-
 Pharmacy Staff Experiences and Needs During Second Dispense of Driving-Impairing Medicines: A Qualitative Study
Pharmacy Staff Experiences and Needs During Second Dispense of Driving-Impairing Medicines: A Qualitative Study -
 Peer-Delivered Hepatitis C Testing and Health Screening Provided in a Community Pharmacy Setting: Proof of Concept
Peer-Delivered Hepatitis C Testing and Health Screening Provided in a Community Pharmacy Setting: Proof of Concept -
 Assessing Pharmacy Costs of Intravenous Push Controlled Substance Waste in Hospital-Based Areas: A Multi-Site Study
Assessing Pharmacy Costs of Intravenous Push Controlled Substance Waste in Hospital-Based Areas: A Multi-Site Study -
 Developing a Theoretically Informed Strategy to Enhance Pharmacist-Led Deprescribing in Care Homes for Older People
Developing a Theoretically Informed Strategy to Enhance Pharmacist-Led Deprescribing in Care Homes for Older People
Journal Description
Pharmacy
Pharmacy
is an international, scientific, peer-reviewed, and open access journal dealing with pharmacy education and practice, and is published bimonthly online by MDPI. The Academy of Pharmaceutical Sciences (APS) is affiliated with Pharmacy and its members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, Embase, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 22.9 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: Reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Journal Clusters-Pharmaceutical Science: Scientia Pharmaceutica, Marine Drugs, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Pharmacy, Future Pharmacology, Pharmacoepidemiology, Drugs and Drug Candidates and Journal of Pharmaceutical and BioTech Industry.
Impact Factor:
1.8 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.0 (2024)
Latest Articles
Oral Contraceptive Knowledge Among Adolescents and Young Women
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010030 - 5 Feb 2026
Abstract
This study aims to describe oral contraceptive knowledge among adolescents and young women, and to examine individuals’ characteristics associated with oral contraceptive knowledge. A cross-sectional survey was administered using an online panel. Females aged 16 to 24 were recruited. Oral contraceptive knowledge was
[...] Read more.
This study aims to describe oral contraceptive knowledge among adolescents and young women, and to examine individuals’ characteristics associated with oral contraceptive knowledge. A cross-sectional survey was administered using an online panel. Females aged 16 to 24 were recruited. Oral contraceptive knowledge was measured using nine items with six domains, including oral contraceptive use, efficacy, indication, mechanism of action, risks, and side effects. A summated score was created, with a score of 9 indicating highest level of knowledge. Multivariable regression was used to examine significant socio-demographics and clinical characteristics. Among the 700 included responses, largest proportion of respondents were White (45.43%) and were covered by public insurance (43.14%). A total of 446 (63.71%) respondents expressed at least slight interest in using over-the-counter oral contraceptives. Overall, the mean score of knowledge was 4.08 out of 9. Most did not correctly answer questions about side effects, the mechanism of action and appropriate use. Similar patterns were observed among those who were interested in over-the-counter oral contraceptives (mean = 4.11). Adolescents and young women had a low level of oral contraceptive knowledge. With a high proportion of individuals interested in over-the-counter oral contraceptives, additional information support is needed to support informed contraception choice and use.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Pharmacy Practice for Women’s/Reproductive Health)
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of Pharmacist-Developed Educational Leaflets for Women’s Health: A Pre–Post Study of Knowledge and Perceived Usefulness
by
Weronika Guzenda, Zuzanna Berdzińska, Piotr Przymuszała, Olga Sierpniowska, Magdalena Jasińska-Stroschein and Magdalena Waszyk-Nowaczyk
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010029 - 5 Feb 2026
Abstract
Background: Written educational materials are widely used in community pharmacies to support patient education, and available evidence suggests their effectiveness in improving short-term knowledge. However, there remains a need for well-documented, practice-oriented evaluations of pharmacist-developed materials in real-world community pharmacy settings. The aim
[...] Read more.
Background: Written educational materials are widely used in community pharmacies to support patient education, and available evidence suggests their effectiveness in improving short-term knowledge. However, there remains a need for well-documented, practice-oriented evaluations of pharmacist-developed materials in real-world community pharmacy settings. The aim of this study was to evaluate the immediate impact of a pharmacist-developed educational leaflet on women’s health knowledge and its perceived usefulness, clarity, and acceptability. Methods: This study evaluated pharmacist-developed educational leaflets addressing women’s health topics using a pre–post study design. The study was conducted in Poland and involved 266 adult women. All participants completed a five-question knowledge test before and immediately after reading the educational leaflet, followed by a self-assessment of perceived usefulness, clarity, and visual appeal. Descriptive statistics were performed to summarize the results. Results: A statistically significant increase in knowledge was observed after exposure to the educational material, with mean scores rising from 2.8 ± 1.2 to 4.6 ± 0.7 (out of 5, p < 0.001). The greatest improvements were noted in topics related to sexually transmitted infection self-testing and pregnancy testing. Most participants rated the leaflet as useful, comprehensible, attractive, and engaging, with higher ratings reported among younger and better-educated respondents. Conclusions: Pharmacist-developed educational leaflets can support short-term knowledge acquisition and are perceived positively by women across age groups. These findings highlight the potential role of community pharmacies in delivering accessible written health education, while underscoring the need for future studies to assess long-term knowledge retention, behavioral outcomes, and topic-specific, targeted materials.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Pharmacy Practice for Women’s/Reproductive Health)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Role of the Pharmacist in Supporting the Use of Connected Health Devices: Example of Connected Watches
by
Cordélia Salomez-Ihl, Léa Liaigre, Wiceme Dala, Ambre Davat, Maud Barbado, Sébastien Chanoine, Philippe Py, Delphine Schmitt, Pascal Defaye and Pierrick Bedouch
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010028 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
The use of Connected Medical Devices (CMDs) is growing significantly throughout the world. Although they are not dispensed in pharmacies and are not part of the pharmacy-only drug dispensing system, clinical pharmacists must be able to support patients in the use of these
[...] Read more.
The use of Connected Medical Devices (CMDs) is growing significantly throughout the world. Although they are not dispensed in pharmacies and are not part of the pharmacy-only drug dispensing system, clinical pharmacists must be able to support patients in the use of these new technologies, which are central to their care. The aim of this study is to identify the role of the community pharmacist in supporting patients who use CMDs, using the case of connected watches in electrophysiology. Semi-structured interviews were conducted between 15 February and 20 April 2024 by a pharmacy student. The questionnaires were drafted in collaboration with a pharmacist, a cardiac electrophysiologist, a methodologist specializing in the evaluation of medical devices, and an ethical philosopher specializing in the support and acceptability of new technologies. The aim of these questionnaires was to study the use of connected watches and support for patients who own them. A total of 4 cardiac electrophysiologists and 10 cardiac electrophysiology patients were interviewed, and then 6 pharmacists were also questioned about the roles identified by physicians and patients. This study identified a major need on the part of specialist physicians for clinical pharmacist support in helping patients use connected watches. Patients expressed a high level of confidence in their pharmacists to support them, and in the motivation of pharmacists’ ability to take up these challenges. A number of challenges remain, such as the effective integration of this support into pharmacy practice, remuneration, and the organization of collaboration between clinical pharmacists and hospital electrophysiologists.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pharmacy Practice and Practice-Based Research)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
International Benchmarking of Pharmacology Curricula and Prescribing Related Learning Outcomes, Implications for Australian Health Professional Education: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
by
Syed Haris Omar and Anna Barwick
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010027 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Pharmacology plays a central role in linking biomedical science concepts with their application in clinical practice across medical and healthcare education. Globally, the pharmacological curriculum has evolved, just like other disciplines, through the integration of case-based, problem-based, and hybrid teaching models that
[...] Read more.
Background: Pharmacology plays a central role in linking biomedical science concepts with their application in clinical practice across medical and healthcare education. Globally, the pharmacological curriculum has evolved, just like other disciplines, through the integration of case-based, problem-based, and hybrid teaching models that led to firm clinical reasoning and long-term learning. Thus, this study aims to evaluate and compare the learning outcomes of pharmacology curricula across the globe by adopting a systematic review and meta-analysis research approach. Methods: This comprehensive review was conducted with transparency and integrity in accordance with Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA 2020) guidelines and was registered with PROSPERO (CRD420251207753). Five electronic databases, including MEDLINE (PubMed), EMBASE, CINAHL, PsycINFO, and the Cochrane Library were searched from January 2000 to October 2025. The Cochrane Library tool was used for the risk of bias assessment of randomised controlled trials, while the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) checklist was used for mixed-design, quasi-experimental, and cross-sectional cohorts. Review Manager 5.4 was used for statistical analysis. Results: Out of 3300 identified studies, 11 met the inclusion criteria, spanning 11 countries (published between 2007 and 2025). Integrated and case-based curricula significantly improved pharmacology knowledge compared to traditional lecture-based methods (SMD = 0.35; 95% CI: 0.07–0.64; I2 = 75%). Student satisfaction also favours integrated learning (OR = 1.53; 95% CI: 1.16–2.02; I2 = 46%). Most included studies were of moderate-to-high methodological quality. Conclusion: Globally, active and integrated pharmacology curricula foster greater cognitive understanding and learner satisfaction than conventional models. However, significant variability persists in resource-limited settings, leading to unequal competency in prescribing and therapeutic reasoning. Australian pharmacology programmes align broadly with international standards but require greater standardisation in assessment and experiential learning.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Roles and Responsibilities in Pharmacy Practice as Determinants of Burnout: A Comparative Cross-Sectional Survey of Community Pharmacists and Pharmacy Assistants in the Northeastern Region of Bulgaria
by
Mariya Ivanova, Antoaneta Tsvetkova and Anna Todorova
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010026 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Burnout is a significant occupational risk among healthcare professionals, including community pharmacy staff, whose differing roles and responsibilities may influence burnout determinants. This study aimed to compare burnout levels and associated work characteristics between master pharmacists (MPs) and assistant pharmacists (APs) working
[...] Read more.
Background: Burnout is a significant occupational risk among healthcare professionals, including community pharmacy staff, whose differing roles and responsibilities may influence burnout determinants. This study aimed to compare burnout levels and associated work characteristics between master pharmacists (MPs) and assistant pharmacists (APs) working in community pharmacies in Northeastern Bulgaria. Methods: A cross-sectional observational survey was conducted between November 2023 and December 2024 using an anonymous, self-administered online questionnaire completed by 221 MPs and 151 APs. Burnout was assessed using the Maslach Burnout Inventory—Human Services Survey for Medical Personnel, measuring emotional exhaustion (EE), depersonalization (DP), and personal accomplishment (PA). Work characteristics were evaluated using items adapted from an internationally recognized European Commission guideline on occupational health and safety risks in the healthcare sector. Results: High levels of EE and DP were observed in both groups, with no statistically significant differences in mean burnout scores. Age and years of professional experience were not significantly associated with burnout. However, work environment factors differed: poor team communication and a negative workplace climate affected both groups, whereas lack of recognition and support was more influential for MPs, and physical workload and frequent interruptions were more prominent stressors for APs. Conclusions: Burnout is prevalent among community pharmacy professionals, with role-specific organizational factors shaping its determinants and highlighting the need for targeted preventive strategies.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Regulation of Food Supplements and Pharmacists’ Responsibility in Professional Practice: A Review
by
Cristina Ioana Niculaș, Sonia Bianca Blaj, Marius Călin Cherecheș, Raul Miron, Daniela Cristina Valea and Daniela Lucia Muntean
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010025 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
(1) Background: Regulations governing food supplements vary considerably across countries, allowing products that are prohibited in one jurisdiction to be legally sold in another. Furthermore, online sales enable and facilitate this practice. Regarding pharmaceutical malpractice, the absence of a standardized European framework complicates
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: Regulations governing food supplements vary considerably across countries, allowing products that are prohibited in one jurisdiction to be legally sold in another. Furthermore, online sales enable and facilitate this practice. Regarding pharmaceutical malpractice, the absence of a standardized European framework complicates the evaluation of pharmacist liability. As a result, the specific elements of the liability framework are defined by the national legislation of each Member State. The aim of our review is to map the global regulatory landscape of food supplements and to examine the pharmacist’s professional responsibilities, including instances of malpractice related to this area. (2) Methods: A literature review covering publications from January 2020 to December 2024 was performed using four databases: Scopus, PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science. The search retrieved 8243 records, of which 77 studies fulfilled the eligibility criteria. The extracted data were organized into five main themes: pharmacist responsibility and malpractice, food supplement regulation, consumer safety, health claims, and pharmacist knowledge. (3) Results: The literature reviewed indicated a relatively low number of malpractice cases within the pharmacy profession compared to other professions. A higher incidence of cases is observed among male pharmacists and those practicing in the private sector. Notably, no cases have been identified addressing pharmacists’ responsibilities in the dispensing of food supplements. In the context of food supplement regulation, the reviewed literature highlights a lack of standardized terminology and harmonized legislation across different jurisdictions. Therefore, products may be classified differently across jurisdictions. Another observed barrier is the considerable variation in market access requirements across countries. Regarding consumer safety, several irregularities have been observed. Substantial non-compliance in both product composition and labeling has been observed, reflecting insufficient quality control measures. Concerning health claims, significant regulatory non-compliance with European Union regulations has been documented. In addition, widespread misleading advertising practices have been observed. With respect to pharmacists’ knowledge, the reviewed literature identifies several professional challenges within pharmacy practice, particularly those concerning the dispensing of food supplements. (4) Conclusions: This research offers a comprehensive analysis of the literature published over the past five years concerning pharmaceutical malpractice cases, as well as an examination of food supplement regulation and the professional responsibilities of pharmacists. A recurring barrier identified is the absence of unified regulatory frameworks worldwide. This results in uncertainty concerning the pharmacist’s professional role and responsibilities.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Good Practices and Challenges in the Collaboration of Pharmacists with General Practitioners—A Scoping Review
by
Evelina Gavazova, Kiril Atliev and Daniela Kafalova
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 24; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010024 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Optimizing medication management and improving patient health outcomes depend primarily on the strength of primary healthcare services, where collaboration between general practitioners (GPs) and pharmacists plays a critical role. This scoping review aimed to identify the main facilitators and barriers influencing pharmacist–GP collaboration.
[...] Read more.
Optimizing medication management and improving patient health outcomes depend primarily on the strength of primary healthcare services, where collaboration between general practitioners (GPs) and pharmacists plays a critical role. This scoping review aimed to identify the main facilitators and barriers influencing pharmacist–GP collaboration. The review was conducted in line with PRISMA-ScR guidelines. A comprehensive search of PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science identified studies published in English between January 2019 and May 2025, of which twenty met the inclusion criteria. Key facilitators of collaboration included pharmacist co-location within GP practices, clearly defined professional responsibilities, access to shared electronic health records, and supportive government policies. Barriers most frequently reported were limited communication pathways, insufficient interprofessional training, and financial constraints. Overall, the findings suggest that effective pharmacist–GP collaboration relies on structural integration, professional trust, and policy initiatives that enable sustained cooperation. Long-term investment in collaborative infrastructure and workforce development will be essential to strengthen primary care, support patient outcomes, and ensure more efficient use of healthcare resources.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Healthcare Professionals’ Perspectives on Barriers and Facilitators to Medication Adherence Post Myocardial Infarction: A Qualitative Study Using the Theoretical Domains Framework
by
Fatma El-Komy, Michelle O’Driscoll, Stephen Byrne, Margaret Bermingham and Laura J. Sahm
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010023 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
Medication adherence following myocardial infarction (MI) is essential for effective secondary prevention, yet adherence rates remain suboptimal. Healthcare professionals (HCPs) are central to promoting adherence through clinical decision-making, patient education, and ongoing behavioural support. Understanding how HCPs perceive and experience the factors’ influencing
[...] Read more.
Medication adherence following myocardial infarction (MI) is essential for effective secondary prevention, yet adherence rates remain suboptimal. Healthcare professionals (HCPs) are central to promoting adherence through clinical decision-making, patient education, and ongoing behavioural support. Understanding how HCPs perceive and experience the factors’ influencing adherence is key to developing effective, context-specific interventions. This study explored HCPs’ perspectives on medication adherence post-MI and identified behavioural determinants influencing medication management across the care pathway. A qualitative descriptive study was conducted using semi-structured interviews with HCPs in the southwest of Ireland. Participants included hospital pharmacists, community pharmacists, general practitioners (GPs), cardiologists, and nurses, recruited through purposive, convenience, and snowball sampling. Interviews were recorded, transcribed verbatim, and analysed using directed content analysis guided by the Theoretical Domains Framework (TDF). Twelve HCPs (eight female) were interviewed between December 2024 and May 2025, including four pharmacists, two GPs, three cardiologists and three nurses. Interviews lasted 30–50 min (mean 41 min). Analysis identified 15 facilitators, 13 barriers, and 7 dual-role determinants across 10 TDF domains. Novel contributions include demonstrating how HCPs’ real-world experiences contextualise adherence issues in the distinct post-MI setting characterised by abrupt care transitions, polypharmacy, and emotional vulnerability and identifying where HCPs feel most constrained and where their expertise could directly inform targeted intervention design. HCPs’ insights reveal complex, context-specific behavioural determinants influencing post-MI medication adherence and highlight the need for multidisciplinary, tailored, and system-level solutions. Enhancing collaboration, supporting patient-centred communication, and addressing resource barriers could empower HCPs to deliver more effective, personalised adherence support and inform the development of targeted intervention strategies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pharmacy Practice and Practice-Based Research)
Open AccessArticle
ACE Inhibitor/ARB Therapy and Other Risk Factors for COVID-19 Infection in Elderly Hypertensive Patients: Sub-Group Analysis Based on a Single-Center, Retrospective, Observational Study in Japan
by
Kazuhiro Furumachi, Akari Higuchi, Tatsuki Kagatsume, Mariko Kozaru, Tsutomu Nakamura, Etsuko Kumagai and Keiko Hosohata
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010022 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) are often used in hypertensive patients. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus responsible for the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, binds the ACE2 receptor on the cell surface. This
[...] Read more.
Background: Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) are often used in hypertensive patients. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus responsible for the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, binds the ACE2 receptor on the cell surface. This study aimed to identify the risk factors influencing COVID-19 infection in hypertensive patients. Methods: This is a part of a single-center, retrospective, observational study investigating patients ≥ 20 years old at Kenwakai Hospital (Nagano, Japan). COVID-19 was diagnosed by polymerase chain reaction. All patients received antihypertensive drugs. Results: Among 316 patients (mean age, 75.0 ± 13.4 years; men, 55.1%), COVID-19 was diagnosed in 39 (12.3%). Multiple logistic regression analysis after adjustment for age, sex, and smoking status identified increased serum creatinine (Scr) as a significant risk factor for COVID-19 (odds ratio [OR] 1.10; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.00–1.20; p = 0.046). Conversely, lower serum chloride was associated with COVID-19 (OR 0.92; 95% CI 0.85–0.99; p = 0.047). There was no significant association between COVID-19 and the use of ACEIs and ARBs. Conclusions: Scr was independently associated with COVID-19 risk, whereas ACEI/ARB use was not associated with COVID-19 risk in Japanese hypertensive patients, suggesting that these users need not discontinue or change their treatment. The study population included a very high proportion of patients with advanced chronic kidney disease, which makes the cohort substantially different from the general hypertensive population. However, our results can help guide targeted treatment strategies, improving patient outcomes in healthcare settings.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Perspectives and Experiences of Doctors and Pharmacists on the Clinical Use of Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Saudi Arabia
by
Dalal Salem Aldossari, Komal Latif, Amjad Nasser Alsadoni, Orjuwan Hasan Alshehri, Rakan Ibrahim Binjathlan, Monirah Mutlaq Alenezy, Taif Farhan Alshahrani, Hana Ahmed Lubbad, Rana Saeed Alshamasi, Abdulmajead Khaled Alanazi, Raed Ghazi Alotaibi, Ghazi Ibrahim Arishi and Sheraz Ali
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010021 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background and objectives: Research into clinicians’ and pharmacists’ experiences and perspectives on direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) use in Saudi Arabia and the broader Middle Eastern area is limited. Therefore, we aimed to evaluate the perspectives and experiences of physicians and pharmacists practicing in
[...] Read more.
Background and objectives: Research into clinicians’ and pharmacists’ experiences and perspectives on direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) use in Saudi Arabia and the broader Middle Eastern area is limited. Therefore, we aimed to evaluate the perspectives and experiences of physicians and pharmacists practicing in Saudi Arabia who prescribe DOACs and dispense DOAC therapy, respectively. Methods: A cross-sectional study was undertaken utilizing an online survey instrument. We collected data via Google Forms. Between June and July 2024, the study questionnaire was distributed to community pharmacists, general practitioners [GPs], cardiologists, residents in internal medicine, and hospital pharmacists (primary and secondary healthcare professionals) working in Saudi Arabia. Results: Comprising 146 doctors and 167 pharmacists, 313 total healthcare professionals participated in the study. Of the weekly DOAC prescriptions, cardiologists had the most at 35%; internal medicine residents came next at 16.3% and general practitioners at 17.5%. Among pharmacists, 16.7% of community pharmacists and 23.9% of hospital pharmacists dispensed DOACs weekly. The most often prescribed and dispensed medications were rivaroxaban, edoxaban, and apixaban. Across all categories, Lexicomp was the most often used tool. Most physicians (98%) said they lowered the DOAC dose when necessary. Especially in dosing, preoperative care, patient education, and medication interaction identification, internal medicine residents and hospital pharmacists expressed more confidence in managing DOACs. In these domains, community pharmacists expressed less trust. Conclusions: This study revealed that most participants preferred newer oral anticoagulants over warfarin and demonstrated a fairly good level of self-perceived knowledge regarding various aspects of the clinical use of DOACs. The study findings highlight the importance of focused training initiatives to standardize the use of DOACs, boost trust among community pharmacists and GPs, and ensure safe and effective patient care.
Full article
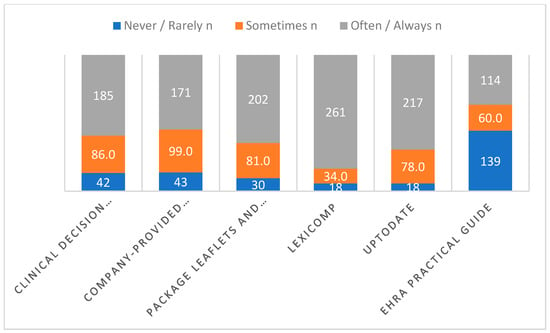
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
An Exploratory Study of Over-the-Counter Medication Counseling Topics in Community Pharmacies and Alignment with Counseling Frameworks
by
Jason S. Chladek, Leena Jaiswal, Jamie A. Stone, Aaron M. Gilson, Taylor L. Watterson, Elin C. Lehnbom, Jukrin Moon, Emily L. Hoffins, Maria E. Berbakov and Michelle A. Chui
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010020 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
Community pharmacists can play an important role in patient safety by consulting patients on over-the-counter (OTC) medications. Several OTC counseling frameworks have been integrated into pharmacy education to guide pharmacists through these consultations, but limited work has been performed to examine how these
[...] Read more.
Community pharmacists can play an important role in patient safety by consulting patients on over-the-counter (OTC) medications. Several OTC counseling frameworks have been integrated into pharmacy education to guide pharmacists through these consultations, but limited work has been performed to examine how these frameworks are applied in real-world settings. The objective of this study was to identify the topics discussed during over-the-counter medication consultations and explore how they align with existing counseling frameworks. Participants were recruited from 10 community pharmacies. Participants were given hypothetical symptoms and asked to select OTCs for self-treatment. The selection process and potential interactions with pharmacy staff were recorded via Tobii Pro Glasses 2. Deductive and inductive content analysis of the recordings were used to compare participant–pharmacist consultations to existing OTC counseling frameworks. In total, 144 participants completed the study, with 32 (22%) having an OTC consultation with the pharmacist. Across all consultations, eight topic categories were identified. The consultations most frequently focused on discussions of product details and did not closely align with the OTC counseling frameworks. Future work should examine if and how this discordance contributes to OTC misuse among those interacting with pharmacists and potentially adapt or develop new frameworks to further support consultations and OTC safety.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Direct Oral Anti-Xa Anticoagulants and the Future of Factor XI/FXIa Inhibition: A New Paradigm in Thrombosis Prevention
by
Francesca Futura Bernardi, Dario Bianco, Rosaria Lanzillo, Natalia Diana, Mario Scarpato, Antonio Lalli, Aniello Corallo, Consiglia Riccardi, Ugo Trama, Alessandro Perrella, Manuela Basaglia, Ada Maffettone, Pierpaolo Di Micco and Carmine Siniscalchi
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010019 - 27 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The introduction of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs), particularly factor Xa (FXa) inhibitors, has transformed the prevention and treatment of thromboembolic events. These agents have largely replaced vitamin K antagonists across most indications due to their predictable pharmacokinetics, reduced rates of intracranial bleeding, and
[...] Read more.
The introduction of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs), particularly factor Xa (FXa) inhibitors, has transformed the prevention and treatment of thromboembolic events. These agents have largely replaced vitamin K antagonists across most indications due to their predictable pharmacokinetics, reduced rates of intracranial bleeding, and overall ease of use. Nevertheless, a substantial residual bleeding risk remains, particularly gastrointestinal bleeding and clinically relevant non-major bleeding in elderly, frail, or polymedicated patients. Furthermore, the management of patients with severe renal dysfunction, active cancer, especially gastrointestinal or genitourinary malignancies and those requiring complex pharmacological regimens, continues to pose significant challenges. These limitations have intensified interest in targeting earlier steps of the coagulation cascade, specifically factor XI (FXI) and its activated form (FXIa). FXI occupies a unique mechanistic position: it contributes substantially to pathological thrombosis while playing only a limited role in physiological hemostasis. Genetic, observational, and mechanistic evidence consistently demonstrates that FXI deficiency confers protection against venous thromboembolism and cardiovascular events while causing minimal spontaneous bleeding. This biological paradigm has catalyzed the development of novel FXI/FXIa inhibitors, including small-molecule agents (asundexian, milvexian) and biological therapies (abelacimab). Clinical trials such as AXIOMATIC-TKR, PACIFIC-AF, and OCEANIC-AF, and ongoing programmes including ASTER and MAGNOLIA suggest that FXI inhibition may preserve antithrombotic efficacy while substantially reducing bleeding risk. This review summarizes the current landscape of oral FXa inhibitors, outlines the biological rationale for FXI/FXIa inhibition, and discusses the evolving clinical evidence supporting what may represent the next major advance in anticoagulant therapy.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Pharmacists’ Work Experiences and Career Dynamics in Saudi Arabia: A Cross-Sector Study
by
Mohammed Alnuhait, Ayidh Alqarni, Leena Alsharafi, Arjwan Alshreef, Renad Althebaiti, Alaa Shahbar, Foud Bahamdain, Abdulhamid Althagafi, Mohamed A. Albekery, Abdullah F. Alharthi and Abdulmalik S. Alotaibi
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010018 - 27 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background: Pharmacists in Saudi Arabia are assuming increasingly diverse and specialized roles amid rapid healthcare transformation. However, evolving expectations and expanding responsibilities may influence their job satisfaction, well-being, and career stability. This study aimed to assess job satisfaction, burnout, well-being, and career intentions
[...] Read more.
Background: Pharmacists in Saudi Arabia are assuming increasingly diverse and specialized roles amid rapid healthcare transformation. However, evolving expectations and expanding responsibilities may influence their job satisfaction, well-being, and career stability. This study aimed to assess job satisfaction, burnout, well-being, and career intentions among pharmacists across multiple practice sectors in Saudi Arabia. Method: A nationwide cross-sectional survey was conducted between December 2024 and January 2025 using an electronic questionnaire distributed to licensed pharmacists. The instrument assessed mental well-being, job satisfaction, burnout, workplace environment, and career mobility. Descriptive and inferential analyses were performed using SPSS version 20.0. Results: A total of 531 pharmacists completed the survey; 65% were male, and 89.3% were Saudi nationals. Sector distribution differed significantly by gender (p < 0.001): females were more represented in clinical and hospital pharmacy, while males predominated in the pharmaceutical industry–related roles. Male pharmacists reported higher work environment scores (p = 0.028) and greater sector mobility (34.2% vs. 23.7%, p = 0.012). Approximately 30.5% of participants had changed their employment sector at least once. Community pharmacists reported the highest burnout levels, whereas those in regulatory and administrative roles demonstrated the greatest job satisfaction (both p < 0.001). Participation in professional development showed strong positive associations with job satisfaction and intention to remain in the current role. Conclusions: Marked variations exist in pharmacists’ well-being, satisfaction, and career mobility across sectors in Saudi Arabia, with notable gender differences. Enhancing professional development, ensuring equitable work environments, and promoting sector-specific support strategies may help inform discussions on pharmacist engagement and retention within the evolving national healthcare system.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Pharmacist Workforce Challenges and Solutions: Perspectives from Research and Practice)
Open AccessArticle
The Prevalence and Impact of Bacteremia Among Neonates Receiving Parenteral Nutrition: A Multicenter Retrospective Study from Saudi Arabia
by
Shaker Althobaiti, Aisha H. Alshehri, Abeer K. Alorabi, Alhussain Alzahrani, Lama Marwan Fetyani, Ebtihal Mohsin Fairaq, Enas Ahmed Abukwaik, Njood Abdulsalam Alharbi, Abrar A. Alotaibi, Safia Ghali Alotibi, Shaimaa Alsulami, Abdullah Althomali and Ahmed Ibrahim Fathelrahman
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010017 - 26 Jan 2026
Abstract
(1) Background: We aimed to determine rates of bacteremia and multidrug resistance (MDR) bacteremia and associated risk factors among neonates receiving parenteral nutrition (PN). (2) Methods: This is a multicenter study conducted in three neonatal intensive care units in Saudi Arabia, including 414
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: We aimed to determine rates of bacteremia and multidrug resistance (MDR) bacteremia and associated risk factors among neonates receiving parenteral nutrition (PN). (2) Methods: This is a multicenter study conducted in three neonatal intensive care units in Saudi Arabia, including 414 neonates who received PN. Associations were assessed using Chi-square or Fisher’s Exact tests when applicable and logistic regression analyses were conducted to determine factors predicting outcomes. Odds ratios with their 95% confidence intervals were computed, and a p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. (3) Results: PN was started within the first 10 days of life in 74.4% of cases. Fat emulsion was administered to 38.9% of the newborns. Blood cultures were positive in 24.9% of patients. Among the positive cultures, 4.9% were confirmed to have MDR bacteria. The mortality rate following bacteremia was 7.8%. The use of fat emulsion (p = 0.003), birth weight < 700 g (p < 0.001), and a gestational age within 27 weeks (p < 0.001) predicted bacteremia. (4) Conclusions: There was an association between the PN and bacteremia. Significant predictors of bacteremia were the use of fat emulsion, birth weight < 700 g, and a gestational age within 27 weeks.
Full article
Open AccessOpinion
Parenteral Nutrition Management from the Clinical Pharmacy Perspective: Insights and Recommendations from the Saudi Society of Clinical Pharmacy
by
Nora Albanyan, Dana Altannir, Osama Tabbara, Abdullah M. Alrajhi, Ahmed Aldemerdash, Razan Orfali and Ahmed Aljedai
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010016 - 26 Jan 2026
Abstract
Parenteral nutrition (PN) is essential for patients who are unable to tolerate oral or enteral feeding, providing them with necessary nutrients intravenously, including dextrose, amino acids, electrolytes, vitamins, trace elements, and lipid emulsions. Clinical pharmacists (CPs) play a critical role in PN management
[...] Read more.
Parenteral nutrition (PN) is essential for patients who are unable to tolerate oral or enteral feeding, providing them with necessary nutrients intravenously, including dextrose, amino acids, electrolytes, vitamins, trace elements, and lipid emulsions. Clinical pharmacists (CPs) play a critical role in PN management by ensuring proper formulation, monitoring therapy, preventing complications, and optimizing patient outcomes. In Saudi Arabia, limited literature exists on CPs’ involvement in total parenteral nutrition (TPN) administration, health information management (HIM) systems, and pharmacist staffing ratios. This paper examines the evolving role of CPs in PN management, addressing key challenges such as the optimal patient-to-CP ratio, the impact of HIM systems on PN prescribing, and the advantages and limitations of centralized versus decentralized PN prescription models. It highlights the need for standardized staffing levels, structured pharmacist training, and improved HIM integration to enhance workflow efficiency and prescribing accuracy. Additionally, the study examines how the adoption of advanced HIM systems can streamline documentation, reduce prescribing errors, and enhance interdisciplinary collaboration. This paper provides a framework for optimizing PN delivery, enhancing healthcare quality, and strengthening CPs’ contributions to nutrition support by addressing these factors. Implementing these recommendations will improve patient outcomes and establish a more efficient PN management system in Saudi Arabia, reinforcing the vital role of CPs in multidisciplinary care.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pharmacy Practice and Practice-Based Research)
Open AccessArticle
Addressing Pharmacy Admissions Declines Through a Student-Led Pre-Health Advising and Leadership System (PAALS): An Implementation Evaluation
by
Ashim Malhotra
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010015 - 25 Jan 2026
Abstract
To enhance PharmD student leadership and advocacy skills, combat the paucity of trained pre-health advisors for pharmacy admissions, augment community relationships, and increase pharmacy admissions volume, we designed, implemented, and assessed PAALS, a Pre-health Academic Advising and Leadership System. PAALS was grounded in
[...] Read more.
To enhance PharmD student leadership and advocacy skills, combat the paucity of trained pre-health advisors for pharmacy admissions, augment community relationships, and increase pharmacy admissions volume, we designed, implemented, and assessed PAALS, a Pre-health Academic Advising and Leadership System. PAALS was grounded in Astin’s Theory of Student Involvement and evaluated using the RE-AIM implementation science framework. RE-AIM measured outcomes across Reach, Effectiveness, Adoption, Implementation, and Maintenance as indicators of PAALS’s scale, fidelity, sustainability, and institutional embedding. Analysis of PAALS using the RE-AIM framework demonstrated the following outcomes: (1) Reach: 42 P1-P3 PharmD students participated as mentors; external partnerships expanded from 2 to 8 regional high schools and community programs; and more than 25 mentored learners successfully matriculated into the PharmD program. (2) Effectiveness: students enacted sustained leadership, advocacy, and mentoring roles. (3) Adoption: voluntary uptake of mentoring and governance roles by PharmD students occurred with repeated engagement by external partner institutions. (4) Implementation: Core program components were delivered consistently using existing institutional resources. (5) Maintenance: PAALS remained operational across five academic years despite student turnover, with leadership succession and institutional embedding sustained across cohorts. Our findings demonstrate that student-led advising and advocacy ecosystems address critical gaps in pharmacy-specific pre-health advising models.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pharmacy Education and Student/Practitioner Training)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Trends in Antipsychotic Drug Use in the United States, 2000–2016
by
Nisrine Haddad, Nawal Farhat, Jennifer Go, Yue Chen, Christopher A. Gravel, Franco Momoli, Donald R. Mattison, Douglas McNair, Abdallah Alami and Daniel Krewski
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010014 - 24 Jan 2026
Abstract
This study evaluated long-term trends in the prevalence of use of atypical and typical antipsychotic drugs (APDs), both as classes of drugs and as individual drugs, among adult inpatients in the United States (US). The Health Facts® database developed by Cerner Corporation
[...] Read more.
This study evaluated long-term trends in the prevalence of use of atypical and typical antipsychotic drugs (APDs), both as classes of drugs and as individual drugs, among adult inpatients in the United States (US). The Health Facts® database developed by Cerner Corporation was used to analyze the prevalence of APD use among adult inpatients aged 18 years or older who were administered at least one antipsychotic medication order during hospitalization between 1 January 2000 and 31 December 2016. The prevalence of APD use was standardized by age, sex, race, and census region. Typical and atypical antipsychotic treatment patterns in the US differed over this period. While the use of atypical APDs increased overall, the use of typical antipsychotic medications decreased, but remained more prevalent. Overall, haloperidol and prochlorperazine were the two most administered antipsychotic medications throughout the study period. From 2000 to 2011, prochlorperazine and haloperidol were the first- and second-most prescribed typical APDs, respectively; haloperidol became the most administered antipsychotic of this class as of 2012. Quetiapine was the most administered atypical antipsychotic medication, followed by risperidone and olanzapine until 2014, after which olanzapine was the second-most administered atypical APD. There was a notable decline in the use of atypical antipsychotics medications between 2005 and 2008, which may reflect the impact of the Food and Drug Administration’s warnings and the American Diabetes Association’s consensus position, but only for a short time. The usage patterns observed in this study support existing evidence of substantial off-label use of antipsychotic drugs in the US.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Optimization of Drug Utilization and Medication Adherence)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comparison of Subcutaneous Versus Intramuscular Estradiol Administration for Feminizing Gender-Affirming Hormone Therapy
by
Abby C. Poage, Jordan M. Rowe, Mary Beth A. Dameron, Abigail M. Bavuso and Andrew J. Smith
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010013 - 23 Jan 2026
Abstract
This single health system, retrospective cohort study compared subcutaneous (SC) versus intramuscular (IM) estradiol administration in 70 adult patients with a diagnosis of gender incongruence or gender dysphoria seen in an LGBTQ Specialty Clinic within a safety-net institution between October 2018 and December
[...] Read more.
This single health system, retrospective cohort study compared subcutaneous (SC) versus intramuscular (IM) estradiol administration in 70 adult patients with a diagnosis of gender incongruence or gender dysphoria seen in an LGBTQ Specialty Clinic within a safety-net institution between October 2018 and December 2024. The primary endpoint was patients who reached therapeutic estradiol levels at 6 months. Secondary endpoints included the incidence of sub- and supra-therapeutic and actual estradiol levels at months 3, 6, 9, and 12 and patients who received pharmacist-led injection technique education. At 6 months, the proportion of patients achieving therapeutic estradiol levels did not differ between IM and SC administration. In exploratory analyses of continuous estradiol concentrations, IM administration was associated with higher measured estradiol levels.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Pharmacy Practice for Women’s/Reproductive Health)
Open AccessArticle
Drug-Drug Interaction Knowledge, Practices, and Barriers in Community Pharmacies: A Cross-Sectional Study from Jazan Region, Saudi Arabia
by
Moaddey Alfarhan, Muath F. Haqwi, Abdulrahman H. Musayyikh, Jala Ashqar, Lama Y. Suwidi, Amal H. Fageh, Enas A. Alajam, Hadi Almansour, Thamir M. Alshammari and Saeed Al-Qahtani
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010012 - 23 Jan 2026
Abstract
(1) Background: Drug–drug interactions (DDIs) are a frequent cause of medication-related harm, particularly in ambulatory care. Community pharmacists are uniquely positioned to identify and manage these risks. This study assessed DDI knowledge, practices, and barriers among community pharmacists in the Jazan Region, Saudi
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: Drug–drug interactions (DDIs) are a frequent cause of medication-related harm, particularly in ambulatory care. Community pharmacists are uniquely positioned to identify and manage these risks. This study assessed DDI knowledge, practices, and barriers among community pharmacists in the Jazan Region, Saudi Arabia. (2) Methods: A structured, self-administered questionnaire was distributed to community pharmacists. The survey assessed DDI knowledge using 26 clinically relevant drug pairings and included questions on professional behavior, training exposure, software use, and educational needs. Descriptive and inferential statistics were applied to identify associations between knowledge scores and demographic or practice-related variables. (3) Results: A total of 219 pharmacists participated in the study. The mean knowledge score was (9.63 ± 4.58) out of 26, reflecting suboptimal to moderate awareness. Female pharmacists demonstrated significantly higher DDI knowledge scores than males (10.74 ± 5.4 vs. 9.08 ± 4.2; p = 0.016). Knowledge scores also differed significantly by academic qualification (p < 0.001), with PharmD holders scoring higher than B. Pharm and postgraduate degree holders. Pharmacists with less than 10 years of experience had significantly higher scores compared with those with longer practice duration (p = 0.002). Additionally, pharmacists who graduated from Saudi institutions scored higher than those trained outside Saudi Arabia (10.22 ± 4.7 vs. 8.44 ± 4.2; p = 0.005). Pharmacists who had received professional development training and those who attended workshops regularly also scored significantly higher. Familiarity with guidelines showed a positive trend. Reported barriers to effective DDI counseling included time constraints, limited patient understanding, and poor collaboration with prescribers. Self-rated awareness of DDIs was positively associated with actual knowledge scores. Pharmacists expressed strong preferences for workshops, online courses, and webinars as future training formats. (4) Conclusions: Pharmacists in the Jazan Region demonstrate moderate awareness of DDIs, with variation influenced by training, experience, and qualifications. Enhancing access to structured professional development and integrating clinical decision support tools could strengthen pharmacists’ role in preventing DDIs in community practice.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pharmacy Practice and Practice-Based Research)
Open AccessArticle
Medication Regimen Complexity and Patient-Reported Adverse Drug Events in Korean Community Pharmacies: A Cross-Sectional Study
by
Sunmin Lee and Kyung sun Oh
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010011 - 22 Jan 2026
Abstract
Evidence linking medication regimen complexity to patient-reported adverse drug events (ADEs) is limited. This study examined the association between regimen complexity and patient-reported ADEs among adults using community pharmacy services. A cross-sectional survey was conducted among adults with prescription experience at community pharmacies
[...] Read more.
Evidence linking medication regimen complexity to patient-reported adverse drug events (ADEs) is limited. This study examined the association between regimen complexity and patient-reported ADEs among adults using community pharmacy services. A cross-sectional survey was conducted among adults with prescription experience at community pharmacies in Korea (14 January–24 February 2025). Data included MRCI-K scores, medication adherence, ADE reports, comorbidities, polypharmacy status, and demographics. Prescription records verified medication counts and drug-related risks. Determinants of regimen complexity were assessed using multivariable linear regression, and predictors of ADE reporting were examined using multivariable logistic regression. Among 201 participants, 101 (50.2%) reported at least one ADE in the past month. Polypharmacy, comorbidities, and multidose dispensing service use were independently associated with higher regimen complexity, whereas higher income, college education, and older age were associated with lower complexity. Higher MRCI-K scores (OR = 0.95, 95% CI 0.91–0.99) and older age (OR = 0.98, 95% CI 0.96–0.99) were associated with lower odds of ADE reporting. Higher medication regimen complexity and older age were associated with reduced reporting of ADEs, suggesting possible under-recognition among these populations. Patient-centered strategies are needed to enhance ADE identification in individuals with complex medication regimens.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Optimization of Drug Utilization and Medication Adherence)

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Pharmacy Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
9 December 2025
Meet Us at the 146th Annual Meeting of the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan (Osaka), 26–29 March 2026, Osaka, Japan
Meet Us at the 146th Annual Meeting of the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan (Osaka), 26–29 March 2026, Osaka, Japan

6 November 2025
MDPI Launches the Michele Parrinello Award for Pioneering Contributions in Computational Physical Science
MDPI Launches the Michele Parrinello Award for Pioneering Contributions in Computational Physical Science

Topics
Topic in
JCM, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Pharmacy, Healthcare
Optimization of Drug Utilization and Medication Adherence
Topic Editors: Enrica Menditto, Sara Mucherino, Ignacio Aznar-LouDeadline: 30 October 2026
Topic in
Biomedicines, Future Pharmacology, Pharmacy, IJMS, Biomolecules, Genes
Prospects of Multi-Target Agonists in Metabolic and Epigenetic Medicine
Topic Editors: Riham Abouleisa, Yanming LiDeadline: 30 November 2026

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Pharmacy
The Evolving Role of the Pharmacist in Improving Vaccination Uptake
Guest Editor: Mary BushellDeadline: 31 March 2026
Special Issue in
Pharmacy
Advancing Pharmacy Education: Integrating Science and Clinical Practice
Guest Editors: Ryoichi Fujiwara, Frank YuDeadline: 15 April 2026
Special Issue in
Pharmacy
Pharmacist Workforce Challenges and Solutions: Perspectives from Research and Practice
Guest Editors: Ioana Popovici, Manuel J. CarvajalDeadline: 30 April 2026
Special Issue in
Pharmacy
Drug Repurposing: Strengthening Outcomes of Existing Pharmaceuticals to Shift Emerging Health Challenges
Guest Editors: Ilko Getov, Hristina LebanovaDeadline: 30 April 2026
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Pharmacy
New Insights into Pharmacy Teaching and Learning during COVID-19
Collection Editors: Darko Modun, Ana Seselja Perisin




