Journal Description
Drugs and Drug Candidates
Drugs and Drug Candidates
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on drug discovery, development, and knowledge, published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 16.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Drugs and Drug Candidates is a companion journal of Pharmaceuticals.
- Journal Clusters-Pharmaceutical Science: Scientia Pharmaceutica, Marine Drugs, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Pharmacy, Future Pharmacology, Pharmacoepidemiology, Drugs and Drug Candidates and Journal of Pharmaceutical and BioTech Industry.
Latest Articles
Non-Pharmacological Activation of the Renal Kallikrein–Kinin System: Dietary Potassium as a Novel Renoprotective Approach
Drugs Drug Candidates 2026, 5(1), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc5010013 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) has emerged as a pervasive global health concern, for which there are no known curative treatments. Consequently, there is an imperative for the implementation of preventive and kidney-protective strategies. The renal kallikrein–kinin system (KKS) is a vasodilator, anti-inflammatory, and
[...] Read more.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) has emerged as a pervasive global health concern, for which there are no known curative treatments. Consequently, there is an imperative for the implementation of preventive and kidney-protective strategies. The renal kallikrein–kinin system (KKS) is a vasodilator, anti-inflammatory, and antifibrotic pathway located in the distal nephron, whose decline contributes to hypertension and CKD progression. In this narrative, non-systematic review, a thorough evaluation of both experimental and clinical data was undertaken to ascertain the interactions between dietary potassium, renal KKS activity, and kidney protection. A particular emphasis was placed on animal models of proteinuria, tubulointerstitial damage, and salt-sensitive hypertension, in conjunction with human studies on potassium intake and renal outcomes. A body of experimental evidence suggests a relationship between potassium-rich diets and renal kallikrein synthesis, urinary kallikrein activity, and up-regulated kinin B2 receptor expression. Collectively, these factors have been shown to result in reduced blood pressure, oxidative stress, apoptosis, inflammation, and fibrosis, and these effects are counteracted by B2 receptor blockade. In humans, higher potassium intake has been shown to enhance kallikrein excretion and lower cardiovascular and renal risk, independently of aldosterone. Conversely, low potassium intake has the potential to exacerbate CKD progression. Notwithstanding the concerns that have been raised regarding the potential necessity of increasing potassium intake in cases of advanced CKD, extant evidence would appear to indicate that potassium excretion persists until late disease stages. The activation and preservation of the renal KKS through a potassium-rich diet is a rational, cost-effective strategy for renoprotection. When combined with sodium reduction and nutritional education, this approach has the potential to halt the progression of CKD and enhance cardiovascular health on a population scale.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Preclinical Research)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Exploring the Chemical Space of Cephalosporins Across Generations
by
Henrique de Aguiar Mello and Itamar Luís Gonçalves
Drugs Drug Candidates 2026, 5(1), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc5010012 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Cephalosporins represent one of the most important classes of β-lactam antibiotics, widely used in clinical practice due to their broad-spectrum activity and favorable safety profile. As generations evolved, structural modifications were introduced to expand antimicrobial coverage and overcome β-lactamase resistance. This study
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Cephalosporins represent one of the most important classes of β-lactam antibiotics, widely used in clinical practice due to their broad-spectrum activity and favorable safety profile. As generations evolved, structural modifications were introduced to expand antimicrobial coverage and overcome β-lactamase resistance. This study aimed to analyze the drug-like properties of cephalosporins across different generations using molecular descriptors to identify structural and pharmacokinetic patterns influencing bioavailability and oral administration profiles. Methods: Thirty-eight cephalosporins representative of different generations were selected. Molecular data were obtained from PubChem, and SMILES were extracted and validated. Molecular descriptors (including MW, logP, TPSA, HBA, HBD, rotatable bonds, and global complexity indices) were calculated using the SwissADME and ChemDes platforms. Statistical analysis included ANOVA followed by post hoc tests, and principal component analysis (PCA). Results: A progressive increase in molecular weight, polarity, and TPSA was observed across generations, with fourth-generation cephalosporins showing significantly higher values compared to first-generation compounds (p < 0.0001). LogP decreased significantly in fourth-generation agents (p < 0.0001), reflecting increased polarity. PCA revealed that most compounds from generations 1–2 cluster in regions consistent with Lipinski’s and Veber’s rules, whereas fourth- and fifth generation - cephalosporins deviated substantially, prioritizing antimicrobial efficacy over oral bioavailability. Recurrent structural modifications such as oximes, tetrazoles, and aminothiazoles were identified, with increasing frequency in modern generations. Conclusions: The evolution of cephalosporins reflects a strategic shift toward enhanced antimicrobial potency and β-lactamase stability at the expense of oral bioavailability. Understanding these structural transitions provides valuable insights for rational drug design, aiming to balance antimicrobial effectiveness with favorable pharmacokinetic profiles essential for therapeutic success.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Marketed Drugs)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Levamisole Potentiation via Thymol and Cinnamaldehyde: Assessment of Pharmacological Interactions in Sheep
by
María Victoria Miró, Paula Ichinose, Mercedes Lloberas, Carlos Lanusse, Guillermo Virkel and Adrián Lifschitz
Drugs Drug Candidates 2026, 5(1), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc5010011 - 31 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: The widespread development of anthelmintic resistance in gastrointestinal nematodes constitutes a major production-limiting factor in grazing ruminants. Resistance mechanisms often involve drug efflux transporters like P-glycoprotein (P-gp). This study aimed to evaluate the potential of the phytochemicals cinnamaldehyde (CNM) and thymol (TML)
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The widespread development of anthelmintic resistance in gastrointestinal nematodes constitutes a major production-limiting factor in grazing ruminants. Resistance mechanisms often involve drug efflux transporters like P-glycoprotein (P-gp). This study aimed to evaluate the potential of the phytochemicals cinnamaldehyde (CNM) and thymol (TML) to modulate P-gp activity and enhance the pharmacokinetic profile and efficacy of levamisole (LVM) in lambs. Methods: An ex vivo diffusion assay using sheep ileum was conducted to assess the influence of CNM, TML, and LVM on the transport of the P-gp substrate Rhodamine 123 (Rho123). Subsequently, a clinical trial was performed in lambs naturally infected with resistant nematodes. Animals received LVM (3.75 mg/kg) subcutaneously, either alone or co-administered with CNM or TML (80 mg/kg). Plasma LVM concentrations were analyzed by HPLC, and anthelmintic efficacy was determined via the Fecal Egg Count Reduction (FECR) test. Results: Ex vivo assays demonstrated that CNM, TML and LVM significantly reduced the efflux ratio of Rho123, confirming P-gp inhibition. The pharmacokinetic parameters of LVM did not differ significantly in the co-administered groups. However, the combination of LVM + TML tended to increase the total systemic exposure of LVM. Although all experimental groups showed a significant reduction in EPG between day 0 and day 7 (FECR 50–58%), the magnitude of this reduction did not differ significantly among treatments. Conclusions: While CNM and TML effectively inhibited P-gp activity ex vivo and slightly modified LVM pharmacokinetics, these effects were insufficient to yield clinically meaningful improvements in its efficacy against nematodes under the tested conditions. Future strategies should focus on optimizing delivery systems to maximize phytochemical–drug interactions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Anti-Parasite Drug Discovery)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Nanoencapsulated Cannabidiol–Cannabigerol Using Eudragit L100: In Vitro and In Vivo Evidence in Murine Colitis Model
by
K. Antonio Cárdenas-Noriega, Joel H. Elizondo-Luévano, Abelardo Chávez-Montes, Luis E. Rodríguez-Tovar, Moisés A. Franco-Molina, Diana G. Zárate-Triviño, Raymundo A. Pérez-Hernández, Adolfo Soto-Domínguez and Uziel Castillo-Velázquez
Drugs Drug Candidates 2026, 5(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc5010010 - 31 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background: Phytocannabinoids such as cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabigerol (CBG) have received increasing attention in the context of inflammatory and intestinal disorders. However, direct comparisons between their individual and combined effects, as well as the influence of delivery systems, remain limited. Objectives: This study
[...] Read more.
Background: Phytocannabinoids such as cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabigerol (CBG) have received increasing attention in the context of inflammatory and intestinal disorders. However, direct comparisons between their individual and combined effects, as well as the influence of delivery systems, remain limited. Objectives: This study evaluated the biological effects of free and nanoencapsulated CBD and CBG, including a cannabinoid–Eudragit L100 formulation, in an in vitro TNBS-treated intestinal cell model and an in vivo murine model of TNBS-induced colitis. Methods: Cytotoxicity and treatment-associated effects of CBD, CBG, their 1:1 combination, and a nanoencapsulated formulation were assessed in TNBS-exposed Caco-2 cells. In parallel, BALB/c mice with TNBS-induced colitis were evaluated for colonic damage and inflammatory markers. Results: CBD and CBG individually showed dose-dependent effects in Caco-2 cells, while their combined administration produced a greater effect than either compound alone at higher concentrations. The nanoencapsulated formulation preserved cellular metabolic activity following TNBS exposure. In vivo, both free combined and nanoencapsulated cannabinoids were associated with reduced epithelial damage and inflammatory alterations. Conclusions: Nanoencapsulation using Eudragit L100 modulated the biological effects of CBD and CBG in experimental models of TNBS-induced intestinal injury.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Preclinical Research)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Rational Design of Mitochondria-Targeted Antioxidants: From Molecular Determinants to Clinical Perspectives
by
Beata Franczyk, Kinga Bojdo, Jakub Chłądzyński, Katarzyna Hossa, Katarzyna Krawiranda, Natalia Krupińska, Natalia Kustosik, Klaudia Leszto, Wiktoria Lisińska, Anna Wieczorek, Jacek Rysz and Ewelina Młynarska
Drugs Drug Candidates 2026, 5(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc5010009 - 20 Jan 2026
Abstract
Oxidative stress, caused by an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species and endogenous antioxidant capacity, is a key etiological factor in numerous pathologies, including neurodegenerative and cardiovascular diseases. The limited clinical efficacy of conventional antioxidants is primarily due to their insufficient
[...] Read more.
Oxidative stress, caused by an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species and endogenous antioxidant capacity, is a key etiological factor in numerous pathologies, including neurodegenerative and cardiovascular diseases. The limited clinical efficacy of conventional antioxidants is primarily due to their insufficient accumulation within the mitochondria, the main site of intracellular ROS generation. This article reviews the design and application of Mitochondria-Targeted Antioxidants, which represent a major advance in precision medicine. The design of these compounds involves linking an antioxidant “payload” to a lipophilic cation, such as the triphenylphosphonium group. This positive charge leverages the negative electrochemical gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane to drive the antioxidant into the organelle. This mechanism allows the drug to reach concentrations over 100 times higher than non-targeted alternatives. The discussion encompasses the structure-activity analysis of the carrier, the payload (e.g., quinone derivatives), and the linker, which determine optimal subcellular partitioning and scavenging efficiency. Preclinical data highlight the therapeutic potential of this approach, showing strong neuroprotection in models of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases, as well as improved outcomes in cardiovascular and ocular health. By restoring redox balance specifically within the mitochondria, these targeted therapies offer a more effective way to treat chronic oxidative damage.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Antioxidant Drug Candidates: Mechanistic and Computational Insights into Free Radical Scavenging and Redox Modulation)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Antischistosomal Activity of 1,4-Dihydropyridines
by
Thaís A. S. Oliveira, Matheus H. M. Zago, Larissa G. Maciel, Yan R. Robles, Lizandra G. Magalhães and Antônio E. M. Crotti
Drugs Drug Candidates 2026, 5(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc5010008 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Recent reports have demonstrated the antiparasitic activity of 1,4-dihydropyridine (1,4-DHPs). This study aimed to assess the in vitro antischistosomal activity of 24 1,4-DHPs against Schistosoma mansoni adult worms. Methods: Sixteen hexahydroquinolines (1–16) and eight Hantzsch esters
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Recent reports have demonstrated the antiparasitic activity of 1,4-dihydropyridine (1,4-DHPs). This study aimed to assess the in vitro antischistosomal activity of 24 1,4-DHPs against Schistosoma mansoni adult worms. Methods: Sixteen hexahydroquinolines (1–16) and eight Hantzsch esters (17–24) previously obtained through a multicomponent Hantzsch reaction were tested in vitro against Schistosoma mansoni adult worms. In silico studies with the most active compounds were also carried out. Results: Among the tested compounds, the Hantzsch esters 20 (diethyl 4-(4-bromophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate) and 21 (diethyl 4-(3-fluorophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate) provided the lowest IC50 (15.2 and 13.1 µM, respectively) and the highest selectivity for this parasite (SI = 2.31 and >4.59, respectively). Conclusions: Docking studies revealed that compound 21 has a high affinity for the S. mansoni target (PDB ID: 6UY4). Furthermore, ADMET predictions indicated that compound 21 meets the drug-likeness criteria without violating any Lipinski, Veber, or Egan’s rules.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Anti-Parasite Drug Discovery)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessCorrection
Correction: Ajith et al. Recent Developments in Electrospun Nanofibers as Delivery of Phytoconstituents for Wound Healing. Drugs Drug Candidates 2023, 2, 148–171
by
Govindaraj Ajith, Ganesan Padmini Tamilarasi, Govindaraj Sabarees, Siddan Gouthaman, Krishnan Manikandan, Vadivel Velmurugan, Veerachamy Alagarsamy and Viswas Raja Solomon
Drugs Drug Candidates 2026, 5(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc5010007 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
In the published manuscript [...]
Full article
Open AccessReview
Phage Therapy: A Promising Approach in the Management of Periodontal Disease
by
Paulo Juiz, Matheus Porto, David Moreira, Davi Amor and Eron Andrade
Drugs Drug Candidates 2026, 5(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc5010006 - 8 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Periodontal disease is a condition marked by the destruction of tooth-supporting tissues, driven by an exaggerated immune response to an unbalanced dental biofilm. Conventional treatments struggle due to antimicrobial resistance and the biofilm’s protective extracellular matrix. This study evaluates the potential of
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Periodontal disease is a condition marked by the destruction of tooth-supporting tissues, driven by an exaggerated immune response to an unbalanced dental biofilm. Conventional treatments struggle due to antimicrobial resistance and the biofilm’s protective extracellular matrix. This study evaluates the potential of bacteriophages as an innovative strategy for managing periodontal disease. Methods: This research employed a qualitative approach using Discursive Textual Analysis, with IRAMUTEQ version 0.8 alpha 7 (Interface de R pour les Analyses Multidimensionnelles de Textes et de Questionnaires) software. The search was conducted in the Orbit Intelligence and PubMed databases, for patents and scholarly articles, respectively. The textual data underwent Descending Hierarchical Classification, Correspondence Factor Analysis, and Similarity Analysis to identify core themes and relationships between words. Results: The analysis revealed an increase in research and patent filings concerning phage therapy for periodontal disease since 2017, emphasizing its market potential. The primary centers for intellectual property activity were identified as China and the United States. The study identified five focus areas: Genomic/Structural Characterization, Patent Formulations, Etiology, Therapeutic Efficacy, and Ecology/Phage Interactions. Lytic phages were shown to be effective against prominent pathogens such as Fusobacterium nucleatum and Enterococcus faecalis. Conversely, the lysogenic phages poses a potential risk, as they may transfer resistance and virulence factors, enhancing pathogenicity. Conclusions: Phage therapy is a promising approach to address antimicrobial resistance and biofilm challenges in periodontitis management. Key challenges include the need for the clinical validation of formulations and stable delivery systems for the subgingival area. Future strategies, such as phage genetic engineering and data-driven cocktail design, are crucial for enhancing efficacy and overcoming regulatory hurdles.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Microbes and Medicines)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessCorrection
Correction: Sathvika et al. Review of Case Study Results: Assessing the Effectiveness of Curcumin, St. John’s Wort, Valerian Root, Milk Thistle, and Ashwagandha in the Intervention for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Drugs Drug Candidates 2024, 3, 838–859
by
Veerabhadrappa Pallavi Sathvika, Prathibha Guttal Subhas, Debayan Bhattacharjee, Vejetha Nagaraj Koppad, Uday Samrat, Sindhu Bindapla Karibasappa and Kadappara Mallikarjun Sagar
Drugs Drug Candidates 2026, 5(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc5010005 - 8 Jan 2026
Abstract
In the original publication [...]
Full article
Open AccessReview
Clinical Pharmacology Packages of FDA-Approved Biologic License Applications in Oncology from 2015 to 2025
by
Kate Gallinero, Hunter Daws, Amanda Singh and Sanela Bilic
Drugs Drug Candidates 2026, 5(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc5010004 - 6 Jan 2026
Abstract
The landscape of oncologic therapies has undergone large changes since the introduction of monoclonal antibody (mAb) based immunotherapies in the late 1990s and early 2000s. MAb-based therapeutics, also called biologics or large molecules, have distinct pharmacological characteristics compared to chemotherapeutics and small molecules.
[...] Read more.
The landscape of oncologic therapies has undergone large changes since the introduction of monoclonal antibody (mAb) based immunotherapies in the late 1990s and early 2000s. MAb-based therapeutics, also called biologics or large molecules, have distinct pharmacological characteristics compared to chemotherapeutics and small molecules. Development of biologics requires thorough assessment of pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) characteristics to ensure safety and demonstration of efficacy. This review provides an overview of the clinical pharmacology packages of biologics for the treatment of oncologic malignancies approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) over the past decade (January 2015 and August 2025). The conduct of population PK (PopPK) and exposure-eesponse (E-R) analyses, as well as assessments for drug–drug interactions (DDIs), immunogenicity, and QT prolongation risk are discussed. The aim of this review is to provide insight into the clinical pharmacology assessments for approval of antibody-based therapies in oncology as well as provide a longitudinal view of clinical pharmacology packages in this space.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Marketed Drugs)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessRetraction
RETRACTED: Lokanath et al. Exploring Chalcone Derivatives as a Multifunctional Therapeutic Agent: Investigating Antioxidant Potential, Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition and Computational Insights. Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4, 16
by
Sujatha M. Lokanath, Manjunatha S. Katagi, Girish S. Bolakatti, Johnson Samuel and Belakatte P. Nandeshwarappa
Drugs Drug Candidates 2026, 5(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc5010003 - 31 Dec 2025
Abstract
The journal retracts the article titled “Exploring Chalcone Derivatives as a Multifunctional Therapeutic Agent: Investigating Antioxidant Potential, Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition and Computational Insights” [...]
Full article
Open AccessCorrection
Correction: Singh et al. Synergistic Interaction of Glycyrrhizin with Norfloxacin Displays ROS-Induced Bactericidal Activity against Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Drugs Drug Candidates 2023, 2, 295–310
by
Vigyasa Singh, Anirban Pal and Mahendra P. Darokar
Drugs Drug Candidates 2026, 5(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc5010002 - 22 Dec 2025
Abstract
In the publication [...]
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Synthesis, In Vitro Antitumor Activity, and In Silico ADMET Evaluation of β-Lapachone-Based Thiosemicarbazones
by
Elizabete Silva de Sousa, Edilane Almeida da Silva, Délis Galvão Guimarães, Ingrid Louise Santos de Souza, Arlan de Assis Gonsalves, Paulo Michel Pinheiro Ferreira, Rayran Walter Ramos de Sousa, Marcília Pinheiro da Costa and Cleônia Roberta Melo Araújo
Drugs Drug Candidates 2026, 5(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc5010001 - 21 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: β-Lapachone and triapine are compounds with recognized antitumor potential—the former is an ortho-naphthoquinone, and the latter a thiosemicarbazone inhibitor of ribonucleotide reductase. This study aimed to synthesize and evaluate new β-lapachone-based thiosemicarbazones (TSC1–TSC6) as potential antineoplastic
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: β-Lapachone and triapine are compounds with recognized antitumor potential—the former is an ortho-naphthoquinone, and the latter a thiosemicarbazone inhibitor of ribonucleotide reductase. This study aimed to synthesize and evaluate new β-lapachone-based thiosemicarbazones (TSC1–TSC6) as potential antineoplastic agents. Methods: Lapachol was isolated from Tabebuia sp. and used to obtain ortho-naphthoquinones (2–4), which served as precursors for thiosemicarbazones (TSC1–TSC6). NMR and HRMS spectra were used to characterize the compounds. Their cytotoxic activity was evaluated in vitro against murine melanoma (B16–F10), colon carcinoma (CT26.WT), and breast cancer (4T1) cell lines, as well as normal fibroblasts (L929). Pharmacokinetic parameters were predicted in silico using ADMETLab 3.0. Results: β-Lapachone exhibited strong cytotoxicity toward tumor cells with moderate effects on normal cells, while thiosemicarbazones of β-lapachone, TSC1, and TSC3 demonstrated lower potency but greater selectivity. The β-lapachone-3-sulfonic acid showed high activity against melanoma and breast cancer cells and low toxicity toward normal cells, indicating tumor selectivity. In contrast, their thiosemicarbazones, TSC2, TSC4, and TSC6, showed weak or no antiproliferative activity. The 3-iodo-β-lapachone was cytotoxic to both tumor and normal cells, whereas its derivative TSC5 demonstrated moderate activity with reduced toxicity. β-Lapachone, β-lapachone-3-sulfonic acid, TSC1, and TSC3 exhibited favorable ADME profiles (QED ≈ 0.61–0.66), suggesting good oral bioavailability. Conclusions: The β-lapachone-3-sulfonic acid and the β-lapachone-based thiosemicarbazones TSC1 and TSC3 emerged as promising lead candidates, combining tumor selectivity, favorable pharmacokinetic properties, and structural innovation for the development of safer and more effective antineoplastic agents.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Medicinal Chemistry and Preliminary Screening)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Molecular Hybridization of Naphthoquinones as Selective Inhibitors of Shikimate Kinase: A Promising Strategy Against Mycobacterium tuberculosis
by
Beatriz C. T. de Oliveira, Dandara de Paula Candido, Acácio S. de Souza, Iva S. de Jesus, Fernando de C. da Silva, Leonardo Bruno P. F. Barreto, Samyra A. da Silveira, Yrneh Y. P. Palacios, Francisco das C. de Souza, Maria Cristina S. Lourenço, Carlos Mauricio R. Sant’Anna, Vitor F. Ferreira and Alcione S. de Carvalho
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(4), 59; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4040059 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Tuberculosis (TB) remains a critical global health concern, exacerbated by the emergence of multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. In the search for novel therapeutic agents, naphthoquinones have garnered interest due to their diverse mechanisms of action and potent
[...] Read more.
Background: Tuberculosis (TB) remains a critical global health concern, exacerbated by the emergence of multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. In the search for novel therapeutic agents, naphthoquinones have garnered interest due to their diverse mechanisms of action and potent antimycobacterial activity. In this study, we report the design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of a novel series of eleven naphthoquinone-based derivatives (compounds 22–32), developed through a molecular hybridization strategy targeting shikimate kinase (Mtb-SK) an essential enzyme present exclusively in M. tuberculosis. Methods: The compounds were synthesized via a straightforward and efficient synthetic route, and preliminary screening identified five molecules with significant anti-TB activity. Notably, compound 26, 4-(4-ethoxyphenyl) amino) Naphthalene-1,2-dione, exhibited a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 21.33 µM, comparable to ethambutol and substantially more potent than pyrazinamide. Results: Molecular docking studies indicated that all active compounds interact favorably within the shikimate binding pocket of Mtb-SK, following the proposed mechanism of action. Additionally, ongoing cytotoxicity assays in HepG2 cells aim to assess the selectivity of these derivatives. Conclusions: These findings support the potential of this new class of naphthoquinones as promising scaffolds for the development of anti-TB agents, contributing to the growing body of research focused on new chemotherapeutic options against tuberculosis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Anti-Parasite Drug Discovery)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Cytotoxic and Antiproliferative Effects of Chlorella vulgaris Lectin on Colon Cancer Cells
by
Vivianne Lays Ribeiro Cavalcanti, Maria Carla Santana de Arruda, Thalya Natasha da Silva Santos, Daniela de Araújo Viana Marques, Romero Marcos Pedrosa Brandão Costa, Luiza Rayanna Amorim de Lima, Ana Lúcia Figueiredo Porto and Raquel Pedrosa Bezerra
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(4), 58; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4040058 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Colon cancer is the third most common type of cancer in the world, characterized by a high risk of metastasis, resistance to various drugs, and late diagnosis. In addition, the drugs used for treatment are associated with serious neurological damage, causing acute
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Colon cancer is the third most common type of cancer in the world, characterized by a high risk of metastasis, resistance to various drugs, and late diagnosis. In addition, the drugs used for treatment are associated with serious neurological damage, causing acute and chronic pain and compromising the patient’s quality of life. Meanwhile, lectins are proteins capable of exerting cytotoxic action on cells from various tumors in a selective manner, without exerting significant toxicity on healthy cells. Despite this, studies on the potential of lectins obtained from microalgae are still scarce in the literature. In this sense, the objective of this study was to evaluate the antitumor activity of lectin isolated from the microalgae Chlorella vulgaris (CvL) on colorectal cancer cells, HT-29. Methods: The purified lectin was tested for cytotoxicity using MTT colorimetric methods, in addition to clonogenicity, cell cycle, apoptosis, and necrosis tests, analyzed by flow cytometry. Results: The assays demonstrated that the lectin was able to induce cell death in the HT-29 tumor line by approximately 83.75% with an IC50 value of 21.5 µg/mL−1, reduced colony formation by more than 90%, was able to regulate the cell cycle by apoptosis, and did not present significant necrosis. These results show that microalgae lectins have the potential to be exploited in the control of neoplastic cells.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Drug Candidates from Natural Sources)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessEditorial
Drugs and Drug Candidates: Constantly Progressing
by
Jean Jacques Vanden Eynde
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(4), 57; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4040057 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
As we are closing Volume 4 of Drugs and Drug Candidates (DDC), this gives me the opportunity to share the journal’s latest developments [...]
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Repositioning Imipramine for Antiparasitic Effects Against Giardia lamblia
by
Xareni Zinereth Herrera-Valero, Sendar Daniel Nery-Flores, Filiberto Gutiérrez-Gutiérrez, Lizeth Guadalupe Campos-Múzquiz, Sandra Cecilia Esparza-González, Raúl Rodríguez-Herrera and Lissethe Palomo-Ligas
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(4), 56; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4040056 - 16 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Giardia lamblia is an intestinal protozoan responsible for giardiasis, a globally prevalent parasitic disease. Current therapeutic options, including nitroimidazoles and benzimidazoles, have increasing treatment failures due to resistance, adverse reactions, and patient non-compliance. Drug repositioning offers a cost-effective strategy for identifying
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Giardia lamblia is an intestinal protozoan responsible for giardiasis, a globally prevalent parasitic disease. Current therapeutic options, including nitroimidazoles and benzimidazoles, have increasing treatment failures due to resistance, adverse reactions, and patient non-compliance. Drug repositioning offers a cost-effective strategy for identifying new antigiardial agents. This study aimed to evaluate the in vitro antiparasitic effects and possible mechanisms of action of the tricyclic antidepressant imipramine against G. lamblia trophozoites. Methods: Trophozoites were exposed to increasing concentrations of imipramine (25–125 µM). Growth inhibition and adhesion capacity were quantified using cell counts. Apoptosis- or necrosis-like death was evaluated through Annexin V/PI staining. The expression and distribution of α-tubulin and lipid rafts were analyzed by immunofluorescence microscopy. Finally, the effect of the drug on encystment efficiency was assessed in vitro. Results: Imipramine inhibited G. lamblia trophozoite growth in a concentration-dependent manner, with an IC50 of 42.31 µM at 48 h. The drug significantly reduced adhesion capacity (>90% at 125 µM) and induced apoptosis-like cell death, as evidenced by Annexin V positivity. Immunofluorescence revealed disruption of α-tubulin distribution and lipid raft organization, accompanied by morphological rounding. Moreover, encystment efficiency decreased in a concentration-dependent mode, suggesting interference in the differentiation process. Conclusions: This investigation describes, for the first time, the antigiardial potential of imipramine, which alters cytoskeletal organization, membrane microdomains, and differentiation pathways, ultimately leading to apoptosis-like cell death. These findings position this compound as a promising lead structure and support further exploration of tricyclic antidepressants as scaffolds for the development and optimization of new antiparasitic agents, as well as future studies on their molecular targets and in vivo efficacy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Anti-Parasite Drug Discovery)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
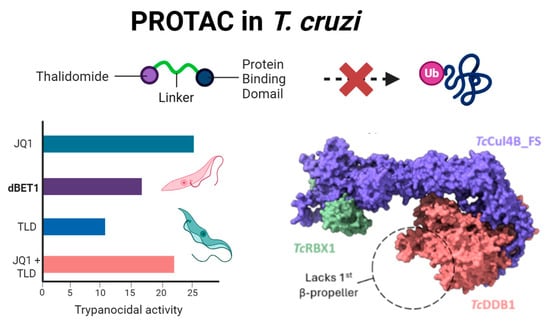
Thalidomide-Based PROTACs: A Viable Strategy Against Trypanosomatids?
by
Romina Manarin, Gianfranco Frattini, Victoria L. Alonso, Victoria Boselli, Giselle R. Bedogni, Elvio Rodríguez Araya, Diego M. Moreno and Esteban Serra
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(4), 55; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4040055 - 10 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: In recent years, compounds known as Proteolysis Targeted Chimeras (PROTACs) have revitalized the field of bioactive molecule design. These compounds promote proteolysis of therapeutic targets by recruiting them to ubiquitin ligases. One of the most commonly used classes of compounds in the
[...] Read more.
Background: In recent years, compounds known as Proteolysis Targeted Chimeras (PROTACs) have revitalized the field of bioactive molecule design. These compounds promote proteolysis of therapeutic targets by recruiting them to ubiquitin ligases. One of the most commonly used classes of compounds in the synthesis of PROTACs are immunomodulatory imides (IMiDs), such as thalidomide (TLD), which interact with the E3 ligase CRL4CRBN via the CULT domain of the cereblon protein (CRBN). This domain has been identified in proteins across various phylogenetic groups, including trypanosomatids, leading to the hypothesis that IMiD-derived PROTACs should be active in these organisms. Methods: The trypanocidal activity of the PROTAC dBET1 and its separated components (JQ1 and TLD) were assayed using a T. cruzi strain expressing β-glalactosidase. Potential CRL4-E3L complexes from humans and trypanosomatids were assembled in silico with MultimerMapper. The IMiD-binding site of HsCRBN and its trypanosomatid homologs were analyzed using molecular dynamics and docking simulations. Results: We demonstrate that the compound dBET1 does not function as a PROTAC in Trypanosoma cruzi. In silico structural analysis of CRL4-E3L complex orthologs revealed that the trypanosomal CULT-containing protein is not part of such a complex. Molecular dynamics simulations showed that the pocket of this CULT domain is smaller than that of mammalian CRBN and cannot accommodate IMiDs within. Conclusions: We underscore the importance of functional and structural validation in drug discovery, particularly when extrapolating mechanisms between evolutionarily distant species. While PROTACs hold promise in human therapeutics, our work advocates for re-evaluating the rationale behind thalidomide-based PROTACs in trypanosomatid research.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Anti-Parasite Drug Discovery)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Aqueous Leaf Extracts of Bauhinia cheilantha (Bong.) Steud.: Phytochemical Profile, Antioxidant Activity and In Vitro Safety Evaluation
by
Palloma Lima de Oliveira, José Rafael da Silva Araújo, Camila Marinho da Silva, Kyria Cilene de Andrade Bortoleti, Silvany de Sousa Araújo, Márcia Vanusa da Silva, Dráulio Costa da Silva, Marcos dos Santos Lima, Ana Paula de Oliveira and Ana Christina Brasileiro-Vidal
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(4), 54; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4040054 - 8 Dec 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Bauhinia cheilantha Bong. Steud. (Leguminosae; “pata-de-vaca”) is traditionally used in folk medicine for its antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, and sedative properties. This study aimed to evaluate aqueous leaf extracts of B. cheilantha, non-delipidated and delipidated, regarding their phytochemical composition, phenolic profile, antioxidant potential,
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Bauhinia cheilantha Bong. Steud. (Leguminosae; “pata-de-vaca”) is traditionally used in folk medicine for its antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, and sedative properties. This study aimed to evaluate aqueous leaf extracts of B. cheilantha, non-delipidated and delipidated, regarding their phytochemical composition, phenolic profile, antioxidant potential, and cytotoxic, genotoxic, and antigenotoxic effects. Methods: Phytochemical screening was performed by TLC, and phenolic compounds were determined by HPLC. Antioxidant activity was assessed using DPPH, ABTS, and phosphomolybdenum assays. Cytotoxicity, genotoxicity, and antigenotoxicity were evaluated in L929 murine fibroblast cells using MTT and cytokinesis-block micronucleus (CBMN) assays. Results: Both extracts contained anthocyanins, phenolics, lignans, saponins, and hydrolyzable tannins. The delipidated extract showed higher total phenolic content (17.54 mg/kg) than the non-delipidated (13.76 mg/kg). Major constituents included kaempferol 3-glucoside, quercetin, hesperidin, naringenin, and t-cinnamic acid. Antioxidant assays revealed EC50 values of 25.84, 13.60, and 66.09 µg/mL for the non-delipidated extract, and 26.19, 16.34, and 52.78 µg/mL for the delipidated extract in the DPPH, ABTS, and phosphomolybdenum assays, respectively. No cytotoxicity was observed, except at 1600 µg/mL for the non-delipidated extract and 800–1600 µg/mL for the delipidated extract. Genotoxicity occurred only at 400 µg/mL. Antigenotoxic evaluation showed that the non-delipidated extract (100 µg/mL) reduced methyl methanesulfonate-induced chromosomal damage in simultaneous and post-treatment conditions, while the delipidated extract was only effective for post-treatment. Conclusions: Aqueous extracts of B. cheilantha exhibit antioxidant and antigenotoxic properties. At active concentrations, they were non-cytotoxic and non-genotoxic. The non-delipidated extract, in particular, showed the strongest genome-protective potential, supporting its traditional use and highlighting its relevance in the development of natural therapeutic agents.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Drug Candidates from Natural Sources)
►▼
Show Figures
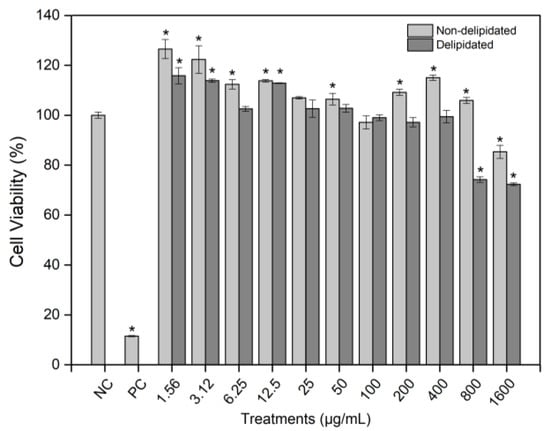
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Synthetic Derivatives of Vinpocetine as Antiproliferative Agents
by
Mihira Gutti, Melanie Tsui, Stella Yang, Selina Xi, Jennifer Luo, Arshia Desarkar, Yining Xie, Mirabelle Feng, Udbhav Avadhani, Shloka Raghavan, Elena Brierley-Green, Erika Yu and Edward Njoo
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(4), 53; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4040053 - 28 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Vincamine is an indole alkaloid initially isolated from plants of the Vinca genus and has previously been demonstrated to have antioxidant, hypoglycemic, and hypolipidemic activities. Vinpocetine, a synthetic derivative of vincamine with an enhanced pharmacological profile, has demonstrated promising antiproliferative properties. While
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Vincamine is an indole alkaloid initially isolated from plants of the Vinca genus and has previously been demonstrated to have antioxidant, hypoglycemic, and hypolipidemic activities. Vinpocetine, a synthetic derivative of vincamine with an enhanced pharmacological profile, has demonstrated promising antiproliferative properties. While previously reported vinpocetine derivatives have undergone extensive investigation for their pharmacological properties, the role of the E-ring ethyl ester in the antiproliferative properties of compounds with this scaffold has not yet been fully described. Methods: Here, the antiproliferative activity of two vinpocetine analogs with modifications at the E-ring was evaluated through cell viability and LDH assays, and their mechanism of action was investigated through cell cycle analysis, apoptosis detection, and reporter assays for Wnt-1, NF-κB, and STAT3 signaling. Results: Cell viability assays revealed that reduction of the ethyl ester to an alcohol exhibited strong dose-dependent antiproliferative activity across five mammalian cell lines, but did not induce significant markers of apoptosis or necrotic death as determined by FITC/Annexin V and cell cycle flow cytometry, respectively. Through label-free cell imaging, we found the antiproliferative activity of vinpocetine alcohol to be correlated with a decrease in membrane integrity in treated cells. We further observe that both analogs exhibit dose-dependent modulation of TCF/LEF, NF-kB, and STAT3 reporter cells, which appears to be coupled with trends in antiproliferative activity. Conclusions: Altogether, this work demonstrates the potential for E-ring modifications of vinpocetine as antiproliferative agents.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Preclinical Research)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
27 January 2026
Meet Us at the 5th Molecules Medicinal Chemistry Symposium, 14–17 May 2026, Beijing, China
Meet Us at the 5th Molecules Medicinal Chemistry Symposium, 14–17 May 2026, Beijing, China

3 December 2025
Meet Us at the 5th Molecules Medicinal Chemistry Symposium, 14–17 May 2026, Beijing, China
Meet Us at the 5th Molecules Medicinal Chemistry Symposium, 14–17 May 2026, Beijing, China

Topics

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
DDC
Therapeutic Protease and Peptidase Inhibitors
Guest Editor: François MarceauDeadline: 30 April 2026
Special Issue in
DDC
Antioxidant Drug Candidates: Mechanistic and Computational Insights into Free Radical Scavenging and Redox Modulation
Guest Editor: Žiko B. MilanovićDeadline: 20 June 2026
Special Issue in
DDC
Microbes and Medicines
Guest Editors: Paul Hyman, Jennifer BennettDeadline: 31 July 2026
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
DDC
Bioinorganic Chemistry in Drug Discovery
Collection Editors: Tanja Soldatović, Snežana Jovanović-Stević
Topical Collection in
DDC
Chirality in Drugs and Drug Candidates
Collection Editors: Carla Fernandes, Maria Emília De Sousa
Topical Collection in
DDC
Heterocycles in Drug Discovery
Collection Editors: Thierry Besson, Nicolas Primas, Jean Jacques Vanden Eynde






