation emerges as a promising strategy to improve EO stability, control release, and reduce toxicity. In this study, Tetradenia riparia essential oil was encapsulated into poly(lactide) (PLA) nanoparticles (NP) using the nanoprecipitation method. Methods: The physicochemical properties of the nanoparticles were characterized, and their antibacterial, antibiofilm, and cytotoxic activities were evaluated. Antibiofilm and antibacterial effects against S. aureus were assessed by the broth microdilution method, while cytotoxicity was determined using a VERO cell line. Results: The nanoparticles exhibited nanometric size, spherical morphology, and homogeneous structure. Both free EO and EO-loaded nanoparticles demonstrated antibacterial and antibiofilm activity against S. aureus. Importantly, EO-loaded nanoparticles were significantly less cytotoxic than free EO. Nanoencapsulation effectively prevented rapid EO evaporation and degradation, thereby enhancing stability. The nanoparticles exhibited a zeta potential of approximately −23.1 mV, indicating adequate colloidal stability. Differential scanning calorimetry revealed a reduction in melting enthalpy from 429.63 J/g (blank nanoparticles) to 115.83 J/g for EO-loaded nanoparticles, indicating decreased polymer crystallinity and a system favorable for controlled EO release. Conclusions: Overall, these findings demonstrate that nanoencapsulation of T. riparia essential oil into PLA nanoparticles preserves antimicrobial efficacy, reduces cytotoxicity, and improves physicochemical stability, supporting the potential of this nanostructured system as a promising strategy for the treatment of S. aureus biofilm-associated infections.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Novel Therapeutic Agents and Innovative Treatment Strategies Against Infectious Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Serotonin, Granisetron, and Temozolomide Alone or in Combination on Neuroblastoma and Glial Cell Lines
by
Özlem Erol Polat, Ferhunde Aysin, Nihal Şimşek Özek and Fikret Çelebi
Future Pharmacol. 2026, 6(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol6010003 - 2 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Neuroblastoma is the most common extracranial solid malignancy in infants and children. High-risk neuroblastoma patients are commonly treated with temozolomide (TMZ), which typically exhibits a poor therapeutic response. Serotonin, also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), plays various essential functions in the human body.
[...] Read more.
Background: Neuroblastoma is the most common extracranial solid malignancy in infants and children. High-risk neuroblastoma patients are commonly treated with temozolomide (TMZ), which typically exhibits a poor therapeutic response. Serotonin, also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), plays various essential functions in the human body. In the central nervous system, it serves as a neurotransmitter. Beyond its physiological roles, 5-HT has recently been identified as a potential growth factor for several human tumors, including gliomas and carcinoid tumors. Recent literature has demonstrated that 5-HT receptor antagonists can inhibit the growth of cancer cells. Furthermore, both 5-HT receptors and their antagonists have been identified as potential anticancer agents, suggesting their significance in the development of new treatment strategies. Objectives: The primary aim of this study was to examine the effects of 5-HT and 5-HT antagonists on tumor (neuroblastoma (SH-SY5Y)) and healthy cells (microglia (HMC3)) and determine the impact of their interaction with the anticancer agent TMZ on cell proliferation/viability and migration. Methods: The study explored the interaction between 5-HT, the 5-HT antagonist granisetron (GRN), the anticancer agent TMZ, and their combinations, specifically assessing their influence on cell proliferation, viability, and migration. Results: As a result, the single and combined applications of 5-HT, TMZ, and GRN, a 5-HT antagonist, inhibited cell growth and proliferation in SH-SY5Y, causing decreased cell viability. Additionally, the combination of 5-HT and GRN increased the efficacy of TMZ. Conclusions: The study findings revealed that 5-HT and 5-HT antagonists may have therapeutic effects by exhibiting antiproliferative effects in SH-SY5Y cells at high concentrations.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
From Painkillers to Antidiabetics: Structural Modification of NSAID Scaffolds for Drug Repurposing
by
Anđela Gogić, Miloš Nikolić, Nikola Nedeljković, Nebojša Zdravković, Marina Vesović and Ana Živanović
Future Pharmacol. 2026, 6(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol6010002 - 2 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The treatment of diabetes in the modern era, with its growing patient population, represents a significant challenge due to the wide range of adverse effects associated with medications that target complex biochemical processes. Consequently, researchers are investigating the hypoglycemic potential of existing drugs.
[...] Read more.
The treatment of diabetes in the modern era, with its growing patient population, represents a significant challenge due to the wide range of adverse effects associated with medications that target complex biochemical processes. Consequently, researchers are investigating the hypoglycemic potential of existing drugs. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used to treat pain, fever, and various inflammatory conditions. Recent studies have shown that NSAIDs, particularly salicylates, can influence glycemia through multiple mechanisms, including inhibition of gastrointestinal enzymes, blockade of KATP channels, activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), and inhibition of NF-κB signaling, among others. Accordingly, this review explores the hypoglycemic potential of NSAIDs as well as their derivatives, and the diverse mechanisms through which these molecules may influence glucose homeostasis.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Leishmanicidal and Immunomodulatory Effects of Ocellatin-PT4 and Ocellatin-PT6 on Amastigotes of Leishmania amazonensis
by
Mayara G. C. Oliveira, Vanessa da Silva Eschimith, Felipe T. B. Kuzniewski, Andreanne G. Vasconcelos, Daniel C. Moreira, Marcelo P. Bemquerer, Danilo Corazza, Jhones N. Dias, Daniel D. R. Arcanjo, Peter Eaton, Maria I. Muniz-Junqueira, José Roberto S. A. Leite, Tatiana K. S. Borges and Selma A. S. Kuckelhaus
Future Pharmacol. 2026, 6(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol6010001 - 21 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Leishmaniasis is a neglected parasitic disease with significant global impact and limited therapeutic options due to the toxicity and cost of current treatments. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) derived from amphibians, such as Ocellatin-PT4 and Ocellatin-PT6, have emerged as promising bioactive molecules due
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Leishmaniasis is a neglected parasitic disease with significant global impact and limited therapeutic options due to the toxicity and cost of current treatments. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) derived from amphibians, such as Ocellatin-PT4 and Ocellatin-PT6, have emerged as promising bioactive molecules due to their antimicrobial properties and low toxicity to mammalian cells. This study evaluated the leishmanicidal and immunomodulatory effects of Ocellatin-PT4 and Ocellatin-PT6 against Leishmania amazonensis amastigotes. Methods: Peptides were tested on axenic amastigotes and macrophages infected with amastigotes. Cytotoxicity was assessed using MTT (0.4–197 µM for Ocellatin-PT4 and 0.3–152.1 µM for Ocellatin-PT6) and vital dye exclusion assays. Reactive oxygen species (ROS), nitric oxide (NO), and lipid droplet (LD) production were quantified to assess immunomodulatory responses. Results: Ocellatin-PT4 and Ocellatin-PT6 significantly reduced the viability of free and intracellular amastigotes at concentrations ≥ 24.7 µM and ≥19 µM, respectively, without affecting J774 macrophage viability. Infected macrophages treated with the peptides showed reduced parasite load and decreased infection index (≥12.3 µM for Ocellatin-PT4 and ≥2.4 µM for Ocellatin-PT6). Both peptides modulated the oxidative stress response: they reduced ROS levels in infected macrophages while only slightly increasing NO production at higher concentrations. Additionally, lipid droplet accumulation, which was increased during infection, was downregulated by both peptides—particularly by Ocellatin-PT6. Conclusions: Ocellatin-PT4 and Ocellatin-PT6 exert leishmanicidal effects and modulate key macrophage functions without cytotoxicity. These peptides represent promising candidates for the development of novel therapies against cutaneous leishmaniasis.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Organoids as a Revolutionary Data Source for Pharmacokinetic Modeling: A Comprehensive Review
by
Lara Marques and Nuno Vale
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(4), 74; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040074 - 15 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The progress of contemporary pharmacology is deeply linked to pharmacokinetics (PK) and its quantitative exploration through PK modeling. By offering a robust mathematical framework to describe and predict drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME), PK modeling is essential for designing and optimizing
[...] Read more.
The progress of contemporary pharmacology is deeply linked to pharmacokinetics (PK) and its quantitative exploration through PK modeling. By offering a robust mathematical framework to describe and predict drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME), PK modeling is essential for designing and optimizing safe and effective dosing regimens and for advancing personalized medicine and model-informed drug development (MIDD). The reliability of population PK (popPK) and physiologically based PK (PBPK) models depends on high-quality experimental data to estimate PK parameters. Traditional PK data sources include clinical studies, preclinical animal models, and human-derived cell lines. Although considered gold standards, these sources have significant drawbacks. Clinical trials are often restricted by ethical, logistical, and financial challenges and often include homogenous populations that fail to reflect real-world interindividual variability. Similarly, animal and cell-based models lack the physiological complexity of humans, leading to discrepancies between preclinical predictions and clinical outcomes. These constraints have stimulated interest in alternative platforms that more faithfully recapitulate human physiology and interindividual diversity. This review explores the potential of organoids as a novel or complementary source of PK-relevant data. Organoids, three-dimensional (3D) stem cell-derived structures, mimic the cellular architecture, functional heterogeneity, and physiological responses of human tissues. In particular, intestinal, liver, and kidney organoids preserve essential cellular features of ADME processes, positioning them as promising tools for integration into popPK and PBPK modeling frameworks.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
In Vitro Antifungal Effect of Selected Essential Oils Against Clinical Isolates Causing Fungal Keratitis: A Preliminary Pharmacological Evaluation
by
Elijah Akegbe, Nuno Mesquita, Célia Cabral, Emília Pereira, Luís Fernandes, Anália do Carmo, Rui Tomé, Dolores Pinheiro, João Pinheiro-Costa, Andreia M. Rosa and Elisa J. Campos
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(4), 73; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040073 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Fungal keratitis (FK) is a current challenge in ophthalmology due to its association with severe visual impairment and the limitations of current antifungal therapies. We aim to evaluate the antifungal activity of essential oils (EOs) from the aromatic and medicinal plants Cymbopogon
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Fungal keratitis (FK) is a current challenge in ophthalmology due to its association with severe visual impairment and the limitations of current antifungal therapies. We aim to evaluate the antifungal activity of essential oils (EOs) from the aromatic and medicinal plants Cymbopogon citratus and Lavandula pedunculata against selected FK pathogens collected from FK patients in two Portuguese hospitals. Methods: The antifungal activity of the EOs was tested at concentrations of 25%, 50%, 75%, and 100% for up to 7 days using the solid-phase disk diffusion in vitro assay. Results: Candida albicans was the most prevalent pathogen (28.6%), followed by Candida parapsilosis (21.4%) and Dicyma olivacea (14.2%). The other identified species were Aspergillus fumigatus and Scedosporium boydii (7.1%). Clinical diagnostic methodologies showed agreement with the molecular identification. Cymbopogon citratus EO showed higher antifungal activity than Lavandula pedunculata EO. The highest antifungal activity was observed against Aspergillus fumigatus and Scedosporium boydii (inhibition zone diameter, IZD = 90.0 mm) after 7 (Cymbopogon citratus EO) or 3 days of incubation (Lavandula pedunculata EO). While the antifungal activity of Cymbopogon citratus EO was maintained during the study (for Aspergillus fumigatus, Candida albicans, and Scedosporium boydii), the antifungal activity of Lavandula pedunculata EO decreased with time. Conclusions: Cymbopogon citratus EO and Lavandula pedunculata EO showed optimal antifungal activity against molds (Aspergillus fumigatus and Scedosporium boydii) after 3 days of incubation. Against yeasts (Candida albicans and Candida parapsilosis), the EOs showed lower activity. Our study sheds light on the development of new pharmacological strategies for FK based on EOs extracted from aromatic and medicinal plants.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Novel Therapeutic Agents and Innovative Treatment Strategies Against Infectious Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Synthesis of New Schiff Bases Derived from Sulfamethoxazole and Aromatic Aldehydes with High Antibiofilm Activity in Rapidly Growing Mycobacteria Samples
by
Fallon dos Santos Siqueira, Josiéli Demétrio Siqueira, Alencar Kolinski Machado, Michele Rorato Sagrillo, Yuri Clemente Andrade Sokolovicz, Marieli Friedrich Loreto, Thiago Augusto de Lima Burgo, Carlos Serpa, Otávio Augusto Chaves, Matiko Anraku de Campos and Davi Fernando Back
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(4), 72; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040072 - 3 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Rapidly growing mycobacteria (RGM) are microorganisms with variable pathogenicity, which can cause different clinical forms of mycobacterioses. They can form structured communities at the liquid-air interface and adhere to animate and inanimate solid surfaces, characterizing one of their most powerful mechanisms of
[...] Read more.
Background: Rapidly growing mycobacteria (RGM) are microorganisms with variable pathogenicity, which can cause different clinical forms of mycobacterioses. They can form structured communities at the liquid-air interface and adhere to animate and inanimate solid surfaces, characterizing one of their most powerful mechanisms of resistance and survival, named biofilms. Objectives: Here, a novel series of sulfamethoxazole (SMTZ) Schiff bases were obtained by the condensation of the primary amine from SMTZ core with six different aldehydes to evaluate their antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities, as well as physicochemical and in silico characteristics. Methods: The compounds L1–L6 included: pyridoxal hydrochloride (L1), salicylaldehyde (L2), 3-methoxysalicylaldehyde (L3), 2-hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde (L4), 3-allylsalicylaldehyde (L5), and 4-(diethylamino)salicylaldehyde (L6). MIC determination was performed against standard strains and seven clinical isolates. Time-kill assays, biofilm inhibition assays, atomic force microscopy, and peripheral blood mononuclear cell cytotoxicity assays were carried out. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations using quantum descriptors, Mulliken charges, Fukui functions, non-covalent interactions (NCI), and reduced density gradient (RDG), along with molecular docking calculations to DHS, LasR, and PqsR, supported the experimental trend. Results: The compounds L1–L6 showed a significant capacity to inhibit the growth of RGM, with MIC values in the range of 0.61 to 1.22 μg mL−1, which are significantly lower than those observed for the parent compound SMTZ, demonstrating superior antimicrobial potency. To deepen antimicrobial activity assays, L1 was chosen for further evaluations and showed a significant ability to inhibit the growth of RGM in both planktonic and biofilm forms. In addition, atomic force microscopy views great changes in topography, electrical force, and nanomechanical properties of microorganisms. The cytotoxic assays with the peripheral blood mononuclear cell model suggest that the new compound may be considered as an antimicrobial alternative, as well as a safe substance showing selectivity indexes in the range of efficacy. Conclusions: Density functional theory (DFT) calculations were performed to obtain quantum descriptors, Mulliken charges, Fukui functions, non-covalent interactions (NCI), and reduced density gradient (RDG), which, with molecular docking calculations to DHS, LasR, and PqsR, supported the experimental trend.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Future Pharmacology 2025)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Antibacterial Mechanisms of 4-Chlorobenzyl p-Coumarate: Inhibition of MepA and NorA Efflux Pumps
by
Éverton Paredes Falcão, Jeremias Justo Emídio, Natália Ferreira de Sousa, Karinne Kelly Gadelha Marques, Janaina Esmeraldo Rocha, Wellington Lima da Silva Sobrinho, João Felipe Bezerra, Luciana Scotti, Marcus Tullius Scotti, Juan Carlos Ramos Gonçalves, Henrique Douglas Melo Coutinho, Damião Pergentino de Sousa and Ricardo Dias de Castro
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(4), 71; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040071 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
Introduction: Bacterial infections, especially those caused by multidrug-resistant strains, remain a major health concern. This study investigates 4-chlorobenzyl p-coumarate, assessing its antibacterial mechanism, pharmacokinetic profile, and potential to modulate antimicrobial resistance. Methods: In silico studies were conducted, including molecular docking, molecular dynamics
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Bacterial infections, especially those caused by multidrug-resistant strains, remain a major health concern. This study investigates 4-chlorobenzyl p-coumarate, assessing its antibacterial mechanism, pharmacokinetic profile, and potential to modulate antimicrobial resistance. Methods: In silico studies were conducted, including molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations, and pharmacokinetic predictions, alongside in vitro assays assessing efflux pump inhibition, antibiotic modulation, and bacterial DNA analysis. Results: The compound showed higher binding affinity and complex stability with the enzyme phosphatidylglycerol phosphate synthase, while also exhibiting reduced residue fluctuations and better flexibility with the NAD+-dependent DNA ligase. Molecular interactions with the efflux proteins MepA and NorA were also observed. Pharmacokinetic predictions indicated a favorable profile, including suitability for oral administration. Experimentally, the compound inhibited the MepA and NorA efflux pumps, modulated the activity of the antibiotics ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin, and reduced DNA concentration in treated cells. Conclusions: The findings suggest that the compound acts through dual mechanisms, with a prediction of activity by disrupting phosphatidylglycerol synthesis and DNA replication while inhibiting and modulating MepA and NorA efflux pumps.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Novel Therapeutic Agents and Innovative Treatment Strategies Against Infectious Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Levosimendan in ECMO: A Paradigm Shift or an Adjunctive Option?
by
Debora Emanuela Torre and Carmelo Pirri
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(4), 70; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040070 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Levosimendan, a calcium-sensitizing inodilator, has emerged as a promising adjunctive therapy in patients undergoing veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (V-A ECMO). Its pharmacodynamic profile, combining positive inotropy with vasodilation and mitochondrial protective effects, offers a unique therapeutic potential in the context of mechanical circulatory
[...] Read more.
Levosimendan, a calcium-sensitizing inodilator, has emerged as a promising adjunctive therapy in patients undergoing veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (V-A ECMO). Its pharmacodynamic profile, combining positive inotropy with vasodilation and mitochondrial protective effects, offers a unique therapeutic potential in the context of mechanical circulatory support. Despite growing interest, the clinical impact of Levosimendan in ECMO remains debated, with heterogeneous evidence regarding its efficacy in improving weaning success, reducing vasopressor requirements or mitigating ischemia-reperfusion injury. This narrative review aims to critically appraise the current literature on Levosimendan use in ECMO settings, exploring its mechanistic rationale, pharmacologic behavior under extracorporeal circulation and potential role in various clinical scenarios including post-cardiotomy shock and refractory cardiogenic failure. The limitations of existing studies are critically examined, underscoring the need for high-quality clinical trials to define appropriate patient selection, optimal timing of administration and dosing strategies. This review synthesizes current evidence to determine whether Levosimendan constitutes a true therapeutic asset or remains merely an adjunctive agent in the complex management of ECMO supported patients.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Natural Product-Based Drug Discovery for Monkeypox Virus: Integrating In Silico Approaches and Therapeutic Development Strategies
by
Aganze Gloire-Aimé Mushebenge and David Ditaba Mphuthi
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(4), 69; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040069 - 26 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The global spread of Monkeypox virus (MPXV) has emerged as a major public health concern, with the 2022 outbreak underscoring the urgent need for effective antiviral therapies. Current treatment options are limited because no drugs specifically target Mpox, and existing recommendations rely on
[...] Read more.
The global spread of Monkeypox virus (MPXV) has emerged as a major public health concern, with the 2022 outbreak underscoring the urgent need for effective antiviral therapies. Current treatment options are limited because no drugs specifically target Mpox, and existing recommendations rely on repurposed smallpox antivirals that may cause resistance. This highlights the critical need for novel therapeutic agents targeting key viral and host factors involved in MPXV pathogenesis. Medicinal plants provide a rich reservoir of bioactive compounds with potential antiviral activity, particularly in low- and middle-income countries where they play an essential role in healthcare. To address this issue, we conducted a review exploring innovative in silico approaches for natural product-based drug discovery against MPXV. Computational studies identified phytochemicals such as curcumin, punicalagin, rosmarinic acid, and quercitrin with strong affinities for key viral proteins including DNA polymerase, TMPK, DdRp, A42R, MTase, p37, and envelope proteins and favorable pharmacokinetic profiles Despite these promising findings, fragmented biological datasets, viral mutability, and limited in vitro and in vivo validation hinder clinical translation. Our analysis highlights integrating AI-driven virtual screening with experimental validation to accelerate MPXV drug discovery, providing a scalable framework for managing emerging viral threats.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Quercetin in Free Form and Nanoemulsion in an In Vivo Model of Parkinson’s Disease
by
Camila de Oliveira Vian, Rafael Felipe De Aguiar, Marcelo Augusto Germani Marinho, Vitória Pereira Mackmillan, Carolina Miranda Alves, Jamile Lima Rodrigues, Fernanda Barros de Miranda, Cristiana Lima Dora, Ana Paula Horn and Mariana Appel Hort
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(4), 68; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040068 - 20 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by motor and cognitive impairments due to dopaminergic neuron loss. The neurotoxin MPTP is commonly used to model PD, as it selectively targets these neurons. Quercetin (QU), a flavonoid with antioxidant properties, has
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by motor and cognitive impairments due to dopaminergic neuron loss. The neurotoxin MPTP is commonly used to model PD, as it selectively targets these neurons. Quercetin (QU), a flavonoid with antioxidant properties, has shown neuroprotective potential, but its poor solubility limits clinical application. Nanoemulsions (NEQU) have emerged as a strategy to enhance its bioavailability and efficacy. Methods: To evaluate the neuroprotective and antioxidant effects of QU and NEQU, zebrafish larvae were exposed to MPTP (50 µM) and assessed for survival, locomotion (total distance traveled), morphological parameters, reactive oxygen species (ROS), lipid peroxidation (via MDA), and reduced glutathione (GSH) levels. Results: Only NEQU pre-treatment reversed MPTP-induced locomotor deficits. Both QU and NEQU (2.5 µM) significantly reduced ROS production and lipid peroxidation, with no effect on GSH levels. Notably, MPTP exposure led to a significant reduction in head size, an unprecedented finding in zebrafish PD models, indicating neurotoxicity. Morphometric analysis showed no change in total body length. However, MPTP significantly decreased swim bladder size and increased yolk sac size. Treatment with QU and NEQU attenuated these swim bladder alterations; no significant differences were observed in other parameters. Conclusions: These findings suggest that quercetin, particularly when nanoencapsulated, is a promising candidate for further development as a therapeutic agent to mitigate PD-related neurodegeneration.
Full article
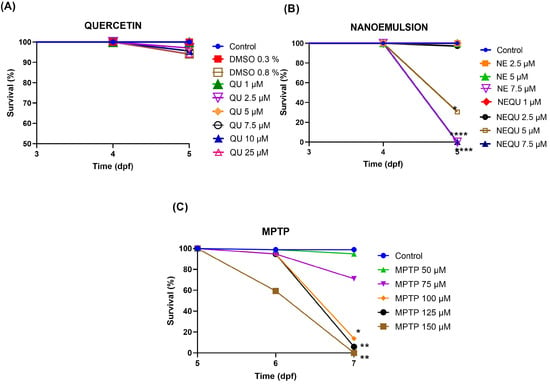
Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Impact of Postural Restrictions on Tetrabenazine Pharmacokinetics in Healthy Volunteers: A Randomized Crossover Study Emphasizing Variance Minimization Strategies in Good Clinical Practice-Guided Bioequivalence Research
by
Nirav Chandegara, Shrikalp Deshpande, Bhupendra Prajapati, Anup Singh and Dignesh Khunt
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(4), 67; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040067 - 10 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Tetrabenazine, a VMAT2 inhibitor used for hyperkinetic disorders, shows considerable pharmacokinetic variability due to extensive first-pass metabolism. Standardization of clinical trial conditions, including posture, may reduce variability and improve bioequivalence assessments. Objective: The aim of this study was to determine the impact
[...] Read more.
Background: Tetrabenazine, a VMAT2 inhibitor used for hyperkinetic disorders, shows considerable pharmacokinetic variability due to extensive first-pass metabolism. Standardization of clinical trial conditions, including posture, may reduce variability and improve bioequivalence assessments. Objective: The aim of this study was to determine the impact of postural restriction on the pharmacokinetics of tetrabenazine and its active metabolite, dihydrotetrabenazine (HTBZ), under controlled conditions. Methods: A randomized, open-label, four-period replicate crossover study enrolled 72 healthy fasted adults who received a single 25 mg tetrabenazine dose under two conditions: 4 h semirecumbent posture versus unrestricted movement. Plasma drug concentrations were measured across 36 h using validated LC–MS/MS method. Pharmacokinetic parameters were estimated via non-compartmental analysis and compared with Wilcoxon signed-rank tests. Results: Postural restriction significantly increased tetrabenazine exposure (AUC0–t: +16.4%, p < 0.0001) and half-life (p = 0.002), with a nonsignificant rise in Cmax. For HTBZ, Cmax decreased (−16.2%, p = 0.018), whereas AUC was unchanged. Parent-to-metabolite ratios increased by 24–29%. Replicate design analyses showed reduced intra-subject variability for tetrabenazine AUC with posture control (~24% vs. >28%). Simulation suggested that posture restriction could lower sample size requirements by 15–30% in two-period average bioequivalence trials. Conclusions: Maintaining a semirecumbent posture after dosing enhances tetrabenazine’s bioavailability, attenuates early metabolite formation, and reduces pharmacokinetic variability. Incorporating posture control into bioequivalence trial protocols may optimize study design, reduce participant exposure, and align with ICH-GCP ethical principles.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Structure-Guided Identification of JAK2 Inhibitors: From Similarity to Stability and Specificity
by
Muhammad Yasir, Jinyoung Park, Jongseon Choe, Jin-Hee Han, Eun-Taek Han, Won Sun Park and Wanjoo Chun
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(4), 66; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040066 - 5 Nov 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) is a pivotal signaling protein implicated in various hematological malignancies and inflammatory disorders, making it a compelling target for therapeutic intervention. Methods: In this study, we employed an integrative computational approach combining ligand-based screening, pharmacophore modeling,
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) is a pivotal signaling protein implicated in various hematological malignancies and inflammatory disorders, making it a compelling target for therapeutic intervention. Methods: In this study, we employed an integrative computational approach combining ligand-based screening, pharmacophore modeling, molecular docking, molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, and MM/PBSA free energy calculations to identify JAK2 inhibitors from the ChEMBL database. A comprehensive virtual screening of over 1,900,000 compounds was conducted using Tanimoto similarity and a validated pharmacophore model, resulting in the identification of 39 structurally promising candidates. Docking analyses prioritized compounds with favorable interaction energies, while MD simulations over 100 ns assessed the dynamic behavior and binding stability of top hits. Results: Four compounds, CHEMBL4169802, CHEMBL4162254, CHEMBL4286867, and CHEMBL2208033, exhibited consistently superior performance, forming stable hydrogen bonds, favorable RMSD profiles (≤0.5 nm), and strong binding interactions, including salt bridges. Notably, the binding free energies revealed ΔG values as low as −29.91 kcal/mol, surpassing that of the reference inhibitor, momelotinib (−24.17 kcal/mol). Conclusions: Among these, CHEMBL4169802 emerged as the most promising candidate due to its synergistic electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions. Collectively, our results highlight these compounds as probable, JAK2-selective inhibitors with strong potential for further biological validation and optimization.
Full article
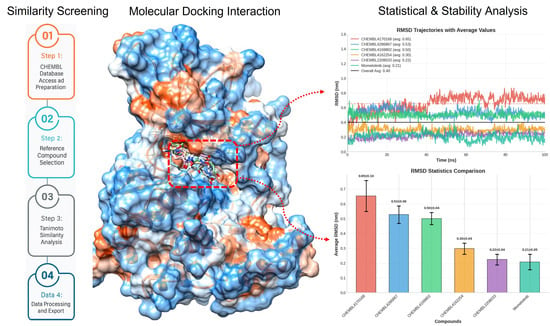
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
In Vitro Effects of Retinoic Acid and Sodium Selenite on Neuroblastoma Cell Line (SH-SY5Y)
by
Milena Mariano Ribeiro, Luíza Siqueira Lima, Nayara de Souza da Costa, Meire Ellen Pereira, Aline S. Fonseca, Luciane R. Cavalli, Quelen I. Garlet, Ana Carolina Irioda and Cláudia S. Oliveira
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(4), 65; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040065 - 4 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Neuroblastoma is a pediatric embryonal tumor of the autonomic nervous system, characterized by high heterogeneity. Recent research has explored the therapeutic potential of retinoic acid and selenium derivatives as antiproliferative agents. This study aims to assess the antiproliferative effects of sodium
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Neuroblastoma is a pediatric embryonal tumor of the autonomic nervous system, characterized by high heterogeneity. Recent research has explored the therapeutic potential of retinoic acid and selenium derivatives as antiproliferative agents. This study aims to assess the antiproliferative effects of sodium selenite and retinoic acid, as well as the conventional chemotherapeutic agents, cyclophosphamide and cisplatin, using the SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell line. Methods: Cells were treated with the compounds at concentrations ranging from 0 to 1000 µM for 72 h. The following assays were performed: cell viability, clonogenic assay, cell migration, cell cycle analysis, and gene expression (BCL2 and BAX). Data were analyzed using the Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s or the Mann–Whitney test (p < 0.05). IC50 values were obtained from dose–response curves. Results: Sodium selenite (100–1000 µM) significantly reduced cell viability by more than 50% (IC50: 166 µM at 72 h). Retinoic acid (300 µM) reduced viability by 65% (IC50: 198 µM at 72 h), and cisplatin (10 µM) reduced viability by 79% (IC50: 3.4 µM at 72 h). All compounds significantly decreased colony formation. Sodium selenite and retinoic acid induced arrest in the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle. Gene expression analysis revealed downregulation of the BCL2 gene by all compounds and upregulation of BAX only by sodium selenite at IC50 concentration. Conclusions: Sodium selenite and retinoic acid showed antiproliferative effects on neuroblastoma cells, suggesting their potential as adjuvant therapeutic agents. To reach this goal, we suggest further investigation of their mechanisms of action and evaluation of the combined strategies.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
27 January 2026
Meet Us at the 5th Molecules Medicinal Chemistry Symposium, 14–17 May 2026, Beijing, China
Meet Us at the 5th Molecules Medicinal Chemistry Symposium, 14–17 May 2026, Beijing, China

9 December 2025
Meet Us at the 146th Annual Meeting of the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan (Osaka), 26–29 March 2026, Osaka, Japan
Meet Us at the 146th Annual Meeting of the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan (Osaka), 26–29 March 2026, Osaka, Japan

Topics
Topic in
Biomedicines, IJMS, Sci. Pharm., Molecules, Future Pharmacology, Biomolecules
Natural Products and Drug Discovery—2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Sonia Piacente, Marta MenegazziDeadline: 30 September 2026
Topic in
Biomedicines, Future Pharmacology, Pharmacy, IJMS, Biomolecules, Genes
Prospects of Multi-Target Agonists in Metabolic and Epigenetic Medicine
Topic Editors: Riham Abouleisa, Yanming LiDeadline: 30 November 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Future Pharmacology
Recent Advances in the Discovery of Anti-Inflammatory Compounds
Guest Editors: Ivan M. Srejović, Nikola Nedeljkovic, Miloš NikolićDeadline: 28 February 2026
Special Issue in
Future Pharmacology
Novel Therapeutic Agents and Innovative Treatment Strategies Against Infectious Diseases
Guest Editor: Sara ConsalviDeadline: 31 March 2026
Special Issue in
Future Pharmacology
Drugs, Growth Factors and Active Molecules for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine
Guest Editor: Natasha MaurmannDeadline: 31 March 2026
Special Issue in
Future Pharmacology
Liposome-Mediated Natural Compounds in Cancer Therapy
Guest Editors: Panayiota Christodoulou, Athanasios SkourasDeadline: 30 April 2026







